
Rhetorical Questions in Essays: 5 Things you should Know

Rhetorical questions can be useful in writing. So, why shouldn’t you use rhetorical questions in essays?
In this article, I outline 5 key reasons that explain the problem with rhetorical questions in essays.
Despite the value of rhetorical questions for engaging audiences, they mean trouble in your university papers. Teachers tend to hate them.
There are endless debates among students as to why or why not to use rhetorical questions. But, I’m here to tell you that – despite your (and my) protestations – the jury’s in. Many, many teachers hate rhetorical questions.
You’re therefore not doing yourself any favors in using them in your essays.
Rhetorical Question Examples
A rhetorical question is a type of metacommentary . It is a question whose purpose is to add creative flair to your writing. It is a way of adding style to your essay.
Rhetorical questions usually either have obvious answers, or no answers, or do not require an answer . Here are some examples:
- Are you seriously wearing that?
- Do you think I’m that gullible?
- What is the meaning of life?
- What would the walls say if they could speak?
I understand why people like to use rhetorical questions in introductions . You probably enjoy writing. You probably find rhetorical questions engaging, and you want to draw your marker in, engage them, and wow them with your knowledge.
1. Rhetorical Questions in Academic Writing: They Don’t belong.
Rhetorical questions are awesome … for blogs, diaries, and creative writing. They engage the audience and ask them to predict answers.
But, sorry, they suck for essays. Academic writing is not supposed to be creative writing .
Here’s the difference between academic writing and creative writing:
- Supposed to be read for enjoyment first and foremost.
- Can be flamboyant, extravagant, and creative.
- Can leave the reader in suspense.
- Can involve twists, turns, and surprises.
- Can be in the third or first person.
- Readers of creative writing read texts from beginning to end – without spoilers.
Rhetorical questions are designed to create a sense of suspense and flair. They, therefore, belong as a rhetorical device within creative writing genres.
Now, let’s look at academic writing:
- Supposed to be read for information and analysis of real-life ideas.
- Focused on fact-based information.
- Clearly structured and orderly.
- Usually written in the third person language only.
- Readers of academic writing scan the texts for answers, not questions.
Academic writing should never, ever leave the reader in suspense. Therefore, rhetorical questions have no place in academic writing.
Academic writing should be in the third person – and rhetorical questions are not quite in the third person. The rhetorical question appears as if you are talking directly to the reader. It is almost like writing in the first person – an obvious fatal error in the academic writing genre.
Your marker will be reading your work looking for answers , not questions. They will be rushed, have many papers to mark, and have a lot of work to do. They don’t want to be entertained. They want answers.
Therefore, academic writing needs to be straight to the point, never leave your reader unsure or uncertain, and always signpost key ideas in advance.
Here’s an analogy:
- When you came onto this post, you probably did not read everything from start to end. You probably read each sub-heading first, then came back to the top and started reading again. You weren’t interested in suspense or style. You wanted to find something out quickly and easily. I’m not saying this article you’re reading is ‘academic writing’ (it isn’t). But, what I am saying is that this text – like your essay – is designed to efficiently provide information first and foremost. I’m not telling you a story. You, like your teacher, are here for answers to a question. You are not here for a suspenseful story. Therefore, rhetorical questions don’t fit here.
I’ll repeat: rhetorical questions just don’t fit within academic writing genres.
2. Rhetorical Questions can come across as Passive
It’s not your place to ask a question. It’s your place to show your command of the content. Rhetorical questions are by definition passive: they ask of your reader to do the thinking, reflecting, and questioning for you.
Questions of any kind tend to give away a sense that you’re not quite sure of yourself. Imagine if the five points for this blog post were:
- Are they unprofessional?
- Are they passive?
- Are they seen as padding?
- Are they cliché?
- Do teachers hate them?
If the sub-headings of this post were in question format, you’d probably – rightly – return straight back to google and look for the next piece of advice on the topic. That’s because questions don’t assist your reader. Instead, they demand something from your reader .
Questions – rhetorical or otherwise – a position you as passive, unsure of yourself, and skirting around the point. So, avoid them.
3. Rhetorical Questions are seen as Padding
When a teacher reads a rhetorical question, they’re likely to think that the sentence was inserted to fill a word count more than anything else.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY LONGER >>>RELATED ARTICLE: HOW TO MAKE AN ESSAY SHORTER
Rhetorical questions have a tendency to be written by students who are struggling to come to terms with an essay question. They’re well below word count and need to find an extra 15, 20, or 30 words here and there to hit that much-needed word count.
In order to do this, they fill space with rhetorical questions.
It’s a bit like going into an interview for a job. The interviewer asks you a really tough question and you need a moment to think up an answer. You pause briefly and mull over the question. You say it out loud to yourself again, and again, and again.
You do this for every question you ask. You end up answering every question they ask you with that same question, and then a brief pause.
Sure, you might come up with a good answer to your rhetorical question later on, but in the meantime, you have given the impression that you just don’t quite have command over your topic.
4. Rhetorical Questions are hard to get right
As a literary device, the rhetorical question is pretty difficult to execute well. In other words, only the best can get away with it.
The vast majority of the time, the rhetorical question falls on deaf ears. Teachers scoff, roll their eyes, and sigh just a little every time an essay begins with a rhetorical question.
The rhetorical question feels … a little ‘middle school’ – cliché writing by someone who hasn’t quite got a handle on things.
Let your knowledge of the content win you marks, not your creative flair. If your rhetorical question isn’t as good as you think it is, your marks are going to drop – big time.
5. Teachers Hate Rhetorical Questions in Essays
This one supplants all other reasons.
The fact is that there are enough teachers out there who hate rhetorical questions in essays that using them is a very risky move.
Believe me, I’ve spent enough time in faculty lounges to tell you this with quite some confidence. My opinion here doesn’t matter. The sheer amount of teachers who can’t stand rhetorical questions in essays rule them out entirely.
Whether I (or you) like it or not, rhetorical questions will more than likely lose you marks in your paper.
Don’t shoot the messenger.
Some (possible) Exceptions
Personally, I would say don’t use rhetorical questions in academic writing – ever.
But, I’ll offer a few suggestions of when you might just get away with it if you really want to use a rhetorical question:
- As an essay title. I would suggest that most people who like rhetorical questions embrace them because they are there to ‘draw in the reader’ or get them on your side. I get that. I really do. So, I’d recommend that if you really want to include a rhetorical question to draw in the reader, use it as the essay title. Keep the actual essay itself to the genre style that your marker will expect: straight up the line, professional and informative text.
“97 percent of scientists argue climate change is real. Such compelling weight of scientific consensus places the 3 percent of scientists who dissent outside of the scientific mainstream.”
The takeaway point here is, if I haven’t convinced you not to use rhetorical questions in essays, I’d suggest that you please check with your teacher on their expectations before submission.
Don’t shoot the messenger. Have I said that enough times in this post?
I didn’t set the rules, but I sure as hell know what they are. And one big, shiny rule that is repeated over and again in faculty lounges is this: Don’t Use Rhetorical Questions in Essays . They are risky, appear out of place, and are despised by a good proportion of current university teachers.
To sum up, here are my top 5 reasons why you shouldn’t use rhetorical questions in your essays:

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Rhetorical Question

Rhetorical Question Definition
What is a rhetorical question? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a person asks, "How many times do I have to tell you not to eat my dessert?" he or she does not want to know the exact number of times the request will need to be repeated. Rather, the speaker's goal is to emphasize his or her growing frustration and—ideally—change the dessert-thief's behavior.
Some additional key details about rhetorical questions:
- Rhetorical questions are also sometimes called erotema.
- Rhetorical questions are a type of figurative language —they are questions that have another layer of meaning on top of their literal meaning.
- Because rhetorical questions challenge the listener, raise doubt, and help emphasize ideas, they appear often in songs and speeches, as well as in literature.
How to Pronounce Rhetorical Question
Here's how to pronounce rhetorical question: reh- tor -ih-kuhl kwes -chun
Rhetorical Questions and Punctuation
A question is rhetorical if and only if its goal is to produce an effect on the listener, rather than to obtain information. In other words, a rhetorical question is not what we might call a "true" question in search of an answer. For this reason, many sources argue that rhetorical questions do not need to end in a traditional question mark. In the late 1500's, English printer Henry Denham actually designed a special question mark for rhetorical questions, which he referred to as a "percontation point." It looked like this: ⸮ (Here's a wikipedia article about Denham's percontation point and other forms of "irony punctuation.")
Though the percontation point has fallen out of use, modern writers do sometimes substitute a traditional question mark with a period or exclamation point after a rhetorical question. There is a lively debate as to whether this alternative punctuation is grammatically correct. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- In general, rhetorical questions do require a question mark.
- When a question is a request in disguise, you may use a period. For instance, it is ok to write: "Will you please turn your attention to the speaker." or "Can you please go to the back of the line."
- When a question is an exclamation in disguise, you may use an exclamation point. For instance, it is okay to write: "Were they ever surprised!"
- When asking a question emotionally, you may use an exclamation point. For instance, " Who could blame him!" and "How do you know that!" are both correct.
Rhetorical Questions vs. Hypophora
Rhetorical questions are easy to confuse with hypophora , a similar but fundamentally different figure of speech in which a speaker poses a question and then immediately answers it. Hypophora is frequently used in persuasive speaking because the speaker can pose and answer a question that the audience is likely to be wondering about, thereby making the thought processes of the speaker and the audience seem more aligned. For example, here is an example of hypophora used in a speech by Dwight Eisenhower:
When the enemy struck on that June day of 1950, what did America do? It did what it always has done in all its times of peril. It appealed to the heroism of its youth.
While Eisenhower asked this question without expecting an answer from his audience, this is an example of hypophora because he answered his own question. In a rhetorical question, by contrast, the answer would be implied in the question—to pose a rhetorical question, Eisenhower might have said instead, "When the enemy struck, who in their right mind would have done nothing to retaliate?"
Rhetorical Questions vs. Aporia
Rhetorical questions are also related to a figure of speech called aporia . Aporia is an expression of doubt that may be real, or which may be feigned for rhetorical effect. These expressions of doubt may or may not be made through the form of a question. When they are made through the form of a question, those questions are sometimes rhetorical.
Aporia and Rhetorical Questions
When someone is pretending doubt for rhetorical effect, and uses a question as part of that expression of doubt, then the question is rhetorical. For example, consider this quotation from an oration by the ancient Greek orator Demosthenes:
I am at no loss for information about you and your family; but I am at a loss where to begin. Shall I relate how your father Tromes was a slave in the house of Elpias, who kept an elementary school near the Temple of Theseus, and how he wore shackles on his legs and a timber collar round his neck? Or how your mother practised daylight nuptials in an outhouse next door to Heros the bone-setter, and so brought you up to act in tableaux vivants and to excel in minor parts on the stage?
The questions Demosthenes poses are examples of both aporia and rhetorical question, because Demosthenes is feigning doubt (by posing rhetorical questions) in order to cast insulting aspersions on the character of the person he's addressing.
Aporia Without Rhetorical Questions
If the expression of doubt is earnest, however, then the question is not rhetorical. An example of aporia that is not also a rhetorical question comes from the most famous excerpt of Shakespeare's Hamlet:
To be or not to be—that is the question. Whether ‘tis nobler in the mind to suffer The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, Or to take arms against a sea of troubles, And by opposing end them?
While Hamlet asks this question without expecting an answer (he's alone when he asks it), he's not asking in order to persuade or make a point. It's a legitimate expression of doubt, which leads Hamlet into a philosophical debate about whether one should face the expected miseries of life or kill oneself and face the possible unknown terrors of death. It's therefore not a rhetorical question, because Hamlet asks the question as an opening to actually seek an answer to the question he is obsessing over.
Rhetorical Question Examples
Rhetorical question examples in literature.
Rhetorical questions are particularly common in plays, appearing frequently in both spoken dialogue between characters, and in monologues or soliloquies, where they allow the playwright to reveal a character's inner life.
Rhetorical Questions in Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice :
In his speech from Act 3, Scene 1 of Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice , Shylock uses rhetorical questions to point out the indisputable similarities between Jews and Christians, in such a way that any listener would find him impossible to contradict:
I am a Jew. Hath not a Jew eyes? Hath not a Jew hands, organs, dimensions, senses, affections, passions? fed with the same food, hurt with the same weapons, subject to the same diseases, healed by the same means, warmed and cooled by the same winter and summer, as a Christian is? If you prick us, do we not bleed? if you tickle us, do we not laugh? if you poison us, do we not die? and if you wrong us, shall we not revenge? If we are like you in the rest, we will resemble you in that. If a Jew wrong a Christian, what is his humility? Revenge. If a Christian wrong a Jew, what should his sufferance be by Christian example? Why, revenge. The villainy you teach me, I will execute, and it shall go hard but I will better the instruction.
Rhetorical questions in Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet :
In this soliloquy from Act 2, Scene 2 of Romeo and Juliet , Juliet poses a series of rhetorical questions as she struggles to grasp the difficult truth—that her beloved Romeo is a member of the Montague family:
Thou art thyself, though not a Montague. What's Montague? it is nor hand, nor foot, Nor arm, nor face, nor any other part Belonging to a man. O, be some other name! What's in a name? that which we call a rose By any other name would smell as sweet; So Romeo would, were he not Romeo call'd Retain that dear perfection which he owes Without that title. Romeo, doff thy name, And for that name which is no part of thee Take all myself.
Rhetorical Question Examples in Political Speeches
Rhetorical questions often "challenge" the listener to contradict what the speaker is saying. If the speaker frames the rhetorical question well, it gives the impression that his or her view is true and that it would be foolish, or even impossible, to contradict the speaker's argument. In other words, rhetorical questions are great for speeches.
Rhetorical Questions in Ronald Reagan's 1980 Republican National Convention Acceptance Address:
In this speech, Reagan uses a series of rhetorical questions—referred to as "stacked" rhetorical questions—to criticize the presidency of his predecessor and running opponent, Jimmy Carter:
Can anyone look at the record of this Administration and say, "Well done"? Can anyone compare the state of our economy when the Carter Administration took office with where we are today and say, "Keep up the good work"? Can anyone look at our reduced standing in the world today say, "Let's have four more years of this"?
Rhetorical Questions in Hillary Clinton's 2016 Democratic National Convention Speech:
In this portion of her speech, Clinton argues that her opponent Donald Trump is not temperamentally fit to become president:
A president should respect the men and women who risk their lives to serve our country—including Captain Khan and the sons of Tim Kaine and Mike Pence, both Marines. So just ask yourself: Do you really think Donald Trump has the temperament to be commander-in-chief?
Rhetorical Question Examples in Song Lyrics
Love has left even the best musicians of our time feeling lost, searching for meaning, and—as you might expect—full of rhetorical questions. Musicians such as Tina Turner, Jean Knight, and Stevie Wonder have all released hits structured around rhetorical questions, which allow them to powerfully express the joy, the pain, and the mystery of L-O-V-E.
Rhetorical Questions in "What's Love Got to do with It" by Tina Turner
What's love got to do, got to do with it What's love but a second hand emotion What's love got to do, got to do with it Who needs a heart when a heart can be broken
Rhetorical Questions in "Mr. Big Stuff" by Jean Knight
Now because you wear all those fancy clothes (oh yeah) And have a big fine car, oh yes you do now Do you think I can afford to give you my love (oh yeah) You think you're higher than every star above
Mr. Big Stuff Who do you think you are Mr. Big Stuff You're never gonna get my love
Rhetorical Questions in "Isn't She Lovely" by Stevie Wonder
Isn't she lovely Isn't she wonderful Isn't she precious Less than one minute old I never thought through love we'd be Making one as lovely as she But isn't she lovely made from love
Stevie Wonder wrote "Isn't She Lovely" to celebrate the birth of his daughter, Aisha. The title is a perfect example of a rhetorical question, because Wonder isn't seeking a second opinion here. Instead, the question is meant to convey the love and amazement he feels towards his daughter.
Why Do Writers Use Rhetorical Questions?
Authors, playwrights, speech writers and musicians use rhetorical questions for a variety of reasons:
- To challenge the listener
- To emphasize an idea
- To raise doubt
- To demonstrate that a previously asked question was obvious
The examples included in this guide to rhetorical questions have largely pointed to the persuasive power of rhetorical questions, and covered the way that they are used in arguments, both real and fictional. However, poets also frequently use rhetorical questions for their lyrical, expressive qualities. Take the poem below, "Danse Russe (Russian Dance)" by William Carlos Williams:
If when my wife is sleeping and the baby and Kathleen are sleeping and the sun is a flame-white disc in silken mists above shining trees,— if I in my north room dance naked, grotesquely before my mirror waving my shirt round my head and singing softly to myself: "I am lonely, lonely. I was born to be lonely. I am best so!" If I admire my arms, my face, my shoulders, flanks, buttocks against the yellow drawn shades,— Who shall say I am not the happy genius of my household?
The rhetorical question that concludes this poem has the effect of challenging the reader to doubt Williams' happiness—daring the listener to question this intimate, eccentric portrait of the poet's private world. By ending the poem in this way, Williams maintains a delicate balance. Throughout the poem, he draws the reader in and confides secrets of his interior life, but the question at the end is an almost defiant statement that he does not require the reader's approval. Rather, the reader—like the mirror—is simply there to witness his happy solitude.
Other Helpful Rhetorical Question Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Rhetorical Questions: A general explanation with a variety of examples, as well as links to specific resources with punctuation rules.
- The Dictionary Definition of Rhetorical Question: A basic definition with some historical information.
- A detailed explanation of rhetorical questions , along with related figures of speech that involve questions.
- A video of Ronald Reagan's 1980 Republican National Convention Speech, in which he asks stacked rhetorical questions.
- An article listing the greatest rhetorical questions in the history of pop music.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1895 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,904 quotes across 1895 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Figurative Language
- Figure of Speech
- Parallelism
- Juxtaposition
- Characterization
- Internal Rhyme
- Colloquialism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Anthropomorphism
- Extended Metaphor
- Polysyndeton
- Blank Verse
- Static Character

