150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples
Looking for good titles for a Holocaust project? This is one of the most tragic parts of WW2 that is definitely worth studying.

🔝 Top 10 Holocaust Questions for Essays
📝 holocaust essay: how to write, 🏆 holocaust essay examples & topics, 📌 holocaust thesis ideas, ✍️ holocaust essay topics for college, 💡 most interesting holocaust topics to write about, ❓ holocaust essay questions.
The most popular Holocaust essay topics are:
- The Holocaust and its causes
- Nazi human experiments as a part of the Holocaust
- Jewish ghettos in Poland
- The establishment of Auschwitz concentration camp
- The consequences of the Holocaust
Below you can find much more ideas. In this article, we’ve collected Holocaust thesis ideas and questions for essays. They will suite for middle school, high school, and college-level assignments. You’ll also find tips on writing your introduction, conclusion, and formulating a thesis statement, together with Holocaust essay examples. Write an ️A+ paper with us!
- What were the ideological causes of the Holocaust?
- How was anti-Jewish legislation in Germany established?
- What were the goals of the Nazi Euthanasia Program?
- How and where were the largest ghettos created?
- How did the concentration camp system expand across Europe?
- What were the three types of ghettos?
- How did the resistance efforts in the ghettos look like?
- Who were the key opponents of Nazism inside and outside Germany?
- How did the US government respond to Nazism?
- What were the consequences of the Holocaust?
The Holocaust has affected millions of people around the world. It is one of the most tragic and problematic topics of history. Holocaust essays help students to understand the issue better, analyzing its causes and consequences.
Organizing an essay on the Holocaust may be challenging, as there are many aspects to cover. We have developed some tips to help you through the process.
First, choose the Holocaust issue you want to discuss. Select one of the titles to work on. Some of the Holocaust essay topics include:
- Concentration camps in today’s Europe
- Lessons from the Holocaust: Fostering tolerance
- Present and future of the Holocaust research
- The causes of the Holocaust and discrimination against Jewish people
- How could people have stopped the Holocaust?
- Political issues behind the Holocaust
- The effects of the Holocaust on its survivors
- The factors and issues that contributed to Nazism
You can choose one of these holocaust essay questions or ask your professor for suggestions. Once that you have selected the topic of your essay, you can start working on the paper.
A well-developed structure is highly significant for an outstanding essay. Here are some tips on how to develop a structure for the paper:
- Think of the Holocaust essay prompts you want to discuss first. You can do preliminary research to see what issues you should cover.
- Ask your professor about the type of essay you should write. If it is an argumentative essay, you will need to leave space for at least one refutation paragraph and a rebuttal paragraph.
- Include an introductory paragraph (or several paragraphs if you are working on a longer essay). This paragraph should include the background information on the Holocaust and the problem you have selected. Discuss the goals of the paper and state your main claim at the end of this section.
- The main arguments of your paper will comprise body paragraphs. You may want to dedicate at least one separate paragraph for each of your claims. The number of body paragraphs is up to you, however, we would recommend including at least three of them. Hint: Make smooth transitions between paragraphs to make your paper look more organized.
- Remember that at least one body paragraph should state the general information about the Holocaust, its causes, and effects. You may discuss statistical data, global consequences, and primary victims.
- While working on a refutation paragraph, do not forget to prove that your arguments are more reasonable that the opposing perspectives. You can dedicate a separate paragraph for a rebuttal.
- A concluding section or a summary should state your main arguments again. You can also include a recommendation if necessary.
- Important tip: Do not make your paragraphs too short or too long. We would recommend writing between 65 and 190 words per paragraph and not more than 35 words per sentence. Making all body paragraphs of similar length is also a good idea that will make your paper look more professional.
- Ask your professor whether you need to include a title page and table of contents. Remember that a reference page is a must, as it includes all sources from the essay.
- If you are not sure that the selected structure is good, search for the holocaust essay titles and examples online and see how other students organize their papers. Avoid copying the works you will find.
Remember to look at the samples on our website to get some ideas for your excellent paper!
- Holocaust and Bosnian Genocide Comparison The current paper aims to compare some of the most notable genocides in history, the Holocaust, and the Bosnian mass murder in terms of their aims, death tolls, tactics, and methods.
- Critique of Elie Wiesel’s Holocaust Book “Night” Like many books on the Holocaust, Elie Wiesel’s Night is a dramatic picture of the horror times in the history of humankind and particularly in the history of the Jewish people.
- The Holocaust: Poem “Tears of Blood” The extermination of the Roma was part of the general policy of the National Socialists to destroy political opponents, homosexual people, terminally and mentally ill, drug addicts, and Jews.
- US Holocaust Policy During World War II However, the anti-Nazi campaign was not successful, and the main reason for this was the harsh foreign policy of the USA.
- Reasons Why the Jews Failed to Resist the Holocaust The award-winning book brings the readers to the lives and experiences of Vladek Spiegelman, a holocaust survivor, and his father during the period.
- Discussion of Holocaust and Immigration In “Holocaust Education and Remembrance in Australia,” Suzanne D.and Suzanne H.discuss the adverse effects and after-issues of immigration among the Jewish community and how it led to the concept that the Holocaust had a long-lasting […]
- The Holocaust and the Nakba: Tragedy and Trauma The Nakba refers to the destruction of hundreds of cities and towns and the Palestinian people’s cultural, economic, political, and social backgrounds.
- Holocaust Commemoration in the US Holocaust Memorial Museum This paper is relevant to the understanding of virtual exhibit since it highlights the major notions of memorialization that are included in the exhibition.
- Holocaust: Traditions and Encounters He was the only presenter in the video: he revealed the question about Sephardic Jews in the Holocaust and answered questions from the audience.
- Holocaust: Taking Steps Toward Evil To the Nazi leader, the Jews were an inferior race and were an alien threat to the German racial purity. The Germans blamed the Jews for having lost the World War 1 and accused them […]
- A Visit to the Holocaust Museum Houston The museum emphasizes the perils of intolerance, bigotry, and apathy by drawing on the lessons of the Holocaust and other massive genocides.
- “Holocaust Horror…” by Moore A considerable number of young people do not have the correct knowledge, and the most disturbing fact is that the Holocaust started to be interpreted in different ways.
- The Relationship Between Epigenetics and the Effects of the Holocaust Tests are most likely to identify existing changes of DNA and the proteins related to DNA, which are responsible for the structure of the DNA and the availability of other elements related to the DNA.
- The Terror of the Holocaust in the Book “Hana’s Suitcase” by Karen Levine The story “Hana’s Suitcase” by Karen Levine is not fiction, where heroes and the plot are the imagination of the author; it is a documentary story where the situation and named people are real, they […]
- The Holocaust and Schindler’s List: Transforming the Human Perception of Violence The World War II genocide of Jews, known as the Holocaust, changed both the Jewish history and the history of the world, transforming the human perception of violence and religious conflicts.
- The Holocaust as a History-Cultural Phenomenon The Holocaust in the narrow sense represents the persecution and mass extermination of Jews who inhabited the German lands, the territories of Hitler’s allies, and the areas occupied during the war.
- Art Spiegelman’s Graphic Novel “Maus I: A Survivor’s Tale”: Author’s Understanding of the Holocaust Spiegelman uses mice to represent Jews because of the oppression they experienced while in Hitler’s concentration camps. The mistreatment the Jews experienced is similar to what mice experience in the presence of cats.
- Holocaust Museum Exhibition “State of Deception” Generally, evaluating a variety of facts from different sources, it becomes evident that the exhibition “State of Deception: The Power of Nazi Propaganda” in the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum can be seen as rather […]
- Holocaust: Ethnic and Cultural Diversity and the Real Face of Prejudice The holocaust refers to the murder of six million European Jews in the course of the Second World War. The holocaust was the highest level of prejudice in society during the time.
- German Attitudes Towards Third Reich and Holocaust Commemoration The Goldhagen debate represents a shift in the attitude of the Germans regarding the commemoration of the Third Reich and the remembrance of the holocaust.
- Jewish Holocaust and the Humour During the Dark Times This is the Jewish long tradition of jokes in Judaism that dates back to the Midrash and the Pentateuch but it generally refers to the more recent group of verbs that were first used in […]
- Human Response to Holocaust in “Nightfather” and “Fugitive Pieces” It is his memory of the nightmare that keeps him imprisoned, he appears in the camp again and again by the volition of his memory that is eager to play painful tricks with him.
- Holocaust Denial: Dynamics of Ethics While keeping this in mind, we will analyze the introduction of “holocaust denial” criminal charges into the penal code of many Western countries that simultaneously take pride in the fact that their democratic form of […]
- American’s Reaction to Jewish Holocaust Later when America joined Russia in the war against the Nazi Regime, the action was selective in that it failed to protect the Jews from genocide.
- Holocaust: From Discrimination to Concentration Camps The discrimination as said at workplaces and other areas was later to escalate to actual killing with the taking of power by the Nazi party establishing legal backing of their activities with the enactment of […]
- Jewish Family’s Experiences During the Holocaust Piecing together everything that I learned from my grandparents and parents, I have come to realize that I was shaped early on by the experience of my ancestors in the Holocaust and in Russia.
- Censorship, Holocaust and Political Correctness In this paper, we will focus on exploring different aspects of formal and informal censorship, in regards to a so-called “Holocaust denial”, as we strongly believe that people’s ability to express their thoughts freely is […]
- The Holocaust: Auschwitz Concentration Camp History In an attempt to dehumanize the victims of the Nazis and as a testament to the resilience of a few of the inmates of the camps, the mentality of the brutal Nazis is worth a […]
- Vatican and Holocaust: Did Pope help Jews The couple later stated that they never wanted the Pope to come out in the open and state that he was against the Nazis because then he will become the center of attention and to […]
- Holocaust: What Were Its Causes and Effects? After the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazis, the goal of the Nazis was to murder every individual of Jewish origin, which the Nazis defined as anyone with a trace of Jewish “blood” dating […]
- Henry Orenstein: Holocaust Survivor and Entrepreneur The Nazi regime, were under the impression that the Germans were ‘racially superior’ to the Jews and believed that the Jews were somehow lesser than them.
