Welcome Guest!
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Writing
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Speaking Part 2
- IELTS Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Practice Tests
- IELTS Listening Practice Tests
- IELTS Reading Practice Tests
- IELTS Writing Practice Tests
- IELTS Speaking Practice Tests
- All Courses
- IELTS Online Classes
- OET Online Classes
- PTE Online Classes
- CELPIP Online Classes
- Free Live Classes
- Australia PR
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Austria Job Seeker Visa
- Sweden Job Seeker Visa
- Study Abroad
- Student Testimonials
- Our Trainers
- IELTS Webinar
- Immigration Webinar

IELTS Direct Question Essays – Structure, Questions, Samples & Tips
Updated On Nov 28, 2023

Share on Whatsapp
Share on Email
Share on Linkedin

Limited-Time Offer : Access a FREE 10-Day IELTS Study Plan!
The IELTS Writing Task 2, has an essay type known as the “Direct Question Essay,” which is a crucial component of the IELTS exam. It evaluates your ability to express your ideas, analyze a given topic, and provide a clear, well-structured response.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the structure of IELTS Writing Task 2 : Direct Question Essays, delve into essential pointers, provide ten valuable tips to ace this task and furnish you with five sample questions and answers to boost your preparation.
Structure of a Direct Question Essay
A Direct Question Essay typically follows a specific format:
I agree that schools should place a greater emphasis on practical life skills. While traditional subjects are essential, practical skills like cooking, budgeting, and home repair equip students for real-life challenges. For instance, teaching basic culinary skills can promote healthier eating habits, reducing the prevalence of diet-related health issues.
Furthermore, budgeting knowledge empowers individuals to manage their finances effectively, reducing the risk of falling into debt. The ability to handle basic home repairs fosters independence and self-reliance, which are valuable qualities in adulthood.
By incorporating practical skills into the curriculum, schools prepare students for the responsibilities they will face in their daily lives. While academic knowledge is important, it is equally crucial to equip individuals with the tools they need to thrive in the real world. Thus, I firmly believe that schools should allocate more resources to teach practical life skills alongside traditional subjects, ensuring a holistic education that sets students on the path to success.
Banning smoking in public places offers numerous advantages. Firstly, it significantly improves public health by reducing exposure to harmful secondhand smoke. Non-smokers, including children and those with respiratory conditions, benefit from cleaner air, leading to a lower incidence of smoking-related health issues.
Secondly, such bans encourage individuals to quit smoking or reduce their consumption. When smoking is restricted in public spaces, smokers may be more inclined to quit as the inconvenience of finding a designated smoking area becomes apparent. This, in turn, decreases the overall demand for tobacco products and contributes to public health.
However, banning smoking in public places can lead to potential disadvantages. Businesses reliant on tobacco sales may experience a decline in revenue, potentially leading to layoffs or closures. Additionally, some smokers may resist the bans, leading to enforcement challenges and potential conflicts in public spaces.
In conclusion, the advantages of banning smoking in public places, such as improved public health and reduced smoking rates, outweigh the disadvantages. While businesses may face challenges, the long-term benefits to society as a whole are substantial.
Key Pointers for Direct Question Essays
- Understand the Question: Read the question carefully to grasp its requirements and focus. Identify keywords that dictate the scope of your response.
- Plan Your Essay: Spend a few minutes brainstorming and outlining your essay. Organize your thoughts and main ideas. A well-structured essay flows more naturally.
- Clarity and Coherence: Use clear and concise language. Ensure that your essay is easy to follow and logically organized. Employ appropriate transitions between sentences and paragraphs.
- Stay on Topic: Avoid straying from the main question. Irrelevant information can reduce the clarity of your essay and affect your score.
- Word Count: Adhere to the word count requirement. Going over or under the limit can result in point deductions.
- Vocabulary and Grammar: Showcase a wide vocabulary range and accurate grammar. Simple and complex sentences should be used appropriately to enhance the quality of your writing.
- Examples and Details: Support your ideas with relevant examples, facts, and details. This strengthens your arguments and demonstrates a deep understanding of the topic.
- Counter Arguments: Address counterarguments when relevant. This shows your ability to consider different perspectives and strengthens your position.
- Time Management: Allocate time wisely. Ensure you have enough time to review and edit your essay before submission.
- Revision: Always review and edit your essay. Look for errors in spelling, grammar, and clarity. A well-edited essay leaves a positive impression.
You can practice more Direct Question Essays here .
Direct Question Essay: A Skill to Learn!
In conclusion, mastering the art of writing Direct Question Essays is achievable with practice, a clear understanding of the format, and attention to key pointers. By following the structure, incorporating the tips provided, and analyzing the sample questions and answers, you can significantly enhance your performance in the IELTS Writing Task 2. So, start practicing and make your writing shine on test day. Good luck!
Here are the 10 examples for the Direct question essay
Also, check :
- Tips to Improve IELTS Writing Skills
- IELTS Writing recent actual test
- IELTS Band 9 essays
- Advantage and Disadvantage Essays
- IELTS Writing Task 1 Connectors
Frequently Asked Questions
How will you write an introduction in the IELTS Direct Question Essay?
What are the common errors the examinees make in the IELTS Direct Question Essay?
How can you score high marks for task achievement in the IELTS Direct Question Essay?
Can I use only one body paragraph in my IELTS Direct Question Essay?
Are IELTS Direct Question Essay and IELTS Double Question Essay the same?
Practice IELTS Writing Task 2 based on Essay types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
I HACK YOUR ACCOUNT
Explore other Direct Question Essays

Raajdeep Saha

Kasturika Samanta

Janice Thompson

Post your Comments
Posted on Apr 15, 2022
Thank you very much for sharing this useful post.I’m sure this educational programs & sectors will be helpful for those who want to improve their skills in learning better English. So I expect you going on this.
Recent Articles

Nehasri Ravishenbagam

Our Offices
Gurgaon city scape, gurgaon bptp.
Step 1 of 3
Great going .
Get a free session from trainer
Have you taken test before?
Please select any option
Get free eBook to excel in test
Please enter Email ID
Get support from an Band 9 trainer
Please enter phone number
Already Registered?
Select a date
Please select a date
Select a time (IST Time Zone)
Please select a time
Mark Your Calendar: Free Session with Expert on
Which exam are you preparing?
Great Going!
Directed Writing: Format, Benefits, Topics, Common Mistakes and Examples
Pankaj dhiman.
- Created on December 5, 2023
What is Directed Writing, Importance, Benefits, Purpose, Tips and Examples of Directed Writing
Directed writing is a form of written assessment, where the students must follow instructions to create a piece of writing. In this Article, we discussed What is directed writing, importance of directed writing, directed writing format, key elements, purpose of directed, common mistakes, topic, tips and examples of directed writing.
What is Directed Writing
In directed writing, the writer is given a specific assignment or challenge that directs the composition’s substance and organization. It is distinguished by its intentional and focused nature, necessitating compliance with particular rules or goals by the writer.
This type of writing is used in professional and academic contexts, where it is used as a useful instrument to evaluate communication abilities.
The value of directed writing comes from its capacity to teach people how to communicate ideas, target audiences with particular messages, and complete tasks as assigned. It places a strong emphasis on communication efficacy and clarity.
Must Read: Notice Writing Format, Importance, Examples and How to Prepare
Importance of Directed Writing
This methodical way of expressing oneself not only develops the capacity for precise idea delivery but also for clear thought presentation. Directed writing is a crucial tool in academic contexts for evaluating students’ comprehension of a subject as well as their capacity for knowledge synthesis and efficient communication.
In the workplace, it becomes essential to express important details, putting forth strong arguments, and creating well-organized reports.
Directed writing also provides a realistic training ground for modifying language, tone, and style to fit various audiences and objectives, which promotes communication versatility and talent that is crucial for negotiating the intricacies of both the personal and professional arenas.
The ability of directed writing to provide people with the means of meaningful, effective, and audience-appropriate communication is ultimately what makes it so important.
Learn more: IGCSE English Language Study Resources
Directed Writing Format
Introduction: .
- Grab the reader’s interest right away with a succinct introduction.
- Clearly state the writing’s goal or aim.
- Give the background information that’s required to establish the scene.
Body Paragraphs:
- Divide the text into thoughtful paragraphs that concentrate on different concepts or facets.
- To ensure unity, keep the paragraphs flowing logically from one another.
- Provide appropriate examples, facts, or evidence to back up your claims or arguments.
Language and Style:
- Convey concepts with language that is straightforward and succinct.
- Observe the proper tone and style for the goal and target audience.
- A statement that is too complicated or full of jargon may make it harder to understand.
Guidelines for Formatting:
- Observe any particular formatting requirements that the question or guidelines may have given.
- Keep the font size constant throughout the document, and choose a readable typeface.
- Observe the necessary margins, indentation, and spacing.
Editing and proofreading:
- Check the article’s overall coherence, consistency, and clarity.
- Verify the text for punctuation, spelling, and grammar faults.
- Make sure that the writing stays within the allotted word count, if any.
About the Prompt’s objective:
- Check to see if the writing directly addresses the prompt or assignment.
- Avoid irrelevant content that could take attention away from the intended objective.
Conclusion:
- Recap the key ideas discussed in the writing’s body.
- Summarize the main point or objective.
- Make a last point that will stick with the audience.
Must Read : IGCSE English Literature Study Resources
Key elements of Directed Writing
Quick understanding:.
- It is essential to fully understand the assignment or prompt that has been assigned.
- Determine the essential needs, including the goal, target audience, and detailed guidelines.
Clearly Stated Introduction:
- Give a succinct opening outlining the writing’s primary idea or goal.
- To help the reader along, state the thesis or main point clearly.
A Well-Maintained Body:
- Make sure each paragraph in the body of the essay is well-developed.
- Each paragraph should concentrate on a distinct topic or point to add to the overall cohesion. To ensure a seamless flow of ideas across paragraphs, use logical transitions.
Editing and revision:
- Verify the text for correct spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
- Make sure the writing follows any formatting requirements that may be provided.
Flexibility:
- Show that you can modify your language and style to fit the demands of the assignment.
- Tailor the writing to suit the intended audience and purpose effectively.
Access the Learning Platform
Benefits of Directed Writing
With so many advantages, directed writing is an essential instrument for improving communication abilities. First of all, it is a focused activity that improves the capacity to express ideas clearly and cohesively. Directed writing helps people concentrate on the crucial components of communication by giving them a task or suggestion, which promotes a methodical and deliberate approach to concept expression.
Must Read : Why and How To Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Student
Another notable advantage of directed writing lies in its capacity to promote critical thinking. By challenging writers to analyze information, structure their thoughts logically, and present compelling arguments, this form of writing fosters intellectual growth. It encourages individuals to think critically about the content they are conveying, enhancing their ability to synthesize and evaluate information coherently and purposefully.
Start today: English Tuition: Best Online English Tutors in Singapore
Purpose of Directed writing
Directed writing serves as an organized means of accomplishing well-defined goals through communication. Directed writing helps people convey ideas intentionally within predetermined boundaries, whether it is in professional papers, assignments, or tests.
It promotes a focused approach and accuracy in communication by providing a defined task or prompt. Beyond only delivering information, this intentional communication fosters critical thinking, organizational, and context-adaptation abilities.
The main objective is to provide people with the tools necessary to express ideas coherently and fulfill the requirements of a particular assignment, which will improve their communication skills in a variety of contexts.
Start Learning : Free IGCSE Resources for Students
Examples of Directed Writing
Academic essays:.
- Responding to essay prompts in standardized tests or academic assignments involves directed writing. Students must adhere to a specific topic, structure, and word limit.
Business Emails:
- Composing emails in a professional setting often requires directed writing. The writer must convey a clear message, follow a formal tone, and adhere to specific guidelines.
Reports and Proposals:
- Writing business reports or project proposals involves directed writing. The author must address a particular issue, provide relevant information, and follow a structured format.
Application Letters:
- Crafting letters of application for jobs, scholarships, or programs is a form of directed writing. The writer must convey their qualifications, intentions, and suitability for the position.
Creative Writing Prompts:
- Even in creative writing, prompts can serve as a form of directed writing. Authors may be tasked with creating a story based on specific themes or constraints.
Topics for Directed Writing
- The impact of social media on student wellbeing
- The importance of time management for academic success
- The role of technology in modern education
- The impact of fracking in Wildlife
- The broader environmental of fracking
- The challenges and opportunities of online learning
- The influence of role models in students life
- Benefits of reading for pleasure in student development
- The importance of digital literacy in 21st Century
Must Read : IGCSE English: Syllabus, Revision Notes & Preparation Tips
Tips for Directed Writing
Understand the Prompt: Ensure a clear understanding of the task or prompt before starting your writing.
Plan Your Structure: Outline your ideas before writing to maintain a logical and organized flow.
Stay Focused on the Task : Address the specific requirements of the task without deviating.
Use Clear Language: Choose words carefully to convey ideas precisely and avoid ambiguity.
Adapt to the Audience : Tailor your language and style to suit the intended audience and purpose.
Revise and Edit: Review your writing for coherence, clarity, and grammatical correctness.
Manage Time Effectively: Allocate time for planning, writing, and revising to meet deadlines.
Support with Examples: Use relevant examples or evidence to strengthen your arguments.
Vary Sentence Structure: Avoid monotony by using a mix of sentence structures for better readability.
Proofread Carefully : Check for spelling, punctuation, and grammatical errors before submitting your work.
Must Read : Cambridge IGCSE: Benefits, Subjects, Grading Scheme, and Tips
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Directed Writing
Lack of Planning: Writing without a clear structure or outline can lead to disorganized content.
Overly Complex Language: Using unnecessarily complex vocabulary that may hinder understanding.
Inconsistent Tone: Failing to maintain a consistent tone appropriate for the purpose and audience.
Rambling or Off-Topic Writing: Straying from the main point and including irrelevant information.
Neglecting Revision: Submitting the first draft without thorough review and edits.
Exceeding Word Limits : Not adhering to specified word counts, can result in loss of marks.
Poor Time Management: Spending too much time on one section and neglecting others.
Inadequate Support for Arguments : Failing to provide sufficient evidence or examples to support claims.
Neglecting Proofreading: Overlooking spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors in the final draft.
Start Homeschooling Today
Online Resources for Directed Writing
In mastering directed writing, it’s crucial to avoid common pitfalls. Steer clear of vague language, prioritize thorough proofreading to eliminate errors, maintain a consistent notice writing format for clarity, consider your target audience’s preferences to enhance engagement, and craft a compelling heading to capture attention effectively.
Additionally, for comprehensive guidance and practice, Tutopiya offers valuable resources. Tutopiya provides specialized online courses, informative writing guides, and practical exercises tailored to notice writing.
With Tutopiya, you can refine your directed-writing skills, ensuring impactful and effective communication in various contexts.
Explore the Learning Platform
See author's posts
Recent Posts
- Mastering IGCSE: Ace Your Exams in 3 Months with Our Unlimited Learning Program
- IGCSE Exam 2024 Revision: 10 Tips and Tricks to Score A*
- How to Ace Your IGCSE Exam in 3 Months: A Comprehensive Guide to Score A*
- Tutopiya’s Shining Star: An Insight into the Teaching Journey of Anshu Gupta
- IGCSE Group Classes in Singapore: Exam Preparation, Pricing, Benefits and Online Resources
- 1:1 IGCSE Online Tutoring in Malaysia: Benefits, Challenges, Online Resources and How to Succeed
- IGCSE Mock Assessment: Prepare with Tutopiya’s Practice Exams
- IGCSE Online Tutors Dubai: Boost Your Grades Now
- How to Stay Calm and Confident in IGCSE Exams
- Avoid These 7 Common IGCSE Exam Mistakes for Better Grades: Tutopiya
Get Started
Learner guide
Tutor guide
Curriculums
IGCSE Tuition
PSLE Tuition
SIngapore O Level Tuition
Singapore A Level Tuition
SAT Tuition
Math Tuition
Additional Math Tuition
English Tuition
English Literature Tuition
Science Tuition
Physics Tuition
Chemistry Tuition
Biology Tuition
Economics Tuition
Business Studies Tuition
French Tuition
Spanish Tuition
Chinese Tuition
Computer Science Tuition
Geography Tuition
History Tuition
TOK Tuition
Privacy policy
22 Changi Business Park Central 2, #02-08, Singapore, 486032
All rights reserved
©2022 tutopiya

