
MLA 9th Edition Formatting
A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide + Free Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Formatting your paper in MLA style can feel like a pretty daunting task . In this post, we’ll show you exactly how to set up your paper for MLA (9th edition), as quickly and easily as possible. We’ll also share our popular free MLA template , to help you fast-track your writing.
Overview: MLA 9th Edition Formatting
- Structure and layout
- General page setup
- The opening section
- The main body
- Works cited (reference list)
- Free MLA 9 template
MLA Structure and Layout
Let’s start by looking at the overall structure of a typical student paper formatted for MLA 9th edition, before diving into the details of each section. For the most part, MLA papers follow a standardised structure, consisting of the following parts:
The opening section : While MLA doesn’t require a dedicated title page (unlike APA ), it does require an opening section that details some important information about yourself, your university and the paper itself.
The main body : The main body begins directly after the opening section on the first page. This is the “heart” of your paper and there are a very specific requirements regarding how you present and format this content.
The appendix (or appendices): While using an appendix in a student paper is relatively uncommon, you’ll place this section directly after the main body section, if required by your university.
The “Works Cited” list : This section is equivalent to what we’d usually call a references page and it’s where you’ll detail all the reference information corresponding to the in-text citations in the main body of your paper.
These four sections form the standard structure and order of a student paper using MLA 9th edition. As we mentioned, not all sections are always required , so be sure to double check what your university expects from you before submitting. Also, it’s always a good idea to ask your university if they have any style requirements in addition to the standard MLA specification.
Now that we’ve got a big-picture view of the typical paper structure, let’s look at the specific formatting requirements for each of these sections.
Generic Page Setup
Before you jump into writing up your paper, you’ll first need to set up your document to align with MLA’s generic page requirements. Alternatively, you can download our MLA paper template (which comes fully preformatted).
MLA 9th edition requires a 1-inch margin on all sides , for all pages. That said, if you’re writing a dissertation, thesis or any document that will ultimately be printed and bound, your university will likely require a larger left margin to accommodate for physical binding.
Fonts & sizing
MLA does not require that you use any specific font, but we do recommend sticking to the tried and tested , well-accepted fonts. For example, you might consider using one of the following:
- Sans serif fonts : Calibri (11), Arial (11), or Lucida Sans Unicode (10)
- Serif fonts : Times New Roman (12), Georgia (11), or Computer Modern (10)
Whichever font you opt for, be sure to use it consistently throughout your paper . Don’t chop and change, or use different fonts for different parts of the document (e.g., different fonts for the body text and the headings). Also, keep in mind that while MLA does not have a specific font requirement, your university may have its own preference or requirement. So, be sure to check with them beforehand regarding any additional specifications they may have.
In general, all text throughout your document needs to be left-aligned and should not be justified (i.e., leave an uneven right edge). You might consider using a different alignment for section headings, but in general, it’s best to keep things simple .
Line spacing
MLA 9th edition requires double line spacing throughout the document . There should also be no extra space before and after paragraphs . This applies to all sections of the paper, including the “Works Cited” page (more on this later).
Page header
Last but not least, you’ll need to set up a running header for your document. This should contain your last name, followed by the page number. Both of these should be positioned in the top right corner of all pages (even the first page). On a related note, there’s no need for you to include any footer content unless your university specifically requests it.
Now that we’ve looked at the generic formatting considerations, let’s dive into the specific requirements for each section of your paper.
The Opening Section
While MLA-formatted papers typically don’t require a title page, there are very specific requirements regarding the opening section of the first page .
Here’s how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition.
- On the first line, write your full name (flush left)
- On a new line, write your professor or instructor’s full name
- On a new line, write the course code and course name
- On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
- On a new line, write the full title of your paper , centre-aligned and using title case (consider using a title case converter if you’re not familiar with this)
- On a new line, begin your body content
All of the above should be in plain, unformatted font – in other words, you don’t need to apply any boldfacing, underlining , etc. That said, you should use italics whenever you’re writing out the titles of other works (for example, titles of books or articles).
To make it all a little more tangible, below is an example of a first page formatted according to the MLA specifications that we just covered.

The Main Body
While the formatting requirements for the body section are relatively light for MLA (at least when compared to APA ), there are still quite a few important things to pay attention to. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
Each of your paragraphs needs to start on a new line , and the first sentence of each paragraph requires a half-inch indent (while the rest of the paragraph is flush left aligned). Note that each paragraph simply starts on a new line and doesn’t require an additional blank line.
MLA 9th edition is fairly flexible in terms of heading formatting. There is no specified formatting, so you can decide what works best for you. However, there are still a few basic rules you need to follow:
- All your headings should be written in title case – never use all caps
- There should be no period following a heading
- Each heading level needs to be uniquely formatted and easily distinguishable from other levels (for example, a distinct difference in terms of boldfacing, underlining or italicisation)
- You can have as many heading levels as you need, but each level must have at least two instances
Abbreviations
When using abbreviations, you’ll need to make sure that you’re using the MLA version of the abbreviation . Below we’ve listed a few common ones you should be aware of:
- Appendix: app.
- Circa: c. or ca.
- Chapter: ch.
- Column: col.
- Definition: def.
- Department: dept.
- Example: e.g.
- Edition: ed.
- Figure: fig.
- Foreword: fwd.
- That is: i.e.
- Journal: jour.
- Library: lib.
- Manuscript(s): MS
- Number: no.
- Quoted in: qtd. in
- Revised: rev.
- Section: sec. or sect.
- Series: ser.
- Translation: trans.
- Version: vers.
- Variant: var.
- Volume: vol.
If you’re interested, you can find a more comprehensive list here . Alternatively, if you have access to the MLA 9th edition handbook, you can find the full list in the first appendix.

In-text citations
MLA 9 has a very specific set of requirements regarding how to cite your sources within the body of your paper. Here are some of the most important things to help you get started with MLA citations.
Author-page number system: in-text citations consist of (at a minimum) the lead author’s last name, followed by the page number of the paragraph you are citing. There is no comma between the two components (only a space).
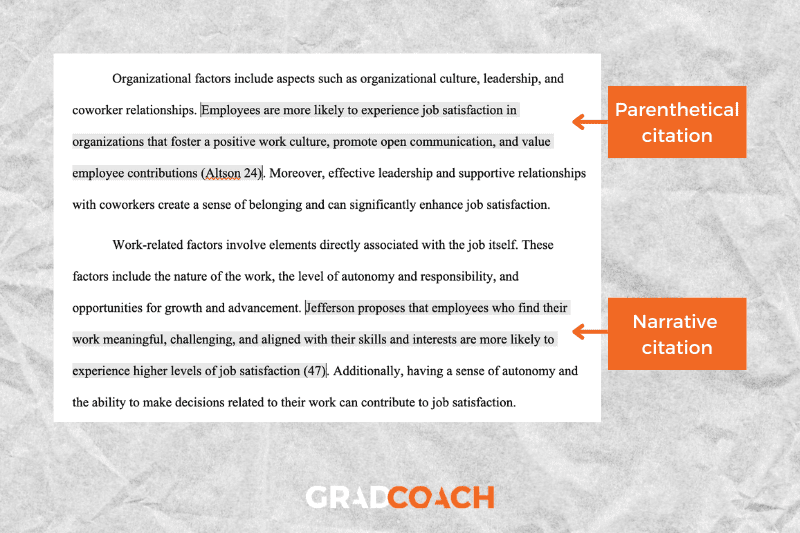
Types of citations: MLA allows two types of in-text citations: parenthetical and narrative . Parenthetical citations feature the author and page number in parentheses (brackets) at the end of the respective sentence. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen 13).
Narrative citations, on the other hand, weave the author’s name into the flow of the sentence and then present the publication date in parentheses at the end of the sentence. Here’s an example:
Jansen states that MLA 9th edition is easy for students to grasp if they visit the Grad Coach blog (13).
In general, it’s a good idea to utilise a mix of both in your writing. Narrative citations are particularly useful when you want to highlight or contrast authors or their viewpoints, while parenthetical citations are useful when you want to strengthen your own academic voice. In other words, both formats have their respective strengths and weaknesses, so try to use citation format strategically in your writing.
Quotations: when quoting text verbatim from a source, there is no need to do anything differently in terms of the citation itself, but do remember to wrap the verbatim text in quotation marks. Here’s an example:
Jansen proposes that MLA 9th edition is “easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog” (13).
Multiple authors: when citing resources that were authored by three or more people, you only need to list the lead author, followed by “et al.”. Here’s an example:
MLA 9th edition is easy to grasp if you visit the Grad Coach blog (Jansen et al. 13).
Below are a few more examples from our free MLA template .
Please keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list of all the MLA 9th edition citation-related requirements – just a shortlist of the most commonly relevant ones. If you’d like to learn more, consult the MLA handbook .
The Works Cited (Reference List)
The final section that you’ll need to pay close attention to is the “Works Cited” page, which should contain a list of reference information for all the sources cited in the body of the paper. Again, MLA has a quite a meaty set of specifications regarding the content and formatting of this list, but we’ll cover the basics here to get your started on the right foot.
Basic setup
Your reference list needs to start on a new page and should be titled “Works Cited”. The title should be unformatted and centred . The reference list should then start on the next line. As with the rest of your document, you should use double line spacing throughout.
When it comes to the reference list itself, you’ll need to keep the following in mind:
- All the sources that you cited in the body of your document should feature in the reference list. Make sure that every citation is accounted for .
- The references should be ordered alphabetically , according to the lead author’s last name .
- The exact information required within each entry depends on the type of content being referenced (e.g., a journal article, web page, etc.)
- Components that may need to feature (other than the author) include the title of the source, the title of the container, other contributors, the article version or number, the publisher, the publication date, and the location.
- All references should be left-aligned and should use a hanging indent – i.e., the second line of any given reference (if it has one) should be indented a half inch.
We have to stress that these are just the basics. MLA 9th edition requires that your references be structured and formatted in a very specific way , depending on the type of resource. If you plan to draft your reference list manually, it’s important to consult your university’s style guide or the MLA manual itself. This leads us to our next point…
In general, it’s a bad idea to write your reference list manually . Given the incredibly high level of intricacy involved, it’s highly likely that you’ll make mistakes if you try to craft this section yourself. A better solution is to use (free) reference management software such as Mendeley or Zotero . Either of these will take care of the formatting and content for you, and they’ll do a much more accurate job of it too.
If you’re not familiar with any sort of reference management software, be sure to check out our easy-to-follow Mendeley explainer video below.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve provided a primer covering how to format your paper according to MLA 9th edition. To recap, we’ve looked at the following:
- The structure and layout
- The general page setup
- The “Works Cited” page (reference list)
Remember to always check your university’s style guide to familiarise yourself with any additional requirements they may. Also, if your university has specified anything that contrasts what we’ve discussed here, please do follow their guidance .
If you need any help formatting your paper for MLA 9, take a look at our “done for you” language editing and proofreading service . Simply send us your document and we’ll take care of all the MLA formatting intracies on your behalf.
You Might Also Like:

Very well recounted!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
MLA Format: A Complete Guide with Examples
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Your instructor has asked you to format your term paper using Modern Language Association (MLA) style. You feel confident enough to produce the paper, but you have never heard of MLA style. Don't panic—we've got you covered.
This article will explain MLA style citation, give examples of MLA formatting for specific aspects of references, provide an MLA format example for each category of source material, and share essay formatting tips that our editors have learned over the years.
You'll even find a free, downloadable MLA Works Cited example page for easy reference. So, if you have a general understanding of what MLA style is and are just looking for examples of MLA citations, we can help with that too!
Free MLA Cheat Sheet
What Is MLA Style?
MLA style is an accepted way to document source material for many types of humanities documents. Some would say it is simpler than other style guides, such as the APA Style Guide or the Chicago Manual of Style .
An MLA citation has two basic requirements:
Brief parenthetical citations in the text
An alphabetical list of the works cited that corresponds to the in-text citations and appears at the end of the paper
In simple terms, you refer to your source material in parentheses throughout the main text—then, at the end of your paper, you list all the sources to which you have referred, in alphabetical order.
Of course, there is so much more to MLA style and MLA formatting than just that. Indeed, the current version of the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (7th Edition) runs to 292 pages! But here are the essential style and formatting points.
MLA Format Citation Example
To start, let's look at a basic example of how to format a citation in MLA.
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Webpage/Chapter/Article." Website/Book Title/Journal Title , edition used, vol. X, no. Y, Publisher,
Day Month Year of Publication, URL/location/page number.
This is MLA format at its simplest.
Why Use MLA Format (or Any Other)?
The main reason for carefully citing source material is to avoid allegations of plagiarism, which—derived from the Latin word for "kidnapping"—refers to stealing someone else's work. The MLA Handbook explains plagiarism in detail. You should feel free to use another person's words, facts, and thoughts in your research paper, but the material you borrow must not be presented as if it were your own creation.
When you write your research paper, remember that you must document everything that you borrow—not only direct quotations and paraphrases but also information and ideas. Our MLA citation guide will walk you through how to properly cite your sources using MLA style.
Who Uses MLA Citation Format?
MLA-style citation is commonly used by writers and students who create content in the humanities.
You'll often see it used for the following subject areas:
Language and literature
Comparative literature
Literary criticism
Cultural studies
Foreign languages
Using MLA's citation guide in these fields of study gives readers an easier option for navigating through your paper. In addition to making you look credible by neatly organizing your sources, MLA citation lends consistency to your work. It provides readers with the opportunity to easily find sources in your paper that interest them.
How to Use MLA Format
The early stages of producing a paper involve copious amounts of reading, research, and note-taking. At this point, it's easy to get confused about who said what. The best way to avoid getting confused right from the start is to keep your ideas, your summary of others' ideas, and direct transcriptions of text clearly marked and separate. Throughout our guide, we'll provide examples of MLA citation to give you a hand.
Make notes on the following elements for ease of reference and proper MLA citation later on:
Author's name
Full title of each publication (from the title page, not the front cover)
City of publication (cite only the first city if there is more than one)
Date of publication
Volume and issue numbers, if available (for journals)
Page numbers you have referenced
Medium of publication or reception (print, web, radio, television, etc.)
Laying the groundwork during your research will make the citation process much easier later on.
MLA Citation Format
Because we know there are many ways to cite a reference in MLA, depending on what source you're using, we've compiled an extensive list of MLA citation examples below.
You'll find MLA citation examples for articles, books, images, interviews, journals, movies, and more to ensure you are citing your sources correctly.
We've done our best to be as thorough as possible. Review how to use in-text citations in MLA below or skip to the ones you need most!
How to Cite Two to Three Authors
If you're citing a book in MLA format with two or three authors, use the examples below to format your citation:
Bringham, Darrin E., and Sally Knope. Resting Heartbeat Science . 12th ed., Wiley, 2001.
Christopherson, Charles, Ronald Swanson, and Roger Koltz. Fog Pirates: On Board the USS Hammerhead . Putters, 2001.
Only the first author is listed by their last name followed by their first name. Any subsequent authors are written normally (first name then last name).
How to Cite More than Three Authors
When there are more than three authors to reference in MLA, format your citation using et al., as shown below:
Niderbacher, Leslie A., et al. Penne and the Jets: A Love Story . Partridge, 2003.
Note that only the first author is fully named, followed by et al.
Related: Learn more about How to Use Et Al. here.
How to Cite No Author
An MLA in-text citation with no author begins with the title . If your in-text citation has no author in MLA, you can also use the title in addition to the page number.
( Encyclopedia of Football 54)
How to Cite a Journal Article
Correct MLA article citation starts with finding good, credible articles. Try looking for peer-reviewed scholarly journal articles in free research databases such as CORE and ScienceOpen.
When searching for the best journals for your topic, try to steer clear of regular search engines like Google or Yahoo. Academic databases like JSTOR and Google Scholar are the best sources for scholarly, peer-reviewed articles .
MLA journal citation elements include the title of the work, author(s), and publication date. While this information is usually found on the first page of an article, its placement can vary. It may be at the top or bottom of the first page or, in the case of database articles, on the results page or the description page.
Related: Check out our list of 17 Research Databases for Free Articles .
MLA Citation for an Article

MLA Article Citation Examples
Lau, Frank. "Vitamin D Insufficiency is Prevalent in Severe COVID-19." Journal of Health , vol. 2, no. 5, Aug. 2020, pp. 34–27.
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838.
Kuehn, Bridget. "Hospitals Turn to Housing to Help Homeless Patients." JAMA , Feb. 2019, pp. 5–9.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.21476.
MLA Website Article Citation Examples
Tomky, Naomi. "Explore the Oregon Coast—but don't touch the 'dragon toes.'" National Geographic , 23 Mar. 2022,
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/article/explore-oregon-coast-but-dont-touch-dragon-toe-barnacles.
Gateley, Cheyne. "Netflix's Password Crackdown Will Be Tougher Than It Seems." Variety , 21 Mar. 2022,
https://variety.com/vip/netflixs-password-crackdown-will-be-tougher-than-it-seems-1235208619/.
Book Citation in MLA
If you're citing passages from a book using MLA, look at the title page of the book to find the information you need to cite the source. The title page can usually be found a couple of pages into the book. This is where you'll find the author(s), date, edition, title, editors (if any), place of publication, and publisher.
MLA Book Citation Examples
Schucman, Helen. A Course in Miracles. Edited by Robert Perry, The Circle of Atonement, Inc., 2017.
MLA Textbook Citation Examples

How to Cite an Image
Image citation in MLA requires you to first define what type of image you're sourcing. Is it an image you saw in person or an image from a website?
Asking yourself this question first will help you decide which format to use to cite your image. Let's look at a few examples below.
MLA Image Citation Examples

How to Cite an Image from a Website
To cite an image from a website in MLA, start with the image creator's last and first name, then add the image title, the website name , day, month, and year published, and the URL.
In the example below, there is no image title, so we're using a description of the image:
Yam, Marcus. Photograph of a man hurrying away from a building hit by Russian bombs. Los Angeles Times , 25 Mar. 2022,
www.latimes.com/world-nation/story/2022-03-25/ukraine-russia-war-biden-heads-to-poland .
Here is an example with an image title:
Clancy, Pat. "Foggy Sunrise." Flickr , 10 Mar. 2022,
https://www.flickr.com/photos/128721907@N02/51958337614/in/explore-2022-03-24/.
MLA Citation: Interview
When citing an interview in MLA, the information you need can vary depending on the type of interview.
For example, if you're citing an interview printed in a magazine, you can find relevant citation information in the title or subtitle of the interview page.
For online interviews, the relevant information can be found on the site where the interview was published. Typically, in the title or near the name of the person who published the interview, you'll find the names of the interviewer and interviewee, as well as the date the interview was published.
Here are a few elements you'll need if you're citing an interview in MLA:
Interviewee's first and last name
Interviewer's first and last name
Interview title
Periodical or journal title (if any)
Type of interview
Date the interview was conducted/published
URL of the interview (if online)
Page numbers of the interview (if in print)
In MLA, if you can't find the author of an interview you're trying to source, this information can be skipped. Instead, you can start your citation with the title of the interview in quotation marks. You can also skip the date of the interview if it is missing, but you should still include the access date if the interview is online.
If, for any reason, you also can't access the title of the interview, MLA allows you to replace the title with a short description. Let's look at a couple of examples below.
MLA Interview Citation Examples

How to Cite a Lecture
When citing a lecture in MLA, start with the speaker's last and first names, followed by the lecture title in quotes, then the course or event name, the day, month, and year, the institution, the location, and the word "Lecture." Below is an example of how to cite a lecture in MLA.
MLA Lecture Citation Example

How to Cite a Movie in MLA
If you need to cite a movie in MLA style, you'll need the title of the film, the director, any relevant contributors, the company that produced/distributed the film, and the release year. Be sure to add the words "Directed by" before the director's name, as you'll see in the examples below.
MLA Movie Citation Examples

How to Cite a Poem
To cite a poem in MLA, begin with listing the author's last name and first, then the poem's title in quotes, followed by the title of the book the poem was found in, and the publisher, year, and page number(s).
MLA Poem Citation Examples

Quotes in MLA Format
When you're using a quote, you're taking the exact words from an original source, so you need to make sure you're citing that source correctly.
In MLA format, quotes should be cited in the main text and on the Works Cited page. Your in-text citation will need the author's last name and the page number where you found the quote , while the Works Cited page will include the full citation. We've included examples of both MLA quote citation formats below.
MLA Short Quote Citation Examples
In-text citation example:
It appears that creating "businesses that diminish the quality of life and well-being of our citizens" (Williamson 109) will only make things worse.
Works Cited example:
Williamson, Marianne. A Politics of Love . Harper One, 2019.
MLA Format for Long Quotes
If you have to cite quotes longer than four lines in your paper, you'll want to use a block quote. The MLA format is the same on the Works Cited page for long and short quotes, but block quotes look different in the main text.
Block quotes are placed in a separate paragraph, indented 1 inch from the left margin. When using a block quote in text, include the last name of the author and page number(s) in parentheses after the closing punctuation at the end of the quote.
Note that block quotes are not enclosed in quotation marks.
How to Cite a Song in MLA
When citing a song in MLA, pay close attention to the medium you used to access it. If you heard the song on a CD or on a streaming service like Spotify, you'll want to include this in your reference.
For in-text citations of songs, you'll include your citation at the end of your paraphrased portion with the last name of the performer and the specific time stamp of the song. Other elements needed for the citation on the Works Cited page include the album name, label, and release date.
MLA Song Citation Examples

How to Cite a Video
An MLA citation for a YouTube video requires a few pieces of information, including the video creator's name, the title of the video, the website hosting the video, the name of the channel or uploader, the day, month , and year the video was published, and its URL.
Regardless of the platform from which you cite a video, MLA requires the same standard information, including the creator of the video, the title, where it was found, who uploaded it, the day, month, and year it was uploaded, and the URL.

