Online Nursing Essays
Top Quality Nursing Papers

Main Tips On How To Write a Case Study Analysis

A nursing case study analysis is like an in-depth exploration. It acts as the lifeline connecting theoretical knowledge to its real-world implications, bridging the gap between understanding symptoms and improving the quality of patient care.
Why is a case study analysis so significant? Case studies are types of essays that breathe life into nursing principles, making them more than abstract concepts. They provide context, create connections, and highlight the real-world impact of nursing decisions. Furthermore, they foster empathy, allowing nursing professionals to perceive each patient as unique with distinctive healthcare needs. This comprehensive guide will serve as your roadmap for how to write a nursing case study analysis.
What is a Case Study Analysis in Nursing?
In the 5th century BC, the philosopher Lao-Tse (also Lao-tzu) wrote, “If you tell me, I will listen. If you show me, I will see. But if you let me experience, I will learn.” And so began one of the first active learning philosophies.
A nursing case study analysis is an immersive journey into a patient’s health scenario. It’s like a detective story, where the nurse or nursing student acts as the investigator, and the patient’s condition is the mystery waiting to be solved. Each patient’s story is unique and requires a thorough examination to extract useful insights. But what exactly does this process involve?
A nursing case study analysis begins with a comprehensive exploration of a patient’s health situation. This includes their health history, current symptoms, and previous treatments. This exploration phase involves collecting data from patient interviews, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. Each data point could be the key to better understanding the patient’s condition.
The next step is to diagnose the issues. This involves understanding the complexities of the patient’s condition—the root causes, contributing factors, and potential risks. The nurse then moves on to planning and implementing interventions. This might involve developing a care plan, suggesting lifestyle modifications, or coordinating with other healthcare professionals for specialized care. These interventions aim to address the diagnosed issues and improve the patient’s health outcomes.
The nurse then moves on to planning and implementing interventions. This might involve developing a care plan, suggesting lifestyle modifications, or coordinating with other healthcare professionals for specialized care. These interventions aim to address the diagnosed issues and improve the patient’s health outcomes.
What is the Purpose of a Case Analysis?
Why do nurses engage in the elaborate process of a case study analysis? What purposes does it serve, and how does it contribute to the broader nursing field?
- Enhancing Patient Care: A nursing case study analysis aims to improve patient care. When a nurse begins analyzing a patient’s case, they are honing their ability to provide effective, personalized care.
- Refining Critical Thinking Skills: A case analysis requires active engagement, thoughtful consideration, and deliberate analysis. Nurses must interpret data, make diagnoses, and plan interventions, all of which demand a high degree of cognitive ability.
- Bridging Theory and Practice: A case study allows nurses to apply theoretical concepts to real-world contexts, demonstrating the practical implications of nursing principles. This deepens their understanding of these concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Fostering Reflective Learning: As nurses evaluate their interventions’ outcomes, they reflect, assessing their actions and learning from their experiences. This cultivates an attitude of continuous learning and promotes personal and professional growth.
Difference Between a Nursing Research Paper and a Case Study
Here are the differences between these two important facets of nursing literature:
Research Paper
A nursing research paper explores a particular topic or concept in depth. Its purpose is to contribute new insights or validate or challenge existing theories. It seeks to add to the collective understanding of a topic and often aims to solve a larger problem or answer a complex question.
A research paper often employs a systematic and structured approach. This might involve a literature review, an experimental study, a survey, or a qualitative investigation, depending on the nature of the research topic. The methodology is often rigorous and has strict guidelines to ensure the validity and reliability of the results.
A research paper generally follows the IMRaD format—Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each section has a specific role, contributing to the overall narrative of the paper.
A case study takes a single patient situation or a unique medical scenario and delves into it with microscopic attention. The primary aim is to apply theoretical knowledge to practical, real-life scenarios, enhancing understanding and application.
The case study method employs a more focused approach. It concentrates on a single instance or scenario, using interviews, observations, and medical records review to gain insights. Its strength lies in its detail and specificity.
A case study begins with an introduction of the patient or the situation, followed by a detailed account of the patient’s history, diagnosis, treatment, and the nurse’s role. The focus is on presenting a chronological and detailed narrative of the patient’s journey.
Types of Nursing Case Studies
Here are the five primary types of case studies:
- Problem-Oriented Case Studies: These studies focus on a specific problem encountered in nursing practice. Whether it’s a challenging patient condition, a complex care scenario, or an organizational issue, problem-oriented case studies zero in on the problem. They detail the problem’s context, dissect its causes, and evaluate the solutions implemented.
- Critical Case Studies: They delve into cases with significant implications for nursing practice. These could be landmark cases, rare medical conditions, or novel nursing interventions. A critical analysis case study aims to illuminate the unique aspects and derive valuable lessons. They often lead to advancements in nursing knowledge, influencing nursing practices and policies.
- Historical Case Studies: As the name suggests, historical case studies delve into past nursing scenarios. They offer a retrospective analysis of a patient case, nursing intervention, or healthcare event. They allow for reflecting on past actions, evaluating their outcomes, and extracting lessons for future practice.
- Illustrative Case Studies: Descriptive or illustrative case studies are designed to ‘illustrate’ or ‘describe’ a particular nursing situation or condition. These case studies provide a detailed narrative of the case, painting a vivid picture for the reader. They serve to familiarize the readers with the case’s intricacies, enhancing their understanding and empathy. They are useful for educating patients or the general public about specific health conditions or nursing procedures.
- Collective Case Studies: Multiple case studies involve the analysis of more than one case. The goal is to derive insights from a collective analysis, recognizing patterns, differences, and similarities across the cases. This type of case study is especially useful for comparing different nursing approaches, understanding the variability in patient responses, or evaluating the impact of a particular nursing intervention across multiple scenarios.
6 Steps for Writing a Case Study Analysis
Writing a nursing case study analysis requires a systematic approach to ensure all necessary details are covered and accurately presented. The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in real-life settings. Here is a step-by-step guide to facilitate this process:
Preparation
Preparation means collecting, collating, and comprehending all available patient case information. First, take the patient’s medical history to understand the current health situation. It may include details about previous diagnoses, treatments, hospitalizations, allergies, and family history of diseases.
Check nursing assessments that were conducted. These assessments serve as a foundation for nursing care, offering vital clues about the patient’s health status at different times. Information about the patient’s vital signs, physical examination findings, lab results, and psychosocial assessments can help unravel the case’s complexity.
Review the treatment plans initiated to have insights into the healthcare team’s approach to managing the patient’s condition. Lastly, include the outcomes. What was the response to the treatments initiated? How did the patient’s condition evolve over time? Outcomes, both expected and unexpected, offer a reality check. They help understand the interventions’ effectiveness and provide opportunities for reflection and learning.
Introduction
Introducing your case study analysis is a gateway to the patient’s story, providing crucial initial details and laying the groundwork for in-depth exploration. Present a snapshot of the patient’s background that involves sharing key details, such as the patient’s age and gender, which can influence disease prevalence, presentation, and response to treatment.
Next, share why the patient sought medical care for a first clue to their health status. Was it a routine check-up that led to an unexpected discovery? Or perhaps the patient presented with specific symptoms, causing them concern? Then, outline the primary health concerns. What were the initial diagnoses or suspicions based on the assessments done? Were there any significant risks identified?
Finally, mention the challenges encountered during care, the strategies to address them, or the valuable lessons gleaned from the case. However, don’t give away too much – just enough to pique their interest and keep them reading.
Background Information
A key element of the background information is the patient’s medical history which sheds light on the patient’s health journey. Past medical diagnoses, treatments, lifestyle habits, and familial health patterns can explain the current health problem and guide future healthcare decisions.
The initial nursing assessments form an integral part of the background information. They include observations about the patient’s symptoms and vital signs and depict their health status at the point of care. Key details such as the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature, pain level, and overall physical and mental state provide crucial baseline data against which progress can be measured.
Diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, or biopsies, offer objective insights into the patient’s condition. The results of these tests can confirm or rule out diagnoses, guide the choice of interventions, and help assess the effectiveness of treatments.
Lastly, highlight significant observations made during the care process. Did the patient’s condition improve or worsen over time? Were there any unexpected reactions or complications? How did the healthcare team respond? These observations offer a real-world view of the patient’s journey, providing an opportunity to reflect on the decisions made and the outcomes achieved.
Proposed Solutions
First, present the nursing interventions proposed to address the patient’s health concerns. Nursing interventions refer to nurses’ actions to improve patient outcomes, such as administering medication, providing health education, or coordinating care with other healthcare professionals.
Then, discuss the rationale behind each intervention. The rationale is the ‘why’ that justifies the ‘what.’ It explains why a particular intervention was chosen over others and how it is expected to contribute to the patient’s recovery or well-being.
Lastly, determine how each intervention was incorporated into the patient’s care plan. How was the medication administered? What teaching strategies were used for health education? How was care coordination achieved? These details help bring the care process to life, giving readers a peek into the realities of nursing practice.
Recommendations
Recommendations derive from carefully evaluating the patient’s journey, considering the outcomes observed, the challenges encountered, and the lessons learned. These recommendations aim to refine and optimize care processes, ensuring that nursing practice evolves and improves continually.
One common type of recommendation involves suggesting alternative interventions. Despite the best efforts, not all interventions yield the desired outcomes. In such cases, it’s beneficial to explore other potential solutions. These alternatives, informed by the latest evidence and expert opinion, can provide fresh approaches to the problem, opening up new avenues for patient recovery.
Another type of recommendation focuses on enhancing the implementation of interventions. Sometimes, the choice of intervention is sound, but the execution may fall short. Here, the recommendations may address areas such as improving the timing or technique of intervention delivery, enhancing patient education and engagement, or strengthening coordination among the healthcare team.
The review begins with a concise summary of the case. It revisits the patient’s background, the identified health concerns, the nursing interventions implemented, the outcomes observed, and the recommendations proposed. This brief recounting of the case helps anchor the detailed analysis in the reader’s mind.
Following the summary, it’s time for reflection. Reflective essay writing encourages practitioners to learn from their experiences and continuously improve their practice. Discuss the lessons learned from the case, the insights gained, and the challenges faced. This reflective dialogue enriches the case study analysis, transforming it from a simple narrative to a springboard for professional development and growth.
Lastly, the review addresses the case’s broader implications for nursing practice. How does this case contribute to our understanding of patient care? What does it reveal about the application of nursing theory in real-world scenarios? How can the insights from this case inform future nursing practice? By exploring these questions, the review extends the relevance of the case beyond its specific context, connecting it to the larger discourse on nursing care.
Nursing Case Study Analysis Example
This fictitious case involves a patient named “John,” who presents with Type 2 Diabetes and related complications.
Introduction John, a 63-year-old male, presented to the clinic complaining of persistent fatigue, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. As a nurse practitioner, I evaluated John’s condition and formulated a care plan. This case study analysis will explore John’s health journey, his health issues, the interventions undertaken, and the lessons gleaned from his case. Background Information John was diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes five years ago. His medical history reveals that he has struggled to maintain his blood glucose levels within the recommended range. Despite being prescribed oral hypoglycemic agents and advised lifestyle modifications, he found adhering to the recommended regimen challenging. A recent HbA1c test showed a level of 9.5%, indicating poorly controlled diabetes. Proposed Solutions Given John’s condition, the mainstay of his management involved rigorous blood glucose control. His existing medication regimen was reviewed and adjusted to improve glycemic control. Simultaneously, a comprehensive diabetes self-management education (DSME) program was designed to enhance John’s understanding of diabetes and empower him to manage his condition effectively. The DSME covered essential topics such as the nature of diabetes, the importance of regular monitoring and medication adherence, diet and exercise guidelines, and coping strategies for managing stress and preventing complications. Recommendations Despite best efforts, John’s struggle with diabetes control highlights the need for individualized and holistic care approaches in managing chronic conditions like diabetes. In retrospect, introducing a more intensive support system early on, including regular follow-ups and mental health support, might have helped John better manage his condition. This case underlines the importance of comprehensive patient education and the need for healthcare professionals to recognize and address the psychosocial factors that can impact chronic disease management. Review John’s case provides valuable insights into the challenges of managing chronic conditions like diabetes. It underscores the need for a holistic and personalized approach to patient care beyond medical interventions. The lessons from this case highlight the importance of ongoing patient education, the need for mental health support in chronic disease management, and the value of early and proactive interventions. I hope that the experiences and reflections from this case will inform and enrich nursing practice, especially in chronic disease management.
Final Thoughts on Case Study Analysis
Writing a nursing case study analysis demands a keen understanding of nursing concepts, critical thinking skills, and the ability to apply theory to practice. But, with a structured approach and thorough preparation, it is a rewarding and educational process that enhances nursing practice, contributes to better patient outcomes, and facilitates lifelong learning.
If you’re a nursing student or professional seeking assistance with your own case study analysis, research summary, argumentative essay, or academic writing, look no further. Our dedicated professional writers are well-versed in nursing principles, theories, and practices, making them perfectly equipped to craft high-quality, insightful, and personalized nursing case study analyses.
Ready to experience the difference? Place your order today, and let us support your journey to academic excellence and professional development. Let’s craft a nursing case study analysis that earns you high grades and enriches your nursing practice.
FAQs on How To Write a Case Study Analysis
What is a case study analysis.
A case study analysis critically evaluates a specific instance or event, often focused on a person or a small group. It helps in applying theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
How do you structure a case study assignment?
A case study format has an introduction, background information, proposed solutions, recommendations, and a review.
What is an example of case analysis?
Case analysis examples could involve examining a patient’s journey through a specific health condition. It would involve analyzing the patient’s health history, symptoms, treatment, and response to the care provided. An in-depth review of all these elements helps to understand the situation better, gain insights, and improve future patient care.
What is the difference between a case study and a case analysis?
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a single individual, group, or event to explore causation and find underlying principles. On the other hand, a case analysis often refers to examining and interpreting the data from the case study to formulate solutions or extract insights.
What are the stages of a case study?
A case study generally involves five stages: preparation, data collection, analysis, formulation of solutions, and essay conclusions or recommendations.
What is the purpose of a case study?
A case study aims to investigate a contemporary phenomenon within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not evident.
What are the qualities of a good case study?
A good case study is relevant, detailed, focused, provides a learning opportunity, and can generate useful results or insights contributing to the broader field of study.