- The Holocaust: Historical Analysis The Holocaust, now the example of Jewish pain, has long stopped to be a piece of history, and is now regarded by spiritual and material alike, as a piece of divinity – a sacred text […]
- The Holocaust: Planned Physical Extermination In this essay, we are going to concentrate particularly on the point of the Holocaust in the countries of Eastern and Western Europe, namely the extermination of Jews that took place in Romania and France […]
- Holocaust Tragedy in Nazi Germany Since the forties of the twentieth century, another such theory, called the Holocaust, came into use in the context of the mass extermination of Jews in Europe by the Nazis. It is the education of […]
- The Holocaust: Problems and Perspectives of Interpretation The sanctity of life should therefore be respected at all costs and so humanity should strive to coexist in peace and harmony in a manner that is sustainable to prevent the reoccurrence of such atrocities […]
- A Visit to the Holocaust Museum in Washington DC People visited the museum to learn about the atrocities caused to the Jews by the Nazi administration, headed by Hitler. The other piece I learned is that in the museum there was a video of […]
- Holocaust in “Maus” Graphic Novel by Art Spiegelman It is quite peculiar that Spiegelman uses only the black-and-white color perhaps, this is another means to emphasize the gloomy atmosphere of the Nazi invasion and the reign of the anti-Semite ideas.
- Post-Holocaust and Imprisonment Literary Works It is possible that Celan uses repetition to express the feelings of repetitiveness that he and the other people felt during the imprisonment.
- Virginia Holocaust Museum’s Genocide Presentation In terms of the educational objective, I aimed to learn the aspects and details of the Holocaust through the artifacts, objects, and things that belonged to people experiencing these events’ atrocities.
- Virginia Holocaust Museum Trip and Experience I wanted to make sure that I could listen to myself and truly feel what the Holocaust was for humanity and is for me. I felt outraged that someone could think they had the right […]
- Virginia Holocaust Museum Field: Trip Reflection I must admit that the very fact of listening to the voice of somebody who went through the horrors of the Holocaust proved to be at least as revealing as all of the artifacts and […]
- The Poetry of the Holocaust Period In conclusion, it seems appropriate to state that Sutzkever is a metaphysical poet as his creative thought focuses on the beauty of nature and the truthful presentation of events.
- The Public Memory of the Holocaust In addition to his pain, Levi concerns the increasing temporal distance and habitual indifference of hundreds of millions of people towards the Holocaust and the survivors1 It causes the feeling of anxiety that was fuelled […]
- History of the Holocaust They can be outlined as follows: the historical legacy of anti-Semitism in Europe, the particulars of the German national character /the fact that the Nazis did succeed in dehumanizing the Jews, and the irrational hatred […]
- Holocaust and Stuttgart Declaration of Guilt This paper is devoted to the analysis of the Holocaust in general and the Stuttgart Declaration of Guilt in particular. The judges represented the states which were the main winners in the war: Great Britain, […]
- Holocaust Memorial Museum Textiles, for example, badges, uniforms, flags, costumes, and banners are also housed in the museum. Other types of materials housed in the museum are works on paper, such as announcements, posters, broadsides, and maps.
- Holocaust in “Survival in Auschwitz” by Primo Levi Another issue that needs to be discussed is that the economy of Germany was hurt because of the World War I, and it has affected the pride of the nation.
- 1942-1945 Holocaust: Nazi Germany’s Political Reasons Started in 1942 and taking place until the end of the war, the Holocaust was the genocide of Jewish people arranged by Hitler and implemented by the Nazi army.
- Holocaust vs. Japanese Colonial Era in Korea The Holocaust in the history of Jewish people, as well as Japanese occupation in the history of Korean people, was one of the greatest tragedies.
- Holocaust, Antisemitism, and Propaganda That is why, nowadays great attention is given to issues which led to the death of millions of people. Being a part of the ideology of Nazism, it led to the elimination of a great […]
- The Holocaust Effects: Books “Tzili” and “Wartime Lies” The natural experiences of growing up are changed and twisted by the war and its horrors, but the specific developments, their perceptions, and impacts are affected by the children’s personalities and circumstances of their lives, […]
- Nazi Medical Experiments During the Holocaust The information is maintained by the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. This photograph is maintained and produced by the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.
- The Holocaust and Jehovas Witnesses The concept of “spiritual resistance” in the case of members of Jehovah’s Witness during the era of the Nazis in Germany focused primarily on continuing the acts associated with their faith despite the persecution they […]
- Holocaust: Nazi Anti-Jewish Policies and Actions The major policy that the Nazi implemented was the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service that excluded Jews from government jobs.
- Holocaust and Nazi’s Racial Imperialism The scholar argues that the event was a result of the racial imperialism championed by the Nazi Party in the country.
- Adolf Hitler and a History of the Holocaust Before going any further it is important to point out the kind of mindset that the German people had back then that made it easier for Hitler to convince them to join him in a […]
- The Holocaust History: the Jewish Community Destruction To achieve its objective, the paper will expound on why the Nazi government targeted the Jews, why did these attacks come during this specific period, the role that average German citizens played and the overall […]
- Holocaust History, Its Definition and Causes Also notable about racism is the fact that it may take several forms and it is not just limited to the literal meaning of racism like the skin color, the size of the eyes, and […]
- Holocaust Experience in the Book ‘Night’ by Elie Wiesel Eliezer’s depiction in the story as the main character in the story is that of a humble and religious young man.
- The Jewish Holocaust Novel ‘Night’ by Eliezer Wiesel Generally, Eliezer admired the fact that his father was prayerful and he kept his utmost faith in God even in the time of oppression.
- History of the Jews and the Holocaust The Nazi regime and its partners became the pioneers of the Holocaust. That being the case, the anti-Semitism ideas and prejudices experienced in Germany before the Second World War led to the infamous Holocaust.
- Denying the Holocaust: The Growing Assault on Truth and Memory by Deborah Lipstadt The book is divided into chapters that focus on the history and methods that are used to distort the truth and the memory of the Holocaust.
- The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum Since its inception in 1993, the museum has served as the nation’s reminder when it comes to issues of the holocaust.
- Iran and Israel’s Nuclear Holocaust and the Gulf Cooperation Council’s Position As such conflict would put a serious threat to the safety of the region, the policy aims at the acceptance of nuclear deal and the development of the effective course of actions aimed at eliminating […]
- Liberal Democracy, Anti-Semitism and the Holocaust The Nazis and other populist political movements in Germany believed that the Jews had undue influence in the country through their prominent positions in the media and the financial system4.
- Was the Holocaust the failure of or the product of Modernity? The date that traditionally marks the beginning of modernist era is 1453, when the City of Constantinople was conquered by the Turkish Ottoman Empire, as far as this date symbolized the end of the Byzantine […]
- Reconsidering the History: Holocaust Denial. The XXI Century Prospects Despite the fact that Holocaust was one of the hideous crimes against the humanity that is never to occur again, some tend to represent the tragic event as the stage of the history that people […]
- Nazi Germany & Holocaust The Nazi movement is a revolutionary movement that was associated with the mass murder of Jews and Communists in an attempt to restore the reputation of Germany at the international level. The Nazi regime under […]
- The Holocaust and Nazi Germany The rise of the Nazis to power in 1933 led to the establishment of thousands of concentration camps, which were centers of mass murders of Jews.
- The Holocaust and Jews Extermination The Nazis perceived Internationalism in the context of the Holocaust to be a global perspective primarily held and advocated by Jews who were using it as a method designed to dominate the whole world.
- The Holocaust: Analysis of Life in the Kovno, Warsaw and Lodz Ghettos Due to the continued capturing and shooting of the Jews at the forts, Rabbi Shapiro felt that the Jews should be separated from the Lithuanians to live into the Ghetto and thus a seven member […]
- How Holocaust Has Been Projected by the Different Historians Over the Years? Several historians claimed that it was unfair as it was an act of barbarism and it promoted wicked behavior with the innocent people of Jewish community while on the other hand, it was said that […]
- Jewish Insight of Holocaust Holocaust, the extermination of Jews from the European land was the example of brutality and viciousness of the Nazi Germany. Meanwhile, many historians were observing the situation critically and wanted to present their ideas about […]
- Shooting At the Holocaust Museum According to the incident report, von Brunn entered the museum and shot the guard. His motive was to hold the board members who were in the building hostage for the economic difficulties that the country […]
- The Nazi Holocaust’s Effects This study aims at analyzing the claim that social and psychological effects of the Holocaust linger in areas of political systems in which the survivors of the holocaust currently reside.
- The History of the Holocaust Hitler said that the root cause of the problems were the despicable Jews of Europe. The direct victims were the Jews but the rest of the world understood the consequences of inaction and the lack […]
- Holocaust and the Cold War Cold war refers to the military and political tension between the United States of America and the Soviet Union immediately after the World War 2.
- Reinhard Heydrich’s Role in the Holocaust With the help of his boss: Himmler[7], they used political forces to influence the police in an attempt to ensure the consolidation of the Nazi administration in the entire nation of Germany[8].
- Doris Bergen: Nazi’s Holocaust Program in “War and Genocide” The discussion of the Holocaust cannot be separated from the context of the World War II because the Nazi ideology of advancing the Aryans and murdering the undesirable people became one of the top reasons […]
- The ‘Banality’ of Abstraction: Western Philosophy’s Failure to Address the Moral Implications of the Holocaust Additionally, I would like to address the relationship of Arendt and Heidegger in the context of The Holocaust, and the effect that it had upon their philosophical works.