Rhetorical Question
Definition of rhetorical question.
A rhetorical question is asked just for effect, or to lay emphasis on some point being discussed when no real answer is expected. A rhetorical question may have an obvious answer, but the questioner asks it to lay emphasis on the point. In literature, a rhetorical question is self-evident and used for style as an impressive persuasive device.
Broadly speaking, a rhetorical question is asked when the questioner himself knows the answer already, or an answer is not actually demanded. So, an answer is not expected from the audience . Such a question is used to emphasize a point or draw the audience’s attention.
Common Rhetorical Question Examples
Rhetorical questions, though almost needless or meaningless, seem a basic need of daily language. Some common examples of rhetorical questions from daily life are as follows:
- “Who knows?”
- “Are you stupid?”
- “Did you hear me?”
Mostly, it is easy to spot a rhetorical question because of its position in the sentence . It occurs immediately after a comment made, and states the opposite of it. The idea again is to make a point more prominent. Some rhetorical question examples are as follows. Keep in mind that they are also called “tag questions” if used in everyday conversation.
- “It’s too hot today, isn’t it? “
- “The actors played the roles well, didn’t they? “
How to Punctuation Rhetorical Questions?
It is not very difficult to tell how to punctuate a rhetorical question. It either ends on a question mark or a period. However, it is to be kept in mind that if the question occurs in the middle of a simple or complex sentence, it does not require any punctuation mark. If, on the other hand, it occurs by the end of the sentence or text, then it needs a question mark. Sometimes writers use an exclamation mark instead of a question mark. That is entirely a contextual requirement that the writer understands and wants to convey to his audiences.
Rhetorical Question and Hypophora
A rhetorical question is a rhetorical device , while a hypophora is a figure of speech . Whereas in a rhetorical question, the person does not need an answer, nor does he/she answers that question, in hypophora, the person posing a question gives its answer as well. It is a simple question with a simple and single sentence answer.
Rhetorical Question and Aporia
Similar to the rhetorical question, aporia is also a rhetorical device. However, it only expresses skepticism to prove something. Therefore, it becomes a question when expressing that uncertainty. On the other hand, a rhetorical question does not express any uncertainty as it does not require an answer and is posed often with the attention to stress upon the idea about which it is posed.
Use of Rhetorical Questions in Sentences
- i am obviously angry. Will you be okay if I punch you?
- Do you wonder why Harry is such a dumb person like he’s lost his mind? Oh well!
- The Earth revolves around the sun. Why? Because rest the of the planets do too.
- Looking at the clock, the father asked his son, ‘What time do you think it is now ?’
- Isn’t he the master of deceptions? Alas, you knew that too?
Examples of Rhetorical Questions in Literature
Rhetorical questions in literature are as important as they are in daily language, or perhaps even more so. The reason is the significant change a rhetorical question can bring about. The absence or presence of a rhetorical question in some of the most famous lines in literature would change the impact altogether. Some examples of rhetorical questions in the literature show that writers sometimes ask questions and then go on to answer them to produce the desired effect.
Example #1: Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
JULIET: ” ’Tis but thy name that is my enemy. Thou art thyself, though not a Montague. What’s Montague ? It is nor hand, nor foot , Nor arm, nor face, nor any other part Belonging to a man. O, be some other name! What’s in a name ? That which we call a rose By any other name would smell as sweet.”
A very good example of a rhetorical question in literature is from Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet . Here, Juliet makes a statement that a man’s name does not define him as a person. She draws attention to this issue by asking two important rhetorical questions, as noted in bold.
Example #2: Ode to the West Wind by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Percy Bysshe Shelley ends his masterpiece Ode to the West Wind with a rhetorical question:
“…O Wind, If Winter comes, can Spring be far behind ?”
In this excerpt, Shelley achieves the desired effect by asking a rhetorical question, rather than making a statement. The answer to this question is not sought; rather, an effect is successfully created giving a fine finishing touch to the ode .
Example #3: Creation by Hladia Porter Stewart
Mrs. Hladia Porter Stewart in her poem Creation employs rhetorical questions to create effect and achieve the desired appeal of the poem.
“What made you think of love and tears And birth and death and pain?”
Without rhetorical questions, it might have been impossible for the poet to express herself as impressively as she does here.
Example #4: The Solitary Reaper by William Wordsworth
“Will no one tell me what she sings?”
Notice, that an answer is not expected to this question. The poet prefers a rhetorical question to a plain statement to emphasize his feelings of pleasant surprise. Thus, the poem’s meaning is enhanced by the use of a rhetorical question.
Example #5: The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare
“If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?”
The character Shylock, in Shakespeare’s play The Merchant of Venice , asks a series of rhetorical questions in this excerpt. The questions don’t necessarily need answers. They are neither questions nor plain statements, but rather something in between the two.
Function of Rhetorical Question
Writers employ rhetorical questions for rhetorical effects, and we cannot easily quantify the impact rendered by a rhetorical question. The idea becomes all the more powerful, and our interest is aroused to continue to read and enjoy the technical and aesthetic beauty that a rhetorical question generates. Moreover, it is a requirement in persuasive speeches.
Synonyms of Rhetorical Question
There is no equivalent meaning to a rhetorical question. The following words may come close in meanings such as explanation, question, inquiry, rebuttal , question, inquiry, and query.
Related posts:
- Rhetorical Device
- Beg The Question
- Hypothetical Question
Post navigation
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
What Is a Rhetorical Analysis and How to Write a Great One

Helly Douglas

Do you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay? Fear not! We’re here to explain exactly what rhetorical analysis means, how you should structure your essay, and give you some essential “dos and don’ts.”
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
How do you write a rhetorical analysis, what are the three rhetorical strategies, what are the five rhetorical situations, how to plan a rhetorical analysis essay, creating a rhetorical analysis essay, examples of great rhetorical analysis essays, final thoughts.
A rhetorical analysis essay studies how writers and speakers have used words to influence their audience. Think less about the words the author has used and more about the techniques they employ, their goals, and the effect this has on the audience.

In your analysis essay, you break a piece of text (including cartoons, adverts, and speeches) into sections and explain how each part works to persuade, inform, or entertain. You’ll explore the effectiveness of the techniques used, how the argument has been constructed, and give examples from the text.
A strong rhetorical analysis evaluates a text rather than just describes the techniques used. You don’t include whether you personally agree or disagree with the argument.
Structure a rhetorical analysis in the same way as most other types of academic essays . You’ll have an introduction to present your thesis, a main body where you analyze the text, which then leads to a conclusion.
Think about how the writer (also known as a rhetor) considers the situation that frames their communication:
- Topic: the overall purpose of the rhetoric
- Audience: this includes primary, secondary, and tertiary audiences
- Purpose: there are often more than one to consider
- Context and culture: the wider situation within which the rhetoric is placed
Back in the 4th century BC, Aristotle was talking about how language can be used as a means of persuasion. He described three principal forms —Ethos, Logos, and Pathos—often referred to as the Rhetorical Triangle . These persuasive techniques are still used today.
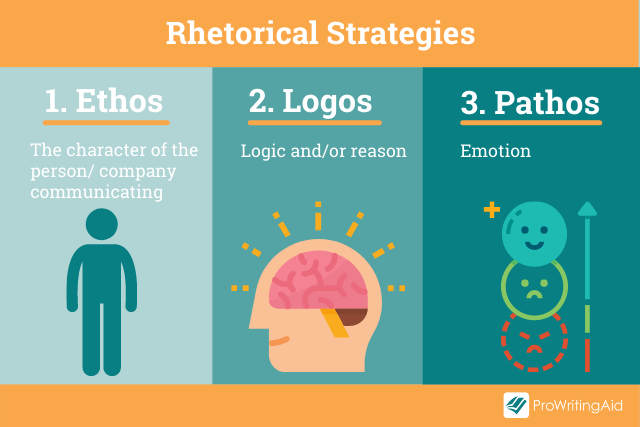
Rhetorical Strategy 1: Ethos
Are you more likely to buy a car from an established company that’s been an important part of your community for 50 years, or someone new who just started their business?
Reputation matters. Ethos explores how the character, disposition, and fundamental values of the author create appeal, along with their expertise and knowledge in the subject area.
Aristotle breaks ethos down into three further categories:
- Phronesis: skills and practical wisdom
- Arete: virtue
- Eunoia: goodwill towards the audience
Ethos-driven speeches and text rely on the reputation of the author. In your analysis, you can look at how the writer establishes ethos through both direct and indirect means.
Rhetorical Strategy 2: Pathos
Pathos-driven rhetoric hooks into our emotions. You’ll often see it used in advertisements, particularly by charities wanting you to donate money towards an appeal.
Common use of pathos includes:
- Vivid description so the reader can imagine themselves in the situation
- Personal stories to create feelings of empathy
- Emotional vocabulary that evokes a response
By using pathos to make the audience feel a particular emotion, the author can persuade them that the argument they’re making is compelling.
Rhetorical Strategy 3: Logos
Logos uses logic or reason. It’s commonly used in academic writing when arguments are created using evidence and reasoning rather than an emotional response. It’s constructed in a step-by-step approach that builds methodically to create a powerful effect upon the reader.
Rhetoric can use any one of these three techniques, but effective arguments often appeal to all three elements.
The rhetorical situation explains the circumstances behind and around a piece of rhetoric. It helps you think about why a text exists, its purpose, and how it’s carried out.
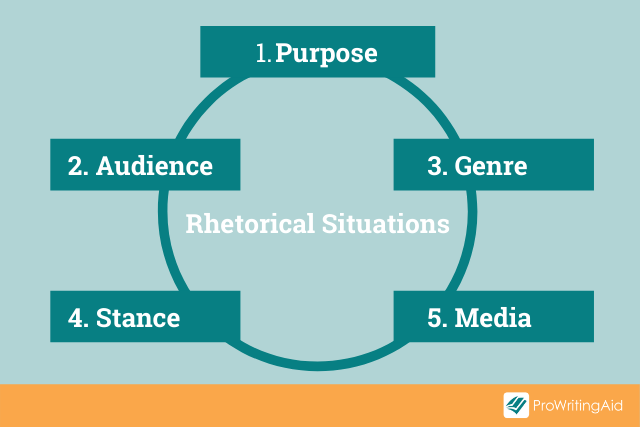
The rhetorical situations are:
- 1) Purpose: Why is this being written? (It could be trying to inform, persuade, instruct, or entertain.)
- 2) Audience: Which groups or individuals will read and take action (or have done so in the past)?
- 3) Genre: What type of writing is this?
- 4) Stance: What is the tone of the text? What position are they taking?
- 5) Media/Visuals: What means of communication are used?
Understanding and analyzing the rhetorical situation is essential for building a strong essay. Also think about any rhetoric restraints on the text, such as beliefs, attitudes, and traditions that could affect the author's decisions.
Before leaping into your essay, it’s worth taking time to explore the text at a deeper level and considering the rhetorical situations we looked at before. Throw away your assumptions and use these simple questions to help you unpick how and why the text is having an effect on the audience.

1: What is the Rhetorical Situation?
- Why is there a need or opportunity for persuasion?
- How do words and references help you identify the time and location?
- What are the rhetoric restraints?
- What historical occasions would lead to this text being created?
2: Who is the Author?
- How do they position themselves as an expert worth listening to?
- What is their ethos?
- Do they have a reputation that gives them authority?
- What is their intention?
- What values or customs do they have?
3: Who is it Written For?
- Who is the intended audience?
- How is this appealing to this particular audience?
- Who are the possible secondary and tertiary audiences?
4: What is the Central Idea?
- Can you summarize the key point of this rhetoric?
- What arguments are used?
- How has it developed a line of reasoning?
5: How is it Structured?
- What structure is used?
- How is the content arranged within the structure?
6: What Form is Used?
- Does this follow a specific literary genre?
- What type of style and tone is used, and why is this?
- Does the form used complement the content?
- What effect could this form have on the audience?
7: Is the Rhetoric Effective?
- Does the content fulfil the author’s intentions?
- Does the message effectively fit the audience, location, and time period?
Once you’ve fully explored the text, you’ll have a better understanding of the impact it’s having on the audience and feel more confident about writing your essay outline.
A great essay starts with an interesting topic. Choose carefully so you’re personally invested in the subject and familiar with it rather than just following trending topics. There are lots of great ideas on this blog post by My Perfect Words if you need some inspiration. Take some time to do background research to ensure your topic offers good analysis opportunities.

Remember to check the information given to you by your professor so you follow their preferred style guidelines. This outline example gives you a general idea of a format to follow, but there will likely be specific requests about layout and content in your course handbook. It’s always worth asking your institution if you’re unsure.
Make notes for each section of your essay before you write. This makes it easy for you to write a well-structured text that flows naturally to a conclusion. You will develop each note into a paragraph. Look at this example by College Essay for useful ideas about the structure.
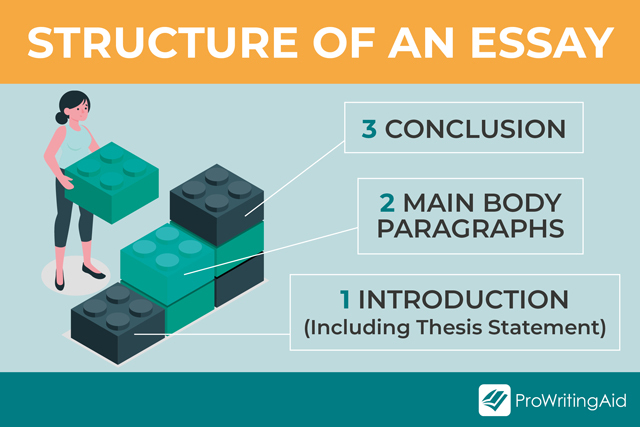
1: Introduction
This is a short, informative section that shows you understand the purpose of the text. It tempts the reader to find out more by mentioning what will come in the main body of your essay.
- Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses
- Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. “implies,” “asserts,” or “claims”
- Briefly summarize the text in your own words
- Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect
Create a thesis statement to come at the end of your introduction.
After your introduction, move on to your critical analysis. This is the principal part of your essay.
- Explain the methods used by the author to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience using Aristotle's rhetorical triangle
- Use quotations to prove the statements you make
- Explain why the writer used this approach and how successful it is
- Consider how it makes the audience feel and react
Make each strategy a new paragraph rather than cramming them together, and always use proper citations. Check back to your course handbook if you’re unsure which citation style is preferred.
3: Conclusion
Your conclusion should summarize the points you’ve made in the main body of your essay. While you will draw the points together, this is not the place to introduce new information you’ve not previously mentioned.
Use your last sentence to share a powerful concluding statement that talks about the impact the text has on the audience(s) and wider society. How have its strategies helped to shape history?
Before You Submit
Poor spelling and grammatical errors ruin a great essay. Use ProWritingAid to check through your finished essay before you submit. It will pick up all the minor errors you’ve missed and help you give your essay a final polish. Look at this useful ProWritingAid webinar for further ideas to help you significantly improve your essays. Sign up for a free trial today and start editing your essays!
You’ll find countless examples of rhetorical analysis online, but they range widely in quality. Your institution may have example essays they can share with you to show you exactly what they’re looking for.
The following links should give you a good starting point if you’re looking for ideas:
Pearson Canada has a range of good examples. Look at how embedded quotations are used to prove the points being made. The end questions help you unpick how successful each essay is.
Excelsior College has an excellent sample essay complete with useful comments highlighting the techniques used.
Brighton Online has a selection of interesting essays to look at. In this specific example, consider how wider reading has deepened the exploration of the text.

Writing a rhetorical analysis essay can seem daunting, but spending significant time deeply analyzing the text before you write will make it far more achievable and result in a better-quality essay overall.
It can take some time to write a good essay. Aim to complete it well before the deadline so you don’t feel rushed. Use ProWritingAid’s comprehensive checks to find any errors and make changes to improve readability. Then you’ll be ready to submit your finished essay, knowing it’s as good as you can possibly make it.
Try ProWritingAid's Editor for Yourself
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Helly Douglas is a UK writer and teacher, specialising in education, children, and parenting. She loves making the complex seem simple through blogs, articles, and curriculum content. You can check out her work at hellydouglas.com or connect on Twitter @hellydouglas. When she’s not writing, you will find her in a classroom, being a mum or battling against the wilderness of her garden—the garden is winning!
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Literary Terms
- Rhetorical Question
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Rhetorical Question
I. What is a Rhetorical Question?
A rhetorical question is a question that is not asked in order to receive an answer from the audience or reader. It’s just posed to make a point. Don’t we do this all the time in everyday speech? Sometimes a rhetorical question will just be left open, but other times the speaker will immediately go on to answer it. In either case, no answer from the audience is expected.
II. Examples of a Rhetorical Question
“What’s the deal with airline food?”
This sort of rhetorical question is often asked by standup comedians. They’re not actually asking the audience to answer the question – they’re just setting up a joke or monologue about the subject of airline food.
“Want to order a pizza?”
“Sure, why not?”
You’ve probably used this rhetorical question before. Rather than just saying “yeah,” you ask a question. But the question is entirely rhetorical. Imagine if someone actually responded by explaining why you shouldn’t order a pizza – you might suspect that they missed your point.
III. The Importance of a Rhetorical Question
Rhetorical questions are so common in everyday speech that it’s hard to define their overall effect. It’s just part of the way people speak in real life, so using a rhetorical question here and there can make your writing sound more natural. In addition, a question gives the feel of a dialogue, because the reader feels as though he or she is being addressed directly by the writer. (The fancy word for this is that rhetorical questions “interpellate” the reader.)
There’s at least one clear purpose for rhetorical questions in formal essays : they’re a great way to move an argument forward (see section 6 for an example). Instead of just saying “I will now talk about x ,” you can ask a question about x and give your reader a better idea of where you’re going. This is a much more natural and conversational way to write. Imagine a dinner party where someone raised their hand and announced what they were going to talk about next – no one does this! But you can easily imagine someone raising a rhetorical question instead. You can mimic this flow of conversation in your writing.
V. Examples of a Rhetorical Question in Literature
“ What’s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet!” (Juliet, Romeo and Juliet )
One of Shakespeare’s most famous lines is a rhetorical question. In this line, Juliet is raising the question to prove a point – that names don’t mean anything and it shouldn’t matter if Romeo’s last name is unacceptable to her parents. She’s asking the question rhetorically, and doesn’t expect that someone will come in and tell her what is in a name.
“Who’s afraid of Virginia Woolf?” (Play by Edward Albee)
This rhetorical question also contains a clever pun. The play is all about a pair of English professors who discuss the work of British author Virginia Woolf; they also sing a humorous version of the song “Who’s Afraid of the Big Bad Wolf?” onstage.
VI. Examples of Rhetorical Question in Pop Culture
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); “If vegetarians eat vegetables, then what do humanitarians eat?”
This joke is an example of a rhetorical question. It doesn’t really need an answer, since the punch line is already implied by the question – do humanitarians eat humans?
“How many roads must a man walk down before you call him a man?” “Seven!” (Mona and Homer Simpson, The Simpsons )
In this episode of The Simpsons , Mona Simpson is singing a famous song by Bob Dylan in which the first line is “How many roads must a man walk down before you call him a man?” Obviously it’s a rhetorical question because the singer doesn’t expect an answer, but Homer fails to understand this and hazards a guess.
VII. Related Terms
An “aporia” is a rhetorical expression of doubt, usually when the author doesn’t actually feel the doubt. An aporia is often expressed in question form, and in these cases it’s an example of a rhetorical question. It’s often used in philosophy and other argument-heavy fields when the author wants to move the conversation forward. Take this line from a philosophy paper, transitioning from one section into another:
Therefore, the democratic citizen should speak as plainly as possible so that his or her fellow-citizens can understand. But what exactly does it mean to “speak plainly” when it comes to complicated political issues? And are there exceptions to the general rule?
In these sentences, the author is getting ready to raise a new point in the argument, and the rhetorical questions help smooth the transition. Obviously, the author isn’t expecting a response – in fact, the author is about to go forward and answer the questions herself.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What Is a Rhetorical Question?

