

The Writing Process
Making expository writing less stressful, more efficient, and more enlightening, search form, you are here, what is a writing process.

“Writing is easy. You just open your veins and bleed.” — Red Smith, Sportswriter
As you might expect, process writing means approaching a writing task according to a formalized series of concrete, discrete steps. Although different versions of the writing process can be found—some with as few as three steps or phases, others with as many as eight—they generally move from a writer-oriented phase of pre-writing through drafting to reader-oriented revising and editing. I generally find that the one I will present below, comprising five steps, is specific enough to make the important steps separate and yet not so complex as to be daunting.
Why even use a formal writing process, though? What can it offer you that the kind of informal processes people typically use don't? Continue.
- Enroll & Pay
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Degree Programs
The Writing Process
The writing process is something that no two people do the same way. There is no "right way" or "wrong way" to write. It can be a very messy and fluid process, and the following is only a representation of commonly used steps. Remember you can come to the Writing Center for assistance at any stage in this process.
Steps of the Writing Process
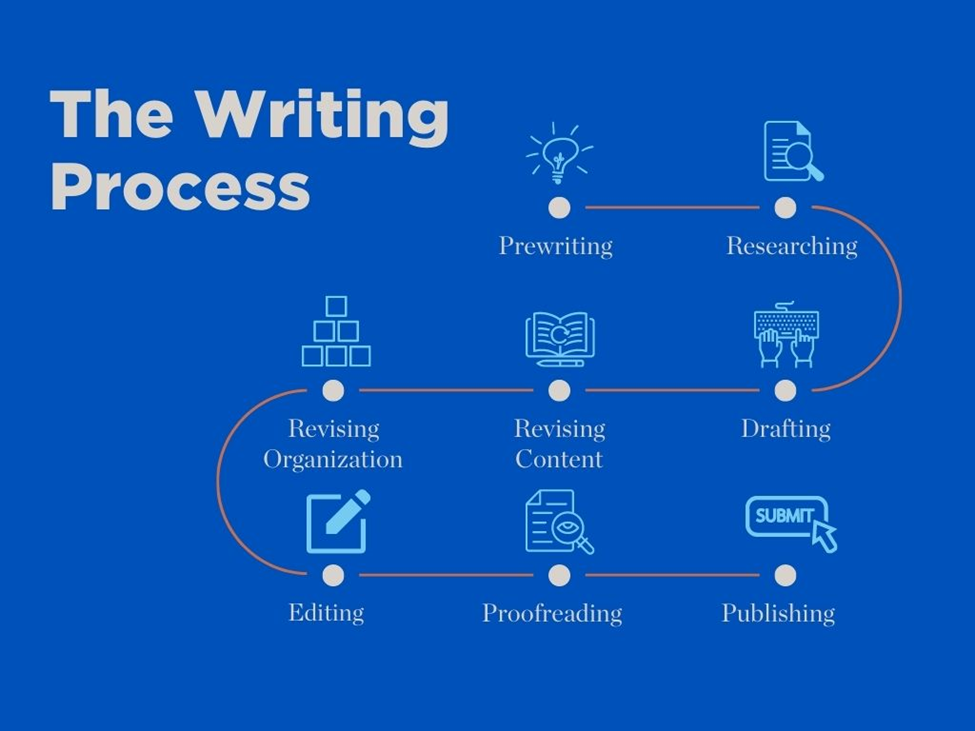
Step 1: Prewriting
Think and Decide
- Make sure you understand your assignment. See Research Papers or Essays
- Decide on a topic to write about. See Prewriting Strategies and Narrow your Topic
- Consider who will read your work. See Audience and Voice
- Brainstorm ideas about the subject and how those ideas can be organized. Make an outline. See Outlines
Step 2: Research (if needed)
- List places where you can find information.
- Do your research. See the many KU Libraries resources and helpful guides
- Evaluate your sources. See Evaluating Sources and Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Make an outline to help organize your research. See Outlines
Step 3: Drafting
- Write sentences and paragraphs even if they are not perfect.
- Create a thesis statement with your main idea. See Thesis Statements
- Put the information you researched into your essay accurately without plagiarizing. Remember to include both in-text citations and a bibliographic page. See Incorporating References and Paraphrase and Summary
- Read what you have written and judge if it says what you mean. Write some more.
- Read it again.
- Write some more.
- Write until you have said everything you want to say about the topic.
Step 4: Revising
Make it Better
- Read what you have written again. See Revising Content and Revising Organization
- Rearrange words, sentences, or paragraphs into a clear and logical order.
- Take out or add parts.
- Do more research if you think you should.
- Replace overused or unclear words.
- Read your writing aloud to be sure it flows smoothly. Add transitions.
Step 5: Editing and Proofreading
Make it Correct
- Be sure all sentences are complete. See Editing and Proofreading
- Correct spelling, capitalization, and punctuation.
- Change words that are not used correctly or are unclear.
- APA Formatting
- Chicago Style Formatting
- MLA Formatting
- Have someone else check your work.
An Overview of the Writing Process
Defining the writing process.