- Conduction of The Holocaust Propaganda against Jews The common media the Nazis used for the campaign against the Jews was the Weekly Nazis newspaper, “The attacker”.
- Does Global English Mean Linguistic Holocaust? It is not difficult to find examples of the extinction of languages in the wake of the introduction of English. Some of the most active areas of extinction include the American West, where a variety […]
- The Horror of the Holocaust in Different Styles of Writing One of the thematic thread that unites these three works of the writers from different countries is their attempt to reproduce how cruel and unfair the actions of the Nazi were. The Holocaust, the judgment […]
- Peter Eisenman; Building Germany, the Holocaust Memorial The Jews were not the Nazi’s only victims during the holocaust, other casualties were the weak and disabled people in the society, who were killed on the pretext of the Euthanasia program.
- The Holocaust: A German Historian Examines the Genocide The Holocaust: A German Historian Examines the Genocide deals with one of the most debatable issues of the history of the twentieth century, i.e.
- The Holocaust: Religion, Race and Ethnicity Discrimination
- Holocaust Resistance: The Largest Jews Revolt Holocaust
- The Violent Conditions and Dehumanization Faced by the Jewish People During the Holocaust
- Analysis of the Causes of the Holocaust in Germany
- The Anger and Bewilderment of Holocaust Survivors
- Racist and Hate Crimes During the Holocaust
- The Long-Lasting Impact of the Holocaust on the Survivors
- The Holocaust, and the Statistics of the Tragic Events
- General Information About the Holocaust Was Genocide Against the Jewish Race
- The Causes and Effects the Holocaust Was Responsible for the Death of 6 Million
- Overview of the Chinese Holocaust and Experiments on Living People
- The Goals and Impact of the Holocaust Camps in Germany
- General Information About the Horrible Events That Took Place During the Holocaust
- The Different Killing Methods Used by the Nazi Germans During the Holocaust
- The U.S. Government’s Disregard of the Jewish Holocaust
- Survivor’s Syndrome Among Holocaust Survivors
- The German Holocaust: Treatment of the Germans After WWII
- Holocaust Survivor Testimonies: Time, Methodology and Memory
- The Link Between Nazi Propaganda and the Holocaust
- Holocaust Survivor Bewilderment and Anger
- Stolen Art Literature and Music of the Holocaust
- The Genesis and History of the Holocaust in Nazi Germany
- The Knowledge About the Holocaust To Avoid the Same Experience
- Analysis of the Holocaust and the Crisis of Human Behavior
- The Horrific Experience and Fate of the Children During the Holocaust
- How Did the Holocaust Affect the Jewish Community?
- How Does the American Holocaust Show the Huge Decline of Native Americans?
- Was German “Eliminationist Anti Semitism” Responsible for the Holocaust?
- How Were Jews Treated During the Holocaust?
- What Is the Relationship Between Holocaust and Genocide?
- How the Holocaust Took Away the Rights of Jewish People?
- What Was the Strength of the Nazis During the Holocaust?
- With Whom Does Responsibility for the Holocaust Ultimately Lie?
- How the Pope Affected the Holocaust?
- What Events Led to the Holocaust in Germany?
- How Was Survival Possible in the Death Camps of the Holocaust?
- Were the Jehovah’s Witnesses Really Affected by the Holocaust?
- Why Does God Permit Tragic Events Like the Holocaust Terrorist Attacks?
- What Was Hitler’s Role in the Holocaust?
- Why Is Peter Eisenman Building a Memorial to the Victims of the Holocaust in Germany?
- How Does the Holocaust Compare to One Other Form of Modern Genocide (Kurdish Genocide)?
- What Are the Problems Between Jews and Christians That Caused the Holocaust?
- How Did Oskar Schindler Act During the Holocaust?
- What Prejudices Were There During the Holocaust?
- How Did People Avoid Removal During the Holocaust?
- What Kind of Medical Experiments Were Carried Out During the Holocaust?
- How Did the Holocaust Affect Ordinary People?
- What Are the Proposals for Preventing a New Holocaust?
- How Did the U.S. React to the Holocaust in Germany?
- Why Was the World Silent During the Holocaust?
- How the Holocaust Affected Its Jewish Victims?
- What Are the Consequences of the Holocaust and Its Consequences for the Jews and the Rest of the Population?
- How the Holocaust Explodes the Concept of Mass Crime?
- Why Are Jews Demanding Compensation for Holocaust Damage?
- What Economic and Social Conditions Led to the Holocaust?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/holocaust-essay-examples/
"150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/holocaust-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/holocaust-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/holocaust-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "150 Holocaust Essay Topics & Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/holocaust-essay-examples/.
- Genocide Essay Titles
- Famine Essay Titles
- Civil War Titles
- Cold War Topics
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- Nazism Topics
- Iraq War Research Ideas
- Pearl Harbor Paper Topics
- Vietnam War Paper Topics
- World War 1 Research Ideas
- Hiroshima Topics
- World War 2 Essay Topics
- Social Justice Essay Ideas
- Disaster Essay Titles
126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles
The Holocaust is one of the most tragic events in world history, and writing an essay about it can help you understand it better. Among these Holocaust essay topics, you can find ideas for different types of middle school or college essays. Use them as the Holocaust essay titles or as a starting point for your dissertation research.
🕎 TOP 7 Holocaust Essay Topics
🏆 good titles for holocaust essays, 🎓 most interesting holocaust research paper topics, 💡 simple holocaust essay ideas, ❓ holocaust questions for essays, 📝 holocaust argumentative essay topics, 🔎 holocaust topics for research paper, ✍️ more holocaust essay titles.
- Holocaust in “The Boy in the Striped Pajamas” Film
- Turning Points of the Holocaust
- Escape from Sobibor: World War 2 Holocaust
- World War II: Holocaust and Discrimination of the Jews
- Holocaust: Jewish Women’s Experiences
- World History: Researching of Holocaust
- “Children in the Holocaust and World War II” by Holliday
- Perpetrators, Bystanders, and Rescuers During the Holocaust The Holocaust was prevalent, with cruelties, tragedies, and atrocities directed at various groups defined by diverse characteristics.
- Holocaust and Its Physical and Mental Consequences This paper is a detailed and thorough study of the physical and mental consequences of the Holocaust on people who survived this terrible period of history.
- The Holocaust Impact on Jewish Theology Holocaust had a major impact on Jewish theology by providing an earth-shattering tragedy the likes of which the Jewish have never seen in the past, to explain.
- Holocaust and War in “Hiroshima” by John Hersey This paper provides a review of John Hersey’s accounts of the holocaust on “Hiroshima” and provides an understanding of how to handle incidences of war.
- Wiesel’s Holocaust Experiences Eliezer Wiesel’s view of human nature and understanding of God radically changed due to his experience of the Holocaust.
- Behavior of Witnesses in “Holocaust by Bullets” by Desbois Desbois’ book “Holocaust by Bullets” documents in detail the experience of witnesses to the persecution of the Jews by the Nazis.
- Holocaust and Moral Objectivism: “Surviving Auschwitz” “Surviving Auschwitz: Children of the Shoah” by WSGVU is a documentary that follows two Holocaust survivors as they visit their hometown and concentration camps.
- The Extent of the Holocaust as a Christian Problem The events of the Holocaust are considered a regrettable lapse in judgment on the part of the German Christian population and should be remembered to prevent such events.
- Holocaust and the United States To the most basic facts, the holocaust saw the death of approximately eleven million people, six million of these being Jews.
- The Armenian Genocide and the Holocaust Comparing the Holocaust and the Armenian Genocide the latter is much simpler in terms of cause, method, and outcome. The Holocaust is the direct result of anti-Semitism.
- Third Reich and Holocaust Commemoration The commemoration of the Third Reich and the holocaust through negative publicity like in Goldhaggen and crimes of the Wehrmacht gives the world a chance to ridicule the country.
- Facts of the Holocaust Holocaust was one of the most terrible events in history if the world marked by extreme violence and hostility.
- American Influence on Stopping Holocaust Had America been involved early and acted accordingly, millions of Jews could have been saved from the Holocaust.
- Holocaust and Genocide Analysis The ideology provided by Nazi underlined the descent of the German people from the Aryan race and rejected all other nations.
- “I, Rigoberta Menchú: An Indian Woman in Guatemala” and “American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World”: Comparison The book titled “I, Rigoberta Menchú: An Indian Woman in Guatemala” is an autobiography of Rigoberta Menchú that is written in the form of the testimonio.
- Herero Holocaust Among European Colonial Genocides The source identifies a pattern of events that preceded the holocaust in Germany. As Ter-Matevosyan notes, the holocaust is one of the worst historic moments in modern history.
- US Holocaust Memorial and American Indian Museums In this paper, I will evaluate the National Museum of the American Indian and the U.S. Holocaust Memorial Museum.
- Holocaust in “Night” Novel by Elie Wiesel While exterminating Jews, the Nazis were also trying to humiliate the ‘chosen people’ in every way possible. Wiesel’s book Night illustrates the validity of this suggestion.
- Antisemitism Controversy and Holocaust Denial Antisemitism has existed for centuries and taken different forms. This is a very dangerous phenomenon as it often resulted in cruel pogroms and even legal persecutions.
- Holocaust Denial and Antisemitism Ideas Antisemitism has existed for centuries and taken different forms. This is a very dangerous phenomenon as it often resulted in cruel pogroms and even legal persecutions.
- “Night” a Book by Elie Wiesel about Holocaust Literature Analysis Night is a book written by Elie Wiesel that focuses on his experiences while imprisoned in one of the Auschwitz concentration camp during the Holocaust.
- Night by Elie Wiesel: A Memoir About the Holocaust Experiences Night by Elie Wiesel describes the little boy Eliezer. In his teens, Eliezer is a perfect embodiment of a child growing up in a perfect society.