3-minute read
- 4th April 2023
Rhetorical questions can be an effective tool for writers and speakers to connect with their audience and convey their message more effectively. In this article, we’ll discuss rhetorical questions, how to use them, and some examples.
Definition of a Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a question that isn’t meant to be answered. It’s asked to make a point or create an effect rather than to elicit an actual response. Here are a few examples:
· Are you kidding me? ‒ Used to express disbelief or shock
· Do you think I was born yesterday? ‒ Used to express suspicion or doubt
· Why not? – Used to express willingness to try something
How to Use a Rhetorical Question
Rhetorical questions are rhetorical devices often used in writing and speech to engage the audience, emphasize a point, or provoke thought. They can be used to introduce a topic, make a statement, or open an argument.
Conversational Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are used in everyday speech and conversations. For example:
· Who knows? ‒ Indicates that no one knows the answer
· Isn’t that the truth? ‒ Used to express agreement with something
Introducing a Topic
Rhetorical questions are a common strategy in essay writing to introduce a topic or persuade the reader . Here are some essay questions with rhetorical questions you could use to introduce the topic:
Essay Question: Why should we care about climate change?
Rhetorical Question Introduction: Would you like to live on a dying planet?
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Essay Question: Are dress codes a good idea for school?
Rhetorical Question Introduction: Wouldn’t you like the freedom to choose what you want to wear?
Famous Examples of Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are a powerful and effective device to use in speech and writing, which is why you can find countless examples, from past and present figures, using them. Here are a few examples:
Here, Obama is using rhetorical questions to emphasize a point to his audience about what type of nation America is. The questions demonstrate his stance on immigration in America.
Dr. King used a variety of literary devices in his writing and speeches to inspire and invoke change and action in his audience. Here, he poses the rhetorical question, “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” to get his audience thinking. There’s no obvious answer here. He’s setting up his response to this seemingly unanswerable question.
Here, Sojourner Truth is speaking at the 1851 Women’s Convention to persuade the audience that women should have the right to vote like men. She’s emphasizing that she can do everything a man can do and more (childbirth), but she can’t vote like a man because she’s a woman.
Rhetorical questions are statements pretending to be a question. They’re not to be answered, as their answer should be obvious or there isn’t an obvious answer.
You can use rhetorical questions to emphasize a point, introduce a topic, or encourage your audience to think critically about an issue. If you’re looking to enhance your speaking or writing, check out our Literary Devices page to learn more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
An Introduction to Rhetorical Questions
Is This a Rhetorical Question?
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A rhetorical question is a question (such as "How could I be so stupid?") that's asked merely for effect with no answer expected. The answer may be obvious or immediately provided by the questioner. Also known as erotesis , erotema, interrogatio, questioner , and reversed polarity question (RPQ) .
A rhetorical question can be "an effective persuasive device, subtly influencing the kind of response one wants to get from an audience " (Edward P.J. Corbett). See Examples and Observations, below. They may also be used for dramatic or comedic effect, and may be combined with other figures of speech , such as puns or double entendres .
In English, rhetorical questions are commonly used in speech and in informal kinds of writing (such as advertisements). Rhetorical questions appear less frequently in academic discourse .
Pronunciation: ri-TOR-i-kal KWEST-shun
Types of Rhetorical Questions
- Anthypophora and Hypophora
Examples and Observations
- "Something [rhetorical] questions all have in common . . . is that they are not asked, and are not understood, as ordinary information-seeking questions, but as making some kind of claim , or assertion, an assertion of the opposite polarity to that of the question." (Irene Koshik, Beyond Rhetorical Questions . John Benjamins, 2005)
- " Marriage is a wonderful institution, but who would want to live in an institution? " (H. L. Mencken)
- "It did not occur to me to call a doctor, because I knew none, and although it did occur to me to call the desk and ask that the air conditioner be turned off, I never called, because I did not know how much to tip whoever might come— was anyone ever so young? " (Joan Didion, "Goodbye to All That." Slouching Towards Bethlehem , 1968)
- "The means are at hand to fulfill the age-old dream: poverty can be abolished. How long shall we ignore this under-developed nation in our midst ? How long shall we look the other way while our fellow human beings suffer? How long" (Michael Harrington, The Other America: Poverty in the United States , 1962)
- "Must I argue the wrongfulness of slavery ? Is that a question for republicans? Is it to be settled by the rules of logic and argumentation, as a matter beset with great difficulty, involving a doubtful application of the principle of justice, hard to understand?" ( Frederick Douglass , "What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?" July 5, 1852)
- "Hath not a Jew eyes? Hath not a Jew hands, organs, dimensions, senses, affections, passions? If you prick us, do we not bleed, if you tickle us, do we not laugh? If you poison us, do we not die? ( Shylock in William Shakespeare's Merchant of Venice )
- "Can I ask a rhetorical question ? Well, can I?" (Ambrose Bierce)
- "Aren't you glad you use Dial? Don't you wish everybody did?" (1960s television advertisement for Dial soap)
- "To actually see inside your ear canal--it would be fascinating, wouldn't it?" (Letter from Sonus, a hearing-aid company, quoted in "Rhetorical Questions We'd Rather Not Answer." The New Yorker , March 24, 2003)
- "If practice makes perfect, and no one's perfect, then why practice?" (Billy Corgan)
- "Isn't it a bit unnerving that doctors call what they do 'practice'?" ( George Carlin )
- "Am I alone in thinking it odd that a people ingenious enough to invent paper, gunpowder, kites, and any number of other useful objects, and who have a noble history extending back three thousand years, haven't yet worked out that a pair of knitting needles is no way to capture food?" (Bill Bryson, Notes From a Small Island . Doubleday, 1995)
- "The Indians [in the Oliver Stone movie The Doors ] serve the same function they did in Dances With Wolves : they make the far more highly paid white movie actors seem soulful and important and in touch with ancient truths. Do Indians enjoy being used this way, as spiritual elves or cosmic merit badges?" (Libby Gelman-Waxner [Paul Rudnick], "Sex, Drugs, and Extra-Strength Excedrin." If You Ask Me , 1994)
Rhetorical Questions in Shakespeare's "Julius Caesar"
Rhetorical questions are those so worded that one and only one answer can be generally expected from the audience you are addressing. In this sense, they are like the unmentioned premises in abbreviated reasoning, which can go unmentioned because they can be taken for granted as generally acknowledged. "Thus, for example, Brutus asks the citizens of Rome: 'Who is here so base that would be a bondman?' adding at once: 'If any, speak, for him have I offended.' Again Brutus asks: 'Who is here so vile that will not love his country?' Let him also speak, 'for him I have offended.' Brutus dares to ask these rhetorical questions, knowing full well that no one will answer his rhetorical questions in the wrong way. "So, too, Marc Antony , after describing how Caesar's conquests filled Rome's coffers, asks: 'Did this in Caesar seem ambitious?' And after reminding the populace that Caesar thrice refused the crown that was offered him, Antony asks: 'Was this ambition?' Both are rhetorical questions to which one and only one answer can be expected." (Mortimer Adler, How to Speak How to Listen . Simon & Schuster, 1983)
Are Rhetorical Questions Persuasive?
"By arousing curiosity, rhetorical questions motivate people to try to answer the question that is posed. Consequently, people pay closer attention to information relevant to the rhetorical question. . . . "At this point, I think it is important to note that the fundamental problem in the study of rhetorical questions is the lack of focus on the persuasive effectiveness of different types of rhetorical questions. Clearly, an ironical rhetorical question is going to have a different effect on an audience than an agreement rhetorical question. Unfortunately, little research has been conducted on how different types of rhetorical questions operate in a persuasive context." (David R. Roskos-Ewoldsen, "What Is the Role of Rhetorical Questions in Persuasion?" Communication and Emotion: Essays in Honor of Dolf Zillmann , ed. by Jennings Bryant et al. Lawrence Erlbaum, 2003)
Punctuating Rhetorical Questions
"From time to time, people become dissatisfied with the broad application of the question mark and try to narrow it down, usually by proposing distinct marks for the different kinds of question. Rhetorical questions have attracted particular attention, as—not requiring any answer—they are so different in kind. An Elizabethan printer, Henry Denham, was an early advocate, proposing in the 1580s a reverse question mark (؟) for this function, which came to be called a percontation mark (from a Latin word meaning a questioning act). Easy enough to handwrite, some late 16th century authors did sporadically use it, such as Robert Herrick. . . . But printers were unimpressed, and the mark never became standard. However, it has received a new lease of life online . . .." (David Crystal, Making a Point: The Persnickety Story of English Punctuation . St. Martin's Press, 2015)
The Lighter Side of Rhetorical Questions
-Howard: We need to ask you a question. - Professor Crawley: Really? Let me ask you a question. What does an accomplished entomologist with a doctorate and twenty years of experience do when the university cuts all his funding? - Rajesh: Ask uncomfortable rhetorical questions to people? (Simon Helberg, Lewis Black, and Kunal Nayyar in "The Jiminy Conjecture." The Big Bang Theory , 2008) -Penny: Sheldon, have you any idea what time it is? - Sheldon: Of course I do. My watch is linked to the atomic clock in Boulder, Colorado. It's accurate to one-tenth of a second. But as I'm saying this, it occurs to me that you may have again been asking a rhetorical question . (Kaley Cuoco and Jim Parsons in "The Loobenfeld Decay." The Big Bang Theory , 2008) -Dr. Cameron: Why did you hire me? - Dr. House: Does it matter? - Dr. Cameron: Kind of hard to work for a guy who doesn't respect you. - Dr. House: Why? - Dr. Cameron: Is that rhetorical ? - Dr. House: No, it just seems that way because you can't think of an answer. ( House, M.D. ) "I forget, which day did God create all the fossils?" (An anti-creationism bumper sticker, cited by Jack Bowen in If You Can Read This: The Philosophy of Bumper Stickers . Random House, 2010) Grandma Simpson and Lisa are singing Bob Dylan's "Blowin' in the Wind" ("How many roads must a man walk down/Before you call him a man?"). Homer overhears and says, "Eight!" -Lisa: "That was a rhetorical question !" -Homer: "Oh. Then, seven!" -Lisa: "Do you even know what 'rhetorical' means?" -Homer: "Do I know what 'rhetorical' means?" ( The Simpsons , "When Grandma Simpson Returns")
- What Is a Rhetorical Question? Definition and Examples
- Question Mark Definition and Examples
- Homer Simpson's Figures of Speech
- An Introduction to Declarative Questions
- Direct Question in Grammar
- Anthypophora and Rhetoric
- epimone (rhetoric)
- Definition and Examples of Sarcasm
- Pathos in Rhetoric
- Rhetorical Questions for English Learners
- Paralepsis (Rhetoric)
- Socratic Dialogue (Argumentation)
- Interrobang (Punctuation)
- Interrogative Sentences
- Persuasion and Rhetorical Definition
- Quotes from Shakespeare Plays

Rhetorical Questions: 30 Effective Examples and Definition
Oct 24, 2023

Rhetorical questions, in particular, possess the unique ability to captivate, engage, and provoke thought. Whether you’re a seasoned orator, a writer, or someone simply looking to enhance their persuasive skills, this article is your definitive guide to mastering this impactful technique. Delve into the world of rhetoric and discover how these 30 examples and expert tips can elevate your communication to new heights.
What Are Rhetorical Questions?
Rhetorical questions are a powerful tool in the realm of persuasive communication. They are a form of interrogative expression used to make a point or convey a message rather than to elicit a direct response. These questions are crafted with a specific intention, often to provoke thought, engage the audience, or emphasize a particular idea. Here’s a clear and easy-to-understand explanation of rhetorical questions:
Rhetorical questions are inquiries posed in conversation or writing that do not require or expect an actual answer. Instead, they serve as a persuasive or rhetorical device, designed to make a statement, emphasize a point, or provoke critical thinking in the audience.
The biggest difference between rhetorical questions and typical questions in that rhetorical questions are not used to gather information or seek a response from others. Rather, they function as a means of guiding the listener or reader’s thoughts in a particular direction. They are strategically employed to emphasize a message, create a sense of engagement, or encourage reflection.
Rhetorical questions are commonly used in persuasive speeches, essays, debates, and everyday communication to achieve various objectives. Here are a few key purposes:
Emphasis – Rhetorical questions can draw attention to a specific idea or argument by framing it as a question. For example, “Do we want to continue down a path of destruction?” emphasizes the gravity of the situation.
Engagement – These questions engage the audience by prompting them to consider the topic more deeply. For instance, “Have you ever wondered what the future holds?” encourages the audience to reflect on possibilities.
Affirmation – Rhetorical questions often lead the audience to agree with the implied answer, reinforcing the speaker’s point. An example is, “Is it not our moral duty to help those in need?” which presupposes that helping others is a moral obligation.
Persuasion – By framing an argument as a rhetorical question, the speaker can guide the audience to a specific conclusion. For instance, “Wouldn’t you agree that a healthier lifestyle leads to a happier life?” implies that the answer is yes.
30 Best Rhetorical Questions Examples
1. What’s not to love about a beautiful sunset? Rhetorical questions like this one evoke a sense of wonder and appreciation, inviting the audience to share the sentiment.
2. Are you going to let fear hold you back from your dreams? This question challenges the audience to confront their fears and consider the impact on their aspirations.
3. Do you think the world would be a better place without acts of kindness? By implying a positive response, this question emphasizes the importance of kindness in society.
4. Can you imagine a world without art and creativity? It highlights the significance of art and creativity in our lives, making the audience reflect on their value.
5. Is it possible to put a price on freedom? This question prompts reflection on the intangible value of freedom.
6. Why do we fall? So we can learn to pick ourselves up. Rhetorical questions like this can be motivational, emphasizing the importance of resilience.
7. Does anyone really believe in a perfect world? It invites contemplation about the idealistic notion of a perfect society.
8. What’s more important than the health and well-being of our children? This question highlights the paramount importance of children’s welfare.
9. Could we exist without the air we breathe? It emphasizes the fundamental nature of oxygen to human existence.
10. Is there a single recipe for happiness that suits everyone? This question suggests the subjectivity of happiness and personal fulfillment.
11. Is it fair to judge a book by its cover? This age-old question prompts reflection on the issue of prejudice and superficial judgments.
12. Can you really put a price on love? This question emphasizes the idea that love is priceless and beyond monetary value .
13. Who doesn’t want to be successful in life? This question assumes that everyone desires success, making the audience ponder their own aspirations.
14. Do you think anyone would willingly choose pain over pleasure? It underlines the universal preference for pleasure and avoidance of pain.
15. Is there anything more refreshing than a cold glass of water on a hot day? This question appeals to our shared experience of relief on a scorching day.
16. What could be more comforting than the embrace of a loved one? This rhetorical question highlights the emotional value of human connection.
17. Can we really call ourselves civilized when we still wage wars? This question provokes thought about the contradiction between civilization and conflict.
18. What’s stopping you from chasing your dreams? I t encourages self-reflection and motivation to overcome obstacles.
19. Is there anything better than the sound of laughter? This question celebrates the universal joy associated with laughter.
20. How can we expect change if we never take action? It underscores the necessity of taking the initiative to bring about change.
21. Do you think the world would be the same without great leaders? This question underscores the impact of influential leaders throughout history.
22. What would life be without a sense of humor? It highlights the role of humor in our lives, promoting its significance.
23. Is there any greater tragedy than the loss of a loved one? This question evokes empathy and reflection on the depth of human emotion.
24. Can you really put a limit on human potential? It challenges the idea of constraining human capabilities.
25. What could be more fundamental than the pursuit of knowledge? This rhetorical question emphasizes the inherent human curiosity and thirst for knowledge.
26. Can you imagine a world without hope? It prompts reflection on the importance of hope in people’s lives.
27. Is there any greater bond than the love between a parent and child? This question celebrates the profound connection between parents and their children.
28. What would life be without challenges to overcome? It highlights the role of adversity in personal growth and development.
29. Is there a more powerful force than the unity of a community? This question emphasizes the strength of community and solidarity .
30. Who would trade the beauty of nature for a concrete jungle? It encourages reflection on the value of preserving natural environments
Why People Use Rhetorical Questions?
Rhetorical questions serve various compelling purposes. Foremost among these is their ability to engage the audience or reader. They break the monotony of one-way communication and encourage active participation, thereby infusing the conversation or written text with dynamism and interactivity. Rhetorical questions also double as persuasive tools since they often imply a specific answer or point of view, subtly guiding the audience to consider the speaker or writer’s perspective.
Moreover, rhetorical questions can stimulate thought and critical thinking, encouraging individuals to ponder complex issues or view a subject from multiple angles. They possess the remarkable capacity to evoke emotions, eliciting empathy, curiosity, or reflection by framing an issue in a relatable manner. Additionally, rhetorical questions can be effectively employed to emphasize key points, rendering them memorable, and drawing attention to the essential aspects of a message.
Tips On How to Make Good Rhetorical Questions
- Consider your audience’s interests, values, and knowledge. Pattern your questions to resonate with their experiences and perspectives.
- Ensure your question is clear and concise . A complex question may confuse your audience and weaken the impact of your message.
- Rhetorical questions should stimulate thought. Make questions that encourage your audience to reflect on the subject matter.
- Rhetorical questions often imply an answer . Ensure that this answer connects with your intended message or argument.
- Use rhetorical questions to evoke emotions . Appeal to your audience’s feelings to make your message more impactful.
- Ensure that your rhetorical question is directly related to the topic at hand. Irrelevant questions can disrupt the flow of your communication.
- Don’t overuse rhetorical questions. Use them strategically to emphasize key points or engage your audience when necessary.
- While rhetorical questions can be powerful, using too many can lessen their impact. Use them sparingly for maximum effect.
- Some questions can be more complex, but be mindful of your audience’s ability to engage with the topic. Balance between simple and hard questions as needed.
- Crafting effective rhetorical questions is a skill that improves with Seeking feedback from peers or mentors to refine your use of rhetorical questions in your communication.
Upon discussing the key points about rhetorical questions, we learned that: the art of using rhetorical questions is a powerful tool in communication. As we’ve explored in this discussion, rhetorical questions can captivate your audience, prompt reflection, and enhance the impact of your message. By understanding your audience, tailoring your questions, and using them strategically, you can become a more persuasive and engaging communicator. Whether you’re delivering a speech, writing an essay, or simply engaging in a meaningful conversation, the use of rhetorical questions can elevate your communication to a new level. So, the next time you seek to make a point, inspire, or provoke thought, consider the art of the rhetorical question, and watch the power of your words come to life.
Read More: 10 Biggest Philosophical Dilemmas Examples
Read also: 30 Effective Guiding Questions Examples
The Most Popular on BitGlint

- Gene-Editing Babies: 20 Pros and Cons to Consider
The topic of gene-editing babies is one that stirs a lot of discussion and debate. It's about scientists using...

Top 30 Individual Autonomy Examples & Why It Matters
Individual autonomy, the capacity to make one's own decisions and govern oneself, stands as a cornerstone of personal...

- Top 20 Cultural Hybridization Examples & Definition
Cultural hybridization is a fascinating phenomenon where different cultures blend to create something entirely new and...

Top 20 Moral Subjectivism Examples & Definition
Moral subjectivism asserts that ethical judgments and moral values are based on individual preferences and...

Top 20 Dualism Examples & Definition
Dualism, a concept deeply rooted in philosophy, theology, and psychology, refers to the existence of two distinct,...

Top 30 Symbolic Archetypes Examples & Their Meaning
Symbolic archetypes are the building blocks of storytelling, weaving deep significance and universal themes into...

Top 20 Pluralism Examples & Definition
Pluralism represents the fabric of a society woven with varied threads – different beliefs, cultures, and...
Get Inspired with BitGlint
AI-powered Personalization & All You Need to Know About It
Top 30 Imperfect Things That Are Beautiful
30 Examples of Perspective: Diverse Viewpoints Explored
UK Citizenship: A Comprehensive Guide How To Get It
Top 20 Benefits of Having a Mentor in Your Life
Top 30 Self-Care Morning Rituals
Top 20 Disadvantages of Credit Cards
30 Best Examples How Can Nature Inspire Us
Top 30 Authoritarianism Examples: Definition & Guide
Guide to Growing Organic Vegetables at Home - 10 Tips
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Articles
- Private Schools: 30 Pros and Cons to Consider
- Genetic Elites vs. The Rest: A New Form of Inequality?
- 30 Best Moral Dilemma Examples