People often think of writing in terms of its end product—the email, the report, the memo, essay, or research paper, all of which result from the time and effort spent in the act of writing. In this course, however, you will be introduced to writing as the recursive process of planning, drafting, and revising.
Writing is Recursive
You will focus as much on the process of writing as you will on its end product (the writing you normally submit for feedback or a grade). Recursive means circling back; and, more often than not, the writing process will have you running in circles. You might be in the middle of your draft when you realize you need to do more brainstorming, so you return to the planning stage. Even when you have finished a draft, you may find changes you want to make to an introduction. In truth, every writer must develop his or her own process for getting the writing done, but there are some basic strategies and techniques you can adapt to make your work a little easier, more fulfilling and effective.
Developing Your Writing Process
The final product of a piece of writing is undeniably important, but the emphasis of this course is on developing a writing process that works for you. Some of you may already know what strategies and techniques assist you in your writing. You may already be familiar with prewriting techniques, such as freewriting, clustering, and listing. You may already have a regular writing practice. But the rest of you may need to discover what works through trial and error. Developing individual strategies and techniques that promote painless and compelling writing can take some time. So, be patient.
A Writer’s Process: Ali Hale
Read and examine The Writing Process by Ali Hale. Think of this document as a framework for defining the process in distinct stages: Prewriting, Writing, Revising, Editing, and Publishing. You may already be familiar with these terms. You may recall from past experiences that some resources refer to prewriting as planning and some texts refer to writing as drafting.
What is important to grasp early on is that the act of writing is more than sitting down and writing something. Please avoid the “one and done” attitude, something instructors see all too often in undergraduate writing courses. Use Hale’s essay as your starting point for defining your own process.
A Writer’s Process: Anne Lamott
In the video below, Anne Lamott, a writer of both non-fiction and fiction works, as well as the instructional novel on writing Bird by Bird: Instructions on Writing , discusses her own journey as a writer, including the obstacles she has to overcome every time she sits down to begin her creative process. She will refer to terms such as “the down draft,” “the up draft,” and “the dental draft.”
As you watch, think about how her terms, “down draft,” “up draft,” “dental draft,” work with those presented by Hale’s The Writing Process . What does Lamott mean by these terms? Can you identify with her process or with the one Hale describes? How are they related?
Also, when viewing the interview, pay careful attention to the following timeframe: 11:23 to 27:27 minutes and make a list of tips and strategies you find particularly helpful. Think about how your own writing process fits with what Hale and Lamott have to say. Is yours similar? Different? Is there any new information you have learned that you did not know before exposure to these works?
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Daryl Smith O' Hare and Susan C. Hines. Provided by : Chadron State College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image: Computer and notebook. Located at : https://unsplash.com/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- A Conversation with Anne Lamott 2007. Provided by : University of California Television (UCTV). Located at : http://youtu.be/PhP5GmybvPM . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
Pasco-Hernando State College
- The Writing Process
- Paragraphs and Essays
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Related Pages
Good writing is usually the result of a process of pre-writing, drafting, reviewing, revising, and rewriting. It’s rare that anyone is able to express his or her thoughts in the best way possible on the first try although the more we practice, the better we become at it. Experienced, published writers readily admit that they have revised their writing several times before publication.
Revise means to see again . After we’ve done our first draft, it’s helpful to leave it for a while before looking at it again. While having others read the paper may help, the goal is to become self-editors and see the writing as others would see it. We need to be sure that it says what we mean to communicate in a way that will show the legitimacy of our position.
A good essay must prove the thesis: a one-sentence statement taking a position. Once you have a thesis, even though you may change it, it’s easier to formulate ideas about the body paragraphs since they just have to prove the thesis.
Proof paragraphs are just reasons why your thesis is right. Just as an essay has a controlling idea expressed is the thesis statement, paragraphs also have a controlling idea expressed in a topic sentence.
While experienced writers sometimes take poetic liberties in some contexts such as fiction or informal writing, good writers know how to use proper grammar and punctuation, and in college writing, it should be used.
Proofreading carefully helps to assure that the writing says what we want it to say and that it uses proper grammar. Sometimes, it helps to read the paper aloud. It’s easy to miss an error.
Whether you are writing a paragraph, an essay, another type of assignment for school such as a reaction paper, or simply a letter, here are key elements to remember.
Subject, Purpose, and Audience
- Subject – (picking the right topic, narrowing the topic, supporting the topic)
- Audience – For whom are you writing? (experts, teachers, general public?)
- Purpose- (explaining, persuading, comparing, entertaining….)
Writing is a Process
- Pre-writing (freewriting, brainstorming, clustering, asking questions (research), keeping a Journal)
- Organizing (grouping, eliminating, adding) and narrowing the topic (focus on a point)
- Rough Draft
- Revising (self check, peer review, tutoring)
- Final Copy (typed)
Pre-writing: Free-writing, Brainstorming, Clustering, Asking Questions (Research), Keeping a Journal
Pre-writing consists of various strategies to help overcome a writing block, to get ideas, or just to get organized. Whether you are writing a letter or doing a writing assignment for school, one or more of the following may be used as needed.
1. Focused Free-writing
More “poetic” than typical prose writing for college classes. Contains many vivid details and extra information that will need to be cut, added to, or rearranged.
2. Brainstorming
A filled page of just word or sentence fragments. Complete sentences are not required, but a large amount of ideas should be present. Add details to fill the page.
3. Clustering
Start with the topic in the center and draw spokes outward as thought take you in new, more detailed directions. A cluster typically takes a full page.
4. Asking Questions (Research)
Ask yourself the reporter’s six questions: Who? What? Where? Why? When, How? Use these questions to focus on what you really want to write about and what you know about.
When accessing sources beyond your own knowledge is appropriate – either you don’t know enough about the topic or the assignment requires outside research – find out what others say about the topic or research question
5. Keeping a Journal
Your journal is a private place where you can develop ideas and ability! When you see something interesting or have a new, exciting thought, write it down and use it for a later writing assignment.
Narrowing the Topic – Focus on a Point
A paragraph, an essay, or a research paper (also called research essay ), each must focus on a point.
- The point of a paragraph is called a topic sentence .
- The topic sentence of a paragraph tells the reader what the paragraph will prove.
- The point of an essay or research paper is called the thesis .
- A thesis tells the reader what the paper will prove.
An essay has different types of paragraphs:
- introduction (introductory paragraph) – gives a background and states the thesis. The topic sentence of an introductory paragraph is called the thesis and belongs at the end of the first paragraph.
- body paragraphs – each of which gives a different reason with supporting details on why the thesis is accurate. The topic sentence of a body paragraph belongs at the beginning of the paragraph.
- concluding paragraph – sums up the proof and restates the thesis and/or draws an implication from the information presented depending on instructor preference. The topic sentence of a concluding paragraph is a restatement of the thesis and may go anywhere in the concluding paragraph.
In some assignments, you are given a question to answer to form a thesis a thesis or topic sentence. This type of assignment usually does not present a problem in finding a focus. For example, if you assignment is to research what treatment is best for a particular disease or whether the cycles of the moon affect human beings, the result of your research will generate an answer to the question which will be your thesis statement: The best treatment for ovarian cancer is …. The topic sentences for your body paragraphs will each be one reason why that treatment is best.
In other cases, you are given a topic and you must narrow your topic to find a focus. Here are some strategies to help develop a one-sentence topic sentence or a thesis:
- Narrow your topic by thinking about what you know about the topic and a specific area that interests you if there is not a research component. For example, if the topic is about how computers have affected our lives, you may think about the various types of computers and focus in on personal computers. The question then becomes “How have personal computers affected our lives.”
- If there is a research component, think about what questions you have about the topic and/or what your exploratory research has found. For example, if you research on the topic of how computers have affected our lives turns up information on the types of computers that are used in appliances that we use every day, you question for focused research may be “How have computers used in household appliances affected our lives?”
- Think about your topic until you can find a main idea or question that is not as broad as the topic your instructor gave you if you were assigned a topic. This should be an idea that is interesting to you and something you know about.
- A thesis statement should include both the subject and the controlling idea.
Drafting, Reviewing, Revising, and Editing
Regardless of the type of writing, the first attempt must be considered a rough draft. Don’t worry too much about grammar. The first goal is to get the ideas down. Generate ideas by reviewing your pre-writing efforts if you use any of those strategies.
- Are there any natural groups that you can arrange your ideas into?
- Take the most promising groups and add information and details.
- Any ideas that do not fit into these groups or don’t have many details should be discarded.
Once the first draft is complete, you must review it to see if the ideas and wording flow logically and support the topic sentence within a paragraph and the thesis if an academic essay. Paragraphs must be limited to information about the topic sentence. Related ideas must be together in one section. There must be an internal organization from paragraph to paragraph that the reader can easily follow. Transitions may be needed from sentence to sentence and paragraph to paragraph for the sentences and/or paragraph to flow from one to the next. See Paragraphs in Related Pages on the right sidebar for more information.
Revise as needed, moving or adding sentences or paragraphs, and modifying wording. The last step is editing where you make sure the writing is grammatical. There must be sentences and not fragments. The punctuation should be accurate. Check for spelling.
Writing an Academic Essay
An academic essay has a particular type of organization with an introduction paragraph with a thesis, body paragraphs which prove the thesis, and a concluding paragraph which sums up the proof and restates the thesis. See Essay Organization for more information.
To write an academic essay, it is helpful to start with an outline.
An outline is a plan of what your essay will look like.
- Start with the thesis statement.
- Then, list the separate reasons why your thesis is accurate as I, II, and so on. These will be the topic sentences for your body paragraphs. The number of paragraphs will be determined by the assigned length of the paper. These must be complete sentences.
- Under each of the topic sentences, include the details that fit into this group.
An essay can be written right from the outline. You would have to add background information before the thesis to complete the introductory paragraph. You would have one paragraph each for sections I, II, III, and IV, depending on how many sections are in your outline. Your concluding paragraph just sums up the proof in the body and restates the thesis.
See Related Pages on the right sidebar.
- Printer-friendly version

Table of Contents
- Collaboration
Information Literacy
Writing process, the writing process – research on composing.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about their work. They've found that the writing process can be seen in three main ways: (1) a series of steps or stages ; (2) a cognitive, problem-solving activity ; and (3) a creative, intuitive, organic, dialogic process that writers manage by listening to their inner speech and following their felt sense . Learn about scholarship on the writing process so you can understand how to break through writing blocks and find fluency as a writer, researcher, and thought leader.