- The Rwandan Genocide as One of the Devastating Genocides Since the Holocaust The historic Rwandan Genocide, organized by Hutu hardliners, resulted in the merciless murder of approximately one million individuals after a three months rampage in 1994.
- Environmental Studies: The Global Warming Holocaust Global climate change is a social issue that has captured the imagination of the world’s population. This issue is discussed in mass media and social media platforms.
- Concentration Camps During the Holocaust
- Saving Jews From the Holocaust Examined in Terms of Cognitive Dissonance Theories
- Nazi Beliefs and the Holocaust
- Holocaust Survivor Bewilderment and Anger
- Life During the Holocaust in the Eyes of Jean Amery
- Comparing Adolf Hitler and Joseph Stalin During the Holocaust
- Christian Churches Should Have Opposed the Nazi Holocaust
- Holocaust, the Rwandan Genocide, and the Asian Genocide
- Stolen Art Literature and Music of the Holocaust
- German Anti-Semitism Was Responsible for the Holocaust
- Political Ideology and Other Factors Leading to the Holocaust
- Dehumanization During the Holocaust and Iranian Revolution
- Holocaust and Its Sociopolitical Causes
- American Foreign Policy During the Holocaust
- Moral Indifference, the Holocaust & the Directive for Genocide
- Croatia Before and After the Holocaust and World War II
- Death and Concentration Camps in the Holocaust History
- Nazi Propaganda During World War Two and the Holocaust
- Holocaust Victim’s Retribution and Reparations
- Nazi Germany and Virginia Holocaust Museum
- Medical Experiments During the Holocaust
- Pre Nazi Holocaust and the Civil War
- Holocaust and Bosnian Genocide Comparisons
- German Battalion 101’s Role in Perpetuating the Holocaust
- Hypothesis Concerning Holocaust Presented by David Cole
- Emotional Changes During the Holocaust
- Jewish Resistance During WWII and the Holocaust
- Holocaust Bystanders: Placing the Blame on Surrounding Citizens and Allied Nations
- Anti-Semitism and the Holocaust
- Japanese Internment Camps and Holocaust Concentration Camps
- Holocaust and the Response of the American Catholic Church
- Armenian Genocide and the Holocaust
- Holocaust Denial Political Agenda
- Nuclear Holocaust United States
- Advancing the Individual’s Knowledge of the Holocaust
- Holocaust: Monuments, Memorials, and Public Demonstrations
- Khmer Rouge and the Cambodian Holocaust
- Challenges Facing the Nazis and Other Jews in the Holocaust
- Holocaust Survivor Testimonies: Time, Methodology, and Memory
- American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World
- How Did the Holocaust Affect the Development of Military Literature?
- How Did the Native American Removal Compared to the Holocaust?
- How Did the Nazis Use Propaganda During the Holocaust?
- How Ordinary Germans and Their Foreign Allies Willingly Participated in the Holocaust?
- How the Holocaust Affected It’s Jewish Victims?
- Were German Citizens Aware of the Holocaust?
- What Did the Holocaust and Japanese Relocation Act Have in Similarities?
- What Theological Questions Relevant to the Study of Judaism Are Raised by the Holocaust?
- What Was the Involvement of Ordinary Germans in the Holocaust?
- Why Germans Scientist, Engineers and Doctors Asked To Participate in the Holocaust?
- Why Should Future Generations Know About the Holocaust?
- Were the Jehovah Witnesses Really Affected by the Holocaust?
- Was German “Eliminationist Antisemitism” Responsible for the Holocaust?
- What Is Meant by Term the Holocaust Industry?
- Why Does God Permit Tragic Events Like the Holocaust Terrorist Attacks?
- Who Says the Holocaust Never Happened and Why Do They Say It?
- What Is the Environmental History of the Holocaust?
- Why Did the World Keep Silent During the Holocaust?
- What Is the Treatment of the Holocaust in High School History Textbooks?
- What Is the Culpability of Accounting in Perpetuating the Holocaust?
- Did Gender Matter During the Holocaust?
- What Are the Reflections on the Historiography of the Holocaust?
- Can There Be a Political Science of the Holocaust?
- How Did Holocaust Show the Problems of Historical Representation?
- Why the Holocaust Does Not Matter to Estonians?
- Bystanders during the Holocaust: should they be morally responsible for not intervening?
- Did the Nuremberg trials achieve justice for Holocaust victims?
- Should teaching the history of the Holocaust be mandatory in schools?
- Should Holocaust denial be legally punishable?
- Does the Holocaust illustrate the dangers of unchecked government power?
- Should Holocaust restitution claims be limited to a specific timeframe?
- The Holocaust and the problem of evil: does this genocide contradict the existence of a benevolent God?
- Should non-Jewish victims of the Holocaust be commemorated equally to Jewish victims?
- Should Holocaust museums adopt a truthful or sensitive approach to showing Holocaust atrocities?
- Is it justifiable for Holocaust victims to seek financial restitution from companies collaborating with Nazis?
- The Holocaust denial: the motivations behind it and its consequences.
- What were the motivations of people participating in the Holocaust genocide?
- The impact of the Holocaust survivors’ testimonies on understanding the history.
- The role of the Holocaust in countering modern hate speech and prejudice.
- Similarities and differences between the Holocaust and other genocides.
- How did the Nazi propaganda incite violence during the Holocaust?
- Evaluating the effectiveness of resistance movements during the Holocaust.
- The psychological effects of the Holocaust on survivors.
- Children’s experiences of separation and survival during the Holocaust.
- Non-Jewish people’s rescue efforts during the Holocaust.
- The ethical challenges involved in the artistic representation of the Holocaust.
- The role of international law in preventing genocide after the Holocaust.
- Beyond Auschwitz: lesser-known Holocaust concentration camps.
- How is the Holocaust remembered and commemorated today?
- The role of ordinary citizens in perpetrating the Holocaust.
- The Warsaw Ghetto uprising and its impact on the Jewish resistance.
- The portrayal of the Holocaust in literature and movies.
- The Holocaust and gender: unique experiences of male and female victims.
- Challenges that followed the liberation of the Nazi concentration camps.
- The effects of the Holocaust on the victims’ descendants.
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, May 10). 126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/holocaust-essay-topics/
"126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles." StudyCorgi , 10 May 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/holocaust-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles'. 10 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/holocaust-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/holocaust-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "126 Holocaust Essay Topics & Research Paper Titles." May 10, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/holocaust-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Holocaust were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 21, 2024 .
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
The Holocaust
By: History.com Editors
Updated: April 11, 2023 | Original: October 14, 2009

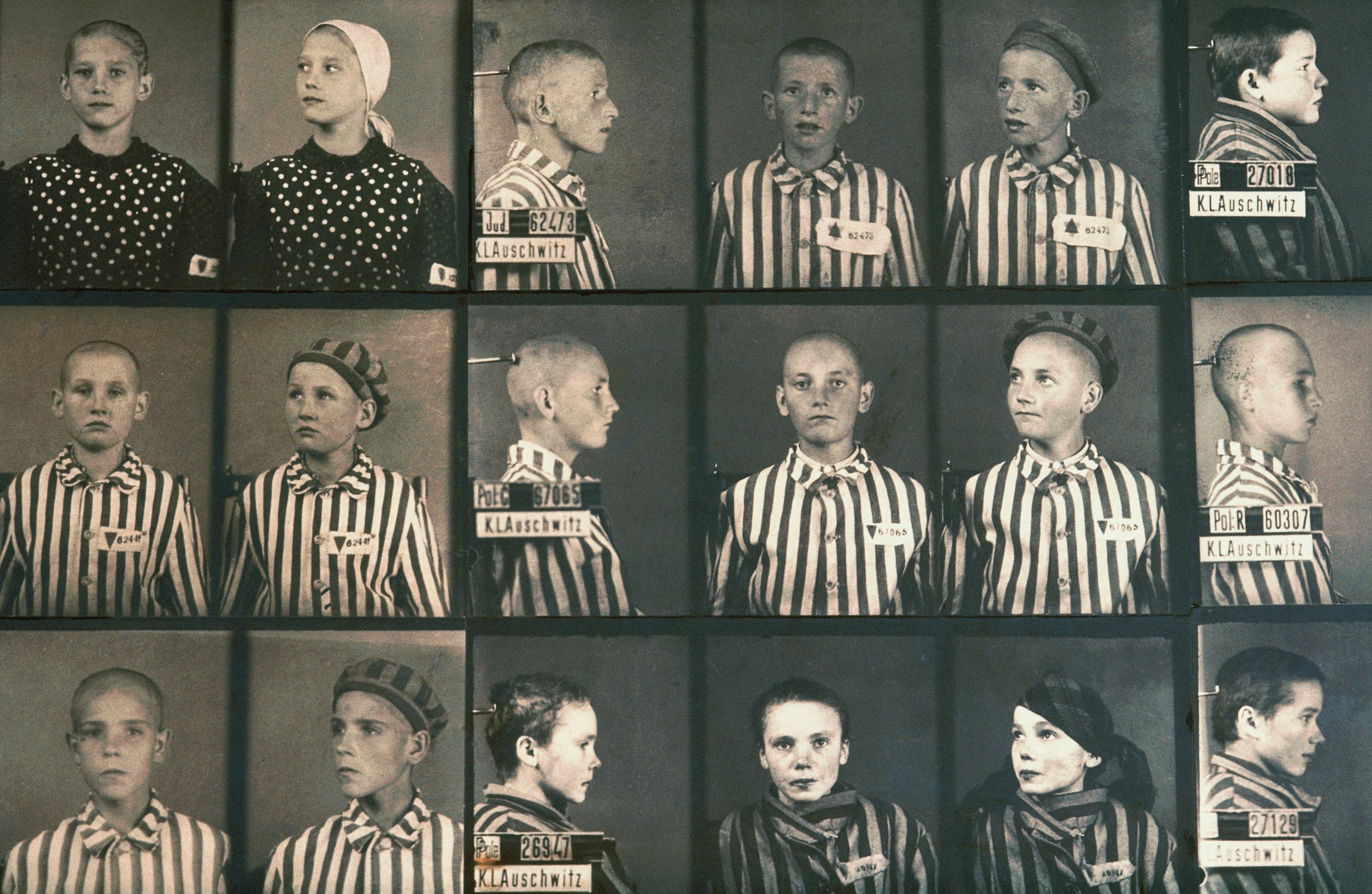
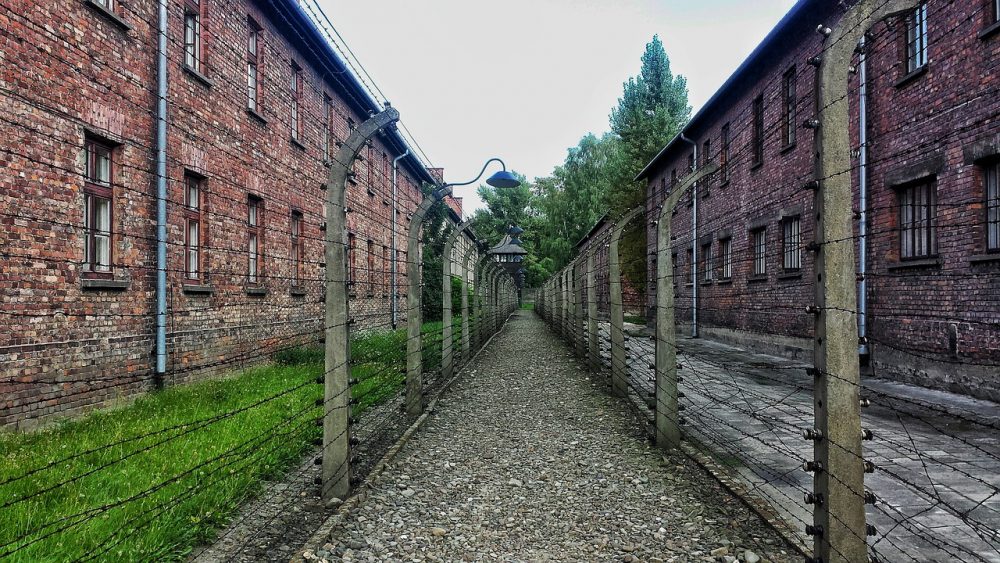
The Holocaust was the state-sponsored persecution and mass murder of millions of European Jews, Romani people, the intellectually disabled, political dissidents and homosexuals by the German Nazi regime between 1933 and 1945. The word “holocaust,” from the Greek words “holos” (whole) and “kaustos” (burned), was historically used to describe a sacrificial offering burned on an altar.