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Study Abroad Test Prep /
Direct Question Essay in IELTS: Everything You Need to Know
- Updated on
- Dec 30, 2023

The IELTS Writing Task 2 demands test takers to write cohesive, nuanced, and insightful essays. Within this section, a diverse spectrum of essay types arises, such as opinion pieces, problem-solution analyses, and advantage/disadvantage examinations. Notably, amongst these stands the Direct Question Essay, characterized by its explicit and directive nature, demanding a clear and concise response within a 250-word limit. To know more about IELTS direct question essays, read the entire blog.
This Blog Includes:
Top 5+ tips for direct question essay ielts, structure of an ielts direct question essay, scoring criteria for direct essay questions, most common ielts direct essay sample questions, ielts direct question essay samples .
Here are the top tips for direct question essays in IELTS writing task 2. Refer to them to bolster your chances of scoring better in IELTS writing.
- Take a good look at the test questions before diving in. It’ll save you time and frustration in the long run, and make sure you’re answering what the examiners want to know.
- You should keep a formal tone while writing direct-question essays in IELTS writing task 2.
- Individuals must stick to the given word limit. Exceeding the word limit can cause you to lose marks and time. Write your essay with a word count of at least 250-270 words.
- Set a time restriction during your preparation to enhance your overall speed and accuracy. During your actual exam, you will get around 40 minutes to write a direct-question essay. Therefore, practising under time constraints can help you get accustomed to the actual time crunch you’ll face during the test.
- A proper content structure must be followed, i.e., begin with an introduction paragraph, a two-body paragraph and end the essay with a concise conclusion.
- Make your intro concise and to the point. In other words, keep them tight, clear, and accurate to the topic.
- The main body paragraphs of your essay should answer the questions asked in the question.
- Refined writing with proper grammar and vocabulary makes a big impression and showcases your language proficiency.
Sticking to the expected structure in IELTS direct question essays is crucial to avoid losing points and improve your chances of scoring better. Refer to the data given below to get a better understanding of the structure of IELTS Direct Question Essays.
Introduction Paragraph
Always start your essay with a concise, articulated and punchy introduction. Intros that pack a punch can rope in a lot of eyeballs and encourage them to read further. Begin with a succinct yet insightful phrasing of the assigned prompt, then offer a taste of the key arguments you’ll elaborate upon in the subsequent paragraphs.
Body Paragraph 1
Directly address the first question in the opening paragraph with a clear and comprehensive response.
Body Paragraph 2
In this paragraph, feel free to explore your second or third questions, bolstering your arguments with illustrative examples for greater clarity and impact.
Conclusion Paragraph
Sum up your entire essay in this paragraph. Ensure that you have included all the major points in this part of the essay.
The IELTS Direct Essay Questions are evaluated on the following factors:
Task Achievement
Your essay should answer all the questions asked on the topic. You should use linkers and examples to make your essay more cohesive, comprehensible and impactful.
Lexical Resource
Diversify your lexical choices to enhance the persuasiveness and sophistication of your written arguments.
Grammatical Range and Accuracy
Evaluate your essay for grammatical inconsistencies that might detract from its persuasiveness and accuracy.
Maintain Coherence
Your IELTS Direct Question Essay should be coherent and comprehensible to the readers. It must be segregated into concise and articulated paragraphs that are easy to read and comprehend.
Here are the most common IELTS Direct Essay Sample Questions.
Refer to the following samples to get a solid idea about IELTS direct question essays and how to answer them.
Q: Online shopping is significantly increasing. What impact does this have on people, what are the disadvantages, and what are the job opportunities?
Ans: The internet’s discovery has transformed numerous facets of people’s lives, giving rise to online shopping and sparking significant societal changes. While it delivers numerous benefits, it also introduces disadvantages that warrant discussion.
One of the main disadvantages of online shopping is that it lacks a tangible experience as consumers can not touch, feel, or try the items they are purchasing beforehand. It not only causes dissatisfaction but has also increased return rates. In addition to this, the impersonal nature of online shopping has led to poor customer service. Apart from this, another significant concern of people is the risk of fraud and identity theft that it carries. With the growing prevalence of online transactions, consumers face a heightened risk of compromising their personal and financial information.
Despite these challenges, the rise of online shopping has created numerous job opportunities. The e-commerce industry is booming and requires a wide range of skills such as web development, digital marketing, logistics, and customer service. Due to this, new jobs have been created, allowing individuals to start their businesses. Furthermore, the need for improved cybersecurity has led to an increase in demand for this field. In today’s fast-paced world, businesses are emphasizing safeguarding their customers’ data and ensuring a secure online shopping experience, making cybersecurity an essential and integral part of the e-commerce industry.
In conclusion, although online shopping comes with a share of drawbacks, it also brings opportunities for various employment prospects. It is crucial for both consumers and businesses to effectively tackle these challenges while capitalizing on the opportunities provided by this expanding industry.
Q: Fast food is a part of life in many places. Some people think this has bad effects on lifestyle and diets. How is the consumption of fast food bad for people? Why should one avoid fast food?
Ans : The omnipresence of fast food in today’s society is undeniable, as it has become an integral part of every individual’s life worldwide. However, fast food’s detrimental effects on our lifestyle and diet are unmistakable, and I wholeheartedly agree with this viewpoint for several reasons.
Fast food is often high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and calories while providing very few nutrients. If someone consumes it regularly, there is a high probability that it can lead to obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and other health-related problems. It is concerning as in the present scenario many countries are facing high rates of childhood obesity cases. In addition to this, the convenience of fast food has encouraged a sedentary lifestyle. Daily consumers tend to invest less time in preparing home-cooked meals and participating in physical fitness activities, contributing to social isolation. This lifestyle shift can have adverse effects on people’s overall well-being.
Moreover, fast food promotes overconsumption through clever marketing strategies. For instance, the ubiquitous practice of offering “value meals” with larger portions at only a slightly higher cost may entice customers to opt for larger servings than they need. Coupled with the addictive appeal of certain fast food ingredients, such as the high levels of salt, sugar, and fat, this marketing approach can significantly contribute to overeating and, consequently, weight gain.
In conclusion, while fast food may be an enticing option for many individuals, it comes with adverse impacts on health and overall lifestyle. Therefore, people need to make conscious decisions regarding their food consumption, and governments should actively play a pivotal role in promoting healthy eating habits. This may involve enacting regulations on fast food advertising, providing education, and encouraging physical activity.
With that, we conclude our foray into IELTS Direct Question Essays.
Ans. The IELTS direct-question essay is divided into an introduction, two body paragraphs and a conclusion.
Ans. Test takers can use a range of linkers, adverbial phrases, references, and punctuations to bolster their overall scores in IELTS writing.
Ans. The IELTS Writing Task 2 requires individuals to complete the task within 40 minutes.
Related Reads:
Visit the Leverage Live page of Leverage edu or contact our study abroad experts at 1800-57-2000 to strengthen your scores and application to secure your spot in your dream college.
Shubham Das
Shubham Das has been working as an educational content writer for the past two years and has a background in filmmaking & screenplay/ teleplay writing. He is fascinated by the human psyche, literature and cinema.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
How To Write A Direct Question Essay
In writing task 2 you will be asked to write a discursive essay ( 250 words minimum ). You will be given a question asking you to give your opinion, discuss a problem or issue. You could also be asked to provide solutions, evaluate a problem, compare and contrast different ideas or challenge an idea. In this post, we will be focussing on how to write a direct question essay .
One of the first things you should do is read the marking criteria to see what the examiners expect. This is really important, as you need to know what they are looking for in the band 7+ boxes.
You should be able to give the examiners exactly what they want, in order to get a 7+ band score.
If you would like to purchase a 29 page PDF download that is easy to read and print out please take a look at the bookshop >
WRITING TASK 2 Direct Question STRUCTURE
The structure that I advise my students to use, will be sure to get you a band score 7+. You need to practice using this structure, with as many questions as you can, before sitting your IELTS test. This writing task 2 structure has been proven to be successful for my students and when perfected, can easily help you to achieve a high band score.
TIP >> Before you start writing, plan your ideas so that you can organise the information clearly. You must read the question and answer the questions asked in your essay. Take 5 minutes and plan out your ideas and examples.
TIP >> It is very important that spend a full 40 minutes on this task as the score you get for writing task 2 is two-thirds of your total writing score. You also need to write a minimum of 250 words and use your own ideas.
TIP >> Remember to write in a formal tone, this is an academic essay, therefore your writing should be formal.
TIP >> The structure may differ depending on the question. Most questions will ask as two questions but other questions may ask further questions. You will have to adjust the structure, to make sure you are answering all parts of the question. This means adding an extra paragraph to answer another question, or to give your opinion.
IT IS A 4-PARAGRAPH STRUCTURE >>
Paragraph 1 – The Introduction
This is the introduction to the essay and where you should start off by paraphrasing the question.
Do you understand what I mean, when I say ‘paraphrase’ the question?
This means that you rewrite the question in your own words using synonyms. You can’t just copy the question again or use the same words in the question. Paraphrase and show off your vocabulary knowledge by using synonyms. When practising your essay writing, use an online thesaurus to help you. This is a great tool and can help you to learn many new words.
Then your next sentence should outline for the examiner exactly what you will discuss in the main body paragraphs. For example, Firstly this essay will discuss……… Secondly this essay will discuss…….
There are two sentences you need in the introduction >>
- Paraphrase the question.
- Outline the specific topics that will be discussed in the main body paragraphs.
Paragraph 2 – Main Body Paragraph 1
In this paragraph, you should answer the first question asked. You should give specific information and only write about one main idea in each main body paragraph.
Start the paragraph by introducing the topic. This is where you need to have a topic sentence. The next sentence(s) should explain the topic, going into detail. The third sentence should give an example that supports the positive aspect.
The example you give could be something from your own experience or made up – it is ok to make up something as the examiners will not fact check your information. They want to see your ability to use English at a certain level. You could make up an example from a report, journal, newspaper or University study to support your view.
This is how the paragraph should look >>
- Introduce the topic (answer the first question)
- Explain/give detail
Paragraph 3 – Main Body Paragraph 2
In this paragraph, you should answer the second question asked. You should give specific information and only write about one main idea in each main body paragraph.
Start the paragraph by introducing the topic. This is where you need to have a topic sentence. The next sentence(s) should explain the topic, going into detail. The third sentence should give an example that supports the view.
The example you give could be something from your own experience or made up – it is ok to make up something as the examiners will not fact check your information. They want to see your ability to use English at a certain level. You could make up an example from a report, journal, newspaper or University study to support your view.
This is how the paragraph should look >>
- Introduce the topic (answer the second question asked)
Paragraph 4 – The Conclusion
In the fourth paragraph, you write the conclusion giving a summary of your main points and give a recommendation. You should not enter any new information or ideas in this paragraph.
- Summary of the main points
- Give a recommendation
* Note – There may be more than 2 questions asked in the main essay question, therefore you can add a third paragraph if necessary. Your essay should never contain more than three main body paragraphs.*
SAMPLE Direct Question ESSAY >>
**All questions have been reported by students who have taken the IELTS exam.**
Creative pleasures such as viewing fine arts, listening to music and watching a play are treated by many as enjoyable and essential as part of their everyday living. Firstly this essay will discuss how the arts are a crucial element in most people’s lives and secondly will discuss how it is vital that creative subjects are included in the school’s curriculum.
Firstly, the creative arts, such as paintings, sculptures, music and theatre have a long and ardent history throughout the ages. They have grown and evolved with the times, appealing to new generations every year, in order to keep being a part of everyday life. People enjoy the arts, often as an escape from their lives, listening to music they enjoy, going to see a play with friends or visiting galleries and museums to see paintings, photography or sculptures. For example, a study from the New York Times in 2017 showed that over 75% of New Yorkers said that they regularly visited the cities art galleries, museums and theatres. A further 35% said that they donated money regularly to art societies, for the preservation of the collections, so they can continue for many years to come.
Secondly, many people develop a love for the arts early in life, when they are at school. In my opinion, I think that a range of arts subjects should be included in the school curriculum, as not all students are ‘left brained’ enjoying logical, core subjects like mathematics. Others are more ‘right brained’ where they enjoy being creative, whether that is in writing, painting or making music. Children should be encouraged to find their talents at school and develop them for their own enjoyment and advancement. For instance, St. Cuthberts school in the north of England dedicated 40% of the curriculum of creative subjects, including fine art, pottery, music, drama and dance. Those subjects proved to enhance school results by over 25% in 2017.
In conclusion, there are clear benefits to individuals who are passionate about the arts and find enjoyment in them regularly. If more people tried to become involved in the arts, then perhaps they would find a way to allow themselves time to become creative or to relax, while learning something new.
(Word Count = 371 / Band Score 9)

- Task Achievement – The answer provides an answer to both questions asked, supported by relevant examples.
- Coherence and Cohesion – The answer has been divided into clear logical paragraphs and each main body paragraph only has one main idea. There are cohesive links between the main body paragraphs (firstly, secondly).
- Lexical Resource – There is evidence of a wide range of vocabulary, with no errors in the text.
- Grammatical Range and Accuracy – The answer has no grammatical errors. The sentences have a wide range of structures.
TIP >> Remember to read the question and plan your answer around what it is asking you to do.
WRITING TASK 2 BAND SCORE 9 CRITERIA >>
If you would like to view more high band score direct question essay examples please click the button below >
We hope you found this post useful in helping you to study for the IELTS Test . If you have any questions please let us know in the comments below or on the Facebook page.
The best way to keep up to date with posts like this is to like us on Facebook , then follow us on Instagram and Pinterest . If you need help preparing for the IELTS Test, join the IELTS Achieve Academy and see how we can assist you to achieve your desired band score. We offer an essay correction service, mock exams and online courses.
Related Posts

Business: IELTS Direct Question Essay Model Answer
Business: IELTS Writing Task 2 Direct Question Essay Band 8 sample answer. The question is:…

IELTS Direct Question Essay Model Answer: Education and Teaching
Education and Teaching: IELTS Writing Task 2 Direct Question Essay Band 8 sample answer. The…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
IELTS Direct Questions Sample Essay Titles
Below is a list of sample essay questions for IELTS direct questions essays which can come in writing task 2. These essay types are also known as two question essays (although it is possible to get more than two questions).
Direct Questions Essay Tips
- spend time planning the answers to the questions
- each question must have one main point as an answer
- put the answer to each question in a separate body paragraph
- follow a safe direct questions essay model
Direct Questions Sample Titles
News plays an important part of most people’s lives. Why is news so important to people? Why is so much news dedicated to bad news? Should the news focus on good news instead?
Most people agree that money cannot be happiness. Why is happiness difficult to define? How can people achieve happiness?
Success is often measured by wealth and material belongings. Do you think wealth is the best measure of success? What makes a successful person?
The internet is a great course of information and has opened up opportunities for people to learn all over the world. Is all information reliable on the internet? What could be done to control information online?
Art and music are considered some of the fundamental elements of all societies. Do you think art and music still have a place in today’s modern world of technology? Should children spend more time learning art and music at school?
It is often said “when is Rome, do as the Romans do”. Do you think people should adapt and accept the culture of the country they are visit? do you think it is possible to learn a culture without learning the language?
Other IELTS Essay Questions
- Opinion Essay Questions
- Solution Essay Questions
- Discussion Essay Questions
- Advantage Disadvantage Essay Questions
- All Essay Questions by Topic
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Recent Lessons
50% discount advanced ielts lessons & e-books final day, answers to age group bar chart lesson, ielts bar chart of age groups 2024, 50% discount: advanced ielts lessons & e-books, ielts topic: urban planning, ielts listening transcripts: when and how to use them.

