What Is a Commentary in an Essay | Writing Guide & Examples
22 December 2023
last updated
When people need to express their thoughts or ideas about something, they need guidelines on how to write a commentary essay. This article begins by defining what is a commentary essay, its meaning, and outlining its basic structure. Some insights students can learn are that introductions should have hooks, background information, and thesis statements. Body paragraphs of a commentary essay should have topic sentences; evidence, mainly quotes; comments after the evidence; and transitions. The conclusion part should restate the thesis and summarize the main ideas. This guideline also gives a sample outline template, possible topics, and a practical example of a commentary essay. Lastly, the article teaches students 10 dos and 10 don’ts and 20 tips for writing a high-standard commentary essay.

How to Write an Outstanding Commentary Essay & Examples
Reading is an academic exercise that develops a person’s mental faculties of intellect, memory, reason, intuition, perception, and imagination. These faculties develop when people utilize what they have acquired through reading to write different types of papers , including essays, reports, and research papers. Therefore, reading and writing are related because they both induce intellectual development. This guideline on how to write a commentary in an essay teaches students and anyone passionate about writing how to create a good argumentative position that meets the quality standards for intellectual discourse and publication. The guideline also offers vital insights, including the definition of what is a commentary essay, its basic essay structure , different types, possible essay topics, 10 dos and 10 don’ts, and 20 tips for producing a high-standard essay. Therefore, reading this guideline is beneficial to students and others who may, from time to time, write a commentary in an essay to communicate ideas to specific audiences.

