Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix

Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It’s a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.
Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing . You must emphasize how each source contributes to current debates, highlighting points of (dis)agreement and putting the sources in conversation with each other.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field or throughout your research paper when you want to position your work in relation to existing research.
Table of contents
Example of synthesizing sources, how to synthesize sources, synthesis matrix, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about synthesizing sources.
Let’s take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it.
This paragraph provides no context for the information and does not explain the relationships between the sources described. It also doesn’t analyze the sources or consider gaps in existing research.
Research on the barriers to second language acquisition has primarily focused on age-related difficulties. Building on Lenneberg’s (1967) theory of a critical period of language acquisition, Johnson and Newport (1988) tested Lenneberg’s idea in the context of second language acquisition. Their research seemed to confirm that young learners acquire a second language more easily than older learners. Recent research has considered other potential barriers to language acquisition. Schepens, van Hout, and van der Slik (2022) have revealed that the difficulties of learning a second language at an older age are compounded by dissimilarity between a learner’s first language and the language they aim to acquire. Further research needs to be carried out to determine whether the difficulty faced by adult monoglot speakers is also faced by adults who acquired a second language during the “critical period.”
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To synthesize sources, group them around a specific theme or point of contention.
As you read sources, ask:
- What questions or ideas recur? Do the sources focus on the same points, or do they look at the issue from different angles?
- How does each source relate to others? Does it confirm or challenge the findings of past research?
- Where do the sources agree or disagree?
Once you have a clear idea of how each source positions itself, put them in conversation with each other. Analyze and interpret their points of agreement and disagreement. This displays the relationships among sources and creates a sense of coherence.
Consider both implicit and explicit (dis)agreements. Whether one source specifically refutes another or just happens to come to different conclusions without specifically engaging with it, you can mention it in your synthesis either way.
Synthesize your sources using:
- Topic sentences to introduce the relationship between the sources
- Signal phrases to attribute ideas to their authors
- Transition words and phrases to link together different ideas
To more easily determine the similarities and dissimilarities among your sources, you can create a visual representation of their main ideas with a synthesis matrix . This is a tool that you can use when researching and writing your paper, not a part of the final text.
In a synthesis matrix, each column represents one source, and each row represents a common theme or idea among the sources. In the relevant rows, fill in a short summary of how the source treats each theme or topic.
This helps you to clearly see the commonalities or points of divergence among your sources. You can then synthesize these sources in your work by explaining their relationship.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Synthesizing sources means comparing and contrasting the work of other scholars to provide new insights.
It involves analyzing and interpreting the points of agreement and disagreement among sources.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field of research or throughout your paper when you want to contribute something new to existing research.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/synthesizing-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, signal phrases | definition, explanation & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
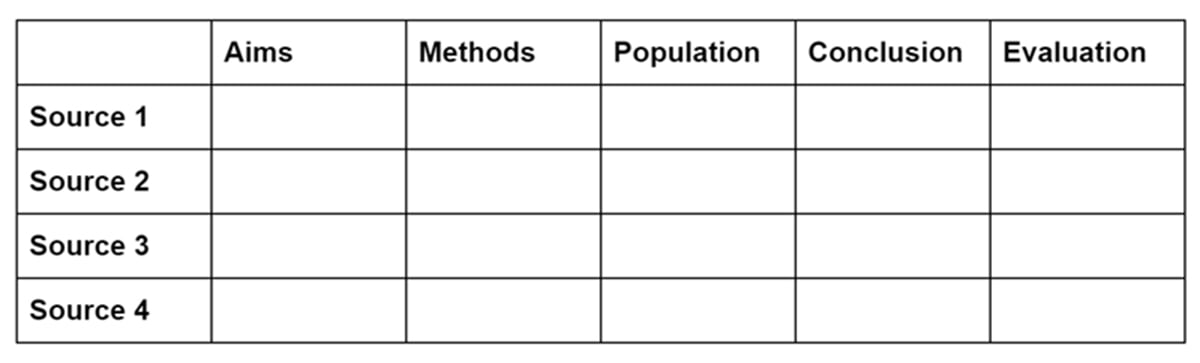
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
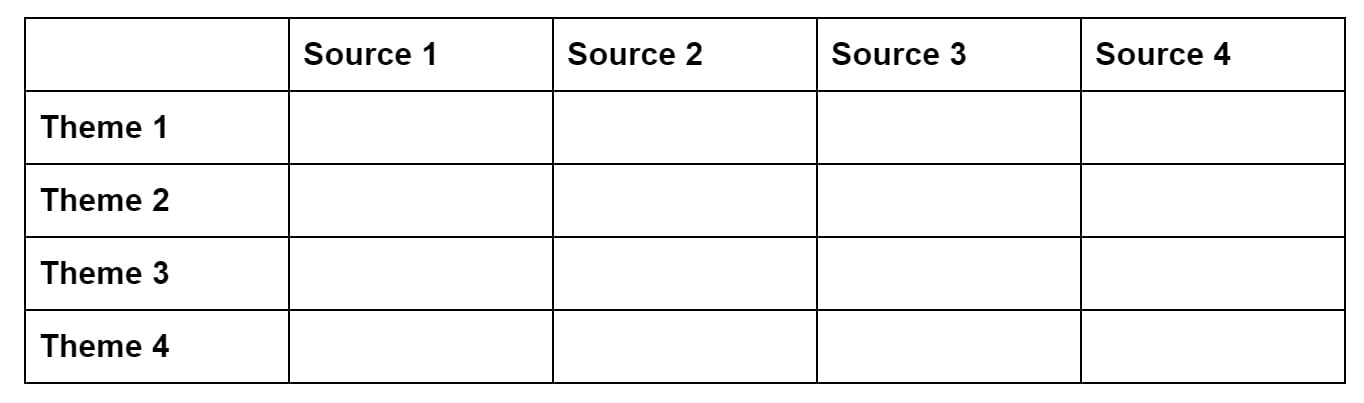
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
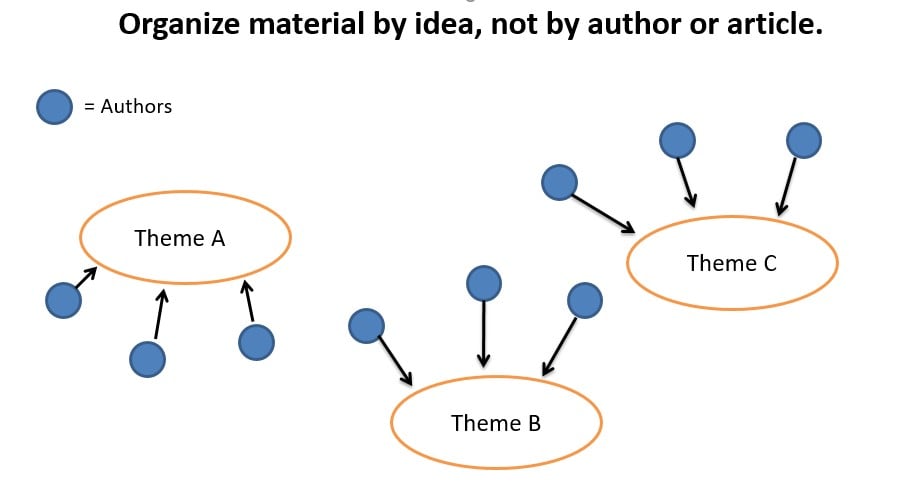
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Synthesizing Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you look for areas where your sources agree or disagree and try to draw broader conclusions about your topic based on what your sources say, you are engaging in synthesis. Writing a research paper usually requires synthesizing the available sources in order to provide new insight or a different perspective into your particular topic (as opposed to simply restating what each individual source says about your research topic).
Note that synthesizing is not the same as summarizing.
- A summary restates the information in one or more sources without providing new insight or reaching new conclusions.
- A synthesis draws on multiple sources to reach a broader conclusion.
There are two types of syntheses: explanatory syntheses and argumentative syntheses . Explanatory syntheses seek to bring sources together to explain a perspective and the reasoning behind it. Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions.
In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the pros and cons of encouraging healthy eating in children, you would want to separate your sources to find which ones agree with each other and which ones disagree.
After you have a good idea of what your sources are saying, you want to construct your body paragraphs in a way that acknowledges different sources and highlights where you can draw new conclusions.
As you continue synthesizing, here are a few points to remember:
- Don’t force a relationship between sources if there isn’t one. Not all of your sources have to complement one another.
- Do your best to highlight the relationships between sources in very clear ways.
- Don’t ignore any outliers in your research. It’s important to take note of every perspective (even those that disagree with your broader conclusions).
Example Syntheses
Below are two examples of synthesis: one where synthesis is NOT utilized well, and one where it is.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for KidsHealth , encourages parents to be role models for their children by not dieting or vocalizing concerns about their body image. The first popular diet began in 1863. William Banting named it the “Banting” diet after himself, and it consisted of eating fruits, vegetables, meat, and dry wine. Despite the fact that dieting has been around for over a hundred and fifty years, parents should not diet because it hinders children’s understanding of healthy eating.
In this sample paragraph, the paragraph begins with one idea then drastically shifts to another. Rather than comparing the sources, the author simply describes their content. This leads the paragraph to veer in an different direction at the end, and it prevents the paragraph from expressing any strong arguments or conclusions.
An example of a stronger synthesis can be found below.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Different scientists and educators have different strategies for promoting a well-rounded diet while still encouraging body positivity in children. David R. Just and Joseph Price suggest in their article “Using Incentives to Encourage Healthy Eating in Children” that children are more likely to eat fruits and vegetables if they are given a reward (855-856). Similarly, Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for Kids Health , encourages parents to be role models for their children. She states that “parents who are always dieting or complaining about their bodies may foster these same negative feelings in their kids. Try to keep a positive approach about food” (Ben-Joseph). Martha J. Nepper and Weiwen Chai support Ben-Joseph’s suggestions in their article “Parents’ Barriers and Strategies to Promote Healthy Eating among School-age Children.” Nepper and Chai note, “Parents felt that patience, consistency, educating themselves on proper nutrition, and having more healthy foods available in the home were important strategies when developing healthy eating habits for their children.” By following some of these ideas, parents can help their children develop healthy eating habits while still maintaining body positivity.
In this example, the author puts different sources in conversation with one another. Rather than simply describing the content of the sources in order, the author uses transitions (like "similarly") and makes the relationship between the sources evident.
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

Synthesizing Research

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
When combining another author’s ideas with your own, we have talked about how using the can help make sure your points are being adequately argued (if you have not read our handout on the evidence cycle, check it out!). Synthesis takes assertions (statements that describe your claim), evidence (facts and proof from outside sources), and commentary (your connections to why the evidence supports your claim), and blends these processes together to make a cohesive paragraph.
In other words, synthesis encompasses several aspects:
- It is the process of integrating support from more than one source for one idea/argument while also identifying how sources are related to each other and to your main idea.
- It is an acknowledgment of how the source material from several sources address the same question/research topic.
- It is the identification of how important factors (assumptions, interpretations of results, theories, hypothesis, speculations, etc.) relate between separate sources.
TIP: It’s a fruit smoothie!
Think of synthesis as a fruit smoothie that you are creating in your paper. You will have unique parts and flavors in your writing that you will need to blend together to make one tasty, unified drink!
Why Synthesis is Important
- Synthesis integrates information from multiple sources, which shows that you have done the necessary research to engage with a topic more fully.
- Research involves incorporating many sources to understand and/or answer a research question, and discovering these connections between the sources helps you better analyze and understand the conversations surrounding your topic.
- Successful synthesis creates links between your ideas helping your paper “flow” and connect better.
- Synthesis prevents your papers from looking like a list of copied and pasted sources from various authors.
- Synthesis is a higher order process in writing—this is the area where you as a writer get to shine and show your audience your reasoning.
Types of Synthesis
Demonstrates how two or more sources agree with one another.
The collaborative nature of writing tutorials has been discussed by scholars like Andrea Lunsford (1991) and Stephen North (1984). In these essays, they explore the usefulness and the complexities of collaboration between tutors and students in writing center contexts.
Demonstrates how two or more sources support a main point in different ways.
While some scholars like Berlin (1987) have primarily placed their focus on the histories of large, famous universities, other scholars like Yahner and Murdick (1991) have found value in connecting their local histories to contrast or highlight trends found in bigger-name universities.

Accumulation
Demonstrates how one source builds on the idea of another.
Although North’s (1984) essay is fundamental to many writing centers today, Lunsford (1991) takes his ideas a step further by identifying different writing center models and also expanding North’s ideas on how writing centers can help students become better writers.
Demonstrates how one source discusses the effects of another source’s ideas.
While Healy (2001) notes the concerns of having primarily email appointments in writing centers, he also notes that constraints like funding, resources, and time affect how online resources are formed. For writing centers, email is the most economical and practical option for those wanting to offer online services but cannot dedicate the time or money to other online tutoring methods. As a result, in Neaderheiser and Wolfe’s (2009) reveals that of all the online options available in higher education, over 91% of institutions utilize online tutoring through email, meaning these constraints significantly affect the types of services writing centers offer.
Discussing Specific Source Ideas/Arguments
To debate with clarity and precision, you may need to incorporate a quote into your statement. Using can help you to thoroughly introduce your quotes so that they fit in to your paragraph and your argument. Remember that you need to use the to bridge between your ideas and outside source material.
Berlin, J. (1987). Rhetoric and reality: Writing instruction in American colleges, 1900-1985 . Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press.
Boquet, E.H. (2001). “Our little secret”: A history of writing centers, pre- to open admissions. In R.W. Barnett & J.S. Blumner (Eds.), The Allyn and Bacon guide to writing center theory and practice (pp. 42-60). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Carino, P. (1995). Early writing centers: Toward a history. The Writing Center Journal , 15 (2), 103-15.
Healy, D. (2001). From place to space: Perceptual and administrative issues in the online writing center. In R.W. Barnett & J.S. Blumner (Eds.), T he Allyn and Bacon guide to writing center theory and practice (pp. 541-554). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Lunsford, A. (1991). Collaboration, control, and the idea of the writing center. The Writing Center Journal , 12 (1), 310-75.
Neaderheiser, S. & Wolfe, J. (2009). Between technological endorsement and resistance: The state of online writing centers. The Writing Center Journal . 29 (1), 49-75.
North, S. (1984). The idea of a writing center. College English , 45 (5), 433-446.
Yahner, W. & Murdick, W. (1991). The evolution of a writing center: 1972-1990. Writing Center Journal , 11 (2), 13-28.
- USU Library
Synthesis: Home
Engaging in synthesis.
Synthesis requires you to make sense of all the relevant ideas in your sources and blend them together with your own thoughts and ideas. Watch this video to learn how to engage in synthesis in order to take research from multiple sources along with your own arguments and turn it into a research paper.
Synthesizing Your Research
Understanding your research.
1. Read through your sources carefully.
2. Identify common themes or sub-topics that keep appearing in the articles you’re reading.

The Research Matrix
- Blank Research Matrix Fill out this blank matrix.
- Blank Synthesis Matrix template (Google Docs)
The research matrix is a helpful tool you can use to synthesize your research along with your own voice. The blank research matrix above can help you organize your paper by main idea, identify connections between your sources, and add your own analysis.

Filling Out Your Matrix
1. Write your topic or research question above the matrix.

2. Write your main ideas for your paper on the left side of the matrix. Helpful Tip: Choose your main ideas AFTER you have read your sources!

3. Write the title, author, or citation of each source in the top row of the matrix.

4. Fill in the matrix boxes with a paraphrase or direct quote that represents how the source discussed that main idea. You do not need every source to address every main idea!

5. Don't forget to nclude your own analysis of the main idea and the sources in the last column on the matrix.

Identify Gaps in Your Research
1. There’s a high likelihood that you will have empty spaces on your research matrix and that’s okay! Small gaps show that there is room for your own voice to join the conversation.

2. Large gaps in your matrix are often a sign that you need to do more research on that main idea. As a rule of thumb you should have at least two sources for each main idea in order to create a meaningful dialogue.

- Last Updated: Mar 13, 2023 1:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usu.edu/synthesizing_info

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Your Guide From Start to Finish

Today, we're swamped with information, like reading 174 newspapers every day. It comes from all over—news, social media, science, and more. This flood might make you feel overwhelmed and lost in a sea of facts and opinions. But being able to make sense of it all is crucial.
This guide isn't just about handling all that info; it's about using it to write awesome essays. We'll show you step by step how to pick a topic and organize your essay. Let's dive in and learn how to turn scattered facts into powerful essays that really stand out.
What Is a Synthesis Essay
The synthesis essay is a powerful tool in writing. It's not just about gathering facts but about connecting them to make a clear and strong argument.
Writing a synthesis essay allows you to dive deep into ideas. You have to find similarities between different sources—like articles, studies, or arguments—and use them to tell a convincing story.
In today's world, where we're bombarded with information, synthesis essays are more important than ever. They let us explore how different ideas fit together and help us express our thoughts on complex topics. Whether you're writing about literature, science, history, or current events, a synthesis essay shows off your ability to analyze and understand a topic from all angles. And if you're struggling with this task, just ask us to ' write paper for me ,' and we'll handle your assignment for you.
Explanatory vs. Argumentative Synthesis Essays
In synthesis writing, there are two main types: explanatory and argumentative. Understanding these categories is key because they shape how you approach your essay.
Explanatory:
An explanatory synthesis essay does just what it says—it explains. These essays aim to give a balanced view of a topic by gathering information from different sources and presenting it clearly. They don't try to persuade; instead, they focus on providing information and making things easier to understand. They're like comprehensive summaries, breaking down complex ideas for a broader audience. These essays rely heavily on facts and expert opinions, avoiding personal bias.
Argumentative:
On the flip side, argumentative synthesis essays are all about persuasion. Their main goal is to take a stance on an issue and convince the reader. They gather information from various sources not only to present different views but also to build a strong argument. Argumentative essays aim to sway the reader's opinion by using gathered information as evidence. These essays express opinions and use rhetorical strategies to persuade.
And if you're keen on knowing how to write an informative essay , we've got you covered on that, too!
Synthesis Essay Structure
To craft a strong synthesis essay, you need a solid foundation. Here's a structured approach to help you nail it:
Introductory Paragraph:
- To kick things off, grab your reader's attention with a catchy hook or interesting fact. Give a bit of background info about your topic and the sources you'll be using, as it can help readers understand your topic better! Then, lay out your main argument in a clear thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs:
- Each paragraph should focus on a different aspect of your topic or source. Start with a topic sentence that links back to your thesis. Introduce the source you're discussing and highlight its main points. Also, using quotes, paraphrases, or summaries from your sources can make your arguments stronger.
Synthesis :
- This part is where your essay comes together. Look for common themes or differences among your sources. Use your analysis to build a strong argument. Don't forget to address any opposing viewpoints if they're relevant!
Conclusion :
- Wrap things up by restating your thesis and summarizing your main points. Explain why your argument is important and what it means in the bigger picture. End with a thought-provoking statement to leave a lasting impression.
References :
- Finally, don't forget to list all your sources properly using the right citation style, like MLA or APA. Do you know that different citation styles have different rules? So, make sure you follow the right one!
Choosing a Synthesis Essay Topic
Picking essay topics is just the beginning. To write a great synthesis essay, you need to carefully evaluate and connect different sources to build a strong argument or viewpoint. Here's a step-by-step infographic guide to help you choose the right synthesis essay topics wisely.