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
4 The Direct Writing Process for Getting Words on Paper
- Published: July 1998
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The direct writing process is most useful if you don’t have much time or if you have plenty to say about your topic. It’s a kind of let’s-get-this-thing-over-with writing process. I think of it for tasks like memos, reports, somewhat difficult letters, or essays where I don’t want to engage in much new thinking. It’s also a good approach if you are inexperienced or nervous about writing because it is simple and doesn’t make as much of a mess as the other ways of getting words on paper I describe in Section II.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Write with Focus
- Read with Purpose
- Build your Community
- Discover Classes & Tools
The Direct Address, Epistolary Essay, and Energizing Your Writing

Jul 19, 2022 by Patrice Gopo published in Writing

The Power of Writing to YOU
Several months ago, I visited the Rubenstein Rare Books & Manuscript Library at Duke University. My purpose? I needed to research an individual for a possible picture book biography. Duke housed my subject’s archives in one of their collections. As I sorted through photographs and papers in the quiet of the reading room, I stopped, every so often, to read a letter addressed from friend to friend, mother to child, sister to sister.
Each time I read a salutation, I navigated a mixture of strange emotions. Maybe a little giddiness at access to words intended to be shared between writer and recipient, as if I now knew a secret. Also, perhaps a dash of impropriety as if I were reading someone else’s mail. Which I was, of course, reading someone else’s mail. I’m sure we’ve all been there before, that sense of reading something written to another, something intended for someone else’s eyes—not necessarily yours.
A particular energy arrives on the page when we read an epistolary essay or direct address essay, this form of writing that the author seemingly intends for someone else. As readers, we find ourselves pulled in because of the excitement of being part of an inside conversation.
Also, maybe we feel just that tiny, delightful touch of sneakiness. Are we supposed to be reading this? Is this a bit like slicing open a letter sent to your sister? Reading your boss’ email? Finding a note slipped into the back of the library book the previous borrower used as a bookmark? No one intended these words for you. Oh, the intrigue!
In my view, the narrator in a direct address essay writes to a “you” character (not to be confused with writing in the second-person point of view). Perhaps a parent, a friend, or a stranger. I consider the epistolary essay to be a subset of the direct address because these essays take the form of a letter. For example: Dear Mom. Love, the narrator. (While I won’t say more about this here, it’s important to note that sometimes the “you” character can be an inanimate object).
One of the noticeable qualities of the direct address or epistolary essay is the sense of intimacy rising from the page. Since the intended reader is no longer a nameless, unknown person, the words often convey a deeper sense of knowing. Of course, increased intimacy isn’t necessarily a characteristic we always want to achieve in every essay. But for certain content, the heightened intimacy contributes to the strength of the writing.
The Writer Benefits of YOU
In addition, I recognize several benefits you as a writer can gain when you use the direct address or epistolary structure:
Circumvent the Internal Critic
When you choose to write your essays directed toward another individual, this can often circumvent that internal critic always wanting to comment from the side. The imaginary audience of possible readers shrinks to just a person: a spouse, a child, a parent, a friend, a stranger you saw at the grocery store. Of course, the presence of one person versus many doesn’t necessarily eliminate the critic’s voice, but it can certainly be a tool that might help.
Bring a Sense of Community
The direct address can bring a sense of community to your writing practice. Often the act of writing is a solitary venture. You craft the words alone. However, with the direct address, you invite another presence into your story, and you remember in a tangible way that you are not alone. This addresses “you” joins with your creative practice.
Communicate a Difficult Subject Matter
The direct address easily becomes a sideways opportunity to explore or communicate topics a reader might directly ignore. The direct address feels somewhat less like the author intends the content for the reader. As a result, the reader can develop more of that “fly on the wall” posture as they engage with the words.

Lower the Stakes
The direct address can reduce the stakes as you are drafting. After all, these are just words you are writing to another person, or it’s just a letter. You may find that you can write with greater ease if you choose a person to write to and then adapt a phrase of encouragement such as, “It’s just a letter. It’s just a letter.”
YOU Leading Us to What’s Next
Up until now, I’ve talked of how the direct address might be a good format for an essay. However, sometimes the direct address is the pathway that leads to the final essay. The direct address can serve as a powerful tool to help you say what you may not have realized you wanted to say. Perhaps you’re trying to write about a conflict with a friend, and you’re struggling to identify the emotion present in a scene. Maybe a helpful strategy is pausing in the work and, instead, writing a letter to that person, an authentic, genuine letter that may enable you to unearth emotions you didn’t realize you had. In the end, you can use this new information to help you craft a stronger essay or other work. Ultimately, the direct address or epistolary form can serve as another pathway to find the deeper material.
Where do YOU go from here?
Maybe you already love the direct address or epistolary essay (yay!). Or perhaps the thought of bringing in this YOU seems strange or unfamiliar. Wherever you may find yourself in the writing journey, here are a couple of writing prompts to help you further engage.
Prompt 1
1. List five conflicts you’ve had with other people; these can range from minor to major; from just today to a lifetime ago.
2. Pick one item from your list and write a letter to the other person involved in the conflict.
3. Reread what you’ve written. Perhaps this is an essay, OR perhaps this content is the springboard for an essay.
Prompt 2
1. Think of an essay where you find yourself stuck.
2. Rewrite this essay but begin with a greeting to someone. Perhaps an old teacher, a friend, a relative, your neighbor, a stranger, whoever you want.
3. See if any new content, emotion, or reflection emerges from bringing another into the writing.
1. Write a letter to your past self or your future self and see what essay may emerge.
2. As with the previous prompts, also examine if this letter brings you new content, emotion, or reflection for future writing.
Of course, feel free to lop off the Salutation and Closing in any of these letters and see what happens.
1. Take an in-progress essay. Choose a person in the essay to address directly rather than refer to in the 3 rd person.
2. Note what happens to your essay when you do this.
I wish YOU the best with bringing in the YOU!
Examples of Direct Address or Epistolary Essays
- This Far: Notes on Love and Revolution by Daniel José Older
- Girl by Jamaica Kincaid (note that this direct address writing is officially categorized as fiction but still is a powerful example)
- Swerve by Brenda Miller
- For a Recently Disco or a Recently Discovered Shipwreck at the Bottom of Lake Michigan by Matthew Olzmann (an example of directly addressing an inanimate object; note that this example is officially categorized as a poem)
- Between the World and Me by Ta-Nehisi Coates is an example of a book-length epistolary essay
Tell us in the comments: Which of these prompts are you going to use to write a direct address or epistolary essay?

Patrice Gopo is the child of Jamaican immigrants and was born and raised in Anchorage, Alaska. She is an award-winning essayist and the author of All the Colors We Will See: Reflections on Barriers, Brokenness, and Finding Our Way (a Fall 2018 Barnes & Noble Discover Great New Writers selection). Her ties to Jamaica and other parts of the world sparked her early desire to travel to the cities and countries she traced on a globe. In time, as she began writing about her experiences, Patrice became interested in how places contribute to the people we become. Ultimately, she hopes her stories celebrate the beauty of living a multifaceted life. Patrice lives with her family in North Carolina—a place she considers another home. All the Places We Call Home is her first picture book.
To connect with Patrice, you can find her on her website or follow her on Facebook , Twitter , and Instagram .
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
Enjoyed this article?
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.
DIYMFA Social

Learn more »
Writer Fuel
Get email updates including a free diy mfa starter kit.
………………………….. This mini-course delivered via email gives you resources so you can jumpstart your personalized program. …………………………..
The Resources
New start here, writing resources.
Use these craft and creativity resources to Write with Focus.
…………………………..
Reading Resources
Discover the basics of Reading With Purpose.
Community Resources
Learn techniques to Build Your Community.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Essay
Last Updated: February 1, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Megaera Lorenz, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 18 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 7,926,087 times.
An essay is a common type of academic writing that you'll likely be asked to do in multiple classes. Before you start writing your essay, make sure you understand the details of the assignment so that you know how to approach the essay and what your focus should be. Once you've chosen a topic, do some research and narrow down the main argument(s) you'd like to make. From there, you'll need to write an outline and flesh out your essay, which should consist of an introduction, body, and conclusion. After your essay is drafted, spend some time revising it to ensure your writing is as strong as possible.
Understanding Your Assignment

- The compare/contrast essay , which focuses on analyzing the similarities and differences between 2 things, such as ideas, people, events, places, or works of art.
- The narrative essay , which tells a story.
- The argumentative essay , in which the writer uses evidence and examples to convince the reader of their point of view.
- The critical or analytical essay, which examines something (such as a text or work of art) in detail. This type of essay may attempt to answer specific questions about the subject or focus more generally on its meaning.
- The informative essay , that educates the reader about a topic.

- How long your essay should be
- Which citation style to use
- Formatting requirements, such as margin size , line spacing, and font size and type
Christopher Taylor, PhD
Christopher Taylor, Professor of English, tells us: "Most essays will contain an introduction, a body or discussion portion, and a conclusion. When assigned a college essay, make sure to check the specific structural conventions related to your essay genre , your field of study, and your professor's expectations."

- If you're doing a research-based essay , you might find some inspiration from reading through some of the major sources on the subject.
- For a critical essay, you might choose to focus on a particular theme in the work you're discussing, or analyze the meaning of a specific passage.

- If you're having trouble narrowing down your topic, your instructor might be able to provide guidance or inspiration.
Planning and Organizing Your Essay

- Academic books and journals tend to be good sources of information. In addition to print sources, you may be able to find reliable information in scholarly databases such as JSTOR and Google Scholar.
- You can also look for primary source documents, such as letters, eyewitness accounts, and photographs.
- Always evaluate your sources critically. Even research papers by reputable academics can contain hidden biases, outdated information, and simple errors or faulty logic.
Tip: In general, Wikipedia articles are not considered appropriate sources for academic writing. However, you may be able to find useful sources in the “References” section at the end of the article.

- You might find it helpful to write your notes down on individual note cards or enter them into a text document on your computer so you can easily copy, paste , and rearrange them however you like.
- Try organizing your notes into different categories so you can identify specific ideas you'd like to focus on. For example, if you're analyzing a short story , you might put all your notes on a particular theme or character together.

- For example, if your essay is about the factors that led to the end of the Bronze Age in the ancient Middle East, you might focus on the question, “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?”

- One easy way to come up with a thesis statement is to briefly answer the main question you would like to address.
- For example, if the question is “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?” then your thesis might be, “Natural disasters during the Late Bronze Age destabilized local economies across the region. This set in motion a series of mass migrations of different peoples, creating widespread conflict that contributed to the collapse of several major Bronze Age political centers.”

- When you write the outline, think about how you would like to organize your essay. For example, you might start with your strongest arguments and then move to the weakest ones. Or, you could begin with a general overview of the source you're analyzing and then move on to addressing the major themes, tone, and style of the work.
- Introduction
- Point 1, with supporting examples
- Point 2, with supporting examples
- Point 3, with supporting examples
- Major counter-argument(s) to your thesis
- Your rebuttals to the counter-argument(s)
Drafting the Essay

- For example, if you're writing a critical essay about a work of art, your introduction might start with some basic information about the work, such as who created it, when and where it was created, and a brief description of the work itself. From there, introduce the question(s) about the work you'd like to address and present your thesis.
- A strong introduction should also contain a brief transitional sentence that creates a link to the first point or argument you would like to make. For example, if you're discussing the use of color in a work of art, lead-in by saying you'd like to start with an overview of symbolic color use in contemporary works by other artists.
Tip: Some writers find it helpful to write the introduction after they've written the rest of the essay. Once you've written out your main points, it's easier to summarize the gist of your essay in a few introductory sentences.

- For example, your topic sentence might be something like, “Arthur Conan Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories are among the many literary influences apparent in P. G. Wodehouse's Jeeves novels.” You could then back this up by quoting a passage that contains a reference to Sherlock Holmes.
- Try to show how the arguments in each paragraph link back to the main thesis of your essay.

- When creating transitions, transitional phrases can be helpful. For example, use words and phrases such as “In addition,” “Therefore,” “Similarly,” “Subsequently,” or “As a result.”
- For example, if you've just discussed the use of color to create contrast in a work of art, you might start the next paragraph with, “In addition to color, the artist also uses different line weights to distinguish between the more static and dynamic figures in the scene.”

- For example, if you're arguing that a particular kind of shrimp decorates its shell with red algae to attract a mate, you'll need to address the counterargument that the shell decoration is a warning to predators. You might do this by presenting evidence that the red shrimp are, in fact, more likely to get eaten than shrimp with undecorated shells.

- The way you cite your sources will vary depending on the citation style you're using. Typically, you'll need to include the name of the author, the title and publication date of the source, and location information such as the page number on which the information appears.
- In general, you don't need to cite common knowledge. For example, if you say, “A zebra is a type of mammal,” you probably won't need to cite a source.
- If you've cited any sources in the essay, you'll need to include a list of works cited (or a bibliography ) at the end.

- Keep your conclusion brief. While the appropriate length will vary based on the length of the essay, it should typically be no longer than 1-2 paragraphs.
- For example, if you're writing a 1,000-word essay, your conclusion should be about 4-5 sentences long. [16] X Research source
Revising the Essay

- If you don't have time to spend a couple of days away from your essay, at least take a few hours to relax or work on something else.

- Excessive wordiness
- Points that aren't explained enough
- Tangents or unnecessary information
- Unclear transitions or illogical organization
- Spelling , grammar , style, and formatting problems
- Inappropriate language or tone (e.g., slang or informal language in an academic essay)

- You might have to cut material from your essay in some places and add new material to others.
- You might also end up reordering some of the content of the essay if you think that helps it flow better.

- Read over each line slowly and carefully. It may be helpful to read each sentence out loud to yourself.
Tip: If possible, have someone else check your work. When you've been looking at your writing for too long, your brain begins to fill in what it expects to see rather than what's there, making it harder for you to spot mistakes.

