- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- Future Fables
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Just the Right Book
- Lit Century
- The Literary Life with Mitchell Kaplan
- New Books Network
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway


The 10 Best Essay Collections of the Decade
Ever tried. ever failed. no matter..
Friends, it’s true: the end of the decade approaches. It’s been a difficult, anxiety-provoking, morally compromised decade, but at least it’s been populated by some damn fine literature. We’ll take our silver linings where we can.
So, as is our hallowed duty as a literary and culture website—though with full awareness of the potentially fruitless and endlessly contestable nature of the task—in the coming weeks, we’ll be taking a look at the best and most important (these being not always the same) books of the decade that was. We will do this, of course, by means of a variety of lists. We began with the best debut novels , the best short story collections , the best poetry collections , and the best memoirs of the decade , and we have now reached the fifth list in our series: the best essay collections published in English between 2010 and 2019.
The following books were chosen after much debate (and several rounds of voting) by the Literary Hub staff. Tears were spilled, feelings were hurt, books were re-read. And as you’ll shortly see, we had a hard time choosing just ten—so we’ve also included a list of dissenting opinions, and an even longer list of also-rans. As ever, free to add any of your own favorites that we’ve missed in the comments below.
The Top Ten
Oliver sacks, the mind’s eye (2010).
Toward the end of his life, maybe suspecting or sensing that it was coming to a close, Dr. Oliver Sacks tended to focus his efforts on sweeping intellectual projects like On the Move (a memoir), The River of Consciousness (a hybrid intellectual history), and Hallucinations (a book-length meditation on, what else, hallucinations). But in 2010, he gave us one more classic in the style that first made him famous, a form he revolutionized and brought into the contemporary literary canon: the medical case study as essay. In The Mind’s Eye , Sacks focuses on vision, expanding the notion to embrace not only how we see the world, but also how we map that world onto our brains when our eyes are closed and we’re communing with the deeper recesses of consciousness. Relaying histories of patients and public figures, as well as his own history of ocular cancer (the condition that would eventually spread and contribute to his death), Sacks uses vision as a lens through which to see all of what makes us human, what binds us together, and what keeps us painfully apart. The essays that make up this collection are quintessential Sacks: sensitive, searching, with an expertise that conveys scientific information and experimentation in terms we can not only comprehend, but which also expand how we see life carrying on around us. The case studies of “Stereo Sue,” of the concert pianist Lillian Kalir, and of Howard, the mystery novelist who can no longer read, are highlights of the collection, but each essay is a kind of gem, mined and polished by one of the great storytellers of our era. –Dwyer Murphy, CrimeReads Managing Editor
John Jeremiah Sullivan, Pulphead (2011)
The American essay was having a moment at the beginning of the decade, and Pulphead was smack in the middle. Without any hard data, I can tell you that this collection of John Jeremiah Sullivan’s magazine features—published primarily in GQ , but also in The Paris Review , and Harper’s —was the only full book of essays most of my literary friends had read since Slouching Towards Bethlehem , and probably one of the only full books of essays they had even heard of.
Well, we all picked a good one. Every essay in Pulphead is brilliant and entertaining, and illuminates some small corner of the American experience—even if it’s just one house, with Sullivan and an aging writer inside (“Mr. Lytle” is in fact a standout in a collection with no filler; fittingly, it won a National Magazine Award and a Pushcart Prize). But what are they about? Oh, Axl Rose, Christian Rock festivals, living around the filming of One Tree Hill , the Tea Party movement, Michael Jackson, Bunny Wailer, the influence of animals, and by god, the Miz (of Real World/Road Rules Challenge fame).
But as Dan Kois has pointed out , what connects these essays, apart from their general tone and excellence, is “their author’s essential curiosity about the world, his eye for the perfect detail, and his great good humor in revealing both his subjects’ and his own foibles.” They are also extremely well written, drawing much from fictional techniques and sentence craft, their literary pleasures so acute and remarkable that James Wood began his review of the collection in The New Yorker with a quiz: “Are the following sentences the beginnings of essays or of short stories?” (It was not a hard quiz, considering the context.)
It’s hard not to feel, reading this collection, like someone reached into your brain, took out the half-baked stuff you talk about with your friends, researched it, lived it, and represented it to you smarter and better and more thoroughly than you ever could. So read it in awe if you must, but read it. –Emily Temple, Senior Editor
Aleksandar Hemon, The Book of My Lives (2013)
Such is the sentence-level virtuosity of Aleksandar Hemon—the Bosnian-American writer, essayist, and critic—that throughout his career he has frequently been compared to the granddaddy of borrowed language prose stylists: Vladimir Nabokov. While it is, of course, objectively remarkable that anyone could write so beautifully in a language they learned in their twenties, what I admire most about Hemon’s work is the way in which he infuses every essay and story and novel with both a deep humanity and a controlled (but never subdued) fury. He can also be damn funny. Hemon grew up in Sarajevo and left in 1992 to study in Chicago, where he almost immediately found himself stranded, forced to watch from afar as his beloved home city was subjected to a relentless four-year bombardment, the longest siege of a capital in the history of modern warfare. This extraordinary memoir-in-essays is many things: it’s a love letter to both the family that raised him and the family he built in exile; it’s a rich, joyous, and complex portrait of a place the 90s made synonymous with war and devastation; and it’s an elegy for the wrenching loss of precious things. There’s an essay about coming of age in Sarajevo and another about why he can’t bring himself to leave Chicago. There are stories about relationships forged and maintained on the soccer pitch or over the chessboard, and stories about neighbors and mentors turned monstrous by ethnic prejudice. As a chorus they sing with insight, wry humor, and unimaginable sorrow. I am not exaggerating when I say that the collection’s devastating final piece, “The Aquarium”—which details his infant daughter’s brain tumor and the agonizing months which led up to her death—remains the most painful essay I have ever read. –Dan Sheehan, Book Marks Editor
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013)
Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass , Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer’s gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there’s one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp. When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex-wife, he found a scene of destruction: The farm’s new owners had razed the land where he had tried to build a life. “I sat among the stumps and the swirling red dust and I cried,” he wrote in his journal.
So many in my generation (and younger) feel this kind of helplessness–and considerable rage–at finding ourselves newly adult in a world where those in power seem determined to abandon or destroy everything that human bodies have always needed to survive: air, water, land. Asking any single book to speak to this helplessness feels unfair, somehow; yet, Braiding Sweetgrass does, by weaving descriptions of indigenous tradition with the environmental sciences in order to show what survival has looked like over the course of many millennia. Kimmerer’s essays describe her personal experience as a Potawotami woman, plant ecologist, and teacher alongside stories of the many ways that humans have lived in relationship to other species. Whether describing Dolp’s work–he left the stumps for a life of forest restoration on the Oregon coast–or the work of others in maple sugar harvesting, creating black ash baskets, or planting a Three Sisters garden of corn, beans, and squash, she brings hope. “In ripe ears and swelling fruit, they counsel us that all gifts are multiplied in relationship,” she writes of the Three Sisters, which all sustain one another as they grow. “This is how the world keeps going.” –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Hilton Als, White Girls (2013)
In a world where we are so often reduced to one essential self, Hilton Als’ breathtaking book of critical essays, White Girls , which meditates on the ways he and other subjects read, project and absorb parts of white femininity, is a radically liberating book. It’s one of the only works of critical thinking that doesn’t ask the reader, its author or anyone he writes about to stoop before the doorframe of complete legibility before entering. Something he also permitted the subjects and readers of his first book, the glorious book-length essay, The Women , a series of riffs and psychological portraits of Dorothy Dean, Owen Dodson, and the author’s own mother, among others. One of the shifts of that book, uncommon at the time, was how it acknowledges the way we inhabit bodies made up of variously gendered influences. To read White Girls now is to experience the utter freedom of this gift and to marvel at Als’ tremendous versatility and intelligence.
He is easily the most diversely talented American critic alive. He can write into genres like pop music and film where being part of an audience is a fantasy happening in the dark. He’s also wired enough to know how the art world builds reputations on the nod of rich white patrons, a significant collision in a time when Jean-Michel Basquiat is America’s most expensive modern artist. Als’ swerving and always moving grip on performance means he’s especially good on describing the effect of art which is volatile and unstable and built on the mingling of made-up concepts and the hard fact of their effect on behavior, such as race. Writing on Flannery O’Connor for instance he alone puts a finger on her “uneasy and unavoidable union between black and white, the sacred and the profane, the shit and the stars.” From Eminem to Richard Pryor, André Leon Talley to Michael Jackson, Als enters the life and work of numerous artists here who turn the fascinations of race and with whiteness into fury and song and describes the complexity of their beauty like his life depended upon it. There are also brief memoirs here that will stop your heart. This is an essential work to understanding American culture. –John Freeman, Executive Editor
Eula Biss, On Immunity (2014)
We move through the world as if we can protect ourselves from its myriad dangers, exercising what little agency we have in an effort to keep at bay those fears that gather at the edges of any given life: of loss, illness, disaster, death. It is these fears—amplified by the birth of her first child—that Eula Biss confronts in her essential 2014 essay collection, On Immunity . As any great essayist does, Biss moves outward in concentric circles from her own very private view of the world to reveal wider truths, discovering as she does a culture consumed by anxiety at the pervasive toxicity of contemporary life. As Biss interrogates this culture—of privilege, of whiteness—she interrogates herself, questioning the flimsy ways in which we arm ourselves with science or superstition against the impurities of daily existence.
Five years on from its publication, it is dismaying that On Immunity feels as urgent (and necessary) a defense of basic science as ever. Vaccination, we learn, is derived from vacca —for cow—after the 17th-century discovery that a small application of cowpox was often enough to inoculate against the scourge of smallpox, an etymological digression that belies modern conspiratorial fears of Big Pharma and its vaccination agenda. But Biss never scolds or belittles the fears of others, and in her generosity and openness pulls off a neat (and important) trick: insofar as we are of the very world we fear, she seems to be suggesting, we ourselves are impure, have always been so, permeable, vulnerable, yet so much stronger than we think. –Jonny Diamond, Editor-in-Chief
Rebecca Solnit, The Mother of All Questions (2016)
When Rebecca Solnit’s essay, “Men Explain Things to Me,” was published in 2008, it quickly became a cultural phenomenon unlike almost any other in recent memory, assigning language to a behavior that almost every woman has witnessed—mansplaining—and, in the course of identifying that behavior, spurring a movement, online and offline, to share the ways in which patriarchal arrogance has intersected all our lives. (It would also come to be the titular essay in her collection published in 2014.) The Mother of All Questions follows up on that work and takes it further in order to examine the nature of self-expression—who is afforded it and denied it, what institutions have been put in place to limit it, and what happens when it is employed by women. Solnit has a singular gift for describing and decoding the misogynistic dynamics that govern the world so universally that they can seem invisible and the gendered violence that is so common as to seem unremarkable; this naming is powerful, and it opens space for sharing the stories that shape our lives.
The Mother of All Questions, comprised of essays written between 2014 and 2016, in many ways armed us with some of the tools necessary to survive the gaslighting of the Trump years, in which many of us—and especially women—have continued to hear from those in power that the things we see and hear do not exist and never existed. Solnit also acknowledges that labels like “woman,” and other gendered labels, are identities that are fluid in reality; in reviewing the book for The New Yorker , Moira Donegan suggested that, “One useful working definition of a woman might be ‘someone who experiences misogyny.'” Whichever words we use, Solnit writes in the introduction to the book that “when words break through unspeakability, what was tolerated by a society sometimes becomes intolerable.” This storytelling work has always been vital; it continues to be vital, and in this book, it is brilliantly done. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Valeria Luiselli, Tell Me How It Ends (2017)
The newly minted MacArthur fellow Valeria Luiselli’s four-part (but really six-part) essay Tell Me How It Ends: An Essay in Forty Questions was inspired by her time spent volunteering at the federal immigration court in New York City, working as an interpreter for undocumented, unaccompanied migrant children who crossed the U.S.-Mexico border. Written concurrently with her novel Lost Children Archive (a fictional exploration of the same topic), Luiselli’s essay offers a fascinating conceit, the fashioning of an argument from the questions on the government intake form given to these children to process their arrivals. (Aside from the fact that this essay is a heartbreaking masterpiece, this is such a good conceit—transforming a cold, reproducible administrative document into highly personal literature.) Luiselli interweaves a grounded discussion of the questionnaire with a narrative of the road trip Luiselli takes with her husband and family, across America, while they (both Mexican citizens) wait for their own Green Card applications to be processed. It is on this trip when Luiselli reflects on the thousands of migrant children mysteriously traveling across the border by themselves. But the real point of the essay is to actually delve into the real stories of some of these children, which are agonizing, as well as to gravely, clearly expose what literally happens, procedural, when they do arrive—from forms to courts, as they’re swallowed by a bureaucratic vortex. Amid all of this, Luiselli also takes on more, exploring the larger contextual relationship between the United States of America and Mexico (as well as other countries in Central America, more broadly) as it has evolved to our current, adverse moment. Tell Me How It Ends is so small, but it is so passionate and vigorous: it desperately accomplishes in its less-than-100-pages-of-prose what centuries and miles and endless records of federal bureaucracy have never been able, and have never cared, to do: reverse the dehumanization of Latin American immigrants that occurs once they set foot in this country. –Olivia Rutigliano, CrimeReads Editorial Fellow
Zadie Smith, Feel Free (2018)