How to Write a Synthesis Essay with Easy Steps
Writing a synthesis essay is similar to a compare and contrast essay . It requires a methodical approach to blend information from different sources into a strong and persuasive argument. Here are some crucial steps and tips to help you along the way.
- Clarify Your Purpose: First, decide if you're writing an explanatory or argumentative synthesis essay. This choice will set the tone and direction for your essay.
- Source Selection and Analysis: Choose credible and relevant sources for your topic, balancing different types like articles, books, and websites. Analyze each source carefully, noting the main ideas and evidence presented.
- Formulate a Strong Thesis Statement: Create a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your essay. It should express your main argument or perspective.
- Structure Your Essay: Organize your essay with a clear synthesis essay outline, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of your topic.
- Employ Effective Transition Sentences: Use transition sentences to connect your ideas and paragraphs smoothly, ensuring a cohesive flow in your essay.
- Synthesize Information: Blend information from your sources within your paragraphs. Discuss how each source contributes to your thesis and highlight common themes or differences.
- Avoid Simple Summarization: Don't just summarize your sources—analyze them critically and use them to build your argument.
- Address Counterarguments (if applicable): Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and counter them with well-supported arguments, showing a deep understanding of the topic.
- Craft a Resolute Conclusion: Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in the conclusion. Emphasize the importance of your argument or insights, and end with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
- Revise and Proofread: Check your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammar mistakes. Ensure your citations are correct and follow the chosen citation style, like MLA or APA.
Ready to Transform Your Synthesis Essay from Bland to Grand?
Let's tap into the magic of our expert wordsmiths, who will create an essay that dances with ideas and dazzles with creativity!
Synthesis Essay Format
Choosing the right citation style can enhance the credibility and professionalism of your paper. The format of your synthesis paper depends on the specific guidelines given by your instructor. They usually fall into one of the popular styles: MLA, APA, or Chicago, each used in different academic fields.

1. MLA (Modern Language Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and page number.
- Includes a 'Works Cited' page at the end listing all sources.
- Focuses on the author and publication date.
- Often used in humanities essays, research papers, and literary analyses.
2. APA (American Psychological Association):
- Uses in-text citations with the author's last name and publication date in parentheses.
- Includes a 'References' page listing all sources alphabetically.
- Emphasizes the publication date and scientific precision.
- Commonly used in research papers, scholarly articles, and scientific studies.
3. Chicago Style:
- Offers two documentation styles: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date.
- Notes-Bibliography uses footnotes or endnotes for citations, while Author-Date uses in-text citations with a reference list.
- Suitable for various academic writing, including research papers and historical studies.
- Provides flexibility in formatting and citation methods, making it adaptable to different disciplines.
Synthesis Essay Example
Here are two examples of synthesis essays that demonstrate how to apply the synthesis process in real life. They explore interesting topics and offer practical guidance for mastering the art of writing this type of paper.
Synthesis Essay Tips
Crafting a strong synthesis essay requires careful planning and effective techniques. Here are five essential tips to help you write your best paper:
- Diverse Source Selection : Choose a range of reliable sources that offer different viewpoints on your topic. Make sure they're recent and relevant to your subject.
- Seamless Source Integration : Avoid just summarizing your sources. Instead, blend them into your essay by analyzing and comparing their ideas. Show how they connect to build your argument.
- Balanced Tone : Maintain an impartial tone in your writing, even if you have personal opinions. Synthesis essays require objectivity, so they present different viewpoints without bias.
- Focus on Synthesis : Remember, synthesis essays are about linking ideas, not just summarizing sources. Explore how your sources relate to each other to create a cohesive argument.
- Address Counterarguments : Like in persuasive essays topics , acknowledge opposing viewpoints and explain why your perspective is stronger. This demonstrates your understanding of the topic and adds depth to your argument.
Concluding Thoughts
When writing a synthesis essay, it's essential to pick trustworthy sources, blend them effectively to build your argument and stay objective. Use smooth transitions, address counterarguments thoughtfully, and focus on analyzing rather than just summarizing. By following these steps, you'll create essays that inform, persuade, and engage your readers!
Want an Essay that Sings, Sparkles, and Stuns?
Fear not! Our expert wordsmiths are here to turn your thoughts into a symphony of ideas!
How Should You Conclude a Synthesis Essay?
Related articles.
.webp)
A Guide to Evidence Synthesis: What is Evidence Synthesis?
- Meet Our Team
- Our Published Reviews and Protocols
- What is Evidence Synthesis?
- Types of Evidence Synthesis
- Evidence Synthesis Across Disciplines
- Finding and Appraising Existing Systematic Reviews
- 0. Develop a Protocol
- 1. Draft your Research Question
- 2. Select Databases
- 3. Select Grey Literature Sources
- 4. Write a Search Strategy
- 5. Register a Protocol
- 6. Translate Search Strategies
- 7. Citation Management
- 8. Article Screening
- 9. Risk of Bias Assessment
- 10. Data Extraction
- 11. Synthesize, Map, or Describe the Results
- Evidence Synthesis Institute for Librarians
- Open Access Evidence Synthesis Resources
What are Evidence Syntheses?
What are evidence syntheses.
According to the Royal Society, 'evidence synthesis' refers to the process of bringing together information from a range of sources and disciplines to inform debates and decisions on specific issues. They generally include a methodical and comprehensive literature synthesis focused on a well-formulated research question. Their aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and unpublished studies. Evidence syntheses are conducted in an unbiased, reproducible way to provide evidence for practice and policy-making, as well as to identify gaps in the research. Evidence syntheses may also include a meta-analysis, a more quantitative process of synthesizing and visualizing data retrieved from various studies.
Evidence syntheses are much more time-intensive than traditional literature reviews and require a multi-person research team. See this PredicTER tool to get a sense of a systematic review timeline (one type of evidence synthesis). Before embarking on an evidence synthesis, it's important to clearly identify your reasons for conducting one. For a list of types of evidence synthesis projects, see the next tab.
How Does a Traditional Literature Review Differ From an Evidence Synthesis?
How does a systematic review differ from a traditional literature review.
One commonly used form of evidence synthesis is a systematic review. This table compares a traditional literature review with a systematic review.
Video: Reproducibility and transparent methods (Video 3:25)
Reporting Standards
There are some reporting standards for evidence syntheses. These can serve as guidelines for protocol and manuscript preparation and journals may require that these standards are followed for the review type that is being employed (e.g. systematic review, scoping review, etc).
- PRISMA checklist Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) is an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
- PRISMA-P Standards An updated version of the original PRISMA standards for protocol development.
- PRISMA - ScR Reporting guidelines for scoping reviews and evidence maps
- PRISMA-IPD Standards Extension of the original PRISMA standards for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of individual participant data.
- EQUATOR Network The EQUATOR (Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research) Network is an international initiative that seeks to improve the reliability and value of published health research literature by promoting transparent and accurate reporting and wider use of robust reporting guidelines. They provide a list of various standards for reporting in systematic reviews.
Video: Guidelines and reporting standards
PRISMA Flow Diagram
The PRISMA flow diagram depicts the flow of information through the different phases of an evidence synthesis. It maps the search (number of records identified), screening (number of records included and excluded), and selection (reasons for exclusion). Many evidence syntheses include a PRISMA flow diagram in the published manuscript.
See below for resources to help you generate your own PRISMA flow diagram.
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Tool
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Word Template
- << Previous: Our Published Reviews and Protocols
- Next: Types of Evidence Synthesis >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 4:35 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/evidence-synthesis
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