- Freelancing
- Trending Stories

What are Rhetorical Questions? A Deep Dive into Their Meaning and Significance. This article provides readers with a comprehensive toolkit for creating questions that resonate with an audience, leaving a lasting impact and influencing their perception.
Rhetorical questions are like special questions in how we talk and write. They don’t need answers, but they make you think or underline a point. You see them a lot in everyday talk, big speeches, ads, and in books. They’re like bridges that connect the person talking or writing with the people listening.
So, what are rhetorical questions? Why are they important? Well, they’re everywhere, so that shows they matter. They help share ideas, whether you’re talking to a big audience or just chatting with friends.
Rhetorical questions are like tools for talking and writing. They make sure people really understand the message. They’re not just for one kind of talk; you can use them in school, at work, or in regular conversations.
Rhetorical questions are like magic because they make you think. They get your brain going and help you understand things better. So, next time you hear one, know it’s not just a question – it’s a way to keep our conversations and thoughts moving.
Table of Contents
What are rhetorical questions and their characteristics?
What are rhetorical questions? Rhetorical questions are like a special type of question. Unlike regular questions that expect answers, rhetorical questions are more like statements in disguise. They’re here to get you thinking, not to hear your response. These questions don’t follow the typical question rules; instead, they’re like a secret weapon for writers and speakers to pack a punch with their ideas.
Rhetorical questions have some special features that make them stand out. They’re like little brain teasers, making you ponder and sparking your thoughts. They often use fancy language tricks like metaphors, exaggeration, or wordplay to make a big impact. For example, when someone asks, “Is the sky blue?” to point out the obvious, they’re using a rhetorical question.
History and origin: What are rhetorical questions?
Rhetorical questions have been around for ages, all the way back to ancient Greece. In those days, people really admired the skill of convincing and public speaking. Wise folks like Aristotle and Plato, famous Greek philosophers, used rhetorical questions in their talks. These questions helped them catch the attention of their listeners and make their arguments strong.
But rhetorical questions didn’t stop there. They found their way into all sorts of communication. They were used in religious sermons, political speeches, and even in the writings of famous authors like William Shakespeare. The fact that they’ve been around for so long shows just how powerful and persuasive they can be.
What are the rhetorical questions’ variations and forms?
Rhetorical questions come in all sorts of variations and forms. They can be sly or right out in the open, serious or funny, and sometimes they really make you think. What are rhetorical questions? Here are a few common types:
1. Hypophora:
2. rhetorical exclamatory questions:, 3. rhetorical tag questions:.
This is when a question is asked, and then the answer is given right away. It’s like a question and a follow-up response all in one. For example, “How can we overcome adversity? The answer lies in our resilience and determination.”
These questions are a mix of rhetorical questions and exclamations. They often express strong feelings or amazement. For instance, “Could you believe the incredible beauty of the sunset?”
These questions are used to seek agreement or confirmation, but the person asking them doesn’t expect a direct answer. For example, “It’s a beautiful day, isn’t it?”
These different flavors of rhetorical questions give communicators a whole toolbox to work with. They help connect with the audience in various ways, making communication more effective and engaging.
What are rhetorical questions’ functions?
Rhetorical questions play a unique role in our conversations and writing. By understanding their role, you can become a more effective communicator in a wide range of contexts. What are rhetorical questions? Here are the various functions of rhetorical questions:
- Engaging the audience:
- Stating a point:
- Challenging assumptions:
- Creating a sense of agreement:
- Capturing attention:
- Aiding recall:
- Stirring emotions:
- Enhancing engagement:
- Repetition:
- Antithesis:
A. Persuasion and argumentation
Rhetorical questions serve as powerful tools for persuasion and argumentation. When used strategically, they can influence the beliefs, opinions, and decisions of an audience. Here’s how:
1. Engaging the audience:
Rhetorical questions invite the audience to actively think about a topic. For example, “Can we afford to ignore the urgent need for change?” This question prompts the audience to consider the consequences of inaction, making them more receptive to the speaker’s viewpoint.
2. Stating a point:
Rhetorical questions can be a subtle way to make a point without coming across as confrontational. For instance, “Is it wise to continue down this unsustainable path?” The question implies that the current path is unwise, without directly stating it.
3. Challenging assumptions:
By posing rhetorical questions, speakers or writers can challenge the audience’s assumptions. For example, “Are we really as secure as we believe?” This question prompts the audience to reevaluate their sense of security, opening them to a new perspective.
4. Creating a sense of agreement:
Rhetorical questions can be used to seek agreement from the audience. When a speaker asks, “Don’t we all want a better future?” They are rallying the audience around a shared ideal.
In persuasive contexts, rhetorical questions can sway opinions, inspire action, and strengthen arguments. They do this by encouraging the audience to see things from the speaker’s viewpoint.
B. Emphasis and engagement
Rhetorical questions are masters of emphasis and engagement, often used to grab attention and hold it. Here’s how they achieve this:
1. Capturing attention:
Rhetorical questions pique the audience’s interest. They disrupt the ordinary flow of information and encourage the audience to focus on the question, preparing them for what comes next.
2. Aiding recall:
Because rhetorical questions prompt the audience to think actively, the information presented following the question is more likely to be remembered. This aids in the retention of key messages.
3. Stirring emotions:
Rhetorical questions can evoke strong emotional responses. They can make the audience feel a sense of urgency, wonder, or empathy. For example, “What if you had the power to change someone’s life?” This question tugs at the heartstrings, creating an emotional connection.
4. Enhancing engagement:
Rhetorical questions engage the audience as active participants in the communication process. This is especially valuable in education, encouraging critical thinking and participation.
In sum, rhetorical questions are essential for holding the audience’s attention. They evoke emotions and emphasize key points, making them a valuable tool in various forms of communication.
C. Rhetorical devices and figures of speech
What are rhetorical questions? Rhetorical questions are intertwined with various rhetorical devices and figures of speech. These devices add depth and artistry to the use of rhetorical questions. Let’s explore a few key examples:
1. Metaphor:
Rhetorical questions often employ metaphors to convey complex ideas. “Is life but a fleeting moment in the grand tapestry of time?” This question uses the metaphor of life as a moment and time as a tapestry to provoke contemplation.
2. Repetition:
Repeated rhetorical questions can have a powerful effect. “Can we change? Can we improve? Can we make a difference?” This repetition reinforces the message and emphasizes the importance of change.
3. Antithesis:
Antithesis involves presenting contrasting ideas. Rhetorical questions can be used to set up antithesis, like, “Do we choose to stand still, or do we dare to move forward?” This contrast encourages the audience to consider both sides of the argument.
4. Hyperbole:
Rhetorical questions sometimes employ exaggeration for effect. “Could that be any more obvious?” This hyperbolic question makes a point by emphasizing the blatant nature of the situation.
Examples: What are rhetorical questions?
You might be wondering, “What are these rhetorical questions all about?” Well, they’re questions that don’t need real answers. They’re used to make a point or get you thinking. Let’s see how they work in real life, from famous speeches to everyday talk.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” Speech:
- Shakespeare’s Hamlet:
- Patrick Henry’s “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” Speech:
- When expressing surprise:
- When offering compliments:
- When seeking agreement:
- In parenting:
- Bounty Paper Towels:
A. From famous speeches and literature
Rhetorical questions have made their mark in famous speeches and literature throughout history. Here, we explore how renowned figures have harnessed the power of rhetorical questions to engage, persuade, and inspire:
1. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” Speech:
In his 1963 speech, Dr. King asked rhetorical questions challenging the status quo and envisioning a fairer society.” Is the American dream an elusive fantasy for some and a harsh reality for others?” These questions highlighted African-American injustices and envisioned a more inclusive future.
2. Shakespeare’s Hamlet:
Shakespeare often used rhetorical questions to explore his characters’ inner thoughts. In “Hamlet,” the titular character muses, “To be or not to be, that is the question.” This profound question encapsulates Hamlet’s contemplation of life, death, and the human condition.
3. Patrick Henry’s “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” Speech:
Delivered in 1775, Henry’s speech was a rallying cry for American independence. He asked, “Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery?” These questions challenged the audience to consider the true cost of submission to British rule.
B. In everyday conversation
Rhetorical questions aren’t just for fancy speeches. We use them in everyday talk to show surprise, give compliments, ask for agreement, or teach.
1. When expressing surprise:
“Could it be any colder today?” This question shows we’re shocked by the freezing weather.
2. When offering compliments:
“Is there anything you can’t do?” This is a way of saying someone is super talented.
3. When seeking agreement:
“Don’t we all want a better life?” This question brings people together by talking about shared goals.
4. In parenting:
Parents use rhetorical questions to teach. “What happens when you don’t finish your homework on time?” It makes kids think about the consequences.
C. In advertising and marketing
Have you ever seen a catchy ad or slogan that made you think? Well, that’s the magic of rhetorical questions in marketing.
Nike’s famous slogan, “Just do it,” is a rhetorical question. It challenges consumers to question their own hesitations and inspires them to take action.
“Think Different.” This tagline poses a rhetorical question, prompting consumers to ponder the benefits of Apple products. It also encourages them to think about individuality and creativity.
3. Bounty Paper Towels:
“Why use ordinary paper towels when you can have the quicker picker-upper?” This question emphasizes Bounty’s paper towels’ benefits, making consumers ponder their superior qualities.
These questions make us curious and get us thinking about the product.
The psychology of rhetorical questions
What are rhetorical questions? Ever wonder why these questions grab our attention? It’s because they work with how our brains think. Let’s explore why they’re so powerful.
- Engaging critical thinking:
- Highlighting key points:
- Retaining information:
- Guiding the audience:
- Creating empathy:
- Eliciting emotional responses:
- Fostering engagement:
- Encouraging critical thinking:
- Stimulating class participation:
- Enhancing memory:
- Improving communication:
A. Cognitive processes and impact on the audience
Rhetorical questions are not just linguistic tools; they have a profound impact on the way our minds work. Let’s learn cognitive processes and how rhetorical questions influence the audience’s thinking:
1. Engaging critical thinking:
Rhetorical questions make us think. When we hear one, our brains look for answers, which helps us think critically.
2. Highlighting key points:
These questions point out important stuff. For example, “What are the consequences of climate change?” makes us focus on how serious climate change is.
3. Retaining information:
When we hear a rhetorical question, we remember the info that comes after it better. This is useful for learning new things.
4. Guiding the audience:
Rhetorical questions guide our thoughts. For instance, “Can we afford to ignore the urgent need for change?” helps us think about how important it is to make a change.
B. Emotional appeal and connection
Rhetorical questions can evoke emotions and establish connections with the audience. Here’s how they accomplish this:
1. Creating empathy:
Rhetorical questions get us involved in the conversation. For example, “Have you ever experienced the feeling of loss?” makes us feel the speaker understands us.
2. Eliciting emotional responses:
By their very nature, rhetorical questions can prompt strong emotional reactions. They can be used to spark feelings of empathy, sadness, wonder, or even anger. However, it depends on the context and content of the question.
3. Fostering engagement:
Rhetorical questions don’t just make us think. They also make us feel. This gets us more interested in the message, and we’re more likely to remember it.

C. Rhetorical questions in education and learning
Rhetorical questions aren’t just for speeches and ads. They’re also used in classrooms to help students learn better.
1. Encouraging critical thinking:
Teachers use rhetorical questions to make students think and analyze things. For example, “What do you think will happen if we change this variable in the experiment?”
2. Stimulating class participation:
Rhetorical questions can make learning fun. When a teacher asks one, it gets students talking and learning together.
3. Enhancing memory:
Rhetorical questions help us remember stuff. This is super helpful for students because they can remember what they learn.
4. Improving communication:
Learning how to use rhetorical questions helps students talk and write better. It’s not just for school; it helps in other parts of life, too!
The psychology behind rhetorical questions shows us how they make us think, feel, and learn in different ways. Whether it’s a big speech, a classroom, or an ad, these questions make a big impact.
Common misconceptions: What are rhetorical questions?
There are some things people get mixed up about rhetorical questions. Let’s clear these up so you can understand them better.
- Response expectation:
- Interrogative structure:
- Loss of impact:
- Insincerity:
- Context matters:
- Cultural differences:
- Linguistic nuances:
- Translation challenges:
A. Rhetorical questions vs. literal questions
People sometimes mix up rhetorical questions with regular ones. Let’s see how they’re different:
1. Purpose:
Regular questions are meant to get answers. Rhetorical questions aren’t looking for answers; they’re making a point or getting us thinking.
2. Response expectation:
When someone asks a regular question like “What time is it?” They want a real answer, like “It’s 3:30.” But with a rhetorical question like “Is this the best you can do?” they don’t want an answer; they’re showing something could be better.
3. Interrogative structure:
Regular questions follow the usual rules, like using question words (who, what, where, when, why). Rhetorical questions often break those rules.
Understanding this difference helps us communicate better. Mixing up rhetorical questions with real ones can cause confusion.
B. Effectiveness and overuse
Rhetorical questions are great, but they lose their power if we use them too much.
1. Loss of impact:
When we use these questions too often, they become less exciting. Imagine if a whole speech was just one question after another. It would get boring, right?
2. Insincerity:
If we use too many rhetorical questions, it might seem like we’re not being honest or we’re trying to trick someone. We don’t want that!
3. Context matters:
Rhetorical questions work best when they fit the situation. In some cases, a simple statement might be better than a question. We should use these questions thoughtfully.
C. Cultural and linguistic variations
The use and understanding of rhetorical questions can vary across cultures and languages. It’s important to recognize this. Common misconceptions in this regard include:
1. Cultural differences:
What is considered persuasive or engaging in one culture might not be so in another? The way rhetorical questions are received and their cultural appropriateness can vary significantly.
2. Linguistic nuances:
Different languages may have their own nuances when it comes to rhetorical questions. Some languages use it more, while others prefer direct expression.
3. Translation challenges:
Translating unanswerable questions between languages can be challenging. This happens because the question might not have the same effect in another language due to language and cultural differences.
It’s important to understand and respect these differences. In a world where we communicate with many cultures and languages, it’s a reminder that good communication is about more than just words. You need to get the culture and language context right to communicate well.
How to use rhetorical questions effectively?
What are rhetorical questions? Are you looking to employ rhetorical questions to enhance your communication skills? In this section, we’ll provide practical guidance on using rhetorical questions effectively.
- Know your purpose:
- Clarity and simplicity:
- Consider your audience:
- Use varied forms:
- Timing matters:
- Visual and auditory impact:
- Prior knowledge:
- Interests and values:
- Age and education level:
- Cultural sensitivity:
- Metaphor and Simile:
- Parallelism:
A. Tips for writers and speakers
Follow these tips for writers and speakers to wield rhetorical questions effectively.
1. Know your purpose:
Clearly define the purpose of your rhetorical question. Are you aiming to engage, persuade, or emphasize a point? Your intent should guide the crafting of the question.
2. Clarity and simplicity:
Keep your rhetorical questions clear and simple. Complex questions can confuse the audience and dilute the impact. Choose words and structures that are easily understood.
3. Consider your audience:
Tailor your questions to your audience’s knowledge, interests, and expectations. Avoid questions that might alienate or confuse them.
4. Use varied forms:
Experiment with different forms of rhetorical questions. Consider hypophora (posing a question and then answering it), rhetorical tag questions (inviting agreement), and exclamatory questions (conveying strong emotions).
5. Timing matters:
Think about the timing of your rhetorical questions. Place them strategically within your speech or text to maximize their effect. A well-timed question can captivate the audience’s attention.
6. Visual and auditory impact:
Use vocal and physical cues to accentuate your rhetorical questions. Adjust your tone, volume, and body language to draw attention to the question.
B. Tailoring rhetorical questions to the audience
Adapting your rhetorical questions is crucial for effective communication. Here’s how to do it:
1. Prior knowledge:
Consider what your audience already knows about the topic. Align questions with your audience’s understanding and guide them to more complex ideas.
2. Interests and values:
Reflect on the interests and values of your audience. Craft questions that resonate with their concerns and priorities. This demonstrates that you understand and empathize with their perspective.
3. Age and education level:
Adjust question complexity based on your audience’s age and education. Use straightforward language for a general audience and intricate questions for experts.
4. Cultural sensitivity:
Be aware of cultural nuances. Certain cultural contexts may require more sensitivity in topic and question choice.. Respect and adapt to these variations.
C. Balancing rhetorical questions with other rhetorical techniques
Rhetorical questions, when combined with other techniques, boost their persuasive power.
1. Anaphora:
Anaphora repeats a word or phrase at the start of sentences. Combining rhetorical questions with anaphora can create a rhythmic and persuasive effect. For instance, “What can we do? What can we change? What can we achieve?”
2. Metaphor and Simile:
Use metaphors and similes alongside rhetorical questions to illustrate your point. For example, “Just as a ship needs a strong captain, do we not need a strong leader in our journey forward?”
3. Parallelism:
Employ parallel sentence structures with rhetorical questions for symmetry and impact. “Are we ready to act? Are we ready to commit? Are we ready to make a difference?”
4. Allusion:
Balancing rhetorical questions with other techniques creates a well-rounded, persuasive message. Each technique enhances engagement and impact, making your message more effective.
Ethical considerations: What are rhetorical questions?
While rhetorical questions can be a valuable tool for communication, there are ethical considerations to keep in mind. Not all situations are suitable for their use, and understanding these considerations is crucial to using rhetorical questions responsibly.
- Transparency:
- Balanced presentation:
- Respect for diverse perspectives:
- Fact-checking:
- Personal integrity:
- Honesty in intention:
- Ethical boundaries:
- Advertising and marketing:
- Public speaking and politics:
- Media and journalism:
A. Avoiding manipulation and deceit
In rhetoric and persuasion, using rhetorical questions effectively balances impact and manipulation. Here’s how to avoid crossing that line:
1. Transparency:
Be transparent about your intentions when using rhetorical questions. If your question is meant to persuade, inform your audience of your perspective. Avoid posing questions solely to manipulate their emotions or opinions.
2. Balanced presentation:
Present a balanced view of the topic at hand. Also, avoid simplifying complex topics with rhetorical questions. Moreover, you should not manipulate the narrative to serve your agenda.
3. Respect for diverse perspectives:
Acknowledge that there may be multiple valid viewpoints on a subject. Avoid using rhetorical questions to belittle or dismiss opposing opinions. Foster respectful and open dialogue instead.
4. Fact-checking:
Make sure your rhetorical questions rely on accurate info. Misrepresenting facts or using false premises can lead to deceit.
B. Maintaining authenticity and honesty
Authenticity and honesty should underpin the use of rhetorical questions:
1. Personal integrity:
Use rhetorical questions that align with your values and beliefs. Avoid employing questions that compromise your personal integrity or authenticity.
2. Honesty in intention:
Reflect on the actual purpose of your rhetorical questions. Do they provoke real thought or just deceive? Ensure your intent is honest.
3. Ethical boundaries:
Recognize the ethical boundaries in various contexts. Consider consequences and prioritize honesty and authenticity in interactions.
C. Ethical guidelines for using rhetorical questions in various contexts
Different contexts may require different ethical considerations when using rhetorical questions:
1. Education:
In educational settings, rhetorical questions can be used to stimulate critical thinking. However, educators must ask unbiased questions. These questions should encourage open discussion, not impose a specific viewpoint.
2. Advertising and marketing:
Ethical advertising and marketing aim to inform and persuade consumers honestly. Rhetorical questions engage but should not deceive. Adhering to advertising standards and being transparent about product claims is essential.
3. Public speaking and politics:
In public discourse, rhetorical questions often appear in speeches and politics. Public figures should use them sincerely, avoiding deception or emotional exploitation.
4. Media and journalism:
Journalists must use rhetorical questions responsibly in news reporting. These questions should make readers think but not manipulate the news.
No matter where you use them, you need to be ethical. Ethical use of rhetorical questions involves open, honest, and respectful discussions.
Following these ethical guidelines allows communicators to use rhetorical questions while maintaining integrity.
Whether you’re a student learning rhetoric or a professional enhancing persuasive skills, understanding ‘what is a rhetorical question’ boosts your language and discourse proficiency.
These questions influence, engage, evoke emotions, encourage critical thinking, and simplify complex ideas. Mastering rhetorical questions shape narratives, inspires action, and leaves a lasting impact.
Study famous speeches, literature, or ads to see how they use rhetorical questions. Practice crafting your own, adapting them to contexts and audiences, and refine your technique.
No Comments
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay–Examples & Template
What is a Rhetorical Analysis Essay?
A rhetorical analysis essay is, as the name suggests, an analysis of someone else’s writing (or speech, or advert, or even cartoon) and how they use not only words but also rhetorical techniques to influence their audience in a certain way. A rhetorical analysis is less interested in what the author is saying and more in how they present it, what effect this has on their readers, whether they achieve their goals, and what approach they use to get there.
Its structure is similar to that of most essays: An Introduction presents your thesis, a Body analyzes the text you have chosen, breaks it down into sections and explains how arguments have been constructed and how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section sums up your evaluation.
Note that your personal opinion on the matter is not relevant for your analysis and that you don’t state anywhere in your essay whether you agree or disagree with the stance the author takes.
In the following, we will define the key rhetorical concepts you need to write a good rhetorical analysis and give you some practical tips on where to start.
Key Rhetorical Concepts
Your goal when writing a rhetorical analysis is to think about and then carefully describe how the author has designed their text so that it has the intended effect on their audience. To do that, you need to consider a number of key rhetorical strategies: Rhetorical appeals (“Ethos”, “Logos”, and “Pathos”), context, as well as claims, supports, and warrants.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos were introduced by Aristotle, way back in the 4th century BC, as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience. They still represent the basis of any rhetorical analysis and are often referred to as the “rhetorical triangle”.
These and other rhetorical techniques can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify the concepts they are based on.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeal #1: ethos.
Ethos refers to the reputation or authority of the writer regarding the topic of their essay or speech and to how they use this to appeal to their audience. Just like we are more likely to buy a product from a brand or vendor we have confidence in than one we don’t know or have reason to distrust, Ethos-driven texts or speeches rely on the reputation of the author to persuade the reader or listener. When you analyze an essay, you should therefore look at how the writer establishes Ethos through rhetorical devices.
Does the author present themselves as an authority on their subject? If so, how?
Do they highlight how impeccable their own behavior is to make a moral argument?
Do they present themselves as an expert by listing their qualifications or experience to convince the reader of their opinion on something?
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos
The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader’s emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a “good cause”. To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories, and employ vivid imagery so that the reader can imagine themselves in a certain situation and feel empathy with or anger towards others.
Rhetorical appeal #3: Logos
Logos, the “logical” appeal, uses reason to persuade. Reason and logic, supported by data, evidence, clearly defined methodology, and well-constructed arguments, are what most academic writing is based on. Emotions, those of the researcher/writer as well as those of the reader, should stay out of such academic texts, as should anyone’s reputation, beliefs, or personal opinions.
Text and Context
To analyze a piece of writing, a speech, an advertisement, or even a satirical drawing, you need to look beyond the piece of communication and take the context in which it was created and/or published into account.
Who is the person who wrote the text/drew the cartoon/designed the ad..? What audience are they trying to reach? Where was the piece published and what was happening there around that time?
A political speech, for example, can be powerful even when read decades later, but the historical context surrounding it is an important aspect of the effect it was intended to have.
Claims, Supports, and Warrants
To make any kind of argument, a writer needs to put forward specific claims, support them with data or evidence or even a moral or emotional appeal, and connect the dots logically so that the reader can follow along and agree with the points made.
The connections between statements, so-called “warrants”, follow logical reasoning but are not always clearly stated—the author simply assumes the reader understands the underlying logic, whether they present it “explicitly” or “implicitly”. Implicit warrants are commonly used in advertisements where seemingly happy people use certain products, wear certain clothes, accessories, or perfumes, or live certain lifestyles – with the connotation that, first, the product/perfume/lifestyle is what makes that person happy and, second, the reader wants to be as happy as the person in the ad. Some warrants are never clearly stated, and your job when writing a rhetorical analysis essay is therefore to identify them and bring them to light, to evaluate their validity, their effect on the reader, and the use of such means by the writer/creator.