How to Cite a Website in MLA
The MLA format for websites requires a few core elements, including the author, title of the source and container, relevant contributors, version, publisher, publication date in day-month-year format, and DOI or URL .
Some of this information can be omitted if it isn't available. See the examples below.
MLA Format for Websites

More about MLA Style and Format
Mla heading format.
When you're writing a paper in MLA format, headings go on the first page . Your heading should include the following information:
Instructor's name
Course name or number
Submission date
Your MLA heading goes in the upper left corner of your paper, double-spaced. Try not to confuse an MLA heading with an MLA header, which is in the upper right corner of every page of your paper and includes your last name and the page number.
MLA Format Heading Examples
Here are two example headings in MLA format for reference. Keep in mind that these should be double-spaced in your paper.
Cody Anderson
Professor Lockhart
Astronomy 103
23 March 2022
Raquel Smith
Professor Snape
Humanities 605
25 February 2021
MLA In-Text Citation
In the next few sections, we'll look at MLA formatting for sources cited within the main text of your paper, also called in-text citations. In-text citations give your reader a clue about where to find the source you referenced in the Works Cited section at the end of your paper.
MLA format for books requires that you briefly acknowledge your sources in the main body of the text by using the author's name and the page number in parentheses.
Note the following example:
(Clinton 440).
The reader knows to consult page 440 of Clinton's book.
Larger Works
If you refer to the title of a large published work in your paper, such as a novel or movie, it should appear as follows:
John Clinton's A Study of Life.
Please note the use of capital letters and italics.
Smaller Works
Titles of smaller works, such as poems, short stories, chapters, and articles, should be written in the text as follows:
Raymond Carver's "Cathedral."
Please note that smaller works are put in quotation marks and are not italicized.
MLA Works Cited
To obtain further information, the reader can refer to the alphabetical references section, called the Works Cited page, at the end of the paper. There, the reader can find the full details of each cited publication.
Note the following MLA Works Cited example:
Clinton, John. A Study of Life . London: Hodder, 1998. Print.
Our John Clinton example is MLA style referencing in its simplest form: one author and one book. MLA citation for multiple authors of a single book and MLA citation for multiple books by a single author tend to complicate matters. However, if you have the basics right and have made good notes for all your source material, these problems are manageable.
Multiple Books by One Author
When citing two or more books by one author in your Works Cited section, MLA requires the author's name in the first entry only. In the next entry, replace the author's name with an em dash (—), a period, and the second book title. The em dash takes the place of the author's name. In terms of the order of the books by one author on your Works Cited page, alphabetize the list by title.
Brunson, Russell. DotCom Secrets . Morgan James Publishing, 2015.
—. Traffic Secrets . Hay House, Inc., 2020.
MLA Format with Multiple Authors
When citing three or more authors in MLA, you'll want to use "et al.," which means "and others."
Levine, Robert S., et al. The Norton Anthology of American Literature . 9th ed., W.W. Norton & Company, 2022.
Missing Items
If you're trying to cite a source in MLA with missing information, you have a few options available to you depending on what information is missing.
If you're missing the author of a source, use the title of the work in its place for both in-text citations and citations in the Works Cited in MLA format. If your title is also missing, use the source instead.
If your source has no page numbers, you can omit these in your citations and use paragraph or line numbers if they are available.
If the date of the publication is missing, you don't have to include it. But if it's a resource you accessed online, include the access date at the end of the citation—for example, "Accessed 14 Sep. 2021."
You can also omit the publisher if this information is missing.
MLA Format Works Cited Page Tips
When formatting your Works Cited page in MLA format, be sure to pay close attention to all the guidelines. MLA requires all lines to be double-spaced with a hanging indent. A hanging indent is when the first line of your reference starts at the beginning of the line while the next lines are indented by an inch and a half from the left.
Free Download
To keep all of these MLA examples in one sheet for easy reference, we've compiled a free download. This way, you can review MLA citation examples anytime you need them, either for your Works Cited page or in-text citations, for multiple types of work.
Once downloaded, you'll have all of the MLA citation examples you need in your back pocket. This guide will give you examples of MLA citations for the following types of sources:
Books (with one author, multiple authors, or no author)
Download our free MLA downloadable here.
Download Now
Writing a paper in mla format.
When writing a paper in MLA format, you'll need to cover your bases when it comes to citing your sources. Not only do your sources need to be correct to account for wherever you're pulling information from, but they also need to follow MLA paper formatting basics .
So far, we've covered how to cite sources in your Works Cited list and in-text citations. Now, let's talk about how to use footnotes in an MLA paper with a couple of examples.
As a general rule, footnotes should be used sparingly in MLA. However, when they are used, there are two types: bibliographical footnotes and content footnotes.
Bibliographical footnotes allow you to add more relevant sources. Content footnotes allow you to add commentary or explanations about your topic. We'll look at examples of both of these below.
MLA Footnote Examples
Bibliographical footnote:
1 See Clinton, John. A Study of Life . Hodder, 1998. Additional references are for this edition and appear within the text.
Content footnote:
1 In a lecture from 2013, Peters mentions his love of science and how science will shape our future.
MLA Title Page Format
The MLA format cover page is not an entirely separate page. It begins with a 1-inch margin, flush left with your name, your instructor's name, the course name or number, and the date typed on separate, double-spaced lines.
The title of your research paper should then be centered on the MLA format title page. There is no need for it to be presented in bold, italics, or capital letters.
MLA Parenthetical Citation
When citing a source in your text in MLA, use a parenthetical citation.
Parenthetical citations in MLA should include the author's last name and the page number where you found the information.
For example: (Lars 86).
MLA Page Number Format
In MLA format, page numbers appear in the top right-hand corner with a 0.5-inch margin from the top and a flush right margin. It is good practice to include your last name before the page number in case pages go astray. Do not use the abbreviation p. before the page number or add any other mark or symbol. You may not need to include a page number on the front page—check with your instructor.
Sometimes, it is appropriate to draw attention to particular words in your paper, but using italics for emphasis ("He really ate a lot ") is inappropriate in research writing and inconsistent with MLA style. Generally, in MLA format, italics should be reserved for titles of longer works (e.g., books, films), non-English words, and words and letters referred to as words and letters.
MLA Format Essay Tips
Your instructor may issue particular instructions if you are to use MLA citation in an essay—if so, follow them. Otherwise, the following MLA essay formatting tips will help you set out your research paper in MLA style.
The MLA Style Guide recommends using a clear typeface (Arial or Times New Roman) in a readable size (at least 11 point).
Justification
Justify the text to the left margin, leaving the right margin ragged. Leave 1-inch margins on the top, bottom, left, and right of the page.
Indent the first word in each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Indent set-off block quotations by 1 inch.
Use double-spacing throughout. In accordance with the MLA guide, use single spaces after periods, commas , exclamation marks, etc.
Good grammar, punctuation , and spelling are essential parts of your research paper—not just when using MLA style citation. There is no room for typos at this level.
Our advice is to check and check again, and don't just rely on your word processor's spell-checker. Get a second pair of eyes to look over your paper. T ry our essay editors to ensure that the MLA formatting is consistent throughout your paper and there are no grammatical errors.
Related: Avoid These Common Mistakes in Academic and Scientific Writing
The importance of citing your references in your essay cannot be understated. Any time you include a piece of information in your essay that you didn't write yourself, MLA requires two forms of citation: one in the main text and one at the end of your paper in the Works Cited section.
MLA Format Essay Example
To see how all these formatting elements come together to make an MLA paper, see the example below.
https://p113.p2.n0.cdn.getcloudapp.com/items/v1ugxp7E/9e3b21d9-758c-4e27-b6cb-caa1059c0547.jpeg?v=559e925043cbfee9fe816e0568ab3d3b
Electronic Sources and MLA Formatting
In this computerized age, electronic publications are widely used as source materials for essays. However, electronic texts are prone to frequent and rapid change—one minute you see them online, and the next they are gone. Therefore, it is important to provide more information when references to electronic works are made.
When accessing electronic information, note the following elements:
Name of the author, editor, etc.
Title of the work
Title of the website (if distinct from the title of the work)
Version/edition used, if applicable
Publisher or sponsor of the site (if not available, use n.p.)
Date of publication (day, month, and year, if available; if no date is available, use n.d.)
Medium of publication (web)
Date of access (day, month, and year)
Note the following example of MLA citation:
Smith, George. "Trees of the Southern Hemisphere." The International Leaf. Barker University, 2008. Web. 6 Feb. 2009.
Please note that the MLA formatting and style guide no longer recommends including the URL of a document. Nevertheless, the URL can be included if it is required by your instructor or if your readers will have difficulty locating the source without it.
MLA Format Letter
Below, you'll find examples of how to apply the MLA letter format. Much of the formatting will be similar to that of MLA-style papers, including using double-spaced lines in your text.
MLA Letter Heading Format
Start your MLA-formatted letter with your two-line mailing address in the upper left-hand corner, an inch from the top of the page. Skip to the next line and add the date in day-month-year format.
On the next line, include the addressee's information, starting with the recipient's title, such as Mr., Ms., or Dr. You can also include their address and contact information.
On yet another line, include your salutation—for example, "Dear Ms. Smith"—followed by a colon. If you don't have a name for the person you're writing to, use the person's title—for example, "Dear Director of Operations."
When writing a letter in MLA format, be sure to use double-spacing throughout as you would in an MLA paper.
Chicago vs. MLA vs. APA Citation
The formatting of citations varies among style guides like Chicago, MLA, and APA. While each style guide has its own way of formatting sources and cover pages, one of the biggest differences is in how they format in-text citations. Let's look at how they differ.
MLA stands for the Modern Language Association and is a style used for papers in the humanities. In-text citations in MLA use the author's last name and page number in parentheses: (Smith 15).
APA stands for the American Psychological Association and is a style used for scientific papers. In-text citations in APA style include a bit more information than those in MLA style. For example, APA uses the author's last name, year of publication, and page number: (Smith, 2021, p. 15).
Chicago style is used mainly for manuscripts by writers, designers, and publishers. In-text citations in this style include the last name of the source, the publication year, and the page number in parentheses, with slightly different formatting than APA: (Smith 2021, 15).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i cite a website in mla.
To cite a website in MLA, start with the author's last name and first name separated by a comma and punctuated with a period. Next, include the title of the article or page in headline case and in quotes with a period, followed by the title of the website in italics. After that, add a comma, the name of the publisher, the publication date in day-month-year format, and the URL.
Shields, Ronan. "'The Threat is Hollow': True Transparency is Some Way Off for Scaled Advertisers." Digiday , Digiday Media, 25
Mar. 2022, https://digiday.com/marketing/the-threat-is-hollow-true-transparency-is-some-way-off-for-scaled-advertisers/.
Basu, Tyler. "How to Build a Personal Brand (Complete Guide)." Thinkific , Thinkific, 7 Sep. 2021,
https://www.thinkific.com/blog/personal-branding-guide/.
For an MLA website in-text citation, simply put the last name of the author in parentheses: (Shields).
How Do I Cite a Journal Article in MLA?
The MLA citation for a journal article begins with the author's last name and first name separated by a comma. Next, include the title of the article in quotes, punctuated by a period, then the journal title in title case and italics, and then a comma before the volume or issue number. This is followed by the date of publication, the page range, and the DOI or URL (without https://). Finally, add the access date if no publication date is listed.
How Do I Write In-Text Citations in MLA?
In-text citations allow readers to identify which of the items on your Works Cited page you're referencing. MLA requires the source's last name to be set in parentheses, followed by the page number where you found the information. Below are a few examples of how to use in-text citations in MLA format.
(Smith and Jones 53)
(Smith et al. 33)
(Smith 56–58)
(Smith 56–58, 73)
How Do I Cite a YouTube Video in MLA?
For MLA YouTube citation, start with the video creator's last name and first name, separated by a comma and punctuated by a period. Next, include the title of the video in quotes, also punctuated by a period (inside the quotation marks).
Add the website hosting the video in italics (in this case, YouTube), the name of the channel or uploader, and the day, month, and year the video was published. Include the URL at the end of the MLA video citation.
Forleo, Marie. "Can You Age in Reverse? Tony Robbins Says Yes." YouTube , uploaded by Marie Forleo, 14 Feb. 2022,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YAb5z7NbMYk.
Snipes, Doc. "15 Tips to Stop Ruminating and Get Out of Your Head." YouTube , uploaded by Doc Snipes, 23 Mar. 2022,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yMZpMtM7TkI.
How Do I Use MLA Format for Headings?
Put your MLA heading in the upper left-hand corner of the first page of your paper , double-spaced. It should have your name, your instructor's name, the course name or number, and the date. Here are two examples of how to format your headings in MLA:
How Do I Cite a Movie in MLA Format?
To cite a movie in MLA style, start with the title of the film in italics, then the name of the director, followed by any relevant contributors. Next, include the company that produced or distributed the film and the release year.
Jaws . Directed by Steven Spielberg, performances by Roy Scheider and Robert Shaw, Universal Pictures, 1975.
To cite a movie from a streaming service such as Netflix, use the following format:
Jaws . Directed by Steven Spielberg, performances by Roy Scheider and Robert Shaw, Universal Pictures, 1975. Netflix app.
How Do I Format My Paper Using MLA?
To recap the most important MLA formatting guidelines, be sure to use 1-inch margins all around your paper, set the font to 12-point Times New Roman (or another easy-to-read font), and double-space the lines in your text. Make sure each word at the start of your paragraphs is indented half an inch from the left margin, and do the same for any block quotations.
You must cite all your sources in MLA, both in the text and on the Works Cited page found at the end of your paper. Use the examples and guidelines above to make sure you're formatting your paper and citations according to MLA guidelines.
How Do I Cite a Person in MLA?
If you're citing an interview, use the last and first name of the person interviewed at the start of your MLA Works Cited citation. Then, add the interview title, periodical title, type of interview, date, and URL of the interview (if online).
If the person you're referencing was interviewed in print, include the page numbers.
For an in-text citation of an interview, use the last name of the person being interviewed—for example: (Smith).
Download our free MLA format PDF for more examples of how to cite a person in MLA for an interview, either one you've conducted yourself or one you found elsewhere.
About the Author