After years of Nazi rule in Germany, dictator Adolf Hitler’s “Final Solution”—now known as the Holocaust—came to fruition during World War II, with mass killing centers in concentration camps. About six million Jews and some five million others, targeted for racial, political, ideological and behavioral reasons, died in the Holocaust—more than one million of those who perished were children.
Historical Anti-Semitism
Anti-Semitism in Europe did not begin with Adolf Hitler . Though use of the term itself dates only to the 1870s, there is evidence of hostility toward Jews long before the Holocaust—even as far back as the ancient world, when Roman authorities destroyed the Jewish temple in Jerusalem and forced Jews to leave Palestine .
The Enlightenment , during the 17th and 18th centuries, emphasized religious tolerance, and in the 19th century Napoleon Bonaparte and other European rulers enacted legislation that ended long-standing restrictions on Jews. Anti-Semitic feeling endured, however, in many cases taking on a racial character rather than a religious one.
Did you know? Even in the early 21st century, the legacy of the Holocaust endures. Swiss government and banking institutions have in recent years acknowledged their complicity with the Nazis and established funds to aid Holocaust survivors and other victims of human rights abuses, genocide or other catastrophes.
Hitler's Rise to Power
The roots of Adolf Hitler’s particularly virulent brand of anti-Semitism are unclear. Born in Austria in 1889, he served in the German army during World War I . Like many anti-Semites in Germany, he blamed the Jews for the country’s defeat in 1918.
Soon after World War I ended, Hitler joined the National German Workers’ Party, which became the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (NSDAP), known to English speakers as the Nazis. While imprisoned for treason for his role in the Beer Hall Putsch of 1923, Hitler wrote the memoir and propaganda tract “ Mein Kampf ” (or “my struggle”), in which he predicted a general European war that would result in “the extermination of the Jewish race in Germany.”
Hitler was obsessed with the idea of the superiority of the “pure” German race, which he called “Aryan,” and with the need for “Lebensraum,” or living space, for that race to expand. In the decade after he was released from prison, Hitler took advantage of the weakness of his rivals to enhance his party’s status and rise from obscurity to power.
On January 30, 1933, he was named chancellor of Germany. After the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934, Hitler anointed himself Fuhrer , becoming Germany’s supreme ruler.
Concentration Camps
The twin goals of racial purity and territorial expansion were the core of Hitler’s worldview, and from 1933 onward they would combine to form the driving force behind his foreign and domestic policy.
At first, the Nazis reserved their harshest persecution for political opponents such as Communists or Social Democrats. The first official concentration camp opened at Dachau (near Munich) in March 1933, and many of the first prisoners sent there were Communists.
Like the network of concentration camps that followed, becoming the killing grounds of the Holocaust, Dachau was under the control of Heinrich Himmler , head of the elite Nazi guard, the Schutzstaffel (SS) and later chief of the German police.
By July 1933, German concentration camps ( Konzentrationslager in German, or KZ) held some 27,000 people in “protective custody.” Huge Nazi rallies and symbolic acts such as the public burning of books by Jews, Communists, liberals and foreigners helped drive home the desired message of party strength and unity.
In 1933, Jews in Germany numbered around 525,000—just one percent of the total German population. During the next six years, Nazis undertook an “Aryanization” of Germany, dismissing non-Aryans from civil service, liquidating Jewish-owned businesses and stripping Jewish lawyers and doctors of their clients.
Nuremberg Laws
Under the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, anyone with three or four Jewish grandparents was considered a Jew, while those with two Jewish grandparents were designated Mischlinge (half-breeds).
Under the Nuremberg Laws, Jews became routine targets for stigmatization and persecution. This culminated in Kristallnacht , or the “Night of Broken Glass” in November 1938, when German synagogues were burned and windows in Jewish home and shops were smashed; some 100 Jews were killed and thousands more arrested.
From 1933 to 1939, hundreds of thousands of Jews who were able to leave Germany did, while those who remained lived in a constant state of uncertainty and fear.

HISTORY Vault: Third Reich: The Rise
Rare and never-before-seen amateur films offer a unique perspective on the rise of Nazi Germany from Germans who experienced it. How were millions of people so vulnerable to fascism?
Euthanasia Program
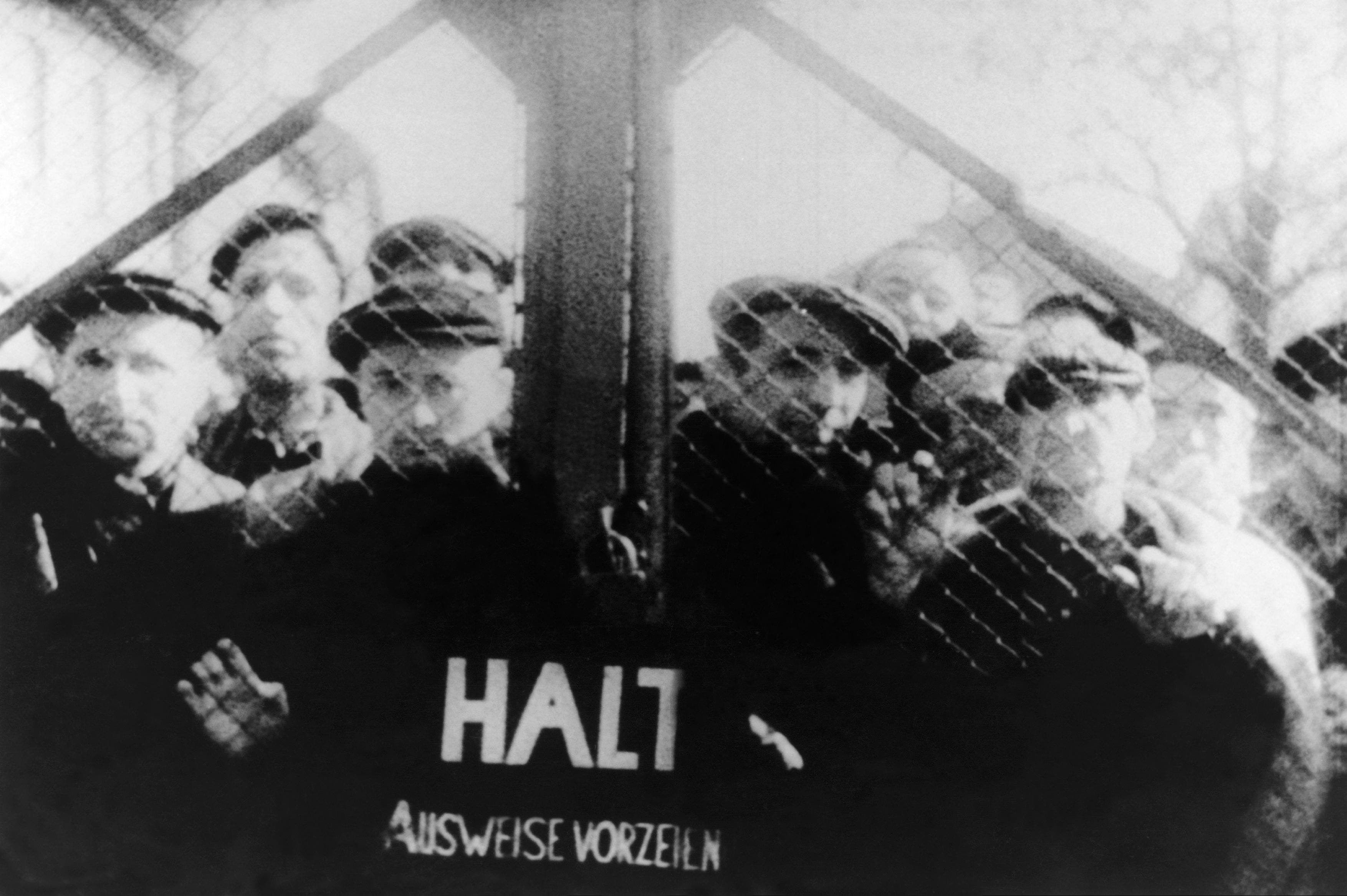
In September 1939, Germany invaded the western half of Poland , starting World War II . German police soon forced tens of thousands of Polish Jews from their homes and into ghettoes, giving their confiscated properties to ethnic Germans (non-Jews outside Germany who identified as German), Germans from the Reich or Polish gentiles.