Synonymous Terms
Composing process.
In writing studies , the writing process may also be known as the composing process . This may be due to the dramatic influence of Janet Emig’s (1971) dissertation, The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Emig’s research employed think-aloud protocols and case-study methods to explore the composing processes of high school students.
Creative Process
In creative writing and literature, the writing process may be known as the creative process .
In the arts and humanities the term creative process is reserved for artistic works, such as paintings, sculptures, performance art, films, and works of literature.
Related Concepts: Composition Studies ; Creativity; Felt Sense ; Growth Mindset ; Habits of Mind ; Intellectual Openness ; Professionalism and Work Ethic ; Resilience ; Self Regulation & Metacognition
What is the Writing Process?
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project.
People experience and define the writing process differently, according to their historical period, literacy history, knowledge of writing tools, media , genres — and more.
One of the takeaways from research on composing is that we’ve learned writers develop their own idiosyncratic approaches to getting the work done. When it comes to how we all develop, research , and communicate information , we are all special snowflakes. For example,
- Hemingway was known for standing while he wrote at first light each morning.
- Truman Capote described himself as a “completely horizontal author.” He wrote lying down, in bed or on a couch, with a cigarette and coffee handy.
- Hunter S. Thompson wrote through the nights, mixing drinking and partying with composing
- J.K. Rowling tracked the plot lines for her Harry Potter novels in a data.
- Maya Angelou would lock herself away in a hotel room from 6:30 a.m. to 2 p.m. so she has no distractions.
Research on composing processes conducted over the past 60 years has led to three major distinct ways of defining and conceptualizing the writing process:
- prewriting , invention , research , collaboration , planning , designing , drafting , rereading , organizing , revising , editing , proofreading , and sharing or publishing
- The writing process refers to cognitive, problem-solving strategies
- The writing process refers to the act of making composing decisions based on nonrational factors such as embodied knowledge , felt sense , inner speech, and intuition.
1. The writing process refers to writing process steps
The writing process is often characterized as a series of steps or stages. During the elementary and middle-school years, teachers define the writing process simply as prewriting , drafting , revising , and editing . Later, in high-school and college, as writing assignments become more challenging, teachers introduce additional writing steps: invention , research , collaboration , designing , organizing , proofreading , and sharing or proofreading.
2. The writing process refers to Problem-Solving Strategies
As an alternative to imagining the writing process to be a series of steps or stages that writers work through in linear manner, Linda Flower and John Hayes suggested in 1977 that writing should be thought of as a “thinking problem,” a “problem-solving process,” a “cognitive problem solving process,” or a “goal-directed thinking process.”
3. The writing process refers to the act of making composing decisions based on flow, felt sense and other elements of embodied knowledge
For some writers, viewing the writing process as a series of steps or problems feels to mechanistic, impersonal and formulaic. Rather than view that the writing process to be a series of writing steps or problem solving strategies , Sondra Perl , an English professor, suggests that composing is largely a process of listening to one’s felt sense — one’s “bodily awareness of a situation or person or event:
“A felt sense doesn’t come to you in the form of thoughts or words or other separate units, but as a single (though often puzzling and very complex) bodily feeling”. (Gendlin 1981, 32-33)

What are Writing Process Steps?
In elementary and middle schools in the U.S., the writing process is often simplified and presented at four or five key steps: prewriting , writing , revising , and editing –and sometimes and publishing or sharing . As students progress through school, the writing process is presented in increasingly complex ways. By high school, teachers present “the writing process steps” as
- Proofreading
- Sharing – Publishing
Is there one perfect way to work with the writing process?
No, there is no one ideal writing process. The steps of the writing process a writer engages in vary from project to project. At times composing may be fairly simple. Some situations require little planning , research , revising or editing , such as
- a grocery list, a to-do list, a reflection on the day’s activity in a journal
- documents you routinely write, such as the professor’s letter of recommendation, a bosses’ performance appraisal, a ground-water engineer’s contamination report.
Over time, writers develop their own unique writing processes. Through trial and error, people can learn what works for them.
Composing may be especially challenging
- when you are unfamiliar with the topic , genre , medium , discourse community
- when the thesis/research question/topic is complicated yet needs to be explained simply
- when you are endeavoring to synthesize other’s ideas and research
- when you don’t have the time you need to perfect the document.
What are the main factors that effect how writers compose documents?
Writers adjust their writing process in response to
- Writers assess the importance of the exigency, the call to write, before commiting time and resources to launching
- the writers access to information
- What they know about the canon, genre, media and rhetorical reasoning
- their writerly background
- the audience
- the schedule.
Why Does the Writing Process Matter?
The writing processes that you use to compose documents play a significant role in determining whether your communications are successful. If you truncate your writing process, you are likely to run out of the time you need to write with clarity and authority .
- Studying the writing processes of successful writers can introduce you to new rhetorical moves, genres , and composing processes. Learning about the composing processes of experienced writers can help you learn how to adjust your rhetorical stance and your writing styles to best accomplish your purpose .
- By examining your writing processes and the writing processes of others, you can learn how to better manage your work and the work of other authors and teams.
- By recognizing that writing is a skill that can be developed through practice and effort, you can become more resilient and adaptable in your writing endeavors.
[ For an example of process pedagogy , see professional writing, which breaks the processes involved in writing a recommendation report down into a 15-week schedule. ]
Do experienced writers compose in different ways than inexperienced writers?
Yes. Experienced writers engage in more substantive, robust writing processes than less experienced writers.
- Experienced writers tend to have more rhetorical knowledge and a better understanding of composing steps and strategies than inexperienced writers.
- Experienced writers tend to be more willing than inexperienced writers to make substantive changes in a draft, often making changes that involve rethinking the meaning of a text. Some professional writers may revise a document hundreds of times before pushing send or publishing it.
- Experienced writers engage in revision as an act of internal conversation, a form of inner speech that they have with themselves and an imagined other–the internalized target audience. In contrast, inexperienced writers tend to confuse editing for revision . They tend to make only a few edits to their initial drafts, focusing primarily on surface-level changes such as correcting grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
- Experienced writers are adept at working collaboratively, leveraging the strengths of team members and effectively coordinating efforts to produce a cohesive final product. Inexperienced writers may struggle with collaboration, communication, and division of labor within a writing team
What is Process Pedagogy?
Process pedagogy, which is also known as the process movement, emerged in the United States during the late 1960s and early 1970s. In The Making of Knowledge in Composition , Steve North (1987) links the emergence of process pedagogy to
- Sputnik and America’s concern it was falling behind Russia
- the GI Bill and the changing demographics of undergraduate students in the post-war era.
Additionally, process pedagogy emerged in response to dissatisfaction with traditional, product-oriented approaches to teaching writing. In the current-traditional paradigm of writing, the focus of the classroom was on “the composed product rather than the composing process; the analysis of discourse into words, sentences, and paragraphs; the classification of discourse into description, narration, exposition, and argument; the strong concern with usage (syntax, spelling, punctuation) and with style (economy, clarity, emphasis)” (Young, 1978, p. 25).
The process movement reflected a sea change on the part of middle schools, high schools, and universities in the U.S. Traditionally, classroom instruction focused on analysis and critique of the great works of literature:
“The student is (a) exposed to the formal descriptive categories of rhetoric (modes of argument –definition, cause and effect, etc. — and modes of discourse — description, persuasion, etc.), (b) offered good examples (usually professional ones) and bad examples (usually his/her own) and (c) encouraged to absorb the features of a socially approved style, with emphasis on grammar and usage. We help our students analyze the product, but we leave the process of writing up to inspiration” (Flower and Hayes, 1977, p. 449).
In contrast to putting the focus of class time on analyzing great literary works, the canon , process pedagogy calls for teachers to put the emphasis on the students’ writing:
- Students need help with prewriting , invention , research , collaboration , writing , designing , revising , organizing , editing , proofreading , and sharing
- Teachers do not comment on grammar and style matters in early drafts. Instead, they focus on global perspectives . They prioritize the flow of ideas and expression over correctness in grammar and mechanics.
- Students engage in prewriting and invention exercises to discover and develop new ideas
- Students repeatedly revise their works in response to self-critique , peer review , and critiques from teachers
- Teachers should provide constructive feedback throughout the writing process.
What does “teach the process and not the product mean”?
“Teach the process not the product ” is both the title of a Donald Murray (1972) article and the mantra of the writing process movement, which emerged during the 1960s.
The mantra to teach the process not the product emerged in response to the research and scholarship conducted by Donald Murray, Janet Emig, Peter Elbow, Ann Berthoff, Nancy Sommers, Sondra Perl, John Hayes and Linda Flower.
What does it mean to describe the writing process as recursive ?
The term recursive writing process simply means that writers jump around from one activity to another when composing . For instance, when first drafting a document, a writer may pause to reread something she wrote. That might trigger a new idea that shoots her back to Google Scholar or some other database suitable for strategic searching .
How do researchers study the writing process?
The writing process is a major subject of study of researchers and scholars in the fields of composition studies , communication, writing studies , and AI (artificial intelligence).
The writing process is something of a black box: investigators can see inputs (e.g., time on task) or outputs (e.g., written discourse ), yet they cannot empirically observe the internal workings of the writer’s mind.
At the end of the day investigators have to jump from what they observe to making informed guesses about what is really going on in the writer. Even if investigators ask a writer to talk out loud about what they are thinking as they compose , the investigators can only hear what the writer is saying: they cannot see the internal machinations associated with the writer’s thoughts. If a writer goes mute, freezes, and just stares blankly at the computer screen, investigators cannot really know what’s going on. They can only speculate about how the brain functions.
Research Methods
To study or theorize about the writing process, investigators may use a variety of research methods .
Doherty, M. (2016, September 4). 10 things you need to know about banyan trees. Under the Banyan. https://underthebanyan.blog/2016/09/04/10-things-you-need-to-know-about-banyan-trees/
Emig, J. (1967). On teaching composition: Some hypotheses as definitions. Research in The Teaching of English, 1(2), 127-135. Retrieved from http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED022783.pdf
Emig, J. (1971). The composing processes of twelfth graders (Research Report No. 13). Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
Emig, J. (1983). The web of meaning: Essays on writing, teaching, learning and thinking. Upper Montclair, NJ: Boynton/Cook Publishers, Inc.
Ghiselin, B. (Ed.). (1985). The Creative Process: Reflections on the Invention in the Arts and Sciences . University of California Press.
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. (1980). Identifying the Organization of Writing Processes. In L. W. Gregg, & E. R. Steinberg (Eds.), Cognitive Processes in Writing: An Interdisciplinary Approach (pp. 3-30). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hayes, J. R. (2012). Modeling and remodeling writing. Written Communication, 29(3), 369-388. https://doi: 10.1177/0741088312451260
Hayes, J. R., & Flower, L. S. (1986). Writing research and the writer. American Psychologist, 41(10), 1106-1113. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.41.10.1106
Leijten, Van Waes, L., Schriver, K., & Hayes, J. R. (2014). Writing in the workplace: Constructing documents using multiple digital sources. Journal of Writing Research, 5(3), 285–337. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2014.05.03.3
Lundstrom, K., Babcock, R. D., & McAlister, K. (2023). Collaboration in writing: Examining the role of experience in successful team writing projects. Journal of Writing Research, 15(1), 89-115. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2023.15.01.05
National Research Council. (2012). Education for Life and Work: Developing Transferable Knowledge and Skills in the 21st Century . Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.https://doi.org/10.17226/13398.
North, S. M. (1987). The making of knowledge in composition: Portrait of an emerging field. Boynton/Cook Publishers.
Murray, Donald M. (1980). Writing as process: How writing finds its own meaning. In Timothy R. Donovan & Ben McClelland (Eds.), Eight approaches to teaching composition (pp. 3–20). National Council of Teachers of English.
Murray, Donald M. (1972). “Teach Writing as a Process Not Product.” The Leaflet, 11-14
Perry, S. K. (1996). When time stops: How creative writers experience entry into the flow state (Order No. 9805789). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses A&I; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (304288035). https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/when-time-stops-how-creative-writers-experience/docview/304288035/se-2
Rohman, D.G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1964). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University.
Rohman, D. G., & Wlecke, A. O. (1975). Pre-writing: The construction and application of models for concept formation in writing (Cooperative Research Project No. 2174). U.S. Office of Education, Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
Sommers, N. (1980). Revision Strategies of Student Writers and Experienced Adult Writers. College Composition and Communication, 31(4), 378-388. doi: 10.2307/356600
Vygotsky, L. (1962). Thought and language. (E. Hanfmann & G. Vakar, Eds.). MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.1037/11193-000
Related Articles:

Discovering Your Unique Writing Process: A Guide to Self-Reflection

Problem-Solving Strategies for Writers: a Review of Research

The 7 Habits of Mind & The Writing Process

The Secret, Hidden Writing Process: How to Tap Your Creative Potential

The Ultimate Blueprint: A Research-Driven Deep Dive into The 13 Steps of the Writing Process
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Joseph M. Moxley
Understanding your writing process is a crucial aspect of developing as a writer. For both students and professional writers, reflection on the process of writing can lead to more effective...

Traditionally, in U.S. classrooms, the writing process is depicted as a series of linear steps (e.g., prewriting, writing, revising, and editing). However, since the 1980s the writing process has also...

In contrast to the prevailing view that the writing process refers to writing steps or problem solving strategies, a third view is that the writing process involves nonrational factors, such...

This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps, or strategies, that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences. Since the 1960s, the writing process has...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

The Writing Process
Definitions.
- Stages of the Writing Process
- Strategies for Good Writing
The Writing Process is a cycle of activities that you complete as you generate ideas, compose those ideas into a document or presentation, and refine those ideas. It is a recursive process, meaning that at any one stage in the process, you may find that you have to return to previous steps to review and refine your methods.
To read more about the elements of the Writing Process, we recommend the following resource:
- Dziak, M. (2018). Writing process (planning, drafting, revising, editing, publishing). Salem Press Encyclopedia. The writing process is the series of actions taken by writers to produce a finished work. Writers, educators, and theorists have defined the writing process in many different ways, but it generally involves prewriting tasks, writing tasks, and post-writing tasks. More specifically, these tasks include planning, drafting, revising, editing, and publishing, in approximately that order.
Benefits of following the Writing Process include:
- The ability to revisit previous work completed to find new ideas or refine existing ones.
- A more organized finished product.
- A less stressful experience, which is one cause of Writer's Block .
- Less time spent in the drafting stage.
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Stages of the Writing Process >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/writingprocess
How to Write a Definition Essay: New Guide with Samples

Have you ever found it difficult to explain certain words or ideas? That's because understanding them isn't always easy. To avoid confusion, it's important to really understand the words we use and be able to explain them well.
That's why teachers often assign definition essays in high school and college. But these essays aren't just about repeating dictionary definitions. They dive deep into complex terms, exploring their rich backgrounds and meanings.
In this article, our rewrite essay service will cover different types of these papers, give you practical tips for writing them, and even provide examples to simplify this journey for you!
What is a Definition Essay
A definition essay is a type of writing assignment where you explain the meaning of a specific word or concept. Instead of just giving a simple definition from the dictionary, you dive deeper into what the word really means and explore its different aspects.
For instance, if you're tasked with defining 'success,' you might discuss what success means to different people, how it can vary based on cultural or societal norms, and whether it's purely based on achievements or encompasses personal fulfillment as well.
The purpose of writing definition essays in school is multifaceted. Firstly, it helps you refine your understanding of language by encouraging you to analyze words more critically. It also fosters your ability to think deeply and express complex ideas clearly. Additionally, it cultivates your skills in research, as you may need to gather evidence and examples to support your interpretation of the word or concept. Now that we've cleared the definition essay meaning, let's explain its common types in detail.
Definition Essay Examples
Here's a definition essay example from our custom essay service to help you understand what a good paper looks like. Take a look at how it's structured and formatted if you want to use it as a reference for your own work. And if you're interested, you can always buy essay cheap and get high-quality paper from our platform anytime.
Stuck on Words?
Our writers excel at turning ordinary ideas into extraordinary narratives.

