- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Write a Good Answer to Exam Essay Questions
Last Updated: March 17, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 642,785 times.
Answering essay questions on an exam can be difficult and stressful, which can make it hard to provide a good answer. However, you can improve your ability to answer essay questions by learning how to understand the questions, form an answer, and stay focused. Developing your ability to give excellent answers on essay exams will take time and effort, but you can learn some good essay question practices and start improving your answers.
Understanding the Question

- Analyze: Explain the what, where, who, when, why, and how. Include pros and cons, strengths and weaknesses, etc.
- Compare: Discuss the similarities and differences between two or more things. Don't forget to explain why the comparison is useful.
- Contrast: Discuss how two or more things are different or distinguish between them. Don't forget to explain why the contrast is useful.
- Define: State what something means, does, achieves, etc.
- Describe: List characteristics or traits of something. You may also need to summarize something, such as an essay prompt that asks "Describe the major events that led to the American Revolution."
- Discuss: This is more analytical. You usually begin by describing something and then present arguments for or against it. You may need to analyze the advantages or disadvantages of your subject.
- Evaluate: Offer the pros and cons, positives and negatives for a subject. You may be asked to evaluate a statement for logical support, or evaluate an argument for weaknesses.
- Explain: Explain why or how something happened, or justify your position on something.
- Prove: Usually reserved for more scientific or objective essays. You may be asked to include evidence and research to build a case for a specific position or set of hypotheses.
- Summarize: Usually, this means to list the major ideas or themes of a subject. It could also ask you to present the main ideas in order to then fully discuss them. Most essay questions will not ask for pure summary without anything else.

- Raise your hand and wait for your teacher to come over to you or approach your teacher’s desk to ask your question. This way you will be less likely to disrupt other test takers.
Forming Your Response

- Take a moment to consider your organization before you start writing your answer. What information should come first, second, third, etc.?
- In many cases, the traditional 5-paragraph essay structure works well. Start with an introductory paragraph, use 3 paragraphs in the body of the article to explain different points, and finish with a concluding paragraph.
- It can also be really helpful to draft a quick outline of your essay before you start writing.

- You may want to make a list of facts and figures that you want to include in your essay answer. That way you can refer to this list as you write your answer.
- It's best to write down all the important key topics or ideas before you get started composing your answer. That way, you can check back to make sure you haven't missed anything.

- For example, imagine that your essay question asks: "Should the FIFA World Cup be awarded to countries with human rights violations? Explain and support your answer."
- You might restate this as "Countries with human rights violations should not be awarded the FIFA World Cup because this rewards a nation's poor treatment of its citizens." This will be the thesis that you support with examples and explanation.

- For example, whether you argue that the FIFA World Cup should or should not be awarded to countries with human rights violations, you will want to address the opposing side's argument. However, it needs to be clear where your essay stands about the matter.
- Often, essay questions end up saying things along the lines of "There are many similarities and differences between X and Y." This does not offer a clear position and can result in a bad grade.

- If you are required to write your answer by hand, then take care to make your writing legible and neat. Some professors may deduct points if they cannot read what you have written.
Staying Calm and Focused

- If you get to a point during the exam where you feel too anxious to focus, put down your pencil (or take your hands off of the keyboard), close your eyes, and take a deep breath. Stretch your arms and imagine that you are somewhere pleasant for a few moments. When you have completed this brief exercise, open up your eyes and resume the exam.

- For example, if the exam period is one hour long and you have to answer three questions in that time frame, then you should plan to spend no more than 20 minutes on each question.
- Look at the weight of the questions, if applicable. For example, if there are five 10-point short-answers and a 50-point essay, plan to spend more time on the essay because it is worth significantly more. Don't get stuck spending so much time on the short-answers that you don't have time to develop a complex essay.

- This strategy is even more important if the exam has multiple essay questions. If you take too much time on the first question, then you may not have enough time to answer the other questions on the exam.

- If you feel like you are straying away from the question, reread the question and review any notes that you made to help guide you. After you get refocused, then continue writing your answer.
- Try to allow yourself enough time to go back and tighten up connections between your points. A few well-placed transitions can really bump up your grade.
Community Q&A
- If you are worried about running out of time, put your watch in front of you where you can see it. Just try not to focus on it too much. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you need more practice, make up your own questions or even look at some practice questions online! Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Look up relevant quotes if your exam is open notes. Use references from books or class to back up your answers.
- Make sure your sentences flow together and that you don't repeat the same thing twice!

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.linnbenton.edu/student-services/library-tutoring-testing/learning-center/academic-coaching/documents/Strategies%20For%20Answering%20Essay%20Questions.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ius.edu/writing-center/files/answering-essay-questions.pdf
- ↑ https://success.uark.edu/get-help/student-resources/short-answer-essays.php
About This Article

To write a good answer to an exam essay question, read the question carefully to find what it's asking, and follow the instructions for the essay closely. Begin your essay by rephrasing the question into a statement with your answer in the statement. Include supplemental facts and figures if necessary, or do textual analysis from a provided piece to support your argument. Make sure your writing is clear and to the point, and don't include extra information unless it supports your argument. For tips from our academic reviewer on understanding essay questions and dealing with testing nerves, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Kristine A.
Did this article help you?

May 29, 2017
Sundari Nandyala
Aug 5, 2016
Oct 1, 2016
Mar 24, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
A How-To Guide for the Short Answer Questions for Highly-Selective Colleges

You know those Common App short answer questions required by USC, Princeton, Columbia, Stanford, Yale, and a bunch of other schools?
Apparently I’ve got a lot to say about them. How do I know?
Because, as I was editing a student's short answers this week, I realized that, as with the Activities List and “Why us” essays , I was repeating myself.
Time to create a guide, I thought.
This is that guide.
With 11 tips.
In a Dos and Dont’s format.
- - -
1. DO: Think of your short answers as an advent calendar.
Consider that each of your short answers, no matter how short, is a tiny window into your soul. Make sure the reader finds something inside that's awesome and different from the window before (like a cool sparkly horse instead of a piece of cheap, melted chocolate).
Can you do that in fifteen words? You can. How?
2. DO: CONSIDER USING the space allotted to explain your answer.
You’re often given space for thirteen words for an answer that could easily be one or two words. So consider using it up! In other words, answer "Why," even if the prompt doesn't ask you to. Do this because your core values may be hard to express in 1-2 words.
Here’s an example question: What's your favorite food?
If you just say “tacos,” what does this reveal about you? Maybe that you live in Austin?
A better answer might be:
My abuela's birria tacos—the recipe has been passed down for generations.
This answer reveals connections to family, culture, and even goats! (Because that's what birria is: goats. #themoreyouknow)
Here’s another example of a just-okay answer: Who is your role model? Louis Zamperini
The admissions officer might read this and think: “Great, no idea who that is.” Don't make your readers Google your answer. They won't.
Instead, expand just a bit:
Olympic athlete Louis Zamperini, who survived concentration camps and overcame severe alcoholism.
IMPORTANT EXCEPTION: If the prompt asks you to describe yourself in five words (ahem, Stanford), then give them five words.
3. DON’T make the short reason you provide (or any of your answers) super obvious.
Bad example: What’s your favorite website?
A: Instagram (social media photo-sharing site)
Yup. That's... pretty much what Instagram is. Thanks for telling me zero about you.
Another bad example: What historical moment or event do you wish you could have witnessed?
A: The Big Bang. It was the beginning of our universe and it would have been amazing to see that.
Yup, that’s… what that was. (Also, FYI, many students write “The Big Bang” for this question.)
Better answer:
A: I want to watch George Washington go shopping. I have an obsession with presidential trivia, and the ivory-gummed general is far and away my favorite. Great leaders aren’t necessarily defined by their moments under pressure; sometimes tiny decisions are most telling--like knickers or pantaloons?
4. DO get specific.
Q: What inspires you?
Non-specific answer:
Documentaries. They are my favorite source of inspiration .
(Side note: Don’t. Sound. Like. A robot.) (Also: using contractions, in this case “they’re,” is fine)
Documentaries. "Forks over Knives" made me go vegan; "Born into Brothels" inspired my Gold Award.
5. DON’T for your favorite quote, say something that you'd find on one of those "Success" posters or a Hallmark card.
Cheesy examples include:
"Life is what you make of it." (or)
"Dreams are X" (or) "Always follow your dreams" (or)
"Life is like a dream and dreams are like life are dreams dreams life life dreams." (You get the idea.
Pretty much anything with "life" or "dreams.")
6. DON’T use Top 50 adjectives on the "3-5 words to describe you" question.
Why not? Again, they don't tell us much.
And what are the Top 50 adjectives? You can probably guess them.
Examples: adventurous, friendly, compassionate, passionate, empathetic, passionate (yeah, I’m making a point here).
Think beyond the generic adjectives.
In fact, don't use adjectives at all. One of my favorite answers for this was "Mulan."

Yeah, that Mulan.
7. DON’T use adjectives that repeat info already clear on your application.
Examples: motivated, hardworking, determined.
Yup. You and every other student with a great GPA.
Which reminds me:
8. DO make sure your adjectives are all clearly different and interesting:
In the example above, they all basically mean the same thing. So make sure they reveal something interesting about you. Tell me whom you’d rather meet:
Someone who is “passionate, persistent, and extroverted?”
Or would you rather meet an “ardent, panglossian visionary?”
Or maybe the “gregarious horse-whispering philosopher queen?”
I have questions for that last girl.
Oh, and hey:
9. DON’T worry so much about pissing people off.
I'm doing that in this guide, using sarcasm and phrases like "pissing people off."
Let me clarify: Students often ask me, "Is [this] okay? Is [that] okay? I don't want them to think that I'm too [blank]."
Oh, you mean you don't want them to think that you have a personality.
I encourage students to take (calculated) risks on these. To push boundaries. To be, I don't know, funny? Human? Compare, for example, the following answers:
(Yale) What's something you can't live without?
Play-it-safe answer:
Me: Zzzzzz.
The Tony Stark-made arc reactor in my chest.
Me: YESSS, LOVE IT.
10. Don't check your humor at the door.
If you're funny in life, feel free to be funny in your short answers. If you're not funny, no need to start now.
Irony is one of the best ways to demonstrate intelligence and sensitivity to nuance.
Check out these just-okay and better examples, all for Yale 2015:
Just Okay Answers:
The two qualities I most admire in other people are… ambition and drive (SMH. Same thing, bro.)
I am most proud of… my passion . (There’s that word again. Also, it’s too abstract in this context. Show, don’t tell.)
I couldn't live without… my cell phone . (Yup, you and everyone else.)
Who or what inspires you… the sunset . (Seriously?)
What do you wish you were better at being or doing? Answering these questions . (Heads-up: meta answers are pretty common.)
Most Yale freshmen live in suites of four to six students. What would you contribute to the dynamic of your suite? Good times and great conversation . (Oh look I'm asleep again.)
Better Answers: (written by a student who was accepted to Yale in 2015):
The two qualities I most admire in other people are… Spock’s logic & Kirk’s passion
I am most proud of… Only cried once during The Notebook (maybe twice)
I couldn't live without… The Tony Stark-made arc reactor in my chest
Who or what inspires you? Shia LaBeouf yelling “Just Do It”
What do you wish you were better at being or doing? Dancing-especially like Drake, Hotline Bling style
Most Yale freshmen live in suites of four to six students. What would you contribute to the dynamic of your suite? A Magical Mystery Tour of Beatles keyboard songs
You totally want to meet this guy, right?
Make the reader totally want to meet you.
A few final tips:
11. DO: Offer a variety of things you're interested in.
If you love science and wrote a supplemental essay about science, don't answer with 20 journals, websites, or publications you’ve read on... science.
Show your interest not in astrophysics but also literature, philosophy, Star Trek, programming, and Godfather 1 and 2 (but not 3).
Here’s one more great set of short answers (for the Columbia supplemental essays):
List a few words or phrases that describe your ideal college community. (150 words or less):
One that allows me to fearlessly voice my opinions and act on my values with organizations such as Students for Human Rights.
A community that encourages me to explore foreign nations and religions through travel programs to foreign nations such as Israel through Columbia Hillel.
One that advances research in international medical practice through publications such as the Journal of Global Health.
A community where importance is given to the arts, with an entire buffet of dance organizations for me to choose from.
One that gives due importance to heartfelt (and cheesy in a good way) traditions such as the Tree Lighting Ceremony.
One that would take the care to distract me from an organic chemistry final with a band concert in the library.
Most importantly, one that is in extremely close proximity to New York pizza.
List the titles of the books you read for pleasure that you enjoyed most in the past year. (150 words or less)
Heart of Darkness, Joseph Conrad; Turtles All The Way Down, John Green; Pride and Prejudice, Jane Austen; To Kill a Mockingbird, Harper Lee; Unfinished Gestures: Devadasis, Memory, and Modernity in South India, Davesh Soneji; Pachinko, Min Jin Lee; 1984, George Orwell; The Noonday Demon, Andrew Solomon; Natyasastra and National Unity, Padma Subrahmanyam
In short, use the other parts of your application to show you are hard-working and responsible. Once you’ve done that, you can have a little fun here.
Another great resource: How to Write the Stanford Roommate Essay
WANT SOME HELP TAKING YOUR short answers TO THE NEXT LEVEL?
Check out session five in my 'how to apply to college' course..

Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- Focus and Precision: How to Write Essays that Answer the Question

About the Author Stephanie Allen read Classics and English at St Hugh’s College, Oxford, and is currently researching a PhD in Early Modern Academic Drama at the University of Fribourg.
We’ve all been there. You’ve handed in an essay and you think it’s pretty great: it shows off all your best ideas, and contains points you’re sure no one else will have thought of.
You’re not totally convinced that what you’ve written is relevant to the title you were given – but it’s inventive, original and good. In fact, it might be better than anything that would have responded to the question. But your essay isn’t met with the lavish praise you expected. When it’s tossed back onto your desk, there are huge chunks scored through with red pen, crawling with annotations like little red fire ants: ‘IRRELEVANT’; ‘A bit of a tangent!’; ‘???’; and, right next to your best, most impressive killer point: ‘Right… so?’. The grade your teacher has scrawled at the end is nowhere near what your essay deserves. In fact, it’s pretty average. And the comment at the bottom reads something like, ‘Some good ideas, but you didn’t answer the question!’.

If this has ever happened to you (and it has happened to me, a lot), you’ll know how deeply frustrating it is – and how unfair it can seem. This might just be me, but the exhausting process of researching, having ideas, planning, writing and re-reading makes me steadily more attached to the ideas I have, and the things I’ve managed to put on the page. Each time I scroll back through what I’ve written, or planned, so far, I become steadily more convinced of its brilliance. What started off as a scribbled note in the margin, something extra to think about or to pop in if it could be made to fit the argument, sometimes comes to be backbone of a whole essay – so, when a tutor tells me my inspired paragraph about Ted Hughes’s interpretation of mythology isn’t relevant to my essay on Keats, I fail to see why. Or even if I can see why, the thought of taking it out is wrenching. Who cares if it’s a bit off-topic? It should make my essay stand out, if anything! And an examiner would probably be happy not to read yet another answer that makes exactly the same points. If you recognise yourself in the above, there are two crucial things to realise. The first is that something has to change: because doing well in high school exam or coursework essays is almost totally dependent on being able to pin down and organise lots of ideas so that an examiner can see that they convincingly answer a question. And it’s a real shame to work hard on something, have good ideas, and not get the marks you deserve. Writing a top essay is a very particular and actually quite simple challenge. It’s not actually that important how original you are, how compelling your writing is, how many ideas you get down, or how beautifully you can express yourself (though of course, all these things do have their rightful place). What you’re doing, essentially, is using a limited amount of time and knowledge to really answer a question. It sounds obvious, but a good essay should have the title or question as its focus the whole way through . It should answer it ten times over – in every single paragraph, with every fact or figure. Treat your reader (whether it’s your class teacher or an external examiner) like a child who can’t do any interpretive work of their own; imagine yourself leading them through your essay by the hand, pointing out that you’ve answered the question here , and here , and here. Now, this is all very well, I imagine you objecting, and much easier said than done. But never fear! Structuring an essay that knocks a question on the head is something you can learn to do in a couple of easy steps. In the next few hundred words, I’m going to share with you what I’ve learned through endless, mindless crossings-out, rewordings, rewritings and rethinkings.
Top tips and golden rules
I’ve lost count of the number of times I’ve been told to ‘write the question at the top of every new page’- but for some reason, that trick simply doesn’t work for me. If it doesn’t work for you either, use this three-part process to allow the question to structure your essay:
1) Work out exactly what you’re being asked
It sounds really obvious, but lots of students have trouble answering questions because they don’t take time to figure out exactly what they’re expected to do – instead, they skim-read and then write the essay they want to write. Sussing out a question is a two-part process, and the first part is easy. It means looking at the directions the question provides as to what sort of essay you’re going to write. I call these ‘command phrases’ and will go into more detail about what they mean below. The second part involves identifying key words and phrases.
2) Be as explicit as possible
Use forceful, persuasive language to show how the points you’ve made do answer the question. My main focus so far has been on tangential or irrelevant material – but many students lose marks even though they make great points, because they don’t quite impress how relevant those points are. Again, I’ll talk about how you can do this below.
3) Be brutally honest with yourself about whether a point is relevant before you write it.
It doesn’t matter how impressive, original or interesting it is. It doesn’t matter if you’re panicking, and you can’t think of any points that do answer the question. If a point isn’t relevant, don’t bother with it. It’s a waste of time, and might actually work against you- if you put tangential material in an essay, your reader will struggle to follow the thread of your argument, and lose focus on your really good points.
Put it into action: Step One

Let’s imagine you’re writing an English essay about the role and importance of the three witches in Macbeth . You’re thinking about the different ways in which Shakespeare imagines and presents the witches, how they influence the action of the tragedy, and perhaps the extent to which we’re supposed to believe in them (stay with me – you don’t have to know a single thing about Shakespeare or Macbeth to understand this bit!). Now, you’ll probably have a few good ideas on this topic – and whatever essay you write, you’ll most likely use much of the same material. However, the detail of the phrasing of the question will significantly affect the way you write your essay. You would draw on similar material to address the following questions: Discuss Shakespeare’s representation of the three witches in Macbeth . How does Shakespeare figure the supernatural in Macbeth ? To what extent are the three witches responsible for Macbeth’s tragic downfall? Evaluate the importance of the three witches in bringing about Macbeth’s ruin. Are we supposed to believe in the three witches in Macbeth ? “Within Macbeth ’s representation of the witches, there is profound ambiguity about the actual significance and power of their malevolent intervention” (Stephen Greenblatt). Discuss. I’ve organised the examples into three groups, exemplifying the different types of questions you might have to answer in an exam. The first group are pretty open-ended: ‘discuss’- and ‘how’-questions leave you room to set the scope of the essay. You can decide what the focus should be. Beware, though – this doesn’t mean you don’t need a sturdy structure, or a clear argument, both of which should always be present in an essay. The second group are asking you to evaluate, constructing an argument that decides whether, and how far something is true. Good examples of hypotheses (which your essay would set out to prove) for these questions are:
- The witches are the most important cause of tragic action in Macbeth.
- The witches are partially, but not entirely responsible for Macbeth’s downfall, alongside Macbeth’s unbridled ambition, and that of his wife.
- We are not supposed to believe the witches: they are a product of Macbeth’s psyche, and his downfall is his own doing.
- The witches’ role in Macbeth’s downfall is deliberately unclear. Their claim to reality is shaky – finally, their ambiguity is part of an uncertain tragic universe and the great illusion of the theatre. (N.B. It’s fine to conclude that a question can’t be answered in black and white, certain terms – as long as you have a firm structure, and keep referring back to it throughout the essay).
The final question asks you to respond to a quotation. Students tend to find these sorts of questions the most difficult to answer, but once you’ve got the hang of them I think the title does most of the work for you – often implicitly providing you with a structure for your essay. The first step is breaking down the quotation into its constituent parts- the different things it says. I use brackets: ( Within Macbeth ’s representation of the witches, ) ( there is profound ambiguity ) about the ( actual significance ) ( and power ) of ( their malevolent intervention ) Examiners have a nasty habit of picking the most bewildering and terrifying-sounding quotations: but once you break them down, they’re often asking for something very simple. This quotation, for example, is asking exactly the same thing as the other questions. The trick here is making sure you respond to all the different parts. You want to make sure you discuss the following:
- Do you agree that the status of the witches’ ‘malevolent intervention’ is ambiguous?
- What is its significance?
- How powerful is it?
Step Two: Plan

Having worked out exactly what the question is asking, write out a plan (which should be very detailed in a coursework essay, but doesn’t have to be more than a few lines long in an exam context) of the material you’ll use in each paragraph. Make sure your plan contains a sentence at the end of each point about how that point will answer the question. A point from my plan for one of the topics above might look something like this:
To what extent are we supposed to believe in the three witches in Macbeth ? Hypothesis: The witches’ role in Macbeth’s downfall is deliberately unclear. Their claim to reality is uncertain – finally, they’re part of an uncertain tragic universe and the great illusion of the theatre. Para.1: Context At the time Shakespeare wrote Macbeth , there were many examples of people being burned or drowned as witches There were also people who claimed to be able to exorcise evil demons from people who were ‘possessed’. Catholic Christianity leaves much room for the supernatural to exist This suggests that Shakespeare’s contemporary audience might, more readily than a modern one, have believed that witches were a real phenomenon and did exist.
My final sentence (highlighted in red) shows how the material discussed in the paragraph answers the question. Writing this out at the planning stage, in addition to clarifying your ideas, is a great test of whether a point is relevant: if you struggle to write the sentence, and make the connection to the question and larger argument, you might have gone off-topic.
Step Three: Paragraph beginnings and endings

The final step to making sure you pick up all the possible marks for ‘answering the question’ in an essay is ensuring that you make it explicit how your material does so. This bit relies upon getting the beginnings and endings of paragraphs just right. To reiterate what I said above, treat your reader like a child: tell them what you’re going to say; tell them how it answers the question; say it, and then tell them how you’ve answered the question. This need not feel clumsy, awkward or repetitive. The first sentence of each new paragraph or point should, without giving too much of your conclusion away, establish what you’re going to discuss, and how it answers the question. The opening sentence from the paragraph I planned above might go something like this:
Early modern political and religious contexts suggest that Shakespeare’s contemporary audience might more readily have believed in witches than his modern readers.
The sentence establishes that I’m going to discuss Jacobean religion and witch-burnings, and also what I’m going to use those contexts to show. I’d then slot in all my facts and examples in the middle of the paragraph. The final sentence (or few sentences) should be strong and decisive, making a clear connection to the question you’ve been asked:
Contemporary suspicion that witches did exist, testified to by witch-hunts and exorcisms, is crucial to our understanding of the witches in Macbeth. To the early modern consciousness, witches were a distinctly real and dangerous possibility – and the witches in the play would have seemed all-the-more potent and terrifying as a result.
Step Four: Practice makes perfect
The best way to get really good at making sure you always ‘answer the question’ is to write essay plans rather than whole pieces. Set aside a few hours, choose a couple of essay questions from past papers, and for each:
- Write a hypothesis
- Write a rough plan of what each paragraph will contain
- Write out the first and last sentence of each paragraph
You can get your teacher, or a friend, to look through your plans and give you feedback . If you follow this advice, fingers crossed, next time you hand in an essay, it’ll be free from red-inked comments about irrelevance, and instead showered with praise for the precision with which you handled the topic, and how intently you focused on answering the question. It can seem depressing when your perfect question is just a minor tangent from the question you were actually asked, but trust me – high praise and good marks are all found in answering the question in front of you, not the one you would have liked to see. Teachers do choose the questions they set you with some care, after all; chances are the question you were set is the more illuminating and rewarding one as well.
Image credits: banner ; Keats ; Macbeth ; James I ; witches .
Comments are closed.