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/essay-types
- ↑ https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/resources/essay-writing/six-top-tips-for-writing-a-great-essay
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/tips-reading-assignment-prompt
- ↑ https://library.unr.edu/help/quick-how-tos/writing/integrating-sources-into-your-paper
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/researching/notes-from-research/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/developing-thesis
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/outlining
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-incorporate-a-counter-argument.html
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.utsc.utoronto.ca/twc/sites/utsc.utoronto.ca.twc/files/resource-files/Intros-Conclusions.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/8-4-revising-and-editing/
- ↑ https://writing.ku.edu/writing-process
About This Article

If you need to write an essay, start by gathering information from reputable sources, like books from the library or scholarly journals online. Take detailed notes and keep track of which facts come from which sources. As you're taking notes, look for a central theme that you're interested in writing about to create your thesis statement. Then, organize your notes into an outline that supports and explains your thesis statement. Working from your outline, write an introduction and subsequent paragraphs to address each major point. Start every paragraph with a topic sentence that briefly explains the main point of that paragraph. Finally, finish your paper with a strong conclusion that sums up the most important points. For tips from our English Professor co-author on helpful revision techniques, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Muhammad Talha Javaid
Feb 7, 2019
Did this article help you?
Gabrielle Mattijetz
May 8, 2017
Shahzad Saleem
Jun 20, 2018
Barbara Gonzalez
Aug 6, 2016
Kniziel Sanders
Oct 17, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

- Integrating Direct Quotations into Your Writing
by acburton | Mar 21, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
If you’ve ever had a professor ask you to “use quotes” or quote other texts in your writing before, you know that it’s no easy task. It can feel awkward sometimes to determine what parts of the text are worth quoting, as well as how to directly quote in your writing without sounding too formulaic or repetitive. Keep reading for some strategies on effectively using direct quotations in your next writing project!
Why do I need to know how to directly quote?
If you’ve seen our blog post on “Quoting Directly,” you know that using direct quotations (or “quotes”) in our writing can be useful for a variety of reasons. By quoting other credible, relevant sources in our own writing projects, we can provide more convincing evidence and reasoning for our own ideas. Direct quotations are a type of support we can provide for our own arguments and claims, as it demonstrates to our readers that other writers agree with what we have to say.
What are different ways to directly quote in my writing so that I don’t sound repetitive?
A common way to integrate “quotes” in our writing is with the use of a signal phrase , which is a short phrase that indicates to readers that the writer is about to introduce another source. For example, we often use the phrase “According to” as a common signal phrase for introducing quotations. However, if we were to use “According to” for every single quotation in our essays, our writing would start to sound awfully repetitive and potentially boring or uninteresting.
So, here are some different approaches you can take for integrating direct quotations to have more variety and style in your writing!
1. Use a signal phrase to introduce the quotation
The two most commonly used signal phrases only require a couple of words, primarily a verb and the author’s name:
- The introductory phrase: “According to (author’s name and/or title of source),”. e.g., “According to Ahmed,” or “According to Ulmer in Internet Invention ,”.
After a signal phrase, you can quote from the text directly. Here are some important reminders to keep in mind whenever you directly quote another source in your own writing:
- Use quotation marks “ “ and copy the passage exactly as it appears in the original text. If there is a grammatical or spelling error in the original source, you can use [sic] to cue to your reader that you did not make the mistake and are intentionally quoting the source material (for more on using [sic] in direct quotations, see our post on Quoting Directly ).
- Long Quotations in MLA format
- Long Quotations in APA format
Note: You can also use a signal phrase after the direct quotation for more variety in your sentence structure and style. You’d follow the same rules, except the quotation would come first, followed by your ‘says’ verb and the author.
It is usually better to lead with the author’s name and a ‘says’ verb because this introduces where the quotation is coming from (ensuring your reader is not confused) and is written in active voice, which is more direct and concise.
Example According to Melissa Dahl, “[Cringe is] the intense visceral reaction produced by an awkward moment, an unpleasant kind of self-recognition where you suddenly see yourself through someone else’s eyes. It’s a forced moment of self-awareness, and it usually makes you cognizant of the disappointing fact that you aren’t measuring up to your own self-concept” (Wynn).
While this is a direct quotation attributed to author Melissa Dahl, the in-text citation is credited to (Wynn) because the writer found this quotation in an original source published by Natalie Wynn. If you directly quote an author or writer whose work is quoted by another source, you cite the source that “houses” the passage. In other words, you cite the author who introduced you to the work. You can still credit the original author by introducing them in your signal phrase, as shown in the example above, but make sure your in-text citation credits the source you found the passage in.
2. Summarize the main ideas of the quotation to create a framework for the quotation, then use a colon to present the quotation.
For this method, you would provide a concise overview of the main ideas from the passage you wish to quote as a way of contextualizing what the source is about. This provides a helpful framework for the reader to understand the purpose and meaning of your quote better.
Example In Rebecca Solnit’s Wanderlust: A History of Walking, she raises several theoretical and philosophical viewpoints concerning both the act of walking, or flânerie, and the walker, or flâneur. On escapism, Solnit posits: “In the city, one is alone because the world is made up of strangers, and to be a stranger surrounded by strangers, to walk along silently bearing one’s secrets and imagining those of the people one passes, is among the starkest of luxuries” (23).
3. Blend a shorter quotation into your own sentence structure
This is the best method to use if you have only a short passage, some key words, or a specific phrase you want to quote in your writing. For this method, you want to build your own original sentence that leads up to the key ideas in your short quotation to blend it together as one cohesive sentence.
Example Within a participatory culture, individuals are often gathered together as a community due to shared interest networks, like video games, in which “members believe that their contributions matter” and there is “some type of informal mentorship whereby what is known by the most experienced is passed along to novices” (Jenkins 7).
Practice in the Writing Center
For more support and guidance on directly quoting, make an appointment with us here at the Writing Center! We can help you integrate “quotes” into your writing projects effectively and with style so that your support is interesting and convincing to readers.
For further reading, check out these resources from the Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages (TESOL) International Association:
- Integrate Quotations in Writing, by Carla Mannix (2017)
- List of Reporting Verbs, from University of Technology Sydney
***Adapted from TESOL International Association Handout “Integrate Quotations in Writing” by Carla Mannix, Nov. 2017
Our Newest Resources!
- Transitioning to Long-form Writing
- Developing a Research Question
- Nurturing a Growth Mindset to Overcome Writing Challenges and Develop Confidence in College Level Writing
- An Introduction to Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Quoting
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
Should college essays touch on race? Some feel the affirmative action ruling leaves them no choice
When the supreme court ended affirmative action, it left the college essay as one of few places where race can play a role in admissions decisions.

Max Decker, a senior at Lincoln High School, sits for a portrait in the school library where he often worked on writing his college essays, in Portland, Ore., Wednesday, March 20, 2024.
Amanda Loman / AP
Like many students, Max Decker of Portland, Oregon, had drafted a college essay on one topic, only to change direction after the Supreme Court ruling in June.
Decker initially wrote about his love for video games. In a childhood surrounded by constant change, navigating his parents’ divorce, the games he took from place to place on his Nintendo DS were a source of comfort.
But the essay he submitted to colleges focused on the community he found through Word is Bond, a leadership group for young Black men in Portland.
As the only biracial, Jewish kid with divorced parents in a predominantly white, Christian community, Decker wrote he felt like the odd one out. On a trip with Word is Bond to Capitol Hill, he and friends who looked just like him shook hands with lawmakers. The experience, he wrote, changed how he saw himself.
“It’s because I’m different that I provide something precious to the world, not the other way around,” wrote Decker, whose top college choice is Tulane, in New Orleans, because of the region’s diversity.
This year’s senior class is the first in decades to navigate college admissions without affirmative action . The Supreme Court upheld the practice in decisions going back to the 1970s, but this court’s conservative supermajority found it is unconstitutional for colleges to give students extra weight because of their race alone.
Still, the decision left room for race to play an indirect role: Chief Justice John Roberts wrote universities can still consider how an applicant’s life was shaped by their race, “so long as that discussion is concretely tied to a quality of character or unique ability.”
Scores of colleges responded with new essay prompts asking about students’ backgrounds.

FILE - Demonstrators protest outside of the Supreme Court in Washington, in this June 29, 2023 file photo, after the Supreme Court struck down affirmative action in college admissions, saying race cannot be a factor.
Jose Luis Magana / AP
Writing about feeling more comfortable with being Black
When Darrian Merritt started writing his essay, his first instinct was to write about events that led to him going to live with his grandmother as a child. Those were painful memories, but he thought they might play well at schools like Yale, Stanford and Vanderbilt.
“I feel like the admissions committee might expect a sob story or a tragic story,” said Merritt, a senior in Cleveland. “I wrestled with that a lot.”
Eventually he abandoned the idea and aimed for an essay that would stand out for its positivity.
Merritt wrote about a summer camp where he started to feel more comfortable in his own skin. He described embracing his personality and defying his tendency to please others. But the essay also reflects on his feelings of not being “Black enough” and getting made fun of for listening to “white people music.”
Related: Oregon colleges, universities weigh potential outcomes of US Supreme Court decision on affirmative action
Essay about how to embrace natural hair
When Hillary Amofa started writing her college essay, she told the story she thought admissions offices wanted to hear. About being the daughter of immigrants from Ghana and growing up in a small apartment in Chicago. About hardship and struggle.
Then she deleted it all.
“I would just find myself kind of trauma-dumping,” said the 18-year-old senior at Lincoln Park High School in Chicago. “And I’m just like, this doesn’t really say anything about me as a person.”
Amofa was just starting to think about her essay when the court issued its decision, and it left her with a wave of questions. Could she still write about her race? Could she be penalized for it? She wanted to tell colleges about her heritage but she didn’t want to be defined by it.
In English class, Amofa and her classmates read sample essays that all seemed to focus on some trauma or hardship. It left her with the impression she had to write about her life’s hardest moments to show how far she’d come. But she and some classmates wondered if their lives had been hard enough to catch the attention of admissions offices.

Hillary Amofa, laughs as she participates in a team building game with members of the Lincoln Park High School step team after school Friday, March 8, 2024, in Chicago. When she started writing her college essay, Amofa told the story she thought admissions offices wanted to hear. She wrote about being the daughter of immigrants from Ghana, about growing up in a small apartment in Chicago. She described hardship and struggle. Then she deleted it all. "I would just find myself kind of trauma-dumping," said the 18 year-old senior, "And I'm just like, this doesn't really say anything about me as a person."
Charles Rex Arbogast / AP
Amofa used to think affirmative action was only a factor at schools like Harvard and Yale. After the court’s ruling, she was surprised to find that race was taken into account even at public universities she was applying to.
Now, without affirmative action, she wondered if mostly white schools will become even whiter.
It’s been on her mind as she chooses between Indiana University and the University of Dayton, both of which have relatively few Black students. When she was one of the only Black students in her grade school, she could fall back on her family and Ghanaian friends at church. At college, she worries about loneliness.
“That’s what I’m nervous about,” she said. “Going and just feeling so isolated, even though I’m constantly around people.”
Related: Some Oregon universities, politicians disappointed in Supreme Court decision on affirmative action
The first drafts of her essay didn’t tell colleges about who she is now, she said.
Her final essay describes how she came to embrace her natural hair. She wrote about going to a mostly white grade school where classmates made jokes about her afro.
Over time, she ignored their insults and found beauty in the styles worn by women in her life. She now runs a business doing braids and other hairstyles in her neighborhood.
“Criticism will persist,” she wrote “but it loses its power when you know there’s a crown on your head!”
Ma reported from Portland, Oregon.
The Associated Press’ education coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org .
OPB’s First Look newsletter
Streaming Now
Weekend Edition Saturday with Scott Simon
site categories
- Edinburgh Film Festival Expands Under Partnership With Fringe Festival Including New Venues And Competition Strands
‘White:’ Steven Waddington To Write And Direct Biopic Based On The Life Of Veteran Snooker Player Jimmy White
By Zac Ntim
International Reporter
More Stories By Zac
- BFI Promotes Melanie Hoyes To Director Of Inclusion
- Locarno Film Festival Teams With Sony & The Academy Museum To Celebrate Columbia Pictures Centennial With ‘The Lady With The Torch’ Retrospective

EXCLUSIVE: Actor Steven Waddington ( The Imitation Game ) has penned a screenplay that he will direct based on the life of veteran Snooker player Jimmy White, with Aneurin Barnard ( Dunkirk ) and Ray Winstone ( Sexy Beast ) signed on to star.
Related Stories

Marvel Cinematic Universe Work Called "Soul-Destroying" By Actor Ray Winstone

Stephen Moyer's Sophomore Feature 'A Bit Of Light' Acquired By Quiver; Anna Paquin, Ray Winstone Star
Produced by Black Water Pictures and Lipsync Productions, the feature shoots in London this April. Winstone and his long-term manager, Michael Wiggs, are also on board as co-producers. The film will mark Waddington’s feature directorial debut.
“I want to illuminate the darkness Jimmy dragged himself through as he lost much more than those famous six World Championship finals,” said Waddington.
“Set during the 80s and 90s when these tournaments were played live to millions at home, this shy, complicated genius tore himself apart behind the scenes – and it’s this vicious, self-inflicted power struggle I want to capture, as his greatest match became Jimmy White Vs his own demons.”
Nicknamed “The Whirlwind” because of his flamboyant style of play, White is one of Snooker’s most popular exports. He is best known for reaching the final of the World Championships on six occasions without winning. White has also been vocal about his struggles with substance abuse, once telling a BBC documentary that at the height of his fame, he plowed through £35,000 ($44,000) on a crack cocaine addiction. White has also successfully battled Cancer and was awarded an MBE in 1999 for his services to the sport of Snooker.
Wiggs added: “Ray and I have admired Steve as an actor for many years, and when we read this incredibly sharp, poignant, and funny script, there was no question that we wanted to get involved.”
Must Read Stories
Fifth season undergoes layoffs in film division, including two vps.

Monster Mash Attacks! $75M Stateside Bow & Kingly Overseas Start
Armorer hannah gutierrez-reed will stay in jail as judge denies new trial, ezra miller’s ‘invincible’ role recast for season 2 of prime video animated series.
Subscribe to Deadline Breaking News Alerts and keep your inbox happy.
Read More About:
No comments.
Deadline is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Deadline Hollywood, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
WELCOME TO THE FAMILY! Please check your email for confirmation from us.
Sob stories? Trauma dumps? Black kids worry about writing college essays after affirmative action ban
When the Supreme Court ended affirmative action in higher education, it left the college essay as one of few places where race can play a role in admissions decisions.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share via Email
- Copy Link Link Copied

CHICAGO (AP) — When she started writing her college essay, Hillary Amofa told the story she thought admissions offices wanted to hear. About being the daughter of immigrants from Ghana and growing up in a small apartment in Chicago. About hardship and struggle.
Then she deleted it all.
“I would just find myself kind of trauma-dumping,” said the 18-year-old senior at Lincoln Park High School in Chicago. “And I’m just like, this doesn’t really say anything about me as a person.”
When the Supreme Court ended affirmative action in higher education , it left the college essay as one of few places where race can play a role in admissions decisions. For many students of color, instantly more was riding on the already high-stakes writing assignment. Some say they felt pressure to exploit their hardships as they competed for a spot on campus.
Amofa was just starting to think about her essay when the court issued its decision, and it left her with a wave of questions. Could she still write about her race? Could she be penalized for it? She wanted to tell colleges about her heritage but she didn’t want to be defined by it.
In English class, Amofa and her classmates read sample essays that all seemed to focus on some trauma or hardship. It left her with the impression she had to write about her life’s hardest moments to show how far she’d come. But she and some of her classmates wondered if their lives had been hard enough to catch the attention of admissions offices.
“For a lot of students, there’s a feeling of, like, having to go through something so horrible to feel worthy of going to school, which is kind of sad,” said Amofa, the daughter of a hospital technician and an Uber driver.
This year’s senior class is the first in decades to navigate college admissions without affirmative action. The Supreme Court upheld the practice in decisions going back to the 1970s, but this court’s conservative supermajority found it is unconstitutional for colleges to give students extra weight because of their race alone.
Still, the decision left room for race to play an indirect role: Chief Justice John Roberts wrote universities can still consider how an applicant’s life was shaped by their race, “so long as that discussion is concretely tied to a quality of character or unique ability.”
“A benefit to a student who overcame racial discrimination, for example, must be tied to that student’s courage and determination,” he wrote.
Scores of colleges responded with new essay prompts asking about students’ backgrounds. Brown University asked applicants how “an aspect of your growing up has inspired or challenged you.” Rice University asked students how their perspectives were shaped by their “background, experiences, upbringing, and/or racial identity.”
Wondering if schools ‘expect a sob story’
When Darrian Merritt started writing his essay, he knew the stakes were higher than ever because of the court’s decision. His first instinct was to write about events that led to him going to live with his grandmother as a child.
Those were painful memories, but he thought they might play well at schools like Yale, Stanford and Vanderbilt.
“I feel like the admissions committee might expect a sob story or a tragic story,” said Merritt, a senior in Cleveland. “And if you don’t provide that, then maybe they’re not going to feel like you went through enough to deserve having a spot at the university. I wrestled with that a lot.”
He wrote drafts focusing on his childhood, but it never amounted to more than a collection of memories. Eventually he abandoned the idea and aimed for an essay that would stand out for its positivity.
Merritt wrote about a summer camp where he started to feel more comfortable in his own skin. He described embracing his personality and defying his tendency to please others. The essay had humor — it centered on a water gun fight where he had victory in sight but, in a comedic twist, slipped and fell. But the essay also reflects on his feelings of not being “Black enough” and getting made fun of for listening to “white people music.”
“I was like, ‘OK, I’m going to write this for me, and we’re just going to see how it goes,’” he said. “It just felt real, and it felt like an honest story.”
The essay describes a breakthrough as he learned “to take ownership of myself and my future by sharing my true personality with the people I encounter. … I realized that the first chapter of my own story had just been written.”
A ruling prompts pivots on essay topics
Like many students, Max Decker of Portland, Oregon, had drafted a college essay on one topic, only to change direction after the Supreme Court ruling in June.
Decker initially wrote about his love for video games. In a childhood surrounded by constant change, navigating his parents’ divorce, the games he took from place to place on his Nintendo DS were a source of comfort.
But the essay he submitted to colleges focused on the community he found through Word is Bond, a leadership group for young Black men in Portland.
As the only biracial, Jewish kid with divorced parents in a predominantly white, Christian community, Decker wrote he constantly felt like the odd one out. On a trip with Word is Bond to Capitol Hill, he and friends who looked just like him shook hands with lawmakers. The experience, he wrote, changed how he saw himself.
Recommended Stories