Definition of What Is a Commentary in an Essay and Its Meaning
From a definition, a commentary is a descriptive account of an event, an expression of opinions about a political, economic, social, or cultural issue, or elucidating a point or topic of public interest. From this perspective, a commentary essay is a document that students write to express opinions about an issue or topic through a descriptive expression and explanation of ideas. In this respect, a commentary essay differs from other types of essays , including an argumentative essay , a personal narrative , a cause and effect essay , compare and contrast essay , or a problem and solution essay , as well as a report and a research paper , because it means expressing the writer’s perspective concerning an issue or topic. Commentaries are products of a critical analysis of societal problems across political, economic, social, and cultural dimensions. When writing a commentary essay, students should analyze and interpret the source under discussion, such as a text, film, article, video, advertisement, event, object, subject, book, poem, speech, presentation, literary work, novel, sculpture, or image, among others, using a basic sandwich rule: giving a commentary after each quote or citation.
Use exceptional writing services that guarantee original and well-researched papers.
Basic Structure of a Commentary Essay
Like other texts, a commentary paper has a basic essay structure that dictates how writers should organize their content. This structure has three components: an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . The introduction is where writers introduce their assigned topics using a hook , context, and an argumentative thesis statement . Although this type of commentary essay is not an argumentative essay, an argumentative thesis indicates the writer’s perspective on the issue, which can be contentious in the eyes of readers. The body of a commentary essay is where authors construct a defense of their perspective through body paragraphs; each body paragraph should have a topic sentence that establishes a claim ; supporting evidence, like quotes, data, or examples; a commentary that analyzes and explains information cited in an essay; and a concluding sentence with a transition to create a logical connection to the next paragraph. In turn, the conclusion restates the thesis and makes a final remark.
5 Main Types of Commentary
Because a commentary in an essay expresses the writer’s perspective about an issue, idea, or topic, it is evident in the body section of a commentary essay, where people describe their perspectives every time they provide evidence. In this respect, there are different types of commentary. The first one is an opinion essay where writers analyze evidence, such as a quote, text, or image, and state their stands with their critics. The second type of a commentary essay is an interpretation, where authors explain a complex concept to enhance the reader’s understanding. The third type is character or subject’s feelings, where students depict the emotional state of the person they have described in a commentary sentence. The fourth type of commentary essay is a personal reaction, where people communicate their stances on an issue, while the fifth type is an evaluation, where writers evaluate a section and gives a critical judgment.
Alternative Commentary Types and Examples
Besides the types of commentary above, students may write alternative commentary types when their essay is part of a bigger writing project, such as a systematic exposition of an idea, theme, or topic. Students must know the unique features of each type, including when to use it, what to focus on, and how to organize a commentary essay’s content.
1️⃣ Close, Direct Analysis of Passages
An example of an alternative commentary is a close, direct analysis of robust passages from the source, such as an article, film, poem, literary work, book, or novel. In this respect, they are standard in bigger writing projects, like expositions or being part of a critic’s work. Students adopt this type of commentary when they have to read a passage in a text or pick a speech in a movie and write a film analysis essay that expresses the writer’s perspective on the central issues, ideas, or concepts. The following example of a commentary essay demonstrates a close, direct examination of the first stanza of the poem “Night Wind” by Christopher Dewdney:
Tonight the wind blows through
all the worlds I have known and
through all the lives I have led.
The wind blows in the trees,
deeper into each.
The wind blows forever,
strains like something
endlessly departing.
Restless, impatient,
it races without burden.
Example of a Commentary on Celebration of Nature in the First Stanza of Christopher Dewdney’s Poem “Night Wind”
Christopher Dewdney’s 1984 poem “Night Wind” celebrates nature by depicting the night wind as a permanent, free expression of nature. The poet describes the wind on a particular night in the first stanza. By using a first-person perspective in the first three lines, Dewdney depicts himself as an observer. This writing style expresses a personal dialogue in which the poet directly relates his senses, experiences, and impressions. Dewdney opens the poem with the words: “Tonight the wind blows through / all the worlds I have known and / through all the lives I have led.” In this passage, the author expresses to the reader how the unity of the wind in whatever time or place leaves a lasting impression on him. Ideally, he views the wind as an omnipresent force but also regards it as very transient and fleeting. The words “endlessly departing” indicate to the reader the sense that the wind encompasses the entire continuum of the poet’s existence. Nonetheless, it is always in a rush to be at another location. The reader gets the impression that wind is a celebration of nature when Dewdney mentions its interactions with nature: “The wind blows in the trees, deeper into each.” This statement induces an imagination of trees fighting against a pervasive wind. The poet ends the stanza by personifying the wind, and he assigns it human qualities of restlessness, impatience, and playfulness. In this respect, the first stanza uses the wind as a reason to celebrate nature.
2️⃣ Commentary Annotations
Annotations are another type of alternative commentary where writers use a short claim on a source, like a text, film, or image. This kind of commentary essay also looks like an annotated bibliography . Typically, writers adopt annotations when they need to explain complex words, phrases, or concepts to readers; give a historical or cultural context of the topic; support or challenge the author’s arguments in an essay; expose literary devices, like contrast, irony, or sarcasm, or rhetorical devices, like ethos, pathos, and logos; provide a personal interpretation of the text under analysis. Therefore, annotations aim to enhance the reader’s understanding of a short passage from a source. Below are three examples of annotations of complex content in writing a commentary essay for Christopher Dewdney’s Poem “Night Wind.”
3 Examples of a Commentary With Annotations
➖ “The night wind is an empire / in exodus, a deliverance / beside the dark shape of trees.”
This statement is in lines 13-15 of Dewdney’s poem, where the poet alludes to a biblical concept, exodus, to express the wind’s freedom. By stating that the wind is “… in exodus, a deliverance…,” Dewdney makes the reader compare the wind to the incident in the book of Exodus in the Bible where Moses leads the children of Israel, God’s chosen people, to Canaan, the promised land, after freeing a life of bondage in Egypt. In this respect, lines 13-15 confirm that the wind is free and expresses nature’s freedom.
➖ “The wind takes / me in its giddy rush and / gathers me into a storm of longing, / rising on wings of darkness.”
In this statement in lines 18-21, the phrase “wings of darkness” emphasizes the wind’s freedom and mystery. The poet contextualizes the wind as an unpredictable force that can take a person anywhere .
➖ “Along oceans and rivers, / the gale’s mysterious, unspoken imperative / is a joyous delirium with / nothing at its end.”
This passage in lines 36-39 expresses Dewdney’s excitement in not knowing where the wind may take him. It suggests that it does not matter where the wind takes him because he is truly free. In essence, the statement makes the reader imagine the wind as a mystery because it can take one anywhere, emphasizing the theme of freedom.
3️⃣ Data Commentary
Data commentary is another type of alternative essay commentary where writers summarize a study by analyzing critical information that helps readers have a sneak peek of the project. The features students should incorporate in a commentary essay include visual illustrations, like charts, diagrams, graphs, and tables, to capture statistical data, allowing readers to compare them easily. In this respect, data commentary reflects the results section of a research paper because that is where scholars use visual illustrations to report statistical data. Another feature is a conclusion summarizing a commentary essay by reiterating the key points and expressing the writer’s final remark, meaning the main perspective on the topic. Lastly, people must provide a reference page listing credible sources they consulted to write data commentaries, such as reports and research articles. Below is an example of data commentary.
Example of Data Commentary
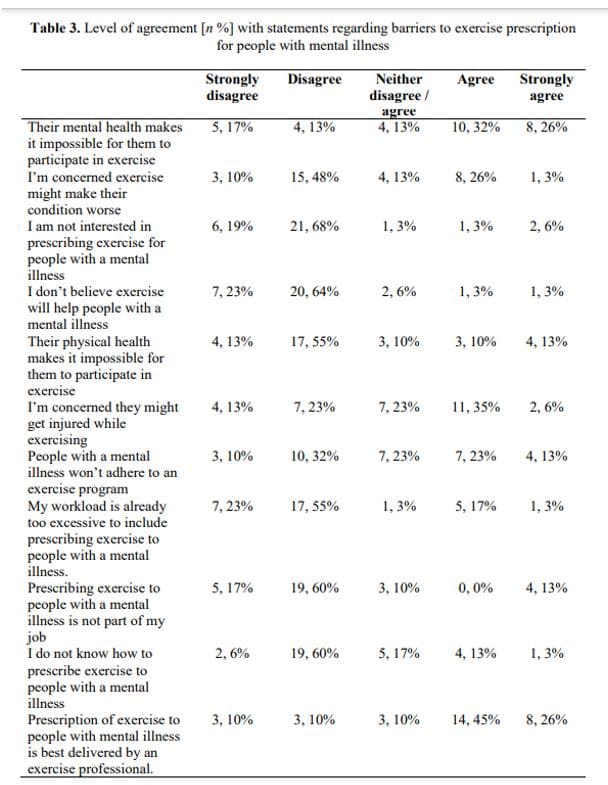
Table 3 shows respondents’ responses to statements about the barriers to exercise prescription for people with mental illness. Those who agreed that patients’ mental health denies them the opportunity to exercise was 58%, while those who agreed that obtaining an injury during exercise is a concern was 45%. There was an overwhelming response by 87% of the respondents who agreed that exercise is beneficial and were interested in prescribing it for patients with mental health problems. However, only 13% agreed that prescribing exercise falls outside their job description. Nonetheless, 16% stated that they did not know how to prescribe exercise for the population. Overall, 71% approved that exercise professionals are best suited to prescribe exercise for people in the population.
Possible Uses of Block Quotations for Writing a Good Commentary Essay
When writing a commentary essay, students can use block quotations to organize comments. However, this feature is suitable mainly for extensive passages. In a simple definition, a block quote is a text that captures direct quotations longer than 40 words, which the writer offsets from the main text and does not include quotation marks. The text appears on a new line with a 0.5 inches indentation or five to seven spaces. Using single space for a block quote is standard, even in an essay requiring double spacing. Hence, students must know how to format block quotes in APA , MLA , Harvard , and Chicago/Turabian referencing styles when writing a commentary essay.
📕 APA Format
There are two ways in which students can write block quotes in the APA style when organizing their commentary essays.
I. The first block captures the author’s name before the quote:
In their tabulation of results, Vancampfort et al. (2019) showed:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (p. 2178).
“[Your comments on a block quote starts here]”
II. Alternatively, a block quote can have the author’s surname at the end:
According to the findings:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (Vancampfort et al., 2019, p. 2178).
📕 MLA Format
Similarly, the MLA style has two ways of formatting a block quote when organizing commentary essays.
I. Having the surname of the author preceding a block quote in an essay:
The results by Vancampfort et al. indicate:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (2178).
II. Having the author’s surname at the end of the quote:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (Vancampfort et al. 2178).
📕 Harvard Format
The Harvard style also has two ways of formatting a block quote when organizing commentary essays.
I. Indicating the author’s surname before a block quote in an essay:
In their findings, Vancampfort et al. (2019) established that:
II. Citing the author’s surname at the end of a block quote:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (Vancampfort et al. 2019, p. 2178).
📕 Chicago/Turabian Format
The Chicago/Turabian style also has two ways of formatting a block quote when organizing commentary essays.
I. Mentioning the author’s surname before a block quote in an essay:
According to Vancampfort et al.:
Almost 75% of the respondents indicated that they would “definitely” attend further training for exercise prescription for people with mental illness, in particular related to how to assess patients and how to motivate them towards an active lifestyle. More than seventy percent of the participants also reported that exercise to people with mental illness is actually best delivered by an exercise professional, although only one respondent referred patients to such an exercise professional (this passage must be formatted as a footnote). 1
II. Showing the author’s surname in a footnote:
Receive personalized assistance from our writers, ensuring your paper is both original and tailored to your needs.
Key Features of Formatting Block Quotes When Writing a Commentary Essay
Looking at the examples of writing a commentary in an essay above, there are some similarities and differences in formatting block quotes. APA and Harvard are similar because they show the research article’s publication year and the page number of the information the writer cites in their commentary essay. The main difference is the arrangement of these details, including the place of putting comas. On the other hand, the MLA and Chicago/Turabian styles are similar in that they do not show the research article’s publication year. The main difference is that the Chicago/Turabian style uses footnotes to show the author(s) and all the bibliography details at the commentary essay’s end. The MLA style shows only the author’s surname and the page number in the text. In turn, people begin writing their commentaries in the following line after a block quote as a standard paragraph in all the formats.
Easy Sample Topics for Writing a Great Commentary Essay
Students should choose easy essay topics when writing a commentary essay to avoid complicating their tasks. Ideally, a specific topic should indicate a particular source document one is commenting on, such as a text, film, or image. The standard practice is that instructors define essay topics or commemorative speech topics students should write about. However, people can choose other themes they are comfortable with if such instructions do not exist for writing a commentary essay. The best approach to choosing an easy topic is to engage with course content and read widely to generate and incubate ideas. When the time for writing a commentary essay comes, one finds it easy to construct arguments fitting the task. The following are possible commentary essay topics because they suggest analyzing and examining a source from the writer’s perspective.
- In Memory of Amelia Earhart: Sky’s Fearless Lady
- The Central Themes in Harper Lee’s novel “To Kill a Mockingbird”
- “The Great Gatsby” Through Contemporary Lens
- The Rhetorical Stance in Jessica Grose’s “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier”
- The Message in Robert Frost’s Poem “The Road Not Taken”
- Maya Angelou’s Magic in “And Still I Rise”
- Demystifying Mental Disorders Through the Film “Black Swan (2010)”
- The Essence of Margaret Atwood’s “Negotiating With the Dead: A Writer on Writing”
Sample Outline Template for Writing a Commentary Essay
- Title of a commentary essay must be precise to an assigned topic.
- Title must be short, clear, and easily understandable.
- Title must be interesting, catchy, and with relevant keywords.
I. Introduction Section of a Commentary Essay
- College essay introduction must have a hook that interests readers enough to grab their attention and stirs a curiosity to continue reading.
- Introduction must refer to a specific source (text, film, or image) and its author(s).
- Introduction must summarize an assigned source that includes the main characters (if any), themes, or concepts.
- Introduction must have a clear thesis statement that states the writer’s claim.
II. Body Section of a Commentary Essay
Body paragraphs (at least three):
- Each body paragraph of a commentary essay must have a topic sentence that emphasizes a single idea central to the main claim in the thesis statement that the writer will defend in the paragraph.
- Each body paragraph must include evidence from a source under analysis, such as a quote, indicating the character responsible and the context.
- Each body paragraph must give a commentary about the evidence through relevant analysis, linking the information to the idea at the beginning of the paragraph and the claim in the thesis.
- Each body paragraph must end with a closing statement and a bridge sentence to facilitate a logical flow to the next paragraph or section.
III. Conclusion Section of a Commentary Essay
Sum up a commentary essay by:
- Restating the thesis.
- Emphasizing the main ideas of a commentary essay.
- Giving a final remark that confirms the importance of the essay topic.
Example of a Commentary Essay
Commentary Essay’s Title: The Rhetorical Stance in Jessica Grose’s “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier”
I. Example of an Introduction of a Commentary Essay
A woman never rests, not with society constantly demanding her value at every turn. This idea is the message in Jessica Grose’s famous article, “Cleaning: The Final Feminist Frontier.” The author argues that cleaning remains a feature of women’s value in society, despite men’s growing involvement in childcare and cooking. The article also opens with personal accounts and convincing facts, suggesting its credibility as a source of information about the dynamics confronting American women. In her article, Grose communicates her message effectively by adopting a rhetorical stance characterized by emotional appeals.
II. Example of Body Paragraphs of a Commentary Essay
A. commentary on the main idea of the article.
Grose opens the article with a personal story of her and her husband cleaning their house after Hurricane Sandy forced them indoors. She uses the uneven distribution of the cleaning task in her marriage to point out the larger feminist issue of who between a husband and wife should do the job. The article gives three reasons why men shy away from the cleaning task, including the fact that it is women who receive praise for a clean house, the media focuses on men’s growing involvement in childcare and cooking, and it is not fun. According to Grose, even distribution of the cleaning task can happen by creating a task chart that shows who does what on the basis of skill and ability and adopting cleaning gadgets to make cleaning more fun.
Throughout the article, Grose uses sources to appeal to the readers’ ethos and build her argument. Some of the sources she uses to achieve these goals include a study by sociologists Judith Treas and Tsui-o Tai and an article by Matthew Krehbiel, North America Fabric Care Brand Manager for P&G. Citing these sources helps the author to build her credibility in the eyes of readers.