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained nearly 20 degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Examples of MLA Citations

MLA Citations: A How-To Guide

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format
MLA Format: Everything You Need to Know Here
Welcome to an overview of “What is MLA Format?” in relation to paper formatting. You’ll find in-depth guidelines, examples, and visual samples to help you easily format your paper. This guide does not serve as a reference for MLA citation format.
For help determining the proper structure for citing, refer to the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here is another informative site which may help with further understanding of MLA citation format.
Guidelines for Formatting a Paper in MLA
- Use white 8 ½ x 11” paper.
- Make 1 inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides.
- The first word in every paragraph should be indented one half inch.
- Indent set-off or block quotations one half inch from the left margin.
- Use any type of font that is easy to read, such as Times New Roman. Make sure that italics look different from the regular typeface.
- Use 12-point size.
- Double space the entire research paper, even the Works Cited page.
- Leave one space after periods and other punctuation marks, unless your instructor tells you to leave two spaces.
These guidelines come from the MLA Style Center’s web page “Formatting a Research Paper.”
MLA Guide Overview
There are various sections in this guide. Each section provides an in-depth overview of the different components to keep in mind when developing an MLA paper.
This guide includes the following sections:
- Format background
- General paper formatting
- MLA heading format & title page instructions
- Running head & page numbers
- Paraphrases
- Abbreviations
- Numbers (includes the use of numbers in MLA outline format)
- Images, tables, and musical scores
- MLA works cited format
- MLA citation format (for in-depth citation rules visit this MLA citation guide or MLA in-text citation guide)
- Edits & proofreading
If you need more guidance, a website like EasyBib.com usually has guides and tools to help you out. There’s also resources on other styles, like our guide on “ APA reference page ”, otherwise known as a “References” page.
MLA Format Background
The Modern Language Association (MLA) is an organization responsible for developing MLA format. It was developed as a means for researchers, students, and scholars in the literature and language fields to uniformly format their papers and assignments. This uniform, or consistent, method to developing a paper or assignment allows for easy reading. Today, MLA is not only used in literature and language subject areas; many others have adopted it as well.
The Modern Language Association released the 9th and most current edition of their MLA Handbook in April 2021. The Handbook provides thorough instructions on citing, as well as guidelines for submitting work that adheres to the Modern Language Association’s rules and standards. Although we’re not affiliated with the MLA, our citation specialists bring you this thoughtful and informative guide on the format.
Looking for information about previous editions to the Handbook ? Want to learn more about the origin of “What is MLA format?” Click here to learn about the previous editions to the Handbook .
Actually, are you looking for help on using another style? See how to cite an APA journal , learn to create an APA book citation , and more!
Formatting the Header in MLA
To create a header for your first page, follow these steps:
- Begin one inch from the top of the first page and flush with the left margin.
- Type your name, your instructor’s name, the course name and number, and the date on separate lines, using double spaces between each.
- Double space once more and center the title. Do NOT underline, bold, or type the title in all capital letters. Only italicize words that would normally be italicized in the text. Example: Character Development in The Great Gatsby
- Do not place a period after the title or after any headings
- Double space between the title and first lines of the text

General Paper Formatting
Paper choice.
While many professors, instructors, and publications allow electronic submission, some prefer printed, hard copies of papers. This section focuses on the type of paper to use for printed submission.
If you choose to print your paper, use white paper only. Do not use ivory, off-white, or any other shades or colors.
Choose a standard, high quality paper to print your project on. Do not use cardstock. It is not necessary to use resum é paper. Use typical, high quality printer or copy paper.
When it comes to size, 8 ½-by-11-inch paper is the recommended size. If you’d like to use a different size, ask your teacher prior to submission.
Use One-Inch Margins in MLA
Use one-inch margins around the entire page. The running head should be the only item seen in the one inch margin (see below for more on running heads).
Most word processing programs automatically default to using one inch margins. Check the page settings section of the program to locate the margin size.

Indenting Paragraphs in MLA
Indent the first word in every paragraph. Sentences should begin one half inch from the left margin.
It is not necessary to manually measure half an inch. Use the “tab” button on the keyboard to create a half inch space.
Double Space Paragraphs in MLA
MLA research paper format requires that the entire research paper or MLA format essay includes double-spaced lines. Double-spaced lines should be found in between the written body of the work, in the heading, and also on the MLA reference page.
While it may seem tempting to place a few extra lines between the heading, title, and beginning of the paper, lines should all be double spaced.
Font and Font Size in MLA
In an MLA paper, it is acceptable to use any font type that is easy to read. Many source types, such as books and articles, use fonts that are easy to read, so if you’re seeking an appropriate font style, look at other sources for guidance. Two of the most commonly used fonts are Arial and Times New Roman.
It is important for the reader to be able to distinguish the difference between italicized and regular font, so if you choose a font style different than Arial or Times New Roman, make sure the difference between the two type styles is evident.
The use of a 12-point font size is recommended as this is the default size for many word processing programs. It is acceptable to use another standard size, such as 11-point or 11.5-point.
Some professors or instructors will provide guidance on how to secure hard copies of projects. If your instructor does not provide you with any expectations or guidance, a simple staple in the top left corner should suffice. If a stapler is not available, some instructors allow paper or binder clips.
Do not fold the top left corner down to secure the pages together. The page could easily unfold, causing a mess of papers. While binders and plastic holders are cute, in reality, they add bulk to a professor or instructor who may like to take the papers home for grading purposes. Keep the binding simple and clean. Staples work best, and binder and paper clips are the next best option.
As always, follow any instructions your professor or teacher may provide. The guidelines found here are simply recommendations.
MLA Heading & Title Page Instructions
The web page “Formatting a Research Paper” gives two options when it comes to creating the header for your project:
- An MLA format heading can be placed at the top of the first page
- A title page can grace the front of the assignment. If you choose to create a title page, keep in mind that there aren’t any official title page or cover page guidelines in MLA format. See more information below.
If choosing option one, creating an MLA heading, you’ll need to include four main components:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s name
- The name and number of the course or class
- The assignment’s due date
The first item typed on the paper should be your full name.
- Position your name one inch from the top and left margins of the page.
- Add a double space beneath your name, and type the name of your instructor.
- Below the professor or instructor’s name should be a double space, followed by the name of the course, class, or section number (if available).
- Below it, include another double space and add the assignment’s due date (Day Month Year).
Here’s an example:

The assignment’s title should be placed below the due date, after a double space. Align the title so it sits in the center of the MLA format paper. The title should be written in standard lettering, without underlines, bold font, italicized font, or any quotation marks. Only include italics or quotation marks if your title includes the title of another source.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment:
Neal E. Bibdarsh
Professor Haujeemoto
English 201
The Trials and Tribulations of Lincoln’s Reciting of “The Gettysburg Address”
*Note: The quotation marks here are around the title of a speech included in the paper’s title.
Most research papers use a standard MLA format heading, like the one seen above. If your instructor requires you to create a standalone title page, ask him or her for specifications. MLA does not have specific instructions for developing an MLA title page. We recommend you use an MLA header for your project.
If your teacher or professor requires a standalone title page, but has not provided any guidance or specifications, here are a few suggestions from EasyBib.com and this MLA guide :
- Center and double space all of the text on your page.
- Place the name of your school at the top of the page.
- Skip down to about the center of the page and type the title of your paper. Do not bold the title, italicize the entire title, place quotation marks around it, or type the title out in capital letters.
- Use italics for the titles of any sources in the title of your paper. Example: An Analysis of Mythical Creatures in Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
- first letter of the title
- first letter of the last word
- first letter of any adjectives, adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs
- If your paper has a subtitle, include on the next line below your title.
- Skip down to the bottom third of the page and add your name, the the name of your instructor, the name/number of the course or class, and the assignment’s due date on four separate lines.
- Keep the font size at 12 pt., or a size close to it, to make it look professional.
- Use the same font as the text of the paper. The Modern Language Association recommends any font that is easy to read and has a clear distinction between italics and standard font. Times New Roman and Arial are recommended, but many other fonts work as well.
- Include a page number in the top right corner of the paper. For more information on how to style page numbers, check out the next section, “Running Head and Page Numbers.”
- We do not recommend adding any images or cover art to the title page.
Click additional information about essays to see an example of a formatted header.
You can either create a title page using the EasyBib Title Page creator or omit the title page completely and use a header.
Running Head & Page Numbers in MLA
A running head is a brief heading that is placed in the top right corner of every page in a project. The Modern Language Association Style Center (online) states that the running head consists of:
- Last name of the paper’s author
- Page number
General tips to keep in mind:
- The running head is placed in the upper right-hand corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin of the page.
- Type your last name before the page number.
- The last name and page number should be separated by a single space.
- Do not place the word “page” or use an abbreviation, such as p. or pg., before the page number.
- Quite often, the running head begins on the second page, but your instructor may ask you to include the running head on the first page of the assignment. As always, if your instructor provides you with specific directions, follow his or her guidelines.