Methods for the synthesis of qualitative research: a critical review
Elaine barnett-page.
1 Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating (EPPI-) Centre, Social Science Research Unit, 18 Woburn Square, London WC1H 0NS, UK
James Thomas
Associated data.
In recent years, a growing number of methods for synthesising qualitative research have emerged, particularly in relation to health-related research. There is a need for both researchers and commissioners to be able to distinguish between these methods and to select which method is the most appropriate to their situation.
A number of methodological and conceptual links between these methods were identified and explored, while contrasting epistemological positions explained differences in approaches to issues such as quality assessment and extent of iteration. Methods broadly fall into 'realist' or 'idealist' epistemologies, which partly accounts for these differences.
Methods for qualitative synthesis vary across a range of dimensions. Commissioners of qualitative syntheses might wish to consider the kind of product they want and select their method – or type of method – accordingly.
The range of different methods for synthesising qualitative research has been growing over recent years [ 1 , 2 ], alongside an increasing interest in qualitative synthesis to inform health-related policy and practice [ 3 ]. While the terms 'meta-analysis' (a statistical method to combine the results of primary studies), or sometimes 'narrative synthesis', are frequently used to describe how quantitative research is synthesised, far more terms are used to describe the synthesis of qualitative research. This profusion of terms can mask some of the basic similarities in approach that the different methods share, and also lead to some confusion regarding which method is most appropriate in a given situation. This paper does not argue that the various nomenclatures are unnecessary, but rather seeks to draw together and review the full range of methods of synthesis available to assist future reviewers in selecting a method that is fit for their purpose. It also represents an attempt to guide the reader through some of the varied terminology to spring up around qualitative synthesis. Other helpful reviews of synthesis methods have been undertaken in recent years with slightly different foci to this paper. Two recent studies have focused on describing and critiquing methods for the integration of qualitative research with quantitative [ 4 , 5 ] rather than exclusively examining the detail and rationale of methods for the synthesis of qualitative research. Two other significant pieces of work give practical advice for conducting the synthesis of qualitative research, but do not discuss the full range of methods available [ 6 , 7 ]. We begin our Discussion by outlining each method of synthesis in turn, before comparing and contrasting characteristics of these different methods across a range of dimensions. Readers who are more familiar with the synthesis methods described here may prefer to turn straight to the 'dimensions of difference' analysis in the second part of the Discussion.
Overview of synthesis methods
Meta-ethnography.
In their seminal work of 1988, Noblit and Hare proposed meta-ethnography as an alternative to meta-analysis [ 8 ]. They cited Strike and Posner's [ 9 ] definition of synthesis as an activity in which separate parts are brought together to form a 'whole'; this construction of the whole is essentially characterised by some degree of innovation, so that the result is greater than the sum of its parts. They also borrowed from Turner's theory of social explanation [ 10 ], a key tenet of which was building 'comparative understanding' [[ 8 ], p22] rather than aggregating data.
To Noblit and Hare, synthesis provided an answer to the question of 'how to "put together" written interpretive accounts' [[ 8 ], p7], where mere integration would not be appropriate. Noblit and Hare's early work synthesised research from the field of education.
Three different methods of synthesis are used in meta-ethnography. One involves the 'translation' of concepts from individual studies into one another, thereby evolving overarching concepts or metaphors. Noblit and Hare called this process reciprocal translational analysis (RTA). Refutational synthesis involves exploring and explaining contradictions between individual studies. Lines-of-argument (LOA) synthesis involves building up a picture of the whole (i.e. culture, organisation etc) from studies of its parts. The authors conceptualised this latter approach as a type of grounded theorising.
Britten et al [ 11 ] and Campbell et al [ 12 ] have both conducted evaluations of meta-ethnography and claim to have succeeded, by using this method, in producing theories with greater explanatory power than could be achieved in a narrative literature review. While both these evaluations used small numbers of studies, more recently Pound et al [ 13 ] conducted both an RTA and an LOA synthesis using a much larger number of studies (37) on resisting medicines. These studies demonstrate that meta-ethnography has evolved since Noblit and Hare first introduced it. Campbell et al claim to have applied the method successfully to non-ethnographical studies. Based on their reading of Schutz [ 14 ], Britten et al have developed both second and third order constructs in their synthesis (Noblit and Hare briefly allude to the possibility of a 'second level of synthesis' [[ 8 ], p28] but do not demonstrate or further develop the idea).
In a more recent development, Sandelowski & Barroso [ 15 ] write of adapting RTA by using it to ' integrate findings interpretively, as opposed to comparing them interpretively' (p204). The former would involve looking to see whether the same concept, theory etc exists in different studies; the latter would involve the construction of a bigger picture or theory (i.e. LOA synthesis). They also talk about comparing or integrating imported concepts (e.g. from other disciplines) as well as those evolved 'in vivo'.
Grounded theory
Kearney [ 16 ], Eaves [ 17 ] and Finfgeld [ 18 ] have all adapted grounded theory to formulate a method of synthesis. Key methods and assumptions of grounded theory, as originally formulated and subsequently refined by Glaser and Strauss [ 19 ] and Strauss and Corbin [ 20 , 21 ], include: simultaneous phases of data collection and analysis; an inductive approach to analysis, allowing the theory to emerge from the data; the use of the constant comparison method; the use of theoretical sampling to reach theoretical saturation; and the generation of new theory. Eaves cited grounded theorists Charmaz [ 22 ] and Chesler [ 23 ], as well as Strauss and Corbin [ 20 ], as informing her approach to synthesis.
Glaser and Strauss [ 19 ] foresaw a time when a substantive body of grounded research should be pushed towards a higher, more abstract level. As a piece of methodological work, Eaves undertook her own synthesis of the synthesis methods used by these authors to produce her own clear and explicit guide to synthesis in grounded formal theory. Kearney stated that 'grounded formal theory', as she termed this method of synthesis, 'is suited to study of phenomena involving processes of contextualized understanding and action' [[ 24 ], p180] and, as such, is particularly applicable to nurses' research interests.
As Kearney suggested, the examples examined here were largely dominated by research in nursing. Eaves synthesised studies on care-giving in rural African-American families for elderly stroke survivors; Finfgeld on courage among individuals with long-term health problems; Kearney on women's experiences of domestic violence.
Kearney explicitly chose 'grounded formal theory' because it matches 'like' with 'like': that is, it applies the same methods that have been used to generate the original grounded theories included in the synthesis – produced by constant comparison and theoretical sampling – to generate a higher-level grounded theory. The wish to match 'like' with 'like' is also implicit in Eaves' paper. This distinguishes grounded formal theory from more recent applications of meta-ethnography, which have sought to include qualitative research using diverse methodological approaches [ 12 ].
Thematic Synthesis
Thomas and Harden [ 25 ] have developed an approach to synthesis which they term 'thematic synthesis'. This combines and adapts approaches from both meta-ethnography and grounded theory. The method was developed out of a need to conduct reviews that addressed questions relating to intervention need, appropriateness and acceptability – as well as those relating to effectiveness – without compromising on key principles developed in systematic reviews. They applied thematic synthesis in a review of the barriers to, and facilitators of, healthy eating amongst children.
Free codes of findings are organised into 'descriptive' themes, which are then further interpreted to yield 'analytical' themes. This approach shares characteristics with later adaptations of meta-ethnography, in that the analytical themes are comparable to 'third order interpretations' and that the development of descriptive and analytical themes using coding invoke reciprocal 'translation'. It also shares much with grounded theory, in that the approach is inductive and themes are developed using a 'constant comparison' method. A novel aspect of their approach is the use of computer software to code the results of included studies line-by-line, thus borrowing another technique from methods usually used to analyse primary research.
Textual Narrative Synthesis
Textual narrative synthesis is an approach which arranges studies into more homogenous groups. Lucas et al [ 26 ] comment that it has proved useful in synthesising evidence of different types (qualitative, quantitative, economic etc). Typically, study characteristics, context, quality and findings are reported on according to a standard format and similarities and differences are compared across studies. Structured summaries may also be developed, elaborating on and putting into context the extracted data [ 27 ].
Lucas et al [ 26 ] compared thematic synthesis with textual narrative synthesis. They found that 'thematic synthesis holds most potential for hypothesis generation' whereas textual narrative synthesis is more likely to make transparent heterogeneity between studies (as does meta-ethnography, with refutational synthesis) and issues of quality appraisal. This is possibly because textual narrative synthesis makes clearer the context and characteristics of each study, while the thematic approach organises data according to themes. However, Lucas et al found that textual narrative synthesis is 'less good at identifying commonality' (p2); the authors do not make explicit why this should be, although it may be that organising according to themes, as the thematic approach does, is comparatively more successful in revealing commonality.
Paterson et al [ 28 ] have evolved a multi-faceted approach to synthesis, which they call 'meta-study'. The sociologist Zhao [ 29 ], drawing on Ritzer's work [ 30 ], outlined three components of analysis, which they proposed should be undertaken prior to synthesis. These are meta-data-analysis (the analysis of findings), meta-method (the analysis of methods) and meta-theory (the analysis of theory). Collectively, these three elements of analysis, culminating in synthesis, make up the practice of 'meta-study'. Paterson et al pointed out that the different components of analysis may be conducted concurrently.
Paterson et al argued that primary research is a construction; secondary research is therefore a construction of a construction. There is need for an approach that recognises this, and that also recognises research to be a product of its social, historical and ideological context. Such an approach would be useful in accounting for differences in research findings. For Paterson et al, there is no such thing as 'absolute truth'.
Meta-study was developed to study the experiences of adults living with a chronic illness. Meta-data-analysis was conceived of by Paterson et al in similar terms to Noblit and Hare's meta-ethnography (see above), in that it is essentially interpretive and seeks to reveal similarities and discrepancies among accounts of a particular phenomenon. Meta-method involves the examination of the methodologies of the individual studies under review. Part of the process of meta-method is to consider different aspects of methodology such as sampling, data collection, research design etc, similar to procedures others have called 'critical appraisal' (CASP [ 31 ]). However, Paterson et al take their critique to a deeper level by establishing the underlying assumptions of the methodologies used and the relationship between research outcomes and methods used. Meta-theory involves scrutiny of the philosophical and theoretical assumptions of the included research papers; this includes looking at the wider context in which new theory is generated. Paterson et al described meta-synthesis as a process which creates a new interpretation which accounts for the results of all three elements of analysis. The process of synthesis is iterative and reflexive and the authors were unwilling to oversimplify the process by 'codifying' procedures for bringing all three components of analysis together.
Meta-narrative
Greenhalgh et al [ 32 ]'s meta-narrative approach to synthesis arose out of the need to synthesise evidence to inform complex policy-making questions and was assisted by the formation of a multi-disciplinary team. Their approach to review was informed by Thomas Kuhn's The Structure of Scientific Revolutions [ 33 ], in which he proposed that knowledge is produced within particular paradigms which have their own assumptions about theory, about what is a legitimate object of study, about what are legitimate research questions and about what constitutes a finding. Paradigms also tend to develop through time according to a particular set of stages, central to which is the stage of 'normal science', in which the particular standards of the paradigm are largely unchallenged and seen to be self-evident. As Greenhalgh et al pointed out, Kuhn saw paradigms as largely incommensurable: 'that is, an empirical discovery made using one set of concepts, theories, methods and instruments cannot be satisfactorily explained through a different paradigmatic lens' [[ 32 ], p419].
Greenhalgh et al synthesised research from a wide range of disciplines; their research question related to the diffusion of innovations in health service delivery and organisation. They thus identified a need to synthesise findings from research which contains many different theories arising from many different disciplines and study designs.
Based on Kuhn's work, Greenhalgh et al proposed that, across different paradigms, there were multiple – and potentially mutually contradictory – ways of understanding the concept at the heart of their review, namely the diffusion of innovation. Bearing this in mind, the reviewers deliberately chose to select key papers from a number of different research 'paradigms' or 'traditions', both within and beyond healthcare, guided by their multidisciplinary research team. They took as their unit of analysis the 'unfolding "storyline" of a research tradition over time' [[ 32 ], p417) and sought to understand diffusion of innovation as it was conceptualised in each of these traditions. Key features of each tradition were mapped: historical roots, scope, theoretical basis; research questions asked and methods/instruments used; main empirical findings; historical development of the body of knowledge (how have earlier findings led to later findings); and strengths and limitations of the tradition. The results of this exercise led to maps of 13 'meta-narratives' in total, from which seven key dimensions, or themes, were identified and distilled for the synthesis phase of the review.
Critical Interpretive Synthesis
Dixon-Woods et al [ 34 ] developed their own approach to synthesising multi-disciplinary and multi-method evidence, termed 'critical interpretive synthesis', while researching access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. Critical interpretive synthesis is an adaptation of meta-ethnography, as well as borrowing techniques from grounded theory. The authors stated that they needed to adapt traditional meta-ethnographic methods for synthesis, since these had never been applied to quantitative as well as qualitative data, nor had they been applied to a substantial body of data (in this case, 119 papers).
Dixon-Woods et al presented critical interpretive synthesis as an approach to the whole process of review, rather than to just the synthesis component. It involves an iterative approach to refining the research question and searching and selecting from the literature (using theoretical sampling) and defining and applying codes and categories. It also has a particular approach to appraising quality, using relevance – i.e. likely contribution to theory development – rather than methodological characteristics as a means of determining the 'quality' of individual papers [ 35 ]. The authors also stress, as a defining characteristic, critical interpretive synthesis's critical approach to the literature in terms of deconstructing research traditions or theoretical assumptions as a means of contextualising findings.
Dixon-Woods et al rejected reciprocal translational analysis (RTA) as this produced 'only a summary in terms that have already been used in the literature' [[ 34 ], p5], which was seen as less helpful when dealing with a large and diverse body of literature. Instead, Dixon-Woods et al adopted a lines-of-argument (LOA) synthesis, in which – rejecting the difference between first, second and third order constructs – they instead developed 'synthetic constructs' which were then linked with constructs arising directly from the literature.
The influence of grounded theory can be seen in particular in critical interpretive synthesis's inductive approach to formulating the review question and to developing categories and concepts, rejecting a 'stage' approach to systematic reviewing, and in selecting papers using theoretical sampling. Dixon-Woods et al also claim that critical interpretive synthesis is distinct in its 'explicit orientation towards theory generation' [[ 34 ], p9].
Ecological Triangulation
Jim Banning is the author of 'ecological triangulation' or 'ecological sentence synthesis', applying this method to the evidence for what works for youth with disabilities. He borrows from Webb et al [ 36 ] and Denzin [ 37 ] the concept of triangulation, in which phenomena are studied from a variety of vantage points. His rationale is that building an 'evidence base' of effectiveness requires the synthesis of cumulative, multi-faceted evidence in order to find out 'what intervention works for what kind of outcomes for what kind of persons under what kind of conditions' [[ 38 ], p1].
Ecological triangulation unpicks the mutually interdependent relationships between behaviour, persons and environments. The method requires that, for data extraction and synthesis, 'ecological sentences' are formulated following the pattern: 'With this intervention, these outcomes occur with these population foci and within these grades (ages), with these genders ... and these ethnicities in these settings' [[ 39 ], p1].
Framework Synthesis
Brunton et al [ 40 ] and Oliver et al [ 41 ] have applied a 'framework synthesis' approach in their reviews. Framework synthesis is based on framework analysis, which was outlined by Pope, Ziebland and Mays [ 42 ], and draws upon the work of Ritchie and Spencer [ 43 ] and Miles and Huberman [ 44 ]. Its rationale is that qualitative research produces large amounts of textual data in the form of transcripts, observational fieldnotes etc. The sheer wealth of information poses a challenge for rigorous analysis. Framework synthesis offers a highly structured approach to organising and analysing data (e.g. indexing using numerical codes, rearranging data into charts etc).
Brunton et al applied the approach to a review of children's, young people's and parents' views of walking and cycling; Oliver et al to an analysis of public involvement in health services research. Framework synthesis is distinct from the other methods outlined here in that it utilises an a priori 'framework' – informed by background material and team discussions – to extract and synthesise findings. As such, it is largely a deductive approach although, in addition to topics identified by the framework, new topics may be developed and incorporated as they emerge from the data. The synthetic product can be expressed in the form of a chart for each key dimension identified, which may be used to map the nature and range of the concept under study and find associations between themes and exceptions to these [ 40 ].
'Fledgling' approaches
There are three other approaches to synthesis which have not yet been widely used. One is an approach using content analysis [ 45 , 46 ] in which text is condensed into fewer content-related categories. Another is 'meta-interpretation' [ 47 ], featuring the following: an ideographic rather than pre-determined approach to the development of exclusion criteria; a focus on meaning in context; interpretations as raw data for synthesis (although this feature doesn't distinguish it from other synthesis methods); an iterative approach to the theoretical sampling of studies for synthesis; and a transparent audit trail demonstrating the trustworthiness of the synthesis.
In addition to the synthesis methods discussed above, Sandelowski and Barroso propose a method they call 'qualitative metasummary' [ 15 ]. It is mentioned here as a new and original approach to handling a collection of qualitative studies but is qualitatively different to the other methods described here since it is aggregative; that is, findings are accumulated and summarised rather than 'transformed'. Metasummary is a way of producing a 'map' of the contents of qualitative studies and – according to Sandelowski and Barroso – 'reflect [s] a quantitative logic' [[ 15 ], p151]. The frequency of each finding is determined and the higher the frequency of a particular finding, the greater its validity. The authors even discuss the calculation of 'effect sizes' for qualitative findings. Qualitative metasummaries can be undertaken as an end in themselves or may serve as a basis for a further synthesis.
Dimensions of difference
Having outlined the range of methods identified, we now turn to an examination of how they compare with one another. It is clear that they have come from many different contexts and have different approaches to understanding knowledge, but what do these differences mean in practice? Our framework for this analysis is shown in Additional file 1 : dimensions of difference [ 48 ]. We have examined the epistemology of each of the methods and found that, to some extent, this explains the need for different methods and their various approaches to synthesis.
Epistemology
The first dimension that we will consider is that of the researchers' epistemological assumptions. Spencer et al [ 49 ] outline a range of epistemological positions, which might be organised into a spectrum as follows:
Subjective idealism : there is no shared reality independent of multiple alternative human constructions
Objective idealism : there is a world of collectively shared understandings
Critical realism : knowledge of reality is mediated by our perceptions and beliefs
Scientific realism : it is possible for knowledge to approximate closely an external reality
Naïve realism : reality exists independently of human constructions and can be known directly [ 49 , 45 , 46 ].
Thus, at one end of the spectrum we have a highly constructivist view of knowledge and, at the other, an unproblematized 'direct window onto the world' view.
Nearly all of positions along this spectrum are represented in the range of methodological approaches to synthesis covered in this paper. The originators of meta-narrative synthesis, critical interpretive synthesis and meta-study all articulate what might be termed a 'subjective idealist' approach to knowledge. Paterson et al [ 28 ] state that meta-study shies away from creating 'grand theories' within the health or social sciences and assume that no single objective reality will be found. Primary studies, they argue, are themselves constructions; meta-synthesis, then, 'deals with constructions of constructions' (p7). Greenhalgh et al [ 32 ] also view knowledge as a product of its disciplinary paradigm and use this to explain conflicting findings: again, the authors neither seek, nor expect to find, one final, non-contestable answer to their research question. Critical interpretive synthesis is similar in seeking to place literature within its context, to question its assumptions and to produce a theoretical model of a phenomenon which – because highly interpretive – may not be reproducible by different research teams at alternative points in time [[ 34 ], p11].
Methods used to synthesise grounded theory studies in order to produce a higher level of grounded theory [ 24 ] appear to be informed by 'objective idealism', as does meta-ethnography. Kearney argues for the near-universal applicability of a 'ready-to-wear' theory across contexts and populations. This approach is clearly distinct from one which recognises multiple realities. The emphasis is on examining commonalities amongst, rather than discrepancies between, accounts. This emphasis is similarly apparent in most meta-ethnographies, which are conducted either according to Noblit and Hare's 'reciprocal translational analysis' technique or to their 'lines-of-argument' technique and which seek to provide a 'whole' which has a greater explanatory power. Although Noblit and Hare also propose 'refutational synthesis', in which contradictory findings might be explored, there are few examples of this having been undertaken in practice, and the aim of the method appears to be to explain and explore differences due to context, rather than multiple realities.
Despite an assumption of a reality which is perhaps less contestable than those of meta-narrative synthesis, critical interpretive synthesis and meta-study, both grounded formal theory and meta-ethnography place a great deal of emphasis on the interpretive nature of their methods. This still supposes a degree of constructivism. Although less explicit about how their methods are informed, it seems that both thematic synthesis and framework synthesis – while also involving some interpretation of data – share an even less problematized view of reality and a greater assumption that their synthetic products are reproducible and correspond to a shared reality. This is also implicit in the fact that such products are designed directly to inform policy and practice, a characteristic shared by ecological triangulation. Notably, ecological triangulation, according to Banning, can be either realist or idealist. Banning argues that the interpretation of triangulation can either be one in which multiple viewpoints converge on a point to produce confirming evidence (i.e. one definitive answer to the research question) or an idealist one, in which the complexity of multiple viewpoints is represented. Thus, although ecological triangulation views reality as complex, the approach assumes that it can be approximately knowable (at least when the realist view of ecological triangulation is adopted) and that interventions can and should be modelled according to the products of its syntheses.
While pigeonholing different methods into specific epistemological positions is a problematic process, we do suggest that the contrasting epistemologies of different researchers is one way of explaining why we have – and need – different methods for synthesis.
Variation in terms of the extent of iteration during the review process is another key dimension. All synthesis methods include some iteration but the degree varies. Meta-ethnography, grounded theory and thematic synthesis all include iteration at the synthesis stage; both framework synthesis and critical interpretive synthesis involve iterative literature searching – in the case of critical interpretive synthesis, it is not clear whether iteration occurs during the rest of the review process. Meta-narrative also involves iteration at every stage. Banning does not mention iteration in outlining ecological triangulation and neither do Lucas or Thomas and Harden for thematic narrative synthesis.
It seems that the more idealist the approach, the greater the extent of iteration. This might be because a large degree of iteration does not sit well with a more 'positivist' ideal of procedural objectivity; in particular, the notion that the robustness of the synthetic product depends in part on the reviewers stating up front in a protocol their searching strategies, inclusion/exclusion criteria etc, and being seen not to alter these at a later stage.