Don’t wait until the last minute
Fill in your requirements and let our experts deliver your work asap.

Nursing Case Study Analysis [10 Examples & How-To Guides]
- Wilson Logan
- August 6, 2022
- blog , Nursing Topics and Ideas
What is a case study analysis?
A case study analysis is a detailed examination of a specific real-world situation or event. It is typically used in business or nursing school to help students learn how to analyze complex problems and make decisions based on limited information.
Preparing a good case study analysis is not an easy task and requires a lot of time and effort. This article provides some tips on how to write a case study analysis that will help you get the most out of your research and provide a solid foundation for your writing.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
Nursing Case Study Analysis
Nurses are constantly faced with decisions that have to be made in a timely and effective manner. Often, these decisions are based on the available information, which may be limited.
In order to make the best possible decisions, nurses need to be able to analyze and interpret data. Nursing case studies are an important tool that can help nurses improve their decision-making skills.
10 Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
How to write case study analysis in nursing.
A case study analysis requires you to investigate a nursing scenario, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidence.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
Nurses have to constantly make decisions that affect the lives of their patients. In order to ensure that these decisions are made correctly, nurses need to have strong problem-solving and critical-thinking skills. Case studies are an excellent way for nurses to hone these skills.
Writing a nursing case study analysis is not as difficult as it may first seem. Follow these steps and you will be well on your way to writing a successful case study analysis.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- Read the case study carefully. As you read, take note of any key facts or information that could be important for your analysis.
- Once you have finished reading the case study, identify the main problem or issue that needs to be addressed.
- Brainstorm possible solutions to the problem or issue . Try to come up with a few different options.
- Choose the best solution based on the information in the case study and your own clinical experience.
- Write up your analysis in a clear and concise manner. Be sure to support your chosen solution with evidence from the case study and your own professional experience .
Here’s How To Write A Nursing Case Study
How do you analyze a case study in nursing?
A nursing case study is an in-depth examination of a single individual. It is usually used to identify new areas of knowledge or to validate existing knowledge.
When analyzing a nursing case study, it is important to consider the following elements:
- The patient’s medical history. This includes any prior illnesses, treatments, and medications.
- The patient’s current condition. This includes symptoms, vital signs, and laboratory results.
- The nurse’s observations. This includes the nurse’s notes on the patient’s condition and behavior.
- The patient’s family and social history. This includes information on the patient’s family, friends, and social support network.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- The patient’s response to treatment. This includes any changes in the patient’s condition or symptoms after receiving treatment.
How nursing practitioners can analyze Patient’s Cases
As a nurse practitioner, you will often be asked to provide a case analysis for your patients. This can be a daunting task, but there are some key elements that you should always include in your analysis.
- The first element is the patient history. This should include any relevant medical history, as well as any personal information that may be pertinent to the case.
- The second element is the physical examination. This should include a thorough examination of the patient, including any relevant test results.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- The third element is the diagnosis. This is where you will provide your assessment of the patient’s condition and identify any potential problems.
- The fourth element is the treatment plan. This is where you will outline the course of treatment that you recommend for the patient.
- The fifth and final element is the prognosis. This is where you will provide your assessment of the likely outcome of the case, based on the information that you have gathered.
Steps of writing nursing case study analysis
Furthermore; there are different ways to approach writing a nursing case study analysis, but there are generally three main steps that need to be followed.
- First, you will need to perform a thorough analysis of the case study. This means looking at all aspects of the case and trying to identify any key issues or problems.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- Once you have done this, you will need to develop a hypothesis or research question that you can test.
- Finally, you will need to write up your findings in a clear and concise manner.
Assuming that you have been given the task of writing a case study analysis, there are a few key steps that you will need to take in order to ensure that your document is well-written and informative.
- Make sure that you understand all of the information presented in the case study , and take note of any key points or details that you think may be important.
- What points do you want to make in your analysis?
- What evidence will you use to support these points?
- Once you have a good idea of what you want to say in your analysis, start organizing your thoughts and putting them into a coherent structure.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- Once you have a rough outline of your case study analysis , start filling in the details. Flesh out your arguments and provide evidence to support them. In addition, make sure to address any counterarguments that could be made against your points.
- Finally, conclude your analysis by summarizing your main points and providing any recommendations or suggestions for further action .
Nursing Case study Analysis Format and Structure
When it comes to writing a case study analysis, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there is a general format and structure that you can follow to ensure your analysis is well-organized and flows smoothly. Here are the basics:
A nursing case study is a detailed study of a patient that is encountered by a nurse. The purpose of the case study is to provide a comprehensive view of the patient’s health condition and history. Nurse practitioners use case studies to enhance their ability to care for patients by providing them with a more complete picture of the patient’s health . Nurse practitioners may use different formats for their nursing case studies. However, all case studies should include certain key elements. These key elements include:
- Patient information – This section should include basic demographic information about the patient, such as age, gender, race/ethnicity, and chief complaint
- Medical history – This section should detail the patient’s past medical history, including any chronic conditions, medications, allergies, and surgeries.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- Family history – This section should detail the patient’s family medical history, including any chronic conditions or genetic diseases that may be relevant to the patient’s current condition.
- Social history – This section should detail the patient’s social circumstances, such as employment status, living situation, and alcohol/drug use.
- Review of symptoms –A physical examination will help you to identify any physical abnormalities that may be causing or contributing to the patient’s condition.
- Diagnostic testing – Diagnostic testing may be necessary in order to confirm or rule out a diagnosis . Common tests used in case analysis include blood work, imaging tests, and biopsies.
- Treatment options – Once a diagnosis has been made, you will need to consider treatment options. Treatment options will vary depending on the diagnosis and the severity of the condition.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
- The prognosis (Evaluation and outcomes) – After considering all of the above factors, you will be able to give the patient a prognosis. The prognosis is an educated guess as to how the condition will progress.
When writing a nursing case study, nurse practitioners should use a clear and concise format. The format should be easy to follow and understand. Nurse practitioners should also include all of the key elements in their nursing case studies.
As a nurse practitioner, you will be required to conduct case analyses on patients in order to make treatment decisions. There are key elements that you will need to take into consideration when conducting a case analysis. These elements include the patient’s history, physical examination, laboratory data, and imaging studies.(Nursing Case Study Analysis)
By taking into consideration all of these elements, you will be able to develop a comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition. This will allow you to make an informed decision about the best course of treatment.

Working On an Assignment With Similar Concepts Or Instructions?
A Page will cost you $12, however, this varies with your deadline.
We have a team of expert nursing writers ready to help with your nursing assignments. They will save you time, and improve your grades.
Whatever your goals are, expect plagiarism-free works, on-time delivery, and 24/7 support from us.
Here is your 15% off to get started. Simply:
- Place your order ( Place Order )
- Click on Enter Promo Code after adding your instructions
- Insert your code – Get20
All the Best,
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, what you'll learn.
Working On A Paper On This Topic?
Use our nursing writing service and save your time. We guarantee high quality, on-time delivery, and 100% confidentiality.
- Nursing Careers
- Nursing Paper Solutions
- Nursing Theories
- Nursing Topics and Ideas
- Nursing Writing Guides
Related Posts
- How to become a Hospice Nurse
- How to Become a Labor and Delivery Nurse
- Role of an Intensive Care Unit Nurse: How to Become, Role and Requirements
Important Links
Knowledge base, paper examples, nursing writing services.
Nursingstudy.org helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Phone: +1 628 261 0844
Mail: [email protected]

We Accept:

@2015-2024, Nursingstudy.org

Nursing Case Study

ScienceDirect posted a nursing ethics case study where an end-stage prostate cancer patient, Mr. Green, confided to nursing staff about his plan to commit suicide. The patient asked the nurse to keep it a secret. The ethical problem is whether the nurse should tell the health care team members about the patient’s thought without his permission. The best ethical decision for this nursing case study was to share this critical information with other health care professionals, which was the action the nurse took. The team adhered to the proper self-harm and suicide protocol. The appropriate team performed a palliative therapy. As a result, the patient didn’t harm himself and died peacefully a few months after he was discharged.
What Is a Nursing Case Study? A nursing case study is a detailed study of an individual patient. Through this type of research, you can gain more information about the symptoms and the medical history of a patient. It will also allow you to provide the proper diagnoses of the patient’s illness based on the symptoms he or she experienced and other affecting factors. Nursing students usually perform this study as part of their practicum, making it an essential experience because, through this research methodology , they can apply the lessons they have learned from school. The situation mentioned above was an excellent example of a nursing case study.
Nursing Case Study Format
1. introduction.
Purpose: Briefly introduces the case study, including the main health issue or condition being explored. Background: Provides context for the patient scenario, outlining the significance of the case in nursing practice. Objectives: Lists the learning objectives or goals that the case study aims to achieve.
2. Patient Information
Demographics: Age, gender, ethnicity, and relevant personal information. Medical History: Past medical history, including any chronic conditions, surgeries, or significant health events. Current Health Assessment: Presents the patient’s current health status, including symptoms, vital signs, and results from initial examinations.
3. Case Description
Clinical Presentation: Detailed description of the patient’s presentation, including physical examination findings and patient-reported symptoms. Diagnostic Findings: Summarizes diagnostic tests that were performed, including lab tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostic procedures, along with their results. Treatment Plan: Outlines the initial treatment provided to the patient, including medications, therapies, surgeries, or other interventions.
4. Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Diagnoses: Identifies the nursing diagnoses based on the assessment data. Goals and Outcomes: Establishes short-term and long-term goals for the patient’s care, including expected outcomes. Interventions: Describes specific nursing interventions planned or implemented to address each nursing diagnosis and achieve the stated goals. Evaluation: Discusses the effectiveness of the nursing interventions, including patient progress and any adjustments made to the care plan.
5. Analysis
Critical Analysis: Analyzes the case in depth, considering different aspects of patient care, decision-making processes, and the application of nursing theories and principles. Reflection: Reflects on the nursing practice, lessons learned, and how the case study has impacted the understanding and application of nursing knowledge.
6. Conclusion
Summary: Provides a concise summary of the key points from the case study, including the patient outcome and the nursing care impact. Implications for Practice: Discusses the implications of the case for nursing practice, including any changes to practice or policy that could improve patient care. Recommendations: Offers recommendations for future care or areas for further study based on the case study findings.
Examples of Nursing Case Study
Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Introduction: A 58-year-old male with a history of hypertension and smoking presents to the emergency department with chest pain. This case study explores the nursing management for patients with AMI. Patient Information: Demographics: 58-year-old male, smoker. Medical History: Hypertension, no previous diagnosis of heart disease. Current Health Assessment: Reports severe chest pain radiating to his left arm, sweating, and nausea. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient appeared in distress, clutching his chest. Diagnostic Findings: ECG showed ST-elevation in anterior leads. Troponin levels were elevated. Treatment Plan: Immediate administration of aspirin, nitroglycerin, and morphine for pain. Referred for emergency coronary angiography. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Acute pain related to myocardial ischemia. Goals: Relieve pain and prevent further myocardial damage. Interventions: Monitoring vital signs, administering prescribed medications, and providing emotional support. Evaluation: Pain was managed effectively, and the patient was stabilized for angiography. Analysis: The timely nursing interventions contributed to stabilizing the patient’s condition, showcasing the critical role nurses play in acute care settings. Conclusion: This case highlights the importance of quick assessment and intervention in patients with AMI, emphasizing the nurse’s role in pain management and support.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes in a Pediatric Patient Introduction: A 10-year-old female diagnosed with type 1 diabetes presents for a routine check-up. This case study focuses on the nursing care plan for managing diabetes in pediatric patients. Patient Information: Demographics: 10-year-old female. Medical History: Diagnosed with type 1 diabetes six months ago. Current Health Assessment: Well-controlled blood glucose levels, but expresses difficulty with frequent insulin injections. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient is active, engaging in school activities but struggles with diabetes management. Diagnostic Findings: HbA1c is 7.2%, indicating good control. Treatment Plan: Insulin therapy, carbohydrate counting, and regular blood glucose monitoring. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Risk for unstable blood glucose levels. Goals: Maintain blood glucose within target range and increase patient comfort with diabetes management. Interventions: Education on insulin pump use, dietary advice, and coping strategies. Evaluation: Patient showed interest in using an insulin pump and understood dietary recommendations. Analysis: This case emphasizes the importance of education and emotional support in managing chronic conditions in pediatric patients. Conclusion: Effective management of type 1 diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that includes education, technological aids, and psychological support.
Elderly Care for Alzheimer’s Disease Introduction: An 82-year-old female with Alzheimer’s disease presents with increased confusion and agitation. This case study examines the complexities of caring for elderly patients with Alzheimer’s. Patient Information: Demographics: 82-year-old female. Medical History: Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis. Current Health Assessment: Increased confusion, agitation, and occasional aggression. Case Description: Clinical Presentation: Patient exhibits signs of advanced Alzheimer’s with memory loss and disorientation. Diagnostic Findings: Cognitive tests confirm the progression of Alzheimer’s. Treatment Plan: Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation, memory aids, and safety measures in the home. Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnoses: Impaired memory related to Alzheimer’s disease. Goals: Reduce agitation and prevent harm. Interventions: Use of calming techniques, establishing a routine, and environmental modifications. Evaluation: Agitation was reduced, and the patient’s safety was improved through environmental adjustments. Analysis: The case underscores the need for tailored interventions to manage Alzheimer’s symptoms and improve the quality of life for the elderly. Conclusion: Nursing care for Alzheimer’s patients requires a multifaceted approach focusing on safety, symptom management, and patient dignity.
Nursing Case Study Topics with Samples to Edit & Download
- Telehealth Nursing
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing
- Geriatric Nursing Care
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care
- Pediatric Nursing
- Emergency and Critical Care Nursing
- Chronic Disease Management
- Nursing Ethics and Patient Rights
- Infection Control and Prevention
- Oncology Nursing
- Nursing Leadership and Management
- Cultural Competence in Nursing
- Substance Abuse and Addiction Nursing
- Technological Innovations in Nursing
- Nursing Education and Training
Nursing Case Study Examples & Templates
1. nursing case study template.

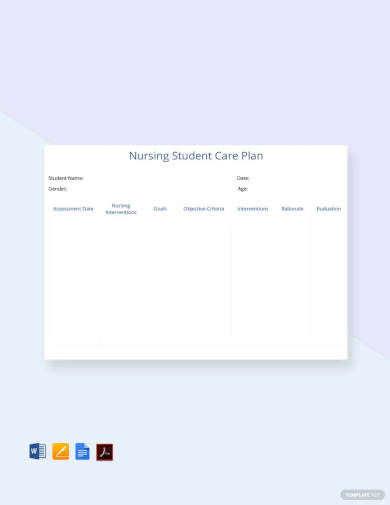
2. Free Nursing Student Care Plan Template
3. Nursing Action Case Study Example

4. Hospital Nursing Care Case Study Example

5. Printable Nursing Health Case Study Example

professays.com
6. Fundamentals of Nursing Case Study Example

secure-ecsd.elsevier.com
7. Sample Nursing Case Study Example

caresearch.com.au
8. Nursing Research Case Study Example
9. Standard Nursing Case Study Example

resourcecenter.ovid.com
10. Nursing Disability Case Study Example

careerswales.com
11. Nursing care Patients Case Study Example

12. School of Nursing Case Study Example

ebn.bmj.com
13. Evaluation of Nursing Care Case Study Example
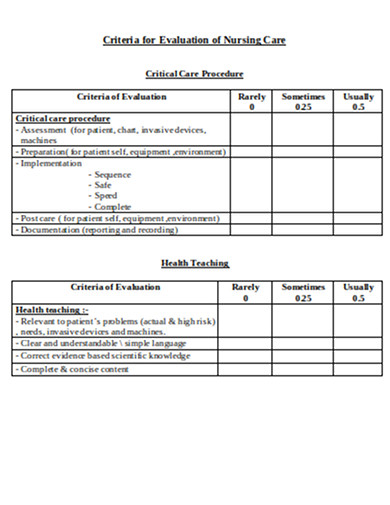
philadelphia.edu
Nursing Case Study Segments
Typically, a nursing case study contains three main categories, such as the items below.
1. The Status of a Patient
In this section, you will provide the patient’s information, such as medical history, and give the current patient’s diagnosis, condition, and treatment. Always remember to write down all the relevant information about the patient. Other items that you can collect in this stage are the reasons for the patient to seek medical care and the initial symptoms that he or she is experiencing. After that, based on the gathered information, you will explain the nature and cause of the illness of the patient.
2. The Nursing Assessment of the Patient
In this stage, you will need to prepare your evaluation of the patient’s condition. You should explain each observation that you have collected based on the vital signs and test results. You will also explain each nursing diagnosis that you have identified and determine the proper nursing care plan for the patient.
3. The Current Care Plan and Recommendations
Describe the appropriate care plan that you can recommend to the patient based on the diagnosis, current status, and prognosis in detail, including how the care plan will affect his or her life quality. If needed, you can also evaluate the patient’s existing care plan and give recommendations to enhance it. It is also crucial to cite relevant authoritative sources that will support your recommendations .
Objectives of Nursing Case Study
Nursing case studies are integral educational tools that bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application in patient care. They serve several key objectives essential for the development of nursing students and professionals. Here are the primary objectives of nursing case studies:
1. Enhance Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning
Case studies encourage nurses to analyze complex patient scenarios, make informed decisions, and apply critical thinking skills to solve problems. They simulate real-life situations, requiring nurses to evaluate data, consider multiple outcomes, and choose the best course of action.
2. Improve Diagnostic Skills
Through the detailed analysis of patient information, symptoms, and diagnostic results, nursing case studies help improve diagnostic skills. They allow nurses to practice interpreting clinical data to identify patient conditions and understand the underlying causes of symptoms.
3. Facilitate Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Nursing case studies provide a direct bridge between classroom learning and clinical practice. They offer a practical venue for applying theoretical knowledge about anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and nursing theories to real-world patient care situations.
4. Promote Understanding of Comprehensive Patient Care
These studies emphasize the importance of holistic care, considering the physical, emotional, social, and psychological aspects of patient well-being. Nurses learn to develop comprehensive care plans that address all facets of a patient’s health.
5. Encourage Reflective Practice and Self-Assessment
Reflecting on case study outcomes enables nurses to evaluate their own decision-making processes, clinical judgments, and actions. This self-assessment promotes continuous learning and professional growth by identifying areas for improvement.
6. Foster Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Case studies often involve scenarios that require collaboration among healthcare professionals from various disciplines. They teach nurses the value of teamwork, communication, and the integration of different expertise to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
7. Enhance Patient Education and Advocacy Skills
By working through case studies, nurses improve their ability to educate patients and families about health conditions, treatment plans, and preventive measures. They also learn to advocate for their patients’ needs and preferences within the healthcare system.
8. Prepare for Real-Life Challenges
Nursing case studies prepare students and new nurses for the unpredictability and challenges of real-life clinical settings. They provide safe, controlled environments to practice responses to emergencies, ethical dilemmas, and complex patient needs without the risk of actual harm.
Steps in Nursing Process
Whether you are handling a patient with schizophrenia, pneumonia, diabetes, appendicitis, hypertension, COPD, etc, you will need to follow specific steps to ensure that you are executing the critical nursing process.
1. Assess the Patient
The first step of the nursing process requires critical thinking skills as it involves gathering both subjective and objective data. Subjective data includes verbal statements that you can collect from the patient or caregiver. In contrast, objective information refers to measurable and tangible data, such as vital signs, height, weight, etc. You can also use other sources of information, such as electronic health records, and friends that are in direct contact with the patient.
2. Diagnose the Patient
This critical step will help you in the next steps, such as planning and implementation of patient care. In this step, you will formulate a nursing diagnosis by applying clinical judgment. As a nurse, the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) will give you an up-to-date nursing diagnosis list, which will allow you to form a diagnosis based on the actual health problem.
3. Plan for a Proper Patient Care Plan
This part is where you will plan out the appropriate care plan for the patient. You will set this goal following the evidence-based practice (EDP) guidelines. The goal you will set should be specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely ( SMART ).
4. Implement the Plan
In this stage, you can execute the plan that you have developed in the previous step. The implementation may need interventions such as a cardiac monitor, medication administration, etc.
5. Evaluate the Results
It is crucial to remember that every time the team does an intervention, you must do a reassessment to ensure that the process will lead to a positive result. You may need to reassess the patient depending on his progress, and the care plan may be modified based on the reassessment result.