Before adding this information manually onto every single page, check to see if the word processor you’re using has the capability to automatically add this information for you. Try looking in the settings area where page numbers or headers can be added or modified.
Google Docs: Adding a header
- Go to the menu section “Insert.”
- Select “Page numbers” and select the option that places the page number in the upper-right corner.
- A page number will appear; your cursor will blink next to it.
- Move your cursor to the left of the page number.
- Type your last name. Add a space between your name and the page number.
- You should now have a properly formatted header on every page!
Microsoft Word Document: Adding a header
- Double-click in the space at the top of the page (where the page number is).
- OR Go to the “Insert” menu, select “Header,” and select “Edit Header.”
- Type your last name next to page number. If it isn’t already right-aligned, go to the “Home” menu and right-align your name.
Quotations in MLA
Quotes are added into assignments to help defend an argument, prove a point, add emphasis, or simply liven up a project.
Quotes should not take up the majority of your paper or assignment. Quotes should be sprinkled sparingly throughout, and quotes longer than 4 lines should be formatted as MLA block quotes . Use direct quotes from outside sources to enhance and expand on your own writing and ideas.
Words from quotes belong to the individual who spoke or wrote them, so it is essential to credit that individual’s work. Credit him or her by adding what is called an “in-text citation” into the body of the project.
There are three ways to add quotes: 1. With the author’s name in the sentence (a citation in prose).
Dan Gutman shares a glimpse into the overall plot by stating, “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman is the author of the book that this quote is pulled from.
2. Without the author’s name in the sentence (a parenthetical citation).
The main character’s confusing experience is realized and explained when he states “I didn’t know it at the time, but a baseball card—for me—could function like a time machine” (Gutman 5).
In the above example, Dan Gutman’s name isn’t included in the sentence. It’s included in the parentheses at the end of the sentence. This is an example of a proper MLA style citation in the body of a project.
3. In a block quote, which is used when a large quote, of 4 lines or more, is added into a project.
Using footnotes and endnotes
The Modern Language Association generally promotes the use of references as described in the sections above, but footnotes and endnotes are also acceptable forms of references to use in your paper.
Footnotes and endnotes are helpful to use in a variety of circumstances. Here are a few scenarios when it may seem appropriate to use this type of referencing:
- When you are referring to a number of various sources, by various authors, in a section of your paper. In this situation, it is a good idea to use a footnote or endnote to share information for parenthetical references. This will encourage the reader to stay focused on the text of the research paper, instead of having to read through all of the reference information.
- When you are sharing additional information that doesn’t quite fit into the scope of the paper, but is beneficial for the reader. These types of footnotes and endnotes are helpful when explaining translations, adding background information, or sharing counterexamples to research.
To include a footnote or endnote, add a superscript number at the end of the sentence the footnote or endnote refers to. They can be included mid-sentence if necessary, but be sure to add it after any punctuation, such as commas or periods. Find a location that doesn’t distract the reader from the content and flow of the paper.
Within the text example:
Numerous well-known children’s books include characters from a wide range of races and ethnicities, thus promoting diversity and multiculturalism.¹
At the bottom of the page (footnote) or at the end of the section (endnote):
¹See Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez. While Parr’s work features characters of various colors, such as pink or blue, children easily correlate it with individuals of different races and ethnicities.
On the last page of the assignment, the writer includes the full references for the books by Isadora, Parr, and Velazquez.
For more on block quotes and a further, detailed explanation on the use of quotes, including MLA footnotes, refer to our MLA In-Text Citation and Parenthetical Citations Guide. In this guide you’ll find further information including directions for the use of quotes without an author, page numbers, and how to properly credit work from electronic sources.
For guides on citations in another style, check out APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation .
Paraphrases in MLA
Paraphrases are created when text or speech from another source are added into a project, but the writer chooses to summarize them and weave in his or her own writing and writing style.
Even though the writer modifies the information from another source, it is still necessary to credit the source using proper format ( Handbook 98). Paraphrased information uses the same MLA reference format as stated in the section directly above this one.
Here is an acceptable paraphrase:
Original text:
“Stay hungry. Stay foolish.” Steve Jobs
Paraphrase:
Steve Jobs encouraged students at Stanford to continue with their determination, drive, and ambitious behavior. They should never be simply satisfied with the status quo. They should continue to push themselves despite possible obstacles and failures.
To develop a well-written paraphrase, follow these simple, step-by-step instructions.
- Find a phrase, sentence, paragraph, or section of original text you’d like to turn into a paraphrase.
- Read the text carefully and make sure you fully comprehend its meaning. A writer can only develop a well-written paraphrase if the information has been fully grasped and understood. If you’re having difficulty understanding the information, take a few minutes to read up on tricky words and background information. If all else fails, ask a friend to see if they’re able to make sense of the concepts.
- After analyzing and completely understanding the original text, put it to the side. Take a moment to think about what you’ve read and connect the idea to your own assignment.
- Now that the information is completely understood, take a moment to rewrite what you’ve read, in your own words and writing style. Do not simply substitute words in the original text with synonyms. That’s plagiarism! Show off and demonstrate your ability to process the original information, connect it to the content in your paper, and write it in your own individual and unique writing style.
- Include an in-text reference next to the paraphrase. All paraphrases include references, similar to direct quotes. See the “Quotations” section of this guide to learn how to properly attribute your paraphrased information.
- Give yourself a pat on the back! Paraphrasing is an important part of the research and writing process.
Wondering if it’s better to quote or paraphrase?
An essential part of the research process involves adding direct quotes and paraphrases into projects. Direct quotes provide word-for-word evidence and allow writers to use another author’s eloquent words and language in their own projects. When it comes to paraphrases, writers are able to take a block of text and shrink the scope of it into the their papers. Paper writers can also use paraphrases to demonstrate their ability to analyze and reiterate information in a meaningful and relevant way.
If you’re wondering which one is better to consistently use, quotes or paraphrases, there’s a clear winner. Paraphrases come out on top. Sure, direct quotes are incredibly beneficial, but copying and pasting too many of these into a project can cause a reader to lose sight of the writer’s own voice. Mixing your own voice with another author’s too much can make for choppy and disjointed reading.
The ultimate goal of a research project is to have your voice and research merged together as one. Paraphrases allow just that. When you combine information from outside sources with your own writing style, it demonstrates your ability as a researcher to showcase your understanding and analyzation of a topic.
Remember, whether you’re adding direct quotes or paraphrases into a project, both types of additions need references. References are placed after the quotes and paraphrases, and also at the end of an assignment.
If you’re looking for additional help with your punctuation or grammar, check out the EasyBib plagiarism checker !
Using Abbreviations in MLA
Abbreviations are commonly used in many source types including websites, blog posts, books, and journal articles. It is acceptable to use abbreviations in all of these sources.
When it comes to school and research assignments, however, the MLA Handbook states that abbreviations should be used rarely in the prose of your paper (293). Spelling out abbreviations into their full words and meanings is recommended. This ensures understanding and avoids any confusion from your reader.
There are times when you may feel it is perfectly acceptable to use an abbreviation rather than its typed out counterpart in a paper. If you do abbreviate, be sure you are using commonly accepted abbreviations, which you can find in the dictionary. You can also review Appendix 1 in the MLA Handbook .
General Abbreviation Tips
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus can be abbreviated to HIV, not H.I.V.
- United States should be US, not U.S.
- Digital video disc should be DVD, not D.V.D.
- For lower case abbreviations, it is acceptable to include periods between the letters.
- The abbreviation, “For example” = e.g.
- If there is a mix of lower case and upper case letters, do not use periods if the majority of the letters are upper case. Examples include PhD and EdD
Abbreviating Months
Type out entire month names when being used in the body of a research paper or assignment.
She rented out the beach house from May through September
When it comes to references, MLA bibliography format requires months longer than four letters to be abbreviated.
- July = July
- November = Nov.
Other abbreviations that are perfectly acceptable to use in a bibliography (not the body of a project) include:
- p. or pp. for page and page numbers
- ch. for chapter
- ed. for edition
- trans. for translation or translated
- vol. for volume
- no. for number
- rev. for revised
Again, these abbreviations should only be used in the final page(s) of a project, the MLA Works Cited list. They should not be used in the body of a project.
For more information on bibliographies, see our MLA format Works Cited List page.
Abbreviating Publishers
One of the quirkiest things about this particular style is how publisher names are structured on the final page of references. Certain words are abbreviated, some words are omitted, and other words are written in full.
Words describing what type of business the publisher is are omitted from the works cited. Here’s a breakdown of the words that should be excluded:
- Co. (Company)
- Corp. (Corporation)
- Inc. (Incorporated)
- Ltd. (Limited)
- The (when at the beginning of the name)
If a publisher’s name contains the words “University” and “Press” (or the equivalent in another language), the words should be abbreviated to the letters “U” and “P” in your citation. But if only one of the words appears, it should be written out normally.
Here are a few examples:
- University of Delaware
- U College of London P
All other words related to the names of publishers should be written out in full.
Abbreviating Titles
Certain classical and biblical works are abbreviated in a bibliography, but also in any parenthetical references in the text.
The official handbook provides a lengthy list, spanning over multiple pages, of the preferred abbreviations to use for classical and biblical works ( Handbook 295-301), but here’s a quick snapshot of some of the commonly used ones:
Hebrew Bible or Old Testament = OT
- Deut. = Deuteronomy
- Gen. = Genesis
- Lev. = Leviticus
- Num. = Numbers
- Ps. = Psalms
New Testament = NT
- 1 Cor. = 1 Corinthians
- Jas. = James
- Matt. = Matthew
Shakespeare:
- Ado = Much Ado about Nothing
- 3H6 = Henry VI, Part 3
- JC = Julius Caesar
- Mac. = Macbeth
- MND = A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- Oth. = Othello
- Rom. = Romeo and Juliet
Again, the titles above are allowed to be abbreviated both in references in parentheses in the body of a project and also on the final page of references. If you’re wondering why, it’s because they’re cited often and it’s unnecessary to type out the entire title names.
Formatting Numbers in MLA
Use of numerals.
If the project calls for frequent use of numbers (such as a scientific study or statistics), use numerals that precede measurements.
- 247 milligrams
Other items to keep in mind:
In divisions, use numbers, ex: In page 5 of the study
Arabic Numbers
When including a number in a paper, spell out the number if it can be written as one word (such as six ) or two words (such as sixty-two ). For fractions, decimals, or longer numbers, type them out using digits. For larger numbers, write the number itself ( Handbook 82-84).
- twenty-seven
- one hundred
If the number comes before a unit of measurement or label, type the number using digits.
- 8 tablespoons
- 3 July 2018
- 25 King Street
More on Numbers
Starting a sentence with a number is generally frowned upon. Try modifying the sentence so that the number, or number word, is found elsewhere.
Instead of:
225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Use this sentence:
A total of 225 children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
If modifying the sentence is not possible or does not work well with the flow of the assignment or paper, type out the written number:
Two hundred twenty five children were found in the warehouse, some malnourished and diseased.
Do not include any ISBN numbers in your paper.
Outline Format
The Modern Language Association does not have any requirements regarding the structure of an outline. If your teacher asks you to create an MLA outline, we recommend using roman numerals, capital and lowercase letters, and numbers.
Here is an example of a recommended outline structure:

In addition to outlines, use roman numerals for suffixes.
- King George IV
Using Images, Tables, & Musical Scores in MLA
Photographs, data sets, tables, graphs, and other images are often added into projects or papers to promote or aid understanding. They provide meaningful visuals for the reader. If the illustration or visual image does not enhance the quality of the paper, do not include it in the project.
Tables and illustrations should be placed as close as possible to the text that they most closely refer to.
For an image to be significant and easily identifiable, place it as close as possible to the text in the project where it is discussed.
It is not acceptable to simply place an image in a project without including identifiable information. All images must include information about its origin.
Here are the directions to properly attribute an image:
- Assign an Arabic number. The image closest to the beginning of the project should be labeled as Fig. 1. The next image in the project should be Fig. 2. and so on.
- Provide a caption. The caption should be a brief explanation or the title of the contents of the image. Place the caption directly next to the label.
- Immediately following the caption, it is acceptable to include attribution information. If the image is not discussed further in the rest of the paper or project, it is acceptable to include the MLA bibliography format citation below the image and omit it from the bibliography or MLA format works cited page.
In the text of the project or paper where the figure is discussed, include the label in parentheses to ensure the reader knows where to find the figure in your paper.
In the text:
Sarah’s tattoo design was filled with two of her favorite flowers: lilies and daffodils along a thinly curved vine (fig. 1).
Image formatting:
(Image Would Be Here) Fig. 1. Sarah’s Tattoo. barneyWILLIAMSable, Deviant Art , 2011, barneywilliamsable.deviantart.com/art/Sarah-s-Tattoo-design-193048938.
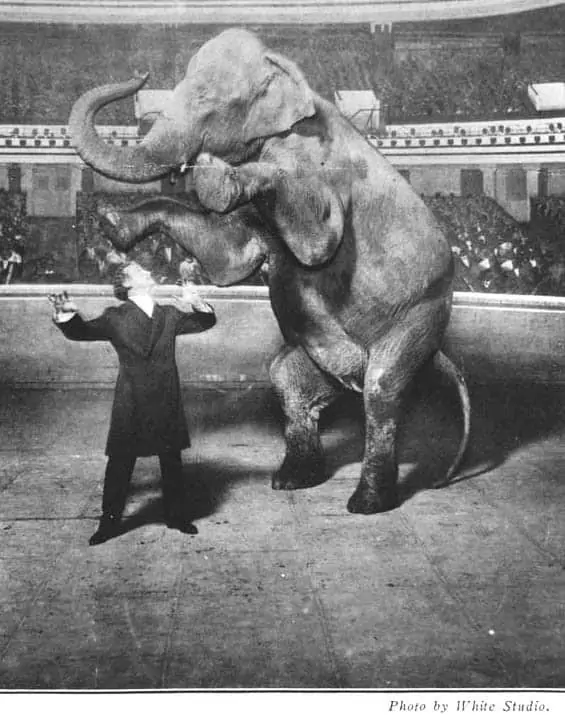