Quality assessment
Another dimension along which we can look at different synthesis methods is that of quality assessment. When the approaches to the assessment of the quality of studies retrieved for review are examined, there is again a wide methodological variation. It might be expected that the further towards the 'realism' end of the epistemological spectrum a method of synthesis falls, the greater the emphasis on quality assessment. In fact, this is only partially the case.
Framework synthesis, thematic narrative synthesis and thematic synthesis – methods which might be classified as sharing a 'critical realist' approach – all have highly specified approaches to quality assessment. The review in which framework synthesis was developed applied ten quality criteria: two on quality and reporting of sampling methods, four to the quality of the description of the sample in the study, two to the reliability and validity of the tools used to collect data and one on whether studies used appropriate methods for helping people to express their views. Studies which did not meet a certain number of quality criteria were excluded from contributing to findings. Similarly, in the example review for thematic synthesis, 12 criteria were applied: five related to reporting aims, context, rationale, methods and findings; four relating to reliability and validity; and three relating to the appropriateness of methods for ensuring that findings were rooted in participants' own perspectives. Studies which were deemed to have significant flaws were excluded and sensitivity analyses were used to assess the possible impact of study quality on the review's findings. Thomas and Harden's use of thematic narrative synthesis similarly applied quality criteria and developed criteria additional to those they found in the literature on quality assessment, relating to the extent to which people's views and perspectives had been privileged by researchers. It is worth noting not only that these methods apply quality criteria but that they are explicit about what they are: assessing quality is a key component in the review process for both of these methods. Likewise, Banning – the originator of ecological triangulation – sees quality assessment as important and adapts the Design and Implementation Assessment Device (DIAD) Version 0.3 (a quality assessment tool for quantitative research) for use when appraising qualitative studies [ 50 ]. Again, Banning writes of excluding studies deemed to be of poor quality.
Greenhalgh et al's meta-narrative review [ 32 ] modified a range of existing quality assessment tools to evaluate studies according to validity and robustness of methods; sample size and power; and validity of conclusions. The authors imply, but are not explicit, that this process formed the basis for the exclusion of some studies. Although not quite so clear about quality assessment methods as framework and thematic synthesis, it might be argued that meta-narrative synthesis shows a greater commitment to the concept that research can and should be assessed for quality than either meta-ethnography or grounded formal theory. The originators of meta-ethnography, Noblit and Hare [ 8 ], originally discussed quality in terms of quality of metaphor, while more recent use of this method has used amended versions of CASP (the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme tool, [ 31 ]), yet has only referred to studies being excluded on the basis of lack of relevance or because they weren't 'qualitative' studies [ 8 ]. In grounded theory, quality assessment is only discussed in terms of a 'personal note' being made on the context, quality and usefulness of each study. However, contrary to expectation, meta-narrative synthesis lies at the extreme end of the idealism/realism spectrum – as a subjective idealist approach – while meta-ethnography and grounded theory are classified as objective idealist approaches.
Finally, meta-study and critical interpretive synthesis – two more subjective idealist approaches – look to the content and utility of findings rather than methodology in order to establish quality. While earlier forms of meta-study included only studies which demonstrated 'epistemological soundness', in its most recent form [ 51 ] this method has sought to include all relevant studies, excluding only those deemed not to be 'qualitative' research. Critical interpretive synthesis also conforms to what we might expect of its approach to quality assessment: quality of research is judged as the extent to which it informs theory. The threshold of inclusion is informed by expertise and instinct rather than being articulated a priori.
In terms of quality assessment, it might be important to consider the academic context in which these various methods of synthesis developed. The reason why thematic synthesis, framework synthesis and ecological triangulation have such highly specified approaches to quality assessment may be that each of these was developed for a particular task, i.e. to conduct a multi-method review in which randomised controlled trials (RCTs) were included. The concept of quality assessment in relation to RCTs is much less contested and there is general agreement on criteria against which quality should be judged.
Problematizing the literature
Critical interpretive synthesis, the meta-narrative approach and the meta-theory element of meta-study all share some common ground in that their review and synthesis processes include examining all aspects of the context in which knowledge is produced. In conducting a review on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups, critical interpretive synthesis sought to question 'the ways in which the literature had constructed the problematics of access, the nature of the assumptions on which it drew, and what has influenced its choice of proposed solutions' [[ 34 ], p6]. Although not claiming to have been directly influenced by Greenhalgh et al's meta-narrative approach, Dixon-Woods et al do cite it as sharing similar characteristics in the sense that it critiques the literature it reviews.
Meta-study uses meta-theory to describe and deconstruct the theories that shape a body of research and to assess its quality. One aspect of this process is to examine the historical evolution of each theory and to put it in its socio-political context, which invites direct comparison with meta-narrative synthesis. Greenhalgh et al put a similar emphasis on placing research findings within their social and historical context, often as a means of seeking to explain heterogeneity of findings. In addition, meta-narrative shares with critical interpretive synthesis an iterative approach to searching and selecting from the literature.
Framework synthesis, thematic synthesis, textual narrative synthesis, meta-ethnography and grounded theory do not share the same approach to problematizing the literature as critical interpretive synthesis, meta-study and meta-narrative. In part, this may be explained by the extent to which studies included in the synthesis represented a broad range of approaches or methodologies. This, in turn, may reflect the broadness of the review question and the extent to which the concepts contained within the question are pre-defined within the literature. In the case of both the critical interpretive synthesis and meta-narrative reviews, terminology was elastic and/or the question formed iteratively. Similarly, both reviews placed great emphasis on employing multi-disciplinary research teams. Approaches which do not critique the literature in the same way tend to have more narrowly-focused questions. They also tend to include a more limited range of studies: grounded theory synthesis includes grounded theory studies, meta-ethnography (in its original form, as applied by Noblit and Hare) ethnographies. The thematic synthesis incorporated studies based on only a narrow range of qualitative methodologies (interviews and focus groups) which were informed by a similarly narrow range of epistemological assumptions. It may be that the authors of such syntheses saw no need for including such a critique in their review process.
Similarities and differences between primary studies
Most methods of synthesis are applicable to heterogeneous data (i.e. studies which use contrasting methodologies) apart from early meta-ethnography and synthesis informed by grounded theory. All methods of synthesis state that, at some level, studies are compared; many are not so explicit about how this is done, though some are. Meta-ethnography is one of the most explicit: it describes the act of 'translation' where terms and concepts which have resonance with one another are subsumed into 'higher order constructs'. Grounded theory, as represented by Eaves [ 17 ], is undertaken according to a long list of steps and sub-steps, includes the production of generalizations about concepts/categories, which comes from classifying these categories. In meta-narrative synthesis, comparable studies are grouped together at the appraisal phase of review.
Perhaps more interesting are the ways in which differences between studies are explored. Those methods with a greater emphasis on critical appraisal may tend (although this is not always made explicit) to use differences in method to explain differences in finding. Meta-ethnography proposes 'refutational synthesis' to explain differences, although there are few examples of this in the literature. Some synthesis methods – for example, thematic synthesis – look at other characteristics of the studies under review, whether types of participants and their context vary, and whether this can explain differences in perspective.
All of these methods, then, look within the studies to explain differences. Other methods look beyond the study itself to the context in which it was produced. Critical interpretive synthesis and meta-study look at differences in theory or in socio-economic context. Critical interpretive synthesis, like meta-narrative, also explores epistemological orientation. Meta-narrative is unique in concerning itself with disciplinary paradigm (i.e. the story of the discipline as it progresses). It is also distinctive in that it treats conflicting findings as 'higher order data' [[ 32 ], p420], so that the main emphasis of the synthesis appears to be on examining and explaining contradictions in the literature.
Going 'beyond' the primary studies
Synthesis is sometimes defined as a process resulting in a product, a 'whole', which is more than the sum of its parts. However, the methods reviewed here vary in the extent to which they attempt to 'go beyond' the primary studies and transform the data. Some methods – textual narrative synthesis, ecological triangulation and framework synthesis – focus on describing and summarising their primary data (often in a highly structured and detailed way) and translating the studies into one another. Others – meta-ethnography, grounded theory, thematic synthesis, meta-study, meta-narrative and critical interpretive synthesis – seek to push beyond the original data to a fresh interpretation of the phenomena under review. A key feature of thematic synthesis is its clear differentiation between these two stages.
Different methods have different mechanisms for going beyond the primary studies, although some are more explicit than others about what these entail. Meta-ethnography proposes a 'Line of Argument' (LOA) synthesis in which an interpretation is constructed to both link and explain a set of parts. Critical interpretive synthesis based its synthesis methods on those of meta-ethnography, developing an LOA using what the authors term 'synthetic constructs' (akin to 'third order constructs' in meta-ethnography) to create a 'synthesising argument'. Dixon-Woods et al claim that this is an advance on Britten et al's methods, in that they reject the difference between first, second and third order constructs.
Meta-narrative, as outlined above, focuses on conflicting findings and constructs theories to explain these in terms of differing paradigms. Meta study derives questions from each of its three components to which it subjects the dataset and inductively generates a number of theoretical claims in relation to it. According to Eaves' model of grounded theory [ 17 ], mini-theories are integrated to produce an explanatory framework. In ecological triangulation, the 'axial' codes – or second level codes evolved from the initial deductive open codes – are used to produce Banning's 'ecological sentence' [ 39 ].
The synthetic product
In overviewing and comparing different qualitative synthesis methods, the ultimate question relates to the utility of the synthetic product: what is it for? It is clear that some methods of synthesis – namely, thematic synthesis, textual narrative synthesis, framework synthesis and ecological triangulation – view themselves as producing an output that is directly applicable to policy makers and designers of interventions. The example of framework synthesis examined here (on children's, young people's and parents' views of walking and cycling) involved policy makers and practitioners in directing the focus of the synthesis and used the themes derived from the synthesis to infer what kind of interventions might be most effective in encouraging walking and cycling. Likewise, the products of the thematic synthesis took the form of practical recommendations for interventions (e.g. 'do not promote fruit and vegetables in the same way in the same intervention'). The extent to which policy makers and practitioners are involved in informing either synthesis or recommendation is less clear from the documents published on ecological triangulation, but the aim certainly is to directly inform practice.
The outputs of synthesis methods which have a more constructivist orientation – meta-study, meta-narrative, meta-ethnography, grounded theory, critical interpretive synthesis – tend to look rather different. They are generally more complex and conceptual, sometimes operating on the symbolic or metaphorical level, and requiring a further process of interpretation by policy makers and practitioners in order for them to inform practice. This is not to say, however, that they are not useful for practice, more that they are doing different work. However, it may be that, in the absence of further interpretation, they are more useful for informing other researchers and theoreticians.
Looking across dimensions
After examining the dimensions of difference of our included methods, what picture ultimately emerges? It seems clear that, while similar in some respects, there are genuine differences in approach to the synthesis of what is essentially textual data. To some extent, these differences can be explained by the epistemological assumptions that underpin each method. Our methods split into two broad camps: the idealist and the realist (see Table Table1 1 for a summary). Idealist approaches generally tend to have a more iterative approach to searching (and the review process), have less a priori quality assessment procedures and are more inclined to problematize the literature. Realist approaches are characterised by a more linear approach to searching and review, have clearer and more well-developed approaches to quality assessment, and do not problematize the literature.
Summary table
N.B.: In terms of the above dimensions, it is generally a question of degree rather than of absolute distinctions.
Mapping the relationships between methods
What is interesting is the relationship between these methods of synthesis, the conceptual links between them, and the extent to which the originators cite – or, in some cases, don't cite – one another. Some methods directly build on others – framework synthesis builds on framework analysis, for example, while grounded theory and constant comparative analysis build on grounded theory. Others further develop existing methods – meta-study, critical interpretive synthesis and meta-narrative all adapt aspects of meta-ethnography, while also importing concepts from other theorists (critical interpretive synthesis also adapts grounded theory techniques).
Some methods share a clear conceptual link, without directly citing one another: for example, the analytical themes developed during thematic synthesis are comparable to the third order interpretations of meta-ethnography. The meta-theory aspect of meta-study is echoed in both meta-narrative synthesis and critical interpretive synthesis (see 'Problematizing the literature, above); however, the originators of critical interpretive synthesis only refer to the originators of meta-study in relation to their use of sampling techniques.
While methods for qualitative synthesis have many similarities, there are clear differences in approach between them, many of which can be explained by taking account of a given method's epistemology.
However, within the two broad idealist/realist categories, any differences between methods in terms of outputs appear to be small.
Since many systematic reviews are designed to inform policy and practice, it is important to select a method – or type of method – that will produce the kind of conclusions needed. However, it is acknowledged that this is not always simple or even possible to achieve in practice.
The approaches that result in more easily translatable messages for policy-makers and practitioners may appear to be more attractive than the others; but we do need to take account lessons from the more idealist end of the spectrum, that some perspectives are not universal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
Both authors made substantial contributions, with EBP taking a lead on writing and JT on the analytical framework. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/9/59/prepub
Supplementary Material
Dimensions of difference . Ranging from subjective idealism through objective idealism and critical realism to scientific realism to naïve realism
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the helpful contributions of the following in commenting on earlier drafts of this paper: David Gough, Sandy Oliver, Angela Harden, Mary Dixon-Woods, Trisha Greenhalgh and Barbara L. Paterson. We would also like to thank the peer reviewers: Helen J Smith, Rosaline Barbour and Mark Rodgers for their helpful reviews. The methodological development was supported by the Department of Health (England) and the ESRC through the Methods for Research Synthesis Node of the National Centre for Research Methods (NCRM). An earlier draft of this paper currently appears as a working paper on the National Centre for Research Methods' website http://www.ncrm.ac.uk/ .
- Dixon-Woods M, Agarwhal S, Jones D, Young B, Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. J Health Serv Res Pol. 2005; 10 (1):45–53b. doi: 10.1258/1355819052801804. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS, Barbour M. Evaluating and synthesizing qualitative research: the need to develop a distinctive approach. J Eval Clin Pract. 2003; 9 (2):179–186. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2753.2003.00371.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C, Popay J. Systematically reviewing qualitative and quantitative evidence to inform management and policy-making in the health field. J Health Serv Res Pol. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):6–20. doi: 10.1258/1355819054308576. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixon-Woods M, Bonas S, Booth A, Jones DR, Miller T, Shaw RL, Smith J, Sutton A, Young B. How can systematic reviews incorporate qualitative research? A critical perspective. Qual Res. 2006; 6 :27–44. doi: 10.1177/1468794106058867. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Mays N, Popay J. Synthesizing Qualitative and Quantitative Health Evidence: a Guide to Methods. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne S, Jenson L, Kearney MH, Noblit G, Sandelowski M. Qualitative metasynthesis: reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qual Health Res. 2004; 14 :1342–1365. doi: 10.1177/1049732304269888. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Systematic Reviews. CRD's Guidance for Undertaking Reviews in Health Care. York: CRD; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-Ethnography: Synthesizing Qualitative Studies. London: Sage; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strike K, Posner G. In: Knowledge Structure and Use. Ward S, Reed L, editor. Philadelphia: Temple University Press; 1983. Types of synthesis and their criteria. [ Google Scholar ]
- Turner S. Sociological Explanation as Translation. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1980. [ Google Scholar ]
- Britten N, Campbell R, Pope C, Donovan J, Morgan M, Pill R. Using meta-ethnography to synthesis qualitative research: a worked example. J Health Serv Res. 2002; 7 :209–15. doi: 10.1258/135581902320432732. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Campbell R, Pound P, Pope C, Britten N, Pill R, Morgan M, Donovan J. Evaluating meta-ethnography: a synthesis of qualitative research on lay experiences of diabetes and diabetes care. Soc Sci Med. 2003; 65 :671–84. doi: 10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00064-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pound P, Britten N, Morgan M, Yardley L, Pope C, Daker-White G, Campbell R. Resisting medicines: a synthesis of qualitative studies of medicine taking. Soc Sci Med. 2005; 61 :133–155. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.11.063. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schutz A. Collected Paper. Vol. 1. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Handbook for Synthesizing Qualitative Research. New York: Springer Publishing Company; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kearney MH. Enduring love: a grounded formal theory of women's experience of domestic violence. Research Nurs Health. 2001; 24 :270–82. doi: 10.1002/nur.1029. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eaves YD. A synthesis technique for grounded theory data analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2001; 35 :654–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2001.01897.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Finfgeld D. Courage as a process of pushing beyond the struggle. Qual Health Res. 1999; 9 :803–814. doi: 10.1177/104973299129122298. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser BG, Strauss AL. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research. New York: Aldine De Gruyter; 1967. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL, Corbin J. Basics of Qualitative Research: Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1990. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL, Corbin J. Basics of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Procedures for Developing Grounded Theory. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Charmaz K. In: Contemporary Field Research: A Collection of Readings. Emerson RM, editor. Waveland Press: Prospect Heights, IL; 1983. The grounded theory method: an explication and interpretation; pp. 109–126. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chesler MA. Professionals' Views of the Dangers of Self-Help Groups: Explicating a Grounded Theoretical Approach. [Michigan]: Department of Sociology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbour Centre for Research on Social Organisation, Working Paper Series; 1987. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kearney MH. Ready-to-wear: discovering grounded formal theory. Res Nurs Health. 1988; 21 :179–186. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-240X(199804)21:2<179::AID-NUR8>3.0.CO;2-G. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Meth. 2008; 8 :45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-8-45. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lucas PJ, Arai L, Baird, Law C, Roberts HM. Worked examples of alternative methods for the synthesis of qualitative and quantitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Meth. 2007; 7 (4) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harden A, Garcia J, Oliver S, Rees R, Shepherd J, Brunton G, Oakley A. Applying systematic review methods to studies of people's views: an example from public health research. J Epidemiol Community H. 2004; 58 :794–800. doi: 10.1136/jech.2003.014829. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paterson BL, Thorne SE, Canam C, Jillings C. Meta-Study of Qualitative Health Research. A Practical Guide to Meta-Analysis and Meta-Synthesis. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao S. Metatheory, metamethod, meta-data-analysis: what, why and how? Sociol Perspect. 1991; 34 :377–390. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritzer G. Metatheorizing in Sociology. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books; 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) http://www.phru.nhs.uk/Pages/PHD/CASP.htm date unknown.
- Greenhalgh T, Robert G, Macfarlane F, Bate P, Kyriakidou O, Peacock R. Storylines of research in diffusion of innovation: a meta-narrative approach to systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2005; 61 :417–30. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.12.001. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn TS. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixon-Woods M, Cavers D, Agarwal S, Annandale E, Arthur A, Harvey J, Hsu R, Katbamna S, Olsen R, Smith L, Riley R, Sutton AJ. Conducting a critical interpretive synthesis of the literature on access to healthcare by vulnerable groups. BMC Med Res Meth. 2006; 6 (35) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gough D. In: Applied and Practice-based Research. 2. Furlong J, Oancea A, editor. Vol. 22. Special Edition of Research Papers in Education; 2007. Weight of evidence: a framework for the appraisal of the quality and relevance of evidence; pp. 213–228. [ Google Scholar ]
- Webb EJ, Campbell DT, Schwartz RD, Sechrest L. Unobtrusive Measures. Chicago: Rand McNally; 1966. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK. The Research Act: a Theoretical Introduction to Sociological Methods. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1978. [ Google Scholar ]
- Banning J. Ecological Triangulation. http://mycahs.colostate.edu/James.H.Banning/PDFs/Ecological%20Triangualtion.pdf
- Banning J. Ecological Sentence Synthesis. http://mycahs.colostate.edu/James.H.Banning/PDFs/Ecological%20Sentence%20Synthesis.pdf
- Brunton G, Oliver S, Oliver K, Lorenc T. A Synthesis of Research Addressing Children's, Young People's and Parents' Views of Walking and Cycling for Transport. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Oliver S, Rees R, Clarke-Jones L, Milne R, Oakley A, Gabbay J, Stein K, Buchanan P, Gyte G. A multidimensional conceptual framework for analysing public involvement in health services research. Health Expect. 2008; 11 :72–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-7625.2007.00476.x. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Qualitative research in health care: analysing qualitative data. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie J, Spencer L. In: Analysing Qualitative Data. Bryman A, Burgess R, editor. London: Routledge; 1993. Qualitative data analysis for applied policy research; pp. 173–194. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles M, Huberman A. Qualitative Data Analysis. London: Sage; 1984. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans D, Fitzgerald M. Reasons for physically restraining patients and residents: a systematic review and content analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2002; 39 :739–743. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7489(02)00015-9. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suikkala A, Leino-Kilpi H. Nursing student-patient relationships: a review of the literature from 1984–1998. J Adv Nurs. 2000; 33 :42–50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2001.01636.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weed M. 'Meta-interpretation': a method for the interpretive synthesis of qualitative research. Forum: Qual Soc Res. 2005; 6 :Art 37. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gough D, Thomas J. Dimensions of difference in systematic reviews. http://www.ncrm.ac.uk/RMF2008/festival/programme/sys1
- Spencer L, Ritchie J, Lewis J, Dillon L. Quality in Qualitative Evaluation: a Framework for Assessing Research Evidence. London: Government Chief Social Researcher's Office; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Banning J. Design and Implementation Assessment Device (DIAD) Version 0.3: A response from a qualitative perspective. http://mycahs.colostate.edu/James.H.Banning/PDFs/Design%20and%20Implementation%20Assessment%20Device.pdf
- Paterson BL. In: Reviewing Research Evidence for Nursing Practice. Webb C, Roe B, editor. [Oxford]: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2007. Coming out as ill: understanding self-disclosure in chronic illness from a meta-synthesis of qualitative research; pp. 73–83. [ Google Scholar ]

Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design (2020)
Chapter: chapter 2 - literature review and synthesis.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
4 Literature Review and Synthesis Literature Review Purpose of Literature Review Performance-based seismic design (PBSD) for infrastructure in the United States is a developing field, with new research, design, and repair technologies; definitions; and method- ologies being advanced every year. A synthesis report, NCHRP Synthesis 440: Performance- Based Seismic Bridge Design (Marsh and Stringer 2013), was created to capture PBSD understanding up to that point. This synthesis report described the background, objec- tives, and research up until 2011 to 2012 and synthesized the information, including areas where knowledge gaps existed. The literature review in this research report focuses on new infor mation developed after the efforts of NCHRP Synthesis 440. The intention is that this research report will fuel the next challenge: developing a methodology to implement PBSD for bridge design. Literature Review Process Marsh and Stringer (2013) performed an in-depth bridge practice review by sending a questionnaire to all 50 states, with particular attention to regions with higher seismic hazards. The survey received responses from a majority of those agencies. This process was continued in the current project with a request for new information or research that the state depart- ment of transportation (DOT) offices have participated in or are aware of through other organizations. The research team reached out to the list of states and researchers in Table 1. An X within a box is placed in front of their names if they responded. The team also examined the websites of the state DOTs that participated to investigate whether something was studied locally, especially work being developed in California. The research team made an additional effort to perform a practice review of bridge designs, research, and other design industries, specifically in the building industry. The building industry has been developing PBSD for more than 20 years, and some of their developments are appli- cable to bridge design. These combined efforts have allowed the research team to assemble an overview of the state of PBSD engineering details and deployment since Marsh and Stringerâs (2013) report was published. NCHRP Synthesis 440 primarily dealt with the effects of strong ground motion shaking. Secondary effects such as tsunami/seiche, ground failure (surface rupture, liquefaction, or slope failure), fire, and flood were outside the scope of this study. Regardless, their impact on bridges may be substantial, and investigation into their effects is undoubtedly important. C H A P T E R 2
Literature Review and Synthesis 5 The following e-mail was sent to the owners and researchers. Dear (individual): We are assisting Modjeski & Masters with the development of proposed guidelines for Performance- Based Seismic Bridge Design, as part of NCHRP [Project] 12-106. Lee Marsh and our Team at BergerABAM are continuing our efforts from NCHRP Synthesis 440, which included a literature review up to December of 2011. From this timeframe forward, we are looking for published research, contractual language, or owner documents that deal with the following categories: 1. Seismic Hazards (seismic hazard levels, hazard curves, return periods, geo-mean vs. maximum direc- tion, probabilistic vs. deterministic ground motions, conditional mean spectrum, etc.) 2. Structure Response (engineering design parameters, materials and novel columns, isolation bearings, modeling techniques, etc.) 3. Damage Limit States (performance descriptions, displacement ductility, drift ratios, strain limits, rotation curvature, etc.) 4. Potential for Loss (damage descriptions, repairs, risk of collapse, economical loss, serviceability loss, etc.) 5. Performance Design Techniques (relating hazard to design to performance to risk, and how to assess [these] levels together) If you are aware of this type of resource, please provide a contact that we can work with to get this information or provide a published reference we can gather. Your assistance is appreciated. We want to minimize your time, and ask that you respond by Wednesday, 8 February 2017. Thank you again, Research Team Synthesis of PBSD (2012â2016) Objectives of NCHRP Synthesis 440 The synthesis gathered data from a number of different but related areas. Marsh and Stringer (2013), herein referred to as NCHRP Synthesis 440, set the basis for this effort. The research report outline follows what has been added to the NCHRP Synthesis 440 effort since 2012. The information gathered that supplements NCHRP Synthesis 440 includes, but is not limited to, the following topics. ⢠Public and engineering expectations of seismic design and the associated regulatory framework Participation State Alaska DOT Arkansas DOT California DOT (Caltrans) Illinois DOT Indiana DOT Missouri DOT Montana DOT Nevada DOT Oregon DOT South Carolina DOT Utah DOT Washington State DOT Table 1. List of state DOT offices and their participation.
6 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design ⢠Seismic hazard analysis ⢠Structural analysis and design ⢠Damage analysis ⢠Loss analysis ⢠Organization-specific criteria for bridges ⢠Project-specific criteria Where new or updated information is available for these areas, a summary is included. Marsh and Stringer (2013) also identified gaps in the knowledge base of PBSD, current as of 2012, that need to be closed. Knowledge gaps certainly exist in all facets of PBSD; however, key knowledge gaps that should be closed in order to implement PBSD are covered. ⢠Gaps related to seismic hazard prediction ⢠Gaps related to structural analysis ⢠Gaps related to damage prediction ⢠Gaps related to performance ⢠Gaps related to loss prediction ⢠Gaps related to regulatory oversight and training ⢠Gaps related to decision making These knowledge gaps have been filled in somewhat in this research report but, for the most part, these areas are still the key concepts that require additional development to further the development of a PBSD guide specification. Public and Engineering Expectations of Seismic Design and the Associated Regulatory Framework The public expectation of a structure, including a bridge, is that it will withstand an earthquake, but there is a limited understanding of what that actually means. Decision makers struggle to understand how a bridge meeting the current requirements of the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (2011), herein referred to as AASHTO guide specifications, will perform after either the expected (design) or a higher level earthquake. Decision makers understand the basis of life safety, wherein the expectation is that no one will perish from a structure collapsing, but often mistakenly believe that the structure will also be usable after the event. In higher level earthquakes, even in some lower level events, this is not true without repair, retrofit, or replacement. In the past decade, there has been an increased awareness by owners and decision makers as to the basis of seismic design. As a result, a need has developed for performance criteria so that economic and social impacts can be interwoven with seismic design into the decision processes (see Figure 1). Several states, including California, Oregon, and the State of Washington, are working toward resiliency plans, although these are developed under different titles or programs within the states. Resiliency has been defined in several ways: (1) amount of damage from an event measured in fatalities, structural replacement cost, and recovery time and (2) the time to resto- ration of lifelines, reoccupation of homes and structures, and, in the short term, resumption of normal living routines. The California DOT Caltrans has generated risk models and is in the process of developing a new seismic design specification to address PBSD in bridge design. The risk models and specifications are not published yet, but the use in PBSD is discussed in greater detail later in this chapter.
Literature Review and Synthesis 7 The State of Washington The State of Washingtonâs resiliency plan, outlined in Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012), works to identify actions and policies before, during, and after an earthquake event that can leverage existing policies, plans, and initiatives to realize disaster resilience within a 50-year life cycle. The hazard level used for trans- portation planning is the 1000 year event. The goals for transportation systems vary depending on the type of service a route provides, as shown in following components of the plan. For major corridors such as Interstates 5, 90, and 405 and floating bridges SR 520, I-90, and Hood Canal, the target timeframe for response and recovery is between 1 to 3 days and 1 to 3 months, depending on location. The current anticipated timeframe based on current capacity and without modifications is between 3 months to 1 year and 1 to 3 years, depending on location. The actual response and recovery time will depend on a number of factors. For example: 1. The number of Washington State DOT personnel who are able to report to work may be limited by a variety of circumstances, including where personnel were at the time of the earthquake and whether they sustained injuries. 2. Bridges and roadways in earthquake-affected areas must be inspected. How long this takes will depend on the number and accessibility of the structures and the availability of qualified inspectors. 3. Some bridges and segments of road may be rendered unusable or only partially usable as a result of the earthquake or secondary effects. The response and recovery timeframe will depend on the number, the location, and the extent of the damage. 4. Certain earthquake scenarios could result in damage to the Ballard Locks and cause the water level in Lake Washington to drop below the level required to operate the floating bridges. 5. Depending on the scenario and local conditions, liquefaction and slope failure could damage both interstates and planned detours. During the first 3 days after the event, the Washington State Department of Transportation (Washington State DOT) will inspect bridges and begin repairs as needed. Washington State DOTâs first priority will be to open key routes for emergency response vehicles. Subsequent phases of recovery will include setting up detours where necessary and regulating the type and Figure 1. PBSD decision-making process (Guidelines Figure 2.0-1). References to guidelines figures and tables within parentheses indicate the proposed AASHTO guidelines.
8 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design volume of traffic, to give the public as much access as possible while damaged roads and bridges are repaired. For major and minor arterials, which encompass arterial roadways (including bridges) other than the interstates (so therefore includes state highways and many city and county roads), the target timeframe for response and recovery is between 0 to 24 hours and 3 months to 1 year, depending on location; the percentage of roadways that are open for use will increase over this period. Anticipated timeframe based on current capacity is between 1 week to 1 month and 1 to 3 years, depending on location; the percentage of roadways that are open for use will increase over this period. The goal of Washington State Emergency Management Councilâs resiliency plan is to establish a means to coordinate agencies, publicâprivate partnerships, and standards toward these resiliency goals. The plan outlines goals for recovery times for transportation systems in terms of hours, days, weeks, months, and years, with targets to achieve different levels of recovery (see Table 2) as follows. Similar recovery timeframe processes were established for service sectors (e.g., hospitals, law enforcement, and education); utilities; ferries, airports, ports, and navigable waterways; mass transit; and housing. The overall resiliency plan also discusses the degree to which the recovery of one component or sector would depend on the restoration of another. The key interdependencies that the participants identified include information and communication technologies, transportation, electricity, fuel, domestic water supplies, wastewater systems, finance and banking, and planning and community development. It appears that the implementation of the Washington State Emergency Management Councilâs initiative, originally assumed to take 2.5 to 3 years in 2012, has not seen significant development since then. However, the Stateâs initiative to develop a more resilient community has been extended down to the county level, with King Countyâs efforts referenced in Rahman et al. (2014) and, at the city level, with the City of Seattle referenced in CEMP (2015). This reflects the commitment needed not only by the legislature and the state departments but also by other agencies (e.g., county, city, or utilities) and the public to take an interest in, and provide funding for, the development of a resiliency plan. The recovery continuum is presented graphically in Figure 2. Developing this relationship with other agency plans is an iterative process that will take time, as shown in Figure 3. Identifying the critical sectors of the agency is necessary to develop a resiliency model and determine how to approach a disaster recovery framework. King County worked from Washington Stateâs initiative to develop Figure 4. The Oregon DOT Oregon DOT has developed a variation of the approach identified by the State of Wash- ington; further discussion is found later in this chapter. Other Resilience Documents The building industry has recently seen the development of two additional documents that address PBSD in terms of expectations and process. The REDi Rating System from REDi (2013) sets an example for incorporating resilience- based design into the PBSD process. This document outlines structural resilience objectives for organizational resilience, building resilience, loss assessment, and ambient resilience to evaluate and rate the decision making and design methodology using PBSD for a specific project.
Literature Review and Synthesis 9 The document is one of the only references that addresses a system to develop probabilistic methods to estimate downtime. The overall intent is to provide a roadmap to resilience. This roadmap is intended to allow owners to resume business operation and to provide livable conditions quickly after an earthquake. The Los Angeles Tall Buildings Structural Design Council (LATBSDC 2014) created an alter- native procedure specific to their location. Design specification criteria are identified and modi- fications are described as appropriate for the PBSD approach to tall buildings in this localized Minimal (A minimum level of service is restored, primarily for the use of emergency responders, repair crews, and vehicles transporting food and other critical supplies.) Functional (Although service is not yet restored to full capacity, it is sufficient to get the economy moving againâfor example, some truck/freight traffic can be accommodated. There may be fewer lanes in use, some weight restrictions, and lower speed limits.) Operational (Restoration is up to 80 to 90 percent of capacity: A full level of service has been restored and is sufficient to allow people to commute to school and to work.) Time needed for recovery to 80 to 90 percent operational given current conditions. Source: Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012). Table 2. Washington Stateâs targets of recovery.
10 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Source: Adapted from FHWA by CEMP (2015). Figure 2. Recovery continuum process. Source: CEMP (2015). Figure 3. Relationship of disaster recovery framework to other city plans. region. This procedure is a good example of how PBSD criteria and methodology need to be established locally, with a knowledge of risk, resources, and performance needs in order to set the criteria for true PBSD. Seismic Hazard Prediction As outlined in NCHRP Synthesis 440, the seismic hazard includes the regional tectonics and the local site characteristics from either a deterministic or probabilistic viewpoint. The deterministic form allows the assessment of shaking at a site as a function of the controlling earthquake that can occur on all the identified faults or sources. The probabilistic approach
Literature Review and Synthesis 11 defines an acceleration used in design that would be exceeded during a given window of time (e.g., a 7% chance of exceedance in 75 years). The following subsections provide a summary of procedures currently used within AASHTO, as well as new issues that should be eventually addressed in light of approaches used by the building industry. AASHTO Probabilistic Approach As summarized in the AASHTO guide specifications, the current approach used by AASHTO involves the use of a probabilistic hazard model with a nominal return period of 1000 years. Baker (2013) noted that the probabilistic seismic hazard analysis involves the following five steps: 1. Identify all earthquake sources capable of producing damaging ground motions. 2. Characterize the distribution of earthquake magnitudes (the rates at which earthquakes of various magnitudes are expected to occur). 3. Characterize the distribution of source-to-site distances associated with potential earthquakes. 4. Predict the resulting distribution of ground motion intensity as a function of earthquake magnitude, distance, and so forth. 5. Combine uncertainties in earthquake size, location, and ground motion intensity, using a calculation known as the total probability theorem. While implementation of the five steps in the probabilistic approach is beyond what most practicing bridge engineers can easily perform, AASHTO, working through the U.S. Geological Survey, developed a website hazard tool that allows implementation of the probabilistic proce- dure based on the latitude and longitude of a bridge site. The product of the website includes peak ground acceleration (PGA), spectral acceleration at 0.2 s (Ss), and spectral acceleration at 1 s (S1). These values are for a reference-site condition comprising soft rock/stiff soil, having a time-averaged shear wave velocity (Vs) over the upper 100 feet of soil profile equal to 2500 feet per second (fps). The Geological Survey website can also correct for local site conditions following procedures in the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design. One of the limitations of the current U.S. Geological Survey hazard website is that it is based on a seismic hazard model developed in 2002. The Geological Survey updated its seismic model in 2008 and then in 2014; however, these updates are currently not implemented within the AASHTO hazard model on the Geological Surveyâs website. Oregon and the State of Washington have updated the seismic hazard map used by the Oregon DOT and the Washington State Source: Rahman et al. (2014). Figure 4. Resilient King County critical sectors and corresponding subsectors.
12 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design DOT to include the 2014 U.S. Geological Survey hazard model; however, most state DOTs are still using the out-of-date hazard model. Use of the outdated hazard model introduces some inconsistencies in ground motion prediction, relative to the current Geological Survey hazard website tool at some locations. Discussions are ongoing between NCHRP and the U.S. Geological Survey to update the 2002 website tool. Another issue associated with the current AASHTO probabilistic method is that it is based on the geomean of the ground motion. In other words, the ground motion prediction equations in the hazard model are based on the geomean of recorded earthquake motions. These motions are not necessarily the largest motion. The building industry recognized that the maximum direction could result in larger ground motions and introduced maximum direction corrections. These corrections increase spectral acceleration by a factor of 1.1 and S1 by a factor of 1.3. The relevance of this correction to bridges is discussed in the next subsection of this review. The building industry also introduced a risk-of-collapse correction to the hazard model results. This correction is made to Ss and S1. The size of the correction varies from approximately 0.8 to 1.2 within the continental United States. It theoretically adjusts the hazard curves to provide a 1% risk of collapse in 50 years. The risk-of-collapse corrections were developed by the U.S. Geological Survey for a range of building structures located throughout the United States. Although no similar corrections have been developed for bridges, the rationale for the adjust- ment needs to be further evaluated to determine if the rationale should be applied to bridge structures. As a final point within this discussion of probabilistic methods within the AASHTO guide specifications, there are several other areas of seismic response that need to be considered. These include near-fault and basin effects on ground motions, as well as a long-period transition factor. The near-fault and basin adjustments correct the Ss and S1 spectral accelerations for locations near active faults and at the edge of basins, respectively. These adjustments typically increase spectral accelerations at longer periods (> 1 s) by 10% to 20%, depending on specifics of the site. The long-period transition identifies the point at which response spectral ordinates are no longer proportional to the 1/T decay with increasing period. These near-fault, basin, and long-period adjustments have been quantified within the building industry guidance documents but remain, for the most part, undefined within the AASHTO guide specifications. As bridge discussions and research move closer to true probabilistic format for PBSD, these issues need to be addressed as part of a future implementation process. Correction for Maximum Direction of Motion Over the last decade, a debate has been under way within the building industry regarding the appropriate definition of design response spectra (Stewart et al. 2011). The essence of the argument relates to the representation of bidirectional motion via response spectra. In both the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (2014), as well as the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (SGS), response spectra are established by defining spectral ordinates at two or three different periods from design maps developed by the U.S. Geological Survey for a return period of 1000 years. The resulting spectra are then adjusted for local site conditions, resulting in the final design spectra. In establishing the design maps for parameters such as Ss and S1, the U.S. Geological Survey has traditionally relied upon probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, which utilizes ground motion prediction equations (GMPEs) defined by the geometric mean of the two principal directions of recorded motion. In 2006, Boore introduced a new rotation independent geometric mean definition termed GMRotI50 (Boore et al. 2006). Then, in 2010, Boore developed a new defini- tion that does not rely upon the geometric mean termed RotD50 spectra, which can be generi- cally expressed as RotDNN spectra, where NN represents the percentile of response (i.e., 50 is