Ahmaud Arbery’s killers seeking to overturn their hate crime convictions
Associated Press
High school teacher and students sue over Arkansas’ ban on critical race theory

House Republicans aim to strip funding from medical schools over diversity programs
Ashlee Banks

DEI programs and concepts that could make someone feel guilty about their race banned in Alabama

America’s youngest teacher is a 16-year-old MBA student
TheGrio Lifestyle

MF Doom and Madlib’s ‘Madvillainy’ — now 20 years old — is the timeless classic album we all thought it would be in 2004
Panama Jackson

Before heading ‘outside,’ spring-clean your finances in 4 steps
Jennifer Streaks
“It’s because I’m different that I provide something precious to the world, not the other way around,” he wrote.
As a first-generation college student, Decker thought about the subtle ways his peers seemed to know more about navigating the admissions process. They made sure to get into advanced classes at the start of high school, and they knew how to secure glowing letters of recommendation.
If writing about race would give him a slight edge and show admissions officers a fuller picture of his achievements, he wanted to take that small advantage.
His first memory about race, Decker said, was when he went to get a haircut in elementary school and the barber made rude comments about his curly hair. Until recently, the insecurity that moment created led him to keep his hair buzzed short.
Through Word is Bond, Decker said he found a space to explore his identity as a Black man. It was one of the first times he was surrounded by Black peers and saw Black role models. It filled him with a sense of pride in his identity. No more buzzcut.
The pressure to write about race involved a tradeoff with other important things in his life, Decker said. That included his passion for journalism, like the piece he wrote on efforts to revive a once-thriving Black neighborhood in Portland. In the end, he squeezed in 100 characters about his journalism under the application’s activities section.
“My final essay, it felt true to myself. But the difference between that and my other essay was the fact that it wasn’t the truth that I necessarily wanted to share,” said Decker, whose top college choice is Tulane, in New Orleans, because of the region’s diversity. “It felt like I just had to limit the truth I was sharing to what I feel like the world is expecting of me.”
Spelling out the impact of race
Before the Supreme Court ruling, it seemed a given to Imani Laird that colleges would consider the ways that race had touched her life. But now, she felt like she had to spell it out.
As she started her essay, she reflected on how she had faced bias or felt overlooked as a Black student in predominantly white spaces.
There was the year in math class when the teacher kept calling her by the name of another Black student. There were the comments that she’d have an easier time getting into college because she was Black.
“I didn’t have it easier because of my race,” said Laird, a senior at Newton South High School in the Boston suburbs who was accepted at Wellesley and Howard University , and is waiting to hear from several Ivy League colleges. “I had stuff I had to overcome.”
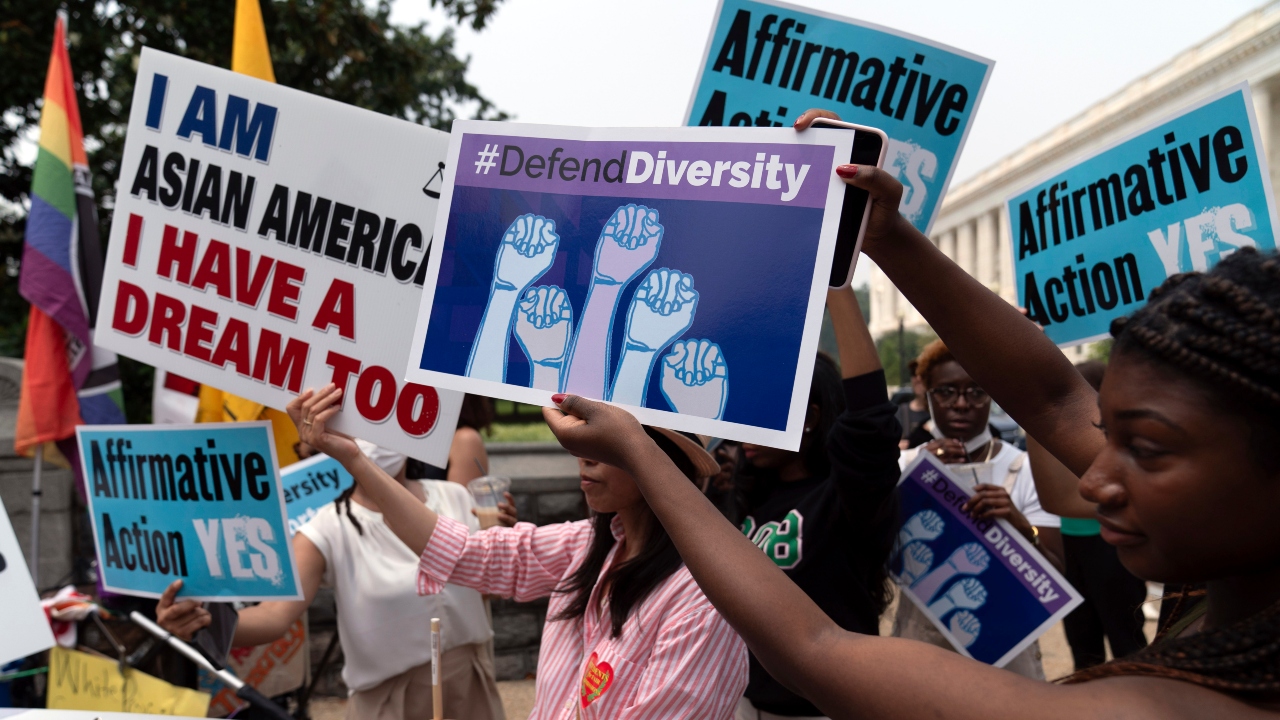

In her final essays, she wrote about her grandfather, who served in the military but was denied access to GI Bill benefits because of his race.
She described how discrimination fueled her ambition to excel and pursue a career in public policy.
“So, I never settled for mediocrity,” she wrote. “Regardless of the subject, my goal in class was not just to participate but to excel. Beyond academics, I wanted to excel while remembering what started this motivation in the first place.”
Will schools lose racial diversity?
Amofa used to think affirmative action was only a factor at schools like Harvard and Yale. After the court’s ruling, she was surprised to find that race was taken into account even at some public universities she was applying to.
Now, without affirmative action, she wondered if mostly white schools will become even whiter.
It’s been on her mind as she chooses between Indiana University and the University of Dayton, both of which have relatively few Black students. When she was one of the only Black students in her grade school, she could fall back on her family and Ghanaian friends at church. At college, she worries about loneliness.
“That’s what I’m nervous about,” she said. “Going and just feeling so isolated, even though I’m constantly around people.”
The first drafts of her essay focused on growing up in a low-income family, sharing a bedroom with her brother and grandmother. But it didn’t tell colleges about who she is now, she said.
Her final essay tells how she came to embrace her natural hair. She wrote about going to a mostly white grade school where classmates made jokes about her afro. When her grandmother sent her back with braids or cornrows, they made fun of those too.
Over time, she ignored their insults and found beauty in the styles worn by women in her life. She now runs a business doing braids and other hairstyles in her neighborhood.
“I stopped seeing myself through the lens of the European traditional beauty standards and started seeing myself through the lens that I created,” Amofa wrote.
“Criticism will persist, but it loses its power when you know there’s a crown on your head!”
Never miss a beat: Get our daily stories straight to your inbox with theGrio’s newsletter.
- Share on Facebook Facebook
- Share on Twitter Twitter
- Share via Email Email
- Copy Link Copy Link Link Copied

STREAM FREE MOVIES, LIFESTYLE AND NEWS CONTENT ON OUR NEW APP
If you want this website to work, you must enable javascript.