Fig. 1. White Studio. “Houdini and Jennie, the Elephant, Performing at the Hippodrome, New York.” Library of Congress , www.loc.gov/item/96518833/.
When adding a table or data set into a project, it is formatted a little differently. Above the data set, include the label “Table” with an Arabic numeral, and title it. The table number and title should be located flush left and on separate lines. The first table seen in the project is labeled as Table 1. The second table in the project is Table 2, and so on. The table’s title should be written in title case form (the first letter of each word is capitalized, except for small, insignificant words).
Underneath the table, provide the source and any notes. Notes should be labeled with a letter, rather than a numeral, so the reader is able to differentiate between the notes of the text and the notes of the table.
International Scholars from India Enrolled at Yale University a
Source: “International Scholars Academic Year 2015-2016.” Yale University , Office of International Students and Scholars, yale.app.box.com/v/scholar-2015-2016. a. The numbers reflect students who are enrolled full-time.
The information included above and below any images or table should be double spaced, similar to the rest of the project or paper.
Musical Scores
Musical scores need to be labeled as well. When including a musical score in a project, label musical scores with “Ex.” which is short for example. This label should be placed below the musical score. Next to the abbreviation “Ex.”, assign the score an Arabic numeral. The first musical score in the project should be labeled as Ex. 1. The second musical score found in an assignment should be labeled as Ex. 2., and so on.
If possible, provide a caption after to the label. If the caption below the sheet music includes enough information about the source, it is not necessary to include the full reference at the end of the assignment.
Here is an example of a possible label and caption:
Ex. 4. Scott Joplin, The Entertainer, piano, C major.
Another example:

Here’s more on tables and illustrations.
Using Lists in MLA
It’s appropriate to add lists into an MLA format essay as long as the proper rules are followed.
Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional vertical style.
Often, you will use a colon between the introductory sentence and the list. But you should not include a colon if the first item in the list is part of the sentence.
List Example #1
Here is an example of how a list may look incorporated into the prose of a research project or assignment:
William Shakespeare wrote numerous plays, many of which were considered tragedies: Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear .
List Example #2 Here is an example of how a list may look in a research project or assignment when the list is part of the introductory sentence:
Many of William Shakespeare’s were tragedies. Some of his most popular tragedies include Romeo and Juliet , Hamlet , Macbeth , Othello , Julius Caesar , and King Lear.
MLA Works Cited Format
EasyBib.com has a full, comprehensive guide to creating a proper works cited MLA format , but here are a few items to keep in mind when developing this portion of a project:
- The list of citations should be the very last page of a research project or essay.
- The top of the page should include the running head and the page number.
- All entries should be placed in alphabetical order by the first item in the MLA format citation.
- The entire page should be double spaced.
For more detailed information, make sure to check out the EasyBib guide to MLA format Works Cited pages.
MLA Citation Format
The majority of this guide focuses on MLA formatting in regards to MLA paper format rules and guidelines. If you’re seeking information related to the proper formatting of an MLA citation, refer to our individual pages and posts on various types of citations.
If you’re simply looking for the general structure for full references, which are found on the final pages of projects, here’s the proper order:
Author’s Last name, Author’s First name. “Title of Source.”* Title of Container , Names of other contributors along with their specific roles, version of the source (if it differs from the original or is unique), any key numbers associated with the source that aren’t dates (such as journal issue numbers or volume numbers), Name of the Publisher, publication date, location (such as the URL or page numbers).
*Note: A title may be in italics instead of quotation marks, depending of the type of source. The general rule is that works that are self-contained (like books, journals, or television shows) are formatted in italics. Works that are part of a larger work (like articles, chapters, or specific episodes) are formatting in quotation marks.
MLA Format Citing FAQs:
“What in the world are containers?”
Containers are what hold the source. If you’re creating a reference for a chapter in a book, the title of the chapter is the title of the source , and the container is the title of the book . The book holds the chapter, so it’s the container. If you’re searching for how to cite a website, here’s a tip: the title of the source is the name of the individual page and the title of the container is the name of the full website.
“This seems like a lot of information for a reference. Is it all necessary?”
The short answer is “No!” When citing, only include the components that help the reader locate the exact same source themselves.
It isn’t necessary to go digging for items such as numbers, version types, or names of other individuals or contributors associated with the source if they aren’t applicable. If you think it’s beneficial for the reader, then include it.
Related to citations, here are helpful pages on:
- MLA citation website format
- Citing a book
- Citing a journal
- What is a DOI ?
- More on PDFs
If you’re looking for an MLA citation generator, head to the EasyBib homepage. Our formatter will help you create citations quickly and easily!
Need APA, too? There are also EasyBib tools and an APA citation website reference guide to help you learn the basics.
Edits and Proofreading
Editing and proofreading your assignment prior to submission is an incredibly important step in the research process. Editing involves checking the paper for the following items:
- Spelling : Are all words spelled correctly? Review all proper names, places, and other unique words to ensure correct spelling. When finished, run the project through a spell checker. Many word processing programs, such as Microsoft Word and Google Drive, provide a free spell checking feature. While spell checks are beneficial, they do not always spot every mistake, so make sure you take the time to read through the assignment carefully. If you’re still not sure if your project contains proper spelling, ask a friend to read through it. They may find a mistake you missed!
- Grammar : Check your assignment to make sure you’ve included proper word usage. There are numerous grammar checkers available to review your project prior to submission. Again, take the time to review any recommendations from these programs prior to accepting the suggestions and revisions.
- Punctuation : Check to make sure the end of every sentence has an ending punctuation mark. Also make sure commas, hyphens, colons, and other punctuation marks are placed in the appropriate places.
- Attribution : Do all quotes and paraphrases include a citation? Did you create an in-text citation for each individual piece of information?
Smart idea: running your paper through a paper checker before you turn it in. EasyBib Plus offers a checker that scans for grammar errors and unintentional plagiarism.
Check out our MLA sample papers . Also, check out the EasyBib MLA Annotated Bibliography Guide.
Don’t forget to use the EasyBib citation generator to develop your Modern Language Association style references.EasyBib.com also has helpful guides on APA format and more styles . Lastly, stay up-to-date on what’s coming by following our EasyBib Twitter account.
Works Cited
“Formatting a Research Paper.” The MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association of America, style.mla.org/formatting-papers/.
MLA Handbook. 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. You can find her here on Twitter. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The works-cited list provides the reader full information so that a reader can locate the source for further use.
Basic formatting
The works-cited list appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes if they are present.
Page margins
All margins (top, bottom, left, and right) should be set at 1 inch.
Running head
Write the running head in the top right of the page at 0.5 inch from the top. Use the running head “Surname Page #.”
The font should be clear enough to read. For example, Times New Roman font set to 12 points.
Formatting entries
Entries should be double-spaced, including a double-space between the heading and the first entry. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Formatting the title
The title should be “Works Cited.” Center the title. Do not bold, italicize, or underline the title. If you cite only one source in the list, the title should be “Work Cited.” If you include sources that you only consulted and didn’t cite directly, the title should be changed accordingly to “Works Cited and Consulted.”
Arranging works cited
Works-cited-list entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name (or the editor’s last name for entire edited collections). Double-space all entries. Begin each entry flush with the left margin. If any entry runs over more than one line, indent the subsequent line(s) 0.5 inch from the left margin (sometimes called a hanging indent).
Example works cited
Damasio, Antonio. The Feeling of What Happens: Body, Emotion and the Making of Consciousness . Vintage, 2000.
Hill, R. T. “Legitimizing Colonial Privilege: Native Americans at a Quincentenary of Discourse.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 16, no. 1, 1996, pp. 92–100.
MacDonald, Shauna M. “Performance as Critical Posthuman Pedagogy.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 164–81.
Zilio, M. “Canada Will Not Move Embassy to Jerusalem, Federal Government Says.” The Globe and Mail . 7 Sept. 2017, www.theglobeandmail.com/news/politics/canada-will-not-move-embassy-to-jerusalem-federal-government-says/article37219576/ .
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed in the text. It is styled in two ways: a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when directly quoting text from the source being cited. When including a page number, do not include a comma or any other punctuation mark between the author’s surname and the page number.
Parenthetical citations usually add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Sometimes they include a page number or other locator. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The spiritual geography of the landscape is explained (Cooper).
If you want to cite a chapter number, a scene, or a line number, follow the abbreviation guidelines below:
When including a more specific locator number rather than a page number, place a comma between the author’s surname and the label.
(Cooper, ch. 2).
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for sources with different numbers or types of authors:
Use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations. If you want to add a page number (or another indicator of the place in a work), add it after the author’s surname without any punctuation between the surname and the page number.
(Abraham 7).
Two authors
Add only the surnames of the authors. Use “and” to separate the two authors.
(Langmuir and Einstein).
Three or more authors
Add only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
(Low et al.).
Corporate author
Shorten the organization name wherever possible, excluding any initial articles and using the shortest noun phrase (e.g., shorten Literary Society of Tamil Culture to Literary Society).
(Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s surname.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is shortened to Fantastic Beasts .
( Fantastic Beasts 160).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, mla format example: sample mla format essay.
- © 2023 by Barbara McLain - The Out-of-Door Academy