In the essay “Meet Justin Bieber!” in Feel Free , Zadie Smith writes that her interest in Justin Bieber is not an interest in the interiority of the singer himself, but in “the idea of the love object”. This essay—in which Smith imagines a meeting between Bieber and the late philosopher Martin Buber (“Bieber and Buber are alternative spellings of the same German surname,” she explains in one of many winning footnotes. “Who am I to ignore these hints from the universe?”). Smith allows that this premise is a bit premise -y: “I know, I know.” Still, the resulting essay is a very funny, very smart, and un-tricky exploration of individuality and true “meeting,” with a dash of late capitalism thrown in for good measure. The melding of high and low culture is the bread and butter of pretty much every prestige publication on the internet these days (and certainly of the Twitter feeds of all “public intellectuals”), but the essays in Smith’s collection don’t feel familiar—perhaps because hers is, as we’ve long known, an uncommon skill. Though I believe Smith could probably write compellingly about anything, she chooses her subjects wisely. She writes with as much electricity about Brexit as the aforementioned Beliebers—and each essay is utterly engrossing. “She contains multitudes, but her point is we all do,” writes Hermione Hoby in her review of the collection in The New Republic . “At the same time, we are, in our endless difference, nobody but ourselves.” –Jessie Gaynor, Social Media Editor
Tressie McMillan Cottom, Thick: And Other Essays (2019)
Tressie McMillan Cottom is an academic who has transcended the ivory tower to become the sort of public intellectual who can easily appear on radio or television talk shows to discuss race, gender, and capitalism. Her collection of essays reflects this duality, blending scholarly work with memoir to create a collection on the black female experience in postmodern America that’s “intersectional analysis with a side of pop culture.” The essays range from an analysis of sexual violence, to populist politics, to social media, but in centering her own experiences throughout, the collection becomes something unlike other pieces of criticism of contemporary culture. In explaining the title, she reflects on what an editor had said about her work: “I was too readable to be academic, too deep to be popular, too country black to be literary, and too naïve to show the rigor of my thinking in the complexity of my prose. I had wanted to create something meaningful that sounded not only like me, but like all of me. It was too thick.” One of the most powerful essays in the book is “Dying to be Competent” which begins with her unpacking the idiocy of LinkedIn (and the myth of meritocracy) and ends with a description of her miscarriage, the mishandling of black woman’s pain, and a condemnation of healthcare bureaucracy. A finalist for the 2019 National Book Award for Nonfiction, Thick confirms McMillan Cottom as one of our most fearless public intellectuals and one of the most vital. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Dissenting Opinions
The following books were just barely nudged out of the top ten, but we (or at least one of us) couldn’t let them pass without comment.
Elif Batuman, The Possessed (2010)
In The Possessed Elif Batuman indulges her love of Russian literature and the result is hilarious and remarkable. Each essay of the collection chronicles some adventure or other that she had while in graduate school for Comparative Literature and each is more unpredictable than the next. There’s the time a “well-known 20th-centuryist” gave a graduate student the finger; and the time when Batuman ended up living in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, for a summer; and the time that she convinced herself Tolstoy was murdered and spent the length of the Tolstoy Conference in Yasnaya Polyana considering clues and motives. Rich in historic detail about Russian authors and literature and thoughtfully constructed, each essay is an amalgam of critical analysis, cultural criticism, and serious contemplation of big ideas like that of identity, intellectual legacy, and authorship. With wit and a serpentine-like shape to her narratives, Batuman adopts a form reminiscent of a Socratic discourse, setting up questions at the beginning of her essays and then following digressions that more or less entreat the reader to synthesize the answer for herself. The digressions are always amusing and arguably the backbone of the collection, relaying absurd anecdotes with foreign scholars or awkward, surreal encounters with Eastern European strangers. Central also to the collection are Batuman’s intellectual asides where she entertains a theory—like the “problem of the person”: the inability to ever wholly capture one’s character—that ultimately layer the book’s themes. “You are certainly my most entertaining student,” a professor said to Batuman. But she is also curious and enthusiastic and reflective and so knowledgeable that she might even convince you (she has me!) that you too love Russian literature as much as she does. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Roxane Gay, Bad Feminist (2014)
Roxane Gay’s now-classic essay collection is a book that will make you laugh, think, cry, and then wonder, how can cultural criticism be this fun? My favorite essays in the book include Gay’s musings on competitive Scrabble, her stranded-in-academia dispatches, and her joyous film and television criticism, but given the breadth of topics Roxane Gay can discuss in an entertaining manner, there’s something for everyone in this one. This book is accessible because feminism itself should be accessible – Roxane Gay is as likely to draw inspiration from YA novels, or middle-brow shows about friendship, as she is to introduce concepts from the academic world, and if there’s anyone I trust to bridge the gap between high culture, low culture, and pop culture, it’s the Goddess of Twitter. I used to host a book club dedicated to radical reads, and this was one of the first picks for the club; a week after the book club met, I spied a few of the attendees meeting in the café of the bookstore, and found out that they had bonded so much over discussing Bad Feminist that they couldn’t wait for the next meeting of the book club to keep discussing politics and intersectionality, and that, in a nutshell, is the power of Roxane. –Molly Odintz, CrimeReads Associate Editor
Rivka Galchen, Little Labors (2016)
Generally, I find stories about the trials and tribulations of child-having to be of limited appeal—useful, maybe, insofar as they offer validation that other people have also endured the bizarre realities of living with a tiny human, but otherwise liable to drift into the musings of parents thrilled at the simple fact of their own fecundity, as if they were the first ones to figure the process out (or not). But Little Labors is not simply an essay collection about motherhood, perhaps because Galchen initially “didn’t want to write about” her new baby—mostly, she writes, “because I had never been interested in babies, or mothers; in fact, those subjects had seemed perfectly not interesting to me.” Like many new mothers, though, Galchen soon discovered her baby—which she refers to sometimes as “the puma”—to be a preoccupying thought, demanding to be written about. Galchen’s interest isn’t just in her own progeny, but in babies in literature (“Literature has more dogs than babies, and also more abortions”), The Pillow Book , the eleventh-century collection of musings by Sei Shōnagon, and writers who are mothers. There are sections that made me laugh out loud, like when Galchen continually finds herself in an elevator with a neighbor who never fails to remark on the puma’s size. There are also deeper, darker musings, like the realization that the baby means “that it’s not permissible to die. There are days when this does not feel good.” It is a slim collection that I happened to read at the perfect time, and it remains one of my favorites of the decade. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Charlie Fox, This Young Monster (2017)
On social media as in his writing, British art critic Charlie Fox rejects lucidity for allusion and doesn’t quite answer the Twitter textbox’s persistent question: “What’s happening?” These days, it’s hard to tell. This Young Monster (2017), Fox’s first book,was published a few months after Donald Trump’s election, and at one point Fox takes a swipe at a man he judges “direct from a nightmare and just a repulsive fucking goon.” Fox doesn’t linger on politics, though, since most of the monsters he looks at “embody otherness and make it into art, ripping any conventional idea of beauty to shreds and replacing it with something weird and troubling of their own invention.”
If clichés are loathed because they conform to what philosopher Georges Bataille called “the common measure,” then monsters are rebellious non-sequiturs, comedic or horrific derailments from a classical ideal. Perverts in the most literal sense, monsters have gone astray from some “proper” course. The book’s nine chapters, which are about a specific monster or type of monster, are full of callbacks to familiar and lesser-known media. Fox cites visual art, film, songs, and books with the screwy buoyancy of a savant. Take one of his essays, “Spook House,” framed as a stage play with two principal characters, Klaus (“an intoxicated young skinhead vampire”) and Hermione (“a teen sorceress with green skin and jet-black hair” who looks more like The Wicked Witch than her namesake). The chorus is a troupe of trick-or-treaters. Using the filmmaker Cameron Jamie as a starting point, the rest is free association on gothic decadence and Detroit and L.A. as cities of the dead. All the while, Klaus quotes from Artforum , Dazed & Confused , and Time Out. It’s a technical feat that makes fictionalized dialogue a conveyor belt for cultural criticism.
In Fox’s imagination, David Bowie and the Hydra coexist alongside Peter Pan, Dennis Hopper, and the maenads. Fox’s book reaches for the monster’s mask, not really to peel it off but to feel and smell the rubber schnoz, to know how it’s made before making sure it’s still snugly set. With a stylistic blend of arthouse suavity and B-movie chic, This Young Monster considers how monsters in culture are made. Aren’t the scariest things made in post-production? Isn’t the creature just duplicity, like a looping choir or a dubbed scream? –Aaron Robertson, Assistant Editor
Elena Passarello, Animals Strike Curious Poses (2017)
Elena Passarello’s collection of essays Animals Strike Curious Poses picks out infamous animals and grants them the voice, narrative, and history they deserve. Not only is a collection like this relevant during the sixth extinction but it is an ambitious historical and anthropological undertaking, which Passarello has tackled with thorough research and a playful tone that rather than compromise her subject, complicates and humanizes it. Passarello’s intention is to investigate the role of animals across the span of human civilization and in doing so, to construct a timeline of humanity as told through people’s interactions with said animals. “Of all the images that make our world, animal images are particularly buried inside us,” Passarello writes in her first essay, to introduce us to the object of the book and also to the oldest of her chosen characters: Yuka, a 39,000-year-old mummified woolly mammoth discovered in the Siberian permafrost in 2010. It was an occasion so remarkable and so unfathomable given the span of human civilization that Passarello says of Yuka: “Since language is epically younger than both thought and experience, ‘woolly mammoth’ means, to a human brain, something more like time.” The essay ends with a character placing a hand on a cave drawing of a woolly mammoth, accompanied by a phrase which encapsulates the author’s vision for the book: “And he becomes the mammoth so he can envision the mammoth.” In Passarello’s hands the imagined boundaries between the animal, natural, and human world disintegrate and what emerges is a cohesive if baffling integrated history of life. With the accuracy and tenacity of a journalist and the spirit of a storyteller, Elena Passarello has assembled a modern bestiary worthy of contemplation and awe. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Esmé Weijun Wang, The Collected Schizophrenias (2019)
Esmé Weijun Wang’s collection of essays is a kaleidoscopic look at mental health and the lives affected by the schizophrenias. Each essay takes on a different aspect of the topic, but you’ll want to read them together for a holistic perspective. Esmé Weijun Wang generously begins The Collected Schizophrenias by acknowledging the stereotype, “Schizophrenia terrifies. It is the archetypal disorder of lunacy.” From there, she walks us through the technical language, breaks down the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual ( DSM-5 )’s clinical definition. And then she gets very personal, telling us about how she came to her own diagnosis and the way it’s touched her daily life (her relationships, her ideas about motherhood). Esmé Weijun Wang is uniquely situated to write about this topic. As a former lab researcher at Stanford, she turns a precise, analytical eye to her experience while simultaneously unfolding everything with great patience for her reader. Throughout, she brilliantly dissects the language around mental health. (On saying “a person living with bipolar disorder” instead of using “bipolar” as the sole subject: “…we are not our diseases. We are instead individuals with disorders and malfunctions. Our conditions lie over us like smallpox blankets; we are one thing and the illness is another.”) She pinpoints the ways she arms herself against anticipated reactions to the schizophrenias: high fashion, having attended an Ivy League institution. In a particularly piercing essay, she traces mental illness back through her family tree. She also places her story within more mainstream cultural contexts, calling on groundbreaking exposés about the dangerous of institutionalization and depictions of mental illness in television and film (like the infamous Slender Man case, in which two young girls stab their best friend because an invented Internet figure told them to). At once intimate and far-reaching, The Collected Schizophrenias is an informative and important (and let’s not forget artful) work. I’ve never read a collection quite so beautifully-written and laid-bare as this. –Katie Yee, Book Marks Assistant Editor
Ross Gay, The Book of Delights (2019)
When Ross Gay began writing what would become The Book of Delights, he envisioned it as a project of daily essays, each focused on a moment or point of delight in his day. This plan quickly disintegrated; on day four, he skipped his self-imposed assignment and decided to “in honor and love, delight in blowing it off.” (Clearly, “blowing it off” is a relative term here, as he still produced the book.) Ross Gay is a generous teacher of how to live, and this moment of reveling in self-compassion is one lesson among many in The Book of Delights , which wanders from moments of connection with strangers to a shade of “red I don’t think I actually have words for,” a text from a friend reading “I love you breadfruit,” and “the sun like a guiding hand on my back, saying everything is possible. Everything .”
Gay does not linger on any one subject for long, creating the sense that delight is a product not of extenuating circumstances, but of our attention; his attunement to the possibilities of a single day, and awareness of all the small moments that produce delight, are a model for life amid the warring factions of the attention economy. These small moments range from the physical–hugging a stranger, transplanting fig cuttings–to the spiritual and philosophical, giving the impression of sitting beside Gay in his garden as he thinks out loud in real time. It’s a privilege to listen. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Honorable Mentions
A selection of other books that we seriously considered for both lists—just to be extra about it (and because decisions are hard).
Terry Castle, The Professor and Other Writings (2010) · Joyce Carol Oates, In Rough Country (2010) · Geoff Dyer, Otherwise Known as the Human Condition (2011) · Christopher Hitchens, Arguably (2011) · Roberto Bolaño, tr. Natasha Wimmer, Between Parentheses (2011) · Dubravka Ugresic, tr. David Williams, Karaoke Culture (2011) · Tom Bissell, Magic Hours (2012) · Kevin Young, The Grey Album (2012) · William H. Gass, Life Sentences: Literary Judgments and Accounts (2012) · Mary Ruefle, Madness, Rack, and Honey (2012) · Herta Müller, tr. Geoffrey Mulligan, Cristina and Her Double (2013) · Leslie Jamison, The Empathy Exams (2014) · Meghan Daum, The Unspeakable (2014) · Daphne Merkin, The Fame Lunches (2014) · Charles D’Ambrosio, Loitering (2015) · Wendy Walters, Multiply/Divide (2015) · Colm Tóibín, On Elizabeth Bishop (2015) · Renee Gladman, Calamities (2016) · Jesmyn Ward, ed. The Fire This Time (2016) · Lindy West, Shrill (2016) · Mary Oliver, Upstream (2016) · Emily Witt, Future Sex (2016) · Olivia Laing, The Lonely City (2016) · Mark Greif, Against Everything (2016) · Durga Chew-Bose, Too Much and Not the Mood (2017) · Sarah Gerard, Sunshine State (2017) · Jim Harrison, A Really Big Lunch (2017) · J.M. Coetzee, Late Essays: 2006-2017 (2017) · Melissa Febos, Abandon Me (2017) · Louise Glück, American Originality (2017) · Joan Didion, South and West (2017) · Tom McCarthy, Typewriters, Bombs, Jellyfish (2017) · Hanif Abdurraqib, They Can’t Kill Us Until they Kill Us (2017) · Ta-Nehisi Coates, We Were Eight Years in Power (2017) · Samantha Irby, We Are Never Meeting in Real Life (2017) · Alexander Chee, How to Write an Autobiographical Novel (2018) · Alice Bolin, Dead Girls (2018) · Marilynne Robinson, What Are We Doing Here? (2018) · Lorrie Moore, See What Can Be Done (2018) · Maggie O’Farrell, I Am I Am I Am (2018) · Ijeoma Oluo, So You Want to Talk About Race (2018) · Rachel Cusk, Coventry (2019) · Jia Tolentino, Trick Mirror (2019) · Emily Bernard, Black is the Body (2019) · Toni Morrison, The Source of Self-Regard (2019) · Margaret Renkl, Late Migrations (2019) · Rachel Munroe, Savage Appetites (2019) · Robert A. Caro, Working (2019) · Arundhati Roy, My Seditious Heart (2019).