Commonly Used Definition Essay Types
When choosing an intriguing term with a rich historical background for your definition essay, it's essential to carefully consider your options and determine the most effective approach. Here are some common types, as suggested by our dissertation writing help :
.webp)
- Analysis : Break down the topic into its constituent parts and define each part separately.
- Classification : Determine the categories under which the topic can be classified.
- Comparison : Highlight the uniqueness of the topic by comparing and contrasting it with more common subjects.
- Details : Identify the key traits and distinctive qualities that best encapsulate the central idea of your essay.
- Negation : Clarify what your topic is, not to narrow down its definition.
- Origins and Causes : Explore the historical origins and background of the concept, examining where it first appeared and any relevant historical details.
- Results, Effects, and Uses : Discuss the consequences, effects, and practical applications of the subject matter.
How to Write a Definition Essay
Just like with any writing, a definition essay structure involves an introduction, body, and conclusion. But what makes it interesting is what you explore in the body paragraphs.
For example, you could organize your definition essay outline by discussing the term from various angles. Start with a personal anecdote or story that illustrates the term in action. Then, provide a definition from a reputable source like a textbook or scholarly article. Next, consider interviewing people from different backgrounds to get their perspectives on the term. You could also analyze how the term has evolved over time, looking at historical examples or cultural shifts. Finally, offer your own interpretation of the term, drawing on your own experiences and insights.
For a more in-depth guide on writing a definition essay, let's explore the following sections provided by our experienced research paper writer .
Definition Essay Introduction
In the beginning stages of a definition essay, your reader gets their first taste of what your topic entails. It's crucial that this introduction is both informative and captivating, setting the stage for the rest of your essay. Here's what you need to include:
- Start with something attention-grabbing, like a thought-provoking question or an interesting fact.
- Provide a brief overview of the topic and why it's important to define it.
- Clearly state the term you're defining and your interpretation of it.
Definition Essay Body Paragraphs
In your essay, break down the phrase into its different parts, look at it from various angles, and then provide a relevant explanation. Depending on what your assignment calls for, you might need more than three paragraphs. Feel free to mix up the order or add sections depending on how complex the term is. Here are some ideas for what you can include:
- Start by talking about where the term came from and how it has changed over time. Understanding its origins can give insight into its meaning and significance.
- Look up the official definition of the term and compare it to your own understanding. This can help clarify any differences and give a broader perspective.
- Share your own thoughts and interpretation of the term, using examples or stories to illustrate your point. Your personal experiences can add depth and context to your analysis.
- Find a definition or explanation from an expert or scholar in the field and discuss how it aligns or differs with your own perspective. This can provide credibility and further insight into the term.
- Explore how the term is used in popular culture and what it reveals about societal values and beliefs. This can shed light on how the term is understood and interpreted in different contexts.
Definition Essay Conclusion
In the concluding paragraph, you should tie everything together neatly. Here's how you can structure your conclusion:
- Remind the reader of your main points and why the definition of the term is important.
- Highlight how having a clear understanding of the term can influence our thoughts and actions. This is where you show the broader significance of your analysis.
- Encourage your audience to apply the term accurately in their own discussions and advocate for precision in defining terms within their communities. This empowers readers to take action based on what they've learned.
Tips for Definition Essay Writing Process
Now that we're nearing the end, you might have already grasped how to write a definition essay. However, if you still feel like you're threading a needle while wearing mittens, fear not! Our essay writer has laid out some nifty guidelines to help you ace this challenge:
.webp)
- Choose a term with depth, something that's not ordinary but has a rich backstory and multiple meanings. Think of it like picking a word that's like a Russian nesting doll – there's plenty to explore.
- Use vivid language to paint a picture that engages the senses. For instance, when talking about 'love,' describe the warmth of a hug, the sweetness of Valentine's chocolates, or the sound of laughter with a partner. It helps your readers feel like they're right there with you.
- Explore both the positive and negative associations of your term. Words aren't simple; they come with different meanings. For example, 'power' can mean strength and influence but can also be linked to negative things like abuse and control.
- Use real-life examples to make your points clear in your definition essay. Whether you're talking about successful people from different fields or sharing stories that illustrate 'love,' concrete examples help readers understand.
- Be creative with your approach. Use metaphors, illustrations, or humor to keep things interesting. Remember, it's your essay – make it come alive!
Final Words
As we wrap up, we trust you've grasped the ins and outs of how to write a definition essay and feel inspired to tackle your own. Nobody wants to be left scratching their head over complex topics, right? So why not leverage our academic writing assistance to your advantage? Whether you need help brainstorming extended topics, crafting a sharp analytical piece, or any other form of writing, we've got you covered. Say goodbye to confusion and ignorance – Order essay and let us guide you toward clarity and knowledge.
Want to Get Your Task Done ASAP?
Leave us a notice and get help from professional writers!
Related Articles
.webp)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
15.7 Definition Essay
Learning objective.
- Read an example of the definition rhetorical mode.
Defining Good Students Means More Than Just Grades
Many people define good students as those who receive the best grades. While it is true that good students often earn high grades, I contend that grades are just one aspect of how we define a good student. In fact, even poor students can earn high grades sometimes, so grades are not the best indicator of a student’s quality. Rather, a good student pursues scholarship, actively participates in class, and maintains a positive, professional relationship with instructors and peers.
Good students have a passion for learning that drives them to fully understand class material rather than just worry about what grades they receive in the course. Good students are actively engaged in scholarship, which means they enjoy reading and learning about their subject matter not just because readings and assignments are required. Of course, good students will complete their homework and all assignments, and they may even continue to perform research and learn more on the subject after the course ends. In some cases, good students will pursue a subject that interests them but might not be one of their strongest academic areas, so they will not earn the highest grades. Pushing oneself to learn and try new things can be difficult, but good students will challenge themselves rather than remain at their educational comfort level for the sake of a high grade. The pursuit of scholarship and education rather than concern over grades is the hallmark of a good student.
Class participation and behavior are another aspect of the definition of a good student. Simply attending class is not enough; good students arrive punctually because they understand that tardiness disrupts the class and disrespects the professors. They might occasionally arrive a few minutes early to ask the professor questions about class materials or mentally prepare for the day’s work. Good students consistently pay attention during class discussions and take notes in lectures rather than engage in off-task behaviors, such as checking their cell phones or daydreaming. Excellent class participation requires a balance between speaking and listening, so good students will share their views when appropriate but also respect their classmates’ views when they differ from their own. It is easy to mistake quantity of class discussion comments with quality, but good students know the difference and do not try to dominate the conversation. Sometimes class participation is counted toward a student’s grade, but even without such clear rewards, good students understand how to perform and excel among their peers in the classroom.
Finally, good students maintain a positive and professional relationship with their professors. They respect their instructor’s authority in the classroom as well as the instructor’s privacy outside of the classroom. Prying into a professor’s personal life is inappropriate, but attending office hours to discuss course material is an appropriate, effective way for students to demonstrate their dedication and interest in learning. Good students go to their professor’s office during posted office hours or make an appointment if necessary. While instructors can be very busy, they are usually happy to offer guidance to students during office hours; after all, availability outside the classroom is a part of their job. Attending office hours can also help good students become memorable and stand out from the rest, particularly in lectures with hundreds enrolled. Maintaining positive, professional relationships with professors is especially important for those students who hope to attend graduate school and will need letters of recommendation in the future.
Although good grades often accompany good students, grades are not the only way to indicate what it means to be a good student. The definition of a good student means demonstrating such traits as engaging with course material, participating in class, and creating a professional relationship with professors. While every professor will have different criteria for earning an A in their course, most would agree on these characteristics for defining good students.
Online Definition Essay Alternatives
Judy Brady provides a humorous look at responsibilities and relationships in I Want a Wife :
- http://www.columbia.edu/~sss31/rainbow/wife.html
Gayle Rosenwald Smith shares her dislike of the name for a sleeveless T-shirt, The Wife-Beater :
- http://faculty.gordonstate.edu/cperkowski/1101/WifeBeater.pdf
Philip Levine defines What Work Is :
- http://www.ibiblio.org/ipa/poems/levine/what_work_is.php
- http://www.poemhunter.com/poem/what-work-is
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.14: Essay Organization
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58331
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Examine the basic organization of traditional essays
Although college essays can offer ideas in many ways, one standard structure for expository essays is to offer the main idea or assertion early in the essay, and then offer categories of support.
One way to think about this standard structure is to compare it to a courtroom argument in a television drama. The lawyer asserts, “My client is not guilty.” Then the lawyer provides different reasons for lack of guilt: no physical evidence placing the client at the crime scene, client had no motive for the crime, and more.
In writing terms, the assertion is the thesis sentence , and the different reasons are the topic sentences . Consider this following example:
- Topic Sentence (reason) #1: Workers need to learn how to deal with change.
- Topic Sentence (reason) #2: Because of dealing with such a rapidly changing work environment, 21st-century workers need to learn how to learn.
- Topic Sentence (reason) #3: Most of all, in order to negotiate rapid change and learning, workers in the 21st century need good communication skills.
As you can see, the supporting ideas in an essay develop out of the main assertion or argument in the thesis sentence.
Essay Organization
The structural organization of an essay will vary, depending on the type of writing task you’ve been assigned, but they generally follow this basic structure:
Introduction
The introduction introduces the reader to the topic. We’ve all heard that first impressions are important. This is very true in writing as well. The goal is to engage the readers, hook them so they want to read on. Sometimes this involves giving an example, telling a story or narrative, asking a question, or building up the situation. The introduction should almost always include the thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs
The body of the essay is separated into paragraphs. Each paragraph usually covers a single claim or argues a single point, expanding on what was introduced in the thesis statement. For example, according to the National Institute of Mental Health, the two main causes of schizophrenia are genetic and environmental. Thus, if you were writing about the causes of schizophrenia, then you would have a body paragraph on genetic causes of schizophrenia and a body paragraph on the environmental causes.
A body paragraph usually includes the following:
- Topic sentence that identifies the topic for the paragraph
- Several sentences that describe and support the topic sentence