What are the Five Rhetorical Situations?
A “rhetorical situation” refers to the circumstance behind a text or other piece of communication that arises from a given context. It explains why a rhetorical piece was created, what its purpose is, and how it was constructed to achieve its aims.
Rhetorical situations can be classified into the following five categories:
Asking such questions when you analyze a text will help you identify all the aspects that play a role in the effect it has on its audience, and will allow you to evaluate whether it achieved its aims or where it may have failed to do so.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Outline
Analyzing someone else’s work can seem like a big task, but as with every assignment or writing endeavor, you can break it down into smaller, well-defined steps that give you a practical structure to follow.
To give you an example of how the different parts of your text may look when it’s finished, we will provide you with some excerpts from this rhetorical analysis essay example (which even includes helpful comments) published on the Online Writing Lab website of Excelsior University in Albany, NY. The text that this essay analyzes is this article on why one should or shouldn’t buy an Ipad. If you want more examples so that you can build your own rhetorical analysis template, have a look at this essay on Nabokov’s Lolita and the one provided here about the “Shitty First Drafts” chapter of Anne Lamott’s writing instruction book “Bird by Bird”.
Analyzing the Text
When writing a rhetorical analysis, you don’t choose the concepts or key points you think are relevant or want to address. Rather, you carefully read the text several times asking yourself questions like those listed in the last section on rhetorical situations to identify how the text “works” and how it was written to achieve that effect.
Start with focusing on the author : What do you think was their purpose for writing the text? Do they make one principal claim and then elaborate on that? Or do they discuss different topics?
Then look at what audience they are talking to: Do they want to make a group of people take some action? Vote for someone? Donate money to a good cause? Who are these people? Is the text reaching this specific audience? Why or why not?
What tone is the author using to address their audience? Are they trying to evoke sympathy? Stir up anger? Are they writing from a personal perspective? Are they painting themselves as an authority on the topic? Are they using academic or informal language?
How does the author support their claims ? What kind of evidence are they presenting? Are they providing explicit or implicit warrants? Are these warrants valid or problematic? Is the provided evidence convincing?
Asking yourself such questions will help you identify what rhetorical devices a text uses and how well they are put together to achieve a certain aim. Remember, your own opinion and whether you agree with the author are not the point of a rhetorical analysis essay – your task is simply to take the text apart and evaluate it.
If you are still confused about how to write a rhetorical analysis essay, just follow the steps outlined below to write the different parts of your rhetorical analysis: As every other essay, it consists of an Introduction , a Body (the actual analysis), and a Conclusion .
Rhetorical Analysis Introduction
The Introduction section briefly presents the topic of the essay you are analyzing, the author, their main claims, a short summary of the work by you, and your thesis statement .
Tell the reader what the text you are going to analyze represents (e.g., historically) or why it is relevant (e.g., because it has become some kind of reference for how something is done). Describe what the author claims, asserts, or implies and what techniques they use to make their argument and persuade their audience. Finish off with your thesis statement that prepares the reader for what you are going to present in the next section – do you think that the author’s assumptions/claims/arguments were presented in a logical/appealing/powerful way and reached their audience as intended?
Have a look at an excerpt from the sample essay linked above to see what a rhetorical analysis introduction can look like. See how it introduces the author and article , the context in which it originally appeared , the main claims the author makes , and how this first paragraph ends in a clear thesis statement that the essay will then elaborate on in the following Body section:
Cory Doctorow ’s article on BoingBoing is an older review of the iPad , one of Apple’s most famous products. At the time of this article, however, the iPad was simply the latest Apple product to hit the market and was not yet so popular. Doctorow’s entire career has been entrenched in and around technology. He got his start as a CD-ROM programmer and is now a successful blogger and author. He is currently the co-editor of the BoingBoing blog on which this article was posted. One of his main points in this article comes from Doctorow’s passionate advocacy of free digital media sharing. He argues that the iPad is just another way for established technology companies to control our technological freedom and creativity . In “ Why I Won’t Buy an iPad (and Think You Shouldn’t, Either) ” published on Boing Boing in April of 2010, Cory Doctorow successfully uses his experience with technology, facts about the company Apple, and appeals to consumer needs to convince potential iPad buyers that Apple and its products, specifically the iPad, limit the digital rights of those who use them by controlling and mainstreaming the content that can be used and created on the device .
Doing the Rhetorical Analysis
The main part of your analysis is the Body , where you dissect the text in detail. Explain what methods the author uses to inform, entertain, and/or persuade the audience. Use Aristotle’s rhetorical triangle and the other key concepts we introduced above. Use quotations from the essay to demonstrate what you mean. Work out why the writer used a certain approach and evaluate (and again, demonstrate using the text itself) how successful they were. Evaluate the effect of each rhetorical technique you identify on the audience and judge whether the effect is in line with the author’s intentions.
To make it easy for the reader to follow your thought process, divide this part of your essay into paragraphs that each focus on one strategy or one concept , and make sure they are all necessary and contribute to the development of your argument(s).
One paragraph of this section of your essay could, for example, look like this:
One example of Doctorow’s position is his comparison of Apple’s iStore to Wal-Mart. This is an appeal to the consumer’s logic—or an appeal to logos. Doctorow wants the reader to take his comparison and consider how an all-powerful corporation like the iStore will affect them. An iPad will only allow for apps and programs purchased through the iStore to be run on it; therefore, a customer must not only purchase an iPad but also any programs he or she wishes to use. Customers cannot create their own programs or modify the hardware in any way.
As you can see, the author of this sample essay identifies and then explains to the reader how Doctorow uses the concept of Logos to appeal to his readers – not just by pointing out that he does it but by dissecting how it is done.
Rhetorical Analysis Conclusion
The conclusion section of your analysis should restate your main arguments and emphasize once more whether you think the author achieved their goal. Note that this is not the place to introduce new information—only rely on the points you have discussed in the body of your essay. End with a statement that sums up the impact the text has on its audience and maybe society as a whole:
Overall, Doctorow makes a good argument about why there are potentially many better things to drop a great deal of money on instead of the iPad. He gives some valuable information and facts that consumers should take into consideration before going out to purchase the new device. He clearly uses rhetorical tools to help make his case, and, overall, he is effective as a writer, even if, ultimately, he was ineffective in convincing the world not to buy an iPad .
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Analysis Essays
What is a rhetorical analysis essay.
A rhetorical analysis dissects a text or another piece of communication to work out and explain how it impacts its audience, how successfully it achieves its aims, and what rhetorical devices it uses to do that.
While argumentative essays usually take a stance on a certain topic and argue for it, a rhetorical analysis identifies how someone else constructs their arguments and supports their claims.
What is the correct rhetorical analysis essay format?
Like most other essays, a rhetorical analysis contains an Introduction that presents the thesis statement, a Body that analyzes the piece of communication, explains how arguments have been constructed, and illustrates how each part persuades, informs, or entertains the reader, and a Conclusion section that summarizes the results of the analysis.
What is the “rhetorical triangle”?
The rhetorical triangle was introduced by Aristotle as the main ways in which language can be used to persuade an audience: Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, Ethos to the writer’s status or authority, and Pathos to the reader’s emotions. Logos, Ethos, and Pathos can all be combined to create the intended effect, and your job as the one analyzing a text is to break the writer’s arguments down and identify what specific concepts each is based on.
Let Wordvice help you write a flawless rhetorical analysis essay!
Whether you have to write a rhetorical analysis essay as an assignment or whether it is part of an application, our professional proofreading services feature professional editors are trained subject experts that make sure your text is in line with the required format, as well as help you improve the flow and expression of your writing. Let them be your second pair of eyes so that after receiving paper editing services or essay editing services from Wordvice, you can submit your manuscript or apply to the school of your dreams with confidence.
And check out our editing services for writers (including blog editing , script editing , and book editing ) to correct your important personal or business-related work.
Pennington Publishing Blog
- Grammar/Mechanics
- Literacy Centers
- Spelling/Vocabulary
- Study Skills
- Uncategorized
Rhetorical Questions in Essays
Rhetorical Questions “Mr. Smith says that I shouldn’t use thought-provoking questions in my thesis statements,” said Issa. “May I read you my thesis?” “Sure. Let’s hear it,” responds Mandy. “My thesis is ‘Do people really want to be successful and happy?’” “Well, it is called a thesis statement , not a thesis question , ” Mandy replied. “Plus, doesn’t the answer appear in the question itself?” “Oh, I get it. It’s one of those rhetorical questions,” says Issa. “But, do you really get it?” asks Mandy. “Ah… A rhetorical question. Very funny.” “Apparently not so funny to Mr. Smith,” says Mandy.
Definition and Examples
A rhetorical question is a statement formed as a question. Rhetorical questions can be manipulative because they are designed to appear objective and open-ended, but may actually lead the reader to a foregone conclusion.
The rhetorical question takes several forms:
- It may answer itself and require no response. Example: Do people want to be successful?
- It may be used to provoke thought. Example: What if this generation could solve hunger?
- It may be used to state the obvious. Example: Can students try a bit harder next time?
- It may have no possible answer. Example: What if there is no answer to this problem?
Read the rules.
Don’t use rhetorical questions as thesis statements. Conclusion paragraphs may include rhetorical questions to provide questions for further study beyond the essay itself.
In the following sentences, [bracket] the rhetorical questions.
- How could they know? Why are the couples traveling to Europe for business?
- Without the tools the project was impossible to complete. Why bother? Does this project have a purpose?
- What is the message within that painting? What if all works of art meant something?
- If love is the answer, what is the question? Why do people fall in love? Does everyone do so?
- What happens when dreams are delayed? Can dreams be real? Or are dreams simply dreams?
Revise the rhetorical question into a statement.
Of what use are rhetorical questions?
- [How could they know?] Why are the couples traveling to Europe for business?
- Without the tools the project was impossible to complete. [Why bother?] [Does this project have a purpose?]
- What is the message within that painting? [What if all works of art meant something?]
- [If love is the answer, what is the question?] [Why do people fall in love?] [Does everyone do so?]
- [What happens when dreams are delayed?] [Can dreams be real?] [Or are dreams simply dreams?]
For more essay rules and practice, check out the author’s TEACHING ESSAYS BUNDLE . This curriculum includes 42 essay strategy worksheets corresponding to teach the Common Core State Writing Standards, 8 on-demand writing fluencies, 8 writing process essays (4 argumentative and 4 informative/explanatory), 64 sentence revision and 64 rhetorical stance “openers,” writing posters, and helpful editing resources.
Differentiate your essay instruction in this comprehensive writing curriculum with remedial writing worksheets, including sentence structure, grammar, thesis statements, errors in reasoning, and transitions.
Plus, get an e-comment bank of 438 prescriptive writing responses with an link to insert into Microsoft Word® for easy e-grading (works great with Google Docs) ,
Download the following 24 FREE Writing Style Posters to help your students learn the essay rules. Each has a funny or ironic statement (akin to “Let’s eat Grandma) to teach the memorable rule.
Writing composition rules , essay rules , essay structure , essay style , essay writing , essay writing rules , five paragraph essays , how to write an essay , Mark Pennington , questions in conclusions , questions in essays , rhetorical devices , rhetorical questions , Teaching Essay Strategies , thesis statement questions , using questions to provoke thought , writing programs
- No comments yet.
- No trackbacks yet.
Links to Programs and Resources
- About the Author/Contact Us
- Free Reading/ELA Assessments
- Free Articles and Resources
- Testimonials
Join the SOR Literacy Hub - Resource Sharing FB Group
https://www.facebook.com/groups/sorliteracyhub
Recent Articles
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | ELL January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | SPED January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | High School January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | Middle School January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | Grade 6 January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | Grade 5 January 2, 2024
- Free Science of Reading Lessons | Grade 4 January 2, 2024
- Reading Intervention Flow Chart December 19, 2023
- Mid-Year Reading Intervention Checklist December 19, 2023
- Reading Rules versus Patterns? December 19, 2023
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Use Rhetorical Questions in Essay Writing Effectively
Table of contents
If you prick us, do we not bleed? If you tickle us, do we not laugh?
If you poison us, do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?
These lines are from William Shakespeare’s play, The Merchant of Venice, wherein he uses consecutive rhetorical questions to evoke a sense of human empathy. This literary technique certainly worked here because the speech manages to move us and pushes us to think.
Writers have been incorporating rhetorical questions together for centuries. So, why not take inspiration and include it in your college essays, too?
A rhetorical question is asked more to create an impact or make a statement rather than get an answer. When used effectively, it is a powerful literary device that can add immense value to your writing.
How do you use rhetorical questions in an essay?
Thinking of using rhetorical questions? Start thinking about what you want your reader to take away from it. Craft it as a statement and then convert it into a rhetorical question. Make sure you use rhetorical questions in context to the more significant point you are trying to make.
When Should You Write Rhetorical Questions in Your Essay?
Are you wondering when you can use rhetorical questions? Here are four ways to tactfully use them to elevate your writing and make your essays more thought-provoking.
#1. Hook Readers
We all know how important it is to start your essay with an interesting essay hook that grabs the reader’s attention and keeps them interested. Do you know what would make great essay hooks? Rhetorical questions.
When you begin with a rhetorical question, you make the reader reflect and indicate where you are headed with the essay. Instead of starting your essay with a dull, bland statement, posing a question to make a point is a lot more striking.
How you can use rhetorical questions as essay hooks
Example: What is the world without art?
Starting your essay on art with this question is a clear indication of the angle you are taking. This question does not seek an answer because it aims to make readers feel that the world would be dreary without art.
#2. Evoke Emotions
Your writing is considered genuinely effective when you trigger an emotional response and strike a chord with the reader.
Whether it’s evoking feelings of joy, sadness, rage, hope, or disgust, rhetorical questions can stir the emotional appeal you are going for. They do the work of subtly influencing readers to feel what you are feeling.
So, if you want readers to nod with the agreement, using rhetorical questions to garner that response is a good idea, which is why they are commonly used in persuasive essays.
Example: Doesn’t everyone have the right to be free?
What comes to your mind when you are met with this question? The obvious answer is – yes! This is a fine way to instill compassion and consideration among people.
#3. Emphasize a Point
Making a statement and following it up with a rhetorical question is a smart way to emphasize it and drive the message home. It can be a disturbing statistic, a well-known fact, or even an argument you are presenting, but when you choose to end it with a question, it tends to draw more emphasis and makes the reader sit up and listen.
Sometimes, rather than saying it as a statement, inserting a question leaves a more significant impact.
Example: Between 700 and 800 racehorses are injured and die yearly, with a national average of about two breakdowns for every 1,000 starts. How many will more horses be killed in the name of entertainment?
The question inserted after presenting such a startling statistic is more to express frustration and make the reader realize the gravity of the situation.
#4. Make a Smooth Transition
One of the critical elements while writing an essay is the ability to make smooth transitions from one point or section to another and, of course, use the right transition words in your essay . The essay needs to flow logically while staying within the topic. This is a tricky skill, and few get it right.
Using rhetorical questions is one way to connect paragraphs and maintain cohesiveness in writing. You can pose questions when you want to introduce a new point or conclude a point and emphasize it.
Example: Did you know that Ischaemic heart disease and stroke are the world’s biggest killers? Yes, they accounted for a combined 15.2 million deaths in 2016.
Writing an essay on the leading causes of death? This is an intelligent way to introduce the reason and then go on to explain it.
What are the types of rhetorical questions?
There are three different kinds of rhetorical questions you can use in your essays:
Epiplexis : This rhetorical question is meant to express disapproval or shame to the reader. It is not meant to obtain an answer; it is a way to convince the reader by demonstrating frustration or grief.
Erotesis : This is used to express strong affirmation or denial. It usually implies an answer without giving the expectations of getting one. Erotesis or erotica is used to push the reader to ponder and reflect.
Hypophora : When a question is raised and is immediately answered, it is referred to as hypophora. It is used in a conversational style of writing and aids in generating curiosity in the reader. It’s also a way to make smooth transitions in the essay while letting the writer completely control the narrative.
What to AVOID while writing rhetorical questions in your essay?
It is important to use them sparingly and wherever appropriate. Rhetorical questions cannot be used in every piece of writing.
Using rhetorical questions in the thesis statement : Asking a rhetorical question in your thesis statement is an absolute no-no because thesis statements are meant to answer a question, not pose another question.
Overusing rhetorical questions : Sub7jecting the reader to an overdose of rhetorical questions, consequently or not, makes for an annoying reading experience.
Using rhetorical questions in research papers : Research papers require you to research a topic, take a stand and justify your claims. It’s a formal piece of writing that must be based on facts and research.
So, keep this literary device for persuasive or argumentative essays and creative writing pieces instead of using them in research papers.
20 Ideas of Good Rhetorical Questions to Start an Essay
- "What if the world could be free of poverty?"
- "Is it really possible to have peace in a world so full of conflict?"
- "Can we ever truly understand the depths of the universe?"
- "What does it really mean to be happy?"
- "Is technology bringing us closer together, or driving us apart?"
- "How far would you go to stand up for what you believe in?"
- "What if we could turn back time and prevent disasters?"
- "Can a single person really make a difference in the world?"
- "Is absolute freedom a blessing or a curse?"
- "What defines true success in life?"
- "Are we truly the masters of our own destiny?"
- "Is there a limit to human creativity?"
- "How does one moment change the course of history?"
- "What if we could read each other's thoughts?"
- "Can justice always be served in an imperfect world?"
- "Is it possible to live without regret?"
- "How does culture shape our understanding of the world?"
- "Are we responsible for the happiness of others?"
- "What if the cure for cancer is just around the corner?"
- "How does language shape our reality?"
While rhetorical questions are effective literary devices, you should know when using a rhetorical question is worthwhile and if it adds value to the piece of writing.
If you are struggling with rhetorical questions and are wondering how to get them right, don’t worry. Our professional essay writing service can help you write an essay using the correct literary devices, such as rhetorical questions, that will only alleviate your writing.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