Emily Temple
Previous article, next article.

- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Suggestions
- A Midsummer Night's Dream
- A Streetcar Named Desire
- Fahrenheit 451
Please wait while we process your payment
Reset Password
Your password reset email should arrive shortly..
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Something went wrong
Log in or create account.
- Be between 8-15 characters.
- Contain at least one capital letter.
- Contain at least one number.
- Be different from your email address.
By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy .
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
- Ad-free experience
- Note-taking
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AP® English Test Prep
- Plus much more
Already have an account? Log in
Choose Your Plan
Group Discount
$4.99 /month + tax
$24.99 /year + tax
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
$24.99 $18.74 / subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
Change
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews April 14, 2024 April 7, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at [email protected] . Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
Your PLUS subscription has expired
- We’d love to have you back! Renew your subscription to regain access to all of our exclusive, ad-free study tools.
- Renew your subscription to regain access to all of our exclusive, ad-free study tools.
- Go ad-free AND get instant access to grade-boosting study tools!
- Start the school year strong with SparkNotes PLUS!
- Start the school year strong with PLUS!
How to Write Literary Analysis
Introduction.
When you read for pleasure, your only goal is enjoyment. You might find yourself reading to get caught up in an exciting story, to learn about an interesting time or place, or just to pass time. Maybe you’re looking for inspiration, guidance, or a reflection of your own life. There are as many different, valid ways of reading a book as there are books in the world.
When you read a work of literature in an English class, however, you’re being asked to read in a special way: you’re being asked to perform literary analysis. To analyze something means to break it down into smaller parts and then examine how those parts work, both individually and together. Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects.
A literary essay isn’t a book review: you’re not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you’d recommend it to another reader. A literary essay also isn’t like the kind of book report you wrote when you were younger, where your teacher wanted you to summarize the book’s action. A high school- or college-level literary essay asks, “How does this piece of literature actually work?” “How does it do what it does?” and, “Why might the author have made the choices he or she did?”
The Seven Steps
No one is born knowing how to analyze literature; it’s a skill you learn and a process you can master. As you gain more practice with this kind of thinking and writing, you’ll be able to craft a method that works best for you. But until then, here are seven basic steps to writing a well-constructed literary essay.
- 1. Ask questions
- 2. Collect evidence
- 3. Construct a thesis
- 4. Develop and organize arguments
- 5. Write the introduction
- 6. Write the body paragraphs
- 7. Write the conclusion
1 Ask Questions
When you’re assigned a literary essay in class, your teacher will often provide you with a list of writing prompts. Lucky you! Now all you have to do is choose one. Do yourself a favor and pick a topic that interests you. You’ll have a much better (not to mention easier) time if you start off with something you enjoy thinking about. If you are asked to come up with a topic by yourself, though, you might start to feel a little panicked. Maybe you have too many ideas—or none at all. Don’t worry. Take a deep breath and start by asking yourself these questions:
What struck you?
Did a particular image, line, or scene linger in your mind for a long time? If it fascinated you, chances are you can draw on it to write a fascinating essay.
What confused you?
Maybe you were surprised to see a character act in a certain way, or maybe you didn’t understand why the book ended the way it did. Confusing moments in a work of literature are like a loose thread in a sweater: if you pull on it, you can unravel the entire thing. Ask yourself why the author chose to write about that character or scene the way he or she did and you might tap into some important insights about the work as a whole.
Did you notice any patterns?
Is there a phrase that the main character uses constantly or an image that repeats throughout the book? If you can figure out how that pattern weaves through the work and what the significance of that pattern is, you’ve almost got your entire essay mapped out.
Did you notice any contradictions or ironies?
Great works of literature are complex; great literary essays recognize and explain those complexities. Maybe the title Happy Days totally disagrees with the book’s subject matter (hungry orphans dying in the woods). Maybe the main character acts one way around his family and a completely different way around his friends and associates. If you can find a way to explain a work’s contradictory elements, you’ve got the seeds of a great essay.
At this point, you don’t need to know exactly what you’re going to say about your topic; you just need a place to begin your exploration. You can help direct your reading and brainstorming by formulating your topic as a question, which you’ll then try to answer in your essay. The best questions invite critical debates and discussions, not just a rehashing of the summary. Remember, you’re looking for something you can prove or argue based on evidence you find in the text. Finally, remember to keep the scope of your question in mind: is this a topic you can adequately address within the word or page limit you’ve been given? Conversely, is this a topic big enough to fill the required length?
Good questions
“Are Romeo and Juliet’s parents responsible for the deaths of their children?”
“Why do pigs keep showing up in Lord of the Flies ?”
“Are Dr. Frankenstein and his monster alike? How?”
Bad questions
“What happens to Scout in To Kill a Mockingbird ?”
“What do the other characters in Julius Caesar think about Caesar?”
“How does Hester Prynne in The Scarlet Letter remind me of my sister?”
2 Collect Evidence
Once you know what question you want to answer, it’s time to scour the book for things that will help you answer the question. Don’t worry if you don’t know what you want to say yet—right now you’re just collecting ideas and material and letting it all percolate. Keep track of passages, symbols, images, or scenes that deal with your topic. Eventually, you’ll start making connections between these examples and your thesis will emerge.
Here’s a brief summary of the various parts that compose each and every work of literature. These are the elements that you will analyze in your essay, and which you will offer as evidence to support your arguments. For more on the parts of literary works, see the Glossary of Literary Terms at the end of this section.
Elements of Story
These are the whats of the work—what happens, where it happens, and to whom it happens.
Elements of Style
These are the hows —how the characters speak, how the story is constructed, and how language is used throughout the work.
Structure and organization
Point of view, figurative language, 3 construct a thesis.
When you’ve examined all the evidence you’ve collected and know how you want to answer the question, it’s time to write your thesis statement. A thesis is a claim about a work of literature that needs to be supported by evidence and arguments. The thesis statement is the heart of the literary essay, and the bulk of your paper will be spent trying to prove this claim. A good thesis will be:
“ The Great Gatsby describes New York society in the 1920s” isn’t a thesis—it’s a fact.
Provable through textual evidence.
“ Hamlet is a confusing but ultimately very well-written play” is a weak thesis because it offers the writer’s personal opinion about the book. Yes, it’s arguable, but it’s not a claim that can be proved or supported with examples taken from the play itself.
Surprising.
“Both George and Lenny change a great deal in Of Mice and Men ” is a weak thesis because it’s obvious. A really strong thesis will argue for a reading of the text that is not immediately apparent.
“Dr. Frankenstein’s monster tells us a lot about the human condition” is almost a really great thesis statement, but it’s still too vague. What does the writer mean by “a lot”? How does the monster tell us so much about the human condition?
Good Thesis Statements
Question: In Romeo and Juliet , which is more powerful in shaping the lovers’ story: fate or foolishness?
Thesis: “Though Shakespeare defines Romeo and Juliet as ‘star- crossed lovers’ and images of stars and planets appear throughout the play, a closer examination of that celestial imagery reveals that the stars are merely witnesses to the characters’ foolish activities and not the causes themselves.”
Question: How does the bell jar function as a symbol in Sylvia Plath’s The Bell Jar ?
Thesis: “A bell jar is a bell-shaped glass that has three basic uses: to hold a specimen for observation, to contain gases, and to maintain a vacuum. The bell jar appears in each of these capacities in The Bell Jar , Plath’s semi-autobiographical novel, and each appearance marks a different stage in Esther’s mental breakdown.”
Question: Would Piggy in The Lord of the Flies make a good island leader if he were given the chance?
Thesis: “Though the intelligent, rational, and innovative Piggy has the mental characteristics of a good leader, he ultimately lacks the social skills necessary to be an effective one. Golding emphasizes this point by giving Piggy a foil in the charismatic Jack, whose magnetic personality allows him to capture and wield power effectively, if not always wisely.”
4 Develop and Organize Arguments
The reasons and examples that support your thesis will form the middle paragraphs of your essay. Since you can’t really write your thesis statement until you know how you’ll structure your argument, you’ll probably end up working on steps 3 and 4 at the same time.
There’s no single method of argumentation that will work in every context. One essay prompt might ask you to compare and contrast two characters, while another asks you to trace an image through a given work of literature. These questions require different kinds of answers and therefore different kinds of arguments. Below, we’ll discuss three common kinds of essay prompts and some strategies for constructing a solid, well-argued case.
Types of Literary Essays
Compare and contrast.
Compare and contrast the characters of Huck and Jim in The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn .
Chances are you’ve written this kind of essay before. In an academic literary context, you’ll organize your arguments the same way you would in any other class. You can either go subject by subject or point by point . In the former, you’ll discuss one character first and then the second. In the latter, you’ll choose several traits (attitude toward life, social status, images and metaphors associated with the character) and devote a paragraph to each. You may want to use a mix of these two approaches—for example, you may want to spend a paragraph apiece broadly sketching Huck’s and Jim’s personalities before transitioning into a paragraph or two that describes a few key points of comparison. This can be a highly effective strategy if you want to make a counterintuitive argument—that, despite seeming to be totally different, the two objects being compared are actually similar in a very important way (or vice versa). Remember that your essay should reveal something fresh or unexpected about the text, so think beyond the obvious parallels and differences.
Choose an image—for example, birds, knives, or eyes—and trace that image throughout Macbeth .
Sounds pretty easy, right? All you need to do is read the play, underline every appearance of a knife in Macbeth , and then list them in your essay in the order they appear, right? Well, not exactly. Your teacher doesn’t want a simple catalog of examples. He or she wants to see you make connections between those examples—that’s the difference between summarizing and analyzing. In the Macbeth example above, think about the different contexts in which knives appear in the play and to what effect. In Macbeth , there are real knives and imagined knives; knives that kill and knives that simply threaten. Categorize and classify your examples to give them some order. Finally, always keep the overall effect in mind. After you choose and analyze your examples, you should come to some greater understanding about the work, as well as your chosen image, symbol, or phrase’s role in developing the major themes and stylistic strategies of that work.
Is the society depicted in 1984 good for its citizens?
In this kind of essay, you’re being asked to debate a moral, ethical, or aesthetic issue regarding the work. You might be asked to judge a character or group of characters ( Is Caesar responsible for his own demise ?) or the work itself ( Is Jane Eyre a feminist novel ?). For this kind of essay, there are two important points to keep in mind. First, don’t simply base your arguments on your personal feelings and reactions. Every literary essay expects you to read and analyze the work, so search for evidence in the text. What do characters in 1984 have to say about the government of Oceania? What images does Orwell use that might give you a hint about his attitude toward the government? As in any debate, you also need to make sure that you define all the necessary terms before you begin to argue your case. What does it mean to be a “good” society? What makes a novel “feminist”? You should define your terms right up front, in the first paragraph after your introduction.
Second, remember that strong literary essays make contrary and surprising arguments. Try to think outside the box. In the 1984 example above, it seems like the obvious answer would be no, the totalitarian society depicted in Orwell’s novel is not good for its citizens. But can you think of any arguments for the opposite side? Even if your final assertion is that the novel depicts a cruel, repressive, and therefore harmful society, acknowledging and responding to the counterargument will strengthen your overall case.
5 Write the Introduction
Your introduction sets up the entire essay. It’s where you present your topic and articulate the particular issues and questions you’ll be addressing. It’s also where you, as the writer, introduce yourself to your readers. A persuasive literary essay immediately establishes its writer as a knowledgeable, authoritative figure.
An introduction can vary in length depending on the overall length of the essay, but in a traditional five-paragraph essay it should be no longer than one paragraph. However long it is, your introduction needs to:
Provide any necessary context.
Your introduction should situate the reader and let him or her know what to expect. What book are you discussing? Which characters? What topic will you be addressing?
Answer the “So what?” question.
Why is this topic important, and why is your particular position on the topic noteworthy? Ideally, your introduction should pique the reader’s interest by suggesting how your argument is surprising or otherwise counterintuitive. Literary essays make unexpected connections and reveal less-than-obvious truths.
Present your thesis.
This usually happens at or very near the end of your introduction.
Indicate the shape of the essay to come.
Your reader should finish reading your introduction with a good sense of the scope of your essay as well as the path you’ll take toward proving your thesis. You don’t need to spell out every step, but you do need to suggest the organizational pattern you’ll be using.
Your introduction should not:
Beware of the two killer words in literary analysis: interesting and important. Of course the work, question, or example is interesting and important—that’s why you’re writing about it!
Open with any grandiose assertions.
Many student readers think that beginning their essays with a flamboyant statement such as, “Since the dawn of time, writers have been fascinated with the topic of free will,” makes them sound important and commanding. You know what? It actually sounds pretty amateurish.
Wildly praise the work.
Another typical mistake student writers make is extolling the work or author. Your teacher doesn’t need to be told that “Shakespeare is perhaps the greatest writer in the English language.” You can mention a work’s reputation in passing—by referring to The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn as “Mark Twain’s enduring classic,” for example—but don’t make a point of bringing it up unless that reputation is key to your argument.
Go off-topic.
Keep your introduction streamlined and to the point. Don’t feel the need to throw in all kinds of bells and whistles in order to impress your reader—just get to the point as quickly as you can, without skimping on any of the required steps.
6 Write the Body Paragraphs
Once you’ve written your introduction, you’ll take the arguments you developed in step 4 and turn them into your body paragraphs. The organization of this middle section of your essay will largely be determined by the argumentative strategy you use, but no matter how you arrange your thoughts, your body paragraphs need to do the following:
Begin with a strong topic sentence.
Topic sentences are like signs on a highway: they tell the reader where they are and where they’re going. A good topic sentence not only alerts readers to what issue will be discussed in the following paragraph but also gives them a sense of what argument will be made about that issue. “Rumor and gossip play an important role in The Crucible ” isn’t a strong topic sentence because it doesn’t tell us very much. “The community’s constant gossiping creates an environment that allows false accusations to flourish” is a much stronger topic sentence— it not only tells us what the paragraph will discuss (gossip) but how the paragraph will discuss the topic (by showing how gossip creates a set of conditions that leads to the play’s climactic action).
Fully and completely develop a single thought.
Don’t skip around in your paragraph or try to stuff in too much material. Body paragraphs are like bricks: each individual one needs to be strong and sturdy or the entire structure will collapse. Make sure you have really proven your point before moving on to the next one.
Use transitions effectively.
Good literary essay writers know that each paragraph must be clearly and strongly linked to the material around it. Think of each paragraph as a response to the one that precedes it. Use transition words and phrases such as however, similarly, on the contrary, therefore, and furthermore to indicate what kind of response you’re making.
7 Write the Conclusion
Just as you used the introduction to ground your readers in the topic before providing your thesis, you’ll use the conclusion to quickly summarize the specifics learned thus far and then hint at the broader implications of your topic. A good conclusion will:
Do more than simply restate the thesis.
If your thesis argued that The Catcher in the Rye can be read as a Christian allegory, don’t simply end your essay by saying, “And that is why The Catcher in the Rye can be read as a Christian allegory.” If you’ve constructed your arguments well, this kind of statement will just be redundant.
Synthesize the arguments, not summarize them.
Similarly, don’t repeat the details of your body paragraphs in your conclusion. The reader has already read your essay, and chances are it’s not so long that they’ve forgotten all your points by now.
Revisit the “So what?” question.
In your introduction, you made a case for why your topic and position are important. You should close your essay with the same sort of gesture. What do your readers know now that they didn’t know before? How will that knowledge help them better appreciate or understand the work overall?
Move from the specific to the general.
Your essay has most likely treated a very specific element of the work—a single character, a small set of images, or a particular passage. In your conclusion, try to show how this narrow discussion has wider implications for the work overall. If your essay on To Kill a Mockingbird focused on the character of Boo Radley, for example, you might want to include a bit in your conclusion about how he fits into the novel’s larger message about childhood, innocence, or family life.
Stay relevant.
Your conclusion should suggest new directions of thought, but it shouldn’t be treated as an opportunity to pad your essay with all the extra, interesting ideas you came up with during your brainstorming sessions but couldn’t fit into the essay proper. Don’t attempt to stuff in unrelated queries or too many abstract thoughts.
Avoid making overblown closing statements.
A conclusion should open up your highly specific, focused discussion, but it should do so without drawing a sweeping lesson about life or human nature. Making such observations may be part of the point of reading, but it’s almost always a mistake in essays, where these observations tend to sound overly dramatic or simply silly.
Take a Study Break

QUIZ: Is This a Taylor Swift Lyric or a Quote by Edgar Allan Poe?