- Remember that information from outside sources should be placed in the middle of the paragraph and not at the beginning or the end of the paragraph so that you have time to introduce and explain the outside content
- Quotation marks placed around any information taken verbatim (word for word) from the source
- Summary sentence(s) that draws conclusions from the evidence
- Transitions or bridge sentences between paragraphs.
- Draw final conclusions from the key points and evidence provided in the paper;
- For example, if you began with a story, draw final conclusions from that story; If you began with a question(s), refer back to the question(s) and be sure to provide the answer(s).
Step through this presentation to review the main components of an essay, then see if you can correctly organize the essay below.
Contributors and Attributions
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing an Essay. Provided by : QUT Cite Write. Located at : http://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/essay.jsp . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of Choosing Paragraph Patterns. Authored by : GrinnPidgeon. Located at : flic.kr/p/a9oiLS. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Essay Structure. Authored by : Marianne Botos, Lynn McClelland, Stephanie Polliard, Pamela Osback . Located at : https://pvccenglish.files.wordpress.com/2010/09/eng-101-inside-pages-proof2-no-pro.pdf . Project : Horse of a Different Color: English Composition and Rhetoric . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Traditional Structure. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/writing-process/essay-writing/essay-writing-traditional-structure-activity/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of writing in the sand. Authored by : Michitogo. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/photos/the-end-sand-end-beach-text-1544913/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
Definition Essay