Literature Review and Synthesis 13 consistent with the median, 0 is the minimum, and 100 is the maximum). The NGAâWest2 project GMPEs utilized RotD50 spectra for the ground motion models; however, the 2009 National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program (NEHRP) provisions adopted a factor to modify the median response, RotD50, to the maximum possible response, RotD100 as the spectra for the design maps (Stewart et al. 2011). Introducing RotD100 resulted in a 10% to 30% increase in spectral ordinates results relative to the geometric mean, which has traditionally been used as a basis of seismic design. In order to appreciate the impact of these choices, a brief discussion of RotDNN spectra is warranted. As described in Boore (2010), for a given recording station, the two orthogonal- component time series are combined into a single time series corresponding to different rotation angles, as shown in Equation 1: aROT(t ; θ) = a1(t)cos(θ) + a2(t)sin(θ) (1) where a1(t ) and a2(t ) are the orthogonal horizontal component acceleration time series and θ is the rotation angle. For example, consider the two orthogonal horizontal component time series, H1 and H2, shown in Figure 5. The single time series corresponding to the rotation angle θ is created by combining the Direction 1 and Direction 2 time series. Then, the response spectrum for that single time series can be obtained, as shown in the figure. The process is repeated for a range of azimuths from 0° to one rotation-angle increment less than 180°. If the rotation-angle increment is θ, then there will be 180/θ single time series, as well as 180/θ corresponding response spectra. For example, if θ = 30°, then there will be six single time series (the original two, as well as four generated time series), as well as six response spectra, as shown in Figure 6. Once the response spectra for all rotation angles are obtained, then the nth percentile of the spectral amplitude over all rotation angles for each period is computed (e.g., RotD50 is the median value and RotD100 is the largest value for all rotation angles). For example, at a given period of 1 s, the response spectra values for all rotation angles are sorted, and the RotD100 value would be the largest value from all rotation angles while RotD50 would be the median. This is repeated for all periods, with potentially different rotation angles, producing the largest Source: Palma (2019). Figure 5. Combination of time series to generate rotation dependent spectra.
14 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design response at any given period (period-dependent rotation angle.) Figure 7 shows an example of the two orthogonal horizontal components, as well as the RotD50 and RotD100 spectra for the as-recorded ground motion from the 2011 Christchurch, New Zealand, earthquake at Kaiapoi North School station. As can be seen in the sample spectra (see Figure 7), the RotD100 spectrum represents a sub- stantial increase in demand when compared with the RotD50 spectrum. The main question facing the bridge community from this point onward is the appropriate selection of response spectra definition. This question can only be answered by developing sample designs to both the RotD50 and RotD100 spectra, which would then be evaluated via no-linear time history analysis. Such a study will require multiple bridge configurations and multiple ground motions. As an example of the potential impact, Figure 8 shows the results of a single-degree-of- freedom bridge column designed according to both RotD50 and RotD100 spectra, along with the resulting nonlinear time history analysis. The column was designed using direct displacement- based design to achieve a target displacement of 45 cm. It is clear from the results in Figure 8d that the nonlinear response of the column designed to the RotD100 spectrum matches the target Source: Palma (2019). Figure 6. Example of time series rotations with an angle increment (p) of 30ç. Source: Palma (2019). Figure 7. Sample spectra for a recorded ground motion pair.
Literature Review and Synthesis 15 reasonably well, while designing to the RotD50 spectrum results in displacements that are much greater than expected. This is, of course, only one result of an axisymmetric system. In the future (and outside the scope of this project), a systematic study could be conducted for both single degree of freedom and multiple degrees of freedom systems. The literature on this topic can be divided into two categories: (1) response spectra definitions and (2) impact on seismic response. The majority of the literature addresses the former. For example, Boore et al. (2006) and Boore (2010) introduced orientation-independent measures of seismic intensity from two horizontal ground motions. Boore et al. (2006) proposed two measures of the geometric mean of the seismic intensity, which are independent of the in-situ orientations of the sensors. One measure uses period-dependent rotation angles to quantify the spectral intensity, denoted GMRotDnn. The other measure is the GMRotInn, where I stands for period-independent. The ground motion prediction equations of Abrahamson and Silva (1997), Figure 8. Single bridge column designed according to both RotD50 and RotD100 spectra (Tabas EQ = Tabas earthquake and displ. = displacement).
16 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Boore et al. (1997), Campbell and Bozorgnia (2003), and Sadigh et al. (1997) have been updated using GMRotI50 as the dependent variable. Since more users within the building industry expressed the desire to use the maximum spec- tral response over all the rotation angles without geometric means, Boore (2010) introduced the measures of ground-shaking intensity irrespective of the sensor orientation. The measures are RotDnn and RotInn, whose computation is similar to GMRotDnn and GMRotInn without computing the geometric means. With regard to impact on seismic response, the opinion paper by Stewart et al. (2011) and the work by Mackie et al. (2011) on the impact of incidence angle on bridge response are relevant. Specifically, Stewart et al. (2011) noted the importance of computational analysis of structures (which had not been done as of 2011) in proposing appropriate spectra definitions. Other Methodologies for Addressing Seismic Ground Motion Hazards There are several other reports that address the question of the methodology that may be utilized in developing the seismic hazard. These recent studies endeavored to create a method- ology that is easier for engineers, as users, to understand how to tie the seismic hazard to the performance expectation. The variability of these approaches also demonstrates the broad range of options and therefore a limited understanding by practitioners in the bridge design industry. Following are some examples that apply to PBSD. Wang et al. (2016) performed a probabilistic seismic risk analysis (SRA) based on a single ground motion parameter (GMP). For structures whose responses can be better predicted using multiple GMPs, a vector-valued SRA (VSRA) gives accurate estimates of risk. A simplified approach to VSRA, which can substantially improve computational efficiency without losing accuracy, and a new seismic hazard de-aggregation procedure are proposed. This approach and the new seismic hazard de-aggregation procedure would allow an engineer to determine a set of controlling earthquakes in terms of magnitude, sourceâsite distance, and occurrence rate for the site of interest. Wang et al. presented two numerical examples to validate the effectiveness and accuracy of the simplified approach. Factors affecting the approximations in the simplified approach were discussed. Kwong and Chopra (2015) investigated the issue of selecting and scaling ground motions as input excitations for response history analyses of buildings in performance-based earthquake engineering. Many ground motion selection and modification procedures have been developed to select ground motions for a variety of objectives. This report focuses on the selection and scaling of single, horizontal components of ground motion for estimating seismic demand hazard curves of multistory frames at a given site. Worden et al. (2012) used a database of approximately 200,000 modified Mercalli intensity (MMI) observations of California earthquakes collected from U.S. Geological Survey reports, along with a comparable number of peak ground motion amplitudes from California seismic networks, to develop probabilistic relationships between MMI and peak ground velocity (PGV), PGA, and 0.3-s, 1-s, and 3-s 5% damped pseudo-spectral acceleration. After associating each ground motion observation with an MMI computed from all the seismic responses within 2 kilometers of the observation, a joint probability distribution between MMI and ground motion was derived. A reversible relationship was then derived between MMI and each ground motion parameter by using a total least squares regression to fit a bilinear function to the median of the stacked probability distributions. Among the relationships, the fit-to-peak ground velocity has the smallest errors, although linear combinations of PGA and PGV give nominally better results. The magnitude and distance terms also reduce the overall residuals and are justifiable on an information theoretical basis.
Literature Review and Synthesis 17 Another approach to developing the appropriate seismic hazard comes out of Europe. Delavaud et al. (2012) presented a strategy to build a logic tree for ground motion prediction in European countries. Ground motion prediction equations and weights have been determined so that the logic tree captures epistemic uncertainty in ground motion prediction for six different tectonic regions in Europe. This includes selecting candidate GMPEs and simultaneously running them through a panel of six experts to generate independent logic trees and rank the GMPEs on available test data. The collaboration of this information is used to set a weight to the GMPEs and create a consensus logic tree. This output then is run through a sensitivity analysis of the proposed weights on the seismic hazard before setting a final logic tree for the GMPEs. Tehrani and Mitchell (2014) used updated seismic hazard maps for Montreal, Canada to develop a uniform hazard spectra for Site Class C and a seismic hazard curve to analyze bridges in the localized area. Kramer and Greenfield (2016) evaluated three case studies following the 2011 Tohoku earthquake to better understand and design for liquefaction. Existing case history databases are incomplete with respect to many conditions for which geotechnical engineers are often required to evaluate liquefaction potential. These include liquefaction at depth, liquefaction of relatively dense soils, and liquefaction of gravelly soils. Kramer and Greenfieldâs investigation of the three case histories will add to the sparse existing data for those conditions, and their interpretations will aid in the validation and development of predictive procedures for liquefaction potential evaluation. Structural Analysis and Design Predicting the structural response to the earthquake ground motions is critical for the PBSD process. NCHRP Synthesis 440 outlined several analysis methods that can be used to accomplish this task. The multimodal linear dynamic procedures are outlined in AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014) and AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011), although the Guide Specifications also include the parameters for performing a model pushover analysis in addition to prescriptive detail practices to ensure energy-dissipating systems behave as intended and other elements are capacity-protected. Other methods of analysis may be better suited for PBSD, but the initial PBSD approach will likely follow the procedures of the AASHTO guide specifications, with multi-level hazards and performance expectations. Limited research and code development have been accomplished since NCHRP Synthesis 440, but one new analysis method, outlined in Babazadeh et al. (2015), includes a three-dimensional finite element model simulation that is used to efficiently predict intermediate damage limit states in a consistent manner, with the experimental observations extracted from the actual tested columns. Other recent articles of structural analysis identified areas of improvement in the current design methodology that may be beneficial to PBSD. Huff and Pezeshk (2016) compared the substitute structure method methodology for isolated bearings with the displacement-based design methodology for ordinary bridges and showed that these two methodologies vary in estimating inelastic displacements. Huff (2016a) identified issues that are generally simplified or ignored in current practice of predicting inelastic behavior of bridges during earthquakes, both on the capacity (in the section of the element type and geometric nonlinearities) and demand (issues related to viscous dampening levels) sides of the process. The current SGS methodology for nonlinear static procedures were compared in Hajihashemi et al. (2017) with recent methodologies for multimodal pushover procedures that take into account all significant modes of the structure and with modified equivalent linearization procedures developed for
18 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design FEMA-440 (FEMA 2005). All of these analysis articles identify areas of current discussion on how to improve the analytical procedures proposed in the SGS. NCHRP Synthesis 440 focused primarily on new analysis methods, but a recent increased focus, in both academia and industry, has to do with new materials and systems and their impacts on PBSD. The evolution of enhanced seismic performance has been wrapped into several research topics, such as accelerated bridge construction (ABC), novel columns, and PBSD. The following are several aspects, though not all-encompassing, which have been improved upon in the last 6 years or so. Improving Structural Analysis Through Better Material Data The analysis and performance of a bridge are controlled with material property parameters incorporated into the seismic analysis models, specifically for the push-over analysis method. AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011) specifies the strain limits to use for ASTM A706 (Grade 60) and ASTM A615 Grade 60 reinforcement. These strain limits come from Caltrans study of 1,100 mill certificates for ASTM A706 Grade 60 in the mid-1990s for projects in Caltrans bridge construction. The results were reported as elongationânot strainâat peak stress, so select bar pull tests were performed to correlate elongation to strain at peak stress. This was assumed to be a conservative approach, though it has recently been validated with a new ASTM A706 Grade 80 study at North Carolina State University by Overby et al. (2015a), which showed Caltrans numbers, by comparison, for Grade 60 are reasonable and conservative. Overby et al. (2015b) developed stress strain parameters for ASTM A706 Grade 80 reinforcing steel. Approximately 800 tests were conducted on bars ranging from #4 to #18 from multiple heats from three producing mills. Statistical results were presented for elastic modulus, yield strain and stress, strain-hardening strain, strain at maximum stress, and ultimate stress. Research is currently under way at North Carolina State University that aims to identify strain limit states, plastic hinge lengths, and equivalent viscous damping models for bridge columns constructed from A706 Grade 80 reinforcing steel. Work is also under way at the University of California, San Diego, on applications of Grade 80 rebar for capacity-protected members such as bridge cap beams. Design Using New Materials and Systems Structural analysis and design are fundamentally about structural response to the earthquake ground motion and the analysis methods used to develop this relationship. The complexity of the analysis depends on the geometry of the structure and elements and the extent of inelastic behavior. This is coupled with the damage, or performance criteria but has been broken out for the purposes of this report and NCHRP Synthesis 440. Next generation bridge columns, often referred to as novel columns, are improving as a tool for engineers to control both the structural analysis, as the make-up of the material changes the inelastic behavior, and the element performance of bridges in higher seismic hazards. The energy-dissipating benefits of low damage materialsâsuch as ultrahigh-performance concrete (UHPC), engineered cementi- tious composites (ECC), and shape memory alloy, fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) wraps and tubes, elastomeric bearings, and post-tensioned strands or barsâcan be utilized by engineers to improve seismic performance and life-cycle costs after a significant seismic event. Recent (Saiidi et al. 2017) studies tested various combinations of these materials to determine if there are columns that can be built with these materials that are equivalent to, or better than, conventional reinforced concrete columns (in terms of cost, complexity, and construction duration) but that improve seismic performance, provide greater ductility, reduce damage, and accommodate a quicker recovery time and reduce loss in both the bridge and the economic environment.
Literature Review and Synthesis 19 Accelerated bridge construction is also a fast-developing field in bridge engineering, with draft guide specifications for design and construction currently being developed for adop- tion by AASHTO for AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). ABC has economic impacts that go beyond seismic engineering, but research is focusing on details and connections for accelerated construction in higher seismic regions, moving two research paths forward at the same time. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) incorporated ABC research with novel column research to evaluate combined novel column materials that can be constructed quickly. The research focused on the performance of materials and how to incorporate them into practice. Key mechanical properties of reinforcing SMA were defined as follows: ⢠Observed yield strength (fyo) is the stress at the initiation of nonlinearity on the first cycle of loading to the upper plateau. ⢠Austenite modulus (k1) is the average slope between 15% to 70% of fyo. ⢠Post yield stiffness (k2) is the average slope of curve between 2.5% and 3.5% of strain on the upper plateau of the first cycle of loading to 6% strain. ⢠Austenite yield strength (fy) is the stress at the intersection of line passing through origin with slope of k1 and line passing through stress at 3% strain with slope of k2. ⢠Lower plateau inflection strength (fi) is the stress at the inflection point of lower plateau during unloading from the first cycle to 6% strain. ⢠Lower plateau stress factor, β = 1 â (fi/fy). ⢠Residual strain (eres) is the tensile strain after one cycle to 6% and unloading to 1 ksi (7 MPa). ⢠Recoverable super-elastic strain (er) is maximum strain with at least 90% strain recovery capacity. Using the ASTM standard for tensile testing, er ⤠6%. ⢠Martensite modulus (k3) is the slope of the curve between 8% to 9% strain, subsequent to one cycle of loading to 6% strain, unloading to 1 ksi (7 MPa) and reloading to the ultimate stress. ⢠Secondary post-yield stiffness ratio, α = k3/k1. ⢠Ultimate strain (eu) is strain at failure. A graphical representation is shown in Figure 9, and minimum and expected mechanical properties are listed in Table 3. Other researchers, such as at the University of Washington, are currently testing grouted bars using conventional grouts and finding that these development lengths can be reduced greatly. However, it is the force transfer of the grouted duct to the reinforcing outside the duct that may Figure 9. NiTi SE SMA nonlinear model.
20 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design require additional length to adequately develop the energy-dissipating or capacity-protecting system that was intended by the designer for performance of the bridge in a high seismic event. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) identified other material properties such as UHPC and ECC, shown in Tables 4 and 5, respectively. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) also addressed grouted splice sleeve couplers, self-consolidating concrete (SCC), and other connection types that could be used in ABC and novel column configurations, testing these materials in the laboratory to see if various combinations produced a logical system to be carried forward in research, design, and implementation. Trono et al. (2015) studied a rocking post-tensioned hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete (HyFRC) bridge column that was designed to limit damage and residual drifts and that was tested dynamically under earthquake excitation. The column utilized post-tensioned strands, HyFRC, and a combination of unbonded and headed longitudinal reinforcement. There have been two projects related to the field of novel columns and ABC through the National Cooperative Highway Research Program. One project was NCHRP Project 12-101, which resulted in NCHRP Report 864, 2 volumes (Saiidi et al. 2017), and the other project was NCHRP Project 12-105, which resulted in NCHRP Research Report 935 (Saiidi et al. 2020). NCHRP Project 12-101 identified three novel column systemsâspecifically, SMA and ECC, ECC and FRP, and hybrid rocking column using post-tensioned strands and fiber-reinforced Parameter Tensile Compressive,ExpectedbExpectedbMinimuma Table 3. Minimum expected reinforcing NiTi SE SMA mechanical properties. Properties Range Poissonâs Ratio 0.2 Creep Coefficient* 0.2 to 0.8 Total Shrinkage** *Depends on curing conditions and age of loading. up to 900x10-6 Equation Compressive Strength (f'UHPC) f'UHPC 20 to 30 ksi, (140 to 200 MPa) Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (5.5 to 8.5)x10 -6/°F, (10 to 15)x10-6/°C Specific Creep* (0.04 to 0.3)x10 -6/psi, (6 to 45)x10-6/MPa A time-dependent equation for UHPC strength is available. Tensile Cracking Strength (ft,UHPC) ft,UHPC = 6.7 (psi) f'UHPCEUHPC = 49000 (psi) 0.9 to 1.5 ksi, (6 to 10 MPa) Modulus of Elasticity (EUHPC) 6000 to 10000 ksi, (40 to 70 GPa) **Combination of drying shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage and depends on curing method. Table 4. UHPC mechanical properties.