Regarding appeals to logos, Grose mentions statistics and interesting facts that help to enhance the logical progression of ideas central to her argument. To emphasize the uneven distribution of the cleaning task, she says, “My husband and I both work…I do the dishes nine times out of ten, and he barely knows how the washer and dryer work.” Such facts confirm and support the idea that women do more household chores than men. She also cites statistics, showing “55 percent of mothers working full-time in America do some housework daily compared to 18 percent of fathers.” In this respect, the article is factual about the uneven distribution of household chores that disadvantages women. As a result, the personal details and statistics from credible sources help Grose to impress upon the reader how society uses the domestic environment to subjugate women.
The article appeals to the readers’ pathos in the beginning and middle sections, where Grose uses emotionally-charged words and phrases to induce the audience’s sympathy. For example, Grose laments that, while she “was eight months pregnant,” her husband experienced the complexity of fighting “a massively pregnant person.” These words evoke an image in the readers’ mind that portrays women as vulnerable in the domestic space because of natural factors, like high emotions and pregnancy. Indeed, readers may feel sympathetic to Grose and the women who generally live in this social context. Moreover, using words and phrases, like ‘argued,’ ‘sucks,’ ‘be shunned,’ ‘be judged,’ and ‘headachey,’ evokes readers’ negative feelings about cleaning. As such, they are more drawn to sympathize with men and view men as selfish.
III. Example of a Conclusion of a Commentary Essay
Grose takes a rhetorical stand throughout the article to persuade her audience of the unfair distribution of cleaning labor in the domestic space. By referencing credible sources, citing statistics and interesting facts, and portraying women as adversely disadvantaged, Grose effectively appeals to the readers’ ethos, logos, and pathos. This rhetorical stand is critical in communicating how society remains unfair to women in the domestic space despite men’s growing involvement in some household chores like childcare and cooking.
4 Easy Steps for Writing a Commentary Essay
Writing a commentary essay is a technical process that requires students to grasp essential details. For example, these details reflect 4 writing steps: preparation, stage setup, writing a first draft, and wrap-up. Typically, each step’s details of writing a commentary essay reflect the wisdom writers should exhibit when creating any scholarly text.
Step 1: Preparation
Preparation is the first step of writing a commentary essay. As the name suggests, it is when writers take time to create a favorable environment to write their papers. The first task is identifying a single source, where students should select good sources they can analyze easily, including poems, novels, or films. The second task is to create a topic, where students must write short topics that communicate a precise message of a commentary essay.
Step 2: Stage Setup
Setting the stage is the second step of writing a commentary essay. The first task is to read, watch, or examine an assigned source to identify key themes and ideas. The second activity is to research reliable sources that help to generate ideas that align with these themes and concepts. The next task is to create a clear essay outline emphasizing the introduction, body, and conclusion with all the essential details.
Step 3: Writing a First Draft of a Commentary Essay
Writing a first draft is the third step in creating a commentary essay, and the focus is generating a paper that can be used for further editing and improvement. As such, students should organize their ideas into text, emphasizing the claim in the thesis statement, ideas in the topic sentences, evidence (quotes), and transitions in the body paragraphs. Students should also ensure the conclusion restates the thesis, summarizes the main ideas of a commentary essay, and gives a final remark about their commentaries, focusing on an assigned source and topic.
Step 4: Wrap-Up
The wrap-up is the last step in writing a commentary essay. The main focus is transforming a first draft into a final text by eliminating all mistakes and flaws. Typically, students should revise all sections that do not make sense to a central claim or those that affect the paper’s logical progression. They should also edit a commentary essay by adding or deleting words and phrases and eliminating grammatical mistakes, missing punctuation, formatting errors, and incorrect citations.
20 Tips for Writing a Commentary Essay
Looking at the information in the preceding sections, writing a great commentary essay is a complex task that requires students to demonstrate knowledge of what it takes to create a quality paper. Some of the tips for writing a commentary essay include identifying a single source, which can be a text, film, or image; noting the source’s basic information, like the author, title, and publication date; identifying the central themes in the source; writing an introduction that emphasizes the source’s basic information; creating a thesis that communicates a claim about the source; adopting the unique structure as above; beginning paragraphs with a topic sentence; incorporating quotes from the source into body paragraphs; commenting on the quotes and their significance; and concluding a commentary essay with a summary that makes a final remark about a single source and topic.
10 things to do when writing a commentary essay include:
- identifying a source for writing a commentary essay;
- reading, watching, or analyzing an assigned source carefully and closely;
- outlining critical details, like themes, ideas, and literary devices;
- writing an introduction with a hook and an argumentative thesis statement;
- providing body paragraphs with topic sentences, concluding sentences, quotes, commentary, and transitions;
- maintaining a formal tone in a commentary essay;
- using the applicable format (APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian) correctly;
- presenting an introduction that summarizes a commentary essay;
- avoiding grammatical mistakes;
- proofreading a final version of a commentary essay.
10 things not to do include:
- failing to document the source’s essential details, like the author’s name and surname;
- concentrating on the introduction more than the body;
- not incorporating quotes in body paragraphs;
- focusing on too many ideas in a commentary essay;
- not defending the claim in the thesis;
- ignoring a unique outline of a commentary essay;
- writing with too many grammatical mistakes;
- using different formatting styles (APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago/Turabian);
- not implementing transitions in body paragraphs;
- creating a commentary essay without a logical flow of ideas and thoughts.
Summing Up on How to Write a Perfect Commentary Essay
- Choose a single source that is simple to analyze.
- Create a clear thesis that emphasizes the focus of a commentary essay, such as a claim.
- Identify passages or themes in an assigned source that help to build an argumentative claim.
- Use an introduction paragraph for its purpose: to introduce a specific topic. As such, it should be short and precise.
- Use a body section for its purpose: to analyze a particular source and defend a central claim comprehensively. Therefore, it should be long and have quotes as evidence.
- Use a conclusion part to summarize a commentary essay, and it should be concise. More importantly, it should leave readers with a lasting impression of a defined source and topic.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
Reducing plastic waste in the ocean: an innovative approach, history of cryptography and its modern applications.
Rhetoric and Composition/Commentaries
- 1 What is a Commentary?
- 2 What Do Commentaries Do?
- 3 Where Can I Find Commentaries?
- 4 What Is In a Commentary?
- 5 How Should Writers Organize Their Commentaries?
- 6.1 Preliminary Inquiry
- 6.2 Background Research
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Explanation
- 7.3 Support
- 7.4 Clarification
- 7.5 Conclusion
- 8.1 "Getting into Character"
- 8.2 Imitation
- 9 References
What is a Commentary? [ edit | edit source ]
A commentary is a response to another person's argument. Commentaries are most often found in expressions of opinions on current issues and events [1] . The purpose of commentaries is to offer new and insightful perspectives so that readers can understand their own stance on an issue or event. Importantly, readers can find commentaries as similar to an op-ed (opinion/editorial) piece in a newspaper or a magazine.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 22:37, 16 November 2012 (UTC)
What Do Commentaries Do? [ edit | edit source ]
Commentaries offer a new angle to an ongoing public conversation [2] . The goal of commentaries is to convince readers that the opinion of the person writing the commentary is more convincing. When writing a commentary, it is important to make clear points that are understood easily by readers. At the same time, readers of commentaries want to learn something new while figuring out how someone else views an issue or event of interest. Most commentaries act on the purpose of making their points memorable [3] .
Where Can I Find Commentaries? [ edit | edit source ]
Commentaries are not difficult at all to find. Readers can find them in print media (e.g., newspapers, magazines) and visual media (e.g., online news). Many letters to the editor and opinion-editorial (op-ed) pieces have a similar style as commentaries do. In addition, blogs and social networking sites like Blogger or Facebook serve the purpose of creating a space for writing commentaries [4] .
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 22:38, 16 November 2012 (UTC)
What Is In a Commentary? [ edit | edit source ]
The content of commentaries (along with letters to the editor and op-ed pieces) have current events or issues as their primary focus [5] . Commentaries often contain an explanation of the current event or issue. Commentaries often offer support for the opinions written in them. As with any writing genre, commentaries focus on topic, angle, purpose, readers (audience), and context. Writers of commentaries, letters to the editor, and op-ed pieces often view a current issue or event from a unique angle that applies to the issue's timely relevance. In rhetoric, this is known as kairos . Kairos is the Greek word meaning "right or opportune time." Writers and readers of commentaries should not confuse kairos with chronos (chronological time). However, if historical criticism applies to the current event, writers should feel free to put that in their commentaries.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 18:40, 6 December 2012 (UTC)
How Should Writers Organize Their Commentaries? [ edit | edit source ]
One method of organizing a commentary comes from Johnson-Sheehan and Paine [6] . The features included in this method of organizing commentaries are:
How Do Writers Know What to Put in Their Commentaries? [ edit | edit source ]
As with reviews, commentaries involve using the techniques of preliminary inquiry and background research without necessarily experiencing the subject under review . However, commentaries are different from reviews in lieu of these features. Writers of commentaries should write about something that is important to them by listening to what others say and reading what others write [7] . Writers of commentaries should also take care to listen to what people are not saying and not writing; this would mean citing a gap in the conversation. Writers of commentaries, in addition, often follow news events found on Web sites, in newspaper, and in magazines [8] . As it is for reviews, writers and readers of commentaries should play the Believing and Doubting Game using the three steps of believing , doubting , and synthesizing . Playing the Believing and Doubting Game can help writers of commentaries see multiple sides of an issue while they tie all of their information together to make it their own.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 19:04, 6 December 2012 (UTC)
Preliminary Inquiry [ edit | edit source ]
Another way of stating this is "finding out what you already know" [9] [10] . The Believing and Doubting Game applies most fittingly here. The three steps of preliminary inquiry are:
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 20:04, 6 December 2012 (UTC)
Background Research [ edit | edit source ]
This next step of the Believing and Doubting Game is also known as "finding out what others know" [13] . Since commentaries are most often responses to current events and issues, writers must comment on how the events are still happening and what that will mean. Not all the facts are present in commentaries because they are happening at that moment. New developments often arise before any publication of the commentary takes place. Nonetheless, sources that writers of commentaries include:
With all of the potential sources to use for writing commentaries, writers should triangulate their sources. [17] . Triangulating sources helps confirm facts to gain a broader understanding of an issue.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 20:27, 6 December 2012 (UTC)
How Do Writers Organize and Draft Their Commentaries? [ edit | edit source ]
As mentioned earlier, the best commentaries often grab the readers' attention immediately. In any format, including the commentary, the best writers often lead readers through a series of argument supporting a specific position. There is often the consideration of what type of information is best suitable for the writer's intended audience. In other words, writers of commentaries must focus on what the audience needs to know.
Introduction [ edit | edit source ]
In the introduction, it is often the case that writers generate reader interest if there is the use of information not previously considered [18] . Within the introduction, it is best to do to two things:
Explanation [ edit | edit source ]
The amount of explanation needed in a commentary depends on how familiar readers are with both the topic and the issue [20] . When explaining the topic and the event, writers should explain what has already happened. Writers should also summarize what others have said about the topic and the issue. If, for example, readers are already familiar with a topic, then the explanation should be very brief. Writers, therefore, should give enough information to remember an event or the origins of an ongoing debate.
If readers are not already familiar with a topic or an issue, then writers should provide enough background to help stimulate the readers' interest [21] . In this case, writers will need to explain who was involved, where and when it happened, how it happened, and why. Additionally, writers should show as many angles to the debate as possible by summarizing what others have said.
Support [ edit | edit source ]
It is impossible to include all the possible information in explaining why a writer's own position is the most credible [22] . Instead, writers often pick the best and most important pieces of evidence while they devote an appropriate amount of time explaining them. In most commentaries, each piece of evidence receive one to two paragraphs of coverage. Each piece of evidence should support the main point (or thesis statement) while each piece should provide a solid structure for taking an angle on the topic and issue at hand.
Clarification [ edit | edit source ]
This section often comes before the conclusion. When writing this section of a commentary, writers should make their readers of the complexities involved in the issue [23] . Here, writers need to make their arguments clear, particularly when they insert new information or events that could complicate the overall argument. In most cases, writers use signal phrases such as:
Most clarifications are only one paragraph in length, depending on the extent of the issue as well as how much readers already know about the topic and the issue. Often, clarification prevents readers from making accusations of writers "painting with too broad a brush"--generalizing too far or failing to consider the fine but important points of an issue [25] .
Conclusion [ edit | edit source ]
Readers should finish reading a commentary with a clear statement of a position writers make. As with any written task, writers often restate the main thesis but in stronger terms. Writers often reemphasize why the topic is important while speculating on what others will say in the future. Many writers of commentaries finish with an anecdote, a figure of speech, a clever turn of phrase, or a lasting image.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 03:24, 7 December 2012 (UTC)
What Is An Appropriate Writing Style for Commentaries? [ edit | edit source ]
Commentaries often use a style that set their arguments apart from writing done for other genres, such as reviews or proposals. [26] With the style, writers should see through the lens of someone making a commentary. Important aspects of commentaries to consider are: how writers want their readers to imagine them and how writers want readers to react to the overall tone.
"Getting into Character" [ edit | edit source ]
Johnson and Sheehan suggest that writers of commentaries play their role "like an actor" [27] . Another term for this is "getting into character." This allows writers of commentaries to write with less constraints. Depending on the tone writers of commentaries wish to convey--whether angry or upbeat--they can let emotions flow onto a screen or page. Writing multiple drafts of commentaries allows writers to explore the specific emotion they use.
Imitation [ edit | edit source ]
Some commentaries work best when they imitate the style of a well-known critic or commentator. Examples of well-known commentators include George Will , Glenn Greenwald Glenn Greenwald , Jeremy Scahill Jeremy Scahill , and Ariana Huffington Ariana Huffington . Writers of commentaries look closely at how other commentators achieve their style or tone [28] . In most cases, writers of commentaries look for details or words used in a particular way; sentence length; analogies, similes, and metaphors to express complex thoughts; and expression of emotions. Writers should, however, best to avoid imitating the style of an article on the topic they want to write about so as to avoid plagiarism.
MichaelPickar ( discuss • contribs ) 21:06, 7 December 2012 (UTC)
References [ edit | edit source ]
- ↑ Writing Today, Custom Edition for St. Cloud State University. Taken from Writing Today, Second Edition by Richard Johnson-Sheehan and Charles Paine, 2012. Print. p. 171.
- ↑ Johnson-Sheen and Paine, p. 171
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 171
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 172
- ↑ Writing Today, p. 172
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 175
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 84.
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 90
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, pp. 175-176
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 176
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 177
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 178
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 179
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 180
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 181
- ↑ Writing Today, p. 181
- ↑ Johnson-Sheehan and Paine, p. 182
- Book:Rhetoric and Composition
Navigation menu