The 7 Most Embarrassing Proposals in Literature

The 6 Best and Worst TV Show Adaptations of Books

QUIZ: Which Greek God Are You?
- Skip to content
Davidson Writer
Academic Writing Resources for Students
Main navigation
Literary analysis: sample essay.
We turn once more to Joanna Wolfe’s and Laura Wilder’s Digging into Literature: Strategies for Reading, Writing, and Analysis (Boston: Bedford/St. Martin’s, 2016) in order to show you their example of a strong student essay that has a strong central claim elucidated by multiple surface/depth arguments supported by patterns of evidence.
Paragraph 1
Sylvia Plath’s short poem “Morning Song” explores the conflicted emotions of a new mother. On the one hand, the mother recognizes that she is expected to treasure and celebrate her infant, but on the other hand, she feels strangely removed from the child. The poem uses a combination of scientific and natural imagery to illustrate the mother’s feelings of alienation. By the end of the poem, however, we see a shift in this imagery as the mother begins to see the infant in more human terms.
Paragraph 2
There are several references to scientific imagery in “Morning Song” that suggest that mother is viewing the baby in clinical, scientific terms rather than as a new life. The poem refers to magnification (4) and reflection (8), both of which are scientific methods. The word “distills” (8) refers to a scientific, chemical process for removing impurities from a substance. The baby’s cry is described as taking “its place among the elements” (3), which seems to refer to the periodic table of elements, the primordial matter of the universe. The watch in the first line is similarly a scientific tool and the gold the watch is made of is, of course, an element, like the baby’s cry. Even the balloons in the last line have a scientific connotation since balloons are often used for measurements and experiments in science. These images all serve to show how the speaker feels distanced from the baby, who is like a scientific experiment she is conducting rather than a human being.
Paragraph 3
Natural imagery also seems to further dehumanize the baby, reducing it to nothing more than its mouth. The baby’s breathing is compared to a moth in line 10, suggesting that the speaker feels the infant is fragile and is as likely to die as a moth dancing around candlelight. A few lines later, the baby’s mouth is compared to another animal—a cat—who greedily opens its mouth for milk. Not only does the speaker seem to feel that the baby is like an animal, but she herself is turned into an animal, as she arises “cow-heavy” (13) to feed the infant. These images show how the speaker sees both the baby and herself as dumb animals who exist only to feed and be fed. Even the morning itself seems to be reduced to another mouth to feed as she describes how the dawn “swallows its dull stars” (16). These lines suggest that just as the sun swallows up the stars, so the baby will swallow up this mother.
Paragraph 4
However, in the last few lines the poem takes a hopeful turn as the speaker begins to view the baby as a human being. The baby’s mouth, which has previously been greedy and animal-like, now becomes a source of music, producing a “handful of notes” (17) and “clear vowels” (18). Music is a distinctly human sound. No animals and certainly not the cats, cows, or moths mentioned earlier in the poem, make music. This change in how the speaker perceives the baby’s sounds—from animalistic cry to human song—suggest that she is beginning to relate the baby as an individual. Even the word “handful” in the phrase “handful of notes” (17) seems hopeful in this context since this is the first time the mother has referred to the baby as having a distinctly human body part. When the baby’s notes finally “rise like balloons” (18), the speaker seems to have arrived at a place where she can celebrate the infant. For the first time, the infant is giving something to the speaker rather than threatening to take something away. The mother seems to have finally accepted the child as an independent human being whose company she can celebrate.
Works Cited
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction
You’ve been assigned a literary analysis paper—what does that even mean? Is it like a book report that you used to write in high school? Well, not really.
A literary analysis essay asks you to make an original argument about a poem, play, or work of fiction and support that argument with research and evidence from your careful reading of the text.
It can take many forms, such as a close reading of a text, critiquing the text through a particular literary theory, comparing one text to another, or criticizing another critic’s interpretation of the text. While there are many ways to structure a literary essay, writing this kind of essay follows generally follows a similar process for everyone
Crafting a good literary analysis essay begins with good close reading of the text, in which you have kept notes and observations as you read. This will help you with the first step, which is selecting a topic to write about—what jumped out as you read, what are you genuinely interested in? The next step is to focus your topic, developing it into an argument—why is this subject or observation important? Why should your reader care about it as much as you do? The third step is to gather evidence to support your argument, for literary analysis, support comes in the form of evidence from the text and from your research on what other literary critics have said about your topic. Only after you have performed these steps, are you ready to begin actually writing your essay.
Writing a Literary Analysis Essay
How to create a topic and conduct research:.
Writing an Analysis of a Poem, Story, or Play
If you are taking a literature course, it is important that you know how to write an analysis—sometimes called an interpretation or a literary analysis or a critical reading or a critical analysis—of a story, a poem, and a play. Your instructor will probably assign such an analysis as part of the course assessment. On your mid-term or final exam, you might have to write an analysis of one or more of the poems and/or stories on your reading list. Or the dreaded “sight poem or story” might appear on an exam, a work that is not on the reading list, that you have not read before, but one your instructor includes on the exam to examine your ability to apply the active reading skills you have learned in class to produce, independently, an effective literary analysis.You might be asked to write instead or, or in addition to an analysis of a literary work, a more sophisticated essay in which you compare and contrast the protagonists of two stories, or the use of form and metaphor in two poems, or the tragic heroes in two plays.
You might learn some literary theory in your course and be asked to apply theory—feminist, Marxist, reader-response, psychoanalytic, new historicist, for example—to one or more of the works on your reading list. But the seminal assignment in a literature course is the analysis of the single poem, story, novel, or play, and, even if you do not have to complete this assignment specifically, it will form the basis of most of the other writing assignments you will be required to undertake in your literature class. There are several ways of structuring a literary analysis, and your instructor might issue specific instructions on how he or she wants this assignment done. The method presented here might not be identical to the one your instructor wants you to follow, but it will be easy enough to modify, if your instructor expects something a bit different, and it is a good default method, if your instructor does not issue more specific guidelines.You want to begin your analysis with a paragraph that provides the context of the work you are analyzing and a brief account of what you believe to be the poem or story or play’s main theme. At a minimum, your account of the work’s context will include the name of the author, the title of the work, its genre, and the date and place of publication. If there is an important biographical or historical context to the work, you should include that, as well.Try to express the work’s theme in one or two sentences. Theme, you will recall, is that insight into human experience the author offers to readers, usually revealed as the content, the drama, the plot of the poem, story, or play unfolds and the characters interact. Assessing theme can be a complex task. Authors usually show the theme; they don’t tell it. They rarely say, at the end of the story, words to this effect: “and the moral of my story is…” They tell their story, develop their characters, provide some kind of conflict—and from all of this theme emerges. Because identifying theme can be challenging and subjective, it is often a good idea to work through the rest of the analysis, then return to the beginning and assess theme in light of your analysis of the work’s other literary elements.Here is a good example of an introductory paragraph from Ben’s analysis of William Butler Yeats’ poem, “Among School Children.”
“Among School Children” was published in Yeats’ 1928 collection of poems The Tower. It was inspired by a visit Yeats made in 1926 to school in Waterford, an official visit in his capacity as a senator of the Irish Free State. In the course of the tour, Yeats reflects upon his own youth and the experiences that shaped the “sixty-year old, smiling public man” (line 8) he has become. Through his reflection, the theme of the poem emerges: a life has meaning when connections among apparently disparate experiences are forged into a unified whole.
In the body of your literature analysis, you want to guide your readers through a tour of the poem, story, or play, pausing along the way to comment on, analyze, interpret, and explain key incidents, descriptions, dialogue, symbols, the writer’s use of figurative language—any of the elements of literature that are relevant to a sound analysis of this particular work. Your main goal is to explain how the elements of literature work to elucidate, augment, and develop the theme. The elements of literature are common across genres: a story, a narrative poem, and a play all have a plot and characters. But certain genres privilege certain literary elements. In a poem, for example, form, imagery and metaphor might be especially important; in a story, setting and point-of-view might be more important than they are in a poem; in a play, dialogue, stage directions, lighting serve functions rarely relevant in the analysis of a story or poem.
The length of the body of an analysis of a literary work will usually depend upon the length of work being analyzed—the longer the work, the longer the analysis—though your instructor will likely establish a word limit for this assignment. Make certain that you do not simply paraphrase the plot of the story or play or the content of the poem. This is a common weakness in student literary analyses, especially when the analysis is of a poem or a play.
Here is a good example of two body paragraphs from Amelia’s analysis of “Araby” by James Joyce.
Within the story’s first few paragraphs occur several religious references which will accumulate as the story progresses. The narrator is a student at the Christian Brothers’ School; the former tenant of his house was a priest; he left behind books called The Abbot and The Devout Communicant. Near the end of the story’s second paragraph the narrator describes a “central apple tree” in the garden, under which is “the late tenant’s rusty bicycle pump.” We may begin to suspect the tree symbolizes the apple tree in the Garden of Eden and the bicycle pump, the snake which corrupted Eve, a stretch, perhaps, until Joyce’s fall-of-innocence theme becomes more apparent.
The narrator must continue to help his aunt with her errands, but, even when he is so occupied, his mind is on Mangan’s sister, as he tries to sort out his feelings for her. Here Joyce provides vivid insight into the mind of an adolescent boy at once elated and bewildered by his first crush. He wants to tell her of his “confused adoration,” but he does not know if he will ever have the chance. Joyce’s description of the pleasant tension consuming the narrator is conveyed in a striking simile, which continues to develop the narrator’s character, while echoing the religious imagery, so important to the story’s theme: “But my body was like a harp, and her words and gestures were like fingers, running along the wires.”
The concluding paragraph of your analysis should realize two goals. First, it should present your own opinion on the quality of the poem or story or play about which you have been writing. And, second, it should comment on the current relevance of the work. You should certainly comment on the enduring social relevance of the work you are explicating. You may comment, though you should never be obliged to do so, on the personal relevance of the work. Here is the concluding paragraph from Dao-Ming’s analysis of Oscar Wilde’s The Importance of Being Earnest.
First performed in 1895, The Importance of Being Earnest has been made into a film, as recently as 2002 and is regularly revived by professional and amateur theatre companies. It endures not only because of the comic brilliance of its characters and their dialogue, but also because its satire still resonates with contemporary audiences. I am still amazed that I see in my own Asian mother a shadow of Lady Bracknell, with her obsession with finding for her daughter a husband who will maintain, if not, ideally, increase the family’s social status. We might like to think we are more liberated and socially sophisticated than our Victorian ancestors, but the starlets and eligible bachelors who star in current reality television programs illustrate the extent to which superficial concerns still influence decisions about love and even marriage. Even now, we can turn to Oscar Wilde to help us understand and laugh at those who are earnest in name only.
Dao-Ming’s conclusion is brief, but she does manage to praise the play, reaffirm its main theme, and explain its enduring appeal. And note how her last sentence cleverly establishes that sense of closure that is also a feature of an effective analysis.
You may, of course, modify the template that is presented here. Your instructor might favour a somewhat different approach to literary analysis. Its essence, though, will be your understanding and interpretation of the theme of the poem, story, or play and the skill with which the author shapes the elements of literature—plot, character, form, diction, setting, point of view—to support the theme.
Academic Writing Tips : How to Write a Literary Analysis Paper. Authored by: eHow. Located at: https://youtu.be/8adKfLwIrVk. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube license
BC Open Textbooks: English Literature Victorians and Moderns: https://opentextbc.ca/englishliterature/back-matter/appendix-5-writing-an-analysis-of-a-poem-story-and-play/
Literary Analysis
The challenges of writing about english literature.
Writing begins with the act of reading . While this statement is true for most college papers, strong English papers tend to be the product of highly attentive reading (and rereading). When your instructors ask you to do a “close reading,” they are asking you to read not only for content, but also for structures and patterns. When you perform a close reading, then, you observe how form and content interact. In some cases, form reinforces content: for example, in John Donne’s Holy Sonnet 14, where the speaker invites God’s “force” “to break, blow, burn and make [him] new.” Here, the stressed monosyllables of the verbs “break,” “blow” and “burn” evoke aurally the force that the speaker invites from God. In other cases, form raises questions about content: for example, a repeated denial of guilt will likely raise questions about the speaker’s professed innocence. When you close read, take an inductive approach. Start by observing particular details in the text, such as a repeated image or word, an unexpected development, or even a contradiction. Often, a detail–such as a repeated image–can help you to identify a question about the text that warrants further examination. So annotate details that strike you as you read. Some of those details will eventually help you to work towards a thesis. And don’t worry if a detail seems trivial. If you can make a case about how an apparently trivial detail reveals something significant about the text, then your paper will have a thought-provoking thesis to argue.
Common Types of English Papers Many assignments will ask you to analyze a single text. Others, however, will ask you to read two or more texts in relation to each other, or to consider a text in light of claims made by other scholars and critics. For most assignments, close reading will be central to your paper. While some assignment guidelines will suggest topics and spell out expectations in detail, others will offer little more than a page limit. Approaching the writing process in the absence of assigned topics can be daunting, but remember that you have resources: in section, you will probably have encountered some examples of close reading; in lecture, you will have encountered some of the course’s central questions and claims. The paper is a chance for you to extend a claim offered in lecture, or to analyze a passage neglected in lecture. In either case, your analysis should do more than recapitulate claims aired in lecture and section. Because different instructors have different goals for an assignment, you should always ask your professor or TF if you have questions. These general guidelines should apply in most cases:
- A close reading of a single text: Depending on the length of the text, you will need to be more or less selective about what you choose to consider. In the case of a sonnet, you will probably have enough room to analyze the text more thoroughly than you would in the case of a novel, for example, though even here you will probably not analyze every single detail. By contrast, in the case of a novel, you might analyze a repeated scene, image, or object (for example, scenes of train travel, images of decay, or objects such as or typewriters). Alternately, you might analyze a perplexing scene (such as a novel’s ending, albeit probably in relation to an earlier moment in the novel). But even when analyzing shorter works, you will need to be selective. Although you might notice numerous interesting details as you read, not all of those details will help you to organize a focused argument about the text. For example, if you are focusing on depictions of sensory experience in Keats’ “Ode to a Nightingale,” you probably do not need to analyze the image of a homeless Ruth in stanza 7, unless this image helps you to develop your case about sensory experience in the poem.
- A theoretically-informed close reading. In some courses, you will be asked to analyze a poem, a play, or a novel by using a critical theory (psychoanalytic, postcolonial, gender, etc). For example, you might use Kristeva’s theory of abjection to analyze mother-daughter relations in Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved. Critical theories provide focus for your analysis; if “abjection” is the guiding concept for your paper, you should focus on the scenes in the novel that are most relevant to the concept.
- A historically-informed close reading. In courses with a historicist orientation, you might use less self-consciously literary documents, such as newspapers or devotional manuals, to develop your analysis of a literary work. For example, to analyze how Robinson Crusoe makes sense of his island experiences, you might use Puritan tracts that narrate events in terms of how God organizes them. The tracts could help you to show not only how Robinson Crusoe draws on Puritan narrative conventions, but also—more significantly—how the novel revises those conventions.
- A comparison of two texts When analyzing two texts, you might look for unexpected contrasts between apparently similar texts, or unexpected similarities between apparently dissimilar texts, or for how one text revises or transforms the other. Keep in mind that not all of the similarities, differences, and transformations you identify will be relevant to an argument about the relationship between the two texts. As you work towards a thesis, you will need to decide which of those similarities, differences, or transformations to focus on. Moreover, unless instructed otherwise, you do not need to allot equal space to each text (unless this 50/50 allocation serves your thesis well, of course). Often you will find that one text helps to develop your analysis of another text. For example, you might analyze the transformation of Ariel’s song from The Tempest in T. S. Eliot’s poem, The Waste Land. Insofar as this analysis is interested in the afterlife of Ariel’s song in a later poem, you would likely allot more space to analyzing allusions to Ariel’s song in The Waste Land (after initially establishing the song’s significance in Shakespeare’s play, of course).
- A response paper A response paper is a great opportunity to practice your close reading skills without having to develop an entire argument. In most cases, a solid approach is to select a rich passage that rewards analysis (for example, one that depicts an important scene or a recurring image) and close read it. While response papers are a flexible genre, they are not invitations for impressionistic accounts of whether you liked the work or a particular character. Instead, you might use your close reading to raise a question about the text—to open up further investigation, rather than to supply a solution.
- A research paper. In most cases, you will receive guidance from the professor on the scope of the research paper. It is likely that you will be expected to consult sources other than the assigned readings. Hollis is your best bet for book titles, and the MLA bibliography (available through e-resources) for articles. When reading articles, make sure that they have been peer reviewed; you might also ask your TF to recommend reputable journals in the field.
Harvard College Writing Program: https://writingproject.fas.harvard.edu/files/hwp/files/bg_writing_english.pdf
In the same way that we talk with our friends about the latest episode of Game of Thrones or newest Marvel movie, scholars communicate their ideas and interpretations of literature through written literary analysis essays. Literary analysis essays make us better readers of literature.
Only through careful reading and well-argued analysis can we reach new understandings and interpretations of texts that are sometimes hundreds of years old. Literary analysis brings new meaning and can shed new light on texts. Building from careful reading and selecting a topic that you are genuinely interested in, your argument supports how you read and understand a text. Using examples from the text you are discussing in the form of textual evidence further supports your reading. Well-researched literary analysis also includes information about what other scholars have written about a specific text or topic.
Literary analysis helps us to refine our ideas, question what we think we know, and often generates new knowledge about literature. Literary analysis essays allow you to discuss your own interpretation of a given text through careful examination of the choices the original author made in the text.
ENG134 – Literary Genres Copyright © by The American Women's College and Jessica Egan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Literary Analysis Essay
Literary Analysis Essay Writing
Last updated on: May 21, 2023
Literary Analysis Essay - Ultimate Guide By Professionals
By: Cordon J.
Reviewed By: Rylee W.
Published on: Dec 3, 2019

A literary analysis essay specifically examines and evaluates a piece of literature or a literary work. It also understands and explains the links between the small parts to their whole information.
It is important for students to understand the meaning and the true essence of literature to write a literary essay.
One of the most difficult assignments for students is writing a literary analysis essay. It can be hard to come up with an original idea or find enough material to write about. You might think you need years of experience in order to create a good paper, but that's not true.
This blog post will show you how easy it can be when you follow the steps given here.Writing such an essay involves the breakdown of a book into small parts and understanding each part separately. It seems easy, right?
Trust us, it is not as hard as good book reports but it may also not be extremely easy. You will have to take into account different approaches and explain them in relation with the chosen literary work.
It is a common high school and college assignment and you can learn everything in this blog.
Continue reading for some useful tips with an example to write a literary analysis essay that will be on point. You can also explore our detailed article on writing an analytical essay .

On this Page
What is a Literary Analysis Essay?
A literary analysis essay is an important kind of essay that focuses on the detailed analysis of the work of literature.
The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to explain why the author has used a specific theme for his work. Or examine the characters, themes, literary devices , figurative language, and settings in the story.
This type of essay encourages students to think about how the book or the short story has been written. And why the author has created this work.
The method used in the literary analysis essay differs from other types of essays. It primarily focuses on the type of work and literature that is being analyzed.
Mostly, you will be going to break down the work into various parts. In order to develop a better understanding of the idea being discussed, each part will be discussed separately.
The essay should explain the choices of the author and point of view along with your answers and personal analysis.
How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay
So how to start a literary analysis essay? The answer to this question is quite simple.
The following sections are required to write an effective literary analysis essay. By following the guidelines given in the following sections, you will be able to craft a winning literary analysis essay.
Introduction
The aim of the introduction is to establish a context for readers. You have to give a brief on the background of the selected topic.
It should contain the name of the author of the literary work along with its title. The introduction should be effective enough to grab the reader’s attention.
In the body section, you have to retell the story that the writer has narrated. It is a good idea to create a summary as it is one of the important tips of literary analysis.
Other than that, you are required to develop ideas and disclose the observed information related to the issue. The ideal length of the body section is around 1000 words.
To write the body section, your observation should be based on evidence and your own style of writing.
It would be great if the body of your essay is divided into three paragraphs. Make a strong argument with facts related to the thesis statement in all of the paragraphs in the body section.
Start writing each paragraph with a topic sentence and use transition words when moving to the next paragraph.
Summarize the important points of your literary analysis essay in this section. It is important to compose a short and strong conclusion to help you make a final impression of your essay.
Pay attention that this section does not contain any new information. It should provide a sense of completion by restating the main idea with a short description of your arguments. End the conclusion with your supporting details.
You have to explain why the book is important. Also, elaborate on the means that the authors used to convey her/his opinion regarding the issue.
For further understanding, here is a downloadable literary analysis essay outline. This outline will help you structure and format your essay properly and earn an A easily.
DOWNLOADABLE LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY OUTLINE (PDF)
Types of Literary Analysis Essay
- Close reading - This method involves attentive reading and detailed analysis. No need for a lot of knowledge and inspiration to write an essay that shows your creative skills.
- Theoretical - In this type, you will rely on theories related to the selected topic.
- Historical - This type of essay concerns the discipline of history. Sometimes historical analysis is required to explain events in detail.
- Applied - This type involves analysis of a specific issue from a practical perspective.
- Comparative - This type of writing is based on when two or more alternatives are compared
Examples of Literary Analysis Essay
Examples are great to understand any concept, especially if it is related to writing. Below are some great literary analysis essay examples that showcase how this type of essay is written.
A ROSE FOR EMILY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE GREAT GATSBY LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
THE YELLOW WALLPAPER LITERARY ANALYSIS ESSAY
If you do not have experience in writing essays, this will be a very chaotic process for you. In that case, it is very important for you to conduct good research on the topic before writing.
There are two important points that you should keep in mind when writing a literary analysis essay.
First, remember that it is very important to select a topic in which you are interested. Choose something that really inspires you. This will help you to catch the attention of a reader.
The selected topic should reflect the main idea of writing. In addition to that, it should also express your point of view as well.
Another important thing is to draft a good outline for your literary analysis essay. It will help you to define a central point and division of this into parts for further discussion.
Literary Analysis Essay Topics
Literary analysis essays are mostly based on artistic works like books, movies, paintings, and other forms of art. However, generally, students choose novels and books to write their literary essays.
Some cool, fresh, and good topics and ideas are listed below:
- Role of the Three Witches in flaming Macbeth’s ambition.
- Analyze the themes of the Play Antigone,
- Discuss Ajax as a tragic hero.
- The Judgement of Paris: Analyze the Reasons and their Consequences.
- Oedipus Rex: A Doomed Son or a Conqueror?
- Describe the Oedipus complex and Electra complex in relation to their respective myths.
- Betrayal is a common theme of Shakespearean tragedies. Discuss
- Identify and analyze the traits of history in T.S Eliot’s ‘Gerontion’.
- Analyze the theme of identity crisis in The Great Gatsby.
- Analyze the writing style of Emily Dickinson.
If you are still in doubt then there is nothing bad in getting professional writers’ help.
We at 5StarEssays.com can help you get a custom paper as per your specified requirements with our do essay for me service.
Our essay writers will help you write outstanding literary essays or any other type of essay. Such as compare and contrast essays, descriptive essays, rhetorical essays. We cover all of these.
So don’t waste your time browsing the internet and place your order now to get your well-written custom paper.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should a literary analysis essay include.
A good literary analysis essay must include a proper and in-depth explanation of your ideas. They must be backed with examples and evidence from the text. Textual evidence includes summaries, paraphrased text, original work details, and direct quotes.
What are the 4 components of literary analysis?
Here are the 4 essential parts of a literary analysis essay;
No literary work is explained properly without discussing and explaining these 4 things.
How do you start a literary analysis essay?
Start your literary analysis essay with the name of the work and the title. Hook your readers by introducing the main ideas that you will discuss in your essay and engage them from the start.
How do you do a literary analysis?
In a literary analysis essay, you study the text closely, understand and interpret its meanings. And try to find out the reasons behind why the author has used certain symbols, themes, and objects in the work.
Why is literary analysis important?
It encourages the students to think beyond their existing knowledge, experiences, and belief and build empathy. This helps in improving the writing skills also.
What is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay?
Interpretation is the fundamental and important feature of a literary analysis essay. The essay is based on how well the writer explains and interprets the work.