Literature Review and Synthesis 21 polymer confinementâand compared them to a conventional reinforced column. The research and properties of the material are provided; incorporating laboratory tests and calibration, design examples are created to help engineers understand how to use these advanced materials in a linear elastic seismic demand model and to determine performance using a pushover analysis. It is worth noting that ductility requirements do not accurately capture the perfor- mance capabilities of these novel columns, and drift ratio limits are being used instead, similar to the building industry. NCHRP Project 12-101 also provided evaluation criteria that can be evaluated and incorporated by AASHTO into a guide specification or into AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011) directly. NCHRP Project 12-105 synthesized research, design codes, specifications, and contract language throughout all 50 states and combined the knowledge base and lessons learned for ABC into proposed guide specifications for both design and construction. This work focused on connections, and most of that information is related to seismic performance of ABC elements and systems. Earthquake resisting elements (ERE) and earthquake resisting systems (ERS) are specifically identified, defined, and prescribed for performance in AASHTO guide specifica- tions (AASHTO 2011) but only implicitly applied in AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). Since NCHRP Project 12-105 is applicable to both of these design resources, ERE and ERS are discussed in terms of how to apply performance to the force-based seismic design practice of AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). The proposed guide specification language also identifies when performance of materials have to be incor- porated into the design, say in higher seismic hazards, and when it is acceptable to apply ABC connections and detailing practices with prescriptive design methodologies. As the industryâs understanding of performance increases, the engineering industry is accepting the benefits that come from a more user-defined engineering practice that is implemented by identifying material properties; evaluating hazards and soil and structural responses; and verifying performance through strain limits, damage limits states, moment curvature, displacements, and ductility. These tools and advancements in ABC and novel column designs, including other material property performance and analytical methodologies, are allowing PBSD to advance in other areas, such as hazard prediction, loss prediction, and the owner decision-making process. Feng et al. (2014a) studied the application of fiber-based analysis to predict the nonlinear response of reinforced concrete bridge columns. Specifically considered were predictions of overall force-deformation hysteretic response and strain gradients in plastic hinge regions. The authors also discussed the relative merits of force-based and displacement-based fiber elements and proposed a technique for prediction of nonlinear strain distribution based on the modified compression field theory. Fulmer et al. (2013) developed a new steel bridge system that is based upon ABC techniques that employ an external socket to connect a circular steel pier to a cap beam through the use of grout and shear studs. The resulting system develops a plastic hinge in the pipe away from the column-to-cap interface. An advantage of the design is ease of construction, as no field welding Properties Range Flexural Strength 1.5 to 4.5 ksi (10 to 30 MPa) Modulus of Elasticity 2600 to 5000 ksi (18 to 34 GPa) Ultimate Tensile Strain 1 to 8% Ultimate Tensile Strength 0.6 to 1.7 ksi (4 to 12 MPa) First Crack Strength 0.4 to 1.0 ksi (3 to 7 MPa) Compressive Strength 3 to 14 ksi (20 to 95 MPa) Table 5. ECC mechanical properties.
22 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design is required: the two assemblies are placed together and the annular space between the column and cap filled with grout. Figure 10 shows the details of this connection, and Figure 11 shows a test of the system. Another system being investigated is isolation bearings or dampening devices. Xie and Zhiang (2016) investigated the effectiveness and optimal design of protective devices for the seismic protection of highway bridges. Fragility functions are first derived by probabilistic seismic demand analysis, repair cost ratios are then derived using a performance-based methodol- ogy, and the associated component failure probability. Subsequently, the researchers tried to identify the optimal design parameters of protective devices for six design cases with various combinations of isolation bearings and fluid dampers and discussed the outcomes. Damage mitigation through isolation and energy dissipation devices is continually improving based on research, development, and implementation in the field. Recent events within the State of Washington, Alaska, and other state agencies have shown that the benefits of these tools can be compromised if the intended performance cannot be sustained for the 75-year design life of the structure. Mackie and Stojadinovic (2015) outlined performance criteria for fabrica- tion and construction that need to be administered properly, and engineers should consider the effects of moisture, salts, or other corrosive environmental conditions that can affect the performance of the isolation or energy-dissipating system. Another constraint with these systems can be the proprietary nature that occurs as a specific isolation or energy-dissipating system is utilized to develop a specific performance expectation that can only be accomplished with the prescribed system. This proprietary nature of these systems can create issues for certain funding sources that require equal bidding opportunities and the project expense that can accompany a proprietary system. To address this type of design constraint, Illinois DOT has been developing an earthquake-resisting system (ERS) to leverage the displacement capacity available at typical bearings in order to provide seismic protection to substructures of typical bridges. LaFave et al. (2013a) identified the effects and design parameters, Source: Fulmer et al. (2013). 5" 4 at 5" O.C. A A A-A Connection Details 45° UT 100% 3 8" 12 Studs Spaced Around Cross Section 30°Typ. 15° Offset Studs Inside Pipe from Cap Beam CL HSS16x0.500 Pipe 24x0.500 2'-0"2 14 " 4 at 5" O.C. 212"-34 "à Shear Studs 1'-11" Pipe Stud Detail Grout Provided By and Placed by NCSU Figure 10. Grouted shear stud bridge system.
Literature Review and Synthesis 23 such as fuse capacity, shear response, and sliding response, which can be used to account for more standard bearing configurations in seismic analysis, especially lower seismic hazard regions. A variation on the use of bearings in order to improve seismic performance of a pier wall configuration was outlined in Bignell et al. (2006). Historically, pinned, rocking, and sliding bearings have been used with interior pier walls and steel girder superstructures. These bearing configurations were compared with replacement elastomeric bearing configurations and details for structural analysis techniques, damage limit states, and structural fragility, and performance through probability distributions were utilized as a PBSD process for determining solutions to seismic isolation and enhanced seismic performance. The foundation conditions, pier wall effects, bearing type, and even embankment effects to structural performance were included in this evaluation. Another approach to enhanced performance is modifications to foundation elements or increased understanding and modeling of soilâstructure interaction, specifically where lateral spread or liquefaction design conditions make conventional bridge design and elements imprac- tical. One example of this is the seismic design and performance of bridges constructed with rocking foundations, as evaluated in Antonellis and Panagiotou (2013). This type of rocking goes beyond the loss of contact area currently allowed in the guide specifications. The applica- tion of columns supported on rocking foundations accommodates large deformations, while there is far less damage, and can re-center after large earthquakes. Another approach is to tie a tolerable displacement of an individual deep foundation element to a movement that would cause adverse performance, excessive maintenance issues, or functionality problems with the bridge structure. Roberts et al. (2011) established a performance-based soilâstructureâinteraction design approach for drilled shafts. Chiou and Tsai (2014) evaluated displacement ductility of an in-ground hinging of a fixed head pile. Assessment formulas were developed for the displacement ductility capacity of a fixed-head pile in cohesion-less soils. The parameters in the formulas included the sectional over-strength ratio and curvature ductility capacity, as well as a modification factor for consider- ing soil nonlinearity. The modification factor is a function of the displacement ratio of the pileâs ultimate displacement to the effective soil yield displacement, which is constructed through a number of numerical pushover analyses. Source: Fulmer et al. (2013). Figure 11. Photograph of completed system before seismic testing showing hinge locations.
24 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Damage Analysis As stated in NCHRP Synthesis 440, it is a fundamental need for the PBSD methodology to determine the type of damage and the likelihood that such damage will occur in the particular components of the structural system. This determination is of vital importance, as the damage sustained by a structure (and its nonstructural components) is directly relatable to the use or loss of a system after an earthquake. Therefore, there is a need to be able to reliably link structural and nonstructural response (internal forces, deformations, accelerations, and displacements) to damage. This is the realm of damage analyses, where damage is defined as discrete observable damage states (e.g., yield, spalling, longitudinal bar buckling, and bar fracture). Although the primary focus of the discussions is on structural components, similar considerations must be made for nonstructural components as well. NCHRP Synthesis 440 outlined an initial discussion on types of structural damage observed during historic earthquakes and laboratory experiments, prefaced the methods that have been developed to predict damage, identified structural details and concepts that could be used to reduce damage even in strong ground shaking, and reviewed post-event inspection tools. The new materials discussed in previous sections also apply to this discussion but are not repeated herein. Accurate damage prediction relies upon accurate definitions of performance limit states at the material level (i.e., strain limits) and the corresponding relationship between strain and displacement. Examples of recent research follow. Research by Feng et al. (2014b, 2014c) used finite element analysis validated by experimental test results to develop a model for predicting the tension strain corresponding to bar buckling. The model considers the impact of loading history on the boundary conditions of longitudinal bar restraint provided by the transverse steel. Goodnight et al. (2016a) identified strain limits to initiate bar buckling based on experimental results from 30 column tests (Equation 2). Following additional bidirectional tests on 12 columns, Equation 2 was revised to Equation 3. In addition, strain limit state equations were proposed for the compression strain in concrete to cause spiral yielding (Goodnight et al. 2017a). Goodnight et al. (2016b) also developed a new plastic hinge length model based on the data collected during those tests, which accounts for the actual curvature distribution in RC bridge columns. The revised model separates the strain penetration component from the flexural component while also recognizing that the hinge length for compression is smaller than that for tension. Brown et al. (2015) developed strain limit state (Equation 4) (tube wall local buckling) and equivalent viscous damping equations for reinforced concrete filled steel tubes (RCFSTs). The recommendations of the authors were based upon reversed cyclic tests of 12 RCFSTs of variable D/t (diameter to thickness) ratios. 0.03 700 0.1 (2)bucklingbar f E P f A s s yhe s ce g ε = + Ï â â² 0.032 790 0.14 (3)bucklingbar f E P f A s s yhe s ce g ε = + Ï â â² 0.021 9100 (4)tension buckling D t yε = â ⥠ε
Literature Review and Synthesis 25 where rs = reinforcement ratio, fyhe = expected yield strength of the steel tube (ksi), Es = elastic modulus of steel (ksi), P = axial load (kip), f â²ce = expected concrete strength (ksi), Ag = gross area of concrete (in.2), D = diameter of tube (in.), t = thickness of tube (in.), and ey = yield strain for steel (in./in.). Loss Analysis The PBSD combines the seismic hazard, structural, and damage analysis into a performance matrix that can be estimated into a loss metric. There are many loss metrics that can be used by, and that are important to, stakeholders and decision makers (discussed in detail in NCHRP Synthesis 440), but all these metrics can be boiled down to three main categories: deaths, dollars, and downtime. Bertero (2014) discussed earthquake lessons, in terms of loss, to be considered in both design and construction of buildings. At the beginning of 2010, two large earthquakes struck the Americas. The January 12, 2010, Haiti earthquake with a magnitude 7.0 produced about 300,000 deaths (second by the number of fatalities in world history after the 1556 Shaanxi, China earthquake). A month later, the February 27, 2010, Maule Chilean earthquake with a magnitude 8.8 (an energy release 500 times bigger than that from the Haiti earthquake) produced 500 deaths, most due to the resulting tsunami. However, the Chilean earthquake caused more than $30 billion of direct damage, left dozens of hospitals and thousands of schools nonoperational, and caused a general blackout for several hours, as well as the loss of service of essential communications facilities, crucial to take control of the chaotic after-earthquake situ- ation. Bertero (2014) compared the severity of both earthquakes and comments on their effects to life and the economy of the affected countries, as well as the features of the seismic codes or the absence of codes. An example of risk analysis with PBSD is utilized in Bensi et al. (2011), with the development of a Bayesian network (BN) methodology for performing infrastructure seismic risk assessment and providing decision support with an emphasis on immediate post-earthquake applications. A BN is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of random variables and their probabilistic dependencies. The proposed methodology consists of four major components: (1) a seismic demand model of ground motion intensity as a spatially distributed random field, accounting for multiple sources and including finite fault rupture and directivity effects; (2) a model for seismic performance of point-site and distributed components; (3) models of system performance as a function of component states; and (4) models of post-earthquake decision making for inspection and operation or shutdown of components. The use of the term Bayesian to describe this approach comes from the well-known Bayes rule, attributed to the 18th-century mathematician and philosopher Thomas Bayes: A B AB B B A B A( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( )= =Pr Pr Pr Pr Pr Pr (5) Pr(AB) is the probability of joint occurrence of Events A and B; Pr(A) is the marginal probability of Event A; Pr(A|B) is the conditional probability of Event A, given that Event B
26 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design has occurred; and Pr(B) is the marginal probability of Event B. The quantity Pr(B | A) is known as the likelihood of the observed Event B. Note that the probability of Event A appears on both sides of Equation 5. The Bayes rule describes how the probability of Event A changes given information gained about the occurrence of Event B. For discrete nodes, a conditional probability table is attached to each node that provides the conditional probability mass function (PMF) of the random variable represented by the node, given each of the mutually exclusive combinations of the states of its parents. For nodes without parents (e.g., X1 and X2 in Figure 12), known as root nodes, a marginal probability table is assigned. The joint PMF of all random variables X in the BN is constructed as the product of the conditional PMFs: (6) 1 p x p x Pa xi ii nâ( ) ( )( )= = Bensi et al. (2011) goes on to introduce BN models further and discusses how to incorporate BN-based seismic demand models into bridge design. The BN methodology is applied to modeling of random fields, construction of an approximate transformation matrix, and numer- ical investigation of approximation methods, including a discussion on the effect of correlation approximations on system reliability. Modeling component performance with BNs to capture seismic fragility of point-site components and distributed components, as well as modeling system performance of BNs with both qualitative and conventional methods, is explained. This reference goes on to identify efficient minimal link set (MLS), minimal cut set (MCS) formulations, optimal ordering of efficient MLS and MCS formulations, and heuristic augmen- tation that can be utilized with the BN methodology. Bensi et al. (2011) continues the PBSD process by addressing the owner decision-making process (see more discussion later in the report) and how to incorporate this model into that process. Two example problems are provided utilizing this methodology, including a California high-speed rail system that incorporates the bridge modeling into the example. Similarly, in Tehrani and Mitchell (2014), the seismic performance of 15 continuous four- span bridges with different arrangements of column heights and diameters was studied using incremental dynamic analysis (IDA). These bridges were designed using the Canadian Highway Bridge Design Code provisions (CSA 2006). The IDA procedure has been adopted by some guidelines to determine the seismic performance, collapse capacity, and fragility of buildings. Similar concepts can be used for the seismic assessment of bridges. Fragility curves can be devel- oped using the IDA results to predict the conditional probability that a certain damage state is exceeded at a given intensity measure value. Assuming that the IDA data are lognormally distributed, it is possible to develop the fragility curves at collapse (or any other damage state) by computing only the median collapse capacity and the logarithmic standard deviation of the IDA results for any given damage state. The fragility curves can then be analytically computed using Equation 7 as follows: ln ln (7)50% TOT P failure S x x S a a C( )( ) ( )= = Φ â β     where function F = cumulative normal distribution function, SCa 50% = median capacity determined from the IDA, and βTOT = total uncertainty caused by record-to-record variability, design requirements, test data, and structural modeling. Figure 12. A simple BN.
Literature Review and Synthesis 27 The seismic risk associated with exceeding different damage states in the columns, includ- ing yielding, cover spalling, bar buckling, and structural collapse (i.e., dynamic instability) was predicted. Some simplified equations were derived for Montreal, Quebec, Canada, to estimate the mean annual probability of exceeding different damage states in the columns using the IDA results. Repair and retrofit procedures are linked to loss predictions, as outlined in the FHWAâs retro- fitting manual (Buckle et al. 2006). Several chapters/articles address analysis, methodologies, effects, analytical tools, and costs for retrofit and repairs to mitigate damage or return a structure to a serviceable condition. Zimmerman et al. (2013) is one example, in which numerical techniques and seismic retrofit solutions for shear-critical reinforced concrete columns was investigated, utilizing test data of a reinforced concrete column with widely spaced transverse reinforcement. The study focused on the analysis method of nonlinear trusses and the retrofit option known as supplemental gravity columns, which is an example of how loss prediction and the analysis process are linked and should be iterated through PBSD. Organization-Specific Criteria for Bridges and Project-Specific Criteria NCHRP Synthesis 440 has two sections of criteria: organization-specific criteria for bridges and project-specific criteria. New information for both of these sections since NCHRP Synthesis 440 published is combined. The California DOT (Caltrans) Caltrans is currently updating their Seismic Design Criteria (SDC) to specify requirements to meet the performance goals for newly designed Ordinary Standard and Recovery Standard con- crete bridges. Nonstandard bridges require Project-Specific Seismic Design Criteria, in addition to the SDC, to address their nonstandard features. For both standard and nonstandard bridges, Caltrans is also categorizing their inventory in terms of Ordinary Bridges, Recovery Bridges, and Important Bridges. Some states have had issues with terms like Important or Essential, as a bridge is considered important to those that utilize each bridge. Caltrans is using these terms to correlate with loss analysis of an ownerâs infrastructure and the time to reopen the bridge to support lifeline and recovery corridors. The bridge performance is also evaluated using a dual-seismic hazard; for Caltrans SDC they are listed as a Safety Evaluation Earthquake (SEE) for Ordinary Bridges. Both SEE and Functional Evaluation Earthquake (FEE) for Recovery Bridges are summarized in Table 6. Caltrans SDC revisions will also provide updates to the design parameters in Chapter 3 of the SDC and updates to both the analysis methods and displacement ductility demand values in Chapter 4 of the SDC. The adjustments to the displacement ductility demand values are revised to limit the bridge displacements beyond the initial yielding point of the ERE, specifically if a recovery standard bridge is being designed. The revisions to their SDC is an example of how PBSD is being gradually introduced as a better method of dealing with the hazards, soilâstructure interaction, analysis tools, methodologies, material properties, damage states, performance, and loss. Similar revisions are being made to Seismic Design Specifications of Highway Bridges, as detailed in Japan Road Association (JRA) revisions in 2012. A synopsis of the revisions is provided in Kuwabara et al. (2013). The JRA specifications apply to Japanese road bridges and consist of five parts: Part I, Common; Part II, Steel Bridges; Part III, Concrete Bridges; Part IV, Substruc- tures; and Part V, Seismic Design. The revisions are based on improvements in terms of safety,
28 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design serviceability, and durability of bridges. Based on those lessons, design earthquake ground motions corresponding to the subduction-type earthquake were revised, and the requirements for easy and secure maintenance (inspection and repair works) for the bridges were clearly specified. JRA has clarified their performance of ERE conventionally reinforced columns for a dual-level (SPL 2 and SPL 3) seismic performance evaluation, as summarized in Table 7. The JRA 2012 revisions also address connection failures between reinforced concrete steel piles and the pile-supported spread footing to improve structural detailing and performance at the head of the piles. This is similar to research performed by the University of Washington, see Stephens et al. (2015) and Stephens et al. (2016) for both Caltrans and Washington State DOT, respectively, to evaluate capacity protecting this region and even considering the development of plastic hinges at these locations for combined hazard events or large lateral spreading and liquefaction occurrences. Caltrans also funded a study by Saini and Saiidi (2014) to address probabilistic seismic design of bridge columns using a probabilistic damage control approach and reliability analysis. Source: Caltrans. BRIDGE CATEGORY SEISMIC HAZARD EVALUATION LEVEL POST EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE STATE EXPECTED POST EARTHQUAKE SERVICE LEVEL Table 6. Caltrans draft proposed seismic design bridge performance criteria. SPL2 SPL3 Note: SPL1: Fully operational is required. Limit state of bridge is serviceability limit state. Negligible structural damage and nonstructural damage are allowed. Table 7. Seismic performance of bridge and limit states of conventionally reinforced concrete bridge column.