Oxford Tutoring
We Teach the Way you Learn!

Elements of an Essay: Writing Commentary
For several weeks now, we have been identifying the essential elements of essays and learning how to incorporate these effectively and successfully. We have discussed that the thesis statement is the glue that holds the entire paper together, the body paragraphs are the meat where the majority of your argument will be found, and last week we looked at how the details are the key to unlocking your argument . Today we are going to take a look at the other extremely important factor in writing a well-thought out essay. It is needed for every single detail that you write. It is the commentary.
Commentary Definition
When you write commentary, you are explaining to your reader how the details relate to the thesis statement. Commentary does not contain facts. Instead, they help explain why the details are relevant to the topic.
Writing Commentary

You are going to need at least two sentences of commentary for every detail sentence. A good rule of thumb is that your commentary should be twice as long as your details. Otherwise, your paper is just full of facts. We want to know how YOU think these facts prove your point and what YOU think they mean.
Here are a few different methods for writing commentary:
1) Opinion: this is where you write your belief, subjective judgment or way of thinking about a detail .
2) Interpretation: your explanation of something that is not clear.
3) Character and Subject’s Feelings: when you describe what the character or subject of the detail is feeling (ideal for literary analysis papers)
4) Personal Reaction: your personal emotions about the detail.
5) Evaluations: your objective judgment of a detail.
Commentary is the Treasure
Your commentary is the treasure that makes your paper shine. It should always strengthen and extend the details. This is your chance to show us what you’ve got. It is where you can impress us with your analysis and interpretation skills.
“What and Why” Method
You may be thinking, “Analysis and interpretation skills? What if I don’t possess those skills?” Well breathe easy, because interpretation is really just a fancy word for “what,” while analysis simply means “why”.
So if you are struggling to write your commentary try using the “what and why” method. First, tell the reader WHAT your detail is talking about by defining or explaining. Next, let your reader know WHY this detail is relevant to your thesis statement.
Starting Commentary Sentences
If you are struggling to start your commentary, consider beginning your commentary in one of the following ways:
“This shows that…”
“This is important because…”
Obviously, you cannot start every sentence you write like that since this would be redundant. However, even if you do not write these phrases at the beginning of all of your sentences, it is helpful even just to think these phrases in order to guide your commentary in the right direction.
Applying Commentary Techniques
Now that we have discussed the different options for writing commentary, and the method for doing so, let’s put them together and see what is looks like.
Commentary Type: Opinion using the “what and why” method

Topic: education
Detail: According to the 2013 National Assessment of Education Progress Reading test, 80% of students score below grade level in reading.
Commentary: Your commentary for this detail will answer the following questions: (1) “WHAT is my opinion?” and (2) “WHY is my opinion relevant to my thesis statement?”
(1) A statistic like this shows the poor state of the education. (2) If we are to help students become successful adults, we need to change the way we are educating our children.
Commentary Type: Interpretation using the “what and why” method
Topic: benefits of college
Detail: First of all, of 2,350,000 college students enrolling per year, only 1,750,000 will graduate.
Commentary: Your commentary for this detail will answer the following questions: (1) “WHAT is my interpretation?” and (2) “WHY is my interpretation relevant to my thesis statement?”
(1) This shows that the high demand placed on students during their college years is too much stress for many. (2) However rigorous it may be though, the pressure and expectations are reflective of a future career and help prepare young adults for these challenges.
Commentary Type: Character or Subject Feelings using the “what and why” method

Topic: cost of higher education
Detail: For example, Benjamin Davis, a recent college graduate with a degree in Business, struggled for many years to find a job because of the recent unemployment struggles in America
Commentary: Your commentary for this detail will answer the following questions: (1) “WHAT is the subject’s feelings?” and (2) “WHY is subjects feelings relevant to my thesis statement?”
(1) He, like most, experiences extreme frustration at spending a great deal of time and money obtaining his degree, but feeling like he has very little advantage over others without a degree when finding a job. (2) As a result, many who find themselves in a similar situation are left wondering if higher education is worth the high cost.
Commentary Type: Personal Reaction using the “what and why” method
Topic: bullying
Detail: Also, a bully might speak cruelly in order to intimidate, steal a student’s belongings, or intentionally exclude one from a group .
Commentary: Your commentary for this detail will answer the following questions: (1) “WHAT is my personal reaction?” and (2) “WHY is my personal reaction relevant to my thesis statement?”
(1) It is extremely upsetting to know that most children undergo this type of treatment at school. (2) It is hurtful, isolating, and can have long-lasting psychological damage on those students who experience bullying often.
Commentary Type: Evaluation using the “what and why” method
Topic: bears
Detail: Naturally, a bear, when threatened, will rise up from the ground, growl loudly, and begin charging at a speed of up to 35 mph.
Commentary: Your commentary for this detail will answer the following questions: (1) “WHAT is my evaluation?” and (2) “WHY is my evaluation relevant to my thesis statement?”
(1) Although this is a frightening experience, it is not entirely the bear’s fault. (2) In fact, most of the time when a bear attacks a person, it is the result of a person not understanding that when going out into the woods, he or she is entering a bear’s environment; forgetting to be respectful and cautious can cause the bear to react thusly.
When To Use Commentary Types
Depending on your assignment, choose the types of commentary that best fits your argument. Use of a variety of different types of commentary to write a well-argued paper.

Go back and look at step two of writing details from last week’s blog. Look at the commentary you wrote and update it to fit into the “what and why” method using some of the above types of commentary. If you did not do that step last week, go ahead and use the worksheet found here.
We hope this helped you when writing commentary. If you still need help, call Oxford Tutoring for support or to schedule a writing tutoring session.
Share this:
Author: oxfordtutoringblog
Oxford Tutoring specializes in K-12 tutoring in English, mathematics, science and test preparation. We provide skill building and homework help in private, one-on-one sessions coordinated with our student’s classroom programs, but focused on the way in which each student learns. Working to better each student’s academic success, Oxford Tutoring personalizes our tutoring approach to best meet the education needs of our students. View All Posts
One thought on “ Elements of an Essay: Writing Commentary ”
- Pingback: Elements of an Essay: Editing and Revising – Oxford Tutoring
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
School of Modern Languages and Cultures
Writing a literary commentary: guidelines, what is a commentary.
- First and foremost, a literary commentary is NOT an essay. The passage in front of you is not, therefore, an invitation to write a general essay about the work from which it has been taken.
- A commentary is an analysis of the given passage, its function and its characteristics. It should examine the key themes and stylistic devices of the passage, showing how the language works to convey (or at times undermine) its content.
- A commentary should relate the passage to the rest of the work (novel, collection of poems, etc.), but remain focused in the main on the details of the passage itself.
- Make sure that your commentary covers the whole passage. For instance, if you are given a poem with five stanzas, you should try to say something about each stanza.
- Use line numbers (in both poetry and prose) in your commentary, rather than wasting time by quoting at length.
- When you do quote, make sure that your comments don't simply repeat what the quotation already says: 'In the line "Il pleut dehors", the poet tells us that it is raining outside ...'
- Avoid verbosity or inaccurate terminology. Clarity and precision are top priorities, and polysyllabic words do not improve a commentary.
- Don't use words like 'effective', 'atmospheric', or 'beautiful' unless you are also explaining what the effect, atmosphere or beauty of the passage are, and how they are achieved.
How should I write my commentary?
There are no fixed rules for writing a commentary, but a general structure will be suggested. You should always PLAN your commentary before you start writing it, following these guidelines where appropriate.
1 Introduction
- Put the passage into context , and summarise its arguments briefly (in a few sentences): do not spend too much time discussing matters outside of the passage.
- You should assume that your reader has read the work from which the passage has been taken.
- You may want to point out the passage's most important thematic and structural aspects in your introduction.
- Introduce the main themes and structural aspects of the passage.
- What kind of passage is it (description/dialogue/free indirect speech), and what is its function (in the rest of the work)?
- What is its overall structure (repetitious/circuIar/leitmotifs/develops to a climax)?
- What is the narrative point of view (first-person/third-person/omniscient or not)?
- What are the register (high/low) and tone (comic/surreal) of the passage?
3 Detailed Analysis
This is the most substantial part of the commentary. It should not be simple description or paraphrase, but an analysis of how the language of the passage functions. The following are aspects of the text that you should look for:
- Sentence structure
- Tense usage
- Word order (balance or lack thereof, harmony, repetition, parallels)
- Figurative language (imagery, metaphors, similes, symbolism, allegory, personification, myth, antithesis, irony, paradox)
- Characterisation (or lack thereof)
- Narrative technique/point of view (first/third person, limited point of view, stream of consciousness)
- Punctuation
- Alliteration, assonance, rhyme (poetry and prose)
Remember that no text is likely to have instances of all of these elements, and that it is best to concentrate on those that are most relevant to the passage in question. Also, you should avoid simply commenting on the appearance of a particular technique: make sure you say why this is worth noticing. Ideally, your comments should cohere to explain how the various linguistic devices combine to produce the overall effect intended by the author.
4 Conclusion
- Summarise your findings, drawing together the different aspects of the text that you have discussed in your commentary.
- Assess briefly the achievements and significance of the passage, both in itself and in relation to the work from which it is taken.