Should you use Rhetoric Questions in an Essay?
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point or to create a dramatic effect rather than to get an answer.
Many college professors discourage using rhetorical questions in essays, and the majority agree that they can be used only in specific circumstances.
While they are helpful for the person writing an essay, if you want to include them in an essay, ensure that you rephrase them into a sentence, indirect question, or statement.
It is essential to say that there is only minimal space for including rhetorical questions in academic writing.
This post will help you discover why professors discourage using rhetorical questions in essays and when it is okay to use them. Let's dive in!
Why do professors discourage the use of rhetorical questions in academic papers?
We love rhetorical questions for the flair they add to written pieces. They help authors achieve some sense of style when writing essays. However, since they have an obvious answer, no answer, or require no answer, they have no place in academic writing, not even the essay hooks. They are a way to engage the audience by letting them keep thinking of the answer as they read through your text. Avoid using rhetorical essays in academic writing unless you are doing creative writing. There is no room for suspense in academic writing. Let’s find out why professors discourage them so badly in any form of academic writing, not just essay writing alone!
1. Because they don't belong in academic writing
Rhetorical questions are awesome; they can help engage your readers and keep them interested in your writing. However, they are only perfect for creative writing, diaries, and blogs and are not appropriate for academic writing. This is because academic writing is about logic, facts, and arguments, while rhetorical questions are about entertainment. The two are incompatible; the questions do not belong in academic writing.
Rhetorical questions are typically utilized in creative writing to create flair and suspense. However, academic writing does not need flair or suspense. Because most academic writing assignments are based on facts, evidence, arguments, and analysis. Thus, there is no need for the creation of flair or suspense. In other words, there is no space for rhetorical questions in academic writing.
Another thing that shows that rhetorical questions don't belong in academic writing is that they are usually written in the first person. The fact that they are written in the first person means they do not fit in academic writing, where students are usually urged to write in the third person. So while it is okay for rhetorical questions to feature in creative writing where the author addresses the reader, it is not okay for the questions to feature in academic writing where everything should be matter-of-fact.
Lastly, rhetorical questions do not belong in academic writing because readers of academic works do not expect to see them. When you start reading an academic paper, you expect answers, and you don't expect suspense, flair, or entertainment. Therefore, you will most likely be confused and even upset when you see rhetorical questions in an academic paper.
2. Because they come across as passive
When writing an academic paper as a student, you are expected to show your mastery of the content; you are expected to demonstrate your command of the content. What you are not likely to do is to pose rhetorical questions, and this is because the questions are passive and, therefore, unsuitable for academic papers. Specifically, passive voice is unsuitable for academic papers because it is dull and lazy. What is appropriate and recommended for academic papers is active voice, and this is because it is clear and concise.
You now know why you should not use passive rhetorical questions in academic papers. Another reason why you should not use passive rhetorical questions is that they will make you sound as if you are unsure of yourself. If you are sure about the points and arguments you are making in your paper, you will not ask passive rhetorical questions. Instead, you will develop your paper confidently from the introduction to the conclusion.
When you ask your readers passive rhetorical questions, you will make them Google or think about the answer. These are not the things that readers want to be doing when reading academic papers. They want to see well-developed ideas and arguments and be informed, inspired, and educated. Thus, you should spare them the need to do things they do not plan to do by not using rhetorical questions in your academic paper.
3. Because they are seen as padding
When your professor sees a rhetorical question in your essay, they will think you are just trying to fill the minimum word count. In other words, they will think you are trying to cheat the system by filling the word count with an unnecessary sentence. This could lead to you getting penalized, which you do not want for your essay if you are aiming for a top grade.
Why do professors see rhetorical questions as padding? Well, it is because struggling students are the ones who typically use rhetorical questions in their essays. Therefore, when professors see these questions, they assume that the student struggled to meet the word count, so they throw in a few rhetorical questions.
4. Because they are hard to get right
It is not easy to ask rhetorical questions correctly, especially in essays. This is because there are several things to consider when asking them, including the location, the words, the punctuation, and the answer. Most of the time, when students ask rhetorical questions in their papers, professors roll their eyes because most students ask them wrong.
The correct way to ask a rhetorical question is to ask it in the right place, in the right way, and to use the correct punctuation. You will discover how to do these things in the second half of this post. Don't just ask a rhetorical question for the sake of it; ask only when necessary.
5. Because professors hate them
If the other reasons why professors discourage rhetorical questions have not convinced you to give up on using them, this one should. Professors hate rhetorical questions, and they don't like them because they feel the questions don't belong in academic papers. Therefore, when you use them, you risk irking your professor and increasing your likelihood of getting a lower grade. So if you don't want a lower grade, you should give rhetorical questions a wide berth.
Your professor might love rhetorical questions. However, including rhetorical questions in your essay is a risk you do not want to take. Because your hunch about them liking rhetorical questions might be wrong, resulting in a bad grade for you.
When to use rhetorical questions in academic papers
You now know professors do not like seeing rhetorical questions in academic papers. However, this does not mean you cannot use them. There are situations when it is okay to use rhetorical questions in your academic papers. Below you will discover the instances when it is appropriate to use rhetorical questions in your essays.
1. When introducing your essay
When introducing your essay, you must try to grab the reader's attention with your first two or three sentences. The best way to do this is to use a hook statement – an exciting statement that makes the reader want to read the rest of the paper to find out more. And the best way to write a hook statement is as a rhetorical question.
When you write your hook statement as a rhetorical question, you will make your reader think about the question and the topic before they continue to read your introduction . This will most likely pique their interest in the topic and make them want to read the rest of your essay.
Therefore, instead of starting your essay with a dull and ordinary hook statement, you should start it with a powerful rhetorical question. This will undoubtedly hook your reader. Below is a good example of a rhetorical question hook statement:
Where could the world be without the United Nations?
Starting your essay with the question above will definitely hook any reader and give the reader an idea of the angle you want to take in your essay.
2. When you want to evoke emotions
Most academic papers are supposed to be written in the third person and should also be emotionless, well-organized, and to the point. However, there are some that can be written in the first person. Good examples of such essays include personal essays and reflective essays.
When you are writing personal essays, it is okay to express emotions. And one of the best ways to do it is by using rhetorical questions. These questions are perfect for evoking emotions because they make the reader think and reflect. And making your reader think and reflect is an excellent way to make them relate to your story.
The most appropriate way to use rhetorical questions to evoke emotions is to make your questions target specific feelings such as rage, hope, happiness, sadness, and so on. Targeted questions will help your reader think about certain things and feelings, which will undoubtedly influence what they will feel thereafter. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to evoke emotions:
Doesn't everyone deserve to be free?
This question makes you feel compassion for those who are not free and makes you think about them and the things they are going through.
3. When you want to emphasize something
Using a rhetorical question to emphasize a point is okay, especially in a personal essay. The right way to do this is to make the statement you want to highlight and ask a rhetorical question immediately after. Emphasizing a statement using a rhetorical question will help drive your message home, and it will also help leave an impact on the reader. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to emphasize the statement before it:
Nearly 1000 racehorses die or get injured every year. Is the killing and maiming of horses justified in this age of cars and underground trains?
The rhetorical question above brings into sharp focus the statement about the number of horses killed yearly and makes the reader think about the number of horses killed or injured annually.
4. When you want to make a smooth transition
One of the best ways to transition from one topic to the next is by using a rhetorical question. It is essential to transition smoothly from one point to the next if you want your essay to have an excellent flow.
A rhetorical question can help you to make a smooth transition from one point to the next by alerting the reader to a new topic. Below is an excellent example of a rhetorical question used to make a smooth transition from one paragraph to the next:
Did you know malaria remains one of Africa's leading causes of infant mortality? The tropical disease accounted for over half a million infant deaths in 2020.
The statement above smartly alerts the reader about a new topic and introduces it in a smooth and calculated manner.
Mistakes to avoid when using rhetorical questions
If you decide to use rhetorical questions in your essays, there are some mistakes you should avoid.
1. Overusing them
Using rhetorical questions in academic papers is okay, but you should never overuse them. The number of rhetorical questions in your essay should never exceed two, and more than two rhetorical questions are just too many for an essay.
2. Using them in research papers
Research papers are the most formal of academic papers. Most professors who give research paper assignments do not fancy seeing rhetorical questions in them. Therefore, you should never use rhetorical questions in research papers.
3. Never use them as your thesis statement
Your thesis statement should be a statement that is logical, concise, and complete. It should never be a question, let alone a rhetorical one.
As you have discovered in this article, rhetorical questions should ideally not be used in essays. This is because they do not belong, professors hate them, and so on. However, as you have also discovered, there are some situations when it is okay to use rhetorical questions. In other words, you can use rhetorical questions in the right circumstances. The fact that you now know these circumstances should enable you to use rhetorical questions in your essays, if necessary, correctly.
You should talk to us if you are too busy to write your essay or edit it to make it professional enough. Our company provides both essay writing and essay editing services at affordable rates. Contact us today for assistance or simply order your essay using our essay order page.
What are rhetorical questions?
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point rather than to get an answer. They are often used in creative writing to create a dramatic effect or a sense of suspense.
When and how to use rhetorical questions in essays
Professors hate rhetorical questions in essays . You should only use them sparingly and when necessary. Otherwise, you should not use them at all.
What mistakes should you avoid when using rhetorical questions in essays?
You should never use a rhetorical question instead of a good thesis statement . You should also never use a rhetorical question in a research paper.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.


The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Rhetorical Question – Definition, Examples & Meaning
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

In the study of language, a rhetorical question is recognized as a figurative inquiry employed in dialogue, not with the expectation of a response, but to highlight a point, provoke thought, or underscore a declaration. This stylistic device is not aimed at gathering information but serves to draw attention, stimulate contemplation, or reinforce an argument. This type of loaded question is a common and effective tool in the realms of literature, marketing, debates, and daily communication.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Rhetorical question in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Rhetorical questions
- 4 The 3 types
- 6 Benefits & problems
- 7 Rhetorical question vs. leading question
Rhetorical question in a nutshell
A rhetorical question is a stylistic device with a rhetorical question mark that seeks no response because the answer is implied or obvious.
Definition: Rhetorical questions
The word rhetorical has its origin in the Greek language as “rhetorikos,” meaning “skilled in speaking.” It is a figure of speech in the form of a question posed for stylistic and dramatic effect rather than to elicit an answer. Unlike regular questions, which seek information or clarification, rhetorical questions are used to make a point , persuade , provoke thought , or create a dramatic effect.
They are designed to encourage the listener or reader to consider the implied answer within the context of the question itself, rather than to respond verbally. They are commonly used in literature, speeches, and everyday conversation to emphasize a point, express irony, or lead the audience toward a particular conclusion. When talking about academic writing , rhetorical questions have no place in it since they are used for creative flair instead of clarity.
- You’re asking me if I want to go on an all-expenses-paid trip? Is the sky blue?
Rhetorical questions are employed across various contexts to engage audiences, provoke thought, emphasize points, or express emotions. Below you will find examples in different contexts and their functions.
Everyday life
Here are common example sentences used in daily communications.
- Do I look like I was born yesterday?
- Is money growing on trees?
- Have you ever seen me arrive late to anything?
Rhetorical questions in literature are often used to provoke thought, emphasize themes, or convey the characters’ emotions succinctly. Here are some short popular examples from various literary works.
- All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others, aren’t they?
- Was he not born of (a) woman?
- Can’t repeat the past? Why, of course, you can!
Below you’ll find several examples that could be seen in marketing and media.
- Want to save money on your car insurance?
- Why settle for less when you can have the best?
- Isn’t it time we talk about mental health?
In speeches and debates, especially of a political nature, rhetorical questions can be used to provoke an audience’s thoughts and guide them to a specific answer.
- How long will we tolerate injustice and remain silent?
- Is it not our duty to ensure every citizen has access to healthcare?
- Do we want to live in a society where education is a privilege and not a right?
Rhetorical questions with obvious answers
Most rhetorical questions asked have an obvious, implied answer.
- Is the sky blue?
- Don’t you want to win?
- Are you serious?
Rhetorical questions that have no answers
More rarely, a rhetorical question is expressed with no real answer implied. These are often used to make a strong negative point or to prompt further discussion.
- Why bother?
The 3 types
Rhetorical questions frequently appear in fiction, non-fiction, speeches, and everyday conversation. Some are so common they’re clichés. Rhetorical questions come in three flavors – anthypophora, erotesis, and epiplexis. Respectively, they argue the point, reinforce a point, or attack the question’s target.
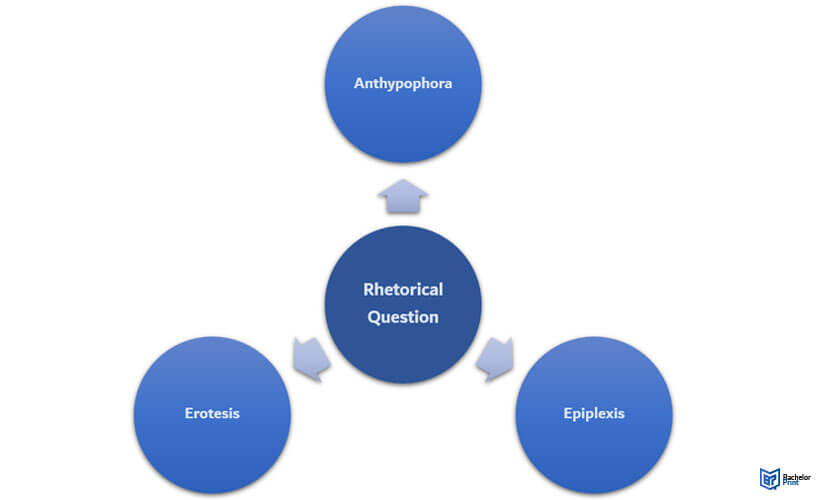
In the world of communication and rhetoric, rhetorical questions are powerful tools that can have profound effects on the listener or reader. Here are some of the theoretical and psychological impacts they have, along with plenty of examples.
Engagement and interest
Rhetorical questions draw the audience’s attention and engage them more deeply in the subject.
- Have you ever wondered what it means to live a good life?
This question invites the audience to reflect personally on the concept of a good life, making them more invested in the ensuing discussion.
They emphasize a point or highlight an issue, making it more memorable or striking.
- Is freedom of speech not the foundation of a democratic society?
By questioning the importance of free speech, the speaker underscores its critical role in democracy.
Provoking thought
Rhetorical questions encourage the audience to critical thinking and reflect on their beliefs or assumptions.
- What does it profit a man if he gains the whole world but loses his soul?
This question, derived from biblical context, prompts deep contemplation about the value of material vs. spiritual wealth.
Expressing irony or sarcasm
They can convey irony or sarcasm , critiquing a situation without directly stating the criticism.
- Oh, because we all have the luxury of time, don’t we?
Used in a context where time is limited, this question sarcastically comments on the unrealistic expectations of having ample time.
Creating a persuasive argument
Rhetorical questions can strengthen a persuasive argument by leading the audience to an intended conclusion.
- Can we really afford to ignore the environmental crisis any longer?
This question implies that the cost of inaction is too high, persuading the audience towards recognizing the urgency of environmental issues.
Building connection
They can create a sense of connection and rapport by involving the audience in the conversation.
- Haven’t we all been in a situation where we wished we had spoken up?
This question resonates with common human experiences, building a bond with the audience.
Challenging assumptions
Rhetorical questions challenge the audience to reconsider their assumptions or preconceived notions.
- Do we truly believe that all men are created equal?
It prompts the audience to reflect on their personal beliefs and the societal values around equality. By questioning the sincerity of the belief in equality, it encourages individuals to consider inconsistencies between stated values and actual practices or policies and societal justice.
Expressing frustration
They can express frustration , disbelief , or incredulity about a situation or behavior.
- Are we seriously still debating this issue?
This question expresses frustration over the prolonged discussion of what the speaker perceives as an obvious or resolved matter.
Benefits & problems
Since we have already discussed possible effects, these questions can offer several benefits in communication, but they also come with potential drawbacks. Understanding both can help in effectively leveraging rhetorical questions for desired outcomes.
Below, you’ll see several advantages rhetorical questions can offer.
While there are numerous advantages, disadvantages can also arise when using rhetorical questions that may make you consider using them.
Rhetorical question vs. leading question
A leading question (also, a suggestive question) is a question that prompts or encourages the desired answer . It’s often used in legal contexts, interviews, or surveys to guide the respondent toward a specific response, sometimes subtly implying it.
The key difference lies in their intent : rhetorical questions aim to engage thought or emphasize a point without expecting a response, while leading questions seek to elicit a specific response, steering the conversation or testimony in a desired direction.
- You saw the defendant at the scene, didn’t you?
- Don’t you agree that the product works wonders?
What's a rhetorical question?
It is a question that is asked for a specific purpose rather than obtaining information.
Why do authors and public speakers use rhetorical questions?
To better illustrate, emphasize, and reiterate the (persuasive) points they want to make. Rhetorical questions can also invite further, unguided thought — even if they’re unanswerable. Open-ended queries make good starting points for free-flowing seminars and rhetorical debates.
Is a rhetorical question ever inappropriate?
Occasionally, it can be. Poorly timed, targeted, or phrased rhetorical questions often appear to talk down to the reader — or appear to tell them what they should think. Accidental, pathetic humor (bathos) may result from questions that are too obscure or niche to be relatable or mistakenly express a truly unpopular opinion.
What is a rhetorical question example?
“How should I know?” is a question that shows frustration, while expecting no answer.
How do you know if a question is rhetorical?
Rhetorical means that it is made for style or effect, meaning a rhetorical question is used for mere effect, rather than an answer or information.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