Literature Review and Synthesis 29 The probabilistic damage control approach uses the extent of lateral displacement nonlinearity defined by Damage Index (DI) to measure the performance of bridge columns. DI is a measure of damage from the lower measure of zero damage to the ultimate measure of a collapse mecha- nism for an element that has been subjected to base excitations. The performance objective was defined based on predefined apparent Damage States (DS), and the DS were correlated to DIs based on a previous study at the University of Nevada, Reno (Figure 13) (Vosooghi and Saiidi 2010). A statistical analysis of the demand damage index (DIL) was performed to develop fragility curves (load model) and to determine the reliability index for each DS. The results of the reliability analyses were analyzed, and a direct probabilistic damage control approach was developed to calibrate design DI to obtain a desired reliability index against failure. The calculated reliability indices and fragility curves showed that the proposed method could be effectively used in seismic design of new bridges, as well as in seismic assessment of existing bridges. The DS and DI are summarized with performance levels defined by Caltrans in Table 8, which shows the correlation between DS and DI. Figure 14 shows a fragility curve using lognormal distribution. Figure 15 shows both the fragility curves (upper two graphs) and reliability indices (lower two graphs) for four column bents (FCBs), with 4-foot diameter columns that are 30 feet in length in Site D for both the 1000 year and 2500 year seismic events. Note: O-ST = ordinary standard bridge, O-NST = ordinary nonstandard bridge, Rec. = recovery bridge, Imp. = important bridge, and NA = not applicable. Damage State (DS) Service to Public Service to Emergency Emergency Repair Design Damage Index (DI) Earthquake Levels (Years) Table 8. Design performance levels. DI P (D I { D S) Figure 13. Correlation between DS and DI.
30 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Figure 14. Fragility curve. 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 P (D I L ) DIL 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 R el ia bi lit y In de x | D S DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 Damage State (DS) 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 R el ia bi lit y In de x | D S DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 Damage State (DS) (a) (b) (d)(c) 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 DIL 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% P (D I L ) Figure 15. Fragility curves and reliability indices for FCBs with 4-foot columns in Site D. The Oregon DOT The Oregon DOT is developing a global plan for addressing resiliency in order to improve recovery for the next Cascadia Earthquake and Tsunami, using PBSD in terms of applying applicable hazards, identifying critical services, developing a comprehensive assessment of structures and systems, and updating public policies. The resilience goals are similar to those discussed at the beginning of this chapter, with the following statement: Oregon citizens will not only be protected from life-threatening physical harm, but because of risk reduction measures and pre-disaster planning, communities will recover more quickly and with less continuing vulnerability following a Cascadia subduction zone earthquake and tsunami.
Literature Review and Synthesis 31 Research has shown that the next great (magnitude 9.0) Cascadia subduction zone earth- quake is pending, as shown in Figure 16. This comparison of historical subduction zone earthquakes in northern California, Oregon, and Washington covers 10000 years of seismic history. The evidence of a pending event has made decision makers and the public take notice and put forth resources to develop strategies revolving around PBSD. Oregonâs performance-based features are modified from NCHRP Synthesis 440 to account for a third hazard condition: Cascadia Subduction Zone Earthquake (CSZE) in Oregon DOTâs Bridge Design and Drafting ManualâSection 1, Design (Oregon DOT 2016a; see also Oregon DOT 2016b). Design of new bridges on and west of US 97 references two levels of perfor- mance criteria: life safety and operational. Design of new bridges east of US 97 requires life safety criteria only. Seismic design criteria for life safety and operational criteria are described as follows. ⢠âLife Safetyâ Criteria: Design all bridges for a 1,000-year return period earthquake (7 percent prob- ability of exceedance in 75 years) to meet the âLife Safetyâ criteria using the 2014 USGS Hazard Maps. The probabilistic hazard maps for an average return period of 1,000 years and 500 years are available at ODOT Bridge Section website, but not available on USGS website. To satisfy the âLife Safetyâ criteria, use Response Modification Factors from LRFD Table 3.10.7.1-1 using an importance category of âother.â ⢠âOperationalâ Criteria: Design all bridges on and west of US 97 to remain âOperationalâ after a full rupture of Cascadia Subduction Zone Earthquake (CSZE). The full-rupture CSZE hazard maps are available at the ODOT Bridge Section website. To satisfy the âOperationalâ criteria, use Response Modification Factors from LRFD Table 3.10.7.1-1 using an importance category of âessential.â When requested in writing by a local agency, the âOperationalâ criteria for local bridges may be waived. The CSZE is a deterministic event, and a deterministic design response spectrum must be generated. To allow for consistency and efficiency in design for the CSZE, an application for generating the design response spectra has been developed by Portland State University (Nako et al. 2009). AASHTO guide specifications values for Table 3.4.2.3-1 are modified into two tables for (1) values of Site Factor, Fpga, at zero-period on the acceleration spectrum and (2) values of Site Factor, Fa, for short-period range of acceleration spectrum. Table 3.4.2.3-2 is replaced with values of Site Factor, Fv, for long-period range of acceleration spectrum. For seismic retrofit projects, the lower level ground motion is modified to be the CSZE with full rupture, as seen in Table 9. Performance levels, including performance level zero (PL0), are specified based on bridge importance and the anticipated service life (ASL) category required. Source: OSSPAC (2013). Figure 16. Cascadia earthquake timeline.
32 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design The South Carolina DOT South Carolina Department of Transportation (South Carolina DOT) has updated its geo- technical design manual (South Carolina DOT 2019). Chapters 12, 13, and 14 for geo technical seismic analysis, hazard, and design, respectively, have been updated to current practices and research, including incorporation of PBSD hazard prediction. South Carolina DOT is also updating their site coefficients to be more appropriate for South Carolinaâs geologic and seismic conditions; see Andrus et al. (2014). Note that with the revisions, South Carolina DOT issued a design memorandum in November 2015 that revised the substructure unit quantitative damage criteria (maximum ductility demand) table (Table 7.1 of the SCDOT Seismic Design Specifications for Highway Bridges). See Table 10. The Utah DOT The Utah DOT and Brigham Young University (see Franke et al. 2014a, 2014b, 2015a, 2015b, 2015c, 2016) are researching the ability for engineers to apply the benefits of the full performance- based probabilistic earthquake analysis without requiring specialized software, training, or education. There is an emphasis on differences between deterministic and performance-based procedures for assessing liquefaction hazards and how the output can vary significantly with these two methodologies, especially in areas of low seismicity. Guidance is provided regarding when to use each of the two methodologies and how to bind the analysis effort. Additionally, a simplified performance-based procedure for assessment of liquefaction triggering using liquefaction loading maps was developed with this research. The components of this tool, as well as step-by-step procedures for the liquefaction initiation and lateral spread displacement models, are provided. The tool incorporates the simplified performance-based procedures determined with this research. National Highway Institute Marsh et al. (2014) referenced a manual for the National Highway Instituteâs training course for engineers to understand displacement-based LRFD seismic analysis and design of bridges, which is offered through state agencies and open to industry engineers and geotechnical engi- neers. This course helps designers understand the principles behind both force-based AASHTO (AASHTO 2014) and displacement-based AASHTO (AASHTO 2011) methodologies, including a deeper understanding of what performance means in a seismic event. Other similar courses are also being offered to industry and are improving the understanding of practicing engineers. Federal Emergency Management Agency The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has developed a series of design guidelines for seismic performance assessment of buildings and three of the five documents EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION BRIDGE IMPORTANCE and SERVICE LIFE CATEGORY Table 9. Modifications to minimum performance levels for retrofitted bridges.
Literature Review and Synthesis 33 are referenced in FEMA (2012a, 2012b, 2012c). A step-by-step methodology and explanation of implementation are provided for an intensity-based assessment and for a time-based assess- ment. The process of identifying and developing appropriate fragility curves is demonstrated. A software program called Performance Assessment Calculation Tool has also been developed with a user manual that is included in the FEMA documents to help engineers apply PBSD to the building industry. Japan Road Association The Japan Road Association (JRA) Design Specifications have been revised based on the performance-based design code concept in response to the international harmonization of design codes and the flexible employment of new structures and new construction methods. Figure 17 shows the code structure for seismic design using the JRA Design Specifications. The performance matrix is based on a two-level ground motion (Earthquakes 1 and 2), with the first one based on an interpolate-type earthquake and magnitude of around 8, and the second one with a magnitude of around 7 with a short distance to the structure. Kuwabara et al. (2013) outlined the incremental revisions from the JRA Design Specif i- cations between 2002 and 2012. These revisions include, but are not limited to, the ductility design method of reinforced concrete bridges, plastic hinge length equation, evaluation of hollow columns, and the introduction of high-strength steel reinforcement. Following the 2016 earthquake in Kumamoto, Japan, a new version of the JRA Design Specifications is in the works. Note: Analysis for FEE is not required for OC III bridges. Source: South Carolina DOT (2015). Design Earthquake Operational Classification (OC)Bridge Systems Table 10. South Carolina DOT substructure unit quantitative damage criteria (maximum ductility demand ld).
34 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Identification of Knowledge Gaps The resources to develop guide specifications for PBSD are improving with examples such as the upcoming Seismic Design Criteria, Version 2 from Caltrans, which will address aspects of PBSD and the building industryâs efforts to develop practices in PBSD and tools for engineers and owners to collaborate on solutions based on performance criteria and expectations. There is still a perception that the bridge industry could better predict likely performance in large, damaging earthquakes than is being done at the present, and there are still gaps in that knowledge base that need to be closed. Most of the knowledge gaps listed in Marsh and Stringer (2013) are still applicable today; see Table 11. The technology readiness levels represent what has been developed and used; what research is done, ongoing, and being discussed; and what only exists in concept. Knowledge gaps certainly exist in all facets of PBSD; however, other key knowledge gaps beyond those listed in NCHRP Synthesis 440 (Marsh and Stringer 2013) that should be closed in order to improve the implementation of PBSD are covered. Objectives of Codes Mandated Specifications Overall Goals Functional Requirements (Basic Requirements) Performance Requirement Level Verification Methods and Acceptable Solutions Can be Modified or May be Selected with Necessary Verifications Importance, Loads, Design Ground Motion, Limit States Principles of Performance Verification Verifications of Seismic Performances (Static and Dynamic Verifications) Evaluation of Limit States of Members (RC and Steel Columns, Bearings, Foundations and Superstructure) Unseating Prevention Systems Principles of Seismic Design Figure 17. Code structure for seismic design using JRA design specifications. TRL Description 0-25 25-50 50-75 75-100 1 PBSD concept exists 2 Seismic hazard deployable 3 Structural analysis deployable 4 Damage analysis deployable 5 Loss analysis deployable 6 Owners willing and skilled in PBSD 7 Design guidelines 8 Demonstration projects 9 Proven effectiveness in earthquake Technology Readiness Level (TRL) % of Development Complete Table 11. Technology readiness levels for PBSD.
Literature Review and Synthesis 35 Gaps related to structural analysis can include minimum and expected properties for reinforcing greater than Grade 80, stainless steel, and other materials that can improve serviceability and in some conditions performance. Oregon DOT has been using stainless steel in their bridges located along the coastline and other highly corrosive environments to extend the service life of the bridge; however, many of these locations are also prone to large CSZE and the use of these materials in earthquake resisting elements is still being developed. In the State of Washingtonâs resiliency plan, outlined in Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012), what is missing is a link between damage levels and return to service. This is a knowledge gap given what we know structurally and what this report is suggesting as a desired goal for post-earthquake recovery. Gaps related to decision makers can include bridge collapse. It is not intended that the PBSD guide specifications will address tsunami events, but the JRA specifications do address tsunami as well as landslide effects. Figures 18 and 19 are examples of these other types of failure systems and show the collapse of bridges caused by effects other than ground motion (Kuwabara et al. 2013). The decision to combine these types of effects with a seismic hazard, even combining liquefaction, down drag, and lateral spreading effects, needs additional clarification and is currently left up to the owner to assess implications of probability, safety, and cost ramifications. Liang and Lee (2013) summarized that in order to update the extreme event design limit states in the AASHTO 2014, combinations of all nonextreme and extreme loads need to be formulated on the same probability-based platform. Accounting for more than one-time variable load creates a complex situation, in which all of the possible load combinations, even many that are not needed for the purpose of bridge design, have to be determined. A formulation of a criterion to determine if a specific term is necessary to be included or rejected is described, and a comparison of the value of a given failure probability to the total pre-set permissible design failure probability can be chosen as this criterion. Figure 18. Collapse of bridge due to landslide. (Note: Reprinted courtesy of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce. Not copyrightable in the United States). Source: Kuwabara et al. (2013).
36 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design While the seismic hazard definition was once thought to be relatively well understood, there is a growing knowledge gap related to the effect of rotation angle on intensity of ground motions and how the use of a geometric mean of the motions, or other methods of including the effect of rotation angle (RotDxx), should be incorporated into seismic design. This issue is not specific to PBSD; like all seismic design methods, PBSD is reliant on a full understanding of the hazard definition for proper implementation. The knowledge gaps identified in NCHRP Synthesis 440 are still applicable. Many of these knowledge gaps will become evident to both engineers and decision makers as the PBSD guidelines are developed. Overall, the baseline information to develop PBSD guide specifica- tions are in place. Industryâs end goal of understanding the relationship between risk-based decision making and design decisions and methodologies to meet performance goals is going to be an iterative process. Figure 19. Collapse of bridge due to tsunami. (Note: Reprinted courtesy of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce. Not copyrightable in the United States). Source: Kuwabara et al. (2013).
Performance-based seismic design (PBSD) for infrastructure in the United States is a developing field, with new research, design, and repair technologies; definitions; and methodologies being advanced every year.
The TRB National Cooperative Highway Research Program's NCHRP Research Report 949: Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design presents a methodology to analyze and determine the seismic capacity requirements of bridge elements expressed in terms of service and damage levels of bridges under a seismic hazard. The methodology is presented as proposed AASHTO guidelines for performance-based seismic bridge design with ground motion maps and detailed design examples illustrating the application of the proposed guidelines and maps.
Supplemental materials to the report include an Appendix A - SDOF Column Investigation Sample Calculations and Results and Appendix B - Hazard Comparison.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan. Revised on May 31, 2023. ... You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field or throughout your research paper when you want to position your work in relation to existing research. Table of contents. Example of ...
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.
An example of a stronger synthesis can be found below. Example 2: Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Different scientists and educators have different strategies for promoting a well-rounded diet while still encouraging body positivity in children. David R.
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
Synthesis of your research findings involves much more than summarizing articles. Summarizing is different from synthesizing. In a summary, you recap key points from a single
In this post, we'll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples. This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp. In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step.
Types of Research Synthesis: Key Characteristics: Purpose: Methods: Product: CONVENTIONAL Integrative Review: What is it? "The integrative literature review is a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated" [, p.356]. ...
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
Synthesis prevents your papers from looking like a list of copied and pasted sources from various authors. Synthesis is a higher order process in writing—this is the area where you as a writer get to shine and show your audience your reasoning. Types of Synthesis Similarity. Demonstrates how two or more sources agree with one another. Example:
When asked to synthesize sources and research, many writers start to summarize individual sources. However, this is not the same as synthesis. In a summary, you share the key points from an individual source and then move on and summarize another source. In synthesis, you need to combine the information from those multiple sources and add your ...
This paper introduces models and techniques for synthesizing multiple qualitative studies on a topic. Qualitative research synthesis is a diverse set of methods for combining the data or the results of multiple studies on a topic to generate new knowledge, theory and applications. Use of qualitative research synthesis is rapidly expanding ...
The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record the main points of argument on the topic at hand. As you examine your first source, you will work ...
Synthesis requires you to make sense of all the relevant ideas in your sources and blend them together with your own thoughts and ideas. Watch this video to learn how to engage in synthesis in order to take research from multiple sources along with your own arguments and turn it into a research paper. Research Synthesis.
Get multiple synthesis essay examples covering a range of topics. Learn how to craft an introduction, thesis, outlines, or write your entire synthesis essay. ... When it comes to a synthesis essay, it is all about the research. You must take a stand, but that position needs to be backed up by credible sources.
Created by Colleen Warwick. Adapted by J. Clevenger 9/2011. Help…I've Been Asked to Synthesize! Writing a strong researched paper requires the ability to synthesize—or combine elements of several sources—to help you make a point. The purpose of the Multiple Source Essay is to give students the chance to practice this process of "synthesis".
students better use synthesis in their writing and will offer strategies in the areas of: (1) pre-writing, (2) writing, (3) recognizing and (4) revising for synthesis. A common strategy for planning a synthesis paper is to create a "grid of common points." To create a grid follow these steps (note: be sure to see example grid on next page): 1.
Commonly used in research papers, scholarly articles, and scientific studies. 3. Chicago Style: Offers two documentation styles: Notes-Bibliography and Author-Date. ... Synthesis Essay Example. Here are two examples of synthesis essays that demonstrate how to apply the synthesis process in real life. They explore interesting topics and offer ...
Their aim is to identify and synthesize all of the scholarly research on a particular topic, including both published and unpublished studies. Evidence syntheses are conducted in an unbiased, reproducible way to provide evidence for practice and policy-making, as well as to identify gaps in the research. Evidence syntheses may also include a ...
1. Introduction. Research or scientific synthesis is the integration and assessment of knowledge and research findings pertinent to a particular issue with the aim of increasing the generality and applicability of, and access to, those findings (Hampton & Parker 2011, Magliocca et al., 2014, Baron et al. 2017).Synthesis of existing research and case studies can also generate new knowledge.
Background. The range of different methods for synthesising qualitative research has been growing over recent years [1,2], alongside an increasing interest in qualitative synthesis to inform health-related policy and practice [].While the terms 'meta-analysis' (a statistical method to combine the results of primary studies), or sometimes 'narrative synthesis', are frequently used to describe ...
A synthesis report, NCHRP Synthesis 440: Performance- Based Seismic Bridge Design (Marsh and Stringer 2013), was created to capture PBSD understanding up to that point. This synthesis report described the background, objec- tives, and research up until 2011 to 2012 and synthesized the information, including areas where knowledge gaps existed.