Stay informed
Receive updates on teaching and learning initiatives and events.
- Resources for teaching
- Assessment design and security
- Tests and exams
Short answer and essay questions
Short answer and essay questions are types of assessment that are commonly used to evaluate a student’s understanding and knowledge.
Tips for creating short answer and essay questions
e.g., What is __? or how could __ be put into practice?
- Consider the course learning outcomes . Design questions that appropriately assess the relevant learning objectives.
- Make sure the content measures knowledge appropriate to the desired learner level and learning goal.
- When students think critically they are required to step beyond recalling factual information , incorporating evidence and examples to corroborate and/or dispute the validity of assertions/suppositions and compare and contrast multiple perspectives on the same argument.
e.g., paragraphs? sentences? Is bullet point format acceptable or does it have to be an essay format?
- Specify how many marks each question is worth .
- Word limits should be applied within Canvas for discursive or essay-type responses.
- Check that your language and instructions are appropriate to the student population and discipline of study. Not all students have English as their first language.
- Ensure the instructions to students are clear , including optional and compulsory questions and the various components of the assessment.
Questions that promote deeper thinking
Use “open-ended” questions to provoke divergent thinking.
These questions will allow for a variety of possible answers and encourage students to think at a deeper level. Some generic question stems that trigger or stimulate different forms of critical thinking include:
- “What are the implications of …?”
- “Why is it important …?”
- “What is another way to look at …?”
Use questions that are deliberate in the types of higher order thinking to promote/assess
Rather than promoting recall of facts, use questions that allow students to demonstrate their comprehension, application and analysis of the concepts.
Generic question stems that can be used to trigger and assess higher order thinking
Comprehension.
Convert information into a form that makes sense to the individual .
- How would you put __ into your own words?
- What would be an example of __?
Application
Apply abstract or theoretical principles to concrete , practical situations.
- How can you make use of __?
- How could __ be put into practice?
Break down or dissect information.
- What are the most important/significant ideas or elements of __?
- What assumptions/biases underlie or are hidden within __?
Build up or connect separate pieces of information to form a larger, more coherent pattern
- How can these different ideas be grouped together into a more general category?
Critically judge the validity or aesthetic value of ideas, data, or products.
- How would you judge the accuracy or validity of __?
- How would you evaluate the ethical (moral) implications or consequences of __?
Draw conclusions about particular instances that are logically consistent.
- What specific conclusions can be drawn from this general __?
- What particular actions would be consistent with this general __?
Balanced thinking
Carefully consider arguments/evidence for and against a particular position.
- What evidence supports and contradicts __?
- What are arguments for and counterarguments against __?
Causal reasoning
Identify cause-effect relationships between different ideas or actions.
- How would you explain why __ occurred?
- How would __ affect or influence __?
Creative thinking
Generate imaginative ideas or novel approaches to traditional practices.
- What might be a metaphor or analogy for __?
- What might happen if __? (hypothetical reasoning)
Redesign test questions for open-book format
It is important to redesign the assessment tasks to authentically assess the intended learning outcomes in a way that is appropriate for this mode of assessment. Replacing questions that simply recall facts with questions that require higher level cognitive skills—for example analysis and explanation of why and how students reached an answer—provides opportunities for reflective questions based on students’ own experiences.
More quick, focused problem-solving and analysis—conducted with restricted access to limited allocated resources—will need to incorporate a student’s ability to demonstrate a more thoughtful research-based approach and/or the ability to negotiate an understanding of more complex problems, sometimes in an open-book format.
Layers can be added to the problem/process, and the inclusion of a reflective aspect can help achieve these goals, whether administered in an oral test or written examination format.
Example 2: Analytic style multiple choice question or short answer
Acknowledgement: Deakin University and original multiple choice questions: Jennifer Lindley, Monash University.
Setting word limits for discursive or essay-type responses
Try to set a fair and reasonable word count for long answer and essay questions. Some points to consider are:
- Weighting – what is the relative weighting of the question in the assessment?
- Level of study – what is the suggested word count for written assessments in your discipline, for that level of study?
- Skills development – what skills are you requiring students to demonstrate? Higher level cognitive skills, such as evaluation and analysis, tend to require a lengthier word count in order to adequately respond to the assessment prompt.
- Referencing – will you require students to reference their sources ? This takes time, which should be accounted for in the total time to complete the assessment. References generally would not count towards the word count. Include clear marking guidelines for referencing in rubrics, including assessing skills such as critical thinking and evaluation of information.
Communicate your expectations around word count to students in your assessment instructions, including how you will deal with submissions that are outside the word count.
E.g., Write 600-800 words evaluating the key concepts of XYZ. Excess text over the word limit will not be marked.
Let students know how to check the word count in their submission:
- Show word count in Inspera – question type: Essay.
Multi-choice questions
Write MCQs that assess reasoning, rather than recall.
Page updated 16/03/2023 (added open-book section)
What do you think about this page? Is there something missing? For enquiries unrelated to this content, please visit the Staff Service Centre
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- School Search
- Guided Tour
Writing samples are an important part of your application to any college. Your responses show how well you would fit with an institution; your ability to write clearly, concisely, and develop an argument; and your ability to do the work required of you should you be accepted. Use both short answer questions and personal essays to highlight your personality and what makes you unique while also showing off your academic talents.
Short Answer Questions
Short answer questions are almost harder to write than a personal essay, since you usually have a word limit. Often, this may be as short as 150 words (a paragraph). This means that your answers must be clear and concise without being so bare bones that you don’t seem to have a personality. In fact, it’s okay if you answer the question in less than the allotted space. Provided you avoid clichés and sarcasm and answer the question wholly, less can be more. Here are some tips to help you ace your short answers:
- Don’t repeat the question.
- Don’t use unnecessarily large words. Not only will you come off as pretentious at best and ignorant at worst, but it’s unlikely that you’ll be able to keep the same tone throughout your response. After all, wouldn’t it be easier for you to read a paragraph that addresses “how to write concisely” rather than one about “how to circumvent the superfluous use of language?” Craft your response so that your reader can easily understand your point without resorting to a thesaurus.
- Answer honestly. If you are asked to discuss one of your favorite things, don’t feel ashamed to tell the truth. Colleges want to get to know you. A “cool” answer isn’t as interesting as your honest, unique one.
- Supplement your résumé. Talk about things that aren’t mentioned anywhere else in your application to show off a different side of your personality.
- Always use details to bring even a short story to life.
- Don’t be afraid of the word limit. Write out your answer without worrying about the length and then go back and delete any unnecessary information. Underline the stand-out points and trim the rest.
- Describe your personal growth. When discussing an activity or event in your life, ask yourself what you learned or took away from it. Colleges like to understand how you’ve been changed by your experiences and see that you possess self-awareness.
- Be specific about each institution. If asked why you want to attend a particular school, make sure to reference any times you visited the campus, met with admissions counselors, or spoke with current students or alumni. Talk about programs that interest you and how you think they will benefit you in the future. Tell your readers why the idea of being a student at their institution excites you. College admissions officers can spot generic answers, so do your research if you don’t know a lot about the school. Talk about each school as if it is your top choice, even if it’s not. Under no circumstances should you say that a particular school is your “safety.”
The Personal Essay
The majority of colleges will ask you to submit at least one personal essay as part of your application. (You can find the 2019–2020 application platform personal essay prompts here , but not all schools use an application platform. In such cases, you will find essay prompts on the school’s own application.) By reading your submission, college admissions officers become familiar with your personality and writing proficiency. Your essay, along with your other application materials, helps them determine if you would be a good fit for the school and if you would be able to keep up with the rigor of the course load. A well-written, insightful essay can set you apart from other applicants with identical grades and test scores. Likewise, a poorly constructed essay can be detrimental to your application.
To ensure that your essay is the best it can be, you will need to spend some time reviewing the essay prompt to understand the question. Not only will you need time to become familiar with the directions, but you will also want to take your time when constructing your essay. No one can sit down and write the perfect essay in one shot. These things take effort, brainpower, and a significant amount of patience. Consider these steps for producing a well-written, thoughtful response to any essay prompt:
- Get moving. The best way to activate your mind is to activate your body. The act of moving forward, whether you are on foot or on a bike, can help you work through the ideas that might feel stuck. Read the prompt thoroughly, and then see what comes to you as your move through your neighborhood.
- Write down your ideas . When you get home, write down the ideas that stood out. Simply put the pen to paper or your hands to the keys and write without worrying about sentence structure or grammar. There’s plenty of time to edit later on.
- Rule out ideas that won’t work. Use the resources in the section below to decide if you are being asked to write a personal, school, or creative/intellectual statement and read through the the corresponding tips. If any of your ideas don’t fall within our guidelines, find a different approach to answering the question or rule out the topic altogether.
- Construct an outline (or two). At most, you will be able to use 650 words to respond to the question, so every statement you make must serve your overall objective. To stay on topic and build your story or argument, it’s helpful to have a map to guide you. Choose a topic or two from you list and give yourself plenty of time to outline each idea. Use bullet points and separate each section by paragraph. You may realize that one topic is too broad and you need to narrow your focus. If you make two outlines, ask a trusted adult to help you decide which one is stronger than the other. Even if you're not a fan of outlines and prefer to write organically, writing down your ideas in a consecutive list and creating a pseudo-outline can still help you maintain organization and flow between ideas when you actually fill in the blanks.
- Fill in the details with positivity. You are now ready to begin your first draft of your essay. Staying positive in your writing, even if you choose to tackle a hard subject, will endear you to admissions officers while negativity, self-pity, and resentment aren’t going to make your case. Use vivid descriptions when telling your story, but don’t stray too far from your main topic as to become dishonest or exaggerated. Admissions officers are well versed in picking out the real from the fake and aren’t going to be impressed by a made-up story.
- Walk away. When you’ve finished your first draft, walk away for a while, even a day or two, and clear your mind. You’ll be able to look at it with fresh eyes later and make edits to strengthen your argument or main idea.
- Ask for the appropriate amount of help. While it is okay to have a parent or teacher read over your essay to make sure that the points you want to make are coming through or to offer minor suggestions, it is under no circumstances acceptable to allow anyone else to make significant changes, alter the voice or message, or write the essay for you. A dishonest application will be noticed and dismissed by admissions officers.
- Edit. For the initial proofreading, read your essay out loud or backwards, sentence by sentence. Reading it in a form that you haven’t gotten used to will make it easier for you to spot grammatical and spelling errors. Then, ask for one family member or friend to read the essay out loud to you. Together, you can listen for things you missed with your eyes.
The Three Types of Essay Questions
There are three types of personal essays: the personal statement, the school statement, and the creative or intellectual statement. These are described below.
The Personal Statement
- Goal: The personal statement should be a window into your inner life. It is a chance to show schools who you are beyond your grades, test scores, and extracurricular activities. An honest, thoughtful reflection will help admissions officers understand your passions, goals, and relationships with family, friends, and other communities.
- Example: “Some students have a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful they believe their application would be incomplete without it. If this sounds like you, then please share your story.” – Common Application, 2015
- Don’t attempt to sum up your life in one statement. Instead, try to pick one significant experience to elaborate on. Use details to paint a picture for the reader. Talk about how you were affected and what changed about your perception of the world. How did the experience bring you to where you are today?
- Don’t reiterate your résumé. Let your résumé, transcripts, and test scores tell one story about you. Use your essay to tell a different one. Think of it not as a place to impress, but as a place to reflect.
- Don’t talk about an experience that isn’t unique. While almost anyone could say that they struggled with history in high school, few could describe the influence that their great-grandfather had on their understanding of U.S. history in the context of World War II. Picking an experience or topic that will set you apart from other applicants is key to catching the eye of the admissions team.
- Don’t write to impress. Schools don’t want you to write about what you think they want to hear. It’s easy for them to tell when you aren’t being genuine. Pick a topic that’s significant and meaningful to you even if it’s not “impressive.” Having personal awareness is impressive on its own.
The School Statement
- Goal: With your school statement, it should be clear that you have done your research on the school to which you are applying. Admissions counselors use the essay to assess your enthusiasm for the school and your commitment to discovering how the education will benefit you in the future. You want them to understand what you are drawn to so they can begin to envision you as a student on campus.
- Example: “Which aspects of Tufts’ curriculum or undergraduate experience prompted your application? In short: Why Tufts?” – Tufts University, 2015
- Don’t make general statements. It’s important to cite specifics instead of referencing the obvious. If a school is highly ranked and is known for its strong liberal arts curriculum, that’s dandy, but it’s common knowledge. Instead, talk about the teachers, programs, school traditions, clubs, and activities that put the school at the top of your list. If possible, reference any times you visited the campus, met with admissions counselors, or spoke with current students or alumni. Show them that you cared to do more than just a simple Google search.
- Don’t use the same essay for every school. It may be tempting to reuse the same essay for every school, but your essay should not be so general that you can sub out each school’s name as if it were a fill-in-the-blank answer. Sure, you may be able to recycle some content that applies to multiple schools on your list, but be sure to round off each essay with tangible information about the institution (references to buildings on campus, your interview, the mascot, an exciting lecture series, etc.). This proves that you aren’t applying to the school on a whim.
- Don’t overlook the facts. Verifying your statements about a school is essential. If you say that you are excited to become a theater major but the college did away with the program five years ago, admissions counselors may not take you seriously. Do yourself a favor and fact-check.
The Creative/Intellectual Statement
- Goal: Colleges ask students creative or intellectual questions to assess their ability to think critically, construct a cohesive argument, and use a nontraditional approach to solve a problem. In short, admissions counselors are looking for students who can think for themselves. They want to see that you are open to new ideas and can support your opinions with thoughtful explanations.
- Example: “What’s so odd about odd numbers?” – University of Chicago, 2014; “Design your own three-and-a-half-week course and describe what you would do.” – Colorado College, 2014
- Don’t tackle the world’s problems. There’s no need to impress colleges with your knowledge of Syria or the spread of Zika virus. Keep it simple. Remember, colleges don’t expect you to be an expert in anything yet.
- Don’t use too many quotes . Your essay is not a collection of other people’s opinions. Back up your arguments, but be selective when using quotes. If you do paraphrase or quote someone’s work, make sure to cite your sources.
- Don’t make it abstract. In an attempt to be creative and original, it’s easy to cross over the line into absurdity, but it’s important to stay grounded.
Page last updated: 05/2019
Related topics:
Understanding application requirements, the common, coalition, and universal college applications explained, how to write your résumé for college applications, asking for letters of recommendation, gap years and college applications, the community college application, acing your college interview.
- Calendar/Events
- One-Stop Resources
- My Wisconsin Portal
- More Resources