How to Write a Rhetorical Question in an Essay

🎓✍️ Acing Your Internal Assessment Has Never Been Easier! ✍️🎓
Are you struggling with your Internal Assessment? Let our experts take care of it! We’ve successfully completed hundreds of IA projects across different IB courses, and we know the IB criterium inside out.
🌟 Our writers are all human and do not use CHAT-GPT, ensuring a unique and personalized touch to your project. Plus, our service is 100% confidential and risk-free, so you can trust us with your academic success.
Don’t miss out on this opportunity to secure the grade you deserve! Get started with our IB IA Writing Service today! 💡📚🔝
Rhetorical questions are an essential part of essay writing and mastering them can significantly improve the quality of your work. A rhetorical question is one that does not require an answer, but rather is used to emphasize a point or create a thought-provoking response from the reader. They are often used to convey a sense of emotion and provide insight into a deeper message.
In this guide, we will discuss the basics of rhetorical questions and how they can be used to strengthen an argument in an essay. We will look at the different types of rhetorical questions and how to use them effectively. We will also cover guidelines for writing rhetorical questions and offer tips on proofreading. By the end of the article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to write effective rhetorical questions in your essays .
A rhetorical question is composed of two elements: the question itself and the context in which it is asked. The question should be phrased in such a way to spark a reaction from the readers. It may be a question that is answered in the essay or simply used as a method of emphasizing a point. The context in which it is asked should be appropriate for the given situation, such as a debate or discussion.
When crafting a rhetorical question, it helps to consider the audience. The question should be relevant to the topic being discussed and the tone should be adjusted to fit the situation. Additionally, the grammar should be accurate and the syntax should be clear. With these elements in place, the question should solidify the writer’s point and add depth to the essay.
Finally, it is important to proofread any rhetorical questions you include in your essay. A poorly placed question can distract from the overall argument and take away from the essay’s effectiveness. Read through your paper to make sure that the question is clear and concise, and that its meaning is not misinterpreted by your reader.
Rhetorical questions can be a powerful tool when used correctly in an essay. As long as you keep in mind the guidelines discussed above, you can successfully add rhetorical questions to your writing in a way that enhances the overall argument.
Remember! Our team of experienced writers are well-versed in the rigorous demands of the IB program and can provide you with high-quality essays that are sure to impress your teachers. Whether you need assistance with research, writing, or editing, we have the skills and expertise to help you excel.
Don’t let the stress of IB writing hold you back. Let us take the reins and deliver top-notch essays that are sure to earn you the grades you deserve. Contact us today to learn more about our IB Writing Service and start your journey to academic success!
What is a Rhetorical Question?
A rhetorical question is a type of question that doesn’t require an answer—in fact, it can be a powerful tool to enhance your writing. Unlike other types of questions, rhetorical questions are made to generate discussion on a particular topic or to evoke an emotional response from the reader. By utilizing rhetorical questions in your essay, you can create a more engaging and effective piece of writing.
Difference between Rhetorical Questions and Other Questions
Rhetorical questions differ from other types of questions in a few important ways. For example, when you ask an open-ended question such as “What is the best way to approach this problem?” you are expecting an answer. With a rhetorical question, however, you are not expecting a direct answer, and the purpose of the question is simply to make a point. Another difference between rhetorical questions and other types of questions is their structure. Rhetorical questions often take the form of a declarative statement, which sets them apart from the more familiar types of questions.
The Power of Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions can be a powerful tool for an essay writer since they can evoke an emotional response from the reader and foster a deeper level of engagement with the material. They also serve to spark further discussion on the topic and can help to better illustrate the writer’s point. By using rhetorical questions in your essay, you can ensure that your writing will be both engaging and effective.
Examples of Rhetorical Questions
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech where the question typically does not expect an answer, but instead serves as a device to create emphasis and provoke thought. Knowing how to skillfully use rhetorical questions in your writing can be a powerful tool and help you create more engaging content. Let’s take a look at some examples of rhetorical questions to better understand how they work.
One classic example of a rhetorical question is “C’mon, what do you think?” This conveys an implied message that the person you are asking should already know the answer or at least think critically about their opinion. It can be used when trying to make a point, or end a discussion.
Another example of a rhetorical question is “Why bother?” This is often used to express a feeling of apathy or suggest that something isn’t worth considering. It can have a persuasive effect as readers may be prompted to consider why they should even bother with something.
Finally, an example of a rhetorical question used for comic relief might be “Do I really need to explain this?” This is often used to show exasperation at a lack of understanding and can be useful for lightening the mood.
When constructing a rhetorical question, there are a few key elements to keep in mind. First, the question should be phrased in a way that does not expect an answer. Second, it should be relevant to the conversation or situation at hand. Finally, the rhetorical question should provide emphasis or clarity to what is being said.
By understanding how to effectively use rhetorical questions, you can add depth and power to your writing. We hope these examples have helped you better understand how to use rhetorical questions in your own writing.
Why Rhetorical Questions Are Important For Essay Writing
A rhetorical question is an important writing skill to have in your arsenal, particularly when it comes to essay writing . So why are rhetorical questions so important when crafting an essay? To put simply, they allow you to ask a question without requiring an answer. This can be a powerful tool to convey a point that you are attempting to make in your essay. By deliberately refraining from providing an answer, the reader is left with a thought-provoking question that will likely stay with them long after they’ve finished your essay.
Rhetorical questions should be used sparingly and judiciously, as overusing them can lead to confusion or give the impression that you haven’t done enough research on the topic at hand. When used effectively, however, they can be a great tool for ensuring that your readers are paying attention to the points you are making and engaging with the material in a meaningful way. One of the key advantages of rhetorical questions is that they can help ensure your essay is memorable and stays with the reader long after they’ve finished reading.
In this sense, a rhetorical question has the power to contribute significantly to your essay’s overall impact. They can also be used as an effective tool to transition between topics, helping to introduce a new idea while adding a sense of mystery and intrigue. Finally, they can be used to further reinforce solutions or arguments in your essay, helping to drive home the point you are trying to make.
As such, it is important to understand the purpose of rhetorical questions and the various ways you can use them to enhance your essay. When used effectively, rhetorical questions can add a great deal of depth and meaning to your essay, and help ensure that your readers stay engaged with your work.
Guidelines for Writing Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions can be a powerful tool when used correctly in an essay. They are designed to draw the reader in and encourage them to think about the topic in new ways. When writing a rhetorical question, there are several guidelines that you should consider in order to make sure that you are conveying your message in the most effective way possible.
First, you should think carefully about the context of your question. Make sure that your question fits in with the rest of the essay’s theme and purpose. Additionally, think about the audience you are writing for and tailor your question so that it speaks to their specific interests and concerns.
Next, when crafting the question itself, make sure to use language that is direct and concise. Avoid using unnecessary words or overly complex sentence structures. Your goal should be to create a clear and direct message that is easy for the reader to comprehend.
You should also strive to craft your rhetorical question in a way that offers the reader an opportunity to think more deeply about the issue. Ask a question that challenges the reader on an intellectual level, encouraging them to view the topic from a new perspective.
Finally, pay careful attention to the structure of your question. Consider whether you should use a positive or negative statement, as this will have a significant impact on how your question is received. Additionally, think about the best way to phrase your question as it relates to the tone of your essay.
By taking the time to consider these guidelines, you can make sure that you are creating effective rhetorical questions that will engage your readers and keep them interested in the topic. If you take the time to craft each one carefully and make sure that it fits in with the overall concept of your essay, then you will be able to create an essay that is sure to leave a lasting impression on your readers.
Structures for Writing Rhetorical Questions
Learning how to effectively write rhetorical questions can make your writing more effective, persuasive, and engaging. Before you begin constructing your own rhetorical questions, it’s important to understand the structures used when crafting them.
Rhetorical questions come in many different forms and have various purposes, so knowing which structure is best suited for your purpose can help get your message across more clearly. Here are some of the most common structures for writing rhetorical questions:
- Meaningful Phrase: A meaningful phrase is a concise way to communicate an idea or an opinion. For example: “What’s the point?”
- Inverted Sentence Structure: This structure involves inverting the normal sentence structure to create a question. For example: “Shouldn’t we be asking why?”
- Parallelism: Parallelism is a technique that involves repeating words, phrases, or sentences in a specific pattern. This can help convey the point of the question more clearly. For example: “What have we done and what are we doing? What will we do?”
- Compound Question: A compound question consists of two or more questions linked together with a conjunction. This can be used to emphasize the importance of the question or to draw attention to multiple aspects of the topic. For example: “Do we really understand the consequences of our actions, and are we prepared to face them?”
- Implied Question: An implied question involves using a statement to imply a question. This structure can be useful if you want to create a certain tone or evoke a particular emotion. For example: “We can’t ignore the fact that this issue has far-reaching effects.”
When crafting rhetorical questions, it’s important to pay attention to the structure of the question in order to ensure that it communicates the desired message. By familiarizing yourself with these common structures, you can create powerful and effective rhetorical questions that will have a lasting impact on your readers.
Techniques for Writing an Effective Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a powerful tool for an essay writer, as it can help to spark the reader’s interest, make them think critically about a topic, and draw their attention to certain details within your essay. To maximize the effectiveness of a rhetorical question, there are several writing techniques that you should keep in mind.
- Be brief: Your rhetorical question should be short and to the point, so that your readers can quickly grasp its meaning. Strive to capture the essence of the thought in just a few words.
- Use assertive language: When writing a rhetorical question, strive to use language that is assertive and authoritative, so that your reader will take the question seriously and take pause to consider its implications.
- Choose the right tone: The tone of your rhetorical question will also be important. Consider the context of the essay and how different tones may affect its impact. Likewise, use carefully chosen words to ensure that the intended meaning is conveyed clearly.
- Be specific: To really drive home the point of your rhetorical question, make sure that it is specific to the topic at hand. A good rhetorical question should be focused enough to make a statement about the topic, yet open-ended enough to raise questions that the reader can explore on their own.
- Keep it relevant: The rhetorical question should be relevant to the essay’s content and should not be seen as an unrelated or unnecessary addition. It should be used to further emphasize a point or to explore an issue more deeply.
By utilizing these techniques and considering their impact, you can write effective rhetorical questions that will contribute to the success of your essay . As with any writing skill, practice makes perfect, so don’t be afraid to experiment with different formats and tone until you feel confident in your ability to craft a powerful rhetorical question.
Dos and Don’ts: Tips for Writing Rhetorical Questions in Your Essay
Writing a rhetorical question in your essay can be a powerful way to engage readers and make an impact on your audience. However, if done incorrectly, these questions can be ineffective and even confusing. To ensure you get the most out of your rhetorical questions, here are some dos and don’ts to follow when incorporating them into your writing.
- Do: Make sure the rhetorical question challenges your reader to think about the topic at hand.
- Don’t: Use rhetorical questions as a crutch instead of offering a well-thought out argument or point of view.
- Do: Write your rhetorical questions in a concise, direct manner.
- Don’t: Waffle with words and clutter your rhetorical questions with excessive modifiers.
- Do: Ask a question that can’t actually be answered, serving to engage the reader instead.
- Don’t: Set up a false dichotomy by asking a rhetorical question that simplifies a complex issue.
- Do: Understand that rhetorical questions can be both positive or negative in nature.
- Don’t: Assume your readers will always interpret your rhetorical questions in the way you intend.
- Do: Frame your rhetorical questions in a way that encourages reflection and thought.
- Don’t: Use rhetorical questions as a tool for manipulation or to push a certain agenda.
Overall, using rhetorical questions in your writing can be a very effective way to engage readers in thoughtful discussion. As long as you consider the intention of your questions, avoid logical fallacies, and keep them concise, your rhetorical questions should make a powerful impact on your audience.
Editing/Proofreading: The Importance of Checking for Unintended Meaning
When it comes to writing a rhetorical question, you must be careful that the words you use do not create an unintended meaning. As rhetorical questions are meant to evoke thought in the reader, it is important to make sure the meaning you intend is conveyed and that any ambiguity is removed in the editing and proofreading process.
Editing and proofreading are key processes to ensuring your rhetorical question conveys the precise message or sentiment that you want it to. A simple misread or misspelling can turn a powerful piece of writing into something completely misconstrued. It is important to review your work several times to ensure that your rhetorical question does not inadvertently provide a different message than what you had intended.
When editing and proofreading your rhetorical questions, pay attention to the wording you use. Make sure that each term is in its correct form and that all words are spelled correctly. Also watch out for any words or phrases that may have multiple meanings that could lead to confusion or misinterpretation. This is why it’s important to read through the question several times and get input from a colleague or second set of eyes for feedback.
In addition to checking for clarity, you should also make sure that your rhetorical question flows naturally and reads well. Pay close attention to the sentence structure and how the words are arranged. Are there any awkward pauses or lengthy phrases that might confuse your readers? You may want to consider restructuring some of your sentences to improve the flow and clarity of the rhetorical question.
Editing and proofreading your rhetorical questions is an important step in the writing process. By taking the time to ensure that your question conveys the message you want and reads clearly, you’ll be able to effectively communicate with your readers and create a powerful impact.
Applications of Rhetorical Questions
A rhetorical question can be an incredibly powerful tool in any type of written communication, beyond just essays. In fact, rhetorical questions can do even more to engage readers and draw attention to certain points that you are making.
Rhetorical questions can be used to emphasize a point, engage readers in some self-reflection, or to simply draw the reader’s attention to something of importance. As such, it is important to be aware of the potential applications and how to use them effectively.
One way to use a rhetorical question to your advantage is to emphasize a key point that you are trying to make. For example, if you are arguing for a particular stance on an issue, you could ask a rhetorical question to draw attention to that point and challenge your readers to think about it. Another effective way to use rhetorical questions is to get your readers to consider their own situation and values. This can help to engage them more with the discussion by asking them to reflect on the material they have read.
When incorporating rhetorical questions into non-essay writing, it is important to keep the following in mind:
- Be selective with the questions you ask – make sure that they are relevant to the topic at hand.
- Keep your questions succinct and avoid using too many words.
- Make sure your questions are clear and easy to understand.
- Maintain a consistent tone throughout your writing.
By following these guidelines, you can harness the power of a rhetorical question to effectively communicate your message and engage your readers. Using rhetorical questions in this way can help to bring your writing to life and create impactful and memorable content.
Writing an effective rhetorical question can be a powerful tool for essay writers. In this guide, we have explored what is a rhetorical question, what are its purposes, and how to write one that truly has an impact on the reader. We’ve discussed common structures, techniques, and guidelines to consider when constructing a rhetorical question.
To conclude, here are the key points to remember when incorporating rhetorical questions into your writing:
- A rhetorical question should always serve a purpose within the essay or written piece.
- Choose the right structure and format for the rhetorical question.
- Employ specific techniques to make the rhetorical question compelling.
- Proofread the question to ensure accuracy and clarity.
If you follow the tips outlined in this guide , you will be able to write a rhetorical question that makes an impact and convinces your readers. So go ahead, give it a try!
Frequently Asked Questions about How to Write a Rhetorical Question in an Essay
- Q: What is a rhetorical question? A: A rhetorical question is a form of question that doesn’t require, or expect, an answer. It is usually used to make a point, create emphasis or draw attention to a certain piece of information.
- Q: What makes a rhetorical question different than other kinds of questions? A: Unlike other types of questions such as closed and open-ended questions, a rhetorical question does not require, nor expect, an answer. It requires the person reading it to reflect, rather than provide an answer.
- Q: What are some examples of rhetorical questions? A: Examples of rhetorical questions include “”How can I be expected to solve this problem?”” or “”What do they expect us to do?””.
- Q: What is the purpose of a rhetorical question in an essay? A: A rhetorical question can be a powerful tool for an essay writer as it invites readers to think critically about the topic being discussed and reflect upon the implications of the argument presented by the essay writer.
- Q: What elements should be included when constructing a rhetorical question? A: When constructing a rhetorical question, ensure that the question contains enough detail to provide context and leave room for interpretation. Additionally, make sure you relate the rhetorical question to your intended outcome.
- Q: Are there different structures and formats to consider when writing a rhetorical question? A: Yes, there are different approaches to writing a rhetorical question, such as questions with ellipses or exclamation mark at the end. Generally, the structure of the sentence should guide you on how best to express the rhetorical question.
- Q: What writing techniques can help enhance the quality of the rhetorical question and contribute to the essay’s effectiveness? A: Using vivid language, concrete examples and references can help to enhance the quality of the rhetorical question and make the essay more effective.
- Q: What Dos and Dont’s should readers be aware of when using rhetorical questions in their essays? A: Do keep your audience in mind when crafting your rhetorical question, ensure the question is relevant to the topic being discussed and pay attention to how it is being used. Don’t forget to proofread to check for errors and ambiguous phrasing.
- Q: Are there any potential applications of rhetorical questions beyond essays? A: Yes, rhetorical questions can also be used in oral presentations, creative writing and even in marketing campaigns.
- Q: What resources are available to help readers further expand upon what they have learnt in the post? A: There are a variety of blog posts, academic articles and books that can help readers gain a deeper understanding of the power and potential of rhetorical questions.

Nick Radlinsky
Nick Radlinsky is a devoted educator, marketing specialist, and management expert with more than 15 years of experience in the education sector. After obtaining his business degree in 2016, Nick embarked on a quest to achieve his PhD, driven by his commitment to enhancing education for students worldwide. His vast experience, starting in 2008, has established him as a reputable authority in the field.
Nick's article, featured in Routledge's " Entrepreneurship in Central and Eastern Europe: Development through Internationalization ," highlights his sharp insights and unwavering dedication to advancing the educational landscape. Inspired by his personal motto, "Make education better," Nick's mission is to streamline students' lives and foster efficient learning. His inventive ideas and leadership have contributed to the transformation of numerous educational experiences, distinguishing him as a true innovator in his field.

Visual Arts IA Topics: The Best Topic Ideas
In the vast world of art, the possibilities for your IA topic are nearly limitless. Yet, this abundance of choice can sometimes feel overwhelming. Whether you’re drawn to traditional painting techniques, the avant-garde movements of the 20th century, or the intersection of digital media and art, your chosen topic should ignite a spark of curiosity and passion within you.

Theatre IA Topics: SL and HL Topic Ideas
Choosing the right topic for IA in the IB Theatre course is a crucial step that significantly influences your research process and overall learning experience. Whether in the Standard Level or Higher Level track, selecting your topic requires careful thought and consideration, aiming to balance personal interest with academic rigor. This guide offers a rich array of topic ideas and research questions to spark your creativity and intellectual curiosity in the vast world of theatre.

Music IA Topics for SL and HL Students
When selecting a topic for your IB Music Internal Assessment, both SL and HL students face a unique set of challenges and opportunities. As a seasoned IB educator with years of experience guiding students through this process, I’ve come to recognize the importance of choosing a topic that aligns with the IB criteria and resonates with your musical interests and strengths.

Film IA Topics: SL and HL Topic Ideas
Choosing a topic for your IB Film Internal Assessment (IA) can be exciting and daunting. Whether you’re enrolled in the Standard Level (SL) or Higher Level (HL), the key is to select an option that not only intrigues you but also meets the criteria of the IB Film course. In this article, we dig into a variety of creative and thought-provoking ideas for both SL and HL Film IA topics.

IB Dance IA Topics: SL and HL Ideas
When it comes to the IB Dance Internal Assessment (IA), students face the exciting challenge of exploring a topic that resonates with their interests and meets the academic rigor of the IB curriculum. I’ve seen how choosing the right topic can set the stage for an enriching learning experience. In this article, I’m thrilled to share some engaging topic ideas for both SL and HL students aimed at sparking creativity and intellectual curiosity.

Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches IA Topics
Writing the Internal Assessment (IA) for IB Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches is a crucial step for any IB student, combining challenge and opportunity in equal measure. This article highlights the diverse and intriguing IA topics available to Standard Level (SL) and Higher Level (HL) students, helping them to use their mathematical skills in creative and meaningful ways.
© 2023 I Bstudenthelp.com. This website is owned and operated by Udeepi OU Harju maakond, Tallinn, Lasnamäe linnaosa, Sepapaja tn 6, 15551. Disclaimer : Services we provide are only to assist the buyer like a guideline to complete any kind of writing assignment. Privacy Policy Terms and Conditions Cookie Policy Revision Policy Refund Policy
31 Useful Rhetorical Devices
What is a rhetorical device and why are they used.
As with all fields of serious and complicated human endeavor (that can be considered variously as an art, a science, a profession, or a hobby), there is a technical vocabulary associated with writing. Rhetoric is the name for the study of writing or speaking as a means of communication or persuasion, and though a writer doesn’t need to know the specific labels for certain writing techniques in order to use them effectively, it is sometimes helpful to have a handy taxonomy for the ways in which words and ideas are arranged. This can help to discuss and isolate ideas that might otherwise become abstract and confusing. As with the word rhetoric itself, many of these rhetorical devices come from Greek.

Ready, set, rhetoric.
The repetition of usually initial consonant sounds in two or more neighboring words or syllables
wild and woolly, threatening throngs
Syntactical inconsistency or incoherence within a sentence especially : a shift in an unfinished sentence from one syntactic construction to another
you really should have—well, what do you expect?
Repetition of a prominent and usually the last word in one phrase or clause at the beginning of the next
rely on his honor—honor such as his?
A literary technique that involves interruption of the chronological sequence of events by interjection of events or scenes of earlier occurrence : flashback
Repetition of a word or expression at the beginning of successive phrases, clauses, sentences, or verses especially for rhetorical or poetic effect
we cannot dedicate—we cannot consecrate—we cannot hallow—this ground
The repetition of a word within a phrase or sentence in which the second occurrence utilizes a different and sometimes contrary meaning from the first
we must all hang together or most assuredly we shall all hang separately
The usually ironic or humorous use of words in senses opposite to the generally accepted meanings
this giant of 3 feet 4 inches
The use of a proper name to designate a member of a class (such as a Solomon for a wise ruler) OR the use of an epithet or title in place of a proper name (such as the Bard for Shakespeare)
The raising of an issue by claiming not to mention it
we won't discuss his past crimes
An expression of real or pretended doubt or uncertainty especially for rhetorical effect
to be, or not to be: that is the question
Harshness in the sound of words or phrases
An inverted relationship between the syntactic elements of parallel phrases
working hard, or hardly working?
A disjunctive conclusion inferred from a single premise
gravitation may act without contact; therefore, either some force may act without contact or gravitation is not a force
The substitution of a disagreeable, offensive, or disparaging expression for an agreeable or inoffensive one
greasy spoon is a dysphemism for the word diner
Repetition of a word or expression at the end of successive phrases, clauses, sentences, or verses especially for rhetorical or poetic effect
of the people, by the people, for the people
Emphatic repetition [ this definition is taken from the 1934 edition of Webster's Unabridged dictionary ]
An interchange of two elements in a phrase or sentence from a more logical to a less logical relationship
you are lost to joy for joy is lost to you
A transposition or inversion of idiomatic word order
judge me by my size, do you?
Extravagant exaggeration
mile-high ice-cream cones
The putting or answering of an objection or argument against the speaker's contention [ this definition is taken from the 1934 edition of Webster's Unabridged dictionary ]
Understatement in which an affirmative is expressed by the negative of the contrary
not a bad singer
The presentation of a thing with underemphasis especially in order to achieve a greater effect : UNDERSTATEMENT
A figure of speech in which a word or phrase literally denoting one kind of object or idea is used in place of another to suggest a likeness or analogy between them ( Metaphor vs. Simile )
drowning in money
A figure of speech consisting of the use of the name of one thing for that of another of which it is an attribute or with which it is associated
crown as used in lands belonging to the crown
The naming of a thing or action by a vocal imitation of the sound associated with it
A combination of contradictory or incongruous words
cruel kindness
The use of more words than those necessary to denote mere sense : REDUNDANCY
I saw it with my own eyes
A figure of speech comparing two unlike things that is often introduced by "like" or "as"
cheeks like roses
The use of a word in the same grammatical relation to two adjacent words in the context with one literal and the other metaphorical in sense
she blew my nose and then she blew my mind
A figure of speech by which a part is put for the whole (such as fifty sail for fifty ships ), the whole for a part (such as society for high society ), the species for the genus (such as cutthroat for assassin ), the genus for the species (such as a creature for a man ), or the name of the material for the thing made (such as boards for stage )
The use of a word to modify or govern two or more words usually in such a manner that it applies to each in a different sense or makes sense with only one
opened the door and her heart to the homeless boy
MORE TO EXPLORE: Rhetorical Devices Used in Pop Songs
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Usage Notes
Prepositions, ending a sentence with, hypercorrections: are you making these 6 common mistakes, a comprehensive guide to forming compounds, can ‘criteria’ ever be singular, singular nonbinary ‘they’: is it ‘they are’ or ‘they is’, grammar & usage, 7 pairs of commonly confused words, did we change the definition of 'literally', more commonly mispronounced words, the tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, 10 bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), eavesdrop, fiasco, and 8 more words with surprising origins, 'when pigs fly' and other barnyard idioms, the words of the week - mar. 29, 9 superb owl words.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
American Jews, Liberalism and Zionism
More from our inbox:, m.i.t. and the gaza war, a pig provides hope for transplant patients, sexual brutality.