Law, Finance Essay
Cordon. is a published author and writing specialist. He has worked in the publishing industry for many years, providing writing services and digital content. His own writing career began with a focus on literature and linguistics, which he continues to pursue. Cordon is an engaging and professional individual, always looking to help others achieve their goals.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- Interesting Literary Analysis Essay Topics for Students

- Write a Perfect Literary Analysis Essay Outline

People Also Read
- mla format paper
- good persuasive essay topics
- expository essay outline
- how to write a bio
- types of argument
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
How to Write a Literary Analysis: 6 Tips for the Perfect Essay
by Kaelyn Barron | 2 comments

Sometimes, you’ll want to read a book just for the pleasure of being entertained and taken to a different time or place, and see the world through the eyes of another.
Other times, however, like when you’re in your English Literature class or reading a classic, you’ll have to dig past the surface and look beyond the words on the page to understand the author’s message.
To do this, you can conduct your own literary analysis, and examine how the author uses various literary devices and techniques to artfully tell their story while delivering a larger message.
What Is a Literary Analysis?
The purpose of a literary analysis is to examine and deconstruct a work of literature to evaluate how the writer uses literary components to convey ideas.
A literary analysis is not a summary; it reaches past basic comprehension and facts. Often, this type of analysis will argue the theme, message, or purpose of a work by analyzing the writer’s use of literary devices and narrative techniques.
How to Write a Literary Analysis
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics.
1. Read the text and identify literary devices.
As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
The following is a checklist of the literary and narrative devices you should take note of while reading. (If possible, marking the text with a pencil can be very helpful.)
- Point of view: First, examine the point of view from which the story is told. Who is the narrator? Is it a character from the story, or an unknown, all-knowing figure? Do they have something at stake? Do you find them to be a reliable narrator? The answers to these questions can help shape your argument.
- Recurring symbols : Things like colors, rivers, and seasons may not seem significant at first glance, but together, and especially if they appear more than once, they can signify a deeper message. (Just look at this analysis of Hemingway’s “Hills Like White Elephants” as an example.) Our guide to symbolism explains some of the most common symbols in literature. If you come across these in a text, highlight or circle them. These symbols can also be part of an extended metaphors, so it’s helpful to keep track of them and look for any possible connections.
- Character motivation : The main character’s motivation is extremely important when it comes to advancing the plot. Ask yourself what the character wants, and what’s keeping them from getting it. Why is that thing important to them? Could it carry any deeper significance that its face value?
- Tone : Evaluate the writer’s tone . Do the words convey an anxious, ominous, or hopeful tone? Is it sad, witty, or whimsical? There are lots of ways to describe tone, and your assessment of this literary device can add important insight to your overall analysis.
- Diction : The author’s word choice, or diction , can also influence the piece’s tone. Do any words seem peculiar? Do you think the author chose that word over other synonyms for a reason? When a word stands out to you, ask yourself why it matters that this particular word was chosen over others.
- Imagery: What types of images does the author paint? This can be done explicitly through vivid descriptions, or implicitly through sensory details, or words that evoke the feelings of a place, emotion, or idea.
- Story structure : How is the story structured, and what impact does this have on the story? Is it told in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? What about the characters, setting, and their relation to the narrative?
- Themes : As you’re taking note of the literary elements outlined above, you’ll likely see certain patterns start to emerge. These patterns represent underlying themes . For example, in The Great Gatsby , recurring images, symbols, and even character motivations point to themes of excess, material wealth, and lost values.
- Characters : Your entire essay might actually be a character analysis, depending on your topic. However, you can also cite characterization as a supporting element to your main argument. For example, a specific character, major or minor, might embody an ideal, which contributes to a larger theme.
2. Develop your thesis.
If you’re writing an essay for your literature class, you’ll likely be given a prompt or question to answer with your essay.
If you’re not assigned a topic, you’ll have to think of one yourself. You may find it helpful to develop questions in order to get started.
The answer to this question is known as your thesis . In order to serve as the foundation for your analysis, your thesis needs to meet several conditions. It must be:
- Arguable : Your thesis should reflect your opinion or interpretation, not a fact. For example, “ The Grapes of Wrath is about a family’s migration from the Oklahoma Dust Bowl to California” is not a good thesis, because that’s a simple fact. However, “ Frankenstein is actually a feminist novel that rejects patriarchy” is an arguable interpretation, and we can argue for or against that statement with supporting evidence.
- Supported through textual evidence : While your thesis shouldn’t be an objective fact, you should still be able to support it with textual evidence and details.
3. Create an outline.
Once you have your thesis, it’s time to make a plan for how you’ll prove your argument. Look back at your notes about the literary and narrative devices above. These will serve as your supporting evidence.
Which elements will help you make the most compelling argument for your thesis? You might choose, for example, to build your argument around imagery, symbolism, and diction.
You can dedicate a section to each of these elements and cite evidence directly from the text to explain why and how they support your thesis.
Create an outline to organize your thoughts, so when it’s time to start writing, you won’t forget where you were going with those points.
4. Cite the evidence.
When you’re making your argument, it’s important that you have concrete evidence from the text to support your claims.
When you can, provide direct quotes and other concrete details. For example, if you’re using symbolism as supporting evidence for why Frankenstein is a feminist text, you should be able to cite passages that illustrate the claim.
5. Write your body paragraphs.
Using your outline and notes from the text, you can now start writing your literary analysis. However, may find it helpful to leave room for your introduction and start by writing the body paragraphs, which contain your main arguments.
You’ll already have all the points and supporting details you need in your outline, so you can jump right in, rather than trying to think of the perfect opening line to your essay.
This strategy can also be beneficial because as you develop your arguments, you may generate new ideas or slightly adjust your thesis.
6. Write your introduction and conclusion.
Once you’ve fleshed out your body paragraphs and written a compelling argument, you can write your introductory paragraph (using the thesis statement you developed earlier), as well as your conclusion, which should neatly tie up your argument and leave your readers with some final insights.
Types of Literary Criticism
When you’re analyzing literature, there are numerous lenses through which you can examine the work. For example, common types of literary criticism include ethical, feminist, historic, and social criticism.
This means that your analysis, interpretation, and evaluation of the work will be through one of those lenses.
Analyzing Literature
The best works of literature are filled with hints that will lead you to a bigger picture, and discovering those clues and how they fit together is what makes reading so fun.
Whether you want to ace your next English essay or refine your critical thinking skills, understanding how to analyze literature will lead you to a more fulfilling reading experience.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- Symbolism: Common Examples in Life and Literature
- The Last Line of The Great Gatsby, Explained
- Extended Metaphors Explained: Definition, Purpose, and Examples from Literature
- 17 of the Most Common Literary Devices Every Reader and Writer Should Know
As a blog writer for TCK Publishing, Kaelyn loves crafting fun and helpful content for writers, readers, and creative minds alike. She has a degree in International Affairs with a minor in Italian Studies, but her true passion has always been writing. Working remotely allows her to do even more of the things she loves, like traveling, cooking, and spending time with her family.
We read a critic generously when they tackle a difficult topic, so one doesn’t judge Barron overly harshly for a seemingly shallow understanding of the subject. The article is useful as a starting point, giving us a chance to consider why so much of the content is ultimately indefensible. This blog has proven a genuinely valuable teaching resource. My students learn a great deal by exploring how this article manages to fall so far short of the promise in its title. Were her approach more thoughtful and erudite, such a rich opportunity to critically engage with literary theory would be denied Barron’s audience.
Hi Gregory, I’m sorry you found the article shallow. I intended it to be an overview for students, to walk them through the process of writing a solid literary analysis essay. What about the content do you find indefensible?

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (46)
- Book Promotion (28)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (53)
- How to Find an Editor (11)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (116)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (73)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (45)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (2)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (17)
- Technology (15)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (59)
- Word Choice (64)
- Writing a Book (62)
- Writing Fiction (195)
- Writing Nonfiction (68)

25 Great Nonfiction Essays You Can Read Online for Free
Alison Doherty
Alison Doherty is a writing teacher and part time assistant professor living in Brooklyn, New York. She has an MFA from The New School in writing for children and teenagers. She loves writing about books on the Internet, listening to audiobooks on the subway, and reading anything with a twisty plot or a happily ever after.
View All posts by Alison Doherty
I love reading books of nonfiction essays and memoirs , but sometimes have a hard time committing to a whole book. This is especially true if I don’t know the author. But reading nonfiction essays online is a quick way to learn which authors you like. Also, reading nonfiction essays can help you learn more about different topics and experiences.
Besides essays on Book Riot, I love looking for essays on The New Yorker , The Atlantic , The Rumpus , and Electric Literature . But there are great nonfiction essays available for free all over the Internet. From contemporary to classic writers and personal essays to researched ones—here are 25 of my favorite nonfiction essays you can read today.

“Beware of Feminist Lite” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
The author of We Should All Be Feminists writes a short essay explaining the danger of believing men and woman are equal only under certain conditions.
“It’s Silly to Be Frightened of Being Dead” by Diana Athill
A 96-year-old woman discusses her shifting attitude towards death from her childhood in the 1920s when death was a taboo subject, to World War 2 until the present day.
“Letter from a Region in my Mind” by James Baldwin
There are many moving and important essays by James Baldwin . This one uses the lens of religion to explore the Black American experience and sexuality. Baldwin describes his move from being a teenage preacher to not believing in god. Then he recounts his meeting with the prominent Nation of Islam member Elijah Muhammad.
“Relations” by Eula Biss
Biss uses the story of a white woman giving birth to a Black baby that was mistakenly implanted during a fertility treatment to explore racial identities and segregation in society as a whole and in her own interracial family.

“Friday Night Lights” by Buzz Bissinger
A comprehensive deep dive into the world of high school football in a small West Texas town.
“The Case for Reparations” by Ta-Nehisi Coates
Coates examines the lingering and continuing affects of slavery on American society and makes a compelling case for the descendants of slaves being offered reparations from the government.
“Why I Write” by Joan Didion
This is one of the most iconic nonfiction essays about writing. Didion describes the reasons she became a writer, her process, and her journey to doing what she loves professionally.
“Go Gentle Into That Good Night” by Roger Ebert
With knowledge of his own death, the famous film critic ponders questions of mortality while also giving readers a pep talk for how to embrace life fully.
“My Mother’s Tongue” by Zavi Kang Engles
In this personal essay, Engles celebrates the close relationship she had with her mother and laments losing her Korean fluency.
“My Life as an Heiress” by Nora Ephron
As she’s writing an important script, Ephron imagines her life as a newly wealthy woman when she finds out an uncle left her an inheritance. But she doesn’t know exactly what that inheritance is.
“My FatheR Spent 30 Years in Prison. Now He’s Out.” by Ashley C. Ford
Ford describes the experience of getting to know her father after he’s been in prison for almost all of her life. Bridging the distance in their knowledge of technology becomes a significant—and at times humorous—step in rebuilding their relationship.
“Bad Feminist” by Roxane Gay
There’s a reason Gay named her bestselling essay collection after this story. It’s a witty, sharp, and relatable look at what it means to call yourself a feminist.
“The Empathy Exams” by Leslie Jamison
Jamison discusses her job as a medical actor helping to train medical students to improve their empathy and uses this frame to tell the story of one winter in college when she had an abortion and heart surgery.
“What I Learned from a Fitting Room Disaster About Clothes and Life” by Scaachi Koul
One woman describes her history with difficult fitting room experiences culminating in one catastrophe that will change the way she hopes to identify herself through clothes.
“Breasts: the Odd Couple” by Una LaMarche
LaMarche examines her changing feelings about her own differently sized breasts.
“How I Broke, and Botched, the Brandon Teena Story” by Donna Minkowitz
A journalist looks back at her own biased reporting on a news story about the sexual assault and murder of a trans man in 1993. Minkowitz examines how ideas of gender and sexuality have changed since she reported the story, along with how her own lesbian identity influenced her opinions about the crime.
“Politics and the English Language” by George Orwell
In this famous essay, Orwell bemoans how politics have corrupted the English language by making it more vague, confusing, and boring.
“Letting Go” by David Sedaris
The famously funny personal essay author , writes about a distinctly unfunny topic of tobacco addiction and his own journey as a smoker. It is (predictably) hilarious.
“Joy” by Zadie Smith
Smith explores the difference between pleasure and joy by closely examining moments of both, including eating a delicious egg sandwich, taking drugs at a concert, and falling in love.
“Mother Tongue” by Amy Tan
Tan tells the story of how her mother’s way of speaking English as an immigrant from China changed the way people viewed her intelligence.
“Consider the Lobster” by David Foster Wallace
The prolific nonfiction essay and fiction writer travels to the Maine Lobster Festival to write a piece for Gourmet Magazine. With his signature footnotes, Wallace turns this experience into a deep exploration on what constitutes consciousness.
“I Am Not Pocahontas” by Elissa Washuta
Washuta looks at her own contemporary Native American identity through the lens of stereotypical depictions from 1990s films.
“Once More to the Lake” by E.B. White
E.B. White didn’t just write books like Charlotte’s Web and The Elements of Style . He also was a brilliant essayist. This nature essay explores the theme of fatherhood against the backdrop of a lake within the forests of Maine.
“Pell-Mell” by Tom Wolfe
The inventor of “new journalism” writes about the creation of an American idea by telling the story of Thomas Jefferson snubbing a European Ambassador.
“The Death of the Moth” by Virginia Woolf
In this nonfiction essay, Wolf describes a moth dying on her window pane. She uses the story as a way to ruminate on the lager theme of the meaning of life and death.

You Might Also Like

beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”
Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
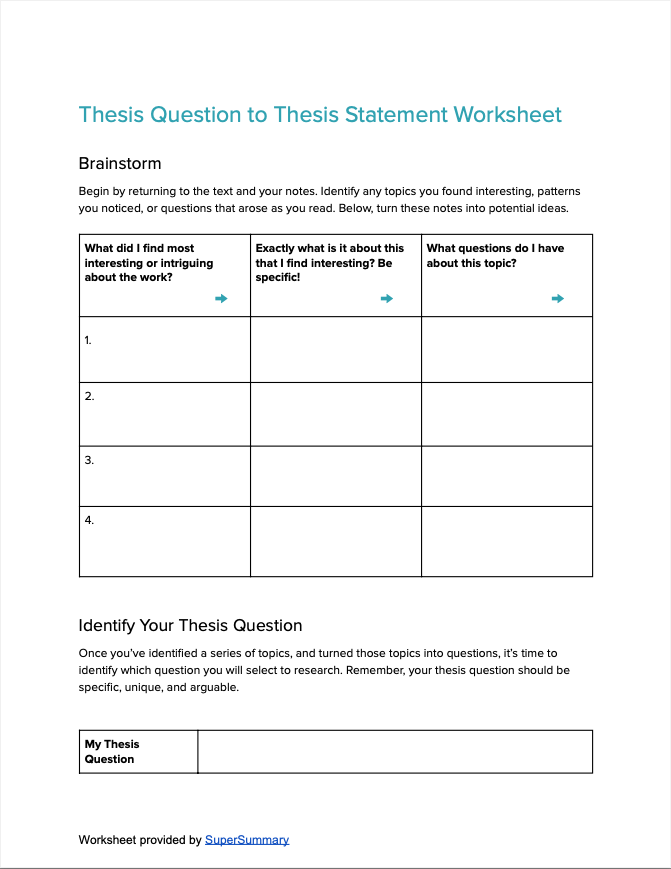
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
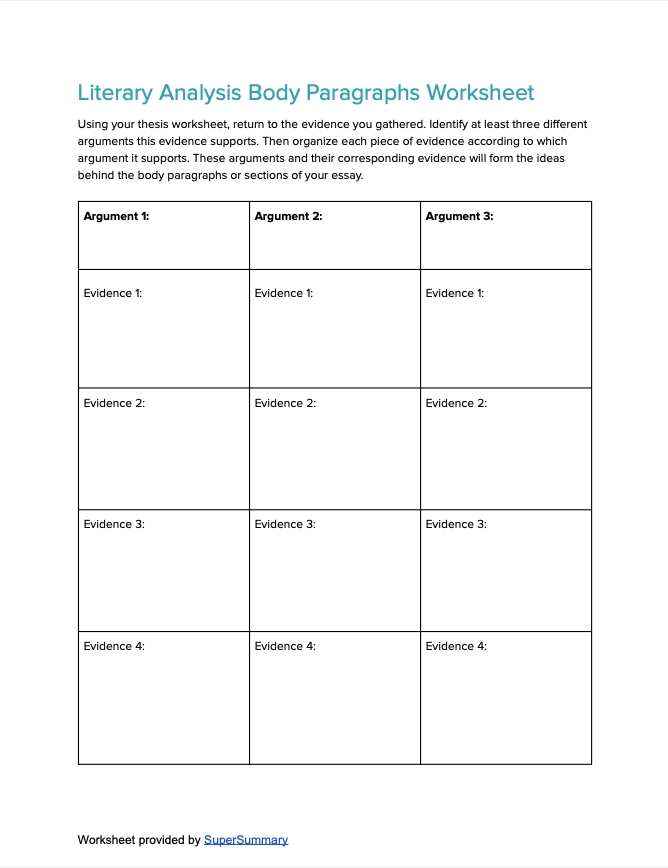
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
Example of an Insightful Literary Analysis Essay

- DESCRIPTION Student writing Insightful Literary Analysis Essay
- SOURCE Wavebreakmedia / iStock / Getty Images Plus
Get a sense of what to do right with this literary analysis essay example. A literary analysis is more than a book report ; it goes deeper into the text, examining the themes, literary devices, characters, and more. To write a great literary analysis essay, you need a good thesis and a good grasp of the novel , story, poem, or other literary work you’re discussing. You also need examples for inspiration.
Sample Literary Analysis Essay for Middle School or High School
At the middle school level, a literary analysis essay can be as short as one page. For high schoolers, the essay may become much longer as they progress. Often, this type of essay will focus on a specific area of literary analysis , such as character development or imagery within a text. Students can sometimes choose the story, novel, or book series they wish to write about, and they learn to use quotes from the text to support their thesis statements.
This sample essay focuses on the character development of Laura in the book By the Shores of Silver Lake by Laura Ingalls Wilder. The thesis statement for this literary analysis essay is, “When her eldest sister loses her sight, Laura must suddenly take on the role of the oldest child in the family and grow in maturity.”
Literary Analysis of By the Shores of Silver Lake
In By the Shores of Silver Lake , Laura Ingalls Wilder focuses on the theme of coming of age, especially as it relates to her main character, Laura. Although this theme runs throughout the novel, it’s especially apparent as Laura’s role in the family changes. The novel begins with Laura’s older sister, Mary, losing her sight due to scarlet fever. This directly affects Laura, who must go from being a middle child to suddenly assuming the role of the oldest and acting as Mary’s eyes. It’s a role she has had no experience with, and as she learns to accept it and grow to meet her responsibilities, she begins to leave childhood behind.
In previous novels in the “Little House” series, Laura and Mary have a typical sibling relationship. Mary is the oldest and is often placed in charge of Laura, such as when Pa and Ma go to town and leave them alone together in the chapter “Keeping House” in On the Banks of Plum Creek . The two sometimes fight, and Laura plainly resents Mary’s bossiness while at the same time looking up to her sister. This relationship changes at the beginning of By the Shores of Silver Lake , which opens with a simple description of Mary’s rapidly fading eyesight and eventual blindness.
Throughout the first chapters, the reader sees the impact of Mary’s blindness on the family’s daily life. Mary can no longer see to care for herself, and as the family sets out on a journey to their new homestead in South Dakota, Laura’s responsibilities increase. She must guide Mary carefully at the depot as they board the train. In the boarding house, she must cut Mary’s meat for her at dinner and help her find her silverware and food. In the wagon that takes them farther west, she must sit on the uncomfortable end of a board seat to give Mary the safer spot in the middle. At the age of 12, Laura must suddenly make countless small adjustments to show she is responsible for Mary’s safety and well-being.
Even more significantly, Laura must “see out loud” for Mary, as is described in the chapter “Riding the Cars”: “On that dreadful morning when Mary could not see even sunshine full in her eyes, Pa had said that Laura must see for her.” Being Mary’s eyes is perhaps one of the most essential duties Laura takes on. She is not only responsible for Mary’s safety and practical needs, but she must also share her outlook on the world in a way that allows Mary to experience it too. This is no light burden, although Laura carries it well.
By the end of the novel, Laura has taken on the role of eldest. She even takes over Mary’s dream of becoming a school teacher. Laura swears to Mary that she will study hard and become a teacher so she can help finance Mary’s college education. She no longer has the option of sitting back and allowing her sister to lead. Instead, she must literally guide her sister from place to place. She must offer direction with her vision and words, and she must provide a means for her sister to achieve her dreams. Although Laura is only 13 at the end of the novel, she has grown significantly in maturity due to her changing role within the family.