Writing My Autobiography

A re you still writing?” he asked.
“I am,” I answered.
“What are you working on at the moment?”
“An autobiography,” I said.
“Interesting,” he replied. “Whose?”
The implication here, you will note, is that mine hasn’t been a life sufficiently interesting to merit an autobiography. The implication isn’t altogether foolish. Most autobiographies, at least the best autobiographies, have been written by people who have historical standing, or have known many important people, or have lived in significant times, or have noteworthy family connections or serious lessons to convey . I qualify on none of these grounds. Not that, roughly two years ago when I sat down to write my autobiography, I let that stop me.
An autobiography, to state the obvious, is at base a biography written by its own subject. But how is one to write it: as a matter of setting the record straight, as a form of confessional, as a mode of seeking justice, or as a justification of one’s life? “An autobiography,” wrote George Orwell, “is only to be trusted when it reveals something disgraceful. A man who gives a good account of himself is probably lying, since any life when viewed from the inside is simply a series of defeats.” Is this true? I prefer to think not.
Autobiography is a complex enterprise, calling for its author not only to know himself but to be honest in conveying that knowledge. “I could inform the dullest author how he might write an interesting book,” wrote Samuel Taylor Coleridge. “Let him relate the events of his own life with Honesty, not disguising the feelings that accompanied them.” One of the nicest things about being a professor, it has been said, is that one gets to talk for fifty minutes without being interrupted. So one of the allurements of autobiography is that one gets to write hundreds of pages about that eminently fascinating character, oneself, even if in doing so one only establishes one’s insignificance.
The great autobiographies—of which there have not been all that many—have been wildly various. One of the first, that of the Renaissance sculptor Benvenuto Cellini, is marked by an almost unrelieved braggadocio: No artist was more perfect, no warrior more brave, no lover more pleasing than the author, or so he would have us believe. Edward Gibbon’s autobiography, though elegantly written, is disappointing in its brevity. That of Jean-Jacques Rousseau, heavily striking the confessional note, might have been told in a booth to a priest. Ben Franklin’s autobiography is full of advice on how the rest of us should live. John Stuart Mill’s is astounding in its account of its author’s prodigiously early education, which began with his learning Greek under his father’s instruction at the age of three. Then there is Henry Adams’s autobiography, suffused with disappointment over his feeling out of joint with his times and the world’s not recognizing his true value. In Making It , Norman Podhoretz wrote an autobiography informed by a single message, which he termed a “dirty little secret,” namely that there is nothing wrong with ambition and that success, despite what leftist intellectuals might claim, is nothing to be ashamed of.
Please note that all of these are books written by men. Might it be that women lack the vanity required to write—or should I say “indulge in”—the literary act of autobiography? In Mary Beard’s Emperor of Rome , I recently read that Agrippina the Younger, the mother of Nero, wrote her autobiography, which has not survived, and which Mary Beard counts as “one of the great losses of all classical literature.” I wish that Jane Austen had written an autobiography, and so too George Eliot and Willa Cather. Perhaps these three women, great writers all, were too sensibly modest for autobiography, that least modest of all literary forms.
A utobiography can be the making or breaking of writers who attempt it. John Stuart Mill’s autobiography has gone a long way toward humanizing a writer whose other writings tend toward the coldly formal. Harold Laski wrote that Mill’s “ Autobiography , in the end the most imperishable of his writings, is a record as noble as any in our literature of consistent devotion to the public good.”
If Mill’s autobiography humanized him, the autobiography of the novelist Anthony Trollope did for him something approaching the reverse. In An Autobiography , Trollope disdains the notion of an author’s needing inspiration to write well. He reports that “there was no day on which it was my positive duty to write for the publishers, as it was my duty to write reports for the Post Office,” where he had a regular job. “I was free to be idle if I pleased. But as I had made up my mind to undertake this second profession [that of novelist], I found it to be expedient to bind myself by certain self-imposed laws.” Trollope recounts—emphasis here on “counts”—that as a novelist he averages forty pages per week, at 250 words per page. He writes: “There are those who would be ashamed to subject themselves to such a taskmaster, and who think that the man who works with his imagination should allow himself to wait till inspiration moves him. When I have heard such doctrine preached, I have hardly been able to repress my scorn.” Trollope then mentions that on the day after he finished his novel Doctor Thorne , he began writing his next novel, The Bertrams . For a long spell the literati refused to forgive Trollope for shearing inspiration away from the creation of literary art, for comparing the job of the novelist to a job at the post office. Only the splendid quality of his many novels eventually won him forgiveness and proper recognition.
A serious biography takes up what the world thinks of its subject, what his friends and family think of him, and—if the information is available in letters, diaries, journals, or interviews—what he thinks of himself. An autobiography is ultimately about the last question: what the author thinks of himself. Yet how many of us have sufficient self-knowledge to give a convincing answer? In her splendid novel Memoirs of Hadrian , Marguerite Yourcenar has Hadrian note: “When I seek deep within me for knowledge of myself what I find is obscure, internal, unformulated, and as secret as any complicity.” The unexamined life may not be worth living, but the scrupulously examined one is rare indeed.
My own life has not provided the richest fodder for autobiography. For one thing, it has not featured much in the way of drama. For another, good fortune has allowed me the freedom to do with my life much as I have wished. I have given my autobiography the title Never Say You’ve Had a Lucky Life , with the subtitle Especially If You’ve Had a Lucky Life . Now well along in its closing chapter, mine, I contend, has been thus far—here I pause to touch wood—a most lucky life.
My title derives from the story of Croesus, who ruled the country of Lydia from circa 585–547 b.c. , and who is perhaps today best known for the phrase “rich as Croesus.” The vastly wealthy Croesus thought himself the luckiest man on earth and asked confirmation of this from Solon, the wise Athenian, who told him that in fact the luckiest man on earth was another Athenian who had two sons in that year’s Olympics. When Croesus asked who was second luckiest, Solon cited another Greek who had a most happy family life. Croesus was displeased but not convinced by Solon’s answers. Years later he was captured by the Persian Cyrus, divested of his kingdom and his wealth, and set on a pyre to be burned alive, before which he was heard to exclaim that Solon had been right. The moral of the story is, of course: Never say you have had a lucky life until you know how your life ends.
I have known serious sadness in my life. I have undergone a divorce. I have become a member of that most dolorous of clubs, parents who have buried one of their children. Yet I have had much to be grateful for. In the final paragraph of a book I wrote some years ago on the subject of ambition, I noted that “We do not choose our parents. We do not choose our historical epoch, or the country of our birth, or the immediate circumstances of our upbringing.” In all these realms, I lucked out. I was born to intelligent, kindly parents; at a time that, though I was drafted into the army, allowed me to miss being called up to fight in any wars; and in the largely unmitigated prosperity enjoyed by the world’s most interesting country, the United States of America.
Writing is a form of discovery. Yet can even writing ferret out the quality and meaning of one’s own life? Alexis de Tocqueville, the endlessly quotable Tocqueville, wrote: “The fate of individuals is still more hidden than that of peoples,” and “the destinies of individuals are often as uncertain as those of nations.” Fate, destiny, those two great tricksters, who knows what they have in store for one, even in the final days of one’s life? I, for example, as late as the age of eighteen, had never heard the word “intellectual.” If you had asked me what a man of letters was, I would have said a guy who works at the post office. Yet I have been destined to function as an intellectual for the better part of my adult life, and have more than once been called a man of letters. Fate, destiny, go figure!
T he first question that arises in writing one’s autobiography is what to include and what to exclude. Take, for starters, sex. In his nearly seven-hundred-page autobiography, Journeys of the Mind , the historian of late antiquity Peter Brown waits until page 581 to mention, in the most glancing way, that he is married. Forty or so pages later, the name of a second wife is mentioned. Whether he had children with either of these wives, we never learn. But then, Brown’s is a purely intellectual autobiography, concerned all but exclusively with the development of the author’s mind and those who influenced that development.
My autobiography, though less than half the length of Brown’s, allowed no such luxury of reticence. Sex, especially when I was an adolescent, was a central subject, close to a preoccupation. After all, boys—as I frequently instructed my beautiful granddaughter Annabelle when she was growing up—are brutes. I came of age BP, or Before the Pill, and consummated sex, known in that day as “going all the way,” was not then a serious possibility. Too much was at risk—pregnancy, loss of reputation—for middle-class girls. My friends and I turned to prostitution.
Apart from occasionally picking up streetwalkers on some of Chicago’s darker streets, prostitution for the most part meant trips of sixty or so miles to the bordellos of Braidwood or Kankakee, Illinois. The sex, costing $3, was less than perfunctory. (“Don’t bother to take off your socks or that sweater,” one was instructed.) What was entailed was less sensual pleasure than a rite of passage, of becoming a man, of “losing your cherry,” a phrase I have only recently learned means forgoing one’s innocence. We usually went on these trips in groups of five or six in one or another of our fathers’ cars. Much joking on the way up and even more on the way back. Along Chicago’s Outer Drive, which we took home in those days, there was a Dad’s Old Fashioned Root Beer sign that read, “Have you had it lately?,” which always got a good laugh.
I like to think of myself as a shy pornographer, or, perhaps better, a sly pornographer. By this I mean that in my fiction and where necessary in my essays I do not shy away from the subject of sex, only from the need to describe it in any of its lurid details. So I have done in my autobiography. On the subject of sex in my first marriage (of two), for example, I say merely, “I did not want my money back.” But, then, all sex, if one comes to think about it, is essentially comic, except of course one’s own.
On the inclusion-exclusion question, the next subject I had to consider was money, or my personal finances. Financially I have nothing to brag about. In my autobiography I do, though, occasionally give the exact salaries—none of them spectacular—of the jobs I’ve held. With some hesitation (lest it seem boasting) I mention that a book I wrote on the subject of snobbery earned, with its paperback sale, roughly half-a-million dollars. I fail to mention those of my books that earned paltry royalties, or, as I came to think of them, peasantries. In my autobiography, I contented myself with noting my good fortune in being able to earn enough money doing pretty much what I wished to do and ending up having acquired enough money not to worry overmuch about financial matters. Like the man said, a lucky life.
If I deal glancingly in my autobiography with sex and personal finances, I tried to take a pass on politics. My own political development is of little interest. I started out in my political life a fairly standard liberal—which in those days meant despising Richard Nixon—and have ended up today contemptuous of both our political parties: Tweedledum and Tweedledumber, as the critic Dwight Macdonald referred to them. Forgive the self-congratulatory note, but in politics I prefer to think myself a member in good standing of that third American political party, never alas on the ballot, the anti-BS party.
Of course, sometimes one needs to have a politics, if only to fight off the politics of others. Ours is a time when politics seems to be swamping all else: art, education, journalism, culture generally. I have had the dubious distinction of having been “canceled,” for what were thought my political views, and I write about this experience in my autobiography. I was fired from the editorship of Phi Beta Kappa’s quarterly magazine, the American Scholar —a job I had held for more than twenty years—because of my ostensibly conservative, I suppose I ought to make that “right-wing,” politics. My chief cancellers were two academic feminists and an African-American historian-biographer, who sat on the senate, or governing board, of Phi Beta Kappa.
T he official version given out by Phi Beta Kappa for my cancellation—in those days still known as a firing—was that the magazine was losing subscribers and needed to seek younger readers. Neither assertion was true, but both currently appear in the Wikipedia entry under my name. The New York Times also printed this “official” but untrue version of my cancellation. In fact, I was canceled because I had failed to run anything in the magazine about academic feminism or race, both subjects that had already been done to death elsewhere and that I thought cliché-ridden and hence of little interest for a magazine I specifically tried to keep apolitical. During my twenty-two years at the American Scholar , the name of no current United States president was mentioned. If anything resembling a theme emerged during my editorship, it was the preservation of the tradition of the liberal arts, a subject on which I was able to acquire contributions from Jacques Barzun, Paul Kristeller, Hugh Trevor-Roper, Frederick Crews, and others.
That I was fired not for anything I had done but for things I had failed to do is an indication of how far we had come in the realm of political correctness. I take up this topic in my autobiography, one theme of which is the vast changes that have taken place in American culture over my lifetime. A notable example is an essay on homosexuality that I wrote and published in Harper’s in 1970, a mere fifty-three years ago. The essay made the points that we still did not know much about the origin of male homosexuality, that there was much hypocrisy concerning the subject, that homosexuals were living under considerable social pressure and prejudice, and that given a choice, most people would prefer that their children not be homosexual. This, as I say, was in 1970, before the gay liberation movement had got underway in earnest. The essay attracted a vast number of letters in opposition, and a man named Merle Miller, who claimed I was calling for genocide of homosexuals, wrote a book based on the essay. Gore Vidal, never known for his temperate reasoning, claimed my argument was ad Hitlerum . (Vidal, after contracting Epstein-Barr virus late in life, claimed that “Joseph Epstein gave it to me.”) I have never reprinted the essay in any of my collections because I felt that it would stir up too much strong feeling. For what it is worth, I also happen to be pleased by the greater tolerance accorded homosexuality in the half century since my essay was published.
The larger point is that today neither Harper’s nor any other mainstream magazine would dare to publish that essay. Yet a few years after the essay was published, I was offered a job teaching in the English Department of Northwestern University, and the year after that, I was appointed editor of the American Scholar. Today, of course, neither job would have been available to me.
Do these matters—my cancellation from the American Scholar , my unearned reputation as a homophobe—come under the heading of self-justification? Perhaps so. But then, what better, or at least more convenient, place to attempt to justify oneself than in one’s autobiography?
Many changes have taken place in my lifetime, some for the better, some for the worse, some whose value cannot yet be known. I note, for example, if not the death then the attenuation of the extended family (nephews, nieces, cousins) in American life. Whereas much of my parents’ social life revolved around an extensive cousinage, I today have grandnephews and grandnieces living on both coasts whom I have never met and probably never shall. I imagine some of them one day being notified of my death and responding, “Really? [Pause] What’s for dinner?”
I take up in my autobiography what Philip Rieff called, in his book of this title, the Triumph of the Therapeutic, a development that has altered child-rearing, artistic creation, and much else in our culture. Although the doctrines of Sigmund Freud, Carl Jung, and others are no longer taken as gospel, their secondary influence has conquered much of modern culture. My parents’ generation did not hold with therapeutic culture, which contends that the essentials of life are the achievement of self-esteem and individual happiness, replacing honor, courage, kindness, and generosity.
In my autobiography, I note that when my mother was depressed by her knowledge that she was dying of cancer, a friend suggested that there were support groups for people with terminal diseases, one of which might be helpful. I imagined telling my mother about such groups, and her response: “Let me see,” she is likely to have said. “You want me to go into a room with strangers, where I will listen to their problems and then I’ll tell them mine, and this will make me feel better.” Pause. “Is this the kind of idiot I’ve raised as a son?”
T hen there is digital culture, the verdict on which is not yet in. Digital culture has changed the way we read, think, make social connections, do business, and so much more. I write in my autobiography that in its consequences digital culture is up there with the printing press and the automobile. Its influence is still far from fully fathomed.
One of my challenges in writing my autobiography was to avoid seeming to brag about my quite modest accomplishments. In the Rhetoric , Aristotle writes: “Speaking at length about oneself, making false claims, taking the credit for what another has done, these are signs of boastfulness.” I tried not to lapse into boasting. Yet at one point I quote Jacques Barzun, in a letter to me, claiming that as a writer I am in the direct line of William Hazlitt, though in some ways better, for my task—that of finding the proper language to establish both intimacy and critical distance—is in the current day more difficult than in Hazlitt’s. At least I deliberately neglected to mention that, in response to my being fired from the American Scholar, Daniel Patrick Moynihan flew an American flag at half-mast over the Capitol, a flag he sent to me as a souvenir. Quoting others about my accomplishments, is this anything other than boasting by other means? I hope so, though even now I’m not altogether sure.
I have a certain pride in these modest accomplishments. Setting out in life, I never thought I should publish some thirty-odd books or have the good luck to continue writing well into my eighties. The question for me as an autobiographer was how to express that pride without preening. The most efficient way, of course, is never to write an autobiography.
Why, then, did I write mine? Although I have earlier characterized writing as a form of discovery, I did not, in writing my autobiography, expect to discover many radically new things about my character or the general lineaments of my life. Nor did I think that my life bore any lessons that were important to others. I had, and still have, little to confess; I have no hidden desire to be spanked by an NFL linebacker in a nun’s habit. A writer, a mere scribbler, I have led a largely spectatorial life, standing on the sidelines, glass of wine in hand, watching the circus pass before me.
Still, I wrote my autobiography, based in a loose way on Wordsworth’s notion that poetry arises from “emotion recollected in tranquility.” Writing it gave me an opportunity to review my life at the end of my life in a tranquil manner. I was able to note certain trends, parallels, and phenomena that have marked my life and set my destiny.
The first of these, as I remarked earlier, was the fortunate time in which I was born, namely the tail end of the Great Depression—to be specific, in 1937. Because of the Depression, people were having fewer children, and often having them later. (My mother was twenty-seven, my father thirty at my birth.) Born when it was, my generation, though subject to the draft—not, in my experience of it, a bad thing—danced between the wars: We were too young for Korea, too old for Vietnam. We were also children during World War II, the last war the country fully supported, which gave us a love of our country. Ours was a low-population generation, untroubled by the vagaries of college admissions or the trauma of rejection by the school of one’s choice. Colleges, in fact, wanted us.
Or consider parents, another fateful phenomenon over which one has no choice. To be born to thoughtless, or disagreeable, or depressed, or deeply neurotic parents cannot but substantially affect all one’s days. Having a father who is hugely successful in the world can be as dampening to the spirit as having a father who is a failure. And yet about all this one has no say. I have given the chapter on my parents the title “A Winning Ticket in the Parents Lottery,” for my own parents, though neither went to college, were thoughtful, honorable, and in no way psychologically crushing. They gave my younger brother and me the freedom to develop on our own; they never told me what schools to attend, what work to seek, whom or when to marry. I knew I was never at the center of my parents’ lives, yet I also knew I could count on them when I needed their support, which more than once I did, and they did not fail to come through. As I say, a winning ticket.
As one writes about one’s own life, certain themes are likely to emerge that hadn’t previously stood out so emphatically. In my case, one persistent motif is that of older boys, then older men, who have supported or aided me in various ways. A boy nearly two years older than I named Jack Libby saw to it that I wasn’t bullied or pushed around in a neighborhood where I was the youngest kid on the block. In high school, a boy to whom I have given the name Jeremy Klein taught me a thing or two about gambling and corruption generally. Later in life, men eight, nine, ten, even twenty or more years older than I promoted my career: Hilton Kramer in promoting my candidacy for the editorship of the American Scholar , Irving Howe in helping me get a teaching job (without an advanced degree) at Northwestern, John Gross in publishing me regularly on important subjects in the Times Literary Supplement , Edward Shils in ways too numerous to mention. Something there was about me, evidently, that was highly protégéable.
I haven’t yet seen the index for my autobiography, but my guess is that it could have been name-ier. I failed, for example, to include my brief but pleasing friendship with Sol Linowitz. Sol was the chairman of Xerox, and later served the Johnson administration as ambassador to the Organization of American States. He also happened to be a reader of mine, and on my various trips to Washington I was often his guest at the F Street Club, a political lunch club where he reserved a private room in which we told each other jokes, chiefly Jewish jokes. I might also have added my six years as a member of the National Council of the National Endowment for the Arts, whose members included the actors Robert Stack and Celeste Holm, the Balanchine dancer Arthur Mitchell, Robert Joffrey, the soprano Renée Fleming, the novelist Toni Morrison, the dancer and choreographer Martha Graham, the architect I. M. Pei, the painter Helen Frankenthaler, and other highly droppable names.
Confronting one’s regrets is another inescapable element in writing one’s autobiography. Ah, regrets: the red MG convertible one didn’t buy in one’s twenties, the elegant young Asian woman one should have asked to dinner, the year one failed to spend in Paris. The greater the number of one’s regrets, the grander their scope, the sadder, at its close, one’s life figures to be. I come out fairly well in the regrets ledger. I regret not having studied classics at university, and so today I cannot read ancient Greek. I regret not having been a better father to my sons. I regret not asking my mother more questions about her family and not telling my father what a good man I thought he was. As regrets go, these are not minor, yet neither have I found them to be crippling.
Then there is the matter of recognizing one’s quirks, or peculiar habits. A notable one of mine, acquired late in life, is to have become near to the reverse of a hypochondriac. I have not yet reached the stage of anosognosia, or the belief that one is well when one is ill—a stage, by the way, that Chekhov, himself a physician, seems to have attained. I take vitamins, get flu and Covid shots, and watch what I eat, but I try to steer clear of physicians. This tendency kicked in not long after my decades-long primary care physician retired. In his The Body: A Guide for Occupants , Bill Bryson defines good health as the health enjoyed by someone who hasn’t had a physical lately. The ancients made this point more directly, advising bene caca et declina medicos (translation on request) . For a variety of reasons, physicians of the current day are fond of sending patients for a multiplicity of tests: bone density tests, colonoscopies, biopsies, X-rays of all sorts, CT scans, MRIs, stopping only at SATs. I am not keen to discover ailments that don’t bother me. At the age of eighty-seven, I figure I am playing with house money, and I have no wish to upset the house by prodding my health in search of imperfections any more than is absolutely necessary.
The older one gets, unless one’s life is lived in pain or deepest regret, the more fortunate one feels. Not always, not everyone, I suppose. “The longer I live, the more I am inclined to the belief that this earth is used by other planets as a lunatic asylum,” said George Bernard Shaw, who lived to age ninety-four. Though the world seems to be in a hell of a shape just now, I nonetheless prefer to delay my exit for as long as I can. I like it here, continue to find much that is interesting and amusing, and have no wish to depart the planet.
Still, with advancing years I have found my interests narrowing. Not least among my waning interests is that in travel. I like my domestic routine too much to abandon it for foreign countries where the natives figure to be wearing Air Jordan shoes, Ralph Lauren shirts, and cargo pants. Magazines that I once looked forward to, many of which I have written for in the past, no longer contain much that I find worth reading. A former moviegoer, I haven’t been to a movie theater in at least a decade. The high price of concert and opera tickets has driven me away. The supposedly great American playwrights—Arthur Miller, Tennessee Williams, Eugene O’Neill, Edward Albee—have never seemed all that good to me, and I miss them not at all. If all this sounds like a complaint that the culture has deserted me, I don’t feel that it has. I can still listen to my beloved Mozart on discs, read Tolstoy, Jane Austen, Dickens, George Eliot, Willa Cather, and the other great novelists, watch the splendid movies of earlier days on Turner Classics and HBO—live, in other words, on the culture of the past.
“Vho needs dis?” Igor Stravinsky is supposed to have remarked when presented with some new phenomena of the avant-garde or other work in the realm of art without obvious benefit. “Vho needs dis?” is a question that occurred to me more than once or twice as I wrote my autobiography. All I can say is that those who read my autobiography will read of the life of a man lucky enough to have devoted the better part of his days to fitting words together into sentences, sentences into paragraphs, and paragraphs into essays and stories on a wide variety of topics. Now in his autobiography all the sentences and paragraphs are about his own life. He hopes that these sentences are well made, these paragraphs have a point, and together they attain to a respectable truth quotient, containing no falsehoods whatsoever. He hopes that, on these modest grounds at least, his autobiography qualifies as worth reading.
Joseph Epstein is author of Gallimaufry , a collection of essays and reviews.
Image by Museum Rotterdam on Wikimedia Commons , licensed via Creative Commons . Image cropped.