Definition Essay - Writing Guide, Examples and Tips
14 min read
Published on: Oct 9, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Interesting Definition Essay Topics for Students
Definition Essay Outline - Format & Guide
Share this article
Many students struggle with writing definition essays due to a lack of clarity and precision in their explanations.
This obstructs them from effectively conveying the essence of the terms or concepts they are tasked with defining. Consequently, the essays may lack coherence, leaving readers confused and preventing them from grasping the intended meaning.
But don’t worry!
In this guide, we will delve into effective techniques and step-by-step approaches to help students craft an engaging definition essay.
Continue reading to learn the correct formation of a definition essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Definition Essay?
Just as the name suggests, a definition essay defines and explains a term or a concept. Unlike a narrative essay, the purpose of writing this essay is only to inform the readers.
Writing this essay type can be deceivingly tricky. Some terms, concepts, and objects have concrete definitions when explained. In contrast others are solely based on the writerâs understanding and point of view.
A definition essay requires a writer to use different approaches when discussing a term. These approaches are the following:
- Denotation - It is when you provide a literal or academic definition of the term.
- Connotation - It is when the writer provides an implied meaning or definition of the term.
- Enumeration - For this approach, a list is employed to define a term or a concept.
- Analogy - It is a technique in which something is defined by implementing a comparison.
- Negation - It is when you define a term by stating what it is not.
A single or combination of approaches can be used in the essay.
Definition Essay Types
There are several types of definition essays that you may be asked to write, depending on the purpose and scope of the assignment.
In this section, we will discuss some of the most common types of definition essays.
Descriptive Definition Essay
This type of essay provides a detailed description of a term or concept, emphasizing its key features and characteristics.
The goal of a descriptive definition essay is to help readers understand the term or concept in a more profound way.
Stipulative Definition Essay
In a stipulative definition essay, the writer provides a unique definition of a term or concept. This type of essay is often used in academic settings to define a term in a particular field of study.
The goal of a stipulative definition essay is to provide a precise and clear definition that is specific to the context of the essay.
Analytical Definition Essay
This compare and contrast essay type involves analyzing a term or concept in-depth. Breaking it down into its component parts, and examining how they relate to each other.
The goal of an analytical definition essay is to provide a more nuanced and detailed understanding of the term or concept being discussed.
Persuasive Definition Essay
A persuasive definition essay is an argumentative essay that aims to persuade readers to accept a particular definition of a term or concept.
The writer presents their argument for the definition and uses evidence and examples to support their position.
Explanatory Definition Essay
An explanatory definition essay is a type of expository essay . It aims to explain a complex term or concept in a way that is easy to understand for the reader.
The writer breaks down the term or concept into simpler parts and provides examples and analogies to help readers understand it better.
Extended Definition Essay
An extended definition essay goes beyond the definition of a word or concept and provides a more in-depth analysis and explanation.
The goal of an extended definition essay is to provide a comprehensive understanding of a term, concept, or idea. This includes its history, origins, and cultural significance.
How to Write a Definition Essay?
Writing a definition essay is simple if you know the correct procedure. This essay, like all the other formal pieces of documents, requires substantial planning and effective execution.
The following are the steps involved in writing a definition essay effectively:
Instead of choosing a term that has a concrete definition available, choose a word that is complicated . Complex expressions have abstract concepts that require a writer to explore deeper. Moreover, make sure that different people perceive the term selected differently.
Once you have a word to draft your definition essay for, read the dictionary. These academic definitions are important as you can use them to compare your understanding with the official concept.
Drafting a definition essay is about stating the dictionary meaning and your explanation of the concept. So the writer needs to have some information about the term.
In addition to this, when exploring the term, make sure to check the termâs origin. The history of the word can make you discuss it in a better way.
Coming up with an exciting title for your essay is important. The essay topic will be the first thing that your readers will witness, so it should be catchy.
Creatively draft an essay topic that reflects meaning. In addition to this, the usage of the term in the title should be correctly done. The readers should get an idea of what the essay is about and what to expect from the document.
Now that you have a topic in hand, it is time to gather some relevant information. A definition essay is more than a mere explanation of the term. It represents the writerâs perception of the chosen term and the topic.
So having only personal opinions will not be enough to defend your point. Deeply research and gather information by consulting credible sources.
The gathered information needs to be organized to be understandable. The raw data needs to be arranged to give a structure to the content.
Here's a generic outline for a definition essay:
Are you searching for an in-depth guide on crafting a well-structured definition essay?Check out this definition essay outline blog!
6. Write the First Draft
Drafting each section correctly is a daunting task. Understanding what or what not to include in these sections requires a writer to choose wisely.
The start of your essay matters a lot. If it is on point and attractive, the readers will want to read the text. As the first part of the essay is the introduction , it is considered the first impression of your essay.
To write your definition essay introduction effectively, include the following information:
- Start your essay with a catchy hook statement that is related to the topic and the term chosen.
- State the generally known definition of the term. If the word chosen has multiple interpretations, select the most common one.
- Provide background information precisely. Determine the origin of the term and other relevant information.
- Shed light on the other unconventional concepts and definitions related to the term.
- Decide on the side or stance you want to pick in your essay and develop a thesis statement .
After briefly introducing the topic, fully explain the concept in the body section . Provide all the details and evidence that will support the thesis statement. To draft this section professionally, add the following information:
- A detailed explanation of the history of the term.
- Analysis of the dictionary meaning and usage of the term.
- A comparison and reflection of personal understanding and the researched data on the concept.
Once all the details are shared, give closure to your discussion. The last paragraph of the definition essay is the conclusion . The writer provides insight into the topic as a conclusion.
The concluding paragraphs include the following material:
- Summary of the important points.
- Restated thesis statement.
- A final verdict on the topic.
7. Proofread and Edit
Although the writing process ends with the concluding paragraph, there is an additional step. It is important to proofread the essay once you are done writing. Proofread and revise your document a couple of times to make sure everything is perfect.
Before submitting your assignment, make edits, and fix all mistakes and errors.
If you want to learn more about how to write a definition essay, here is a video guide for you!
Definition Essay Structure
The structure of a definition essay is similar to that of any other academic essay. It should consist of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
However, the focus of a definition essay is on defining and explaining a particular term or concept.
In this section, we will discuss the structure of a definition essay in detail.
Introduction
Get the idea of writing an introduction for a definition essay with this example:
Body Paragraphs
Here is an example of how to craft your definition essay body paragraph:
Types of the Term/Concept
If applicable, the writer may want to include a section that discusses the different types or categories of the term or concept being defined.
This section should explain the similarities and differences between the types, using examples and anecdotes to illustrate the points.
Examples of the Term/Concept in Action
The writer should also include real-life examples of the term or concept being defined in action.
This will help the reader better understand the term or concept in context and how it is used in everyday life.
Conclusion
This example will help you writing a conclusion fo you essay:
Definition Essay Examples
It is important to go through some examples and samples before writing an essay. This is to understand the writing process and structure of the assigned task well.
Following are some examples of definition essays to give our students a better idea of the concept.
Understanding the Definition Essay
Definition Essay Example
Definition Essay About Friendship
Definition Essay About Love
Family Definition Essay
Success Definition Essay
Beauty Definition Essay
Definition Essay Topics
Selecting the right topic is challenging for other essay types. However, picking a suitable theme for a definition essay is equally tricky yet important. Pick an interesting subject to ensure maximum readership.
If you are facing writerâs block, here is a list of some great definition essay topics for your help. Choose from the list below and draft a compelling essay.
- Authenticity
- Sustainability
- Mindfulness
Here are some more extended definition essay topics:
- Social media addiction
- Ethical implications of gene editing
- Personalized learning in the digital age
- Ecosystem services
- Cultural assimilation versus cultural preservation
- Sustainable fashion
- Gender equality in the workplace
- Financial literacy and its impact on personal finance
- Ethical considerations in artificial intelligence
- Welfare state and social safety nets
Need more topics? Check out this definition essay topics blog!
Definition Essay Writing Tips
Knowing the correct writing procedure is not enough if you are not aware of the essayâs small technicalities. To help students write a definition essay effortlessly, expert writers of CollegeEssay.org have gathered some simple tips.
These easy tips will make your assignment writing phase easy.
- Choose an exciting yet informative topic for your essay.
- When selecting the word, concept, or term for your essay, make sure you have the knowledge.
- When consulting a dictionary for the definition, provide proper referencing as there are many choices available.
- To make the essay informative and credible, always provide the origin and history of the term.
- Highlight different meanings and interpretations of the term.
- Discuss the transitions and evolution in the meaning of the term in any.
- Provide your perspective and point of view on the chosen term.
Following these tips will guarantee you better grades in your academics.
By following the step-by-step approach explained in this guide, you will acquire the skills to craft an outstanding essay.
Struggling with the thought, " write my college essay for m e"? Look no further.
Our dedicated definition essay writing service is here to craft the perfect essay that meets your academic needs.
For an extra edge, explore our AI essay writer , a tool designed to refine your essays to perfection.
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Elite College Admissions Have Turned Students Into Brands

By Sarah Bernstein
Ms. Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist in Brooklyn.
“I just can’t think of anything,” my student said.
After 10 years of teaching college essay writing, I was familiar with this reply. For some reason, when you’re asked to recount an important experience from your life, it is common to forget everything that has ever happened to you. It’s a long-form version of the anxiety that takes hold at a corporate retreat when you’re invited to say “one interesting thing about yourself,” and you suddenly believe that you are the most boring person in the entire world. Once during a version of this icebreaker, a man volunteered that he had only one kidney, and I remember feeling incredibly jealous of him.
I tried to jog this student’s memory. What about his love of music? Or his experience learning English? Or that time on a summer camping trip when he and his friends had nearly drowned? “I don’t know,” he sighed. “That all seems kind of cliché.”
Applying to college has always been about standing out. When I teach college essay workshops and coach applicants one on one, I see my role as helping students to capture their voice and their way of processing the world, things that are, by definition, unique to each individual. Still, many of my students (and their parents) worry that as getting into college becomes increasingly competitive, this won’t be enough to set them apart.
Their anxiety is understandable. On Thursday, in a tradition known as “Ivy Day,” all eight Ivy League schools released their regular admission decisions. Top colleges often issue statements about how impressive (and competitive) their applicant pools were this cycle. The intention is to flatter accepted students and assuage rejected ones, but for those who have not yet applied to college, these statements reinforce the fear that there is an ever-expanding cohort of applicants with straight A’s and perfect SATs and harrowing camping trip stories all competing with one another for a vanishingly small number of spots.
This scarcity has led to a boom in the college consulting industry, now estimated to be a $2.9 billion business. In recent years, many of these advisers and companies have begun to promote the idea of personal branding — a way for teenagers to distinguish themselves by becoming as clear and memorable as a good tagline.
While this approach often leads to a strong application, students who brand themselves too early or too definitively risk missing out on the kind of exploration that will prepare them for adult life.
Like a corporate brand, the personal brand is meant to distill everything you stand for (honesty, integrity, high quality, low prices) into a cohesive identity that can be grasped at a glance. On its website, a college prep and advising company called Dallas Admissions explains the benefits of branding this way: “Each person is complex, yet admissions officers only have a small amount of time to spend learning about each prospective student. The smart student boils down key aspects of himself or herself into their personal ‘brand’ and sells that to the college admissions officer.”
Identifying the key aspects of yourself may seem like a lifelong project, but unfortunately, college applicants don’t have that kind of time. Online, there are dozens of lesson plans and seminars promising to walk students through the process of branding themselves in five to 10 easy steps. The majority begin with questions I would have found panic-inducing as a teenager, such as, “What is the story you want people to tell about you when you’re not in the room?”
Where I hoped others would describe me as “normal” or, in my wildest dreams, “cool,” today’s teenagers are expected to leave this exercise with labels like, Committed Athlete and Compassionate Leader or Environmentally Conscious Musician. Once students have a draft of their ideal self, they’re offered instructions for manifesting it (or at least, the appearance of it) in person and online. These range from common-sense tips (not posting illegal activity on social media) to more drastic recommendations (getting different friends).
It’s not just that these courses cut corners on self-discovery; it’s that they get the process backward. A personal brand is effective only if you can support it with action, so instead of finding their passion and values through experience, students are encouraged to select a passion as early as possible and then rack up the experience to substantiate it. Many college consultants suggest beginning to align your activities with your college ambitions by ninth grade, while the National Institute of Certified College Planners recommends students “talk with parents, guardians, and/or an academic adviser to create a clear plan for your education and career-related goals” in junior high.
The idea of a group of middle schoolers soberly mapping out their careers is both comical and depressing, but when I read student essays today, I can see that this advice is getting through. Over the past few years, I have been struck by how many high school seniors already have defined career goals as well as a C.V. of relevant extracurriculars to go with them. This widens the gap between wealthy students and those who lack the resources to secure a fancy research gig or start their own small business. (A shocking number of college applicants claim to have started a small business.) It also puts pressure on all students to define themselves at a moment when they are anxious to fit in and yet changing all the time.
In the world of branding, a word that appears again and again is “consistency.” If you are Charmin, that makes sense. People opening a roll of toilet paper do not want to be surprised. If you are a teenage human being, however, that is an unreasonable expectation. Changing one’s interests, opinions and presentation is a natural part of adolescence and an instructive one. I find that my students with scattershot résumés are often the most confident. They’re not afraid to push back against suggestions that ring false and will insist on revising their essay until it actually “feels like me.” On the other hand, many of my most accomplished students are so quick to accept feedback that I am wary of offering it, lest I become one more adult trying to shape them into an admission-worthy ideal.
I understand that for parents, prioritizing exploration can feel like a risky bet. Self-insight is hard to quantify and to communicate in a college application. When it comes to building a life, however, this kind of knowledge has more value than any accolade, and it cannot be generated through a brainstorming exercise in a six-step personal branding course online. To equip kids for the world, we need to provide them not just with opportunities for achievement, but with opportunities to fail, to learn, to wander and to change their minds.
In some ways, the college essay is a microcosm of modern adolescence. Depending on how you look at it, it’s either a forum for self-discovery or a high-stakes test you need to ace. I try to assure my students that it is the former. I tell them that it’s a chance to take stock of everything you’ve experienced and learned over the past 18 years and everything you have to offer as a result.
That can be a profound process. But to embark on it, students have to believe that colleges really want to see the person behind the brand. And they have to have the chance to know who that person is.
Sarah Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