Where to find nursing case studies?
Nursing case studies can be found in a variety of academic, professional, and medical resources. Here are some key places to look for nursing case studies:
- Academic Journals : Many academic journals focus on nursing and healthcare and publish case studies regularly. Examples include the “Journal of Clinical Nursing,” “Nursing Case Studies,” and “American Journal of Nursing.”
- University and College Libraries : Many academic institutions provide access to databases and journals that contain nursing case studies. Libraries often have subscriptions to these resources.
- Online Medical Libraries : Websites like PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Wiley Online Library offer a vast collection of nursing and medical case studies.
- Professional Nursing Organizations : Organizations such as the American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National League for Nursing (NLN) often provide resources, including case studies, for their members.
- Nursing Education Websites : Websites dedicated to nursing education, such as Lippincott NursingCenter and Nurse.com, often feature case studies for educational purposes.
- Government Health Websites : The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) sometimes publish case studies related to public health nursing and disease outbreaks.
- Nursing Textbooks and eBooks : Many nursing textbooks and eBooks include case studies to illustrate key concepts and scenarios encountered in practice.
- Online Nursing Forums and Communities : Forums and online communities for nursing professionals may share or discuss case studies as part of their content.
- Conference Proceedings : Nursing and healthcare conferences often include presentations of case studies. Many of these are published in the conference proceedings, which may be accessible online.
Carrying out a nursing case study can be a delicate task since it puts the life of a person at stake. Thus, it requires a thorough investigation. With that said, it is essential to gain intensive knowledge about this type of study. Today, we have discussed an overview of how to conduct a nursing case study. However, if you think that you are having problems with your writing skills , we recommend you to consider looking for an essay writing service from the experts in the nursing department to ensure that the output follows the appropriate writing style and terminology.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
📕 Studying HQ
10 nursing case study analysis examples [format + structure], bob cardens.
- August 6, 2022
If you are a nursing student, you may be asked to write a case study analysis. This can be a daunting task, but it is possible to do if you follow some simple steps. Here we include Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples to help you get started.
First, read the case study and make sure you understand the situation. Next, identify the key players involved and their role in the case. Finally, analyze the data presented and draw your own conclusions.
Writing a case study analysis can be challenging, but it is also an excellent way to learn more about nursing care. By taking the time to understand the situation and identify the key players, you will be able to gain valuable insights that can be applied to future cases.
What You'll Learn
10 Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
Nursing case study analysis format and structure.
When it comes to writing a case study analysis, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, there is a general format and structure that you can follow to ensure your analysis is well-organized and flows smoothly. Here are the basics:
A nursing case study is a detailed study of a patient that is encountered by a nurse. The purpose of the case study is to provide a comprehensive view of the patient’s health condition and history. Nurse practitioners use case studies to enhance their ability to care for patients by providing them with a more complete picture of the patient’s health. Nurse practitioners may use different formats for their nursing case studies. However, all case studies should include certain key elements. These key elements include:
As a nursing practitioner, you will be responsible for analyzing patient cases and providing care based on your findings. There are key elements that you must take into account when performing a case analysis in order to ensure that you are providing the best possible care for your patients.
- The first element is the patient’s history. You will need to obtain a complete medical history in order to understand the background of the case and identify any potential risk factors.
- Next, you will need to perform a physical examination of the patient. This will help you to identify any physical signs or symptoms that may be related to the case.
- You will also need to order and review any laboratory tests or imaging studies that have been performed on the patient. These results can provide valuable information about the patient’s condition.
- Once you have gathered all of this information, you will need to start piecing together the puzzle to form a diagnosis. This process will involve synthesizing all of the information you have gathered and making a determination about what is causing the patient’s symptoms.
- Once you have made a diagnosis, you can start developing a treatment plan. This plan should be tailored specifically to the needs of the individual patient.
When writing a nursing case study, nurse practitioners should use a clear and concise format. The format should be easy to follow and understand. Nurse practitioners should also include all of the key elements in their nursing case studies. Nursing Case Study Analysis Examples
![10 nursing case study analysis examples [format + structure] 1 Nursing case study analysis examples](https://i0.wp.com/studyinghq.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/113124-84-CHECK.png?resize=84%2C84&ssl=1)
How to write a case study assignment
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a real-life situation or incident, as a way to illustrate content and theory to students. It is usually presented as a written report, but can also be done in the form of a presentation, video, or multimedia production.
Case studies are used in many different disciplines, including business, law, psychology, nursing, social work, and medical sciences.
A case study assignment is a type of paper that requires you to analyze a real-life or fictional situation and offer possible solutions. This can be a challenging task, but if you follow some basic guidelines, you can write a successful case study assignment.
Here are some tips on how to write a case study assignment:
- Read the case study carefully. Make sure you understand the situation and the problem that needs to be solved.
- Research the subject matter. You will need to have a good understanding of the relevant theories and concepts in order to offer possible solutions.
- Read the case study carefully. This may seem obvious, but it is important to get a clear understanding of the situation before you start writing. Make sure you have all the relevant facts and figures to hand before you start.
- Identify the key issues. Once you have read and understood the case study, you need to identify the key issues that it raises. These will form the basis of your analysis.
- Research the law/theory applicable to the key issues. Once you have identified the key issues, you need to research the law or theory that applies to them. This will help you to form your arguments and conclusions.
- Write your paper. Be sure to present your analysis in a clear and concise manner. Your paper should be well-organized and well-written
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free Study Database for Essays
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved
How to Write a Nursing Case Study [Examples, Format, & Tips]
✒️ case study topics for nursing students.
- 🩺️ The Basics
- 💉 Nursing Case Study: Writing Rules
📑 Nursing Case Study Format
📝 nursing case study examples.
- ⏱️ Tips on Quick Writing
🔗 References
A nursing case study is an in-depth analysis of the health situation of an individual patient.

The analysis is based on:
- medical history,
- other relevant criteria.
In most cases, you will be asked to diagnose to suggest the first aid measures. Alternatively, nurses can be asked to describe a patient in their practice and analyze the correctness of their actions. The purpose is to recreate a realistic hospital setting in the classroom and make students reflect on the treatment process from diagnosis to treatment.
- Anaphylactic shock in a teenager with peanut allergy.
- Non-compliant patient with diabetes: ways to improve adherence.
- Telehealth intervention for managing chronic disease.
- Communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy in a rural community.
- Postpartum hemorrhage in a new mother: risk factors and interventions.
- Ways to improve recognition of dehydration in aging adults.
- The effective ways of maintaining work-life balance for nurses.
- Cultural competency in providing care to migrants and refugees.
- Why should every patient’s medical history remain confidential?
- The use of massage therapy in relieving pain.
- The challenges facing medicine in 2024.
- How does modern technology impact nursing?
- The significance of regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider.
- What are the primary treatments for postpartum depression?
- The use of steroids in cancer treatment.
🩺️ Nursing Case Study: What Is It About?
As a nursing student, you should understand that no two patients are the same. Each has a unique clinical record and condition. And although most nursing case study tasks will ask you to suggest a diagnosis or treatment, your focus should rest on the patient.
Busy nurses can sometimes see their patients in the framework of an illness to be treated or a procedure to be fulfilled. But you should do your best to remember that each patient is a living person with a complex set of needs, emotions, and preferences. A ready-made textbook answer is rarely the best solution for them. Moreover, it rarely helps to analyze a condition in isolation from the patient.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don’t do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types.
Once again:
A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient’s condition. Meanwhile, a nursing essay will explore the disease, prevention methods, treatment, or possible consequences of the disease.
Even if the case is hypothetical, it should focus on the suggested reality. On the other hand, essays are usually literature-based. You are expected to do some reading for a case study too, but you should research and present the information within the context of the patient. In simple terms, a case study uses information in the actual application, and an essay uses it for the sake of generalized suggestions.
💉 How to Write a Nursing Case Study: 3 Key Rules
- Do the fieldwork. Before setting your hands to writing, you should collect all of the available materials: clinical notes, results of medical tests, x-rays, sickness records, etc. Use this information to draw a clear picture of the story. It is always helpful to ask yourself, “What is interesting or unusual about this patient’s condition?” In the course of writing, recall your answer from time to time not to get lost in words. It will help you to convey a definite and appropriate message.
- Stick to the facts. A nursing case study should be an accurate description of the actual situation. Restrain from speculating about the inherent mechanisms of the illness or the general treatment methodology. In fact, students are rarely prepared enough to discuss pathology and physiology. Leave this to reputable experts. The best result you can provide in a case study is an honest account of clinical events.
- Concentrate on the patients and their progress. Remember that a nursing case study is a story of a patient’s progress and not a narrative about their nurse. No matter how efficiently the medical specialist acted, it would be incorrect to add any praiseful remarks. The optimal way is to tell the story in its logical and time order and outline the result of treatment. In this case, the outcome will speak for itself.
Introduction
It is where you should tell the reader why this case is interesting . Place your study in a social or historical context. If, during your preliminary research, you found some similar cases, describe them briefly. If you had a hard time diagnosing the patient or your proposed treatment is complicated, mention it here. Don’t forget to cite the references to each of them!
The introduction should not exceed several paragraphs. The purpose is to explain why the reader will benefit from reading about the case.