Articles by Joseph Epstein
Want more articles like this one delivered directly to your inbox?
Sign up for our email newsletter now!
Is a robot writing your kids’ essays? We asked educators to weigh in on the growing role of AI in classrooms.
Educators weigh in on the growing role of ai and chatgpt in classrooms..

Remember writing essays in high school? Chances are you had to look up stuff in an encyclopedia — an actual one, not Wikipedia — or else connect to AOL via a modem bigger than your parents’ Taurus station wagon.
Now, of course, there’s artificial intelligence. According to new research from Pew, about 1 in 5 US teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork. Kids in upper grades are more apt to have used the chatbot: About a quarter of 11th- and 12th-graders who know about ChatGPT have tried it.
For the uninitiated, ChatGPT arrived on the scene in late 2022, and educators continue to grapple with the ethics surrounding its growing popularity. Essentially, it generates free, human-like responses based on commands. (I’m sure this sentence will look antiquated in about six months, like when people described the internet as the “information superhighway.”)
Advertisement
I used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: “Write an essay on ‘The Scarlet Letter.’” Within moments, ChatGPT created an essay as thorough as anything I’d labored over in AP English.
Is this cheating? Is it just part of our strange new world? I talked to several educators about what they’re seeing in classrooms and how they’re monitoring it. Before you berate your child over how you wrote essays with a No. 2 pencil, here are some things to consider.
Adapting to new technology isn’t immoral. “We have to recalibrate our sense of what’s acceptable. There was a time when every teacher said: ‘Oh, it’s cheating to use Wikipedia.’ And guess what? We got used to it, we decided it’s reputable enough, and we cite Wikipedia all the time,” says Noah Giansiracusa, an associate math professor at Bentley University who hosts the podcast “ AI in Academia: Navigating the Future .”
“There’s a calibration period where a technology is new and untested. It’s good to be cautious and to treat it with trepidation. Then, over time, the norms kind of adapt,” he says — just like new-fangled graphing calculators or the internet in days of yore.
“I think the current conversation around AI should not be centered on an issue with plagiarism. It should be centered on how AI will alter methods for learning and expressing oneself. ‘Catching’ students who use fully AI-generated products ... implies a ‘gotcha’ atmosphere,” says Jim Nagle, a history teacher at Bedford High School. “Since AI is already a huge part of our day-to-day lives, it’s no surprise our students are making it a part of their academic tool kit. Teachers and students should be at the forefront of discussions about responsible and ethical use.”

Teachers and parents could use AI to think about education at a higher level. Really, learning is about more than regurgitating information — or it should be, anyway. But regurgitation is what AI does best.
“If our system is just for students to write a bunch of essays and then grade the results? Something’s missing. We need to really talk about their purpose and what they’re getting out of this, and maybe think about different forms of assignments and grading,” Giansiracusa says.
After all, while AI aggregates and organizes ideas, the quality of its responses depends on the users’ prompts. Instead of recoiling from it, use it as a conversation-starter.
“What parents and teachers can do is to start the conversation with kids: ‘What are we trying to learn here? Is it even something that ChatGPT could answer? Why did your assignment not convince you that you need to do this thinking on your own when a tool can do it for you?’” says Houman Harouni , a lecturer on education at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Harouni urges parents to read an essay written by ChatGPT alongside their student. Was it good? What could be done better? Did it feel like a short cut?
“What they’re going to remember is that you had that conversation with them; that someone thought, at some point in their lives, that taking a shortcut is not the best way ... especially if you do it with the tool right in front of you, because you have something real to talk about,” he says.
Harouni hopes teachers think about its implications, too. Consider math: So much grunt work has been eliminated by calculators and computers. Yet kids are still tested as in days of old, when perhaps they could expand their learning to be assessed in ways that are more personal and human-centric, leaving the rote stuff to AI.
“We could take this moment of confusion and loss of certainty seriously, at least in some small pockets, and start thinking about what a different kind of school would look like. Five years from now, we might have the beginnings of some very interesting exploration. Five years from now, you and I might be talking about schools wherein teaching and learning is happening in a very self-directed way, in a way that’s more based on … igniting the kid’s interest and seeing where they go and supporting them to go deeper and to go wider,” Harouni says.
Teachers have the chance to offer assignments with more intentionality.
“Really think about the purpose of the assignments. Don’t just think of the outcome and the deliverable: ‘I need a student to produce a document.’ Why are we getting students to write? Why are we doing all these things in the first place? If teachers are more mindful, and maybe parents can also be more mindful, I think it pushes us away from this dangerous trap of thinking about in terms of ‘cheating,’ which, to me, is a really slippery path,” Giansiracusa says.
AI can boost confidence and reduce procrastination. Sometimes, a robot can do something better than a human, such as writing a dreaded resume and cover letter. And that’s OK; it’s useful, even.
“Often, students avoid applying to internships because they’re just overwhelmed at the thought of writing a cover letter, or they’re afraid their resume isn’t good enough. I think that tools like this can help them feel more confident. They may be more likely to do it sooner and have more organized and better applications,” says Kristin Casasanto, director of post-graduate planning at Olin College of Engineering.
Casasanto says that AI is also useful for de-stressing during interview prep.
“Students can use generative AI to plug in a job description and say, ‘Come up with a list of interview questions based on the job description,’ which will give them an idea of what may be asked, and they can even then say, ‘Here’s my resume. Give me answers to these questions based on my skills and experience.’ They’re going to really build their confidence around that,” Casasanto says.
Plus, when students use AI for basics, it frees up more time to meet with career counselors about substantive issues.
“It will help us as far as scalability. … Career services staff can then utilize our personal time in much more meaningful ways with students,” Casasanto says.
We need to remember: These kids grew up during a pandemic. We can’t expect kids to resist technology when they’ve been forced to learn in new ways since COVID hit.
“Now we’re seeing pandemic-era high school students come into college. They’ve been channeled through Google Classroom their whole career,” says Katherine Jewell, a history professor at Fitchburg State University.
“They need to have technology management and information literacy built into the curriculum,” Jewell says.
Jewell recently graded a paper on the history of college sports. It was obvious which papers were written by AI: They didn’t address the question. In her syllabus, Jewell defines plagiarism as “any attempt by a student to represent the work of another, including computers, as their own.”
This means that AI qualifies, but she also has an open mind, given students’ circumstances.
“My students want to do the right thing, for the most part. They don’t want to get away with stuff. I understand why they turned to these tools; I really do. I try to reassure them that I’m here to help them learn systems. I’m focusing much more on the learning process. I incentivize them to improve, and I acknowledge: ‘You don’t know how to do this the first time out of the gate,’” Jewell says. “I try to incentivize them so that they’re improving their confidence in their abilities, so they don’t feel the need to turn to these tools.”
Understand the forces that make kids resort to AI in the first place . Clubs, sports, homework: Kids are busy and under pressure. Why not do what’s easy?
“Kids are so overscheduled in their day-to-day lives. I think there’s so much enormous pressure on these kids, whether it’s self-inflicted, parent-inflicted, or school-culture inflicted. It’s on them to maximize their schedule. They’ve learned that AI can be a way to take an assignment that would take five hours and cut it down to one,” says a teacher at a competitive high school outside Boston who asked to remain anonymous.
Recently, this teacher says, “I got papers back that were just so robotic and so cold. I had to tell [students]: ‘I understand that you tried to use a tool to help you. I’m not going to penalize you, but what I am going to penalize you for is that you didn’t actually answer the prompt.”
Afterward, more students felt safe to come forward to say they’d used AI. This teacher hopes that age restrictions become implemented for these programs, similar to apps such as Snapchat. Educationally and developmentally, they say, high-schoolers are still finding their voice — a voice that could be easily thwarted by a robot.
“Part of high school writing is to figure out who you are, and what is your voice as a writer. And I think, developmentally, that takes all of high school to figure out,” they say.
And AI can’t replicate voice and personality — for now, at least.
Kara Baskin can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her @kcbaskin .
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
Direct quotes in APA Style
Published on November 12, 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 16, 2022.
A direct quote is a piece of text copied word-for-word from a source. You may quote a word, phrase, sentence, or entire passage.
There are three main rules for quoting in APA Style:
- If the quote is under 40 words, place it in double quotation marks .
- If the quote is 40 words or more, format it as a block quote .
- Cite the author, year, and page number with an APA in-text citation .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a direct quote, quoting a source with no page numbers, quoting 40 words or more (apa block quotes), making changes to direct quotes in apa, frequently asked questions about apa style.
To cite a quote in APA, you always include the the author’s last name, the year the source was published, and the page on which the quote can be found. The page number is preceded by “p.” (for a single page) or “pp.” (for a page range).
There are two types of APA in-text citation : parenthetical and narrative.
In a parenthetical citation, you place the entire citation in parentheses directly after the quote and before the period (or other punctuation mark).
In a narrative citation, the author(s) appear as part of your sentence. Place the year in parentheses directly after the author’s name, and place the page number in parentheses directly after the quote.
Remember that every in-text citation must correspond to a full APA reference at the end of the text. You can easily create your reference list with our free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA references
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Some source types, such as web pages , do not have page numbers. In this case, to cite a direct quote, you should generally include an alternative locator, unless the source is very short.
The locator may be a chapter or section heading (abbreviated if necessary), a paragraph number, or a combination of the two. Use whichever locator will help your reader find the quote most easily.
For sources such as movies , YouTube videos , or audiobooks, use a timestamp to locate the beginning of the quote.
- Section heading
- Paragraph number
- Section and paragraph
If the quote contains 40 words or more, it must be formatted as a block quote. To format a block quote in APA Style:
- Do not use quotation marks.
- Start the quote on a new line.
- Indent the entire quote 0.5 inches.
- Double-space the entire quote.
Like regular quotes, block quotes can be cited with a parenthetical or narrative citation. However, if the block quote ends with a period, place the citation after the period.
- Parenthetical
Block quoting is particularly useful when you want to comment on an author’s language or present an argument that you will then critique. By setting the quote on a new line and indenting it, the passage is clearly marked apart from your own words. Therefore, no quotation marks are necessary. (O’Connor, 2019, p. 38)
Block quoting is particularly useful when you want to comment on an author’s language or present an argument that you will then critique. By setting the quote on a new line and indenting it, the passage is clearly marked apart from your own words. Therefore, no quotation marks are necessary. (p. 38)
Block quotes with multiple paragraphs
If the block quote contains multiple paragraphs, indent the first line of each paragraph after the first.
Block quoting is particularly useful when you want to comment on an author’s language or present an argument that you will then critique. By setting the quote on a new line and indenting it, the passage is clearly marked apart from your own words. Therefore, no quotation marks are necessary.
However, it is important not to rely on long quotes to make your point for you. Each quote must be introduced and explained or discussed in your own words. (O’Connor, 2019, p. 38)
In general, a direct quote should be an exact reproduction of the original. However, there are some situations where you may need to make small changes.
You may change the capitalization of the first word or the final punctuation mark in order to integrate the quote grammatically into your sentence, as long as the meaning is not altered.
Any other changes must be marked following these APA guidelines.
Shortening a quote
If you want to omit some words, phrases, or sentences from the quote to save space, use an ellipsis (. . .) with a space before and after it to indicate that some material has been left out.
If the part you removed includes a sentence break, add a period before the ellipsis to indicate this.
- No sentence break
- Sentence break
Clarifying a quote
Sometimes you might want to add a word or phrase for context. For example, if a pronoun is used in the quote, you may add a name to clarify who or what is being referred to.
Any added text should be enclosed in square brackets to show that it is not part of the original.
Adding emphasis to quotes
If you want to emphasize a word or phrase in a quote, italicize it and include the words “emphasis added” in square brackets.
Errors in quotes
If the quote contains a spelling or grammatical error, indicate it with the Latin word “sic”, italicized and in square brackets, directly after the error.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To include a direct quote in APA , follow these rules:
- Quotes under 40 words are placed in double quotation marks .
- Quotes of 40 words or more are formatted as block quote .
- The author, year, and page number are included in an APA in-text citation .
You need an APA in-text citation and reference entry . Each source type has its own format; for example, a webpage citation is different from a book citation .
Use Scribbr’s free APA Citation Generator to generate flawless citations in seconds or take a look at our APA citation examples .
When you quote or paraphrase a specific passage from a source, you need to indicate the location of the passage in your APA in-text citation . If there are no page numbers (e.g. when citing a website ) but the text is long, you can instead use section headings, paragraph numbers, or a combination of the two:
(Caulfield, 2019, Linking section, para. 1).
Section headings can be shortened if necessary. Kindle location numbers should not be used in ebook citations , as they are unreliable.
If you are referring to the source as a whole, it’s not necessary to include a page number or other marker.
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (meaning “and others”) is used to shorten APA in-text citations with three or more authors . Here’s how it works:
Only include the first author’s last name, followed by “et al.”, a comma and the year of publication, for example (Taylor et al., 2018).
In an APA in-text citation , you use the phrase “ as cited in ” if you want to cite a source indirectly (i.e., if you cannot find the original source).
Parenthetical citation: (Brown, 1829, as cited in Mahone, 2018) Narrative citation: Brown (1829, as cited in Mahone, 2018) states that…
On the reference page , you only include the secondary source (Mahone, 2018).
In academic writing , there are three main situations where quoting is the best choice:
- To analyze the author’s language (e.g., in a literary analysis essay )
- To give evidence from primary sources
- To accurately present a precise definition or argument
Don’t overuse quotes; your own voice should be dominant. If you just want to provide information from a source, it’s usually better to paraphrase or summarize .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 16). Direct quotes in APA Style. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/direct-quotes/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, beginner's guide to apa in-text citation, creating apa reference entries, apa format for academic papers and essays, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