- LEARN Center
- Research-Based Teaching Tips
Short Answer & Essay Tests
Strategies, Ideas, and Recommendations from the faculty Development Literature
General Strategies
Save essay questions for testing higher levels of thought (application, synthesis, and evaluation), not recall facts. Appropriate tasks for essays include: Comparing: Identify the similarities and differences between Relating cause and effect: What are the major causes of...? What would be the most likely effects of...? Justifying: Explain why you agree or disagree with the following statement. Generalizing: State a set of principles that can explain the following events. Inferring: How would character X react to the following? Creating: what would happen if...? Applying: Describe a situation that illustrates the principle of. Analyzing: Find and correct the reasoning errors in the following passage. Evaluating: Assess the strengths and weaknesses of.
There are three drawbacks to giving students a choice. First, some students will waste time trying to decide which questions to answer. Second, you will not know whether all students are equally knowledgeable about all the topics covered on the test. Third, since some questions are likely to be harder than others, the test could be unfair.
Tests that ask only one question are less valid and reliable than those with a wider sampling of test items. In a fifty-minute class period, you may be able to pose three essay questions or ten short answer questions.
To reduce students' anxiety and help them see that you want them to do their best, give them pointers on how to take an essay exam. For example:
- Survey the entire test quickly, noting the directions and estimating the importance and difficulty of each question. If ideas or answers come to mind, jot them down quickly.
- Outline each answer before you begin to write. Jot down notes on important points, arrange them in a pattern, and add specific details under each point.
Writing Effective Test Questions
Avoid vague questions that could lead students to different interpretations. If you use the word "how" or "why" in an essay question, students will be better able to develop a clear thesis. As examples of essay and short-answer questions: Poor: What are three types of market organization? In what ways are they different from one another? Better: Define oligopoly. How does oligopoly differ from both perfect competition and monopoly in terms of number of firms, control over price, conditions of entry, cost structure, and long-term profitability? Poor: Name the principles that determined postwar American foreign policy. Better: Describe three principles on which American foreign policy was based between 1945 and 1960; illustrate each of the principles with two actions of the executive branch of government.
If you want students to consider certain aspects or issues in developing their answers, set them out in separate paragraph. Leave the questions on a line by itself.
Use your version to help you revise the question, as needed, and to estimate how much time students will need to complete the question. If you can answer the question in ten minutes, students will probably need twenty to thirty minutes. Use these estimates in determining the number of questions to ask on the exam. Give students advice on how much time to spend on each question.
Decide which specific facts or ideas a student must mention to earn full credit and how you will award partial credit. Below is an example of a holistic scoring rubric used to evaluate essays:
- Full credit-six points: The essay clearly states a position, provides support for the position, and raises a counterargument or objection and refutes it.
- Five points: The essay states a position, supports it, and raises a counterargument or objection and refutes it. The essay contains one or more of the following ragged edges: evidence is not uniformly persuasive, counterargument is not a serious threat to the position, some ideas seem out of place.
- Four points: The essay states a position and raises a counterargument, but neither is well developed. The objection or counterargument may lean toward the trivial. The essay also seems disorganized.
- Three points: The essay states a position, provides evidence supporting the position, and is well organized. However, the essay does not address possible objections or counterarguments. Thus, even though the essay may be better organized than the essay given four points, it should not receive more than three points.
- Two points: The essay states a position and provides some support but does not do it very well. Evidence is scanty, trivial, or general. The essay achieves it length largely through repetition of ideas and inclusion of irrelevant information.
- One point: The essay does not state the student's position on the issue. Instead, it restates the position presented in the question and summarizes evidence discussed in class or in the reading.
Try not to bias your grading by carrying over your perceptions about individual students. Some faculty ask students to put a number or pseudonym on the exam and to place that number / pseudonym on an index card that is turned in with the test, or have students write their names on the last page of the blue book or on the back of the test.
Before you begin grading, you will want an overview of the general level of performance and the range of students' responses.
Identify exams that are excellent, good, adequate, and poor. Use these papers to refresh your memory of the standards by which you are grading and to ensure fairness over the period of time you spend grading.
Shuffle papers before scoring the next question to distribute your fatigue factor randomly. By randomly shuffling papers you also avoid ordering effects.
Don't let handwriting, use of pen or pencil, format (for example, many lists), or other such factors influence your judgment about the intellectual quality of the response.
Write brief notes on strengths and weaknesses to indicate what students have done well and where they need to improve. The process of writing comments also keeps your attention focused on the response. And your comments will refresh your memory if a student wants to talk to you about the exam.
Focus on the organization and flow of the response, not on whether you agree or disagree with the students' ideas. Experiences faculty note, however, that students tend not to read their returned final exams, so you probably do not need to comment extensively on those.
Most faculty tire after reading ten or so responses. Take short breaks to keep up your concentration. Also, try to set limits on how long to spend on each paper so that you maintain you energy level and do not get overwhelmed. However, research suggests that you read all responses to a single question in one sitting to avoid extraneous factors influencing your grading (for example, time of day, temperature, and so on).
Wait two days or so and review a random set of exams without looking at the grades you assigned. Rereading helps you increase your reliability as a grader. If your two score differ, take the average.
This protects students' privacy when you return or they pick up their tests. Returning Essay Exams
A quick turnaround reinforces learning and capitalizes on students' interest in the results. Try to return tests within a week or so.
Give students a copy of the scoring guide or grading criteria you used. Let students know what a good answer included and the most common errors the class made. If you wish, read an example of a good answer and contrast it with a poor answer you created. Give students information on the distribution of scores so they know where they stand.
Some faculty break the class into small groups to discuss answers to the test. Unresolved questions are brought up to the class as a whole.
Ask students to tell you what was particularly difficult or unexpected. Find out how they prepared for the exam and what they wish they had done differently. Pass along to next year's class tips on the specific skills and strategies this class found effective.
Include a copy of the test with your annotations on ways to improve it, the mistakes students made in responding to various question, the distribution of students' performance, and comments that students made about the exam. If possible, keep copies of good and poor exams.
The Strategies, Ideas and Recommendations Here Come Primarily From:
Gross Davis, B. Tools for Teaching. San Francisco, Jossey-Bass, 1993.
McKeachie, W. J. Teaching Tips. (10th ed.) Lexington, Mass.: Heath, 2002.
Walvoord, B. E. and Johnson Anderson, V. Effective Grading. San Francisco, Jossey-Bass, 1998.
And These Additional Sources... Brooks, P. Working in Subject A Courses. Berkeley: Subject A Program, University of California, 1990.
Cashin, W. E. "Improving Essay Tests." Idea Paper, no. 17. Manhattan: Center for Faculty
Evaluation and Development in Higher Education, Kansas State University, 1987.
Erickson, B. L., and Strommer, D. W. Teaching College Freshmen. San Francisco:
Jossey-Bass, 1991.
Fuhrmann, B. S. and Grasha, A. F. A Practical Handbook for College Teachers. Boston:
Little, Brown, 1983.
Jacobs, L. C. and Chase, C. I. Developing and Using Tests Effectively: A Guide for Faculty.
San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1992.
Jedrey, C. M. "Grading and Evaluation." In M. M. gullette (ed.), The Art and Craft of Teaching.
Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1984.
Lowman, J. Mastering the Techniques of Teaching. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1984.
Ory, J. C. Improving Your Test Questions. Urbana:
Office of Instructional Res., University of Illinois, 1985.
Tollefson, S. K. Encouraging Student Writing. Berkeley:
Office of Educational Development, University of California, 1988.
Unruh, D. Test Scoring manual: Guide for Developing and Scoring Course Examinations.
Los Angeles: Office of Instructional Development, University of California, 1988.
Walvoord, B. E. Helping Students Write Well: A Guide for Teachers in All Disciplines.
(2nded.) New York: Modern Language Association, 1986.
We use cookies on this site. By continuing to browse without changing your browser settings to block or delete cookies you agree to the UW-Whitewater Privacy Notice .
- A-Z Directory
- Campus Maps
- Faculties and Schools
- International
- People and Departments
- Become A Student
- Give to Memorial
- Faculty & Staff
- Online Learning
- Self Service
- Other MUN Login Services
- Academic Success Centre
- Learning skills resources
Exam Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Exams
Essay exams involve a significant written component in which you are asked to discuss and expand on a topic. These could include written responses in the form of a formal essay or a detailed short-answer response.
- Short answer vs essay questions
Preparing for an essay exam
Answering essay questions.
Check out our visual resources for " Test Taking Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Questions " below!
What is the difference between a short answer and an essay question?
- Both short-answer and essay questions ask you to demonstrate your knowledge of course material by relating your answer to concepts covered in the course.
- Essay questions require a thesis (argument) and supporting evidence (from course material - lectures, readings, discussions, and assignments) outlined in several paragraphs, including an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Short-answer questions are more concise than essay answers - think of it as a “mini-essay” - and use a sentence or two to introduce your topic; select a few points to discuss; add a concluding sentence that sums up your response.
- Review your course material - look for themes within the topics covered, use these to prepare sample questions if your instructor has not given direction on what to expect from essay questions.
- Create outlines to answer your practice questions. Choose a definite argument or thesis statement and organize supporting evidence logically in body paragraphs. Try a mnemonic (like a rhyme or acronym) to help remember your outline.
- Practice! Using your outline, try using a timer to write a full response to your practice or sample questions within the exam time limit.
- Review the question carefully. Think about what it is asking - what are you expected to include? What material or examples are relevant?
- Underline keywords in the question to identify the main topic and discussion areas.
- Plan your time. Keep an eye on the time allowed and how many essay questions you are required to answer. Consider the mark distribution to determine how much time to spend on each question or section.
- Make a plan. Take a few minutes to brainstorm and plan your response - jot down a brief outline to order your points and arguments before you start to write.
- Include a thesis statement in your introduction so that your argument is clear, even if you run out of time, and help structure your answer.
- Write a conclusion , even if brief - use this to bring your ideas together to answer the question and suggest the broader implications.
- Clearly and concisely answer the question :
- In your introduction, show that you understand the question and outline how you will answer it.
- Make one point or argument per paragraph and include one or two pieces of evidence or examples for each point.
- In your conclusion, summarize the arguments to answer the question.
"Test Taking Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Questions"
Does your next test have short answer or essay questions? Let's look at how to prepare for these type of questions, how to answer these types of questions, and strategies to keep in mind during the exam. Fight exam writer's block and achieve your best marks yet!
- "Test Taking Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Questions" PDF
- "Test Taking Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Questions" Video
Looking for more strategies and tips? Check out MUN's Academic Success Centre online!
Carnegie Mellon University. (n.d.). Successful exam strategies. Carnegie Mellon University: Student Academic Success. Retrieved April 1, 2022 from https://www.cmu.edu/student-success/other-resources/fast-facts/exam-strategies.pdf
Memorial University of Newfoundland. (n.d.). Exam strategies: Short answer & essay exams. Memorial University of Newfoundland: Academic Success Centre. Retrieved April 1, 2022 from https://www.mun.ca/munup/vssc/learning/exam-strategies-essays.php
Trent University. (n.d.). How to understand and answer free response or essay exam questions. Trent University: Academic Skills. Retrieved April 1, 2022 from https://www.trentu.ca/academicskills/how-guides/how-study/prepare-and-write-exams/how-understand-and-answer-free-response-or-essay-exam
University of Queensland Australia. (n.d.). Exam tips. University of Queensland Australia: Student support, study skills. Retrieved April 1, 2022 from https://my.uq.edu.au/information-and-services/student-support/study-skills/exam-tips
University of Waterloo. (n.d.). Exam questions: Types, characteristics, and suggestions. University of Waterloo: Centre for Teaching Excellence. Retrieved April 1, 2022 from https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/teaching-resources/teaching-tips/developing-assignments/exams/questions-types-characteristics-suggestions
- Learning supports
- Peer-Assisted Learning
- Help centres
- Study spaces
- Graduate student supports
- Events and workshops
- Faculty & staff resources
Related Content
Personal Essay and Short Answer Prompts
Personal essay prompts.
To help us get to know you in the application review process, you are required to submit a personal essay. For insight and advice about how to approach writing your personal essay, see our Expert Advice page.
- Common Application first-year essay prompts
- Common App transfer essay prompt: Please provide a personal essay that addresses your reasons for transferring and the objectives you hope to achieve.
- Coalition, powered by Scoir first-year and transfer essay prompts
Short Answer Question
For both first-year and transfer applicants, we ask you to complete a short answer essay (approximately 250 words) based on one of two prompts.
- Vanderbilt University values learning through contrasting points of view. We understand that our differences, and our respect for alternative views and voices, are our greatest source of strength. Please reflect on conversations you’ve had with people who have expressed viewpoints different from your own. How did these conversations/experiences influence you?
- Vanderbilt offers a community where students find balance between their academic and social experiences. Please briefly elaborate on how one of your extracurricular activities or work experiences has influenced you.
College Reality Check
How to Answer Short-Answer Questions in College Application
Short-answer questions specified in the Common App or Coalition App are answered with concise and specific responses that tackle the prompts without going beyond the word count limit. They are college-specific questions, which means that students applying to, say, Harvard University cannot provide the same answers to short-answer questions asked by, say, Carnegie Mellon University or Stanford University.
Read on if the colleges you are applying to require applicants to answer some short-answer questions.
In this post, we will talk about the reasons why some college admissions officers ask short-answer questions as well as how you are supposed to answer short-answer questions asked by some of the most popular institutions.
What are Short-Answer Questions?
Short-answer questions are prompts that require responses from college applicants using considerably fewer words than long-form essays, such as personal statements and supplemental essays. Some short answer essays have word limits ranging from 100 to 250, while others may specify exactly the number of words applicants may use, such as only 1 or 3.
Although requiring much fewer words than supplementals, short-answer questions are not any less difficult to answer since you will have to express yourself succinctly given that you have to stay within the word count limit.
What is the Primary Purpose of Short-Answer Questions?
The primary purpose of short-answer questions is for college admissions officers to gain additional insight into an applicant’s personality, experiences, interests and academic and career goals, which may not necessarily be covered by his or her application materials. It also allows them to see an applicant’s communication and writing skills.
In some instances, short-answer questions may serve as a tie-breaker when college admissions officers cannot decide which applicants with the same academic profiles they should admit.
Do All Colleges Require Short-Answer Questions?
Not all colleges and universities require short-answer questions. Some institutions that require them may no longer require long-form supplemental essays, while others may still do. Some schools may make it mandatory for applicants to answer short-answer questions, while others may present them as optional additions to their supplementals.
Here’s a resource by the College Board that provides you with guidance on what sort of writing questions you can expect within individual college questions — just click on the schools you are planning on applying to.
How to Answer Short-Answer Questions
When answering short-answer questions, understand each of the questions very well and determine what college admissions officers are looking for exactly. So, in other words, it’s important that you correctly address each and every prompt. It’s also a must that you answer short-answer questions without going beyond the word count limit.
Let’s talk about how to answer short-answer questions asked by some of the most popular colleges in the country:
Brown University
Brown’s short-answer questions can be very short — answers can range anywhere from a few words to a few sentences. For instance, the question “What 3 words best describe you?” should be answered in 3 words only, while the rest should be answered in no more than 100 words. There’s also a Brown short-answer question that should be answered in just 1 sentence.
The California Institute of Technology applicants are required to answer 3 short-answer questions. Topics range from STEM experiences, creativity and Caltech values that speak to them, and the word limit ranges from 100 to 400. There are 3 optional short-answer questions that let applicants show more of their personality plus 1 optional academic short-answer question.
Carnegie Mellon
Most colleges that accept the Common App and Coalition App require applicants to write a personal statement and some supplemental essays. Instead of writing a college-specific essay, Carnegie applicants are required to answer a series of short-answer questions to give everyone a chance to talk about their talents and interests.
Columbia University
As of this writing, there are 9 Columbia short-answer questions. Word limit can range from 100 to 150. Columbia asks short-answer questions to know about an applicant’s academic, extracurricular and intellectual interests. Of course, the Ivy League school also wants to learn about why an applicant feels that Columbia would be the perfect fit for his or her undergraduate education.
Cornell University
Other than the school-specific short-answer questions specified in the Common App and Coalition App, some applicants to Cornell may be given the opportunity to answer optional short-answer questions, depending on the college or department. The general consensus is that every opportunity for Cornell’s admissions officers to know the applicant more should be grabbed.
Duke University
Duke requires applicants to answer only 1 supplemental essay, which is just 250 words long. But there are 4 optional short-answer questions, whose maximum word count each is similar to that of the mandatory supplemental. Given that Duke has a low acceptance rate of 6%, it’s a good idea for applicants to shine by answering the optional short-answer questions.
Harvard University
Harvard itself says that your application to the Ivy League school isn’t complete without answering a series of short-answer questions. When answering Harvard short-answer questions, stick to the 200-word limit. Harvard advises applicants to reflect on how their experiences and extracurriculars have shaped them and how they will engage with others on campus.
Instead of asking applicants to answer some long-form essays in addition to the personal statement, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology requires them to answer several different short-answer questions. MIT advises applicants to talk about the things that inspire them and demonstrate that they are thoughtful individuals much like the institution’s attendees.
Princeton University
In addition to the 2 supplementals, Princeton applicants must also answer 3 short-answer questions, each with a 50-word limit. There are no wrong and right answers when it comes to short-answer questions. Applicants are also encouraged to be themselves given that short-answer questions are there to provide more insight into those who like to attend the Ivy League.
Rice University
After writing their personal statements, Rice applicants must also write additional school-specific essays — 1 long essay and 2 short-answer questions. The short-answer questions have a 150-word limit, and applicants should grab this opportunity to demonstrate their interest in attending for they are asked about the program of their choosing and the Rice experience they want.
Stanford University
Stanford applicants must answer a total of 5 short-answer questions, each with a 50-word limit. A couple of those ask applicants to specify a date and list 5 things. Rather than just mentioning an event and enumerating things, applicants are encouraged to elaborate to allow Stanford’s admissions officers to see aspects of themselves that their applications may have stifled.
Texas A&M University
It was only in 2020 when Texas A&M started requiring applicants to answer short-answer questions. Some programs, such as engineering, require applicants to answer additional short-answer questions. According to Texas A&M itself, applicants must also apply the same amount of thought and care when answering short-answer questions as supplemental essays.
UC Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley refers to short-answer questions as personal insight questions, and applicants’ answers to them are reviewed by both admissions and scholarships officers. According to UC Berkeley itself, it uses short-answer questions in the admissions process in many ways, including deciding between 2 applicants with very similar academic records.
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has a unique approach to short-answer questions: instead of the applicants giving complete free-response answers, they are asked to fill in the blanks using 25 words or less. Some examples of these fill-in-the-blank types of short-answer questions include “The quality I most admire in myself” and “One protagonist I identify with”.
Yale University
The number of short-answer questions Yale applicants must answer can vary, depending on the application platform used. For instance, those who are using QuestBridge will have to answer 3, while those who are using the Common App or Coalition App will have to answer 7. All Yale short-answer questions are personal, and applicants are encouraged to reflect deeply.