Some useful aids to commentary-writing
- Nurse, P. (ed.), The Art of Criticism: Essays in French Literary Analysis (Edinburgh, 1969) (sample commentaries of French literary texts)
- Biard, J. D., Lexique pour I 'explication de texte (Exeter, 1980)
- Benac, H., Vocabulaire de la dissertation (Paris, 1949)
(Binac and Biard provide lists of technical terms used in close analysis of a literary text in French, and give explanations and examples of usage)
How To Write A Commentary Essay
- Essay Writing FAQ

A commentary essay is a type of essay that provides an analysis or interpretation of a text. Commentary essays are typically longer than regular essays, and they provide in-depth analysis of the text.
There are a few things to keep in mind when writing a commentary essay. First, be sure to read the text carefully and make sure that you understand it. Next, identify the main points of the text and develop a thesis statement that reflects your interpretation of the text. Then, support your thesis with evidence from the text. Be sure to use clear and concise language, and avoid making any assumptions about the text.
Finally, be sure to revise your essay thoroughly. Check for grammar mistakes, ensure that your argument is clear and concise, and make sure that your evidence supports your thesis.
What are the five parts of a commentary?
When it comes to commenting on a text, there are five main areas that you need to focus on:
1. The Introduction
This is where you introduce the text and give a brief overview of what it is about. You should also state your thesis – or the main point you are trying to make about the text.
2. The Main Body
This is where you expand on your thesis, providing evidence and examples to support your argument.
3. The Conclusion
This is where you summarize your main points and draw conclusions from them.
4. The Literature Review
This is a section where you discuss the work of other scholars who have written about the text you are commenting on.
5. The Bibliography
This is a section where you list all of the sources you have consulted in writing your commentary.
How do you start off a commentary?
When starting a commentary, it is important to introduce who you are and what your qualifications are. This will help to establish your credibility as an expert on the topic at hand. You should also provide a brief overview of the issue or event that you will be commenting on. This will help your readers to understand the context of your remarks.
It is also important to be clear and concise in your remarks. Avoid making any unsupported statements, and back up your arguments with evidence. Be sure to stay on topic, and avoid digressing into unrelated topics.
Finally, always be respectful in your comments, and avoid attacking or insulting others. Remember that a commentary is a forum for thoughtful discussion, not a venue for personal attacks.
What is an example of a commentary?
A commentary is a type of essay that provides an analysis and interpretation of a text. It typically includes an explanation of the author’s purpose in writing the text, as well as an examination of the text’s structure and rhetorical devices. A commentary may also include an evaluation of the text’s strengths and weaknesses.
How do you write a commentary for an essay?
Commentaries are written to explain and analyze a text. They can be written for essays, papers, or other writing assignments. The purpose of a commentary is to help the reader understand the text by providing information about the author, the context, and the meaning of the text.
When writing a commentary, it is important to first read and understand the text. After reading the text, you should outline the main points and ideas that you want to discuss. Next, you should write a paragraph explaining each point. Be sure to provide evidence from the text to support your analysis. Finally, you should conclude your commentary by discussing the implications of the text and what you think the author was trying to say.
Where is commentary in an essay?
Commentary is an important part of an essay, but it can be difficult to know where to put it. Here are a few tips on where to put commentary in an essay.
The best place for commentary is after the main points of your essay. This is where you can expand on your points and give your readers more information. You can also use commentary to explain why you think the points you made are important.
You can also use commentary to introduce your arguments. This is a good way to introduce your readers to your point of view and to explain why you think your argument is important.
Finally, you can use commentary to wrap up your essay. This is a good place to restate your main points and to give your readers a summary of your argument.
What is a commentary statement?
A commentary statement is a type of financial statement that is used to provide additional information about the financial condition of a company. This statement is typically used to explain the results of the company’s operations, to give insights into the company’s financial position, and to provide explanations of significant changes in the company’s financial position.
What are the types of commentary?
There are many different types of commentary. Some of the most common types are:
1. Literary commentary 2. Film commentary 3. Art commentary 4. Music commentary 5. Theatre commentary
Each type of commentary has its own unique set of rules and guidelines. Literary commentary, for example, typically focuses on the meaning and interpretation of a text, while music commentary often focuses on the structure and composition of a piece.
It is important to be aware of the different types of commentary when writing or reviewing any form of art. Understanding the purpose and function of commentary can help you to better appreciate and understand the work being discussed.
What are the three types of commentary?
There are three types of commentary:
1. Explanatory: This type of commentary seeks to explain the text or passage in question. It may provide background information, discuss the author’s intent, or offer other insights into the work.
2. Critical: This type of commentary evaluates the text or passage, often offering a literary or historical analysis. It may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the work, its themes and motifs, and other elements.
3. interpretive: This type of commentary provides an interpretation of the text or passage. It may offer a personal response to the work, explore its symbolism or meaning, or discuss its impact on culture or society.
What is the commentary is main point?
The commentary is the main point of a text. It is the part of the text that provides analysis and interpretation of the text. The commentary is often used to provide information about the author’s thoughts and feelings about the text. It can also provide information about the historical or cultural context of the text.
How do you start a commentary?
Commentary is a form of writing that provides analysis and interpretation of a text. It can be used to discuss a work of fiction, a piece of nonfiction, a poem, or a song. In order to write a commentary, you first need to read the text closely and make sure you understand it fully. Then, you can begin to formulate your thoughts and ideas about the text.
Some people find it helpful to outline their commentary before they write it. Others prefer to just start writing and let the thoughts flow. It’s important to be clear and concise when writing a commentary, and to avoid simply summarizing the text. Instead, offer your own insights and analysis.
Make sure to support your points with evidence from the text, and be sure to cite any sources you might use. A well-written commentary can provide a deeper understanding of a text and help readers to appreciate it more fully.
What is an example for commentary?
Commentary is a type of writing that is used to provide analysis and interpretation of a text. It can be used to provide additional information about the text, or to offer a different perspective on the text. Commentary can be helpful for readers who want to gain a deeper understanding of a text, or who want to see how different people interpret a text.
One of the best ways to understand commentary is to look at some examples. Here is an example of commentary from a book review:
“The author’s use of language is beautiful and fluid, and her story is one that will stay with you long after you finish the book.”
This is a comment about the author’s use of language and the impact the book had on the reader. It is not a direct quote from the book, but it offers insight into the author’s writing style and the themes of the book.
Here is another example of commentary, this time from a movie review:
“The acting is terrific, and the story is suspenseful and thrilling.”
This is a comment about the acting and the story of the movie. It is not a direct quote from the movie, but it offers insight into the quality of the acting and the plot of the movie.
As you can see, commentary can be a great way to provide additional information or interpretation about a text. It can help readers to gain a deeper understanding of the text, and it can also be a fun way to discuss different aspects of a text.
How do you start a commentary after a quote?
When you are writing a commentary after a quote, you want to make sure that you introduce the quote properly and that you provide some context for it. You also want to make sure that your commentary is clear and concise.
To introduce a quote, you should provide the name of the person who said it and the date.
You should also provide a brief summary of the quote. After you introduce the quote, you should provide your commentary.
In your commentary, you should provide your analysis of the quote and you should provide your opinion on it. You should also provide some background information on the quote and on the person who said it. You should also provide a discussion of the implications of the quote.
When you are writing a commentary after a quote, it is important to be clear and concise. You should make sure that your commentary is easy to follow. You should also make sure that your commentary is interesting and engaging.
What are the basic information of a commentary?
Commentaries are a type of literary work that provide interpretation and analysis of a text. They can be used to provide additional information about the text, to offer a different perspective on the text, or to help the reader understand the text better.
There are a few basic pieces of information that all commentaries should include. This information includes the title of the work being commented on, the name of the author of the commentary, the date of the commentary, and the place of publication. Additionally, most commentaries include a table of contents, a preface or introduction, and a conclusion.
The title of the work being commented on is the first piece of information that is included. This is followed by the name of the author of the commentary. The date of the commentary is next, followed by the place of publication.
Most commentaries also include a table of contents. This table of contents should list the headings and subheadings that are included in the commentary, as well as the page numbers on which they can be found.
The preface or introduction is generally a short section that introduces the reader to the work being commented on. It may include information about the author of the work, the date of the work, and the place of publication. It may also include a brief summary of the work.
The conclusion is the final section of the commentary. It generally wraps up the commentary by summarizing the main points that were made. It may also include a discussion of the implications of the commentary.
How do you write a commentary example?
When it comes to writing a commentary, there are a few things that you need to keep in mind. First, a commentary is a type of essay that provides your thoughts and analysis on a text. It is not a summary of the text. Second, a good commentary will be well-organized and well-written. Lastly, a good commentary should be clear and concise.
To write a good commentary, you need to first read and understand the text that you are commenting on. Next, you need to outline your thoughts and organize them in a logical manner. Once you have outlined your thoughts, you can then begin writing your commentary. be sure to proofread your work before submitting it.
What should I write in commentary?
When it comes to writing commentary, there are a few things that you should keep in mind. First and foremost, your commentary should be concise and to the point. You don’t want to overload your readers with too much information, so make sure to focus on the most important points.
In addition, you should always be clear and concise when explaining your analysis. Avoid using complex language or jargon that your readers may not be familiar with.
Finally, make sure to back up your points with concrete evidence. This will help to strengthen your argument and make your commentary more persuasive.
How do you start a commentary sentence?
A commentary sentence is a sentence that provides additional information or commentary on a preceding sentence or statement. Commentary sentences are often used to clarify or explain a point, and can be used to introduce new information, provide a contrast, or offer a different perspective.
When starting a commentary sentence, it is important to ensure that it is logically connected to the sentence or statement that it is commenting on. In order to do this, it is often helpful to use a signal phrase to introduce the commentary sentence. Some common signal phrases include “commenting on,” “speaking to,” “in response to,” and “related to.”
It is also important to ensure that the commentary sentence is properly constructed, and that all of the information it contains is relevant to the point that is being made. In order to avoid rambling or going off on a tangent, it is often helpful to focus the commentary sentence on a specific point or idea.
Finally, it is important to make sure that the commentary sentence is clearly written and easy to understand. In order to ensure this, it is often helpful to use clear and concise language, and to avoid using complex or technical terms.
Cora Carver is an educational blogger and mother of two. She has a passion for helping others learn and grow, and she uses her blog to share her knowledge and experiences with others.
View all posts
coracarver11
Cora Carver is an educational blogger and mother of two. She has a passion for helping others learn and grow, and she uses her blog to share her knowledge and experiences with others. View all posts by coracarver11
Comments are closed.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Occupations
- Media Careers
How to Write a Commentary
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Richard Perkins . Richard Perkins is a Writing Coach, Academic English Coordinator, and the Founder of PLC Learning Center. With over 24 years of education experience, he gives teachers tools to teach writing to students and works with elementary to university level students to become proficient, confident writers. Richard is a fellow at the National Writing Project. As a teacher leader and consultant at California State University Long Beach's Global Education Project, Mr. Perkins creates and presents teacher workshops that integrate the U.N.'s 17 Sustainable Development Goals in the K-12 curriculum. He holds a BA in Communications and TV from The University of Southern California and an MEd from California State University Dominguez Hills. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 674,808 times.
At some point in your life, you'll probably have to write a commentary. Whether you're a teacher, editor, student, or amateur critic, knowing how to constructively analyze someone's work is a useful skill. There isn't a magical formula for writing a commentary. The commentary you write depends upon what you're reviewing, why you're giving feedback, and what you think about the work. No matter what you’re working on, having a clear goal and strong writing will help make your commentary successful.
Writing a Literary Commentary