Case Presentation
- Why did the patient seek medical help? (Describe the symptoms.)
- What is known about the patient? (Mention only the information that influenced your diagnosis. Otherwise, explain why some information is irrelevant to the diagnosis.)
- Stick to the narrative form. (Make it a story!)
- What are the variants for diagnosis? (Make a shortlist of possible disorders that fall under the patient’s symptoms. But make it specific: not just “pneumonia” but “bilateral pneumonia,” for example. Besides, this point is optional.)
- What were the results of your clinical examination? (If you saw the patient in person.)
- Explain the results of lab tests. (The words “positive” or “negative” are not always clear.)
Actions and Their Results
This section describes the care that has been provided and/or is planned. You can answer the following questions in narrative form . If some information is missing, skip the point:
- What preliminary actions have been taken? (Be specific: not just “wound care,” but “wound cleaning and dressing.”)
- How long has the patient been under care?
- Has the previous treatment given any visible result?
- Why was it suspended or finished?
- Why did the patient withdraw from treatment (if applicable)?
- How could you improve the patient’s condition if the result was negative?
- If the disease is incurable (like in the case of diabetes), which activities would stabilize the patient’s condition?
- If possible, include the patient’s reports of their own physical and mental health.
In this section, you should identify your questions about the case. It is impossible to answer all of them in one case study. Likewise, it is unreal to suggest all the relevant hypotheses explaining the patient’s condition. Your purpose is to show your critical thinking and observation skills. Finalize your conclusion by summarizing the lessons you learned from the nursing case study.
Whenever you directly or indirectly cite other sources or use data from them, add these books and documents to the references list. Follow the citation style assigned by your professor. Besides, 15 items are already too much. Try to make a list of up to 10. Using textbooks as references can be viewed as bad manners.
Include all the tables, photographs, x-rays, figures, and the journal of medication usage in this section. Unless required otherwise in the assignment, start each item from a new page, naming them “Appendix A,” “Appendix B…”.
Below you will find case study samples for various topics. Using them as a reference will improve your writing. If you need more ideas, you are welcome to use our free title-generating tool .
- Case study: healing and autonomy.
- Sara’s case study: maternal and child nursing.
- COPD medical diagnostics: case study.
- Care standards in healthcare institutions: case study.
- Acute bacterial prostatitis: case study analysis.
- Alzheimer disease: the patient case study.
- The treatment of foot ulcers in diabetic patients: case study.
- Hypertension: C.D’s case study.
- Myocardial infarction: cardiovascular case study.
- Major depressive disorder case.
- Case study of the patient with metabolic syndrome .
- Pulmonary analysis case study .
- Older adults isolation: Case study .
- The holistic care: Case study .
- Medical ethics: Case study .
- Patient diagnoses and treatment: Case study .
- Obesity case study: Mr. C .
- Nurse Joserine: Case study problems .
- Chronic stable angina: Case study .
- Fetal abnormality: Case study .
- Researching SOAP: Case study .
- Case study for a patient with hormonal disorders .
- Obesity in the elderly: The case study .
- “Walking the Tightrope”: A case study analysis .
- ARNP approach: Case study analysis .
- Case study on biomedical ethics in the Christian narrative .
- Thermal injury: Case study .
- Ethical dilemma in nursing: Case study .
- Asthma: A case study of the patient .
- Asthma discharge plan: Mini case study .
- Case study: An ethics of euthanasia .
- Case study: Head-to-toe assessment steps .
- Pain management strategies: Case study .
- Case study: Inflammatory bowel disease .
- Sleep deprivation and insomnia: The case study .
- The case study of a heart failure .
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: Disease case study .
- Case study: Hardy Hospital case summary .
- Obesity and its complications: Case study .
- Angina disease case study .
- Nursing ethics case study .
- Case study of a patient: Assessment and treatment plan .
- Cecile case study: Mrs. J .
- Nursing power in the emergency department: Case study .
- Heart failure case study: Mrs. J .
- Application of ethics in nursing: Case study .
- Sudden visual impairment: Case study .
- Epidemiology case study: Outbreak at Watersedge — Public health discovery game .
- Wellness of senior citizens: Case study .
- Healthcare organization evaluation: Case study of Banner Health .
⏱️ Bonus: Tips on Writing a Case Study in Record Time
Need to prepare a case study on nursing or in another field? Below you’ll find a collection fo tips that will help you do it as quickly as possible!
3 Shortcuts for a Quick Start
If you’re about to start writing a case study, you should check yourself if you’re not doing any of the following:
- spending too much time on selecting a topic;
- reading too much before selecting a topic;
- making conclusions too early – creating bias.
Instead of killing time doing the three useless things discussed above, consider these:
- Choose approach. Note that there are 2 major approaches to case studies: the analytical approach (investigating possible reasons without making any conclusions) and problem-oriented approach (focusing on a particular problem and investigating it).
- Skim some sources (DON’T READ THEM). Select several sources. Simply skim abstracts and conclusions.
- Start making notes early. Simply reading is ineffective unless you’re lucky to have a phenomenal memory. Always make notes of any useful arguments.
4 Shortcuts Not to Get Stuck in the Middle
Even if you kick started your case study, it’s too early to celebrate it. Consider the following traps in the middle of the project:
- Watch the structure. The classic logical structure is your formula of success. It will help you move from one point to another without the unnecessary procrastination:
- Respect the logic. Make your case study flow – make logical transitions between the different parts and make it consistent. Avoid changing your position throughout the paper.
- Be detail-oriented. Any trifle deserves attention when you write a case study.
- Avoid bias. Be sure that all your opinions are based on the specific arguments form the case study. Avoid pouring your biased views into the project.
3 Shortcuts for a Happy Ending
- Offer a realistic solution. College case study is a rehearsal of real-life situations. Take the responsibility for your suggestions.
- Keep your conclusion short. Avoid repeating the details and don’t include any new information.
- Consider creating a Power Point. If your task is not only writing a case study, but also presenting it – why not create PowerPoint slides to help you?
As the last step on your way to a perfect nursing case study, prepare the title page. Its format usually depends on the professor’s requirements. But if you know the citation style, our Title Page Maker is a perfect tool to apply the right formatting and accelerate the process. And if you have any know-how on how to write a medical case study, you are very welcome to share it with other students in the comments below.
❓ Nursing Case Study: FAQ
What is a case study in nursing.
A nursing case study explores the condition of a patient. It is based on previous clinical records, lab reports, and other medical and personal information. A case study focuses on the patient and describes the treatment that was (or should be) applied and its (expected) outcome.
How to Write a Nursing Case Study?
- Collect the bulk of data available about the patient.
- Read literature about the diagnosed condition.
- Focus on the individual patient and their symptoms.
- Describe the situation and outline its development in time.
- Analyze the actions of the medical personnel that have been done.
- Plan further treatment of the patient.
Why Are Case Studies Good for Nursing Students?
Nursing case studies offer you a priceless opportunity to gain experience of different patient conditions and cure methods without visiting the clinic. You can think about whether the proposed treatment was appropriate or wrong and suggest a better solution. And the best thing, your teacher will indicate your mistakes (and no patient will be hurt in the process).
Why Are Case Studies Important in Nursing?
- You learn to distinguish the relevant data and analyze it.
- You learn to ask the right questions.
- You learn to evaluate the severity of symptoms.
- You learn to make better diagnoses.
- You train your critical thinking in terms of treatment methods
- Case studies are in-class simulators of authentic atmosphere in a clinical ward.
- What is a case study? | Evidence-Based Nursing
- Case Studies – Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Case Study Research Design in Nursing
- Case study report for Nursing | Learning Lab – RMIT University
- Case Study or Nursing Care Study? – jstor
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.

How to Write a Case Study Paper for Nursing
A well-written case study paper for a nursing program requires some planning and consideration. All too often, students begin writing before they complete appropriate, preliminary steps. Ideally, before you start a paper, you should already have determined the focus and format of it. You will then follow this up with a fact-gathering step in which you will gather and collate the content of your paper. Finally, there is the construction/execution step in which you will write the paper in a standard format (such as the APA style) and edit it.
A nursing case study paper contains several sections that fall into three categories:
1. The status of the patient
- Demographic data
- Medical History
- Current diagnosis and treatment
2. The nursing assessment of the patient
- Vital signs and test results
- Nursing observations (i.e., range of motion, mental state)
3. Current Care Plan and Recommendations
- Details of the nursing care plan (including nursing goals and interventions)
- Evaluation of the current care plan
- Recommendations for changes in the current care plan
Patient Status
The first portion of the case study paper will talk about the patient — who they are, why they are being included in the study, their demographic data (i.e., age, race), the reason(s) they sought medical attention and the subsequent diagnosis. It will also discuss the role that nursing plays in the care of this patient.
Next, thoroughly discuss any disease process. Make sure you outline causes, symptoms, observations, and how preferred treatments can affect nursing care. Also, describe the history and progression of the disease. Some important questions for you to answer are: 1) What were the first indications that there was something wrong, and 2) What symptoms convinced the patient to seek help?
Nursing Assessment
When you are discussing the nursing assessment of the patient, describe the patientΓÇÖs problems in terms of nursing diagnoses. Be specific as to why you have identified a particular diagnosis. For example, is frequent urination causing an alteration in the patientΓÇÖs sleep patterns? The nursing diagnoses you identify in your assessment will help form the nursing care plan.
Current Care Plan and Recommendations for Improvement
Describe the nursing care plan and goals, and explain how the nursing care plan improves the quality of the patientΓÇÖs life. What positive changes does the nursing care plan hope to achieve in the patientΓÇÖs life? How will the care plan be executed? Who will be responsible for the delivery of the care plan? What measurable goals will they track to determine the success of the plan?
The final discussion should be your personal recommendations. Based on the current status of the patient, the diagnosis, prognosis, and the nursing care plan, what other actions do you recommend can be taken to improve the patientΓÇÖs chances of recovery? You must support your recommendations with authoritative sources and cite appropriately per APA style guidelines.
Creating a well-written nursing case study paper doesnΓÇÖt need to be a grueling challenge. It can be gratifying, and itΓÇÖs good practice for assessing patients while out in the field, too. Keep in mind that your instructor will not only grade you on the quality of the content of your paper but by how you apply the APA style, as well. If you find that you are spending too much time formatting your paper, consider using formatting software as a helpful tool to ensure accuracy, so you donΓÇÖt lose points on a well-written paper because of some formatting errors.
For more information about APA or MLA formats, contact us today.
David Plaut
David Plaut is the founder of Reference Point Software (RPS). RPS offers a complete suite of easy-to-use formatting template products featuring MLA and APA style templates, freeing up time to focus on substance while ensuring formatting accuracy. 
Reference Point Software is not associated with, endorsed by, or affiliated with the American Psychological Association (APA) or with the Modern Language Association (MLA).
Tags: medical writing tips , nurse writing tips , reference point software
Comments are closed.

How to Write a Nursing Case Study Paper (A Guide)