Below is a sample essay in MLA format.
Sample MLA Essay
Barbara McLain
Dr. Joe Moxley
Linguistics
10 May 2022
The Pronoun Controversy
The way we use pronouns—in particular the use of the traditionally plural pronouns they/them in reference to individuals—has recently been the subject of intense debate and even outrage. This furor over pronoun use feels very current, but linguistic scholars will tell you that the disagreement is almost 700 years old [1] . [BM1] The initial emergence of controversy was purely grammatical: English is lacking an important part of speech. Pronouns are paired with antecedents, the more specific nouns that precede them. But a problem arises when a sentence uses a singular gender-neutral common noun (like student, official, or customer) because English does not have a singular gender-neutral pronoun to pair with these words. The available pronouns that agree in number with our many gender-neutral common nouns ask you to assume that students are all either male or female (“he” or “she”). [BM2] The pronoun debate that we are seeing litigated in the court of public opinion, however, isn’t really a grammatical debate so much as a social one. This is also not new. Pronouns have found themselves at the center of a values debate since the suffragist movement almost 200 years ago.
In the absence of a singular gender-neutral pronoun, grammarians decreed that masculine pronouns—he, him, and his—could also be used generically to refer to both males and females. But this choice amounted to more than a fussy rule for grammar sticklers. Dr. Dennis Baron, professor Emeritus at the University of Illinois and author of What’s Your Pronoun , [BM3] cites the 1871 Dictionary Act as the moment the generic “he” was written into law: “[W]ords importing the masculine gender may be applied to females [Statutes at Large, 41st Congress, session III, ch. 71, p. 431]” (qtd. in Baron “On the Birthday”). [BM4] The dual use of a pronoun was not unheard of (“you”, for instance, can be both singular and plural), but this dual use did create ambiguity, especially with regard to the interpretation of the law. Of particular importance is the word “may,” which signified that the courts had discretion in determining when the use of “he” applied also to women, and when it did not. [BM5]
Perhaps not coincidentally, prior to the passage of the Dictionary Act, in 1869 suffragists argued that if the use of the generic “he” in criminal law applied to women, then the generic “he” in voting law should apply to women as well (Baron, “On the Birthday”). [BM6] Given that 19 th amendment would not be ratified for another 60 years, this argument was clearly unsuccessful at the time. Because “he” could be either masculine or generic, it was up to our courts to interpret its use. Surprising no one, the courts determined that “he” in laws regarding punitive measures like jailable offenses and paying taxes applied generically, while “he” in laws related to the right to vote, the right to practice law, and the right to run for congress (among many others) applied only to men. This uneven application of the generic “he” reveals something important about the pronoun debate: It has never been a debate about grammar. The rules regarding pronouns are inextricably tied to issues of gender and power, rights and equality. [BM7] But the grammatical inconvenience of this missing part of speech resulted in calls for a gender-neutral singular pronouns predating even the suffragist movement. The singular “they” first appeared in writing in 1370 and in 1792, a Scottish economist suggested adopting “ou” as a gender-neutral singular pronoun (Baron, “Pronoun Showdown”). Many alternatives have since been proposed, but none have had staying power.
In the absence of a widely accepted alternative [BM8] , students were instructed, as noted above, to default to male singular pronouns in these cases. For example, if a student wishes to be excused from physical education, he must submit an appeal to the school board. The generic “he,” hilariously described by Baron as “the grammatical equivalent of manspreading,” dates back centuries, and the reason for its adoption had little to do with clarity (“Pronoun Showdown”). Baron quotes John Lyly on this subject in 1567: “The Masculine Gender is more worthy than the Feminine, and Feminine more worthy than the Neuter” ( qtd. in Baron, “Pronoun Showdown”).
More appalling than this reasoning is the fact that this solution remained the standard until the late 20th century, when the rule evolved into the more inclusive but much clunkier “he or she.” E.g. If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, he or she must submit an appeal to the school board. Even as late as 1985, though, only about half of editors surveyed preferred “he or she” over the generic “he”(Watkins). Beyond syntactic awkwardness, this option is also not fully inclusive. “He or she” excludes those who fall outside the gender binary.
Another option is to change the structure of the sentence to avoid the problem. E.g. If students wish to be excused from physical education, they must submit an appeal to the school board. However, writing around the problem is not always possible. The fact is that the lack of an ungendered singular pronoun is a failure of the English language, and the question of how to deal with it continues to be polarizing, with no option whipping up a fury otherwise unheard of in discussion of grammar than the option to adapt “they” to be both plural and singular. [BM9]
Critics of the use of the singular “they” have existed since its inception. Baron notes that in 1794, after being criticized by writer Don Alonzo for using the singular “they,” writers of the offending passage offered this arch reply: “With regard to our using the plural pronoun “them” . . . — as we wished to conceal the gender, we would ask . . . Don [Alonzo] to coin us a substitute”(Baron, “Pronoun Showdown”). Aside from a feeble call for change in The Atlantic in 1879 (Baron, “Pronoun Showdown”), the writing community seemed to side with Mr. Alonzo. As of 1985, newspaper and magazine editors surveyed continued to be overwhelmingly against the use of the singular “they” (Watkins). [BM10]
Pronouns Today
The tide appears, at long last, to be turning. Indeed “they” was the Merriam-Webster word of the year in 2019 (“Word of the Year”). [BM11] Dr. Baron argues that the singular “they” is ideal, as it sounds natural enough that many people accidentally use it already and the larger writing community agrees. The Washington Post , which follows its own style guide, was an early adopter, switching to the use the singular “they” in 2015 (Andrews). The MLA and APA eventually followed suit to fully endorsed the singular “they” as well. The Associated Press, while still recommending writing around the need for a singular gender-neutral pronoun, has also okayed its use (Andrews). The Chicago Manual of Style stops short of a full endorsement, and like the AP suggests write-arounds (“Chicago Style”). They are unanimous, however, in their endorsement of using the singular “they” in reference to specific people. This is important: If a person’s preferred pronouns are they/them, the stylebooks agree that the use of the singular “they” is not just polite but correct.
There are, naturally, still detractors. For those who argue against the singular “they” on grammatical grounds, I think it’s safe to say they have missed the point. First, the English language is evolving and has always done so. The rate at which words disappear from our lexicon is eclipsed only by the rate at which new words are added. An average of 800-1000 new words are added to English dictionaries every year (“Updates to the OED”). Some of this has to do with objects we no longer use (like floppy disks), and some words simply become unfashionable (like groovy). Old English bears only a passing resemblance to its youngest descendant, and even early modern English seems foreign enough to induce genuine anxiety in teenagers toting Shakespeare home in their backpacks each night. [BM12]
And the changes are not limited to our vocabulary—our grammar changes, too (albeit more slowly). “You” for instance, was initially plural (along with “ye”, while “thee” and “thou” were the corresponding singular pronouns). Eventually “you” became singular as well, and supplanted the other pronouns (Yagoda). It is hard to understand how anyone who studies language enough to harbor strong opinions about grammar could find merit in the argument that English shouldn’t change.
Second, our language is a reflection of our culture, and this is where the real debate lives. The generic “he” emerged as a way of subjugating women, deemed “less worthy” so many years ago. It was used to write women out of the law and out of participation in public life. Today’s debate is a new version of the same song [BM13] . When critics of the singular “they” insist on limiting us to “he” or “she,” it is an attempt to write everyone who falls outside of the gender binary not just out of participation, but out of existence.
But take heart. In the end, our language is not swayed by calls, no matter how fervent, to freeze in time. Our language changes as we do, and we have changed. The position of the major stylebooks is not a harbinger of what is to come. It is a record of a change that is already here.
[1] Dr. Dennis Baron in “Pronoun Showdown” argues the first use of the singular “they” appeared in writing in 1370, and the first call for an alternative pronoun appeared in 1792.
[BM1] This is an example of an explanatory footnote, which MLA recommends using sparingly.
[BM2] Introductions are serve two purposes: 1) to introduce any relevant background and 2) to establish the argument. This section provides important explanation and context.
[BM3] When using a source for the first time, best practice is to fully introduce the source to establish it as credible.
[BM4] Sources that reference outside research can be cited with the addition of “qtd. in” in the parenthetical citation.
[BM5] An important part of analysis is often looking closely at the impact of language choices. This analysis takes a closer look at the significance of the word “may” in the preceding evidence.
[BM6] When you’ve used two sources by the same author, include the title along with the author’s last name.
[BM7] Analysis should do more than summarize the information in the quote. In this example, the analysis connects the way pronouns are treated in law to the central argument about the social implications of grammatical choices.
[BM8] One method for effective transitions to is make a clear connection between the last issue addressed and the issue to come. In this case, the previous paragraph ended with a discussion of alternative pronouns, and so the paragraph that follows begins by explaining how the lack of alternative pronouns led to the generic masculine.
[BM9] The end of this paragraph serves as a transition to the next. The writer introduces the issue in preparation for the following paragraph, which explains how long the issue has been polarizing.
[BM10] Rather than looking at evidence in isolation, try to synthesize it in a way that highlights the relationship between multiple sources.
[BM11] When a source has no author, cite the title (or an abbreviated version of the title).
[BM12] While using evidence from experts is important, it’s also valid—and important—to use your own knowledge or reasoning to make a point. In this case, the writer doesn’t need an expert to tell them that the English language has evolved. She can tell just by looking at old, middle, early modern, and modern English.
[BM13] When writing argumentative rather than expository writing, the evidence you introduce should be more than informational. In this case, the writer introduced the way the generic masculine was used to exclude women in law for the purpose of drawing a parallel later in the argument to reasons behind today’s debate.
Andrews, Travis M. “The Singular, Gender-Neutral ‘They’ Add to Associated Press Stylebook.” The Washington Post. 28 March 2017. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2017/03/28/the-singular-gender-neutral-they-added-to-the-associated-press-stylebook/.
Baron, Dennis. “On the birthday of the (legal) generic masculine, let’s declare it legally dead.” The Web of Language , 24 Feb. 2016, https://blogs.illinois.edu/view/25/331699.
—. “Pronoun Showdown: Gender Neutrality and Neutral Pronouns in Language.” 11 April 2016. University of Illinois/Facebook. http://faculty.las.illinois.edu/debaron/essays/Pronoun_showdown_2016.pdf
“Chicago Style for the Singular They.” CMOS Shop Talk : From the Chicago Manual of Style . 3
April 2017, https://cmosshoptalk.com/2017/04/03/chicago-style-for-the-singular-they/. Accessed 25 April 2022.
Meyers, Miriam Watkins. “Current Generic Pronoun Usage: An Empirical Study.” American Speech , vol. 65, no. 3, [Duke University Press, American Dialect Society], 1990, pp. 228–37, https://doi.org/10.2307/455911.
“Updates to the OED.” The Oxford English Dictionary . https://public.oed.com/updates/. Accessed 23 April 2022.
“Word of the Year: They.” Merriam-Webster’s Words of the Year. 2019. https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/word-of-the-year-2019-they/they.
Yagoda, Ben. “’You’, ‘Thou’ or ‘Ye’: An Outline of the Modern Usage of the All-Purpose Second Person in English.” Principa Toscuola . 9 July 2019, https://principatoscuola.it/you-thou-or-ye-an-outline-of-the-modern-usage-of-the-all-purpose-second-person-in-english/. When You Catch an Adjective, Kill It: The Parts of Speech, For Better an/or Worse, Broadway Books, 2007.

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
Using MLA Format

Document Sources
Works cited quick guide.
Learn how to use the MLA format template.
Digital Citation Tool
Build citations with our interactive template.
In-Text Citations
Get help with in-text citations.
Endnotes and Footnotes
Read our guide about using notes in MLA style.

Set Up Your Paper
Setting up a research paper.
Get our guidelines for setting up academic research papers.
Formatting Captions
Learn how to format captions.
Sample Papers
Read sample papers written in MLA style.
Annotated Bibliographies
Learn how to set up an annotated bibliography.