Independent Education Consultant, Editor-in-chief. I have a graduate degree in Electrical Engineering and training in College Counseling. Member of American School Counselor Association (ASCA).
Similar Posts

How to Write Best College Transfer Essay: Secrets, Tips and Tricks

How to Close a College Essay (With 10 Examples)

10 Best Common App Essay Ideas

Can a Good College Essay Get You Into Your Dream College?

Unlocking the Hidden Power of Supplemental Essays

AI and College Admissions essays: Cheating, Plagiarism, Inequality and Other Issues
Essay or short-answer questions
Updated 29 Jul 2021
Essay and short-answer questions are ones for which you enter free-form text. As you type, your answer appears as plain text. Complete essay/short answer questions on a computer, not on a smartphone.
- You can submit an essay or short answer only once. As with all assignment answers, your work is not saved until you submit it. When you choose Submit, the following message appears: "Are you satisfied with your answer? You will not be able to modify your answer after you submit it."
- Consider using a word processor for longer essays. Check your spelling and grammar before saving your essay answers and pasting them into Mastering. This also reduces the chance of losing any work in case of a session timeout or lost Internet connection.
- Your instructor must grade these kinds of answers , even if they are short. All other answers in Mastering assignments are automatically scored.
Your essay answers are limited to about 500 words or 3800 characters maximum, including spaces. This information appears above the answer box for all Mastering essay or short answer questions.
You can enter any alphanumeric characters and symbols available from your keyboard. You can also use keyboard shortcuts to copy, cut, and paste text in the question's answer box. Your submitted answer appears to your instructor as plain text without any line breaks.
- You cannot format text (bold, italic, etc.) or use spaces to align text.
- The Tab key is reserved for navigation, so it is unavailable for answer formatting.
If you write your essay in a word processor, use only plain text. Any other formatting (italic, bold, underline, color, highlight, size, superscript, or subscript) or special characters you add using a word processing application will be converted to plain text when you paste your answer into the Mastering answer box.
When you open the assignment, any ungraded essay or short answer items show as Complete with a 0% Score. If you select this 0% score, the Item Score Details page shows “Pending” for both the Correct Answer Credit and Part Total Score until your instructor grades the item.
See also Grading of essay and short-answer questions .
Skip to main content
- Duke University
- Pratt School of Engineering
Short Answer Essays
Short essay questions are required—post your responses in the application