Click Image to View and Download PDF
- DESCRIPTION Literary Analysis Essay Example
- SOURCE Created by Beth Wiggins for LoveToKnow
Why This Essay Is Successful
There are several qualities that make this an insightful literary analysis essay:
- Clear thesis statement - The thesis statement is clear and each point in the essay relates back to it.
- Supporting evidence - The details from the text, including quotes and specific examples, help to prove the thesis.
- Good introduction - The introduction clearly establishes the literary text being discussed and the thesis that will be proven in the essay.
- Strong conclusion - The conclusion restates the thesis and uses parallel structure to give the essay a sense of importance and finality.
- Transitions - Each paragraph in this essay begins or ends with a transition , allowing the words to flow smoothly from one section to the next.
Remember Your Style
As you write your essay don’t forget to document your sources and use the proper style guide. Whether you’re writing an essay in MLA style or a different style, you’ll find that proper formatting will help you get a better grade on any literary essay.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.3: Prewriting for Literature Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40503

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
The first step in writing a literary analysis essay is actually completing the reading. Sometimes the professor will give you a prompt before you read. If this is the case, look for material which relates to the prompt as you read. If the professor did not give you a prompt, look for any material in the assigned reading that piques your interest or relates to class discussions. Highlight or underline any moments in the reading which stick out to you: something you don't understand, something that relates to a topic you care about, or something weird or surprising. Keeping track of patterns, themes, or literary devices is a great way to engage with a work of literature and prepare for a future discussion or essay.
Completing the Reading
One time, I was talking with my sister-in-law about her experience in nursing school. Whereas her brother had barely achieved Cs in college, she somehow maintained a 4.0, even though she was simultaneously working and caring for her two young daughters.
"What is your secret to success?" I asked.
"Actually doing the assigned readings," she laughed, "most of my peers didn't. And it showed."
As a college professor who teaches reading-heavy classes, this is not a shock to me. After all, most students taking the required writing and literature courses do not wish to become English majors. They sometimes see their literature class as a means to an end: at best, a stepping stone towards their future career; at worst, a time-suck of hoops to jump through. Also, because of today's gig economy, many students are juggling multiple jobs in addition to multiple college classes. This makes it tempting for students to want to skip the readings and just read SparkNotes. Truth be told, students who pursue this method, depending on their BSing skills, might be able to pass a literature class. But for the vast majority of students, this popular high school tactic will not work at the college level. More importantly, it means students miss out on many of the exciting benefits of diving deep into analysis, discussion, and engaging with the text.
Of course, I want my students to fall in love with the written word. I want my passion for literature to be contagious, to light students' hearts and minds on fire with a hunger for the beauty of syntax and diction and literary devices. But I also completely understand that students have limited time. Therefore, I recommend prioritizing the writing process so students can make the most efficient use of their time. In the long run, while it might seem like skipping the readings saves time, completing the readings is actually the best way for students to optimize their time. This is because a strong essay depends on a deep understanding of the literature. If the class features examinations, these almost always test students on whether they completed and understand the readings. Finally, class will be more fun for students if they understand what their peers are talking about in class discussion, and what their professor is talking about during lectures.
Students who complete the readings and annotate as they go will find it much easier to flip back through their notes to find relevant quotations and information. They usually break the readings into small, manageable chunks of twenty to thirty minutes at a time. This helps their brains absorb the information better and retain information for writing and tests.
Students skipping reading often end up performing more work when it comes to writing an essay because they will spend so much time looking up text summaries on the internet (which may or may not be accurate or pertain to the intricacies of the assignment). They will also have to go back and re-read the text to find quotations that fit their prompt. Their essays usually fail because they do not fulfill the in-depth analysis required by the assignments.
So, long story short: even the most practically-minded, time-crunched students would do well to perform the readings. And, while in pursuit of success, a previously literature-averse student might find themselves liking literature more than they thought they would. Just like watching a favorite movie or show, reading a good book can be fun and relaxing!
Active versus Passive Reading
Many students, when first reading academic material, read it like they would a timeline of Facebook or Instagram posts: not fully attentive, skimming over the material in search of something interesting. Or they might read them with full attention, but simply read without questioning or engaging with the material. The difference between a student who is successful in a literature class and a student who is not successful is often that the successful student participates in active reading.
In a literature class, students encounter a lot of literature, written by many different authors. Annotating, or taking notes on the assigned literature as you read, is a way to have a conversation with the reading. This helps you better absorb the material and engage with the text on a deeper level. There are several annotation methods. These are like tools in a student's learning utility belt. Try them all out to discover which tools or combinations of tools help you learn best!
Margin Notes & Highlighting
One of the best ways to interact with a text is to write notes as you read. Underlining and/or highlighting relevant passages, yes, but also responding to the text in the margins. For instance, if a character I love makes a bad choice (like Sydney Carton in Charles Dickens' A Tale of Two Cities ), I will write, "Nooooo, Sydney Carton, don't sacrifice yourself for Lucie's sake!" This helps me remember the events of the plot. Many students also find it helpful to summarize each chapter or section of the literature as they read it. For example, a student said it was helpful for them to draw a picture representing every stanza of "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud" by William Wordsworth to help them understand what was being said. Other ideas include:
- Circling unfamiliar words
- Writing questions in the margins
- Color-coded highlighting to track various literary devices (i.e., blue for metaphors, pink for symbolism, and so forth)
Sticky Notes
For students who would like to sell their textbooks back to the bookstore, writing notes in the margins might not be a practical choice, as it may devalue the textbook or the bookstore may refuse to take it back. For these students, I recommend using sticky notes instead. If sticky notes are cost-prohibitive, most colleges have plenty of scrap paper students can use as bookmarks to stick between pages. This is also an eco-friendly way to re-use paper!
Reading Journal
Another option many students find helpful is keeping a reading journal. Students can write notes in their journals as they read. This helps students keep track of readings and materials in a chronological fashion. Just like when annotating the text directly or upon sticky notes, the most effective use of a reading journal, for learning purposes, is going to be active engagement with the text rather than passive absorption. That is, try to summarize the plot of what you read every time you read. Also, ask questions about the text. If you can record quotes and paraphrase along with in-text parenthetical citations (i.e., the page number where you found the material), this will optimize your time because you already have quotes ready to go when you write an essay!
Example of an Annotated Passage
Using the guidelines above, let's consider this excerpt from a scholarly article by Jacob Michael Leland, "'Yes, That is a Roll of Bills in My Pocket': The Economy of Masculinity in The Sun Also Rises."
A great deal of critical attention has been paid to masculine agency and its displacement in Ernest Hemingway's fiction. The story is familiar by now: the Hemingway hero loses some version of his maleness to the first World War and he replaces it with a tool—in Upper Michigan, a fishing rod or a pocket knife; in Africa, a hunting rifle—a new object that emblematizes his mastery over his surroundings and whose status as a fetishized commodity and Freudian symbolic significance is something less than subtle. In The Sun Also Rises , this pattern repeats itself, but with important differences that arise from the novel's cosmopolitan European setting. Mastery over the elements, here, has more to do with economic agency and control over social relationships than with nature and survival. The stakes are different, too; in the modern European city, the Hemingway hero recovers not only masculinity but also American identity in social and sexual interaction. (37)
In researching The Sun Also Rises for a project, Ling Ti found Leland's article. What follows is her annotated copy of the above excerpt:

Reflecting on Assigned Literature
Studies show reflecting on reading is one of the best ways to learn. This is called metacognition, or thinking about thinking. It is a way to keep track of the knowledge you have learned as you go. Students who reflect on their reading and learning tend to, as a whole, perform better on essays and examinations. So how can you take advantage of this skill?
If you have a prompt, choose a prompt and read through the assigned literature again, noting any quotes which may relate to the assigned topic. It is recommended at this point that you keep track of your observations in a document: either on a computer (Word, Google Docs) or on a physical piece of paper. Write down any quotations along with page numbers (fiction, nonfiction), line numbers (poem), or act, scene, line numbers (drama). This way, you have all potential evidence in one place, and it makes for easy in-text citations when it comes to knitting the evidence together to form an essay. In fact, it is highly recommended that students start an informal Works Cited page to keep track of every source consulted. This makes it much easier to avoid plagiarism by practicing ethical citation habits. For more information about citations, please see the Citations and Formatting Chapter.
Start with a hypothesis or focus but be willing to refine, adjust, or completely discard it if new evidence refutes it. An essay is not a stagnant piece, but a living, breathing thought experiment. Many students feel reluctant to change their thesis or major parts of their essays because they are afraid it means the previous writing was wasted. As a professional writer, editor, and scholar, I want to clue students in on a secret:
There is no such thing as wasted writing.
Even writing that does not end up in the final draft is worthwhile because it is a chance to experiment with ideas. It helps students find a path toward stronger ideas. Just like a gardener might allow branches of a tree to grow to see which ones bear flowers and fruit and then prune the weak, unproductive branches to make the plant stronger and more beautiful, so too must a writer be willing to cut out branches of reasoning which no longer serve the essay. But before you know which ideas or thoughts are worth pursuing, you first have to give them space to grow. You never know what idea branches might prove fruitful!
Contributors and Attributions
- Adapted from "Reading Like a Professional" in Writing and Literature: Composition as Inquiry, Learning, Thinking, and Communication by Dr. Tanya Long Bennett of the University of North Georgia, CC BY-SA 4.0

75 Short Short Stories
Stories to enjoy when you have five minutes to spare, grouped by category to suit your mood: Witty Stories , Introspective Stories , Morality Tales , Other-Worldly Stories , Feel-Good/Love Stories , Dramatic Stories , and Political Farce Stories
Had a rough day? Cheer up with 50 Great Feel-Good Stories and a generous helping of comforting Foodie Stories
Witty Stories

Introspective Stories

Morality Tales

Other-Worldly Stories

Feel-Good/Love Stories

Dramatic Stories

Political Farce
Looking for more? Check out our Favorite Short Stories Collection . You may also enjoy 100 Great Poems Read about the authors' own stories in American Biographies

- short story
Short Story Literature
The short story is a form of literature that has been around for centuries. It offers readers the opportunity to experience different worlds and characters in a condensed format, often focusing on one particular moment or event. A good short story can captivate its audience and leave them wanting more, making it an invaluable tool for writers looking to tell stories within a limited space. This article will explore what makes a great short story, as well as some examples from classic literature.
What Makes a Great Short Story?
At their core, all great stories have certain elements in common: interesting characters, vivid settings, powerful conflicts, and their resolution (or lack thereof). In the case of short stories, however, there are other key aspects that distinguish them from longer works of fiction. They must be concise, yet engaging enough to draw readers into the narrative within just a few pages. The writer needs to quickly create an atmosphere by using strong descriptions without sacrificing clarity or going off track too much; this means choosing words carefully, with each sentence contributing something meaningful towards telling the tale at hand rather than getting bogged down with unnecessary details that could detract from the story.
The best writers know how to capture emotion through succinct yet evocative language—showing rather than telling whenever possible—while still providing sufficient background information. This helps readers understand why the events are happening, even if they don't fully grasp everything right away (this can be especially tricky when dealing with shorter pieces). Additionally, many successful authors also utilize creative techniques such as symbolism or unreliable narrators or characters whose perspectives challenge our preconceived notions about life itself, thereby allowing us a glimpse into alternative realities where anything might happen. Ultimately, no matter what approach is taken, all these components need to work together seamlessly before any kind of true masterpiece can emerge from them. They need to be combined with effortless grace, like the fine artistry of a painting coming alive on canvas.
Examples From Classic Literature
There are countless examples throughout history showcasing the incredibly skillful use of writing craftsmanship, used expressively in storytelling through a mastery of technique displayed in various forms across genres. These include classic literature's quality works: from Edgar Allen Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado" and Nathaniel Hawthorne's "Young Goodman Brown"—both of which capture terror, suspense, thriller, and horror—to personal, individualized intimate accounts such as Eudora Welty's "A Worn Path", Katherine Mansfield's "Miss Brill", Ernest Hemingway's "Hills Like White Elephants", and Flannery O'Connor's "W All of these provide unique snapshots of the different lives lived by people who experience struggle, triumph, heartache, joy, love, hate, sadness, anger, fear, anxiety, hope, courage, despair, faith, or redemption. Each of them encapsulates an entire universe of emotions, thoughts, and feelings into two paragraphs or less. While this is obviously a difficult task, these amazing authors accomplish this masterfully and prove time and again the power of brevity, that beauty lies within simplicity, and that the complexity of the human condition can be understood by devoting proper attention and care, and by employing properly crafted words.
Thank You, Ma'am is a short story written by Langston Hughes in 1958. It follows the story of Mrs. Luella Bates Washington Jones and her encounter with an adolescent boy who attempts to steal her purse late at night on the streets of Harlem. Instead of punishing him for his crime, she takes him home and teaches him an important lesson about respect and kindness that he will never forget. This classic piece of literature has become one of Hughes's most popular works due to its powerful themes surrounding morality, empathy, compassion, and redemption.
Lamb to the Slaughter is a classic short story written by Roald Dahl in 1954. It tells the story of Mary Maloney, an expectant mother who murders her husband with a frozen leg of lamb when he unexpectedly announces that he is leaving her.
The Tell-Tale Heart is a short story by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in 1843. It follows an unnamed narrator who insists on his sanity after murdering an old man with a “vulture eye.” In the tale, the narrator attempts to convince readers of his mental stability while describing a murder he committed and disposing of its evidence.
A Rose for Emily by William Faulkner is a classic example of Southern Gothic literature. Published in 1930, the short story explores themes such as death, loneliness, and isolation through its protagonist, Miss Emily Grierson. Set in a small Mississippi town at the turn of the century, this dark tale follows an eccentric woman’s life over four decades. The narrative style is highly experimental; it jumps back and forth between past and present to slowly reveal secrets from her mysterious past.
J.D. Salinger's short story, "A Perfect Day for Bananafish," is a classic piece of literature that examines the themes of alienation and psychological struggle in post-World War II America. The protagonist, Seymour Glass, is an isolated young man who has recently returned from war with deep emotional wounds. He spends his day at the beach, where he meets Muriel and her daughter, Sybil. While there, Seymour engages in a playful interaction with Sybil by playing bananafish—a game involving him pretending to be a fish eating bananas out of her shoe—which ultimately reveals his profound loneliness and desire to connect with others despite his inability to do so due to mental illness or trauma. In this way, "A Perfect Day for Bananafish" explores how even during times of joyous playfulness, we can still feel disconnected from those around us because of our inner struggles and experiences that prevent us from fully engaging with life as it should be lived.
A Jury of Her Peers is a classic short story by American author Susan Glaspell. Written in 1916, the story explores gender roles and social expectations through its examination of two women's different reactions to an event that occurs within their community. The narrative follows Mrs Hale and Mrs Peters as they investigate the scene surrounding the death of Minnie Wright, who is accused of murdering her husband. As they explore the home more closely, it becomes clear that there are clues that may exonerate Minnie from any wrongdoing; however, these remain hidden to those outside her immediate circle.
Ursula K. Le Guin's short story "The Ones Who Walk Away from Omelas" is an allegory of morality and the concept of utopia. It tells the story of a utopian society that lives in perfect harmony, where everyone is happy and prosperous—except for one child who suffers greatly in order to ensure this happiness. This suffering serves as a reminder that even paradise has its dark side; it challenges readers to consider what they are willing to accept in exchange for their own personal peace and comfort.
In the world of literature, "What We Talk About When We Talk About Love" is a short story by Raymond Carver that explores the complexities and nuances of love. The title comes from a line in Gertrude Stein's poem Sacred Emily that reads: "What is the answer?/ In that there is no answer / What was the question? / Oh yes, what is love?'" This phrase captures both the confusion and uncertainty associated with understanding what it means to be in love.
- Thank You, M'am
- Lamb to the Slaughter
- The Tell-Tale Heart
- A Rose for Emily
- A Perfect Day for Bananafish
- A Jury of Her Peers
- The Ones Who Walk Away From Omelas
- What We Talk About When We Talk About Love
- The Fall of the House of Usher
- The Pit and the Pendulum
- The Lottery
- Legend of Sleepy Hollow
- The Cask of Amontillado
- The Landlady
- The Monkey's Paw
- The Masque of the Red Death
- The Story of an Hour
- Where Are You Going, Where Have You Been?
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- A Good Man Is Hard to Find
- The Lady, or the Tiger?
- An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge
- Young Goodman Brown
- To Build a Fire
- Hills Like White Elephants
- The Scarlet Ibis
When we read stories sometimes, or even when we may watch a movie you realize the author uses something called symbolism. When using symbolism in stories you can use an object or a place to represent the true meaning of what is really trying to be to be told in the story. In the two stories, “The story of an Hour” and “The Lottery” the two authors of these short stories incorporate symbolism all throughout their short stories. Symbolism play a huge role in both of the amazing stories. In the
In the short stories, “The Story of an Hour” by Kate Chopin and “Wildwood” by Junot Diaz, there are a similar type of theme and main character. Both short stories utilize a theme of freedom and a main character that goes along with the theme. The main character is one that is “held back” and wants to have freedom, but there is an antagonist that is preventing that from happening. However, towards the end of the story, there is a plot twist and change in the mindset of the main character. Both stories
their suspenseful text. In various short stories, mystery elements create suspense in a variety of ways. The short stories, “Lamb to the Slaughter,” by Roald Dahl, “The Adventure of the Speckled Band,” by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, and “Invitation to a Murder,” by Josh Pachter create suspense as a result of the mystery elements they contain. “Lamb to the Slaughter” is one of the many examples of texts that includes suspense, which the author created throughout the story. First off, Roald Dahl’s shocking
We have read two short stories, “The Ravine” and “Fine”. In both, they have very strong main characters who deal with many conflicts. The stories revolve around the idea of facing fear, which can involve some internal conflicts when you have to choose what to do. Both stories have very different settings and conflicts, yet they are very similar in some ways, which you will find. The first story we read was titled “The Ravine”. Vinny, the main character, experienced some tough decisions to make
writers, who write masterpieces, wisely use “the elements of the short story” to engage readers. Character, setting, plot, conflict, theme, and other elements are practically used to create climax, bring up questions, form suspense or mystery, and make the story captivating. “The Office” by Alice Munro and “A Rose for Emily” by William Faulkner are epitomes of greatly written short stories due to perfect usage of “the elements of the short story.” Both authors use setting, character, and point of view to
Kimberly Hinojos Paper 2: Causal Claim for Invierno 02/20/18 In the short story Invierno written by Junot Diaz, the main character Yunior and his family move to the United States from the Dominican Republic during the winter and become frustrated with the limitations set upon them by his father. In this story, Yunior speaks about the change that moving to New Jersey has on his mother and his perspective. Further, he goes into great detail about how he and his mother and brother are locked in their