Get Writing and Teaching Tips
Ask the mla.
Browse answers and ask MLA editors questions.
Writing Tips
Improve your writing with these suggestions.
Teaching Resources and Advice
Get teaching advice, lesson plans, and activities.
Test your knowledge with these fun quizzes.
Recent questions from Ask the MLA
How do i cite a work that has incorrect citation information on its cover sheet.
Some works, especially works contained in databases, may list citation information for the work on a cover sheet or in a footer. If that citation… Read More
How do I cite Twitter now that its name has changed to X?
In 2023 the social media platform Twitter changed its name to X . What does this change mean for citations? When you cite a post published… Read More
How do I cite several e-mails sent on the same day to the same correspondent?
If you are citing several e-mails sent on the same day to the same correspondent, use the subject line of the e-mail to differentiate between… Read More
What should I do if an author’s last name is not provided in a source?
If an author’s last name is not provided in the source you are consulting, you may opt to follow the guidance provided in section 5.122… Read More
How do I cite one person’s testimony in a congressional hearing?
Your source for congressional testimony may be a transcript, audio recording, or video recording of all or part of a hearing. Style each source using… Read More
How do I cite a video game?
To cite a video game, follow the template of core elements, as you would for any other source. Below we provide in-depth explanations for each… Read More
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
However, this guide will highlight a few concerns when citing digital sources in MLA style.
Best Practices for Managing Online Sources
Because online information can change or disappear, it is always a good idea to keep personal copies of important electronic information whenever possible. Downloading or even printing key documents ensures you have a stable backup. You can also use the Bookmark function in your web browser in order to build an easy-to-access reference for all of your project's sources (though this will not help you if the information is changed or deleted).
It is also wise to keep a record of when you first consult with each online source. MLA uses the phrase, “Accessed” to denote which date you accessed the web page when available or necessary. It is not required to do so, but it is encouraged (especially when there is no copyright date listed on a website).
Important Note on the Use of URLs in MLA
Include a URL or web address to help readers locate your sources. Because web addresses are not static (i.e., they change often) and because documents sometimes appear in multiple places on the web (e.g., on multiple databases), MLA encourages the use of citing containers such as Youtube, JSTOR, Spotify, or Netflix in order to easily access and verify sources. However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs.
Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL.
Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a “permalink,” which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a “share” or “cite this” button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use that instead of a URL.
Abbreviations Commonly Used with Electronic Sources
If page numbers are not available, use par. or pars. to denote paragraph numbers. Use these in place of the p. or pp. abbreviation. Par. would be used for a single paragraph, while pars. would be used for a span of two or more paragraphs.
Basic Style for Citations of Electronic Sources (Including Online Databases)
Here are some common features you should try to find before citing electronic sources in MLA style. Not every web page will provide all of the following information. However, collect as much of the following information as possible:
- Author and/or editor names (if available); last names first.
- "Article name in quotation marks."
- Title of the website, project, or book in italics.
- Any version numbers available, including editions (ed.), revisions, posting dates, volumes (vol.), or issue numbers (no.).
- Publisher information, including the publisher name and publishing date.
- Take note of any page numbers (p. or pp.) or paragraph numbers (par. or pars.).
- DOI (if available, precede it with "https://doi.org/"), otherwise a URL (without the https://) or permalink.
- Date you accessed the material (Date Accessed). While not required, saving this information it is highly recommended, especially when dealing with pages that change frequently or do not have a visible copyright date.
Use the following format:
Author. "Title." Title of container (self contained if book) , Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs and/or URL, DOI or permalink). 2 nd container’s title , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Citing an Entire Web Site
When citing an entire website, follow the same format as listed above, but include a compiler name if no single author is available.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site. Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), DOI (preferred), otherwise include a URL or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
Editor, author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site . Version number, Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), URL, DOI or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
The Purdue OWL Family of Sites . The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008.
Felluga, Dino. Guide to Literary and Critical Theory . Purdue U, 28 Nov. 2003, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/theory/. Accessed 10 May 2006.
Course or Department Websites
Give the instructor name. Then list the title of the course (or the school catalog designation for the course) in italics. Give appropriate department and school names as well, following the course title.
Felluga, Dino. Survey of the Literature of England . Purdue U, Aug. 2006, web.ics.purdue.edu/~felluga/241/241/Home.html. Accessed 31 May 2007.
English Department . Purdue U, 20 Apr. 2009, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/. Accessed 31 May 2015.
A Page on a Web Site
For an individual page on a Web site, list the author or alias if known, followed by an indication of the specific page or article being referenced. Usually, the title of the page or article appears in a header at the top of the page. Follow this with the information covered above for entire Web sites. If the publisher is the same as the website name, only list it once.
Lundman, Susan. “How to Make Vegetarian Chili.” eHow , www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html. Accessed 6 July 2015.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview. ” WebMD , 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
Citations for e-books closely resemble those for physical books. Simply indicate that the book in question is an e-book by putting the term "e-book" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
Silva, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing. E-book, American Psychological Association, 2007.
If the e-book is formatted for a specific reader device or service, you can indicate this by treating this information the same way you would treat a physical book's edition number. Often, this will mean replacing "e-book" with "[App/Service] ed."
Machiavelli, Niccolo. The Prince , translated by W. K. Marriott, Kindle ed., Library of Alexandria, 2018.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application. These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
An Image (Including a Painting, Sculpture, or Photograph)
Provide the artist's name, the work of art italicized, the date of creation, the institution and city where the work is housed. Follow this initial entry with the name of the Website in italics, and the date of access.
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800. Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Museo Nacional del Prado , www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/the-family-of-carlos-iv/f47898fc-aa1c-48f6-a779-71759e417e74. Accessed 22 May 2006.
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine . 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive , www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
If the work cited is available on the web only, then provide the name of the artist, the title of the work, and then follow the citation format for a website. If the work is posted via a username, use that username for the author.
Adams, Clifton R. “People Relax Beside a Swimming Pool at a Country Estate Near Phoenix, Arizona, 1928.” Found, National Geographic Creative, 2 June 2016, natgeofound.tumblr.com/.
An Article in a Web Magazine
Provide the author name, article name in quotation marks, title of the web magazine in italics, publisher name, publication date, URL, and the date of access.
Bernstein, Mark. “ 10 Tips on Writing the Living Web. ” A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
An Article in an Online Scholarly Journal
For all online scholarly journals, provide the author(s) name(s), the name of the article in quotation marks, the title of the publication in italics, all volume and issue numbers, and the year of publication. Include a DOI if available, otherwise provide a URL or permalink to help readers locate the source.
Article in an Online-only Scholarly Journal
MLA requires a page range for articles that appear in Scholarly Journals. If the journal you are citing appears exclusively in an online format (i.e. there is no corresponding print publication) that does not make use of page numbers, indicate the URL or other location information.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Article in an Online Scholarly Journal That Also Appears in Print
Cite articles in online scholarly journals that also appear in print as you would a scholarly journal in print, including the page range of the article . Provide the URL and the date of access.
Wheelis, Mark. “ Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention. ” Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
An Article from an Online Database (or Other Electronic Subscription Service)
Cite online databases (e.g. LexisNexis, ProQuest, JSTOR, ScienceDirect) and other subscription services as containers. Thus, provide the title of the database italicized before the DOI or URL. If a DOI is not provided, use the URL instead. Provide the date of access if you wish.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. “ Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates. ” Environmental Toxicology, vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library , https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20155. Accessed 26 May 2009.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal, vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest , https://doi.org/10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
E-mail (including E-mail Interviews)
Give the author of the message, followed by the subject line in quotation marks. State to whom the message was sent with the phrase, “Received by” and the recipient’s name. Include the date the message was sent. Use standard capitalization.
Kunka, Andrew. “ Re: Modernist Literature. ” Received by John Watts, 15 Nov. 2000.
Neyhart, David. “ Re: Online Tutoring. ” Received by Joe Barbato, 1 Dec. 2016.
A Listserv, Discussion Group, or Blog Posting
Cite web postings as you would a standard web entry. Provide the author of the work, the title of the posting in quotation marks, the web site name in italics, the publisher, and the posting date. Follow with the date of access. Include screen names as author names when author name is not known. If both names are known, place the author’s name in brackets.
Author or compiler name (if available). “Posting Title.” Name of Site , Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), URL. Date of access.
Salmar1515 [Sal Hernandez]. “Re: Best Strategy: Fenced Pastures vs. Max Number of Rooms?” BoardGameGeek , 29 Sept. 2008, boardgamegeek.com/thread/343929/best-strategy-fenced-pastures-vs-max-number-rooms. Accessed 5 Apr. 2009.
Begin with the user's Twitter handle in place of the author’s name. Next, place the tweet in its entirety in quotations, inserting a period after the tweet within the quotations. Include the date and time of posting, using the reader's time zone; separate the date and time with a comma and end with a period. Include the date accessed if you deem necessary.
@tombrokaw. “ SC demonstrated why all the debates are the engines of this campaign. ” Twitter, 22 Jan. 2012, 3:06 a.m., twitter.com/tombrokaw/status/160996868971704320.
@PurdueWLab. “ Spring break is around the corner, and all our locations will be open next week. ” Twitter , 5 Mar. 2012, 12:58 p.m., twitter.com/PurdueWLab/status/176728308736737282.
A YouTube Video
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author’s name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once. If the author is different from the uploader, cite the author’s name before the title.
McGonigal, Jane. “Gaming and Productivity.” YouTube , uploaded by Big Think, 3 July 2012, www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkdzy9bWW3E.
“8 Hot Dog Gadgets put to the Test.” YouTube, uploaded by Crazy Russian Hacker, 6 June 2016, www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBlpjSEtELs.
A Comment on a Website or Article
List the username as the author. Use the phrase, Comment on, before the title. Use quotation marks around the article title. Name the publisher, date, time (listed on near the comment), and the URL.
Not Omniscient Enough. Comment on “ Flight Attendant Tells Passenger to ‘Shut Up’ After Argument Over Pasta. ” ABC News, 9 Jun 2016, 4:00 p.m., abcnews.go.com/US/flight-attendant-tells-passenger-shut-argument-pasta/story?id=39704050.

VIDEO
COMMENTS
MLA Formatting and Style Guide; MLA General Format MLA Formatting and Style Guide; MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics; MLA Formatting Lists MLA Formatting Quotations; MLA Endnotes and Footnotes; MLA Works Cited Page: Basic Format; MLA Works Cited Page: Books; MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals; MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications)
MLA format is a widely used citation style for academic papers. Learn how to format your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our free template and examples. Watch our 3-minute video to see how easy it is to apply MLA rules to your document.
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
MLA Sample Paper #1. If you've been wondering how to produce a research paper that is strong in both formatting and writing, you've come to the right place. Check out our first sample paper below. It is a helpful and clearly labeled visual aid to refer to. Note that while these sample papers do not include MLA abstracts, you should check ...
Annotated Argumentative Bibliography (8th edition). Causal Argumentative Essay (9th edition). Classification and Division Essay From a Beginning Writing Class (8th edition). Compare and Contrast Essay From a Beginning Writing Class (9th edition). Compare and Contrast Essay From a Literature Course (8th edition). Definition Argumentative Essay (9th edition) ...
The nine core elements of MLA citations. 1. Author. Begin each source entry with the name of the author (s) or creator (s). The name of the first author is always inverted (Last name, First name). When a source has two authors, the second author's name is shown in the normal order (First name Last name).
Here's how you can set your first page up for MLA 9th edition. On the first line, write your full name (flush left) On a new line, write your professor or instructor's full name. On a new line, write the course code and course name. On a new line, write the full date spelt out (e.g., 15 June 2023)
MLA Format Essay Tips. Your instructor may issue particular instructions if you are to use MLA citation in an essay—if so, follow them. Otherwise, the following MLA essay formatting tips will help you set out your research paper in MLA style. ... MLA Format Essay Example. To see how all these formatting elements come together to make an MLA ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Ask the MLA; Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style; Using MLA Format; Works Cited: A Quick Guide; Teaching Resources. A Century of Queer Korean Fiction: An Interview with Samuel Perry Toward Educational Justice: An Interview with the Editors of Teaching Literature and Writing in Prisons. Henrique ...
MLA formatting rules. 1 The sources page is referred to as the works cited page. It appears at the end of the paper, after any endnotes. 2 The entire paper is double-spaced, including block quotations and the references on the works cited page. 3 Use block quotes for quotations that are four lines or longer.
Here is an example of an MLA header for an MLA format essay, paper, or assignment: Neal E. Bibdarsh. Professor Haujeemoto. English 201. 2 Nov 2017. ... Lists created using MLA essay format look different than a grocery list or any other type of vertical listing of items. Items in a list are included in your prose, rather than the traditional ...
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
Formatting an essay according to a certain style affects the way your assignment looks physically and to how you format your citations. How to Format your paper in MLA . The guidelines below are the general MLA formatting guidelines; however, make sure to prioritize following any specific formatting instructions that your instructor has ...
Below is a sample essay in MLA format. Sample MLA Essay Barbara McLain Dr. Joe Moxley Linguistics 10 May 2022 The Pronoun Controversy The way we use pronouns—in particular the use of the traditionally plural pronouns they/them in reference to individuals—has recently been the subject of intense debate and even outrage. This furor over pronoun.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
The driver who killed Morgan Pena in Pennsylvania received two tickets and a $50 fine--and retained his driving privileges (Pena). In Georgia, a young woman distracted by her phone ran down and killed a two-year-old; her sentence was ninety days in boot camp and five hun-dred hours of community service (Ippolito J1).
MLA format for academic papers and essays Apply MLA format to your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our 3-minute video, template, and examples. 1568. MLA titles: Formatting and capitalization rules MLA titles are capitalized, and appear either in italics (e.g. a book title) or in quotation marks (e.g. an article title). ...
Get started with MLA style. Learn how to document sources, set up your paper, and improve your teaching and writing. Document Sources Works Cited Quick Guide Learn how to use the MLA format template. Digital Citation Tool Build citations with our interactive template. In-Text Citations Get help with in-text citations. Endnotes and Footnotes Read our …
General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Works Cited Page. Resources on writing an MLA style works cited page, including citation formats ... Other MLA Resources. Formatting Lists Formatting Quotations Endnotes and Footnotes Abbreviations MLA Sample Paper Tables, Figures, and Examples MLA PowerPoint Presentation MLA ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.