Most nursing students dread writing a nursing case study analysis paper, yet it is a mandatory assignment; call it a rite of passage in nursing school. This is because it is a somewhat tricky process that is often overwhelming for nursing students. Nevertheless, by reading this guide prepared by our best nursing students, you should be able to easily and quickly write a nursing case study that can get you an excellent grade.
How different is this guide from similar guides all over the internet? Very different!
This guide provides all the pieces of information that one would need to write an A-grade nursing case study. These include the format for a nursing case study, a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing case study, and all the important tips to follow when writing a nursing case study.
This comprehensive guide was developed by the top nursing essay writers at NurseMyGrade, so you can trust that the information herein is a gem that will catapult your grades to the next level. Expect updates as we unravel further information about writing a nursing case study.
Now that you know you’ve discovered a gold mine , let’s get right into it.
What Is a Nursing Case Study?
A nursing case study is a natural or imagined patient scenario designed to test the knowledge and skills of student nurses. Nursing case study assignments usually focus on testing knowledge and skills in areas of nursing study related to daily nursing practice.
As a nursing student, you must expect a nursing case study assignment at some point in your academic life. The fact that you are reading this post means that point is now.
While there is no standard structure for writing a nursing case study assignment, some things or elements must be present in your nursing assignment for your professor to consider it complete.
In the next section, you will discover what your instructor n expects in your nursing case study analysis. Remember, these are assignments where you are given a case study and are expected to write a case analysis report explaining how to handle such scenarios in real-life settings.
The Nursing Case Study Template
The typical nursing case study has nine sections. These are:
- Introduction
- Case presentation (Patient info, history, and medical condition)
- Diagnosis/Nursing assessment
- Intervention/Nursing care plan
- Discussion and recommendations
The Structure of a Nursing Case Study Analysis
You now know what nursing professors expect in a nursing case study analysis. In this section, we will explain what to include in each section of your nursing case study analysis to make it an excellent one.
1. Title page
The title page is essential in all types of academic writing. You must include it in your nursing case study analysis or any other essay or paper. And you must include it in the format recommended by your college.
If your college has no specific title page format, use the title page format of the style requested in the assignment prompt. In nursing college, virtually all assignments should be written in Harvard or APA format .
So, check your assignment prompt and create your title page correctly. The typical title page should include the topic of your paper, your name, the name of your professor, the course name, the date you are submitting the paper, and the name of your college.
2. Abstract
Most nursing professors require you to include an abstract in your nursing case study analysis. And even when you are not explicitly required to write one, it is good to do so. Of course, you should consult with your professor before doing so.
When writing an abstract for your paper, make sure it is about 200 words long. The abstract should include a brief summary of the case study, including all the essential information in the patient presentation, such as the history, age, and current diagnosis.
The summary should also include the nursing assessment, the current interventions, and recommendations.
3. Introduction
After writing the title page and the abstract, start writing the introduction. The introduction of a nursing case study analysis must briefly include the patient’s presentation, current diagnosis and medication, and recommendations. It must also include a strong thesis statement that shows what the paper is all about.
You shouldn’t just write an introduction for the sake of it. If you do so, your introduction will be bland. You need to put in good effort when writing your introduction. The best way to do this is to use your introduction to show you understand the case study perfectly and that you will analyze it right.
You can always write your introduction last. Many students do this because they believe writing an introduction last makes it more precise and accurate.
4. Case Presentation (Status of the Patient)
After introducing your nursing case study analysis, you should present the case where you outline the patient's status. It is usually straightforward to present a case.
You must paraphrase the patient scenario in the assignment prompt or brief. Focus on the demographic data of the patient (who they are, age, race, height, skin tone, occupation, relationships, marital status, appearance, etc.), why they are in the case study or scenario, reasons they sought medical attention, chief complaint, and current diagnosis and treatment. You should also discuss the actions performed on the patient, such as admission to the ICU, taking vital signs, recommending tests, etc.
In short, everything necessary in the patient scenario should be in your case presentation. You only need to avoid copying the patient scenario or case study word-for-word when writing your case presentation.
5. Diagnosis and Assessment
After the case presentation, you should explain the diagnosis. In other words, you should explain the condition, disease, or medical situation highlighted in the case presentation. For example, if the patient is a heavy smoker and he has COPD, it is at this point that you explain how COPD is linked to heavy smoking.
This is the section where you thoroughly discuss the disease process (pathophysiology) by highlighting the causes, symptoms, observations, and treatment methods. You should relate these to the patient’s status and give concrete evidence. You should describe the progression of the disease from when the client was admitted to a few hours or days after they were stabilized. Consider the first indication of the disease that prompted the patient to seek further medical assistance.
Your paper should also elucidate the diagnostic tests that should be conducted and the differential diagnosis. Ensure that each is given a well-founded rationale.
When explaining the condition, go deep into the pathophysiology. Focus specifically on the patient’s risk factors. Ensure you get your explanation from recent nursing literature (peer-reviewed scholarly journals published in the last 5 years). And do not forget to cite all the literature you get your facts from.
In short, this section should explain the patient’s condition or suffering.
6. Nursing Intervention
After the diagnosis and nursing assessment section, your nursing case study analysis should have an intervention section. This section is also known as the nursing care planning section. What you are supposed to do in this section is to present a nursing care plan for the patient presented in the patient scenario. You should describe the nursing care plan and goals for the patient. Record all the anticipated positive changes and assess whether the care plan addresses the patient's condition.
A good nursing care plan details the patient’s chief complaints or critical problems. It then describes the causes of these problems using evidence from recent medical or nursing literature. It then details the potential intervention for each problem. Lastly, it includes goals and evaluation strategies for the measures. Most professors, predominantly Australian and UK professors, prefer if this section is in table format.
Some nursing professors regard the intervention section (or nursing care plan section) as the most critical part of a nursing case study. This is because this part details precisely how the student nurse will react to the patient scenario (which is what the nursing professors want to know). So, ensure you make a reasonable effort when developing this section to get an excellent grade.
7. Discussion and Recommendations
The intervention section in a nursing case study is followed by a discussion and recommendations section. In this section, you are supposed to expound on the patient scenario, the diagnosis, and the nursing care plan. You should also expound on the potential outcomes if the care plan is followed correctly. The discussion should also explain the rationale for the care plan or its significant bits.
Recommendations should follow the discussion. Recommendations usually involve everything necessary that can be done or changed to manage a patient’s condition or prevent its reoccurrence. Anything that enhances the patient’s well-being can be a recommendation. Just make sure your key recommendations are supported by evidence.
8. Conclusion
This is the second last section of a typical nursing case study. What you need here is to summarize the entire case study. Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations.
At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible.
9. References
This is the last section of a nursing case study. No nursing case study is complete without a references section. You should ensure your case study has in-text citations and a references page.
And you should make sure both are written as recommended in the assignment. The style section is usually Harvard or APA. Follow the recommended style to get a good grade on your essay.
Step-By-Step Guide to Writing a Nursing Case Study
You know all the key sections you must include in a nursing case study. You also know what exactly you need to do in each section. It is time to learn how to write a nursing case study. The process detailed below should be easy to follow because you know the typical nursing case study structure.
1. Understand the Assignment
When given a nursing case study assignment, the first thing you need to do is to read. You need to read two pieces of information slowly and carefully.
First, you need to read the prompt itself slowly and carefully. This is important because the prompt will have essential bits of information you need to know, including the style, the format, the word count, and the number of references needed. All these bits of information are essential to ensure your writing is correct.
Second, you need to read the patient scenario slowly and carefully. You should do this to understand it clearly so that you do not make any mistakes in your analysis.
2. Create a Rough Outline
Failure to plan is a plan to fail. That is not what you are in it for anyway! In other words, do not fail to create an outline for your case study analysis. Use the template provided in this essay to create a rough outline for your nursing case study analysis.
Ensure your outline is as detailed as it can be at this stage. You can do light research to achieve this aim. However, this is not exactly necessary because this is just a rough outline.
3. Conduct thorough research
After creating a rough outline, you should conduct thorough research. Your research should especially focus on providing a credible and evidence-based nursing assessment of the patient problem(s). You should only use evidence from recent nursing or medical literature.
You must also conduct thorough research to develop an effective intervention or nursing care plan. So when researching the patient’s problem and its diagnosis, you should also research the most suitable intervention or do it right after.
When conducting research, you should always note down your sources. So for every piece of information you find, and what to use, you should have its reference.
After conducting thorough research, you should enhance your rough outline using the new information you have discovered. Make sure it is as comprehensive as possible.
4. Write your nursing case study
You must follow your comprehensive outline to write your case study analysis at this stage. If you created a good outline, you should find it very easy to write your nursing case study analysis.
If you did not, writing your nursing case study will be challenging. Whenever you are stuck writing your case study analysis paper, you should re-read the part where we explain what to include in every section of your analysis. Doing so will help you know what to write to continue your essay. Writing a nursing case study analysis usually takes only a few hours.
5. Reference your case study
After writing your case study, ensure you add all in-text citations if you have not already. And when adding them, you should follow the style/format recommended in the assignment prompt (usually APA or Harvard style).
After adding in-text citations exactly where they need to be and in the correct format, add all the references you have used in a references page. And you should add them correctly as per the rules of the style you were asked to use.
Do not forget to organize your references alphabetically after creating your references page.
6. Thoroughly edit your case study
After STEP 5 above, you need to edit your case study. You should edit it slowly and carefully. Do this by proofreading it twice. Proofread it slowly each time to discover all the grammar, style, and punctuation errors. Remove all the errors you find.
After proofreading your essay twice, recheck it to ensure every sentence is straightforward. This will transform your ordinary case study into an A-grade one. Of course, it must also have all the standard sections expected in a case study.
Recheck your case study using a grammarly.com or a similar computer grammar checker to ensure it is perfect. Doing this will help you catch and eliminate all the remaining errors in your work.
7. Submit your case study analysis
After proofreading and editing your case study analysis, it will be 100% ready for submission. Just convert it into the format it is required in and submit it.
Nursing Case Study Tips and Tricks
The guide above and other information in this article should help you develop a good nursing case study analysis. Note that this guide focuses entirely on nursing case scenario-based papers, not research study-based nursing case studies. The tips and tricks in this section should help you ensure that the nursing case study analysis you create is excellent.
1. Begin early
The moment you see a nursing case study assignment prompt, identify a date to start writing it and create your own deadline to beat before the deadline stated in the prompt.
Do this and start writing your case study analysis early before your deadline. You will have plenty of time to do excellent research, develop an excellent paper, and edit your final paper as thoroughly as you want.
Most student nurses combine work and study. Therefore, if you decide to leave a nursing case study assignment until late to complete it, something could come up, and you could end up failing to submit it or submitting a rushed case study analysis.
2. Use the proper terminology
When writing an essay or any other academic paper, you are always encouraged to use the most straightforward language to make your work easy to understand. However, this is not true when writing a nursing case study analysis. While your work should certainly be easy to understand, you must use the right nursing terminology at every point where it is necessary. Failure to do this could damage your work or make it look less professional or convincing.
3. Avoid copying and pasting
If you are a serious nursing student, you know that copying and pasting are prohibited in assignments. However, sometimes copying and pasting can seem okay in nursing case studies. For example, it can seem okay to copy-paste the patient presentation. However, this is not okay. You are supposed to paraphrase the verbatim when presenting the patient presentation in your essay. You should also avoid copy-pasting information or texts directly. Every fact or evidence you research and find should be paraphrased to appear in your work. And it should be cited correctly.
4. Always ask for help if stuck
This is very important. Students are usually overwhelmed with academic work, especially a month or two to the end of the semester. If you are overwhelmed and think you will not have the time to complete your nursing case study analysis or submit a quality one, ask for help. Ask for help from a nursing assignment-help website like ours, and you will soon have a paper ready that you can use as you please. If you choose to get help from us, you will get a well-researched, well-planned, well-developed, and fully edited nursing case study.
5. Format your paper correctly
Many students forget to do proper formatting after writing their nursing case study analyses. Before you submit your paper, make sure you format it correctly. If you do not format your paper correctly, you will lose marks because of poor formatting. If you feel you are not very confident with your APA or Harvard formatting skills, send your paper to us to get it correctly formatted and ready for submission.
Now that you are all set up …
Our company has been among the best-rated nursing homework help companies in the last few years. Thousands of students have benefitted from our many academic writing guides. Many more have benefitted from direct help given by our experts.
- How to write a nursing philosophy statement.
- Writing an abstract poster presentation.
We have experienced nursing experts available every day of the week to provide nursing assignment help. They can easily research and write virtually any nursing assignment, including a nursing case study. So, if the information provided in this article isn’t making you feel any optimistic about writing an excellent nursing case study, get help from us.
Get help by ordering a custom nursing case study through this very website. If you do so, you will get a 100% original paper that is well-researched, well-written, well-formatted, and adequately referenced. Since the paper is original, you can use it anywhere without problems.
Thousands of students trust our company every week, month, and year. Be like them! Trust us for 100% confidentiality and speedy delivery.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Exploring the Change Theories in Nursing

Why you should Pursue Continuing Education as a Nurse?