COACHING + PUBLISHING

FORMATTING + DESIGN

FREELANCE COMMUNITY
Where to Submit Short Stories: 30 Options for Writers
by Farrah Daniel | Aug 23, 2023

Good news! You can finally stop stressing about where and how to submit your short stories—we compiled a list for you.
Trying to find a sense of community comes with the territory of being a writer. Whether you’re looking for the right writing contests or residencies , it’s hard to know where to begin and how to find the right home for your personal work.
In this guide, you’ll find 30+ magazines and literary journals that publish short fiction (and nonfiction). Our list includes a mix of publications across various genres and styles, ranging from prestigious, highly competitive options to those specifically seeking new and emerging voices.
Plus, international writers, a lot of these are open to you, too!
Table of Contents
30 outlets that publish short stories.
While we’ll give you a brief idea of the flavor of each magazine and site, you’ll definitely want to spend some time reading your target publications before submitting to become familiar with the sort of pieces they prefer.
Many of these short story publishers accept original submissions that are simultaneously submitted elsewhere. Just make sure to withdraw your submitted submissions if you get your story published!
Ready to get started? Here’s where to submit short stories.
1. The New Yorker
Might as well start with a bang, right? Adding publication in The New Yorker to your portfolio puts you in a whole new league, though it won’t be easy. Author David. B. Comfort calculated the odds of acceptance at 0.0000416 percent !
It accepts both standard short fiction as well as humorous short fiction for the “Shouts & Murmurs” section. No word counts are mentioned, though a quick scan of the column shows most pieces are 600 to 1,000 words.
Deadline: Open
Payment: Huge bragging rights; pay for unsolicited submissions isn’t specified. As of this post’s publication, no rates specifically for short stories
2. The Atlantic
Another highly respected magazine, The Atlantic , publishes both big names and emerging writers in fiction and nonfiction. Submission guidelines advise, “A general familiarity with what we have published in the past is the best guide to what we’re looking for.”
Deadline: Open. Fiction stories are submitted to [email protected]
Payment: Unsolicited submissions are generally unpaid
3. The Threepenny Review
The 3P Review is quarterly arts magazine focuses on literature, arts and society, memoir and essay. Short stories should be no more than 4,000 words, while submissions to the “Table Talk” section (pithy, irreverent and humorous musings on culture, art, politics and life) should be 1,000 words or less.
Deadline: January 1 to April 30
Payment: $400 for short stories; $200 for Table Talk pieces
4. One Story
One Story is just what the name says: a literary magazine that publishes one great short story every three to four weeks , and nothing more.
Its main criteria for a great short story ? One “that leaves readers feeling satisfied and [is] strong enough to stand alone.” Stories can be any style or subject but should be between 3,000 and 8,000 words.
Deadline: January 15 – May 31 | September 3 – November 14
Payment: $500 plus 25 contributor copies
Thought-provoking is the name of the game if you want to get published in AGNI . Its editors look for pieces that hold a mirror up to the world around us and engage in a larger, ongoing cultural conversation about nature, mankind, the society we live in and more.
There are no word limits, but shorter is generally better; “The longer a piece is, the better it needs to be to justify taking up so much space in the magazine,” note the submission guidelines.
Deadline: Open September 1 to December 15; February 15 to May 31
Payment: $10 per printed page (up to a max of $150) plus a year’s subscription, two contributor’s copies and four gift copies

6. Kindle Vella
Rather than seeking a magazine or journals editorial approval, you can publish directly to Kindle Vella’s short story program. Here, your work will go directly to market and its success will be determined by the general public, not by an editorial team. You also don’t have to wait months on a response as to whether your short story will be published. You can upload and be published on Kindle Vella in under 48 hours.
For a full review of Kindle Vella, read this article .
Payment: Royalties on KDP reads
7. Barrelhouse
Published by an independent nonprofit literary organization, Barrelhouse’s biannual print journal and online issue seek to “bridge the gap between serious art and pop culture.” Its editors look for quality writing that’s also edgy and funny—as they say, they “want to be your weird Internet friend.”
There’s no hard word count, but try to keep your submission under 8,000 words.
Deadline: Currently open for book reviews only. Check the webpage to see all open categories and sign up for the email list to receive updates on submissions
Payment: $50 to print and online contributors; print contributors also receive two contributor copies
8. The Cincinnati Review
The Cincinnati Review publishes work by writers of all genres and at all points of their careers. Its editors want “work that has energy,” that is “rich in language and plot structure” and “that’s not just ecstatic, but that makes its reader feel ecstatic, too.”
Fiction and nonfiction submissions should be no more than 40 double-spaced pages.
Deadline: The review accepts submissions during three time periods, September, December, and May. Submit earlier in the month because they will stop accepting submissions when their cap is reached.
Payment: $25 per page for prose in journal
9. The First Line
This cool quarterly is all about jumpstarting that pesky writer’s block . Each issue of The First Line contains short fiction stories (300 to 5,000 words) that each begin with the same pre-assigned first line.
If you really want to get ambitious, you can also write a four-part story that uses each of that year’s first lines (which is due by the next year’s spring issue deadline). To find each issue’s assigned first line, check out the submission guidelines.
Deadline: February 1 (spring); May 1 (summer); August 1 (fall); November 1 (winter)
Payment: $25 to $50 (fiction); $25 (nonfiction) plus a contributor’s copy
10. The Georgia Review
Another one high on the prestige list, The Georgia Review features a wide variety of essays, fiction, book reviews, and more across a wide range of topics. You can read specific requirements for each in the submission guidelines, but the common theme among them all is quality, quality, quality.
Bear in mind submitting requires a $3 processing fee if you’re not a subscriber.
Deadline: Opens on August 15
Payment: $50 per printed page; contributors also receive a one-year subscription to the quarterly and a 50% discount on additional copies of that issue
Freelance Writer’s Pitch Checklist Grab it for free 👇
Convince more editors to say YES to your pitches!
We’ll also send you our weekly newsletter, which offers helpful advice for freelancing and publishing. You can unsubscribe at any time.
11. Boulevard Magazine
Boulevard Magazine is always on the lookout for “less experienced or unpublished writers with exceptional promise.” It accepts prose pieces (fiction and nonfiction) up to 8,000 words (note: no science fiction, erotica, westerns, horror, romance or children’s stories).
There is an online submission fee of $3. Free if submitting by post.
Deadline: Open November 1 to May 1
Payment: $100 to $300
Story Magazine is, you guessed it, all about the story, whatever shape it takes. Each issue—printed tri-annually in February, June, and November—is “devoted to the complex and diverse world of narrative with a focus on fiction and nonfiction.” Luckily, you don’t have to stick to any formal guidelines in regards to style, content, or even length; they consider all “short” narrative length work, from flash fiction to novellas. There is a $3 submission fee.
Payment: Regular payment rate is $10 per page upon publication
13. Vestal Review
Prefer to keep your short stories extra short ? Vestal Review publishes flash fiction of no more than 500 words. Its editors are open to all genres except for syrupy romance, hard science fiction and children’s stories, and they have a special fondness for humor. R-rated content is OK, but stay away from anything too racy, gory or obscene.
There is a submission fee of $2 for each submission.
Deadline: Submission periods are February to May and August to November
Payment: The author of an accepted print submission gets $25 and a print copy; $10 for accepted web submissions
14. Flash Fiction Online
Flash Fiction Online allows for slightly longer flash stories—between 500 and 1,000 words. Its editors like sci-fi and fantasy but are open to all genres (except for nonfiction and poetry!). As with Vestal, stay away from the heavier stuff like erotica and violence. What they’re looking for is developed, empathetic characters and discernible, resolved plots. Unlike many of the other publications, they will accept previously published work, which you’d submit in the reprint category.
Deadline: Open each month for submissions from the 1st to the 21st of the month.
Payment: $80 per story; two cents per word for reprints
15. Black Warrior Review
Black Warrior Review publishes a mix of work by up-and-coming writers and nationally known names. Fiction pieces of up to 7,000 words should be innovative, challenging, and unique; its editors value “absurdity, hybridity, the magical [and] the stark.”
BWR also accepts flash fiction under 1,000 words and nonfiction pieces (up to 7,000 words) that complicate western traditions of truth-telling, and “foregrounds the history of emotions rather than the history of facts.” There is a $3 submission fee.
Deadline: Submission periods are December 1 to March 1 and June 1 to September 1
Payment: A one-year subscription to BWR and a nominal lump-sum fee (amount not disclosed in its guidelines)

16. The Sun Magazine
The Sun Magazine offers some of the biggest payments we’ve seen, and while its guidelines specifically mention personal writing and provocative political/cultural pieces, they also say editors are “open to just about anything.”
Works should run no more than 7,000 words. Submit something the editors love, and you could get a nice payday.
Payment: $300 to $2,000
17. Virginia Quarterly (VQR)
A diverse publication that features both award-winning and emerging writers, VQR accepts short fiction (3,500 to 8,000 words) but is not a fan of genre work like romance, sci-fi and fantasy. It also takes nonfiction (3,500 to 9,000 words) like travel essays that examine the world around us.
Deadline: Submissions read July 1 to July 31
Payment: Generally $1,000 and above for short fiction and prose (approximately 25 cents per word) with higher rates for investigative reporting; $100 to $200 for content published online
18. Ploughshares
Ploughshares’ award-winning literary journal is published by Boston’s Emerson College. They accept fiction and nonfiction under 7,500 words and require a $3 service fee if you submit online (it’s free to submit by mail, though they prefer digital submissions). You can also submit your significantly longer work (7,500 to 20,000 words) to the Ploughshares Solos series !
Deadline: June 1 to January 15 at noon Eastern Time
Payment: $45 per printed page (for a minimum of $90 per title and a maximum of $450 per author); plus two contributor copies of the issue and a one-year subscription
19. Carve Magazine
Writers are in for a treat! Carve Magazine accepts poetry, short stories and nonfiction submissions, not exceeding 10,000 words. They accept literary fiction only and are not open to genre fiction (i.e. thriller, horror, romance, etc.). They also accept novel excerpts but only those that can stand alone in the story. There’s a $3 submission fee, but you can subscribe to the magazine to skirt past it.
Deadline: Open all-year-round from anywhere in the world
Payment: Pays $100 and offers feedback on 5 to 10% of declined submissions
20. Daily Science Fiction
Sci-fi and fantasy writers, this one’s for you. Daily Science Fiction is looking for character-driven fiction, and the shorter, the better. While their word count range is 100 to 1,500 words, they might consider flash series—AKA three or more flash tales built around a common theme.
Deadline: Open except for the period between December 24 to January 2
Payment: Eight cents per word, with the possibility of additional pay for reprints in themed Daily Science Fiction anthologies
JMWW is a literary journal that publishes fiction stories with up to 300 words and flash fiction of no longer than 1.500 words, and it’s open to any genre as long as the story is well-crafted. To up your chances of catching the editors’ eyes, note that they like “strong characters whose motivations are not always known to us but can be explained within the confines of common sense,” as well as surprise endings (nothing gimmicky).
Payment: No pay specified
22. Smokelong Quarterly
SmokeLong , a literary mag devoted to flash fiction, publishes flash narratives up to 1000 words—and that’s a firm word limit, so be sure to stick to it. The SLQ aesthetic remains “an ever-changing, ever-elusive set of principles,” but it most likely has to do with these kinds of things: language that surprises and excites, narratives that strive toward something other than a final punch line or twist, and more which you can see in the submission guidelines. Think you can handle that?
Payment: $50 per story upon publication in the quarterly issue
23. The Master’s Review
The Master’s Review’s New Voices category is open to any new or emerging author who has not published a work of fiction or narrative nonfiction of novel length—not including authors with short story collections. Submit your flash fiction of 1,000 words or your piece of fiction or narrative nonfiction of up to 7,000 words. Though, editors are honest: There are no submission fees, but they’re highly selective.
Payment: A flat rate of $100 for flash-length stories; $200 for short fiction
24. Ruminate Magazine
Both emerging and established writers are encouraged to submit fiction or creative nonfiction stories that “engages the contemplative spirit of our journal and embraces curiosity and discovery rather than resolution.” Both genres are capped at a word count of 5,500 words.
Want another option? There’s no pay for this one (just contributor copies), but The Waking is Ruminate Magazine’s online publication space and they’re looking for short-form prose, fiction and nonfiction that is “holy, nutritious and crucial.” Keep your submissions to 1,000 words or less.
Deadline: July 2, 2020; fiction reading periods are April 1 to June 30; January 15 to June 30 for nonfiction
Payment: $20 per 400 words, plus contributor copies
25. Asimov’s Science Fiction
Have you ever wondered where George R. R. Martin’s Daenerys Targaryen first appeared on the printed page? Well, this is it! An established market for science fiction stories, Asimov’s Science Fiction magazine has won numerous Hugo and Nebula Awards, and the writers they’ve published have led successful careers .
They want you to submit your character-oriented, “serious, thoughtful, yet accessible fiction,” but there’s room for humor as well. While science fiction dominates what the magazine publishes, you’re welcome to submit borderline fantasy, slipstream and surreal fiction—steer clear of sword and sorcery, explicit sex or violence. While there’s no specific word count, ASF seldom buys stories shorter than 1,000 words or longer than 20,000 words.
Payment: 8 to 10 cents per word for short stories up to 7,500 words; 8 cents per word for each word over 7,500
Check out this helpful video from our friends at selfpublishing.com for writing a short story.
26. Slice Magazine
Got a fresh voice and a compelling story to share? This one’s for you. To bridge the gap between emerging and established authors, SLICE offers a space where both are published side-by-side. In each issue, a specific cultural theme becomes the catalyst for articles, interviews, stories and poetry from renowned writers and lesser-known voices alike. Short fiction and nonfiction submissions should be 5,000 words max.
Deadline: Slice published their final issue in the fall of 2021 and are no longer looking for submissions
Payment: $400 for stories and essays; $150 for flash fiction pieces; $100 for poems
27. Cricket Media
Cricket Media wants to publish your finest quality writing for children of all ages in one of its four literary magazines—you have options! Open to submissions from writers of every level of experience, CM’s mags are interested in a lot of things, no matter what genre: realistic contemporary fiction, historical fiction, science fiction and fantasy, folk tales, myths and legends, humor, and even westerns. Their advice? Focus on telling a good story that’s well-plotted, character-driven and has a satisfying conclusion.
Most stories are 1200 to 1800 words in length; however, they occasionally serialize longer stories of up to 6,000 words.
Deadline: Varies; check the guidelines to learn the deadlines for each lit mag
Payment: Up to 25 cents per word
28. The Dark Sire
Horror writers, you’re up! A fairly new literary journal, The Dark Sire is a quarterly online and print journal that “explores speculative fiction works for enthusiasts” of gothic, horror, fantasy and psychological realism in short fiction, poetry and art. Subjects of particular interest include: vampires, monsters, old castles, dragons, magic, mental illness, hell, disease and decay of society. No word count.
Payment: None, but they promote writers through author events , social media outreach and the (in development) TDS podcast
29. The Common
Based at Amherst College, The Common is an award-winning print and digital literary journal published biannually in the fall and spring. They seek fiction and nonfiction stories and dispatches (800-word notes, news and impressions from around the world) that “embody a strong sense of place: pieces in which the setting is crucial to character, narrative, mood and language.” Stick to a 10,000 word-count and you’re solid. There is a $3 submission fee.
Deadline: Reading periods are March 1 to June 1 and September 1 to December 1; subscribers can submit for free year-round
Payment: $100 for fiction and nonfiction submissions; $50 per dispatch
30. The Antioch Review
The Antioch Review is currently paused and not accepting submissions. Check back in the future.
The Antioch Review rarely publishes more than three short stories per issue, but its editors are open to new as well as established writers. Authors published here often wind up in Best American anthologies and as the recipients of Pushcart prizes.
To make the cut, editors say, “It is the story that counts, a story worthy of the serious attention of the intelligent reader, a story that is compelling, written with distinction.” Word count is flexible, but pieces tend to be under 5,000.
Deadline: When operational, open except between June 1 to August 31. No electronic submissions
Payment: $20 per printed page plus two contributor copies
31. Literary Orphans
Literary Orphans is currently paused and not accepting submissions. Check back in the future.
Fiction comes first for this short fiction and art magazine. Editors want your fiction of any genre, but they have a need for micro-fiction, flash, and short stories that are 2,000 words or less (but 1,500 is their sweet spot!). Creative nonfiction is also accepted for the bi-monthly Literary Orphans issue on the main website; just keep your story to 5,000 words max. Plus, teens under 19, there’s a category for you, too. Submit a story of no more than 3,000 words to its “TEEN SPIRIT” section
Because they receive a high volume of submissions, editors ask that you submit your *best* piece. But here’s where it gets interesting: If you can’t choose just one, send both! (As long as both stories combined don’t surpass 2,000 words.)
Deadline: Currently no open calls for submission, but check back in the future!
Payment: Not specified
Short Story Submission Tips
With hard work and patience you can see your short stories published!
Here are a few tips to keep in mind when looking to submit short stories
- Take time to read through the literary magazines before you submit . You will have a better idea of what they are looking and know which magazines fit best with your writing style
- Read the submission details before you submit . Each publication has different specifications for submissions – make sure you fulfill their requirements
- Be patient . Many of these publications have a small team and a lot of submissions. It is normal to wait several months before hearing whether an article will be published or not
- Keep track of which articles you have submitted to which publications . Because can submit the same short story to multiple publications, you will need to withdraw that article if it gets published. You don’t want to accidentally publish the same piece in multiple places
- Don’t give up! While you might receive multiple rejections before you get your first piece published, with hard work it will be worth the wait once you get your first piece in print!
The original version of this story was written by Kelly Gurnett . We updated the post so it’s more useful for our readers.
Photo via Nito/ Shutterstock
Craft Essays
- Teaching Resources

Flying Still Matters

Like Nothing Ever Happened

Switched On

From Scratch

“Taste Test!”