To the Editor:
Re “ American Jews in the Age of Palestine ,” by Peter Beinart (Opinion guest essay, March 24):
There is a fundamental flaw in the article. Zionism does not require backing the Israeli government; it does assume backing for the State of Israel.
The nation is and has been divided, and choosing to support the liberal elements of Israeli society, during a period when the ultra right controls the government, is not a rupture. It is a choice to support what many of us believe to be Jewish values, with the domination of the Palestinians being un-Jewish.
Yes, there is a rupture between Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and the Jewish diaspora, but that does not translate to a rupture with Israel, at least not yet.
Steven Goldberg Brooklyn
Peter Beinart claims that the Anti-Defamation League is aligning itself with “Republicans who want to silence ‘woke’ activists on campus.” That’s a distortion of our record. Since 1913, the ADL has hewed to a strictly nonpartisan strategy in calling out antisemitism — whether it emanates from the far left or the extreme right, or anywhere in between.
Moreover, Mr. Beinart’s assertion that we are stifling pro-Palestinian speech is ludicrous. Since Oct. 7, there have been at least 2,874 anti-Israel rallies across the U.S., many held on or near campuses. There’s no shortage of sit-ins, opinion essays, protests and other public manifestations on behalf of the Palestinian cause.
Students are entitled to their First Amendment right to protest, but when free speech devolves into intimidation and threats, we must call it out without hesitation. At stake are the safety and security of Jewish students.
Jonathan A. Greenblatt New York The writer is C.E.O. and national director of the Anti-Defamation League.
I am an American Jew who can be both liberal regarding American politics and Zionist in my support for Israel. There is no conflict in my position.
America and Israel are both democratic liberal states. Hamas is a radical, violent militant group that is a threat to Israel and hardly created a haven for the Palestinians who live under its rule.
I would support a liberal Palestinian state and hope it will one day emerge to receive the loyalty and support of Palestinians wherever they now live. But liberal states need to be formed by a people united by a willingness to abide by a rule of law.
A Jewish state has been so formed in Israel, and is now defending its sovereignty against brutal attacks by terrorists, while we in the U.S. contend with forces of chaos in our political system that threaten our rights and liberties.
I want to defend liberalism in my country and Zionism for those Israelis who are defending their country.
Doris Fine Berkeley, Calif.
Peter Beinart’s essay reminds us all of an essential point: Israel-Palestine will remain the home of millions and millions of Jews and Palestinians. Any proposed solution must grapple with that central fact.
Jeremy Pressman West Hartford, Conn. The writer is a professor of political science and the director of Middle East studies at the University of Connecticut. He is the author of “The Sword Is Not Enough: Arabs, Israelis and the Limits of Military Force.”
It’s on behalf of 30 M.I.T. faculty members from various disciplines that we write to address recent events at M.I.T. concerning the war in Gaza.
Antisemitism is rising nationally and on our campus, necessitating urgent education about its origins and practices. But accusations of antisemitism are used to suppress free speech, particularly in support of Palestinian rights.
M.I.T. students advocating Palestinian liberation face doxxing, threats and false labeling as “pro-Hamas.” Criticism of Israel’s government is wrongly equated with antisemitism, suppressing speech for Palestinian rights.
Biased media coverage has isolated and created fear among Jewish students who support a cease-fire. This fear extends to Arab, Muslim and Palestinian communities.
As an academic institution, M.I.T. must prioritize difficult conversations, reflection and learning over suppression and intimidation. We must foster an inclusive environment that promotes dialogue and understanding.
We must address rising antisemitism and the suppression of free speech without perpetuating fear. M.I.T. should strive for a respectful environment that encourages open dialogue and supports the rights, humanity and dignity of all communities. No Palestinian exception.
Michel DeGraff Tanalís Padilla The writers are professors at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Re “ Patient Mends After Receiving a Pig’s Kidney ” (front page, March 22):
As one who spent much of my career as a spokesperson for an internationally renowned organ transplant center, I read the news of the pig kidney transplant with great interest.
Back in the mid-1980s and into the ’90s, I worked with many patients’ families desperate to both raise the money necessary to pay for then often-uninsured transplants and generate enough awareness to obtain horrendously scarce donor organs. I can’t tell you how many families cracked under the pressure.
Words from pioneering surgeons and other scientists about the future possibility of using animal organs (even then, usually pigs) were of small comfort to people needing help then. And not 30 years hence.
But maybe, just maybe, this news out of Boston about a transplant from a genetically modified pig may be what so many have been waiting for all these years. For the sake of those eager to do nearly anything to save their child, spouse or parent, I hope the genuine worries about such procedures prove to be minimal.
If you’ve ever seen a parent lose a child because an organ wasn’t available, you’d share this hope too.
Mary Stanik Tucson, Ariz.
Re “ Looking Away From an Epidemic of Rape ,” by Maebel Gebremedhin (Opinion guest essay, March 22):
As a Marine Corps and an O.S.S. officer combating the Nazi occupation of Yugoslavia, my father, the actor and writer Sterling Hayden, witnessed many of the most gruesome realities of war. But there was one event that I believe scarred his psyche more profoundly than any other.
One evening, along with a group of Josip Broz Tito’s Partisan fighters, he entered a small village that had been razed by the Ustashe, the fascist Croatian militia allied with the Germans. Years later he would describe what they found:
“Not a house stands, nothing but burned stone shells of chimneys gaunt under scorched trees and over all the terrible stench of fried flesh and bone mingled with burned wood. And by the bank of the Sava the nine girls all in a row upside down they are hung by their ankles to split rails with legs far apart and breasts sliced off and the helves of axes and the handles of rakes rammed to the bloody hilt through areas where life might otherwise have been conceived.”
Grotesque sexual sadism has been present in wars throughout recorded history. That this demonic behavior erupts so often is one of the darkest indictments of the human imagination.
David Hayden Wilton, Conn.
Should you stop writing checks? Banks wish you would to thwart fraud

A big banking industry group, not surprisingly perhaps, suggests that consumers stop writing paper checks to stamp out the proliferation of check washing scams. Stop writing checks?
It's seriously one of the suggestions now that check fraud has exploded by 385% since the pandemic, according to U.S. Treasury Department data. Banks are forced to spend more to beef up their technology to prevent criminal check fraud, and, even then, plenty of fake checks continue to get cashed.
It's a massive headache for bankers, the U.S. Postal Service, and consumers who become victims of crooks and loopholes in a regulatory system that can work against them.
The stolen check can be washed clean of the original ink with household chemicals. Criminals may replace the "payee" and often the dollar amount to fuel the fraud. And fraudsters can copy and print multiple washed checks for future use or to sell to other criminals.
The $150 check you wrote could end up being written by crooks for several hundred dollars or more. If the fraud isn't spotted, the money ends up with the criminals. But your bill won't get paid. Your signature remains in place so it looks like you wrote the check.
Worse yet, you're going to have to undergo an investigation with the bank to get your money back. Consumers report waiting months or even years to get thousands of dollars back. Some do not get any money back.
We never had to go to such lengths to analyze if we should or shouldn't write a check. But high-profile cases — such as a crackdown on a massive mail fraud ring that targeted high-end neighborhoods in Oakland County to steal checks, credit cards and personal information from mailboxes from late 2018 through at least March 2019 — make it clear that check writing cannot be treated casually.
During tax season, many people will be writing checks to pay their income taxes. Yet, should you really do that? Might be better to pay taxes through an electronic funds withdrawal and have money taken out your bank account.
Consumer protections aren't strong
A Los Angeles consumer had written a $21,000 check to pay his federal taxes in 2021, sent the check by mail, and later discovered that the check was stolen, signed by someone else and deposited into a different account at another bank, not the U.S. Treasury, according to a KCAL-TV news report last April.
But the consumer's bank would not credit his account until the bank that accepted the fake check reimbursed the victim's bank. It took two years for the consumer to get several thousand dollars back.
Checks are largely governed by state law through the Uniform Commercial Code, which gives consumers up to a year to inform their bank of a fraudulent or altered check.
But — and pay attention here — banks can and do shorten the time for notification as part of their account agreements, according to Carla Sanchez-Adams, a senior attorney at the National Consumer Law Center.
Many banks, she said, limit the time to somewhere between 14 days and 30 days. Check your account agreement.
"It's incredibly difficult," Sanchez-Adams said.
More: It’s hard to reverse scams on peer-to-peer payment apps like Venmo, PayPal, Zelle
Sometimes, it's hard to spot the fraud. Criminals do not always change the amount on the check. You might see that an $800 check was cashed to cover your rent and not realize that someone else cashed that check.
In testimony before the Senate Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs Committee in February, Sanchez-Adams said one consumer told the National Consumer Law Center that "he had no idea his check had been altered until his landlord — a family friend — eventually told him months later that he had not received the rent."
Many consumers have not received paper copies of their checks for years. And more changes are ahead for many.
Bank of America, for example, told customers that starting May 17, its statements sent in the mail will no longer include images of canceled checks. Such images can be viewed online, and copies are available by request for free.
Sanchez-Adams said she personally doesn't use checks, unless she's able to hand them to someone, given the efforts by criminal activity. She treats a check like cash. "Would you send cash in the mail?" she asks.
How check fraud works today
When it comes to check fraud, criminals often fish out mail from blue U.S. postal boxes, rob carriers at gunpoint, and even try to bribe postal workers to get their hands on master keys that can be sold on the dark web for thousands of dollars and later used to open collection boxes.
Sure, crooks will steal cash or gift cards that people send in the mail, too. But they can steal even more money by getting their hands on paper checks.
Some stolen checks end up being sold online to other crooks. Many times, people can be recruited by criminals to cash the phony checks for them, often using fake IDs, or encouraged to open accounts that can be used to cash altered checks.
Criminals also aim to steal "personal checks, business checks, tax refund checks, and checks related to government assistance programs, such as Social Security payments and unemployment benefits," according to a 2023 alert by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network.
The alert noted: "Business checks may be more valuable because business accounts are often well-funded and it may take longer for the victim to notice the fraud."
Consumers reported losing $209 million in 2023 to fraud involving checks, which is close to the $210 million reported lost to fraud involving payment apps, according to data from the latest Consumer Sentinel Network Data Book. The network is managed by the Federal Trade Commission but compiles consumer complaints from a variety of sources. Only 8,603 complaints involving check fraud were made to the various agencies. By contrast, 63,305 complaints were made involving payment apps.
But the losses are far deeper than those reports. The Treasury Department announced in February that it had recovered more than $375 million after implementing enhanced fraud detection using artificial intelligence at the beginning of fiscal year 2023.
More: Phony postage stamp discounts are scamming online buyers: What to know
Who writes checks anymore?
Many people already are paying their bills online, using direct pay, or using mobile apps, not writing checks. Even so, nearly 13 million checks are still being written each day, according to banking industry data.
"There's no way to stop check fraud without stopping checks at some point," said Paul Benda, executive vice president of risk, fraud and cybersecurity at the American Bankers Association at a banking industry conference in Washington, D.C., on March 20.
He called check fraud "a pain point for the industry."
In March, the American Bankers Association and the U.S. Postal Inspection Service joined forces in an educational campaign to combat the "rapid rise in check fraud."
Pandemic 'turbocharged' financial crimes
But why now? Check fraud isn't new. Street gangs ramped up some white collar crimes, such as check fraud and credit card fraud, more than 25 years ago, thanks to home computers and other technology. So why the dramatic uptick since the pandemic?
"If you look in general, it seems like the pandemic really turbocharged fraud," Benda told me in a phone interview. "We can't necessarily say why."
He pointed to the success that crooks had making fraudulent claims for generous unemployment insurance benefits during the pandemic. The U.S. Government Accountability Office estimated that fraud accounted for anywhere from 11% to 15% of the total amount of unemployment insurance benefits paid nationwide during the pandemic. The dollars lost, according to the GAO report issued in September 2023, were likely "between $100 billion and $135 billion."
"I think there were a lot of first-time fraudsters," Benda said, "that were able to file a claim and didn't get caught."
It seems like, he said, criminal gangs have "industrialized fraud."
Checks, he said, aren't a form of payment that banks really like, Benda said. "Electronic payments are faster and more secure."
How do you protect yourself from check washing scams
Many banks, Benda said, are encouraging customers to stop using checks and move more toward electronic payments. Banks have hired more staff, he said, to review checks on the same day they come in to look for altered checks. Tellers are trained to look for phony checks and fake IDs. But it's a constant battle and costly proposition.
If you're still using checks, you're encouraged to do such things as use a gel pen or pens with indelible black ink so it is more difficult for a criminal to wash your checks. Other tips include:
- Don't mail a bill with a check from a mailbox. If possible, instead go inside the post office to drop off a bill. Never leave mail in your own mailbox overnight.
- Call to make sure the check was received by a business, charity or family member. Contact the bank immediately if you spot a problem.
- Pay attention to who cashes the check. Some scammers don't change the amount on the check but will change the payee.
- Don’t write your Social Security number, credit card information, driver’s license number or phone number on checks.
- Report stolen mail as soon as possible by submitting an online complaint to the Postal Inspection Service at www.uspis.gov/report or calling 877-876-2455.
- Consumers are asked to report crimes or call 911 when they suspect that someone might be trying to rob a mail carrier.
How Postal Service is cracking down on crimes
In May 2023, the U.S. Postal Service and the U.S. Postal Inspection Service launched the Project Safe Deliver y campaign to reduce mail theft and better protect postal employees.
The U.S. Postal Inspection Service now is offering rewards of up to $150,000 now, up from $50,000 in the past, for information leading to the identification, arrest, and prosecution of those rob letter carriers.
Individuals who are convicted of mail theft can face up to five years in prison, possession of postal keys up to 10 years in prison and those who rob letter carriers can face up to 25 years in prison, according to the U.S. Postal Inspection Service.
In the Oakland County mail theft and identity theft case, four men were sentenced — Deavon Allen, Cole Patrick Castelow, Malik Frazier and Ronald Reese — by U.S. District Judge Terrence Berg in U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan in 2023 and 2024. Sentences were: Castelow, 72 months in prison; Frazier, 51 months; Allen, 27 months, and Reese, 18 months. Restitution was ordered, joint and several with the co-defendants in the case, in the total amount of $141,419.21.
Michael Martel, postal inspector and public information officer for the U.S. Postal Inspection Service, said much is being done to frustrate criminals by making it harder for them to gain access to the mail in traditional mailboxes.
So far, the Postal Service has replaced more than 15,000 blue boxes in key areas with a new high-security blue collection box. The outside is similar but the inside has enhanced security features. The post office also has already replaced 28,000 antiquated arrow locks with electronic mechanisms that can better ensure the safety of the mail after a robbery. The key alone, Martel said, won't give someone access to the mail in these cases.
Martel said criminal groups "are increasingly organized. We're seeing multiple robberies committed by the same parties."
More: Fraud and scams cost consumers a record $10 billion in 2023, according to FTC
Martel said the goal of the Postal Service is to make the mail stream safe, not necessarily discouraging consumers from using checks. "We always advise customers to never send cash," he said.
Contact personal finance columnist Susan Tompor: [email protected] . Follow her on X (Twitter) @ tompor .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If your rhetorical question isn't as good as you think it is, your marks are going to drop - big time. 5. Teachers Hate Rhetorical Questions in Essays. This one supplants all other reasons. The fact is that there are enough teachers out there who hate rhetorical questions in essays that using them is a very risky move.
Revised on July 23, 2023. A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting ...
Rhetorical Question Examples in Political Speeches. Rhetorical questions often "challenge" the listener to contradict what the speaker is saying. If the speaker frames the rhetorical question well, it gives the impression that his or her view is true and that it would be foolish, or even impossible, to contradict the speaker's argument.
A rhetorical question is asked just for effect, or to lay emphasis on some point being discussed when no real answer is expected. A rhetorical question may have an obvious answer, but the questioner asks it to lay emphasis on the point. In literature, a rhetorical question is self-evident and used for style as an impressive persuasive device.
Name the author of the text and the title of their work followed by the date in parentheses. Use a verb to describe what the author does, e.g. "implies," "asserts," or "claims". Briefly summarize the text in your own words. Mention the persuasive techniques used by the rhetor and its effect.
An "aporia" is a rhetorical expression of doubt, usually when the author doesn't actually feel the doubt. An aporia is often expressed in question form, and in these cases it's an example of a rhetorical question. It's often used in philosophy and other argument-heavy fields when the author wants to move the conversation forward.
Epiplexis. Epiplexis is a type of rhetorical question that is used to rebuke or reprimand the audience. It challenges and engages the audience in a pointed and sometimes confrontational manner. This type of rhetorical device is meant to persuade (or shame) the audience into accepting the speaker's perspective. I can't believe you skipped class.
Learn to Use Rhetorical Questions. If overused, too many rhetorical questions might make you come off as too sarcastic or even arrogant. But when used skillfully and in combination with other rhetorical devices, such as ethos, pathos, and logos, rhetorical questions can enhance your speech and writing by emphasizing key points.
How to Use a Rhetorical Question. Rhetorical questions are rhetorical devices often used in writing and speech to engage the audience, emphasize a point, or provoke thought. They can be used to introduce a topic, make a statement, or open an argument. Conversational Rhetorical Questions. Rhetorical questions are used in everyday speech and ...
A rhetorical question is a question asked merely for effect with no answer expected. Learn more about these questions and how to spot them. ... Essays in Honor of Dolf Zillmann, ed. by Jennings Bryant et al. Lawrence Erlbaum, 2003) Punctuating Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are commonly used in persuasive speeches, essays, debates, and everyday communication to achieve various objectives. Here are a few key purposes: Emphasis - Rhetorical questions can draw attention to a specific idea or argument by framing it as a question.
4. Enhancing engagement: Rhetorical questions engage the audience as active participants in the communication process. This is especially valuable in education, encouraging critical thinking and participation. In sum, rhetorical questions are essential for holding the audience's attention.
Rhetorical appeal #2: Pathos. The purpose of Pathos-driven rhetoric is to appeal to the reader's emotions. A common example of pathos as a rhetorical means is adverts by charities that try to make you donate money to a "good cause". To evoke the intended emotions in the reader, an author may use passionate language, tell personal stories ...
Rhetorical Questions in Essays. "Mr. Smith says that I shouldn't use thought-provoking questions in my thesis statements," said Issa. "May I read you my thesis?". "Sure. Let's hear it," responds Mandy. "My thesis is 'Do people really want to be successful and happy?'". "Well, it is called a thesis statement, not a ...
Rhetorical questions cannot be used in every piece of writing. Using rhetorical questions in the thesis statement : Asking a rhetorical question in your thesis statement is an absolute no-no because thesis statements are meant to answer a question, not pose another question.
Rhetorical questions, on the other hand, are distinguished by their function. They can invite agreement, stir up emotion, or increase audience engagement. They also contribute to rhythm. Writers and speakers create rhythm in part by varying sentence lengths and types: adding questions is one way to achieve that. ... For more writing and ...
Rhetorical Question Examples in Speeches and Essays. Politicians and important speakers use rhetorical questions all the time, that's because a rhetorical question asks the audience to think about something important, often to take action or vote in a certain way. Here are some examples.
Rhetorical questions are questions asked to make a point rather than to get an answer. They are often used in creative writing to create a dramatic effect or a sense of suspense. When and how to use rhetorical questions in essays. Professors hate rhetorical questions in essays. You should only use them sparingly and when necessary.
Definition: Rhetorical questions. The word rhetorical has its origin in the Greek language as "rhetorikos," meaning "skilled in speaking.". It is a figure of speech in the form of a question posed for stylistic and dramatic effect rather than to elicit an answer. Unlike regular questions, which seek information or clarification ...
Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected].
Use assertive language: When writing a rhetorical question, strive to use language that is assertive and authoritative, so that your reader will take the question seriously and take pause to consider its implications. Choose the right tone: The tone of your rhetorical question will also be important. Consider the context of the essay and how ...
An expression of real or pretended doubt or uncertainty especially for rhetorical effect. to be, or not to be: that is the question. cacophony | see definition ». Harshness in the sound of words or phrases. chiasmus | see definition ». An inverted relationship between the syntactic elements of parallel phrases.
The writing you submit should be fundamentally your own — it should not be plagiarized, created by someone else or generated by artificial intelligence. Your open letter should be original for ...
Ms. Rodden is a professional climber and the author of the forthcoming memoir, "A Light Through the Cracks." I don't know what time it was when my husband at the time, the rock climber Tommy ...
Responses to a guest essay by Peter Beinart. Also: M.I.T. and the Gaza war; organ transplants; sexual brutality.
Many people already are paying their bills online, using direct pay, or using mobile apps, not writing checks. Even so, nearly 13 million checks are still being written each day, ...