6 Best Essay Writing Services: Review Of Most Legit Essay Writing Sites In 2024
E ssay writing can be intimidating for students across all levels of education, from high school to college. Often, they grapple with initiating or organizing their thoughts. Additionally, tight deadlines leave little room for thorough research and gathering credible facts. Without adequate assistance, students may submit poorly written papers.
Struggling students, especially those with declining academic performance, often face a crisis of confidence. Crafting a high-quality essay requires extensive research on the topic and strict adherence to guidelines. Depending on one’s proficiency, this process could span weeks or months. In these moments of need, essay writing services emerge as beacons of hope, offering a lifeline to students seeking respite from the academic whirlwind.
In this article, we delve into the various types of services, highlighting their benefits and risks. So, buckle up and embark on this journey of discovery as we unravel the mysteries of essay writing services and navigate the academic maze together.
Top 6 Websites For Online Writing Services
Through careful research and assessment, these are the best essay writing websites that meet our standards.
- ProwWritngCrew – Best College Essay Writing Service - 5/5 ✅
- EssayMasterz – Cheap Essay Writing Service - 4.86/5✅
- EssayScribez – Professional University Essay Writing Service - 4.85/5✅
- SkilledEssayWriter – Best Paper Writing Site for Students - 4.83/5✅
- EssayLegends – Fastest Essay Writing Service - 4.82/5✅
- QualityEssayWriter – The Most Affordable Essay Writing Service - 4.0/5✅
Each online writing service offers unique strengths and considerations. ProwWritingCrew stands out for its high-quality college essays, albeit at a higher price point. EssayMasterz prioritizes affordability without compromising quality, although ensuring consistency is crucial.
EssayScribez specializes in professional university-level essays with mid-range pricing, suitable for polished work. SkilledEssayWriter caters to student needs with a user-friendly interface, though its specialization may limit versatility. EssayLegends promise quick turnaround times, yet thoroughness may be sacrificed for speed.
QualityEssayWriter provides budget-friendly options covering a wide range of topics, but quality assurance is essential. Consider your priorities, whether it's quality, affordability, or speed before making your choice. Here is a detailed analysis of these websites with prices, pros and cons.
1. ProWritingCrew.com
ProWritingCrew.com stands out as one of the top contenders in the realm of essay writing services. With a user-friendly interface and a team of experienced writers, this platform offers a wide range of services at competitive prices.
Additionally, ProWritingCrew offers clients a streamlined ordering process and direct communication with their assigned writers. This ensures that specific requirements are well-understood and met accurately.
The platform takes pride in its punctual delivery, even for urgent orders. Whether you need help with essays, research papers, or any academic assignment, ProWritingCrew is committed to providing exceptional service customized to your needs.
Prices
The company offers affordable prices for their services. To have your papers written, the cost begins at $32 per page high school level with a minimum of 4 hours of deadline. Pricing varies based on the assignment type and urgency.
Additionally, they provide discounts through promo codes. For example, spending over $500 on the platform earns you a 5% discount. Rest assured, all payments are processed securely through reputable gateways, ensuring the safety of your personal information.
The platform provides excellent customer service, with responsive support agents available round-the-clock to address queries and concerns. Here is the list of pros of this service.
- Original Writing – complete all papers from scratch.
- Money-back Guarantee – if your essay has any genuine issues.
- Timely Delivery – 97% of assignments are completed on time.
- Plagiarism Check.
- 500+ Expert Writers.
The website stands out as one of the best services that write papers for you. However, some users have reported occasional inconsistencies in quality and pricing discrepancies.
- Revision Policy – Some clients perceive the revision process as restrictive or cumbersome.
- Subject Availability – The availability of writers for specific niche subjects or specialized topics may be limited.
2. EssayMasterz.com
EssayMasterz.com prides itself on delivering high-quality papers tailored to each client's requirements. With a diverse pool of writers specializing in various subjects, this platform ensures personalized attention to every order.
From academic essays to research papers, EssayMasterz collaborates closely with clients to create meticulously crafted content that meets the highest standards.
The pricing varies based on the type of paper. For instance, research papers begin at approximately $12 per page. While coursework writing services start at around $32 per page. If you require an essay writer, their services are available starting at $ 6 per page at the school level.
The website also offers you a 20% discount for your first order. It is a huge relief for someone who is trying paper writing services for the first time,
These are the pros of EssayMasterz.
- Impeccable grammar.
- Adherence to deadlines.
- Unlimited revisions after two weeks of completing the order.
- Available 24\7.
- Higher Pricing – some users find the pricing slightly higher compared to other services.
- Limited Discount Offers – offers fewer discount opportunities for loyal customers.
However, the best thing about them is they are continuously seeking customer reviews and improving their services.
3. EssayScribez.com
EssayScribez.com caters to students seeking reliable essay writing solutions with a focus on quality and professionalism. The platform offers a seamless ordering process and guarantees original, well-researched content.
Moreover, EssayScribez.com guarantees original, well-researched content that meets academic standards and helps students achieve their educational goals. Whether you’re facing tight deadlines or need assistance with complex topics, EssayScribez.com is your go-to destination for high-quality writing services.
EssayScribez provides a pricing system that caters to various needs. Their rates are influenced by factors such as urgency, academic level, and word count, ensuring affordability for all. Prices begin at $12 per page for college-level writing with a 14-day delivery.
For more advanced levels (Master’s or Ph.D.), the cost ranges from $14 to $60 per page. If you require expedited service, you can receive your work within 24 hours for an additional fee.
EsasyScribez has gained a reputation within years of its launch. Their key to success is staying loyal to their customers by not compromising on quality.
- Transparent Pricing.
- Comprehensive research.
- Accept PayPal payments.
- 300+ Active writers.
- PhD level academic proficiency.
EssayScribez is a newly launched service despite the short period it has gained a lot of positive reviews. With a burst of positive reviews, there are a few neutral and negative reviews also present.
- Interface Usability – Some users have recommended enhancements to the website’s interface to improve usability and navigation.
- Pricing Discrepancies – Although the pricing is competitive, there have been occasional instances where users noticed discrepancies in the final billing.
4. SkilledEssayWriter.com
SkilledEssayWriter is renowned for its commitment to excellence and customer satisfaction. With a team of seasoned writers, this platform delivers top-notch essays tailored to each student's academic level and requirements.
They deliver customized essays that align with individual academic levels and specific requirements. The platform prioritizes customer satisfaction. Whether it’s prompt responses, revisions, or addressing queries, SkilledEssayWriter.com ensures a seamless experience.
SkilledEssayWriter takes into account students’ budget constraints. Their pricing structure is flexible, adapting to factors like urgency, academic level, and word count, ensuring affordability. For instance:
- An undergraduate-level essay costs $16 with a 14-day delivery.
- A Master level essay is priced at $60.
- For a PhD level essay, the cost is $80. If you require expedited service, the price will adjust based on your specified deadline.
- High-Quality Complex Papers – delivers excellent quality papers, ensuring attention to formatting, structure, depth, and uniqueness.
- Customizable Requests – Your requirements will be followed meticulously.
- Expertise Across Disciplines.
- Interactive Communication.
- Handling Challenging Topics – Writers adeptly manage challenging topics and meet specific requirements.
- Urgent delivery for complex papers can take a while.
- Some errors are found in the final draft.
5. EssayLegend.com
EssayLegend.com emerges as a reliable option for students seeking premium-quality essays at competitive prices. The platform boasts a team of skilled writers capable of tackling diverse topics with precision and expertise.
From academic essays to research papers, their writers bring depth and insight to each piece. The platform maintains rigorous quality standards. Essays undergo thorough checks to ensure originality, coherence, and adherence to guidelines.
EssayLegend offers a flexible pricing structure, catering to students with diverse budgets. Their rates range from a minimum of $12 per page (for 550 words) with a 4-hour deadline to a maximum of $32 per page.
Clients can conveniently estimate the cost of their order using the website’s pricing calculator, which provides a detailed breakdown of associated fees. Rest assured, EssayLegend delivers fair and affordable pricing while maintaining high-quality service.
- The platform provides informative writer profiles, enabling clients to choose the right person for the job. With various filters, you can find a writer who aligns with your requirements.
- Discounts – As your order contains more pages, the discount increases, allowing you to save up to 40%.
- Urgent delivery – you can place an order for a minimum of 4 hours deadline.
- Plagiarism Reports – clients can request a free Turnitin plagiarism report for any order. This commitment to originality is commendable.
- Some users have reported occasional discrepancies in content quality and adherence to instructions.
- You cannot call the support team.
6. QualityEssayWriter.com
QualityEssayWriter.com is synonymous with professionalism, reliability, and excellence in essay writing services. With a focus on customer satisfaction, this platform offers a plethora of benefits, including personalized assistance, round-the-clock support, and free revisions.
Whether it’s the middle of the night or the crack of dawn, QualityEssayWriter.com is there for its clients. The 24/7 customer support team promptly addresses queries, concerns, and urgent requests, providing peace of mind to students navigating tight deadlines.
QualityEssayWriter offers competitive pricing for academic papers. Starting at $12 per page, the cost depends on your academic level, field of study, and project submission deadline. Additionally, their refund policy provides reassurance.
Upon registering with your email address and placing your first order, you’ll receive a 9% discount. However, one challenge faced by the company is sourcing enough native American and British speakers for their services.
- Swift Delivery – Need an urgent essay? QualityEssayWriter has you covered. Their rapid delivery option can have your essay ready in as little as three hours, without compromising quality.
- User-Friendly Website – The intuitive website design ensures a seamless experience, and the order form presents clear and concise questions to guide you through the process.
- Extra Features, Beyond writing, QualityEssayWriter provides essential features at no extra cost. These include formatting, an outline, a professional-looking title page, and even a plagiarism report.
- Expensive for tight deadlines.
- Occasionally, there might be a short delay in receiving a response from the writer as they could be occupied with other tasks.
Conclusion of Best Essay Writing Service:
In conclusion, as students explore their academic journey, they encounter a wide range of choices for obtaining essay writing help. From exploring the best paper writing services to seeking out top essay writers, this journey has been both enlightening and empowering. Quality, affordability, and reliability are key considerations as students confidently choose from the best essay writers online and top essay writing service providers.
Without a doubt, leveraging platforms such as ProWritingCrew to QualityEssayWriter for essay orders provides multiple benefits. These services act as a vital support system for students as they tackle the challenging requirements of academic success.
In this dynamic landscape, the pursuit of excellence remains crucial. As students navigate the academic maze, legitimate paper writing services and reputable essay writing providers offer valuable guidance and support.
However, with a plethora of options available, choosing the right essay writing service can be akin to navigating a maze. Each platform promises impeccable writing, timely delivery, and unmatched quality, leaving students perplexed and overwhelmed by the abundance of choices. In this competitive landscape, it becomes imperative to discern between the myriad offerings and select the service that best aligns with one’s academic needs and preferences.
Throughout our investigation, we’ve encountered a diverse range of essay-writing websites, each with its unique strengths and considerations. Whether you’re searching for the best online essay writing service or evaluating the top essay writers, students now know how to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.

Green Chemistry
Probing laser-induced structural transformation of lignin into few-layer graphene.
Laser induced graphene (LIG) is a versatile form of graphene materials synthesized through direct laser writing (DLW) onto a carbon-rich precursor. Lignin is a promising natural precursor for LIG. However, the lack of understanding of the relationship between lignin chemistry and LIG properties limits the effective utilization of lignin. Herein, we aim to understand the structural evolution of lignin into few-layer graphene during direct laser writing via the combined experimental investigation and reactive force field molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. Strong correlations are found between structural features of lignin and LIG characteristics, especially the sheet resistance (electrical conductivity) and defects in graphene domains. Specifically, higher molecular weight lignin demonstrates a superior propensity for generating the graphitic structure in the turbostratic matrix of LIG. This phenomenon leads to better graphene quality in terms of morphological continuity, conductivity, and graphene domains. The glass transition temperature (Tg) of fractionated lignin was identified to have the strongest linear correlation with both sheet resistance and defects density in LIG. Additionally, the MD simulations shed light on the role of closely positioned carbon atoms in the initial substrate, highlighting their facilitative effect on the formation of large graphene domains. The proposed LIG formation pathway offers a new avenue for lignin refinery, facilitating an efficient production of graphene materials from renewable resources.
Supplementary files
- Supplementary information PDF (1493K)
Article information
Download citation, permissions.
H. Zhang, Q. Li, K. D. Hammond, X. He, J. Lin and C. Wan, Green Chem. , 2024, Accepted Manuscript , DOI: 10.1039/D3GC03603K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The IELTS Writing Task 2, has an essay type known as the "Direct Question Essay," which is a crucial component of the IELTS exam. It evaluates your ability to express your ideas, analyze a given topic, and provide a clear, well-structured response. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the structure of IELTS Writing Task 2: Direct ...
Purpose of Directed writing. Directed writing serves as an organized means of accomplishing well-defined goals through communication. Directed writing helps people convey ideas intentionally within predetermined boundaries, whether it is in professional papers, assignments, or tests. It promotes a focused approach and accuracy in communication ...
You should keep a formal tone while writing direct-question essays in IELTS writing task 2. Individuals must stick to the given word limit. Exceeding the word limit can cause you to lose marks and time. Write your essay with a word count of at least 250-270 words. Set a time restriction during your preparation to enhance your overall speed and ...
How To Write A Direct Question Essay. In writing task 2 you will be asked to write a discursive essay ( 250 words minimum ). You will be given a question asking you to give your opinion, discuss a problem or issue. You could also be asked to provide solutions, evaluate a problem, compare and contrast different ideas or challenge an idea.
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in universities and scholarly publications. You'll encounter it in journal articles and books on academic topics, and you'll be expected to write your essays, research papers, and dissertation in academic style. Academic writing follows the same writing process as other types of texts, but ...
This concludes my mini series looking at my top tips for each of the core skills assessed in paper 1. This video offers my top tips for the directed writing ...
Below is a list of sample essay questions for IELTS direct questions essays which can come in writing task 2. These essay types are also known as two question essays (although it is possible to get more than two questions). Direct Questions Essay Tips. spend time planning the answers to the questions; each question must have one main point as ...
The direct writing process is most useful if you don't have much time or if you have plenty to say about your topic. It's a kind of let's-get-this-thing-over-with writing process. I think of it for tasks like memos, reports, somewhat difficult letters, or essays where I don't want to engage in much new thinking.
1. Write a letter to your past self or your future self and see what essay may emerge. 2. As with the previous prompts, also examine if this letter brings you new content, emotion, or reflection for future writing. Of course, feel free to lop off the Salutation and Closing in any of these letters and see what happens.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
There is no one correct way to write an essay. Writing is a cyclical process. A writer may start by writing the introduction, get stuck, start writing a body paragraph, and then suddenly get inspiration for something else to put in the introduction. If the writer has a clear outline, it is perfectly fine to switch between sections of the paper ...
In a directed writing task, students are given a brief and must produce a piece of written work in line with what it asks. The brief outlines the type of writing that must be produced, such as a formal letter, a speech, or a newspaper article. It also contains a scenario that the student must write about. This could be anything, from a proposal ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
5. Write an outline to help organize your main points. After you've created a clear thesis, briefly list the major points you will be making in your essay. You don't need to include a lot of detail—just write 1-2 sentences, or even a few words, outlining what each point or argument will be.
List the author's name and a 'says'-style verb. e.g., "Ahmed asserts," or "Ulmer discusses,". Some 'says' verbs include: After a signal phrase, you can quote from the text directly. Here are some important reminders to keep in mind whenever you directly quote another source in your own writing: Use quotation marks " " and ...
2.1. Direct Writing and Translated Writing Although research on machine translated writing with a focus on analyzing the quality of the essays or written products are lacking within the field of ELT, previous research on direct writing versus translated writing may provide some preliminary evidence on the effects of MT on L2 writing.
essays—not that kind of writing. It's a how-to manual for high-quality arguments. There are four main components: - Chapters: Each provides guidance, not rules, because there are always exceptions to the rules in academic writing. - Practicums: These boxes give step-by-step instructions to help you build ideas and write papers.
How to present direct quotations in writing. Avoid direct quotations that "float" as their own separate sentences. Instead, integrate the quote into your sentences. Remember: you're using the quotation to support your ideas, so you need to help readers see how and why it's relevant to your point. Ex. "Floating" quotation 1: Toni ...
The best way to do that is to present the ideas in your own words with a reference. So remember, it is important that you only use direct quotations where necessary. Using excessive direct quotations, or quotations that are too long, can lead the marker (or reader) to believe that you are using quotations to avoid having to explain difficult ...
Max Decker, a senior at Lincoln High School, sits for a portrait in the school library where he often worked on writing his college essays, in Portland, Ore., Wednesday, March 20, 2024.
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12.. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a time-saving tool for teachers, was purchased last ...
(The essay-writing businesspeople are probably using these, too, so you're better off eliminating the middleman and using them on your own.) The best AI essay-helper tools.
EXCLUSIVE: Actor Steven Waddington (The Imitation Game) has penned a screenplay that he will direct based on the life of veteran Snooker player Jimmy White, with Aneurin Barnard (Dunkirk) and Ray ...
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
Black kids worry about writing college essays after affirmative action ban. When the Supreme Court ended affirmative action in higher education, it left the college essay as one of few places ...
The essay attracted a vast number of letters in opposition, and a man named Merle Miller, who claimed I was calling for genocide of homosexuals, wrote a book based on the essay. Gore Vidal, never known for his temperate reasoning, claimed my argument was ad Hitlerum .
Kara Baskin used ChatGPT to plug in this prompt: "Write an essay on 'The Scarlet Letter.'" Within moments, the software created an essay as thorough as anything she'd labored over in AP ...
A direct quote is a piece of text copied word-for-word from a source. You may quote a word, phrase, sentence, or entire passage. There are three main rules for quoting in APA Style: If the quote is under 40 words, place it in double quotation marks. If the quote is 40 words or more, format it as a block quote.
Prices. The pricing varies based on the type of paper. For instance, research papers begin at approximately $12 per page. While coursework writing services start at around $32 per page.
Laser induced graphene (LIG) is a versatile form of graphene materials synthesized through direct laser writing (DLW) onto a carbon-rich precursor. Lignin is a promising natural precursor for LIG. However, the lack of understanding of the relationship between lignin chemistry and LIG properties limits the effective utilization of lignin.