AI for Product Innovation
- In what way do you think artificial intelligence is (or will be) changing your field or industry?
- Please tell us about your motivation for applying to the AI for Product Innovation graduate program or certificate – what do you hope to get out of the experience?
- If you could apply AI to build anything to solve a significant problem in the world, what problem would you choose to solve and what might you build?
Biomedical Engineering
- Why are you applying for the MEng program in biomedical engineering at Duke University?
- How will the MEng program help you to achieve the next goal?
- Why are you selecting the Duke MEng program over the Duke MS program?
Civil Engineering
- What is your definition of personal success?
- How do you think the Master’s program at Duke University will help you on the path to success as you define it?
Climate & Sustainability Engineering
Computational mechanics & scientific computing, cybersecurity.
- What activity or experience, not in your resume/CV, sets you apart from other Cyber applicants? (Note that “good grades” typically do not set candidates apart.)
- What was the most complicated thing you’ve ever designed/built, either physical or virtual? Please describe it here
- In your opinion, what do you feel is the most pressing Cyber need or opportunity? How do you see yourself addressing this?
Design & Technology Innovation
- Tell us about a project you worked on (professional or personal) and walk us through how you leveraged design and innovation methods during it, for success or failure. Highlight and explain some key decisions you made throughout.
- Describe what you hope to be working on in ten years. How and why do you think the program will help you achieve that?
Please select one of these principles and explain how you hope to contribute and grow regarding that principle at Duke.
Electrical & Computer Engineering
- What have you done in the past that makes you well suited to the Duke ECE MEng program?
- What is it about Duke's ECE MEng Program that attracted your attention and got you to apply? What do you think you will be able to do with what you learn in the Duke ECE MEng program?
- Also, if applicable, indicate your interest in attending as a part-time student
Environmental Engineering
Financial technology.
- FinTech is all about creating new and innovative solutions, in your opinion what is the most creative fintech solution of the past 20 years and why do you consider it the most creative?
- Often successful FinTech solutions are new, but sometimes they are new applications of existing solutions. What was the most creative solution to a problem that you’ve ever designed/built, either physical or virtual? Please include details.
- The emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms in recent years could cause significant changes to traditional banking systems and financial markets. These platforms operate on a blockchain, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. As a prospective Fintech graduate student, you are presented with the following hypothetical scenario
• What would it look like if you were to design a bridge between this new DeFi platform and traditional financial institutions? The bridge should prioritize seamless integration and mutual growth for both sectors."
Game Design, Development & Innovation
- Your unique perspectives, experiences and passions will impact the Masters in Game Design, Development, and Innovation program. How will you contribute to the diversity of the cohort, enhance the overall learning experience, and help the program grow?
- What was the most complicated project, either physical or virtual, game or other project, that you’ve ever designed/built? Describe any challenges you faced and how you overcame them. Please describe it here and, if applicable, include a link to an online portfolio, or feel free to provide a link to other media as part of your response.
- What new technology or games do you hope to develop? How will this program help you reach your career aspirations?
Materials Science & Engineering
- What was the most complicated thing you’ve ever designed/built, either physical or virtual? Please describe it here and include a link to an online portfolio of your work or a well-labeled graphic as part of the response.
- What do you think the most important problems engineers should solve are and why? How do you find yourself contributing to big ideas?
- How do you feel Duke will assist you on your path to personal success and how will you contribute to the success of our community? Please give specific examples from what you have learned about our school.
Mechanical Engineering
Medical technology design.
- Why are you applying for the Master of Engineering in MedTech Design?
- How will the MEng program in MedTech Design help you to achieve your goals?
- Please explain any experience you’ve had in design, either through coursework and internships.
Photonics & Optical Sciences
- Why do you want to study photonics at Duke?
- Why is the program right for you, and why are you right for the program?
- How will Duke help you meet your future goals?
Risk Engineering
Sample Short Answer Essay on Running
- Essay Samples & Tips
- College Admissions Process
- College Profiles
- College Rankings
- Choosing A College
- Application Tips
- Testing Graphs
- College Financial Aid
- Advanced Placement
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., English, University of Pennsylvania
- M.A., English, University of Pennsylvania
- B.S., Materials Science & Engineering and Literature, MIT
The Common Application no longer requires a short answer essay from all applicants, but many colleges continue to include the short answer as part of a supplement. The short answer essay prompt typically states something like this:
"Briefly elaborate on one of your extracurricular activities or work experiences ."
Colleges like this type of question because it gives their applicants the opportunity to identify an activity that is meaningful to them and to explain why it is meaningful. This information can be useful to colleges with holistic admissions as they try to identify students who will bring interesting skills and passions to the campus community.
Sample Short Answer Essay
Christie wrote the following sample short answer essay to elaborate upon her love of running:
It is the simplest of movements: right foot, left foot, right foot. It is the simplest of actions: run, relax, breathe. For me, running is both the most basic and the most complex activity I perform in any day. While my body adjusts to the challenges of gravel paths and steep inclines, my mind is free to drift, to sift through whatever needs sorting or disposing—the upcoming day's tasks, an argument with a friend, some nagging stress. As my calf muscles loosen and my breathing settles into its deep rhythm, I am able to release that stress, forget that argument, and set my mind in order. And at the midway point, two miles into the course, I stop at the hilltop vista overlooking my little town and the surrounding woodlands. For just a moment, I stop to listen to my own strong heartbeat. Then I run again.
Critique of the Short Answer Essay
The author has focused on a personal activity, running, not any history-making achievement, team triumph, world-changing social work, or even a formal extracurricular activity . As such, the short answer essay does not highlight any kind of remarkable accomplishment or personal talent.
But think about what this short answer essay does reveal; the author is someone who can find pleasure in the "simplest" of activities. She is someone who has found an effective way of dealing with stress and finding peace and equilibrium in her life. She reveals that she is in tune with her self and her small-town environment.
This one little paragraph gives us the impression that the author is a thoughtful, sensitive, and healthy person. In a short space, the essay reveals the maturity of the writer; she is reflective, articulate, and balanced. These are all dimensions of her character that will not come across in her lists of grades, test scores, and extracurricular activities. They are also personal qualities that will be attractive to a college.
The writing is also solid. The prose is tight, clear, and stylistic without being over-written. The length is a perfect 823 characters and 148 words. This is a typical length limit for a short-answer essay. That said, if your college is asking for just 100 words or something longer, be sure to follow their instructions carefully.
Role of Essays and Your College Application
Keep in mind the role of any essays, even short ones, that you submit with your college application. You want to present a dimension of yourself that isn't readily apparent elsewhere in your application materials. Reveal some hidden interest, passion, or struggle that will give the admissions folks a more detailed portrait of yourself.
The college has asked for a short essay because it has holistic admissions ; in other words, the school tries to evaluate the whole applicant through both quantitative. A short answer essay gives the college a useful window into the applicant's interests.
Christie succeeds on this front. For both the writing and the content, she has written a winning short answer essay. You may want to explore another example of a good short answer on working at Burger King as well as learn lessons from a weak short answer on soccer and a weak short answer on entrepreneurship. In general, if you follow the advice on writing a winning short answer and avoid common short answer mistakes, your essay will strengthen your application and help make you an attractive candidate for admission.
- Sample Short Answer on Soccer
- Sample College Application Short Answer Essay
- Common Application Short Answer Essay on Entrepreneurship
- Short Answer Response on Working at Burger King
- How Long Should Your Common Application Short Answer Essay Be?
- Short Answer Mistakes
- Common Application Short Answer Tips
- Ideal College Application Essay Length
- What Are the Best Extracurricular Activities?
- How to Ace Your University of Wisconsin Personal Statements
- "Grandpa's Rubik's Cube"—Sample Common Application Essay, Option #4
- Tips for Writing a Winning College Application Essay
- 5 Tips for a College Admissions Essay on an Important Issue
- Common Application Essay on a Meaningful Place
- What Colleges Look for in an Applicant
- Common Application Essay, Option 1: Share Your Story
Studying & Test Taking

- Introduction
- What to Study?
- Create a Study Space
- Build Healthy Habits
- Practice Tests
- Mnemonic Devices
- Essay Outlining
- Study Groups
- Preparing for Tests & Exams
- Multiple Choice
Short Answer
- Coping with Test Anxiety
- Feedback Form
- Co-Curricular Recognition Form
- Faculty Resources
Short Answer questions can be difficult for students. While not as lengthy as an essay question, you are still expected to cover enough material in the question to get full marks.
Unlike multiple choice and true/false questions, short answer questions have no possible answers written down for you—you have to recall and summarize ideas in your own words.
Despite the added difficulty, there are still some tricks you can use when writing responses to short answer questions.
Keyword Clues in Short Answer Questions
Here are some typical words (instructions) you might find in a short-answer test and their meaning. Understanding the question ensures that you respond to it fully—and earn full marks!
Short Answer Quick Tips
- Read the questions carefully : Take your time to make sure you fully understand what is being asked of you.
- Do not over analyze : Go with your first instinct on your answer.
- Don't leave the answer blank! You can still get partial marks for having some of the answer.
- Make sure you answer the entire question : That's why reading the question carefully is so important.
- Check how many marks each question is worth : Each point you write down will be worth one mark in your final grade. For example, if the short answer question is worth five (5) marks, write down five (5) points in your answer.
- Last Updated: Jan 12, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://sheridancollege.libguides.com/studyingandtesttaking
Connect with us

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
31 Short Answer/Essay Questions
Try these AFTER you have thoroughly studied the chapter. You should not have to look back at the text to answer them (only to check your answer!). Remember, the point is NOT to memorize parts of the textbook but rather to understand the material and describe it in your OWN WORDS.
If you are going to write more than a couple of paragraphs, think about the structure of your answer.
- Describe two ways in which people can alter consciousness without using drugs.
- What impact do opioids have on human consciousness and behaviour? Give examples to illustrate your answer.
- Contrast Freud’s theory of dreaming with the activation-synthesis theory.
- Describe the different phases of sleep.
Introduction to Psychology Study Guide Copyright © 2021 by Sarah Murray is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Best Preparation Tips for Short Answer Tests
Most tests contain at least a few short answer questions. The following are proven study and test preparation strategies that will help improve your performance on short answer/essay questions and tests.
Best Short Answer Test Preparation Tips and Strategies
Study for understanding.
Teachers, professors and instructors typically give short answer and/or essay tests to see how well students have grasped course concepts, their meanings and significance. This has both pros and cons with respect to test preparation and performance.
The con is that you can’t just just memorize information and expect to do well on a short answer test – you must understand course material and concepts.
The pro is that even if you can’t remember a specific term, as long as you have a general understanding of the concept in question, you can still develop an answer that is likely to get you full or partial credit.
When preparing for short answer tests focus on understanding rather than memorization of facts.
Focus on topics and concepts
As with all types of test questions, the best way to prepare is by studying and becoming intimately familiar with course content, concepts and material. During lectures, try to decipher what types of topics and concepts will be covered on the test by looking for hints provided by the professor.
While it’s still important to memorize facts and information, try and do so within the framework of important topics that are being explored and concepts that are being taught.
Employ self testing
Make a guess as to what types of concepts will be covered on a test and create some practice questions to prepare yourself for the test. If accessible, study from previous class tests.
Use flashcards
Many students benefit by creating flashcards. On one side of a card, write definitions or other facts, and on the opposite side, write the definition.
If in doubt, make an educated guess
If you are completely unsure about a question, make an educated guess since there is usually no penalty for doing so. Show your work because teachers often provide partial credit if work is shown. Make sure the work you show is accurate.
Answer the easy questions first
When encountering confusing questions, move on to easier ones. Return to tackle more challenging questions once you’ve answered all the questions for which you know the answer. In some cases, you can decipher clues to answers for difficult questions from questions you’ve already answered.
Read all instructions
It’s critical to carefully read instructions for each short answer question. What exactly is the question asking you? Often short answer questions will ask you to describe, list, compare, contrast, identify, analyze, summarize, or a combination of these. If you describe when you’re supposed to compare, or summarize when you’ve been instructed to analyze, your test performance is going to decrease.
Budget your time
With short answer/essay tests it’s easy to lose track of time. At the beginning of the test check to see how many questions on the test and if the test is divided up into sections. Make sure to allocate a specific amount of time per section and per question.
You don’t want to get halfway through the test and realize you only have a few minutes left. Some short answer questions may be worth substantially more than others. Make sure to allocate time to those questions that are worth the most.
Reread each question
Always reread the question after answering it. It’s not uncommon for a short answer question to have multiple parts. For example: “Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of social oppression with respect to gender inequality. List the differences in their views.” Answering only part of the short answer question will likely result in only partial credit.
Ask for clarification
If you don’t understand a question or find it is a bit confusing, ask your instructor for clarification. Don’t be scared to ask. Chances are there are several other students who are struggling to understand it as well.
Be thorough. But be concise
While opinions may differ, most teachers believe a short answer question typically requires a “short” answer. That doesn’t mean an answer lacking depth analysis or information. It simply means an answer that is concise and includes just enough information to accurately and fully answer the question being asked.
Typically an answer that’s longer than necessary isn’t going to cause you to lose points, as long as your information is correct. However, if you include incorrect information in your short answer, you’ll likely lose points.
The 6 Basic Types of Short-answer Questions
There are six basic types of short-answer questions. Understanding each will improve your performance on short-answer quizzes, tests and exams. When answering short-answer questions, make sure the format and type of answer you provide matches the type of question being asked.
1. Definition questions
Definition questions require you to define a concept.
- Question: “What is a supply curve?”
- Answer: “A supply curve shows the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied. Typically, the price appears on the left vertical axis and the quality supplied on the horizontal axis.”
2. Explanation questions
Explanation questions require you to explain why something is true or how something functions.
- Question: “Why is the supply curve upward-sloping for most goods and services?”
- Answer: “The supply curve is upward-sloping because as the price the market pays increases for goods and services the volume that suppliers are willing to produce increases.”
3. Example questions
Example questions simply require a specific real-world example of a concept or phenomenon.
- Question: “Provide two examples of pairs of goods that are substitutes.”
- Answer: “Margarine and butter, and tea and coffee are examples of pairs of goods that are substitutes.”
4. Relationship questions
Relationship questions require you to state or show how two or more things relate to one another. Are they complementary? Are they the same? Are they different? Are they opposites? How does the existence of one affect the other? Etc. Relationship questions can be a bit more challenging than other types of short answers but are very doable if you’re prepared.
- Question: “In a competitive market, what is the relationship between supply and demand?”
- Answer: “Demand refers to the quality of a good or service consumers are willing to buy at a given price. Supply represents the quantity of a good supplied by producers at various prices. The price resulting from where supply and demand meet is referred to as the equilibrium price.”
5. Calculation questions
As the name suggests, calculations questions require you to calculate or compute a numerical answer or response.
- Question: “If the demand for used motorcycle purchases in the United States is represented by P = 1000 – .2Q and the supply of used motorcycles is represented by P = 400 + .2Q what is the market equilibrium price and quantity?”
- Answer: “The market equilibrium price (P) is 700. The market equilibrium quantity (Q) is 1,500.”
6. Graphing questions
Graphing questions typically require an answer in the form of a graph.
- Question: “Draw a diagram of a supply curve that shows the relationship between quantity supplied and price.”
- The answer is shown below.
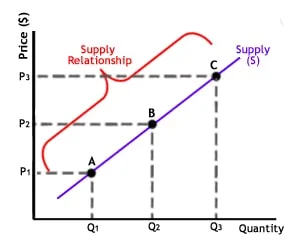
Short-answer versus Short Essay Questions
Students often confuse short-answer questions with short essay questions. While these two question forms share some common characteristics, they are different. The following are the differences between short answer questions and essay questions that students need to know for test taking.
- Short Answer: Someone who assigned the material (teacher, professor, etc.) who has an expert level of the information.
- Short Essay: Someone who has never read or seen the assigned material or topic.
Level of expertise
- Short Answer: Assumes that the reader of the answer is an expert. The reader of the short answer is checking the knowledge of the author of the answer against a specific standard.
- Short Essay: Assumes the reader is not familiar or educated on the topic being addressed. As part of the essay an overview should be provided.
Length of answer
- Short Answer: Typically, very short–no more than 3 to 4 sentences. The more concise the better.
- Short Essay: Answer may vary in length, but ranges from 200-800 words or more.
- Short Answer: Typically comes from a very narrow arena of fact-based knowledge. Details and examples provided in answers are usually limited to assigned/required readings.
- Short Essay: Even though the short essay typically focuses on one specific issue or topic, the information presented in the essay may come from a variety of sources.
Answer format
- Short Answer: The answer format for a short answer will usually be a single sentence or paragraph. Short answers are concise and word selection is important to maximize effect.
- Short Essay: The answer format for short essays, unlike short answers, includes at minimum three paragraphs: the introduction; the body; and the conclusion. The introduction provides a general overview. The body provides the detail of the essay and varies from 1-8 paragraphs (200-800+ words). The conclusion is the wrap-up of the essay and reiterates the main points being communicated. It may also suggest an action.
Similar Posts:
- Guide on College and University Admissions
- 25 Tips For Improving Student’s Performance Via Private Conversations
- 68 Best Chemistry Experiments: Learn About Chemical Reactions
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Princeton’s “More About You” Questions: Examples + Tips
Princeton asks applicants to respond to three short-answer questions in a section titled “More About You.” These questions have a 50-word limit, which can be extremely daunting.
This post will go over the purpose of these questions, tips for writing strong responses, as well as real example responses and analysis.
Princeton “More About You” Questions
The three “More About You” questions in the 2022-2023 admissions cycle were:
- What is a new skill you would like to learn in college?
- What brings you joy?
- What song represents the soundtrack of your life at this moment?
These are questions that might come up in casual conversation, and the goal is to learn “more about you” in a down-to-earth way. This is an opportunity to humanize your application and show more of your “fun” side.
Tips for Princeton’s “More About You” Questions
These short-answer questions are really unlike other parts of your application. Here are our expert tips for writing an engaging response that will win over admissions officers.
1. Be more casual
These are casual questions, so you want your response to feel down-to-earth as well. There’s no need for academic writing here, or even complete sentences. You can even use slang!
Just make sure that your response is still well-written; it should feel like a response in a conversation to an acquaintance or stranger, not like something you’d text a friend.
2. Maximize the word count.
Do not repeat the question in your response. You only have 50 words, so make the most of them! Dive right into your answer.
3. Pay attention to presentation.
Grammatical and formatting mistakes will stand out even more in a short-answer question. Other than maybe using some stylistic fragments, make sure your grammar is correct. You should especially double-check spacing and punctuation/
4. Get an extra set of eyes on your responses.
While most students think to get their college essays edited, these short-answers may not feel like they need an extra set of eyes. Since these are still an important part of your application to Princeton, we recommend having someone else look over your responses. A friend is a great choice since these are more casual questions, and your friend can let you know if your personality shines through.
We also recommend using our free Peer Essay Review platform , where you can get feedback from another student. And, you can review other students’ essays to improve your own writing. If you prefer to have an admissions expert review your essay, you can do so as well on CollegeVine.
Princeton “More About You” Examples
Here are a couple strong responses to the “More About You” questions, as well as analysis on what the writers did well and what could be improved.
Example 1: Joy
Prompt: What brings you joy? (50 words)
The ancient, burlesque sounds of the violin. I love the feeling of completion, when I can finally play a piece I’ve been working at for months. The glide of a slur, the bounce of the spiccato, plentiful accents and tones; The diversity of music lights a fire in my heart.
What the Response Did Well
This answer feels authentic. The student’s use of unique descriptors like “burlesque” and “bounce” communicate to the reader that they have a unique relationship with the violin — one that brings them joy in a specific and special way.
At the same time, the idea of “the feeling of completion” bringing joy is extremely relatable. This student pulls off unique and relatable in the same short answer.
What Could Be Improved
Small mistakes make big impressions in short answers. For example, the word following a semicolon should not be capitalized. While this kind of grammar error could go unnoticed in a larger essay, it stands out when it is one of fifty words.
Example 2: Soundtrack
Prompt: What song represents the soundtrack of your life at the moment? (50 words)
As I sit lost in thought, an urge to stand and pace overwhelms me. The floorboards creaking echoes through the quiet–a familiar symphony accompanying my musings. New ideas take form, energizing, exciting me. In a way, floorboards are my muses fostering my creativity and inspiration, my growth and learning.
This student’s answer is more memorable than traditional answers due to their unique interpretation of the word “soundtrack.” I’m sure this is the only creaking floorboards essay that was submitted to Princeton last year! Originality and setting yourself apart from others is of the utmost importance during the college admissions process.
Admissions officers spend very little time reading short responses and don’t want to parse through your words to find your answer. Because of its roundabout structure, this response requires a second read for an aha moment (“Ohhh the creaking floorboards are the soundtrack!”).
Additionally, your response to a short answer question doesn’t have to be eloquent or figurative. It can be more like an answer to an interview question — to the point, memorable, and honest. This student might have been better off with a casual structure, writing something like:
The sound I hear most often is the creaking of my floorboards, so I’ll call that the soundtrack of my life. I pace when memorizing things, when trying to inspire creativity, when working through complex ideas. My floorboards are probably tired, but pacing is my method.
Finally, like with Example 6, the use of a double hyphen instead of an em dash (—) stands out in a short answer question. Ensure that your grammar is impeccable in your short answers.
More Princeton Essay Resources
How to Write the Princeton Essays
Princeton Essay Examples
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


