contact @ anglaisbac.com

Writing / Expression écrite au bac d’anglais
Scared of essays ? No worries. You are in the right spot to find all the info you need.
To start with, a brief video to remind you of the most common mistakes in the baccalauréat.
To check if you won’t make these mistakes, here is a little online exercise .
The most common exercise given is the essays. Here is a quick video about the method. You can also have a look at the page dedicated to « Argumentative essays «
and a PDF document to remind you of some basic rules :
[bsk-pdf-manager-pdf id= »19″]
Need help with vocabulary :
[bsk-pdf-manager-pdf id= »21″]
[bsk-pdf-manager-pdf id= »22″]
[bsk-pdf-manager-pdf id= »23″]

Assessment grid for writing
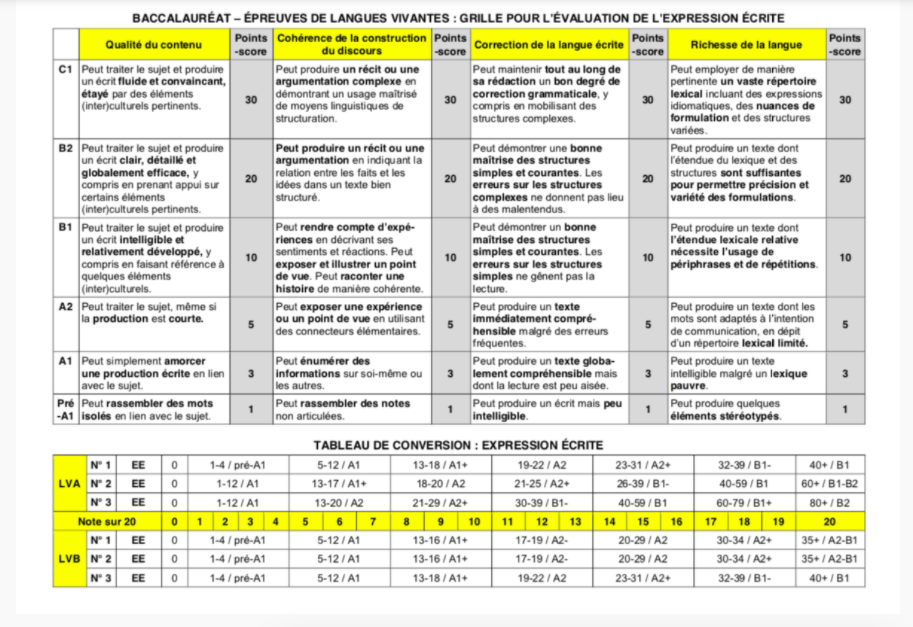
Now, just pick the type of work you’d like to study :
Argumentative Essays
Narrative Essays
Letters / Emails
Diary Entries
Or check the Games section for some fun activities related to writing.
Some links about writing here
Writing an article
Topic outline.
The purpose of an article is often to inform and persuade the reader.
Articles give the reader information about a certain topic, bringing together and discussing different perspectives to provide a balanced argument which lets the reader make up their own mind about the topic.
Articles can also be used to persuade the reader that a certain viewpoint is correct. For example, articles in newspapers or magazines might express a particular viewpoint or perspective; this may be positive or negative depending on the topic.
The ways you use language and organise your ideas when writing an article will depend on the audience and the purpose you are writing for.
- think about the audience that the article is for – w hen writing an article, you do not usually know your readers personally and so you will need to think about their likely interests and experience before you write
- how you expect, or want, your audience to react – re member that the tone of most articles should be semi-formal, so before deciding on your tone imagine your article being read out loud and how that might sound to your reader. For example, an article reviewing a film may be humorous, even sarcastic, but that would not work well for more serious readers or topics
- the purpose for the article – is th e purpose, or reason, for writing your article to persuade your readers to agree with you or to invite your readers to think about different points of view and decide for themselves? For example, do you need to sound reliable and well informed, or choose words that strongly convey a particular emotion?
- how to keep your readers interest – ima gine how boring it would be for your reader if you used the same kind of sentences and simple repetitive vocabulary all the way through your article. Try to include a range of grammatical structures and relevant vocabulary to make sure that your reader wants to keep reading.
- Plan a route through your article before you start writing it – th e structure of an article is usually in three parts. For example:
- An introduction – engage your reader’s interest and introduce your argument or the main points of the topic to be discussed.
- A middle – develop relevant and interesting points about the topic to interest and/or convince your readers to think about a particular perspective.
- An end – d raw your points together and leave your reader with a clear impression of the argument you want them to believe or the viewpoints you would like them to consider.
- Organise your ideas into paragraphs as appropriate – this will help you to develop and support your points convincingly, to build your argument and/or offer a full explanation of a particular point of view.
- Show your reader at a glance what your article is about – articles usually have a suitable headline to attract their readers’ attention and you can choose to use subheadings (a bit like mini headlines) to help break your article up and move your reader on. Do not overdo these, but well-chosen subheadings can help to catch and keep your reader’s attention, as well as sum up the main points you are making.
- Show the connections between ideas in sentences and paragraphs – for example, where a new point or idea follows on from what you have already said you might use linking words or phrases such as, 'in addition’, ‘likewise’ or ‘similarly’.
- Example of an article

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Link Words online Exercise. Writing a dialogue in the BAC. Writing a letter or an email in the BAC. Writing an argumentative essay in the BAC. Writing in the bac. Common Errors in writing. Erreurs à éviter à l’écrit au bac d’anglais. Erreurs récurrentes en expression personnelle. Exam Vocabulary.
Organisation. Plan a route through your article before you start writing it – the structure of an article is usually in three parts. For example: An introduction – engage your reader’s interest and introduce your argument or the main points of the topic to be discussed. A middle – develop relevant and interesting points about the topic ...