Puddle Jumper (excerpt)

Maternity as a Country

Driving Home from the Kink Club

after creating change

Issue 75 / January 2024

Teaching with Brevity
The brevity blog.
- The Art of Traumedy Writing: Or, How to Make Your Mother Cry at Your Life, and Laugh at Your Death
- The Magic Question: Getting Real Feedback You Can Actually Use
- Mao’s Head: The Quest for the Perfect Title
- Get On Board: Keeping Readers on the Dramatic Train
- Crabby Hermits and Simone Biles: Using Satire and Experimental Forms

© 2024 Brevity: A Journal of Concise Literary Nonfiction. All Rights Reserved!
Designed by WPSHOWER
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
John Barth, towering literary figure and revered mentor, dies at 93
Barth, a johns hopkins graduate who later taught at his alma mater for more than two decades, was known for his postmodernist, unpredictable fiction and his exacting, generous teaching.
By Rachel Wallach
John Barth, A&S '51, '52 (MA), groundbreaking and prolific author, revered teacher, and professor emeritus in The Writing Seminars at Johns Hopkins University, died Tuesday. He was 93.
Image caption: John Barth
Best known for his postmodernist, unpredictable fiction and his exacting and generous teaching, Barth served on the Johns Hopkins faculty from 1973 until he retired in 1995. He is the author of 17 novels and collections of short fiction and three collections of essays. He won a National Book Award, F. Scott Fitzgerald Award for Outstanding Achievement in American Fiction, a Lannan Foundation Lifetime Achievement Award, and the PEN/Malamud Award for Excellence in the Short Story.
"Not just a master of fiction and of the literary essay, John Barth was a rhetorician on the order of a Samuel Johnson," said Jean McGarry , A&S '83 (MA), Academy Professor and Barth's former student and then colleague in The Writing Seminars. "Well-read and deeply thoughtful, it was a pleasure to be in his company, whether as his student or colleague. Passionate about literature, and with peerless taste, he was full of wit and wisdom, and had an almost scientific gift for anatomizing the elements of fiction: bones, flesh, nerves, heart, and lungs. He was also funny, tall, and handsome, and never missed a trick. In a rare way, he epitomized his fiction in his own gallant and witty person."
Barth's upbringing on Maryland's Eastern Shore left a powerful echo in the coastal settings of many of his books as well as the understated, southern lilt to his voice. After almost embarking on a career as a jazz drummer, Barth stumbled into what was then Johns Hopkins' Writing, Speech, and Drama department. In a 1999 oral history with the Sheridan Libraries' Mame Warren that revealed a self-deprecating sense of humor, he credits his "a la carte" education (his job reshelving books from wheeled carts in the classics and Oriental Seminary stacks of the old Gilman library) with filling in much of the literary background he had not yet accrued.
After earning his master's degree at Hopkins, Barth served on the faculty of Penn State, SUNY Buffalo, and Boston University before returning to Hopkins as professor in what had then become The Writing Seminars with a joint appointment in the English department. He invited authors including Salman Rushdie, Grace Paley, John Updike, Raymond Carver, Joyce Carol Oates, and Italo Calvino to read from their work, and they did.
As a teacher, he was famous for never imposing his own style on his students, instead imparting to them a sense of both imagination and craftsmanship. His keen ear as a reader made him a deeply admired mentor; leading by example, he showed students how to dissect stories, listen for style and voice, and discern worthy storytelling—whether in their own writing or that of others.
"One of the delights of sitting in his classroom was hearing him X-ray a story, finding its hidden bone structure and energy source, and still be helpful in cutting away the fat," McGarry wrote for a festschrift for Barth in 2015.
John Barth, writer who pushed storytelling's limits, dies at 93
John barth, novelist who orchestrated literary fantasies, dies at 93.
Michael Martone, A&S '79 (MA), remembers driving to Cambridge, Maryland, for the viewing when Barth's father died. "What I remember is that he told us three stories about funerals he had attended with the usual perfect presentation of his storytelling. It was amazing," said Martone, professor emeritus in the University of Alabama's Department of English. "That even in the midst of that moment he was composing the narratives that would become part of his future narratives and mine. He was all about the story and the famous Freytag pyramid. Stories have beginnings, middles, and ends, and each part needed tending, revising, and amending. And each part is connected, entwined, and harmonic.
"He was my teacher but also my first and always 'outside' reader," Martone added, noting that Barth had pledged on the first day of class to read his former students' published work if they sent it to him. "I did for forty-plus years, everything I published in magazines and books. And he responded every time with a brief note of receipt and a message of thanks and 'keep going, don't stop.'"
Image caption: John Barth is seated at the head of the table in the old board room at Shriver Hall in this image from the 1970s.
Image credit : Courtesy of the Ferdinand Hamburger Archives, Johns Hopkins University
Barth's fiction has been described as striking a commanding balance between postmodern self-consciousness and wordplay, and displays the characterization and compelling plot more common in more traditional genres. In works described as playful and challenging, funny and deadly serious, his plots fragment and his points of view shift. He covered ground from the Chesapeake Bay to the Bronze Age city Mycenae to a generic housing development. His translated works found wide audiences in languages including Finnish, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Japanese, and Polish, and continue to make significant appearances in public readings, recordings, adaptations, reviews, and critical essays.
Barth's writing veered from the existential to comical nihilism to metafiction; in 1987's "The Tidewater Tales," a minimalist novelist and maximalist oral historian tell each other stories while sailing around the Chesapeake. "Lost in the Funhouse" features a 13-year-old boy exploring Ocean City, Maryland, with his family and simultaneously commenting on his own story, leaving readers reeling between the plot and the commentary as if visiting a boardwalk funhouse. Other best-known works include "The Sot-Weed Factor," "The Floating Opera," "Giles Goat-Boy," and "Chimera," for which he received the National Book Award for fiction in 1973
In 1995, Barth retired from Hopkins and became a senior fellow at Washington College in Chestertown, Maryland. He received an honorary Doctor of Humane Letters degree from Hopkins in 2011, was a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, and was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters.
The Johns Hopkins Sheridan Libraries hold collections of Barth's manuscripts and books from his personal library, acquired in 2014 . A 2015 exhibit introduced the collection to the public . Typescript drafts with Barth's handwritten corrections offer a glimpse into his writing process, while reviews and critical analyses reveal evolving attitudes toward postmodernism and meta-fiction. The Sheridan Libraries are also processing newly acquired materials, including a set of letters between Barth and his long-time friend and fellow writer Daniel Tamkus. Additional papers can be found at the Library of Congress .
Tagged literature , writing seminars , obituaries , john barth
Related Content

A remembrance of John Barth

Teacher, teacher

A Literary Revival
You might also like, news network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
Advertisement
Supported by
Literary Magazine Retracts Israeli Writer’s Essay as Staffers Quit
An Israeli writer’s essay about seeking common ground with Palestinians led to the resignation of at least 10 staff members at Guernica.
- Share full article

By Marc Tracy
Guernica, a small but prestigious online literary magazine, was thrown into turmoil in recent days after publishing — and then retracting — a personal essay about coexistence and war in the Middle East by an Israeli writer, leading to multiple resignations by its volunteer staff members, who said that they objected to its publication.
In an essay titled “From the Edges of a Broken World,” Joanna Chen, a translator of Hebrew and Arabic poetry and prose, had written about her experiences trying to bridge the divide with Palestinians, including by volunteering to drive Palestinian children from the West Bank to receive care at Israeli hospitals, and how her efforts to find common ground faltered after Hamas’s Oct. 7 attack and Israel’s subsequent attacks on Gaza.
It was replaced on Guernica’s webpage with a note, attributed to “admin,” stating: “Guernica regrets having published this piece, and has retracted it,” and promising further explanation. Since the essay was published, at least 10 members of the magazine’s all-volunteer staff have resigned, including its former co-publisher, Madhuri Sastry, who on social media wrote that the essay “attempts to soften the violence of colonialism and genocide” and called for a cultural boycott of Israeli institutions.
Chen said in an email that she believed her critics had misunderstood “the meaning of my essay, which is about holding on to empathy when there is no human decency in sight.”
“It is about the willingness to listen,” she said, “and the idea that remaining deaf to voices other than your own won’t bring the solution.”
Michael Archer, the founder of Guernica, said that the magazine would publish a response in the coming days. “The time we are taking to draft this statement reflects both our understanding of the seriousness of the concerns raised and our commitment to engaging with them meaningfully,” he wrote in a text.
The essay was published on March 4 and taken down a few days later, according to the Wayback Machine, where the first-person essay is still available in archived form.
Chen, who was born in England and moved to Israel with her family when she was 16, writes in the essay about trying to reconnect with a Palestinian friend and former colleague after the Oct. 7 attacks, and of not knowing how to respond when her friend texted back reports of Israeli attacks on a hospital complex in Gaza.
“Beyond terrible, I finally wrote, knowing our conversation was over,” Chen’s essay said. “I felt inexplicably ashamed, as if she were pointing a finger at me. I also felt stupid — this was war, and whether I liked it or not, Nuha and I were standing at opposite ends of the very bridge I hoped to cross. I had been naïve; this conflict was bigger than the both of us.”
Chen said in the email that she had worked on the essay — her second for Guernica — with the magazine’s editor in chief and publisher, Jina Moore Ngarambe. Over emails and in a one-hour phone conversation, Chen said, “I was offered the distinct impression my essay was appreciated. I was given no indication that the editorial staff was not onboard.”
She still has not heard from anyone at Guernica, she said Tuesday.
Ngarambe, who in 2017 and 2018 worked at The New York Times as its East Africa bureau chief, did not reply to requests for comment on Monday and Tuesday.
In the days following the essay’s online publication last week, several Guernica staffers announced their resignations on X, calling the essay a betrayal of the editorial principles of the magazine, a nonprofit that was founded in 2004.
April Zhu, who resigned as a senior editor, wrote that she believed the article “fails or refuses to trace the shape of power — in this case, a violent, imperialist, colonial power — that makes the systematic and historic dehumanization of Palestinians (the tacit precondition for why she may feel a need at all to affirm ‘shared humanity’) a non-issue.”
Summer Lopez, the chief of free expression programs at PEN America, the writers’ group, said that “a writer’s published work should not be yanked from circulation because it sparks public outcry or sharp disagreement.”
“The pressures on U.S. cultural institutions in this moment are immense,” Lopez said in a statement. “Those with a mission to foster discourse should do so by safeguarding the freedom to write, read, imagine and tell stories.”
In a mission statement on its website, Guernica states that it is “a home for incisive ideas and necessary questions.”
Marc Tracy is a Times reporter covering arts and culture. He is based in New York. More about Marc Tracy
Our Coverage of the Israel-Hamas War
News and Analysis
Faced with deepening Democratic resistance to arming Israel , President Biden threatened to condition future support on how Israel addresses concerns about civilian casualties and the humanitarian crisis in Gaza . The threat is not idle, aides said, but Biden hopes to force a course correction rather than follow through.
A grandmother taken captive on Oct. 7 by Hamas was probably killed when an Israeli helicopter, in response to the attack, fired on the vehicle in which she was being held , said Israel’s military.
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel is facing challenges on multiple fronts: domestic support is eroding, there is international fury over the death toll in Gaza, and the fallout from the killing of seven aid workers has heightened global anger.
Internal Roil at TikTok: TikTok has been dogged for months by accusations that its app has shown a disproportionate amount of pro-Palestinian and antisemitic content to users. Some of the same tensions have also played out inside the company.
Palestinian Detainees: Israel has imprisoned more than 9,000 Palestinians suspected of militant activity . Rights groups say that some have been abused or held without charges.
A Hostage’s Account: Amit Soussana, an Israeli lawyer, is the first former hostage to speak publicly about being sexually assaulted during captivity in Gaza.
A Power Vacuum: Since the start of the war, Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of Israel has done little to address the power vacuum that would appear after Israeli forces leave Gaza. The risks of inaction are already apparent in Gaza City .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013) Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass, Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer's gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there's one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp.When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Paragraph 1. Sylvia Plath's short poem "Morning Song" explores the conflicted emotions of a new mother. On the one hand, the mother recognizes that she is expected to treasure and celebrate her infant, but on the other hand, she feels strangely removed from the child. The poem uses a combination of scientific and natural imagery to ...
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
A literary analysis essay asks you to make an original argument about a poem, play, or work of fiction and support that argument with research and evidence from your careful reading of the text. It can take many forms, such as a close reading of a text, critiquing the text through a particular literary theory, comparing one text to another, or ...
A literary analysis essay is an important kind of essay that focuses on the detailed analysis of the work of literature. The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to explain why the author has used a specific theme for his work. Or examine the characters, themes, literary devices, figurative language, and settings in the story.
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
Besides essays on Book Riot, I love looking for essays on The New Yorker, The Atlantic, The Rumpus, and Electric Literature. But there are great nonfiction essays available for free all over the Internet. From contemporary to classic writers and personal essays to researched ones—here are 25 of my favorite nonfiction essays you can read today.
Step 1: Read the Text Thoroughly. Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
Get a sense of what to do right with this literary analysis essay example that will offer inspiration for your own assignment. ... At the middle school level, a literary analysis essay can be as short as one page. For high schoolers, the essay may become much longer as they progress.
The first step in writing a literary analysis essay is actually completing the reading. Sometimes the professor will give you a prompt before you read. If this is the case, look for material which relates to the prompt as you read. ... So, long story short: even the most practically-minded, time-crunched students would do well to perform the ...
Short Essays for Students. This page contains short essays and other non-fiction writing for students or anyone who wants to read and think about an opinion piece. It will only take a few minutes or less to read any of these texts. They are all under 2,000 words. Each non-fiction selection has a short summary or teaser and some possible themes ...
1. Read and analyze the text. In order to understand how to start a literary analysis essay, you need to realize the importance of strong research. Before you begin writing your essay, make sure to thoroughly go through your text and take detailed notes. Observe and note the words used by the author, the structure and tone of the piece, the ...
Lucy Calkins: Literary Essays Texts: Whole Group Classroom Short Texts for Modeling: (writing inside the story, close reading, characters, conversational prompts, provocative ideas, thesis, framing essay, stories as evidence, summaries, lists, craftmanship, polishing) Spaghetti by Cynthia Rylant (referenced in Units of Study Lessons)
Short Stories to enjoy when you have 5 minutes to spare, sorted by category so you can find what suits your mood. Stories average 1,000 words, including morality tales, feel-good/love stories, other-worldly stories, witty stories, dramatic stories, and farce/political stories. Featured authors include Mark Twain, Anton Chekhov, Kate Chopin, James Baldwin, H.H. Munro (SAKI), Virginia Woolf, O ...
The Tell-Tale Heart is a short story by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in 1843. It follows an unnamed narrator who insists on his sanity after murdering an old man with a "vulture eye.". In the tale, the narrator attempts to convince readers of his mental stability while describing a murder he committed and disposing of ...
The 3P Review is quarterly arts magazine focuses on literature, arts and society, memoir and essay. Short stories should be no more than 4,000 words, while submissions to the "Table Talk" section (pithy, irreverent and humorous musings on culture, art, politics and life) should be 1,000 words or less. Deadline: January 1 to April 30
Our CRAFT ESSAY section (found in our top menu) features Krys Malcolm Belc exploring why the short essay form is such a potent mode of expression for trans stories and Silas Hansen offering the benefits of writing yourself as you are, even if that's not always the person readers might expect you to be:
John Barth, A&S '51, '52 (MA), groundbreaking and prolific author, revered teacher, and professor emeritus in The Writing Seminars at Johns Hopkins University, died Tuesday. He was 93. John Barth. Best known for his postmodernist, unpredictable fiction and his exacting and generous teaching, Barth served on the Johns Hopkins faculty from 1973 ...
Heidi Levine. By Marc Tracy. March 12, 2024. Guernica, a small but prestigious online literary magazine, was thrown into turmoil in recent days after publishing — and then retracting — a ...