- Your thesis is your argument or your point of view. This is where you take a stance, and spend the rest of the essay supporting your thesis.
- Maybe you are writing a commentary on Great Expectations . Your thesis could be, “Not only is Dickens’ tale engaging, it is also an insightful commentary on the differences between social classes in industrial Britain.”
- You might write at the top of your outline, “Important Themes in Great Expectations”. You could then make bullet points such as “Setting”, “Ambition”, “Class”, etc.

- You might start by saying, “ Great Expectations is full of imagery that makes the reader feel as if they are in 19th century England with Pip. Dickens’ novel about class, ambition, and love sheds important light on the social divides of the time.”
- You could then list the themes that you will discuss in the body of your commentary.

- An excellent specific example to illustrate this theme is pointing out that the character remains in her wedding dress, despite being jilted decades before.

- You might write something like, “Miss Havisham is an example of the theme that love can sometimes go terribly wrong. This is also an important theme when examining the relationship between Pip and Estella.”
- Make sure to use smooth transitions. When you move to a new example, use a good transition word or phrase. Some examples are “similarly”, “conversely”, and “again”.

- In your commentary on Great Expectations , you would want to make sure that you emphasize your summary again: this is a good example of class divisions and how ambition is not always the best quality.
- You might also choose to compare it to another book from the same period to illustrate why the work by Dickens is significant. However, you generally shouldn’t introduce new information in your conclusion.
Creating Data Commentary

- You might also be asked by your boss or teacher to write a data commentary. Make sure to ask about their expectations, such as length.

- For example, if the research is about the graduation rate in the Chicago Public Schools, you need to explain the numbers and illustrate why the results are important.

- You might say something like, “As shown in Figure 1.2, the costs of healthcare have risen at a steady rate since 2000.”

- As in the rest of your data commentary, your conclusion should refer to specific pieces of data.

- You should include a specific section for resources at the end of your data commentary.
- Any time you cite numbers or a quote, make sure to provide a reference.
Commentary Outlines

Expert Q&A

- If you are writing a commentary for a class, make sure to carefully follow the instructions. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Make sure to carefully edit and polish your writing. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.bucks.edu/media/bcccmedialibrary/pdf/HOWTOWRITEALITERARYANALYSISESSAY_10.15.07_001.pdf
- ↑ Richard Perkins. Writing Coach & Academic English Coordinator. Expert Interview. 1 September 2021.
- ↑ http://www.udc.edu/docs/asc/Outline_Structure_for_Literary_Analysis_Essay_HATMAT.pdf
- ↑ https://www.germanna.edu/wp-content/uploads/tutoring/handouts/Literary-Analysis.pdf
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/writing-data-commentary/
- ↑ https://ebooks.hslu.ch/academicwriting/chapter/4-5-results/
- ↑ https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/arts/modernlanguages/intranet/undergraduate/skills/commesswriting/commentarywriting/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4789530/
About This Article