Surrounded by high walls and barbed wire, the Jewish ghettoes in Poland functioned like captive city-states, governed by Jewish Councils. In addition to widespread unemployment, poverty and hunger, overpopulation and poor sanitation made the ghettoes breeding grounds for disease such as typhus.
Meanwhile, beginning in the fall of 1939, Nazi officials selected around 70,000 Germans institutionalized for mental illness or physical disabilities to be gassed to death in the so-called Euthanasia Program.
After prominent German religious leaders protested, Hitler put an end to the program in August 1941, though killings of the disabled continued in secrecy, and by 1945 some 275,000 people deemed handicapped from all over Europe had been killed. In hindsight, it seems clear that the Euthanasia Program functioned as a pilot for the Holocaust.

'Final Solution'
Throughout the spring and summer of 1940, the German army expanded Hitler’s empire in Europe, conquering Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg and France. Beginning in 1941, Jews from all over the continent, as well as hundreds of thousands of European Romani people, were transported to Polish ghettoes.
The German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941 marked a new level of brutality in warfare. Mobile killing units of Himmler’s SS called Einsatzgruppen would murder more than 500,000 Soviet Jews and others (usually by shooting) over the course of the German occupation.
A memorandum dated July 31, 1941, from Hitler’s top commander Hermann Goering to Reinhard Heydrich, chief of the SD (the security service of the SS), referred to the need for an Endlösung ( Final Solution ) to “the Jewish question.”

Yellow Stars
Beginning in September 1941, every person designated as a Jew in German-held territory was marked with a yellow, six-pointed star, making them open targets. Tens of thousands were soon being deported to the Polish ghettoes and German-occupied cities in the USSR.
Since June 1941, experiments with mass killing methods had been ongoing at the concentration camp of Auschwitz , near Krakow, Poland. That August, 500 officials gassed 500 Soviet POWs to death with the pesticide Zyklon-B. The SS soon placed a huge order for the gas with a German pest-control firm, an ominous indicator of the coming Holocaust.
Holocaust Death Camps
Beginning in late 1941, the Germans began mass transports from the ghettoes in Poland to the concentration camps, starting with those people viewed as the least useful: the sick, old and weak and the very young.
The first mass gassings began at the camp of Belzec, near Lublin, on March 17, 1942. Five more mass killing centers were built at camps in occupied Poland, including Chelmno, Sobibor, Treblinka, Majdanek and the largest of all, Auschwitz.
From 1942 to 1945, Jews were deported to the camps from all over Europe, including German-controlled territory as well as those countries allied with Germany. The heaviest deportations took place during the summer and fall of 1942, when more than 300,000 people were deported from the Warsaw ghetto alone.
Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
Amid the deportations, disease and constant hunger, incarcerated people in the Warsaw Ghetto rose up in armed revolt.
The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising from April 19-May 16, 1943, ended in the death of 7,000 Jews, with 50,000 survivors sent to extermination camps. But the resistance fighters had held off the Nazis for almost a month, and their revolt inspired revolts at camps and ghettos across German-occupied Europe.
Though the Nazis tried to keep operation of the camps secret, the scale of the killing made this virtually impossible. Eyewitnesses brought reports of Nazi atrocities in Poland to the Allied governments, who were harshly criticized after the war for their failure to respond, or to publicize news of the mass slaughter.
This lack of action was likely mostly due to the Allied focus on winning the war at hand, but was also partly a result of the general incomprehension with which news of the Holocaust was met and the denial and disbelief that such atrocities could be occurring on such a scale.
'Angel of Death'
At Auschwitz alone, more than 2 million people were murdered in a process resembling a large-scale industrial operation. A large population of Jewish and non-Jewish inmates worked in the labor camp there; though only Jews were gassed, thousands of others died of starvation or disease.
In 1943, eugenics advocate Josef Mengele arrived in Auschwitz to begin his infamous experiments on Jewish prisoners. His special area of focus was conducting medical experiments on twins , injecting them with everything from petrol to chloroform under the guise of giving them medical treatment. His actions earned him the nickname “the Angel of Death.”
Nazi Rule Ends
By the spring of 1945, German leadership was dissolving amid internal dissent, with Goering and Himmler both seeking to distance themselves from Hitler and take power.
In his last will and political testament, dictated in a German bunker that April 29, Hitler blamed the war on “International Jewry and its helpers” and urged the German leaders and people to follow “the strict observance of the racial laws and with merciless resistance against the universal poisoners of all peoples”—the Jews.
The following day, Hitler died by suicide . Germany’s formal surrender in World War II came barely a week later, on May 8, 1945.
German forces had begun evacuating many of the death camps in the fall of 1944, sending inmates under guard to march further from the advancing enemy’s front line. These so-called “death marches” continued all the way up to the German surrender, resulting in the deaths of some 250,000 to 375,000 people.
In his classic book Survival in Auschwitz , the Italian-Jewish author Primo Levi described his own state of mind, as well as that of his fellow inmates in Auschwitz on the day before Soviet troops liberated the camp in January 1945: “We lay in a world of death and phantoms. The last trace of civilization had vanished around and inside us. The work of bestial degradation, begun by the victorious Germans, had been carried to conclusion by the Germans in defeat.”
Legacy of the Holocaust
The wounds of the Holocaust—known in Hebrew as “Shoah,” or catastrophe—were slow to heal. Survivors of the camps found it nearly impossible to return home, as in many cases they had lost their entire family and been denounced by their non-Jewish neighbors. As a result, the late 1940s saw an unprecedented number of refugees, POWs and other displaced populations moving across Europe.
In an effort to punish the villains of the Holocaust, the Allies held the Nuremberg Trials of 1945-46, which brought Nazi atrocities to horrifying light. Increasing pressure on the Allied powers to create a homeland for Jewish survivors of the Holocaust would lead to a mandate for the creation of Israel in 1948.
Over the decades that followed, ordinary Germans struggled with the Holocaust’s bitter legacy, as survivors and the families of victims sought restitution of wealth and property confiscated during the Nazi years.
Beginning in 1953, the German government made payments to individual Jews and to the Jewish people as a way of acknowledging the German people’s responsibility for the crimes committed in their name.
The Holocaust. The National WWII Museum . What Was The Holocaust? Imperial War Museums . Introduction to the Holocaust. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum . Holocaust Remembrance. Council of Europe . Outreach Programme on the Holocaust. United Nations .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
My Homework Done
Expert Writing Services
- How It Works
- Buy homework
- Ace my homework
- Homework writers
- Homework help
- Assignment writing
- Homework Solutions
- Homework Answers
- No Need To Study
- High school
- McGraw-Hill Connect
- Myaccountinglab
- Precalculus
- Word Problem
- Computer Science
- Language arts
- Engineering
- Biochemistry
- Microbiology
Homework is easy with expert tips and advice. And even easier when you have an expert to do it for you.

80 Deep Holocaust Research Topics To Explore

Be it history or the sciences, the holocaust has played a key role in shaping theories and ideologies. How do you make your paper on the holocaust standout? What is it that you would be keen to know and research on? If you are finding it hard to put things in perspective, here is a list of topics on concentration camp research paper. It aims to help students and create a resource they can consult for writing research papers on the holocaust.
Table of Contents
Classic holocaust topics for research, holocaust argumentative essay topics, holocaust writing prompts for cause and effect, topics for comparison and contrast, art-based research papers on holocaust.
These holocaust research paper topics have inspired many students across the world. Go through these questions or topics to get inspired. They are sure to help you create interesting papers on the event.
To write a holocaust research paper use these topics as a foundation to start with and build upon.
- Ann Frank’s father — A Detailed character sketch
- Milestones in the life of Adolf Hitler
- Childhood events that shaped Adolf Hitler
- Prosecution of tribunes and war criminals during the Second World War
- The liberation of the concentration camps
- The heroic acts of Oskar Schindler
- Anti-Jew laws adopted in Nazi Germany
- The Schutzstaffel and their role during the holocaust
- The resistance of Denmark and the rescue of Jews of Danish origin
- Role of Pope Pius XII during the Holocaust
- Countries that have adopted laws of Holocaust Denial and why
- The heroic acts of Irena Sendler during the holocaust
- Does the Holocaust question God’s existence?
- Why is it important for young people to visit Holocaust memorials?
- Christian and catholic community – their responses on the holocaust, then and now
- The persecution of homosexuals during the holocaust
- Twin experiments during the holocaust
- How and why did the Germans allow a phenomenon like a holocaust to occur?
- Holocaust – The various stages
- What initiated the Holocaust?
- Deprivation of basic human rights in concentration camps
- The personal history of Eva Braun
- Insights into the life of a Holocaust Survivor
- What do German schoolchildren learn about the Holocaust?