- Schoology Learning
Short Answer/Essay: Standard Question Type
Use the Short Answer/Essay question type to ask questions requiring students to provide a written response. Students can also Insert images, links, and other supporting materials in their responses.
Question Setup
Write your question or writing prompt in the Compose question field.

The Rich Text Editor appears when your click your cursor into the Compose question field. Hover your mouse over the individual icons to view the tooltip explaining the function of each button.

You may copy and paste images into this area from a browser only. If you wish to insert an image directly from your device, use the Image tool in the Rich Text Editor.
Enable rich text options in the Text f ormatting options for students area . By default, students are permitted to include bolded, italicized, underlined, bulleted, or numbered text in their responses.

Click the highlighted rich text option to remove that option for students.

Enter a word limit for student responses in the Word limit field and determine whether to allow submissions over the word limit or not.

Enter instructions into the Placeholder text for students to display a text string that will be the default in the answer box when the student sees the question. For example, "Type your answer here."

Scoring Instructions
If you are creating a Short Answer/Essay question in AMP, you will have access to a Scoring Instructions field. As an instructor, you can access this field while scoring a student’s submission.
Align Learning Objectives or Rubrics
Click Learning Objectives to open the Learning Objectives browser window.

Click Browse/Search to find and add specific objectives.

Click Manage for objectives already aligned to the question.

Click Confirm to save the learning objectives.
Click Align Rubric to create a new rubric, or to add one from your Resources.

Once a rubric has been aligned, you can click the rubric icon (four squares) to view the preview rubric or click X to remove the rubric from the question.
Check the Show to students box to display the rubric to students when they are taking the test.

Preview and Edit Question
To see how the question will appear to a student taking it in an assessment, click Preview Question .

Once you are finished editing the question, click Save .
Please note, these errors can depend on your browser setup.
If this problem persists, please contact our support.

Tips to answer multiple-choice, short-answer, and essay-type questions in exams
E xams are a stressful affair and they require smart strategies and techniques to excel. While in-depth learning is crucial, different types of questions demand specific strategies and approaches for solving.
Exams may appear in several formats including multiple choice questions, short answers and essays, each requiring different techniques of answering.
Below is a comprehensive guide to solving exams with different types of question patterns:
TIPS TO ANSWER MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
- The first and foremost thing to do is to read the questions properly. Often, students miss out on important details due to a lack of focus. Paying attention to each and every piece of information and reading with attention is crucial.
- After reading the question, try to predict the answer without referring to the given options. This increases your chances of selecting the correct answer through educated guessing.
- Using the process of elimination can do wonders. In this method, you eliminate the options you believe are incorrect. This narrows down your choices and aids in identifying the correct response.
- Paying attention to words such as 'always,' 'never,' 'sometimes,' 'most,' 'only,' 'many,' 'but,' and 'often' can help us better understand the sentence. These words tend to alter the meaning of the sentence and hence should be paid attention to and read properly.
- Â Understanding concepts thoroughly enables you to grasp the context of questions accurately and answer them correctly.
TIPS TO ANSWER SHORT QUESTIONS
- Read the question properly and comprehend it well. Understand whether you need to give a definition, provide examples, write a brief summary or offer comparisons.
- Write the answer to the point, avoiding unnecessary explanations and using keywords. This increases your chances of scoring higher.
- Use simple language and avoid complex terms, as they can confuse the examiner. The simpler your answer, the higher your score.
- Write your answers in a logical and organised manner. Structure your answers with separate paragraphs, bullet points, flowcharts, tables, etc., as this makes it easier for the examiner to read and understand your answer.
- During the preparatory phase, use colourful pens, flashcards, charts, and drawings to learn concepts well. This method helps in recollecting the answers during exams.
- Indulge in self-testing methods by practicing sample question papers, demo tests, and solving previous year question papers to understand the probable questions and the exam pattern.
- Having a time management strategy in place is important. Allocate time for different types of questions and try to solve them within the given time frame.
TIPS TO WRITE ESSAYS
- Understand the topic well and follow the instructions.
- Brainstorm ideas on the topic and plan the points you intend to include.
- Begin with an informative yet concise introduction, followed by a detailed body and a conclusion that summarizes your essay.
- Ensure the essay is well-structured and divided into a minimum of 3-4 paragraphs.
- Use quotations and examples to support the information you have written.
- Adhere to the specified time and word limits.
- Ensure your essay is written in simple and clear language.
- Always remember to proofread the essay to eliminate grammatical and spelling errors.
- Make reading a regular practice to enhance language proficiency and facilitate a smoother flow of thoughts.
By implementing such strategic approaches, you can efficiently answer your questions. It is important to study diligently and practice with sample papers.
During the exam, take the time to read the question paper properly during the allocated reading time and manage your time effectively.
- Article by Nischal Narayanam, mathematical child prodigy, winner of the National Child Award (Gold Medal), youngest double Guinness World Record holder in memory power, first Indian to win the World Memory Championship title, youngest CA, and Founder and Mentor at Nischals
Watch Live TV in English
Watch Live TV in Hindi

To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Garrett M. Graff
The 4 Big Questions the Pentagon’s New UFO Report Fails to Answer

After a year of eyebrow-raising headlines about government whistleblowers alleging that the military was running secret programs focused on alien spaceships and a months-long study and dogged investigative work through the shadows of classified Pentagon programs, the United States Defense Department announced Friday that it found no evidence that the government is covering up contact with extraterrestrials.
The first sentence of the 63-page report on the government’s involvement with unidentified anomalous phenomenon—a report mandated and driven by Congress—seemingly left no wiggle room: The study “found no evidence that any USG [US government] investigation, academic-sponsored research, or official review panel has confirmed that any sighting of a UAP represented extraterrestrial technology. All investigative efforts, at all levels of classification, concluded that most sightings were ordinary objects and phenomena and the result of misidentification.”
The report was issued by the Pentagon’s All-domain Anomaly Resolution Office (AARO), the unit created and tasked in recent years with studying UAP sightings and untangling the truth of the government’s knowledge and understanding of generations of UFO reports. It follows media interviews and a blockbuster congressional hearing last summer where whistleblower David Grusch testified that the government was engaged in a decades-long cover-up of crashed alien spacecraft and in possession even of “ non-human biologics ,” e.g., alien bodies. Grusch and other witnesses and whistleblowers came forward to congressional committees and Pentagon investigators and hinted at astounding possibilities, including that the government was running secret UFO crash-retrieval programs, and defense contractors were running covert programs, hidden even from budget appropriators, to reverse-engineer captured alien technology.
There were many reasons to doubt the full expanse of the testimony by Grusch and others. Much of it was second-hand, and after spending two years writing a book on the government, UFOs, and the search for extraterrestrial life, I said last summer that many of the claims seemed more like an “intergalactic game of telephone,” where people with limited visibility into secret Pentagon and intelligence programs were misidentifying or misinterpreting more mundane program. But that’s not to say that the new AARO report is the end of the story nor that its conclusion should be the end of public interest in UFOs, UAPs, and the secret frontiers of government science.
In fact, while the report’s conclusion surprised almost no one except the most ardent of believers—people who might not be all that inclined to believe the Pentagon’s disavowal anyway—the report in its own way raises as many new questions as it answers, questions that could, with time, prove revolutionary to technology and science.
AARO investigators, for instance, dug through the claims of witnesses and whistleblowers and successfully traced back the underlying research projects, Special Access Programs (SAPs), and classified compartments. As the report says, “AARO investigated numerous named, and described, but unnamed programs alleged to involve UAP exploitation conveyed to AARO through official interviews,” and ultimately, “conclude[d] many of these programs represent authentic, current and former sensitive, national security programs, but none of these programs have been involved with capturing, recovering, or reverse-engineering off-world technology or material.”