To write a commentary, write about your observations and analysis of the text you read. You should craft a clear and specific thesis statement about the novel, poem, or play you are evaluating. Your thesis statement should explain your stance or argument about the text. Use this thesis statement to build a brief outline of your commentary and then choose specific details from the text to support your argument. Then, add an introduction to give your reader some context for the themes you will discuss. For tips from our Education reviewer on how to write a data commentary, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Nov 15, 2016
Did this article help you?
Eserbellra Marylao
Mar 20, 2016
Abee Victory
Sep 17, 2020
Aug 19, 2022
Prudence Orji
May 5, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Teacher Habits
Helping Teachers inside the Classroom and Out
How to Write an Explanatory Essay: Topics, Outline, Example
Have you ever been tasked with writing an explanation essay and wondered where to start? You’re not alone! Many students struggle with the challenge of presenting complex ideas in a concise and engaging manner. Fear not; with the right approach, learning how to write an explanation essay can be a rewarding experience that enhances your understanding of a topic and sharpens your writing skills.
In this blog post, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of crafting an exemplary explanation essay. We will explore the definition and purpose of explanatory essays, offer tips on topic selection, outline development, and delve into the essentials of how to write an explanatory essay. By the end of this post, you will be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to tackle any explanatory essay assignment that comes your way.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Explanatory essays, akin to expository essays , provide an unbiased and objective analysis of a topic with the aim of informing and clarifying.
- Choosing the right topic for your explanatory essay involves selecting a neutral, engaging, and relevant topic supported by ample researchable information.
- Writing an explanatory essay requires conducting thorough research, utilizing transitions & linking words judiciously, citing sources accurately & revising/editing to ensure high quality work.
Explanatory Essays: Definition and Purpose
An expository essay, also known as an explanatory essay or an explanatory paper, is a type of explanatory writing wherein one is required to describe and elucidate a particular point of view, incident, event, or situation. Unlike argumentative or persuasive essays, the goal of explanation essays, including expository essays, is to offer an unbiased and objective analysis of a topic, aiming to inform and clarify without arguing or persuading. By presenting information in a clear and organized manner, explanatory essays help readers develop a better understanding of the subject matter.
Explanatory essays follow the traditional explanatory essay format, which includes an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The thesis statement, located in the introduction, is a specific and argumentable statement that concisely presents the primary concept of the essay. The body paragraphs provide evidence and explanations to support the thesis, while the conclusion ties everything together and leaves the reader with a clear understanding of the author’s presentation.
Choosing the Right Topic for Your Explanatory Essay
Selecting an appropriate topic is a crucial step in crafting a successful explanatory essay. A well-written explanation essay seeks to offer an unbiased and objective analysis of a topic, with the intention of informing and elucidating without trying to convince. Therefore, it is essential to choose a topic that is neutral, engaging, and aligns with your interests and the interests of your target audience.
To generate ideas for an explanation essay, consider topics that you have personal experience with or are genuinely curious about. It is also important to ensure that the topic can be effectively researched and that there is ample information available to compose a comprehensive paper. Once you have a list of potential topics, evaluate them based on their relevance to the assignment and your familiarity with the subject matter. This will help you select a topic that will not only be engaging to your readers but also enjoyable for you to research and write about.
Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the backbone of your explanation essay, as it sets the stage for the rest of the paper. A strong explanation essay thesis statement should be concise, debatable, and supportable, summarizing the main idea and purpose of the essay. It is important to invest time and effort into crafting a compelling thesis statement, as it will guide your research and shape the overall structure of your essay.
To develop an effective thesis statement, start by identifying the primary concept or argument that you want to convey in your essay. Then refine your statement to ensure that it is succinct and specific, while still being arguable and justifiable.
If you find yourself struggling to create a strong thesis statement, consider drafting a rough version and returning to it after you have completed the rest of the paper. This will allow you to refine your statement based on the evidence and arguments presented in your essay.
Developing an Effective Explanatory Essay Outline
An effective explanatory essay outline is essential for organizing your thoughts and ideas in a logical manner, ensuring a smooth flow throughout your essay. The outline should include an introduction, body, and conclusion, each containing specific information arranged in a logical manner to ensure the continuity of the paper. By creating a detailed outline, you can easily identify any gaps in your research or argumentation and make revisions as needed.
In the following subsections, we will delve into strategies for writing an engaging explanatory essay introduction, structuring body paragraphs, and crafting a compelling conclusion. These techniques will help you create an effective explanatory essay outline that will serve as a roadmap for your writing process.
Introduction Strategies
The introduction is the first part of your essay that your readers will encounter, and it plays a crucial role in grabbing their attention and setting the stage for the thesis statement. To create an engaging introduction, you can employ various hooks, such as rhetorical questions, quotes, or statistics, to capture the reader’s interest and provide a foundation for your thesis statement.
An effective introduction should also provide a concise overview of the subject matter and the primary concepts that the reader will encounter while perusing the essay. This background information helps your readers understand the context of your essay and prepares them for the arguments and evidence presented in the body paragraphs. By crafting an engaging and informative introduction, you set the tone for the rest of your essay and encourage your readers to continue reading.
Structuring Body Paragraphs
Structuring body paragraphs involves presenting evidence to support your thesis statement while ensuring clarity and logical organization. Each body paragraph should focus on a particular aspect of the topic and provide evidence to back it up. This can include facts, quotes, statistics, survey results, and examples that help validate your arguments and substantiate your assertions.
To ensure clarity and logical organization in your body paragraphs, you can employ various techniques, such as utilizing transitions between paragraphs, supplying examples to elucidate points, and employing linking words to connect ideas. Transitions and linking words, such as “however,” “therefore,” “in addition,” and “furthermore,” can help guide your readers through your essay and make it easier for them to follow your ideas and arguments.
By carefully structuring your body paragraphs, you can create a coherent and persuasive explanatory essay that effectively supports your thesis statement.
Crafting a Compelling Conclusion
The conclusion of your explanation essay is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers. A compelling conclusion should summarize the main points presented in your essay, restate your thesis statement, and offer recommendations or a call to action. This helps to reinforce the key ideas and arguments in your essay and leaves your readers with something to ponder.
When crafting your conclusion, it is important to avoid introducing new information or arguments, as this can confuse your readers and weaken the overall impact of your essay. Instead, focus on providing a concise and convincing summary of the evidence presented in your essay and how it supports your thesis statement. By doing so, you can leave your readers with a clear understanding of your essay’s purpose and a sense of closure.
Writing Your Explanatory Essay: Step-by-Step Process
Now that you have a solid understanding of the key components of an explanation essay, it is time to embark on the writing process. In this section, we will outline a step-by-step process for writing an explanatory essay, which includes conducting thorough research, utilizing transitions and linking words, and citing sources to avoid plagiarism.
By following this step-by-step process, you can ensure that your explanation essay is well-structured and informative, providing your readers with a clear understanding of the subject matter. With practice and persistence, you can master the art of explanatory essay writing and create engaging, persuasive essays that effectively convey complex ideas.
Conducting Thorough Research
Conducting thorough research is essential for an explanation essay, as it helps gather credible evidence (facts, quotes, statistics, survey results, and examples) to support your thesis statement. Begin by selecting a topic that is of personal interest and has some familiarity. Once you have chosen a topic, conduct preliminary research to ensure that there is sufficient information available to compose a comprehensive paper.
When gathering information for your essay, it is crucial to utilize dependable sources, such as scholarly articles, books, and websites. Be sure to take notes and keep track of the sources you have used, as this will make it easier to reference them in your essay and avoid plagiarism. By conducting thorough research, you can ensure that your essay is well-supported and provides a comprehensive analysis of the topic.
Utilizing Transitions and Linking Words
Utilizing transitions and linking words is crucial for ensuring a smooth flow throughout your explanation essay and making it easier for readers to follow your ideas and arguments. Examples of transitions and linking words include phrases such as “however”, “therefore”, “in addition” and “furthermore”.
Incorporating these transitions and linking words in your essay helps guide your readers through the progression of your arguments and enhances the overall readability of your paper. Be sure to use them judiciously and avoid overusing a specific transition or linking word, as this may become repetitive and detract from the flow of your essay.
By employing a variety of transitions and linking words, you can create a cohesive and engaging explanatory essay that effectively conveys your ideas.
Citing Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism
Citing sources accurately and consistently is crucial for avoiding plagiarism and ensuring the credibility of your explanation essay. When composing an explanation essay, sources are typically cited following either MLA, APA, or Harvard formatting. In-text citations generally include the author’s name and the year the source was published, and for direct quotations, the page number must also be specified.
By accurately citing your sources, you not only give credit to the original authors, but also demonstrate your commitment to academic integrity and the credibility of your essay. Be sure to double-check your citations and proofread your essay for any errors or inconsistencies in your referencing style. By doing so, you can avoid plagiarism and ensure that your essay is a credible and accurate representation of your research and ideas.
Analyzing Explanatory Essay Examples
Analyzing explanatory essay examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, style, and content of successful essays, helping you improve your own writing. By examining well-written examples, you can gain a better understanding of the key elements of an explanation essay, such as the thesis statement, the organization of body paragraphs, and the overall flow of the essay.
When analyzing explanatory essay examples, pay close attention to the clarity of the explanations, the use of evidence to support the argument, and the general structure and format of the essay. Also, consider the effectiveness of the thesis statement and the essay in conveying information.
By studying and learning from exemplary essays, you can refine your own writing and create an engaging, informative, and well-structured explanation essay. In fact, knowing how to write an explanation essay is essential for developing your skills in this area.
Tips for Revising and Editing Your Explanatory Essay
Once you have completed your explanation essay, it is essential to revise and edit your work to ensure that it is of high quality and free of mistakes. Start by reviewing your essay for clarity, organization, and logical flow. Check that your thesis statement is clear and concise, and that your body paragraphs effectively support your argument.
During the revision process, ask yourself the following questions: Is the essay organized effectively? Are the transitions between paragraphs seamless? Are there any grammatical or orthographic errors? Are sources referenced accurately? If necessary, make any revisions to improve the overall quality and coherence of your essay.
Finally, proofread your essay for any remaining errors and inconsistencies. Consider presenting your essay to a trusted friend or classmate for feedback, as they may be able to spot mistakes that you may have missed. By revising and editing your essay, you can ensure that it is polished, engaging, and free of errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the format of an explanatory essay.
An explanation essay format typically consists of an introduction, three body paragraphs with one subtopic per paragraph, and a conclusion. It is a basic essay structure which can be further expanded as needed.
Formal language should be used and the goal is to make a connection with the reader through the text.
What is the best way to start an explanatory essay?
To begin an explanation essay, start with an attention-grabbing statement or question that draws your readers in. This should be written in a formal tone, and include a clear conclusion in the first sentence without an introduction or summary.
What are the main parts of an explanatory essay?
An explanation essay typically consists of an introduction with a hook, some background information, and a thesis statement.
It then progresses to further explain the topic and draw a conclusion.
How do you write a 5 paragraph explanatory essay?
To write a five-paragraph explanatory essay, you must create an introduction that introduces the main topic and states the thesis, three body paragraphs to support the thesis, and a concluding paragraph to wrap up the points made in the essay.
The tone should be formal throughout, with clear connections to the reader.
What is the main difference between an explanatory essay and an argumentative essay?
Explanatory essays seek to explain a topic without presenting an argument, while argumentative essays make an assertion and support it with evidence.
These two types of essays have different goals and require different approaches. Explanatory essays focus on providing information and context, while argumentative essays focus on making a persuasive argument.
When writing an essay, it is important to write an explanation.
In conclusion, writing an exemplary explanation essay requires a clear understanding of the topic, careful planning, thorough research, and effective organization. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this blog post, you can create engaging, informative, and persuasive explanatory essays that effectively convey complex ideas. With practice and persistence, you can master the art of explanatory essay writing and tackle any assignment that comes your way.
AP ® Lang teachers: looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Coach Hall Writes
clear, concise rhetorical analysis instruction.
How to Write Commentary for Rhetorical Analysis
February 4, 2022 by Beth Hall
Wondering how to write commentary for rhetorical analysis? When writing a rhetorical analysis essay, having well thought out and strong commentary will make a significant difference in your writing.
So, what exactly is commentary? And how can you deliver high-quality commentary in your rhetorical analysis?
Commentary is your analysis and interpretation of the passage. Commentary explains how the evidence you present in the body paragraph proves your thesis. For more information about what commentary is, click here .
Your body paragraphs in your rhetorical analysis will consist of a topic sentence, analysis, and commentary. Many students think evidence is the most important piece, and while evidence is certainly important, commentary is paramount because it is what contains your argument and analysis. You can think of your evidence as answering the “what” and commentary answering the “how” or “why.”
In order to effectively write commentary in your body paragraphs, you need to have an understanding of the rhetorical situation. The rhetorical situation includes the following elements: the writer or speaker, the audience, the (historical) context, the exigence (ie. what prompted the writer to write), the purpose, and the message or argument.
The rhetorical situation is key to your commentary because it is what you are analyzing. Your commentary should address why the rhetorical choice the author is making is important to the rhetorical situation. (You can learn more about the rhetorical situation by reading this blog.)
How to Develop Your Commentary
Many students don’t develop their commentary enough because they aren’t sure what to say, or they feel they are running out of time.
When writing a rhetorical analysis essay, be sure to include precise verbs to convey what the writer is “doing.”
Here’s a list of rhetorically accurate verbs:
- Acknowledges
Once you’ve made a claim about what the writing is “doing” (the rhetorical choice they are making,) then you need to explain the significance of that choice. Why is the writer “doing” that? This is commentary.
Here are some verbs that can help you generate commentary:
- demonstrates
- illustrates
- underscores
The step to knowing how to write commentary for rhetorical analysis is knowing the right kinds of questions to ask. When you are addressing the rhetorical situation, you want to do more than scratch the surface level. Let’s look at examining the writer or speaker, for example. You may ask some of the following questions to help you create commentary about the rhetorical choice you are analyzing:
- What are the speaker’s qualifications?
- What does the choice reveal about the speaker’s beliefs/values/needs?
- What do the choices reveal about the speaker’s relationship with the audience?
If you want more questions to guide you on analyzing the rhetorical situation, check out this blog.
How do I write a body paragraph with commentary?
Now that you know the parts that make up the commentary, and you understand how to examine the rhetorical situation, let’s put it all together. Let’s look at an excerpt of a body paragraph, and notice how commentary is used.
Albright references recent political examples in which countries could have settled but chose the more arduous path instead. By noting that America “must choose to turn inward” or “seize opportunities,” Albright suggests the value of making challenging, sometimes “trailblazing” decisions as opposed to selecting the easier, more isolating path . While this comment also serves as affirmation of President Clinton’s leadership and thus a subtle reminder of Albright’s credentials as Secretary of State , the contrast between “turning inward” and “seizing opportunities” introduces Albright’s message of perseverance.
In just this small excerpt, you can see how different elements (underlined) of the rhetorical situation are being addressed. When you are writing your own body paragraphs, it may be helpful to color-code the different elements of the rhetorical situation and identify them in your writing. This will help you check to make sure most of the elements are present.
How do you fix limited commentary?
If you find yourself writing with cliches, idioms, vague wording, or sentences that don’t directly address the rhetorical situation, you are likely writing limited commentary. You want each sentence to address your specific passage, so aim to create specific, clear analysis.
Here is what your writing may look like if you have limited commentary:
- You use phrases like “the author uses diction”
- You use cliches like “opens the reader’s eyes”
- You use idioms like “touches the audience’s heart”
This type of writing is common and also fixable. Once you’ve identified these mistakes in your writing, you want to work on changing them.
First, you can fix phrases such as “the author uses” by strengthening your word choice. You want to add a descriptor or adjective in front of the item you are referring to, such as diction. This might mean changing “diction” to “patriotic diction.” Then, analyze why the author uses this rhetorical choice.
Second, you want to avoid cliches. Try rewording the cliche. Instead of “opens the reader’s eyes” try “forces the reader to consider.” This makes our language more precise and helps you expand your commentary.
Lastly, you want to stay away from idioms. These prepackaged expressions don’t tell the reader the why and the how behind the author’s writing choices. Instead of saying “touches the audience’s heart” try to identify what the writer is doing to evoke that emotional response. Specify which emotion the audience is experiencing and why the writer wants to elicit such an emotion.
Now that you know how to write commentary for rhetorical analysis, go rock your next AP® Lang essay!
DISCLAIMER: I am not affiliated with The College Board. The advice and opinions expressed in this blog post are my own.
AP® Lang Teachers
Looking to help your students improve their rhetorical analysis essays?
Latest on Instagram