Integrating Spiritual Texts in a Nursing Paper (A Guide)
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Case study: 33-year-old female presents with chronic sob and cough.
Sandeep Sharma ; Muhammad F. Hashmi ; Deepa Rawat .
Affiliations
Last Update: February 20, 2023 .
- Case Presentation
History of Present Illness: A 33-year-old white female presents after admission to the general medical/surgical hospital ward with a chief complaint of shortness of breath on exertion. She reports that she was seen for similar symptoms previously at her primary care physician’s office six months ago. At that time, she was diagnosed with acute bronchitis and treated with bronchodilators, empiric antibiotics, and a short course oral steroid taper. This management did not improve her symptoms, and she has gradually worsened over six months. She reports a 20-pound (9 kg) intentional weight loss over the past year. She denies camping, spelunking, or hunting activities. She denies any sick contacts. A brief review of systems is negative for fever, night sweats, palpitations, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, neural sensation changes, muscular changes, and increased bruising or bleeding. She admits a cough, shortness of breath, and shortness of breath on exertion.
Social History: Her tobacco use is 33 pack-years; however, she quit smoking shortly prior to the onset of symptoms, six months ago. She denies alcohol and illicit drug use. She is in a married, monogamous relationship and has three children aged 15 months to 5 years. She is employed in a cookie bakery. She has two pet doves. She traveled to Mexico for a one-week vacation one year ago.
Allergies: No known medicine, food, or environmental allergies.
Past Medical History: Hypertension
Past Surgical History: Cholecystectomy
Medications: Lisinopril 10 mg by mouth every day
Physical Exam:
Vitals: Temperature, 97.8 F; heart rate 88; respiratory rate, 22; blood pressure 130/86; body mass index, 28
General: She is well appearing but anxious, a pleasant female lying on a hospital stretcher. She is conversing freely, with respiratory distress causing her to stop mid-sentence.
Respiratory: She has diffuse rales and mild wheezing; tachypneic.
Cardiovascular: She has a regular rate and rhythm with no murmurs, rubs, or gallops.
Gastrointestinal: Bowel sounds X4. No bruits or pulsatile mass.
- Initial Evaluation
Laboratory Studies: Initial work-up from the emergency department revealed pancytopenia with a platelet count of 74,000 per mm3; hemoglobin, 8.3 g per and mild transaminase elevation, AST 90 and ALT 112. Blood cultures were drawn and currently negative for bacterial growth or Gram staining.
Chest X-ray
Impression: Mild interstitial pneumonitis
- Differential Diagnosis
- Aspiration pneumonitis and pneumonia
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Immunodeficiency state and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
- Carcinoid lung tumors
- Tuberculosis
- Viral pneumonia
- Chlamydial pneumonia
- Coccidioidomycosis and valley fever
- Recurrent Legionella pneumonia
- Mediastinal cysts
- Mediastinal lymphoma
- Recurrent mycoplasma infection
- Pancoast syndrome
- Pneumococcal infection
- Sarcoidosis
- Small cell lung cancer
- Aspergillosis
- Blastomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Actinomycosis
- Confirmatory Evaluation
CT of the chest was performed to further the pulmonary diagnosis; it showed a diffuse centrilobular micronodular pattern without focal consolidation.
On finding pulmonary consolidation on the CT of the chest, a pulmonary consultation was obtained. Further history was taken, which revealed that she has two pet doves. As this was her third day of broad-spectrum antibiotics for a bacterial infection and she was not getting better, it was decided to perform diagnostic bronchoscopy of the lungs with bronchoalveolar lavage to look for any atypical or rare infections and to rule out malignancy (Image 1).
Bronchoalveolar lavage returned with a fluid that was cloudy and muddy in appearance. There was no bleeding. Cytology showed Histoplasma capsulatum .
Based on the bronchoscopic findings, a diagnosis of acute pulmonary histoplasmosis in an immunocompetent patient was made.
Pulmonary histoplasmosis in asymptomatic patients is self-resolving and requires no treatment. However, once symptoms develop, such as in our above patient, a decision to treat needs to be made. In mild, tolerable cases, no treatment other than close monitoring is necessary. However, once symptoms progress to moderate or severe, or if they are prolonged for greater than four weeks, treatment with itraconazole is indicated. The anticipated duration is 6 to 12 weeks total. The response should be monitored with a chest x-ray. Furthermore, observation for recurrence is necessary for several years following the diagnosis. If the illness is determined to be severe or does not respond to itraconazole, amphotericin B should be initiated for a minimum of 2 weeks, but up to 1 year. Cotreatment with methylprednisolone is indicated to improve pulmonary compliance and reduce inflammation, thus improving work of respiration. [1] [2] [3]
Histoplasmosis, also known as Darling disease, Ohio valley disease, reticuloendotheliosis, caver's disease, and spelunker's lung, is a disease caused by the dimorphic fungi Histoplasma capsulatum native to the Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River valleys of the United States. The two phases of Histoplasma are the mycelial phase and the yeast phase.
Etiology/Pathophysiology
Histoplasmosis is caused by inhaling the microconidia of Histoplasma spp. fungus into the lungs. The mycelial phase is present at ambient temperature in the environment, and upon exposure to 37 C, such as in a host’s lungs, it changes into budding yeast cells. This transition is an important determinant in the establishment of infection. Inhalation from soil is a major route of transmission leading to infection. Human-to-human transmission has not been reported. Infected individuals may harbor many yeast-forming colonies chronically, which remain viable for years after initial inoculation. The finding that individuals who have moved or traveled from endemic to non-endemic areas may exhibit a reactivated infection after many months to years supports this long-term viability. However, the precise mechanism of reactivation in chronic carriers remains unknown.
Infection ranges from an asymptomatic illness to a life-threatening disease, depending on the host’s immunological status, fungal inoculum size, and other factors. Histoplasma spp. have grown particularly well in organic matter enriched with bird or bat excrement, leading to the association that spelunking in bat-feces-rich caves increases the risk of infection. Likewise, ownership of pet birds increases the rate of inoculation. In our case, the patient did travel outside of Nebraska within the last year and owned two birds; these are her primary increased risk factors. [4]
Non-immunocompromised patients present with a self-limited respiratory infection. However, the infection in immunocompromised hosts disseminated histoplasmosis progresses very aggressively. Within a few days, histoplasmosis can reach a fatality rate of 100% if not treated aggressively and appropriately. Pulmonary histoplasmosis may progress to a systemic infection. Like its pulmonary counterpart, the disseminated infection is related to exposure to soil containing infectious yeast. The disseminated disease progresses more slowly in immunocompetent hosts compared to immunocompromised hosts. However, if the infection is not treated, fatality rates are similar. The pathophysiology for disseminated disease is that once inhaled, Histoplasma yeast are ingested by macrophages. The macrophages travel into the lymphatic system where the disease, if not contained, spreads to different organs in a linear fashion following the lymphatic system and ultimately into the systemic circulation. Once this occurs, a full spectrum of disease is possible. Inside the macrophage, this fungus is contained in a phagosome. It requires thiamine for continued development and growth and will consume systemic thiamine. In immunocompetent hosts, strong cellular immunity, including macrophages, epithelial, and lymphocytes, surround the yeast buds to keep infection localized. Eventually, it will become calcified as granulomatous tissue. In immunocompromised hosts, the organisms disseminate to the reticuloendothelial system, leading to progressive disseminated histoplasmosis. [5] [6]
Symptoms of infection typically begin to show within three to17 days. Immunocompetent individuals often have clinically silent manifestations with no apparent ill effects. The acute phase of infection presents as nonspecific respiratory symptoms, including cough and flu. A chest x-ray is read as normal in 40% to 70% of cases. Chronic infection can resemble tuberculosis with granulomatous changes or cavitation. The disseminated illness can lead to hepatosplenomegaly, adrenal enlargement, and lymphadenopathy. The infected sites usually calcify as they heal. Histoplasmosis is one of the most common causes of mediastinitis. Presentation of the disease may vary as any other organ in the body may be affected by the disseminated infection. [7]
The clinical presentation of the disease has a wide-spectrum presentation which makes diagnosis difficult. The mild pulmonary illness may appear as a flu-like illness. The severe form includes chronic pulmonary manifestation, which may occur in the presence of underlying lung disease. The disseminated form is characterized by the spread of the organism to extrapulmonary sites with proportional findings on imaging or laboratory studies. The Gold standard for establishing the diagnosis of histoplasmosis is through culturing the organism. However, diagnosis can be established by histological analysis of samples containing the organism taken from infected organs. It can be diagnosed by antigen detection in blood or urine, PCR, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The diagnosis also can be made by testing for antibodies again the fungus. [8]
Pulmonary histoplasmosis in asymptomatic patients is self-resolving and requires no treatment. However, once symptoms develop, such as in our above patient, a decision to treat needs to be made. In mild, tolerable cases, no treatment other than close monitoring is necessary. However, once symptoms progress to moderate or severe or if they are prolonged for greater than four weeks, treatment with itraconazole is indicated. The anticipated duration is 6 to 12 weeks. The patient's response should be monitored with a chest x-ray. Furthermore, observation for recurrence is necessary for several years following the diagnosis. If the illness is determined to be severe or does not respond to itraconazole, amphotericin B should be initiated for a minimum of 2 weeks, but up to 1 year. Cotreatment with methylprednisolone is indicated to improve pulmonary compliance and reduce inflammation, thus improving the work of respiration.
The disseminated disease requires similar systemic antifungal therapy to pulmonary infection. Additionally, procedural intervention may be necessary, depending on the site of dissemination, to include thoracentesis, pericardiocentesis, or abdominocentesis. Ocular involvement requires steroid treatment additions and necessitates ophthalmology consultation. In pericarditis patients, antifungals are contraindicated because the subsequent inflammatory reaction from therapy would worsen pericarditis.
Patients may necessitate intensive care unit placement dependent on their respiratory status, as they may pose a risk for rapid decompensation. Should this occur, respiratory support is necessary, including non-invasive BiPAP or invasive mechanical intubation. Surgical interventions are rarely warranted; however, bronchoscopy is useful as both a diagnostic measure to collect sputum samples from the lung and therapeutic to clear excess secretions from the alveoli. Patients are at risk for developing a coexistent bacterial infection, and appropriate antibiotics should be considered after 2 to 4 months of known infection if symptoms are still present. [9]
Prognosis
If not treated appropriately and in a timely fashion, the disease can be fatal, and complications will arise, such as recurrent pneumonia leading to respiratory failure, superior vena cava syndrome, fibrosing mediastinitis, pulmonary vessel obstruction leading to pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure, and progressive fibrosis of lymph nodes. Acute pulmonary histoplasmosis usually has a good outcome on symptomatic therapy alone, with 90% of patients being asymptomatic. Disseminated histoplasmosis, if untreated, results in death within 2 to 24 months. Overall, there is a relapse rate of 50% in acute disseminated histoplasmosis. In chronic treatment, however, this relapse rate decreases to 10% to 20%. Death is imminent without treatment.
- Pearls of Wisdom
While illnesses such as pneumonia are more prevalent, it is important to keep in mind that more rare diseases are always possible. Keeping in mind that every infiltrates on a chest X-ray or chest CT is not guaranteed to be simple pneumonia. Key information to remember is that if the patient is not improving under optimal therapy for a condition, the working diagnosis is either wrong or the treatment modality chosen by the physician is wrong and should be adjusted. When this occurs, it is essential to collect a more detailed history and refer the patient for appropriate consultation with a pulmonologist or infectious disease specialist. Doing so, in this case, yielded workup with bronchoalveolar lavage and microscopic evaluation. Microscopy is invaluable for definitively diagnosing a pulmonary consolidation as exemplified here where the results showed small, budding, intracellular yeast in tissue sized 2 to 5 microns that were readily apparent on hematoxylin and eosin staining and minimal, normal flora bacterial growth.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
This case demonstrates how all interprofessional healthcare team members need to be involved in arriving at a correct diagnosis. Clinicians, specialists, nurses, pharmacists, laboratory technicians all bear responsibility for carrying out the duties pertaining to their particular discipline and sharing any findings with all team members. An incorrect diagnosis will almost inevitably lead to incorrect treatment, so coordinated activity, open communication, and empowerment to voice concerns are all part of the dynamic that needs to drive such cases so patients will attain the best possible outcomes.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Histoplasma Contributed by Sandeep Sharma, MD
Disclosure: Sandeep Sharma declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Muhammad Hashmi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Deepa Rawat declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Sharma S, Hashmi MF, Rawat D. Case Study: 33-Year-Old Female Presents with Chronic SOB and Cough. [Updated 2023 Feb 20]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review Palliative Chemotherapy: Does It Only Provide False Hope? The Role of Palliative Care in a Young Patient With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Adenocarcinoma. [J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017] Review Palliative Chemotherapy: Does It Only Provide False Hope? The Role of Palliative Care in a Young Patient With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Adenocarcinoma. Doverspike L, Kurtz S, Selvaggi K. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2017 May-Jun; 8(4):382-386. Epub 2017 May 1.