Will Knight

Aarian Marshall

But what, then, were those programs? Herein lies the most intriguing—and potentially ground-breaking—question that the Pentagon study leaves us wondering: What exactly are the secret compartmentalized programs that the whistleblowers and government witnesses misidentified as being related to UAP technology? What, exactly, are the Pentagon, intelligence community, or defense contractors working on that, from a concentric circle or two away inside the shadowy world of SAPs, looks and sounds like reverse-engineering out-of-this-world technology or even studying so-called “non-human biologics”?
There are at least four clear possibilities.
First, what exotic technological possibilities have been recovered from unknown terrestrial sources? For example, if the government is working on reverse-engineering technologies, those technologies are likely from advanced adversary nation-states like China, Russia, and Iran, and perhaps even quasi-allies like Israel that may be more limited in their technology-sharing with the US. What have other countries mastered that we haven’t?
Second, what technologies has the US mastered that the public doesn’t know about? One of the common threads of UFO sightings across decades have been secret military aircraft and spacecraft in development or not yet publicly acknowledged. For example, the CIA estimated that the U-2 spy plane in the 1950s accounted for as much as half of reported UFO sightings. And the AARO report spends a half-dozen pages documenting how confusion over subsequent generations of secret US government aircraft appear to have also contributed to the great intergalactic game of telephone of UFO programs inside the government, including modern Predator, Reaper, and Global Hawk drones. AARO investigated one claim where a witness reported hearing a former US military service member had touched an extraterrestrial spacecraft, but when they tracked down the service member, he said that the conversation was likely a garbled version of the time he touched an F-117 Nighthawk stealth fighter at a secret facility.
There are surely other secret craft still in testing and development now, including the B-21 stealth bomber, which had its first test flight in November and is now in testing at Edwards Air Force Base in California, as well as others we don’t know about. The government can still surprise us with unknown craft—like the until-then-unknown modified stealthy helicopter left behind on the Pakistan raid to kill Osama bin Laden. And some of these still-classified efforts are likely causing UFO confusion too: AARO untangled one witness’s claim of spotting a UAP with “peculiar characteristics” at a specific time and place and were able to determine, “at the time the interviewee said he observed the event, the DOD was conducting tests of a platform protected by a SAP. The seemingly strange characteristics reported by the interviewee match closely with the platform’s characteristics, which was being tested at a military facility in the time frame the interviewee was there.” So what was that craft—and what were its “peculiar characteristics?”
Relatedly, the US military has a classified spaceship, the X-37B, that has regularly orbited around the Earth since its first mission in 2010—it just blasted off on its seventh and most recent mission in December—and its previous, sixth, mission lasted a record-breaking 908 days in orbit . The Pentagon has said remarkably little about what it does up there for years at a time. What secret space-related or aviation-related programs is the government running that outsiders confuse as alien spacecraft?
The third likely area of tech development that might appear to outsiders to be UFO-related is more speculative basic research and development: What propulsion systems or material-science breakthroughs are defense contractors at work on right now that could transform our collective future? Again, AARO found such confusion taking place: After one witness reported hearing that “aliens” had observed one secret government test, AARO traced the allegation back to find “the conversation likely referenced a test and evaluation unit that had a nickname with ‘alien’ connotations at the specific installation mentioned. The nature of the test described by the interviewee closely matched the description of a specific materials test conveyed to AARO investigators.” So what materials were being tested there?
There are some puzzling materials-science breadcrumbs wrapped throughout the AARO report. It found one instance where “a private sector organization claimed to have in its possession material from an extraterrestrial craft recovered from a crash at an unknown location from the 1940s or 1950s. The organization claimed that the material had the potential to act as a THz frequency waveguide, and therefore, could exhibit ‘anti-gravity’ and ‘mass reduction’ properties under the appropriate conditions.” Ultimately, though, the new report concluded, “AARO and a leading science laboratory concluded that the material is a metallic alloy, terrestrial in nature, and possibly of USAF [US Air Force] origin, based on its materials characterization.”
Fourth and lastly is the category of the truly weird: Scientists at the forefront of physics point out that we should be humble about how little of the universe we truly understand; as Harvard astronomy chair Avi Loeb explains, effectively all that we’ve learned about relativity and quantum physics has unfolded in the span of a single human lifespan, and astounding new discoveries continue to amaze scientists. Just last summer, scientists announced they’d detected for the first time gravitational waves criss-crossing the universe that rippled through space-time, and astrophysicists continue to suspect that the universe is far weirder than we think. (Italian astrophysicist Carlo Rovelli last year posited the existence of “ white holes ” that would be related to black holes, which, he pointed out, were still a mystery just 25 years ago when he was starting his career.)
Answers here could be almost unfathomably weird—think parallel dimensions or the ability to travel at a fraction of the speed of light. And one of the most intriguing questions left by the UAP “game of telephone” is whether there are truly astounding advances in physics that government scientists, defense contractors, or research laboratories or centers could be feeling around that could also appear from the outside to be UFO-related.
Indeed, the AARO report references that at least some chunk of the “alien confusion” inside government may have grown out of a now well-known but then-secret effort in the late 2000s and early 2010s by Nevada entrepreneur Robert Bigelow’s aerospace company to study UAPs and paranormal activity by the Defense Intelligence Agency, through $22 million in funding secured by then-Senate majority leader Harry Reid. That effort, known as the Advanced Aerospace Weapons System Application Program (AAWSAP), included digging—without official authorization—into paranormal activity at a ranch out west, among other activities. Not much came out of that effort—and the AARO report dismissively notes that AAWSAP’s “scientific papers were never thoroughly peer-reviewed.” But people in and around the world of “ufology” have long noted that one of those papers intriguingly studied “Warp Drive, Dark Energy, and the Manipulation of Extra Dimensions.” Did the Pentagon know more about the outer boundaries of physics than it let on?
While other physicists who have reviewed that speculative 34-page AAWSAP report have said it had little real-world utility, it hints at how our modern understanding of the world around us may still be transformed by the unknown and future discoveries.
After reading thousands of pages of government studies, extraterrestrial research, and scientific papers related to the possibility of intelligent life elsewhere in the universe, I’ve come to believe that in some ways aliens might be the least interesting answer to the questions around UAPs and UFOs. Similarly, the AARO report may one day be seen as closing the door on alien spacecraft while opening the door to something even more fantastical.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: Introducing Politics Lab , your guide to election season
Google used her to tout diversity. Now she’s suing for discrimination
Our in-house physics whiz explains how heat pumps work
The big questions the Pentagon’s new UFO report fails to answer
AirPods Pro or AirPods Max? These are the best Apple buds for your ears

Dell Cameron

Peter Guest

Andy Greenberg

Matt Burgess

Andrew Couts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Typical definition questions would look like this: Question: Define acid precipitation. Strong answer: Acid precipitation is rain, snow or fog with a pH lower than the pH of un‐contaminated rain. Avoid answers like: Acid rain damages lakes and trees, and kills fish. This answer assumes that acid rain is the same as acid precipitation and what ...
Start with an introductory paragraph, use 3 paragraphs in the body of the article to explain different points, and finish with a concluding paragraph. It can also be really helpful to draft a quick outline of your essay before you start writing. 3. Choose relevant facts and figures to include.
10. Don't check your humor at the door. If you're funny in life, feel free to be funny in your short answers. If you're not funny, no need to start now. Irony is one of the best ways to demonstrate intelligence and sensitivity to nuance. Check out these just-okay and better examples, all for Yale 2015:
Step Four: Practice makes perfect. The best way to get really good at making sure you always 'answer the question' is to write essay plans rather than whole pieces. Set aside a few hours, choose a couple of essay questions from past papers, and for each: Write a hypothesis.
require students to construct responses (e.g., short answer, fill in the blank). Essay questions are different from these other constructed response items because they require ... Again, determine whether the given example contains the basic elements of an essay question and then compare your answer with the explanation below the example.
Short answer and essay questions are types of assessment that are commonly used to evaluate a student's understanding and knowledge. Tips for creating short answer and essay questions Consider longer-answer formats that will better test student knowledge because they do not solely rely on recognition or recall of items.
Use both short answer questions and personal essays to highlight your personality and what makes you unique while also showing off your academic talents. Short Answer Questions. Short answer questions are almost harder to write than a personal essay, since you usually have a word limit. Often, this may be as short as 150 words (a paragraph).
For essay questions, consider drafting a brief outline before writing your answer. Organise your thoughts logically, outlining the main points you want to cover to ensure a coherent and structured response. 5. Be Concise and Clear. In short answer and essay questions, aim for clarity and brevity while addressing all aspects of the prompt.
Writing Effective Test Questions. State the question clearly and precisely. Avoid vague questions that could lead students to different interpretations. If you use the word "how" or "why" in an essay question, students will be better able to develop a clear thesis. As examples of essay and short-answer questions:
Exam Strategies: Short Answer & Essay Exams. Essay exams involve a significant written component in which you are asked to discuss and expand on a topic. These could include written responses in the form of a formal essay or a detailed short-answer response. Short answer vs essay questions. Preparing for an essay exam. Answering essay questions.
Short Answer Question. For both first-year and transfer applicants, we ask you to complete a short answer essay (approximately 250 words) based on one of two prompts. Vanderbilt University values learning through contrasting points of view. We understand that our differences, and our respect for alternative views and voices, are our greatest ...
The answer also has proper grammar and spelling and doesn't take long to read. These are all bonuses that make this answer such a good example of how to respond to essay questions. Question #2: Enumerate the three ways in which psychologists have tried to comprehend human perception.
Short answer and essay questions give insight into a student's ability to generate a response in an assessment. Learn the basics of test-taking, and identify the strengths and limitations that ...
Short-answer questions are prompts that require responses from college applicants using considerably fewer words than long-form essays, such as personal statements and supplemental essays. Some short answer essays have word limits ranging from 100 to 250, while others may specify exactly the number of words applicants may use, such as only 1 or ...
Updated 29 Jul 2021. Essay and short-answer questions are ones for which you enter free-form text. As you type, your answer appears as plain text. Complete essay/short answer questions on a computer, not on a smartphone. You can submit an essay or short answer only once. As with all assignment answers, your work is not saved until you submit it.
Short Answer Essays. Short essay questions are required—post your responses in the application.
Sample Short Answer Essay. Christie wrote the following sample short answer essay to elaborate upon her love of running: It is the simplest of movements: right foot, left foot, right foot. It is the simplest of actions: run, relax, breathe. For me, running is both the most basic and the most complex activity I perform in any day.
Short Answer. Short Answer questions can be difficult for students. While not as lengthy as an essay question, you are still expected to cover enough material in the question to get full marks. Unlike multiple choice and true/false questions, short answer questions have no possible answers written down for you—you have to recall and summarize ...
31 Short Answer/Essay Questions. 31. Short Answer/Essay Questions. Try these AFTER you have thoroughly studied the chapter. You should not have to look back at the text to answer them (only to check your answer!). Remember, the point is NOT to memorize parts of the textbook but rather to understand the material and describe it in your OWN WORDS ...
Short-answer versus Short Essay Questions. Students often confuse short-answer questions with short essay questions. While these two question forms share some common characteristics, they are different. The following are the differences between short answer questions and essay questions that students need to know for test taking.
Princeton asks applicants to respond to three short-answer questions in a section titled "More About You.". These questions have a 50-word limit, which can be extremely daunting. This post will go over the purpose of these questions, tips for writing strong responses, as well as real example responses and analysis.
To see how the question will appear to a student taking it in an assessment, click Preview Question. To exit the preview screen and return to the question editor, click Edit Question. Once you are finished editing the question, click Save. Use the Short Answer/Essay question type to ask questions requiring students to provide a written response ...
tips to answer short questions Read the question properly and comprehend it well. Understand whether you need to give a definition, provide examples, write a brief summary or offer comparisons.
The Pentagon says it's not hiding aliens, but it stops notably short of saying what it is hiding. Here are the key questions that remain unanswered—some answers could be weirder than UFOs.