Sponsored Content | Essay Writing Services & AI Tools – Top Picks…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Advertise with us
- Public Notices
- Local Guide
- Real Estate
- Today’s Ads
- Special Sections
Sponsored Content
Sponsored content | essay writing services & ai tools – top picks for students in 2024 (summer review).

Sponsored Content | Sugar Defender Reviews (Urgent Consumer Alert) Does It Work? Real Claims or Fake Official Website Results?

Sponsored Content | Top 11 Best Shampoo for Hair Growth Compared

Sponsored Content | Artrinol Reviews – Does It Work? Real Official Website Claims or Fake Results?

Sponsored Content | KeraBiotics Reviews – Does It Work? Real Official Website Claims or Fake Toenail Fungus Results?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
The writing process can be broken into five steps: Prewriting: planning such as research, brainstorming, outlining, and thesis development. Drafting: writing the material in its intended format ...
As you might expect, process writing means approaching a writing task according to a formalized series of concrete, discrete steps. Although different versions of the writing process can be found—some with as few as three steps or phases, others with as many as eight—they generally move from a writer-oriented phase of pre-writing through ...
Step 1: Prewriting. Think and Decide. Make sure you understand your assignment. See Research Papers or Essays. Decide on a topic to write about. See Prewriting Strategies and Narrow your Topic. Consider who will read your work. See Audience and Voice. Brainstorm ideas about the subject and how those ideas can be organized.
Here's a step by step guide to the writing process. Keep what works for you and discard the rest. Your material and process will guide you to your own set of rules. 1. Prewriting. "I will always jot down things, little ideas. I may never go back to them. I may never see them again.
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps, or strategies, that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences.. Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps, stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, editing.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
Writing is Recursive. You will focus as much on the process of writing as you will on its end product (the writing you normally submit for feedback or a grade). Recursive means circling back; and, more often than not, the writing process will have you running in circles. You might be in the middle of your draft when you realize you need to do ...
Writing is a Process. Pre-writing (freewriting, brainstorming, clustering, asking questions (research), keeping a Journal) ... Writing an Academic Essay. An academic essay has a particular type of organization with an introduction paragraph with a thesis, body paragraphs which prove the thesis, and a concluding paragraph which sums up the proof ...
1. The writing process refers to writing process steps. The writing process is often characterized as a series of steps or stages. During the elementary and middle-school years, teachers define the writing process simply as prewriting, drafting, revising, and editing.Later, in high-school and college, as writing assignments become more challenging, teachers introduce additional writing steps ...
Writing is Recursive. You will focus as much on the process of writing as you will on its end product (the writing you normally submit for feedback or a grade). Recursive means circling back; and, more often than not, the writing process will have you running in circles. You might be in the middle of your draft when you realize you need to do ...
Exercise 1. Using the topic for the essay that you outlined in Section 8.2 "Outlining", describe your purpose and your audience as specifically as you can. Use your own sheet of paper to record your responses. Then keep these responses near you during future stages of the writing process.
Definitions. The Writing Process is a cycle of activities that you complete as you generate ideas, compose those ideas into a document or presentation, and refine those ideas. It is a recursive process, meaning that at any one stage in the process, you may find that you have to return to previous steps to review and refine your methods.
"Writing" is usually understood as the expression of thought. This book redefines "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking. Better living through interpretation: that's the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it's a
Here's what you need to include: Start with something attention-grabbing, like a thought-provoking question or an interesting fact. Provide a brief overview of the topic and why it's important to define it. Clearly state the term you're defining and your interpretation of it. Definition Essay Body Paragraphs.
Class participation and behavior are another aspect of the definition of a good student. Simply attending class is not enough; good students arrive punctually because they understand that tardiness disrupts the class and disrespects the professors. They might occasionally arrive a few minutes early to ask the professor questions about class ...
Writing is a recursive process of forming, developing, and clarifying our ideas, causing them to evolve in unexpected directions. To produce ideas worth sharing, we need to slow down the process of analysis, taking the time to carefully examine each of its components. This page titled 2.3: An Overview of the Writing Process is shared under a CC ...
A process essay is commonly written either to explain how something works or to guide a reader through the process of completing a particular task, states the process essay definition. Process essays also go under the "How-to articles" title and aim to teach the target audience how to achieve certain goals or complete specific assignments.
Topic Sentence (reason) #1: Workers need to learn how to deal with change. Topic Sentence (reason) #2: Because of dealing with such a rapidly changing work environment, 21st-century workers need to learn how to learn. Topic Sentence (reason) #3: Most of all, in order to negotiate rapid change and learning, workers in the 21st century need good ...
Bring to light your personal comprehension and experience. 4. State a definition essay thesis. It plays a great role in the whole work, concentrating both the author and the readers on the matter. The thesis reflects the main key points, supporting the definition of the selected concept. 5.
Definition Essay. Definition is a rhetorical style that uses various techniques to impress upon the reader the meaning of a term, idea, or concept. Definition may be used for an entire essay but is often used as a rhetorical style within an essay that may mix rhetorical styles. For example, you may need to use definition in order to fully ...
Writing a definition essay is simple if you know the correct procedure. This essay, like all the other formal pieces of documents, requires substantial planning and effective execution. ... Although the writing process ends with the concluding paragraph, there is an additional step. It is important to proofread the essay once you are done writing.
Ms. Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist in Brooklyn. "I just can't think of anything," my student said. After 10 years of teaching college essay writing, I was ...
With a user-friendly interface, this AI essay writer tool streamlines the writing process, enhancing productivity and efficiency. The platform's range of writing tools has earned recognition ...