- Review Breathlessness with pulmonary metastases: a multimodal approach. [J Adv Pract Oncol. 2013] Review Breathlessness with pulmonary metastases: a multimodal approach. Brant JM. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2013 Nov; 4(6):415-22.
- A 50-Year Old Woman With Recurrent Right-Sided Chest Pain. [Chest. 2022] A 50-Year Old Woman With Recurrent Right-Sided Chest Pain. Saha BK, Bonnier A, Chong WH, Chenna P. Chest. 2022 Feb; 161(2):e85-e89.
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Duong TVH, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review Domperidone. [Drugs and Lactation Database (...] Review Domperidone. . Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). 2006
Recent Activity
- Case Study: 33-Year-Old Female Presents with Chronic SOB and Cough - StatPearls Case Study: 33-Year-Old Female Presents with Chronic SOB and Cough - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills, referencing.
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Case study report for nursing
Part 1: What is it and why?
This video introduces the concept of the case study and identifies how case studies differ to other written assignments.
The most important thing in writing up a case study report is that first, second, and thirdly: It is about the patient, not the condition nor the treatment. Students often put the emphasis on the condition or the treatment because the question usually focuses on this. While you need to explore these things, you still have to bring it back to the patient, and keep the patient central to the whole assignment.
We can understand if busy medical professionals start to see their patients in terms of a condition to be fixed, or a procedure to be performed. But ideally, we should remember that a patient is a person with a complex array of needs and preferences. This means that a simple textbook answer is not always best for them.
In your career, you will need to negotiate adjustments and anticipate problems particular to the patient. It does not make sense to discuss a condition in isolation from the individual. Each patient has their own unique kaleidoscope of history, personality type, fears, medical challenges, needs during recovery, so forth and so on. You need to see their condition or their treatment overall, as part of the whole person. Writing a case study teaches you to do that, if you don’t explore the condition or treatment as part of a holistic system, you case study becomes theoretical, it becomes another essay.
Let’s compare the case study to the essays you might have already written. The case study in nursing explores a particular patient’s situation, while your essays will more likely have focused on disease, a treatment, a concept, or a system. A case study is very grounded in the real and the now, even if the patient is a hypothetical invention. It still provides some fairly authentic experience with dealing with an individual patient.
Essays, on the other hand, tend to be literature-based. Of course, you need to do a lot of research and reading for your case study too, but the difference is for a case study you must always view and evaluate the information in the context of your patient. So in a case study, you need to show that you can find and apply information to you patient. For an essay you need to look at the information itself, pull it apart and evaluate it for its own sake.
So even if the question looks like an essay, don’t be distracted. There is still an expectation to relate this to the patient. It is possible to explore the content and theory in a generalised way throughout the assignment, but the beginning of the assignment (and the beginning of each paragraph, in fact) should foreground you're patient and their relationship to this theory.
Part 2: Research and writing
This video provides tips on how to research and structure paragraphs in order to keep a patient centred emphasis in the writing.
An essay, as opposed to a case study, usually has an question or a thesis which defines the boundaries of what you research, You aim to keep it within those parameters. and you delve as deeply as you can into the material. It loses focus if you include stuff outside of the topic.
With a case study, however, your focus is the patient so you need to cast your net widely and generously at first to find something that is relevant to them. And then when you find something relevant, you need to research deeply. So, doing a good case study report involves a lot more reading than you might think. You’ll have to research both generally and deeply.
There can be a lot of research, and fairly unguided research involved in a case study. Don’t assume it’s like a reading comprehension exercise, the problems are not always clearly defined and the solutions have not necessarily been covered in lectures. Think of your case study as a mystery puzzle with a few clues scattered through it.
In reality, patients do not arrive with instructions, so it’s up to the professional to notice that it is obvious and to think outside of the box. It is up to you to anticipate problems for the patient, it is up to you to follow through with the threads of any clues, and to see if they offer any valuable information, and these may only be hinted at indirectly. With years of nursing experience, the clues and danger signs get easier to spot, but it is very challenging for a beginner if you don’t know what to look for, and that is why the broad reading is important.
So, every piece of information about your patient is valuable. When the information is given in the assignment, the facts are not random facts, they have usually been included for a reason, so use them and use them as much as you can. You may, on the other hand, have been told very little in the assignment and be expected to elicit the information yourself from the patient, through a blog, or a question-and-answer session. Asking for more details about their own condition just gives you more details about their condition, and unless you have some reasoning in mind for asking about that, more details per se is usually not that very helpful.
Instead, ask about things that may affect the treatment or recovery; ask about things that may complicate matters. Smoking, relevant illnesses, lack of family support, strenuous lifestyles or jobs are all factors that may generate important decisions about how the patient is treated or cared for. The secret to keeping it about the patient is to keep them foremost into the discussion. You do this by making them the subject of each paragraph, and you do this by making them feature in the topic sentence: at the beginning and, if possible, a summary sentence at the end.
In the middle of a paragraph, you have more flexibility to talk about the procedure or the condition in a more general way. But, at the end of the day, you need to remind us of how this is important for your patient. If you don’t, your writing becomes an essay rather than a case study. And if you feel like you’re being asked to research and to discuss material that is not directly relevant to your patient, you can make it relevant by at least explaining why it is not relevant. Remember, everything you write about should be in relation to your patient.
So remember, it is all about the patient, keep everything relevant to the patient; keep the patient in mind throughout the research and the writing. Explore and discuss what the question requires, but theory for the sake of theory should be avoided. Your mission is to find the best solutions available for your patient, and develop the best understanding that you can of your patient.
You have now complete the Case Study module. We hope you have enjoyed the content. For more study skill resources, please visit the RMIT Learning Lab.
- Writing a case study
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study during One Shift. This case study will focus on the implementation and evaluation stages of the nursing process while doing one shift in Theatres. I will highlight the involvement of physiological, pharmacological and psycho-sociological aspects of my given care. The patient's history and current situation will be examined ...
August 17, 2023. Nursing Paper Solutions. NursingStudy.org is your ultimate resource for nursing case study examples and solutions. Whether you're a nursing student, a seasoned nurse looking to enhance your skills, or a healthcare professional seeking in-depth case studies, our comprehensive collection has got you covered.
6 Steps for Writing a Case Study Analysis. Writing a nursing case study analysis requires a systematic approach to ensure all necessary details are covered and accurately presented. The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in real-life settings. Here is a step-by-step guide to facilitate this process:
1. Nursing Case Study Example - Meadowvale University School Of Nursing -. The case analysis explores some of the ways in which the curriculum development leader can adopt measures that enhance faculty support and development in the task of curriculum development (Nursing Case Study Analysis) Problem-solving case analysis. 2.
Case studies encourage nurses to analyze complex patient scenarios, make informed decisions, and apply critical thinking skills to solve problems. They simulate real-life situations, requiring nurses to evaluate data, consider multiple outcomes, and choose the best course of action. 2. Improve Diagnostic Skills.
This essay delves into the craft of writing nursing case studies, examining essential techniques and providing pertinent instances to shed light on industry-standard operating procedures ...
The nursing case study example on Death and Dying and answers questions on Suffering and the Fallenness of the World, Suffering and the Hope of Resurrection, Value of Life, Euthanasia, and Morally Justified Options, also offers an analysis of the sin of suicide. Explores Ethical end of life decision making.
In a nursing case study, your task is to analyze a disorder or illness as a part of a specific medical situation. If you don't do that, your case study becomes an essay (theoretical and generalized). It is the difference between the two assignment types. Once again: A case study in nursing emphasizes the particular patient's condition.
A nursing case study paper contains several sections that fall into three categories: 1. The status of the patient. Demographic data. Medical History. Current diagnosis and treatment. 2. The nursing assessment of the patient. Vital signs and test results.
Ensure your summary has at least the case presentation, the nursing assessment/diagnosis, the intervention, and the key recommendations. At the very end of your conclusion, add a closing statement. The statement should wrap up the whole thing nicely. Try to make it as impressive as possible. 9.
Sample case study for nursing students can be a valuable tool in your preparation, helping you to develop critical thinking skills and apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios. That's why we've put together a list of 5 nursing case study examples, complete with answer guides, to help you prepare for the NCLEX -style questions you'll ...
Sample Undergraduate 2:1 Nursing Case Study. Author: Barclay Littlewood , Modified: 16 July 2023. See for yourself why we're the world's leading academic writing company. One of our expert writers has created this bespoke sample Nursing case study that shows the incredible quality that's guaranteed with every piece of work ordered.
Case Presentation. History of Present Illness: A 33-year-old white female presents after admission to the general medical/surgical hospital ward with a chief complaint of shortness of breath on exertion. She reports that she was seen for similar symptoms previously at her primary care physician's office six months ago.
EXAMPLE ANALYTICAL ESSAY This example of an analytical essay is presented in association with Price, B and Harrington, A (2010) Critical Thinking and Writing for Nursing Students, Exeter, Learning Matters. Readers are introduced to the process of critical and reflective thinking and the translation of these into coursework that will help them ...
tion to the word limits for some journal papers. Examples of case studies Example 1: nurses' paediatric pain management practices One of the authors of this paper (AT) has used a case study approach to explore nurses' paediatric pain management practices. This involved collecting several datasets: 1. Observational data to gain a picture ...
Let's compare the case study to the essays you might have already written. The case study in nursing explores a particular patient's situation, while your essays will more likely have focused on disease, a treatment, a concept, or a system. A case study is very grounded in the real and the now, even if the patient is a hypothetical invention.
Click on a case study below to view in our Nursing Case Study Examples course which holds all of our 40+ nursing case studies with answers. Acute Kidney Injury Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Cardiogenic Shock Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Breast Cancer Nursing Case Study. Continue Case Study. Respiratory Nursing Case Study.
Case Study: Mental Health Problems. 3997 words (16 pages) Essay in Nursing The purpose of this assignment is to select a client with the diagnosis of enduring mental illness and carry out an assessment based on the presenting problem of the chosen patient and the psychosocial intervention during his treatment.
Mrs P - A Clinical Case Study. Mrs P is a 78 year old lady who currently lives alone in a centrally located council owned property in a town in the West Midlands. Mrs P was married in the 1950's and her husband worked in an engineering factory until he had to retire due to ill health and he then unfortunately passed away in the mid 1990's.
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
Undertaking the clinical reasoning cycle while working with the case study of Mr George, the importance of the reasoning process has been understood. Proper nursing abilities and competencies as well as reviewing the in-depth data of the patient may need for acquiring effective health outcomes for the patients (White and Ewan,2013).
Case Study of a Care Plan for a Patient suffering multiple health problems. In this assignment it will define and discuss a nursing intervention for a client with a long enduring mental health illness. A systematic approach will be used the nursing process and the role of the mental health nurse will be clearly identified in providing care for ...
Introduction. This reflective case study will provide an account of the nursing management of a Mr Singh a 79 year old gentleman who developed a pressure sore whilst a hospital inpatient. The aim of the case study is to enhance the reader's knowledge of the importance of a structured approach to the management of the complex problems he ...