These holocaust research questions present two perspectives of a given topic. They focus on the concentration research camp paper, as well as, the papers on arts and science during the holocaust. The argumentative holocaust paper topics give you a lot of scope for research.
- Should holocaust be addressed in college and classrooms?
- Arguments that debunk the holocaust denial.
- Holocaust lessons for humanity
- Is one person responsible for the holocaust?
- Holocaust: Result of war or a systematically planned action?
- Would the international community intervene if a Holocaust was to repeat itself today?
- Were all Nazi soldiers, pro-genocide?
- Why must we remember the Holocaust?
- Could early destruction of concentration camps by allies have prevented the horrors of the Holocaust?
- The holocaust is the result of Hitler’s ideologies about race. Is this statement entirely true?
- What makes the Holocaust unique?
- Did stereotypes have any role to play in the Holocaust?
- Could more resistance from European citizens and Jewish people have stopped the Holocaust?
- Events contributing to the rise of Hitler
- Is it possible for the recurrence of the Holocaust in modern times?
- Was inaction the sole contributor for mass genocide during World War II?
These holocaust research topics look into the massive effects of the Holocaust. Some of these can be felt even today.
- What were the consequences of the Holocaust?
- Provide a holocaust thesis statement on the effects of the Holocaust on Modern Europe.
- The effect of the holocaust on Jewish people
- The effect of the holocaust on other minorities
- Did the Holocaust impact the formation of the EU?
- How did the Holocaust affect Israel?
- Origins and reasons for the Anti-Semitism ideology.
- The effect of the bystander effect on social attitudes towards WWII.
- The effect of the Holocaust on Western civilization.
- The role of anti-Semitism in the Holocaust.
- Increase in atheism after WWII
- Perception of Jewish people after WWII.
- Effects of the Holocaust on modern social ideologies.
- The role of the Holocaust in history
- The perception of Germany post Holocaust
These holocaust research topics compare similar events and ideologies that are connected to the holocaust.
- German Holocaust versus the American Indian Holocaust.
- Compare the lives of Primo Levi and Elie Wiesel in concentration camps.
- Jewish and Black Holocausts
- Japanese Internment camps in the USA versus concentration camps in Germany
- Rwanda genocide versus Holocaust
- Dachau versus Auschwitz
- Similarities between the Holocaust and slavery
- Jewish refugees versus modern Syrian refugees.
- Cambodian genocide versus the Holocaust
- Jewish partisan and spiritual resistance.
These holocaust research questions delve into the artistic representation of the Holocaust.
- Schindler’s List: A representation of Holocaust
- Character sketch of Nechama Tec in the book “Dry Tears”
- Influence of concentration camps on characters in the book, “Night”
- Review of the Pianist
- Holocaust’s famous monuments
- Do movies trivialize the genocide?
- Do Holocaust movies reduce racial discrimination in modern society?
- How literature honours Holocaust victims.
- “March to Freedom” by Edith Singer and human resilience.
- Review of “Dry Tears” by Nechama Tec
- Guilt concept in the graphic novel “Maus” by Art Spiegelman
- Review of “The diary of Anne Frank”
- How personal diaries changed the perception of the Holocaust.
- Is it moral to create art about the Holocaust?
- Can holocaust movies prevent its recurrence?
For more prompts and writing help in various styles, get in touch with our skilled professionals today.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
What americans know about the holocaust.

Last year, Pew Research Center conducted its second U.S. religious knowledge survey , designed to gauge Americans’ familiarity with a variety of religion-related facts. (The first was conducted in 2010 .) This time, we also included a few questions aimed at measuring how much Americans know about the Holocaust, resulting in this report.
The new data is based on a survey of 10,971 U.S. adults conducted in February 2019. Most of the people surveyed (10,429) were members of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel. An additional 542 respondents were sampled from the Ipsos KnowledgePanel – all of them Jewish, Mormon or Hispanic Protestant, to bolster the samples for these subgroups. Both the online survey panels used as a basis for this study recruited panelists by phone or mail via random sampling to ensure that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. Recruiting panelists this way gives us confidence that any sample can represent the whole population (watch our Methods 101 explainer on random sampling).
To further ensure that each survey reflects a balanced cross-section of the nation, the data are weighted to match the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology and the methodology for this report .
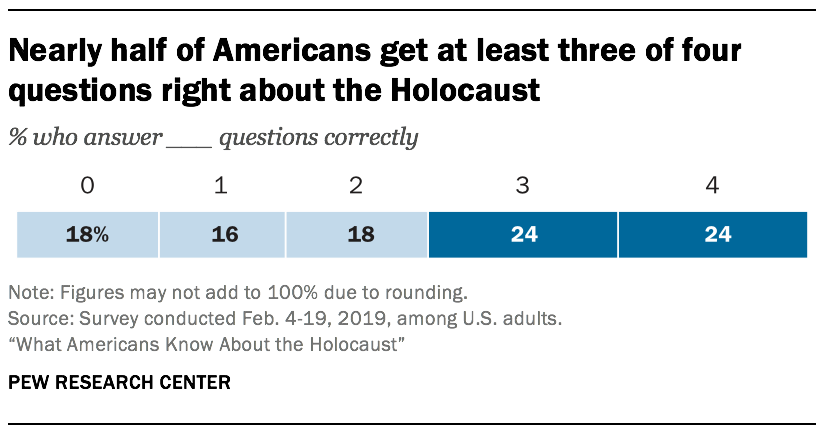
Most U.S. adults know what the Holocaust was and approximately when it happened, but fewer than half can correctly answer multiple-choice questions about the number of Jews who were murdered or the way Adolf Hitler came to power, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.
When asked to describe in their own words what the Holocaust was, more than eight-in-ten Americans mention the attempted annihilation of the Jewish people or other related topics, such as concentration or death camps, Hitler, or the Nazis. Seven-in-ten know that the Holocaust happened between 1930 and 1950. And close to two-thirds know that Nazi-created ghettos were parts of a city or town where Jews were forced to live.
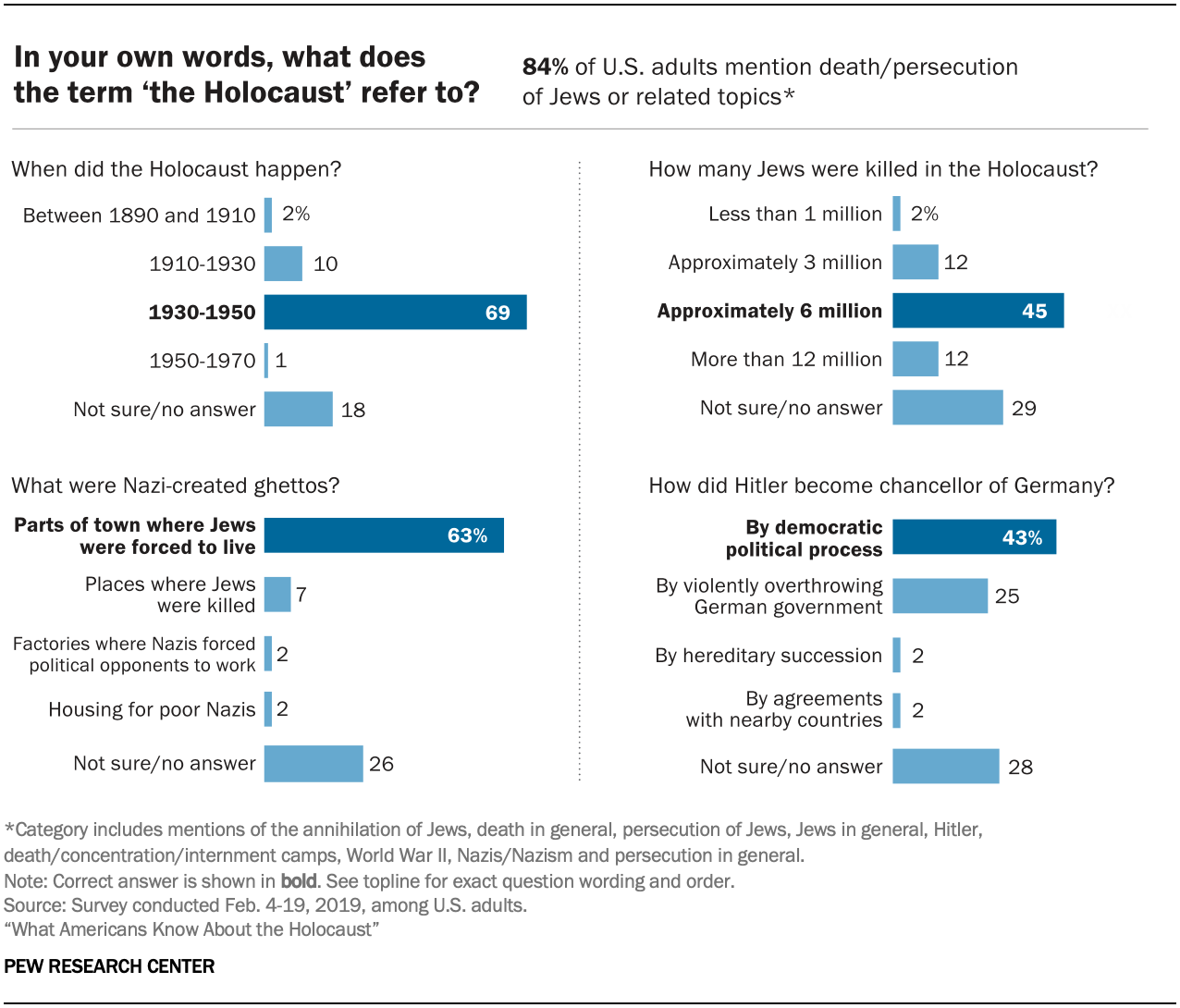
Fewer than half of Americans (43%), however, know that Adolf Hitler became chancellor of Germany through a democratic political process. And a similar share (45%) know that approximately 6 million Jews were killed in the Holocaust. Nearly three-in-ten Americans say they are not sure how many Jews died during the Holocaust, while one-in-ten overestimate the death toll, and 15% say that 3 million or fewer Jews were killed.