Shop My TPT Store

OASIS: Writing Center
Common assignments: commentary versus opinion, commentary and argumentation.
In order to synthesize your sources, you must first analyze them to help provide rationale for why they are a part of your literature review and what role they play within your field. In order to demonstrate analysis, you must provide your commentary on the sources you discuss beyond simply summarizing them.
Consider the following, analysis-free excerpt. This approach is typical in first drafts of literature reviews:
....is to deny the student (Sigree, 1999). As Harper (2001) noted, instructors cannot identify every one of their students' emotional intelligences (EI). Faculty members do not have the time, and students simply are not that forthcoming with their learning preferences (Harper, 2001). Furthermore, as Harper warned, if instructors decide to attempt a complete analysis of every student's EI, they will inevitably hold the entire class back. After all, taking time to adequately diagnose a student's EI means less time for helping students meet the expectations set forth by the No Child Left Behind Act (Harper, 2001). Finkelstein and Kramer's (2002) findings…
There is no analysis or critique in this excerpt. There is strong paraphrasing, and this passage provides a decent overview of Harper, but it addresses only Harper's ideas and does not explain why this information is important and how it relates to the author's overall purpose for the paper. The reader needs to know the answer to "So what, and who cares?"
What is missing from this summary is context and analysis. Consider the following revision:
....is to deny the student (Sigree, 1999). Harper (2001), however, disagreed with Sigree's (1999) assertion. Harper noted that despite the obvious benefits of diagnosing a student's emotional intelligence (EI; Jones & Hammer, 1998; Mooney, 1998; Sigree, 1999), instructors cannot identify every one of their students' EIs (Harper, 2001). Faculty members do not have the time, and students are not that forthcoming with their learning preferences (Harper, 2001). For Harper (2001), though, the real issue was not with instructors' belief in EI, but rather in how this belief affected classroom logistics. Instructors who follow Earnhart's (1996) advice to "Take the time to understand how each of your students learn" (p. 33) are being impractical, Harper argued. Taking time to adequately diagnose a student's EI means less time for helping students meet the expectations set forth by the No Child Left Behind Act (Harper, 2001). Although Earnhart's (1996) vision is ideal, Harper takes a more practical stance. With Harper's (2001) concerns in mind, I cannot endorse Finkelstein and Kramer’s (2002) findings…
Here, the author is synthesizing the literature. We know, based on the author's direction, how Harper interacts with the other literature on the topic. We know that Harper is probably in the minority, and we know what the author's take on Harper is. Finally, we know how and why the author is using Harper: Harper will be used to refute Finkelstein and Kramer, which presumably is the author's intent or thesis. Notice how the author demonstrated analysis and synthesis in just a few additional sentences.
Related Resource
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Synthesizing Your Sources
- Next Page: Literature Review Matrix
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.3: Strong paragraphs start with good evidence
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 15674
(1100 words)
Support your thesis with evidence AND analysis
A paragraph is a group of sentences that present, develop, and support a single idea. That’s it. There’s no prescribed length or number of sentences. In academic writing, body paragraphs need to work together with the thesis to support your main point. If your thesis states where your essay wants to go, then your body paragraphs need to show the reader how you get there. Paragraphs rarely stand alone, so most often the main topic of the paragraph serves the main concept or purpose of a larger whole; for example, the main idea of a paragraph in an essay should serve to develop and support the thesis of the essay.
By reading and annotating your sources, and by responding and analyzing to those sources, you should have developed lots of ideas that can now form the beginnings of your paragraphs. If you don't have ideas about your sources yet, STOP WRITING AND READ AGAIN. When writing with and about sources, you want to have the ideas before you start writing. If you start your paragraphs without evidence with the intention of add the evidence later, you are likely to fall into the trap of confirmation bias : only seeing the evidence you want to see. And, adding the evidence later makes it harder to develop your ideas sufficiently.
Topic Sentence
The job of the topic sentence is to control the development and flow of the information contained in the paragraph. The topic sentence takes control of the more general topic of the paragraph and shapes it in the way that you choose to present it to your readers. It provides a way through a topic that is likely much broader than what you could ever cover in a paragraph, or even in an essay. This more focused idea, your topic sentence, helps you determine the parts of the topic that you want to illuminate for your readers—whether that’s a college essay or a thank you letter to your Aunt Martha. The following diagram illustrates how a topic sentence can provide more focus to the general topic at hand.

Select the Most Effective Primary Support for a Thesis Statement
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts, such as statistics, are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, facts still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it will require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument. Always be sure you gather your facts from credible sources.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic. Use judgments from experts in the field as they are the more credible sources for the topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who directly observed an instance of what you are writing about; testimony adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Include Supporting Detail Sentences for the Topic Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the the topic sentence, which is underlined.
J.D. Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Adding Explanation and Elaboration in your Body Paragraphs
In addition to supporting details, college level paragraphs add quite a bit of explanation and elaboration in body paragraphs. Development of explanation and elaboration is one of the big differences between high school and college-level writing. Rather than just appearing in one paragraph all by itself -- possibly in a conclusion -- explanation and elaboration should appear through your essay. Some sentence stems you can use to help you develop your explanation and elaboration appear in the following list.
Sentence Stems for Elaboration
- X matters because ___________.
- X is important because ___________.
- X is crucial in terms of today’s concern over ___________ because ___________.
- Ultimately, what is at stake here is ___________.
- These points have important consequences for the broader discussion about ___________.
- The discussion of X is in fact addressing the larger matter of ___________.
- These conclusions have significant implications for ___________.
- X should in fact concern anyone who cares about ___________.
These 4 videos review the paragraph ideas shared on this page
Authored by: GoReadWriteNow. License: All Rights Reserved . License Terms: Standard YouTube
Contributors
- Adapted from Writing for Success. Provided by: The Saylor Foundation. License: CC-NC-SA 3.0 and The Word on College Reading and Writing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a student writing a commentary essay, it is important to understand the differences between analyzing, summarizing, and evaluating. To help comprehend these contrasts, let's take a look at four main points: 1. Analyzing - Looking closely at something and breaking it down into smaller parts to better understand it.
A commentary essay is a written piece that provides an opinion on a particular subject. This type of essay is usually written in response to another piece, such as a blog post, article, or book passage. In a commentary essay, the writer will typically offer their own take on the situation, using evidence and examples to support their claims.
A commentary essay is a type of academic writing that aims to analyze and provide an in-depth interpretation of a particular text or topic. It offers a critical examination and evaluation of the subject matter, exploring various perspectives and providing evidence-based arguments to support the author's viewpoint.
1️⃣ Close, Direct Analysis of Passages. An example of an alternative commentary is a close, direct analysis of robust passages from the source, such as an article, film, poem, literary work, book, or novel. In this respect, they are standard in bigger writing projects, like expositions or being part of a critic's work.
A commentary is a response to another person's argument. Commentaries are most often found in expressions of opinions on current issues and events [1]. The purpose of commentaries is to offer new and insightful perspectives so that readers can understand their own stance on an issue or event. Importantly, readers can find commentaries as ...
2) Interpretation: your explanation of something that is not clear. 3) Character and Subject's Feelings: when you describe what the character or subject of the detail is feeling (ideal for literary analysis papers) 4) Personal Reaction: your personal emotions about the detail. 5) Evaluations: your objective judgment of a detail.
First and foremost, a literary commentary is NOT an essay. The passage in front of you is not, therefore, an invitation to write a general essay about the work from which it has been taken. A commentary is an analysis of the given passage, its function and its characteristics. It should examine the key themes and stylistic devices of the ...
What Is the Purpose of a Commentary in Writing? The commentary's primary objective is to help readers grasp the topic better. Most subjects may be unclear to ordinary readers, and it's easy to misunderstand the mentioned points. Commentary essays come through by evaluating and analyzing various topics and concepts within a broader societal scope.
A commentary essay is a type of essay that provides an analysis or interpretation of a text. Commentary essays are typically longer than regular essays, and they provide in-depth analysis of the text. ... It typically includes an explanation of the author's purpose in writing the text, as well as an examination of the text's structure and ...
As the spotlight intensifies, I unveil the essay's purpose, signaling the thematic overture that will unfold. Also, this introduction, akin to an opening act, aims to engage and captivate, preparing the audience for the insightful commentary that awaits in the ensuing scenes of my written performance. ... In a commentary essay, the thesis ...
Analysis—what we're calling commentary—is the student's opinion about the way evidence proves the truth of a topic sentence, which defends the truth of the controlling thesis statement. Here's how the connecting works. A rhetorical analysis essay has a thesis, which is a controlling idea. All ideas within the essay defend this one.
Make sure to use smooth transitions. When you move to a new example, use a good transition word or phrase. Some examples are "similarly", "conversely", and "again". 6. Write a strong conclusion. Your conclusion is the piece that will tie the rest of your commentary together. Make sure to include a summary of your argument.
Explanatory Essays: Definition and Purpose. An expository essay, also known as an explanatory essay or an explanatory paper, is a type of explanatory writing wherein one is required to describe and elucidate a particular point of view, incident, event, or situation. Unlike argumentative or persuasive essays, the goal of explanation essays ...
The commentary part of any essay is always the most difficult. It is the part of the essay in which the writer analyzes evidence, and this analysis speaks to the writer's own unique voice. While we have standard, formulaic ways to teach other parts of the essay such as thesis statements, blending quotes, topics sentences, etc., commentary is ...
In order to effectively write commentary in your body paragraphs, you need to have an understanding of the rhetorical situation. The rhetorical situation includes the following elements: the writer or speaker, the audience, the (historical) context, the exigence (ie. what prompted the writer to write), the purpose, and the message or argument.
Writing commentary is undoubtedly the most difficult part of writing any essay. All other parts of the essay are more formulaic in nature. But when it comes to commenting on evidence, there is no formula. This blog post explores strategies for teaching students how to write commentary for the literary analysis essay.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Commentary and Argumentation. In order to synthesize your sources, you must first analyze them to help provide rationale for why they are a part of your literature review and what role they play within your field. In order to demonstrate analysis, you must provide your commentary on the sources you discuss beyond simply summarizing them.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
An expository essay should take an objective approach: It isn't about your personal opinions or experiences. Instead, your goal is to provide an informative and balanced explanation of your topic. Avoid using the first or second person ("I" or "you"). The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your ...
Paragraphs rarely stand alone, so most often the main topic of the paragraph serves the main concept or purpose of a larger whole; for example, the main idea of a paragraph in an essay should serve to develop and support the thesis of the essay. ... This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Commentary or explanation in an essay provides further analysis and understanding. Commentary involves personal opinions, while explanation is more objective. Explanation: Commentary or explanation in an essay serves the purpose of providing further analysis, interpretation, and evaluation of the topic or evidence presented.