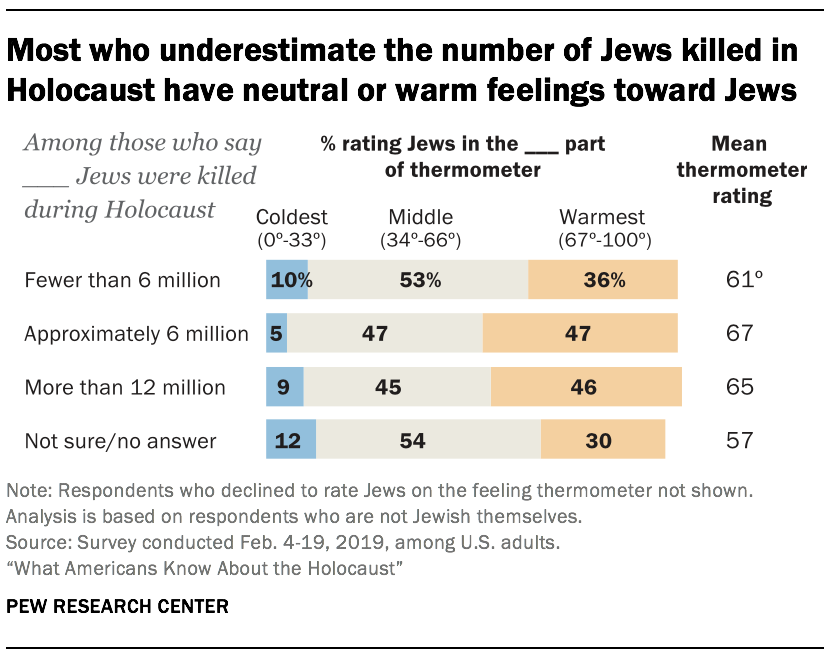
While the survey cannot answer this question directly, the data suggests that relatively few people in this group express strongly negative feelings toward Jews. On a “ feeling thermometer ” designed to gauge sentiments toward a variety of groups, nine-in-ten non-Jewish respondents who underestimate the Holocaust’s death toll express neutral or warm feelings toward Jews, while just one-in-ten give Jews a cold rating. Similar shares express cold feelings toward Jews among those who overestimate the number of Holocaust deaths (9%) and among those who say they do not know how many Jews died in the Holocaust or decline to answer the question (12%).
These are among the key findings of a survey conducted online Feb. 4 to 19, 2019, among 10,971 respondents. The study was conducted mostly among members of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (a nationally representative panel of randomly selected U.S. adults recruited from landline and cellphone random-digit-dial surveys and an address-based survey), supplemented by interviews with members of the Ipsos KnowledgePanel. The margin of sampling error for the full sample is plus or minus 1.5 percentage points.
A previously published report on this survey explored the public’s answers to 32 knowledge questions about a wide range of religious topics, including the Bible and Christianity, Judaism, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, atheism and agnosticism, and religion and public life. In addition to the 32 questions about religious topics, the survey included five factual questions to test knowledge of the Holocaust: one open-ended question and four multiple-choice questions.
The four multiple-choice questions also were included in a separate survey of approximately 1,800 U.S. teens (ages 13 to 17). Overall, the teens display lower levels of knowledge about the Holocaust than their elders do. Like the adults, however, teens fare best on the questions about when the Holocaust occurred and what ghettos were. About half or more of teens answer those questions correctly. By comparison, 38% of teens know that approximately 6 million Jews perished in the Holocaust, and just one-third know that Hitler came to power through a democratic process. See here for details.
The Holocaust knowledge questions were designed to measure some basic facts about the Holocaust, including when it happened and who it involved. However, the questions were not meant to include all of the most essential facts about the Holocaust.
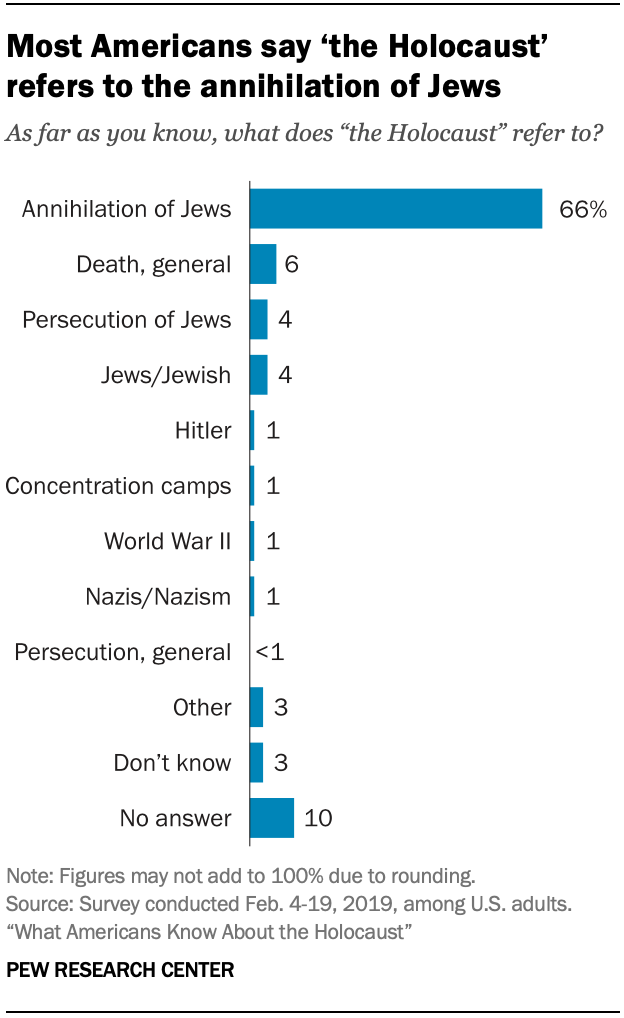
Just 3% of Americans mention something else, and an equal share say they don’t know. One-in-ten decline to answer the question.
Jews, atheists and agnostics get more questions right about the Holocaust
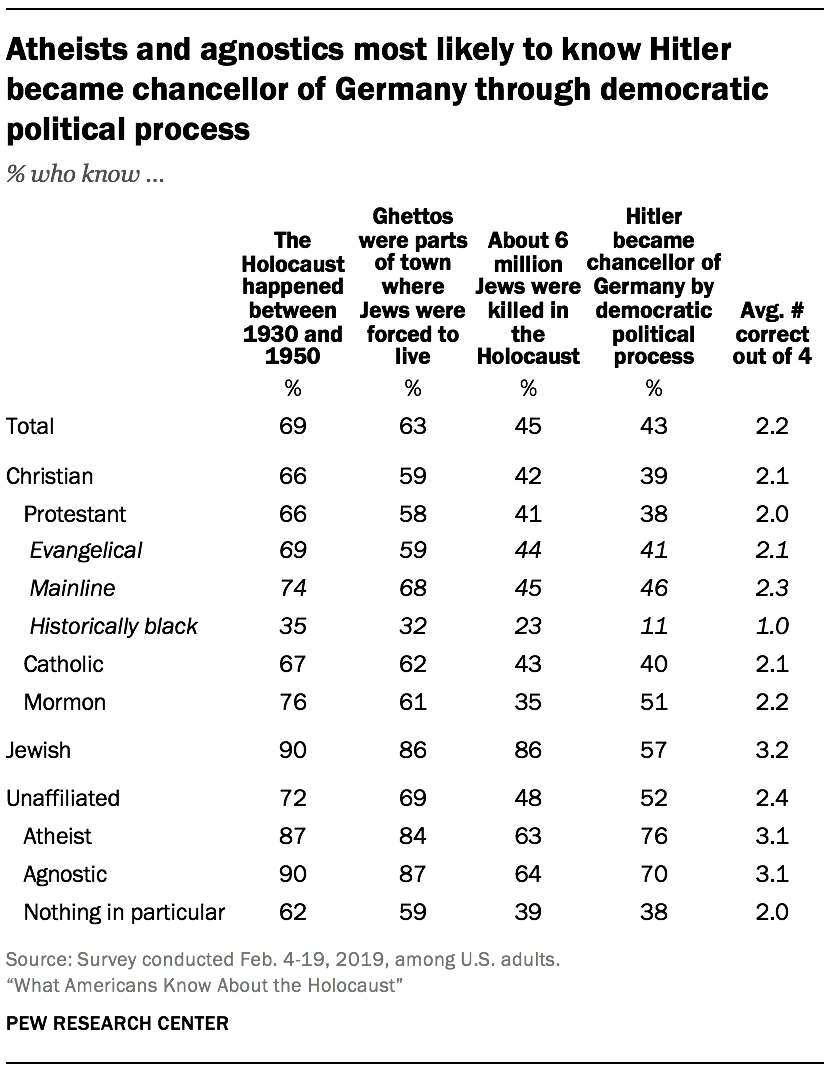
Nearly nine-in-ten U.S. Jews (90%), agnostics (90%) and atheists (87%) know that the Holocaust happened between 1930 and 1950. Similarly, an overwhelming majority of agnostics (87%), Jews (86%) and atheists (84%) know that ghettos were parts of a town or city where Jews were forced to live.
U.S. Jews are more likely than atheists and agnostics to know how many Jews were killed in the Holocaust. Nearly nine-in-ten Jews know that about 6 million Jews were killed in the Holocaust, compared with two-thirds of agnostics (64%) and atheists (63%) who get this question right. By contrast, more atheists and agnostics than Jews correctly answer the question about how Hitler became chancellor of Germany: Three-quarters of atheists (76%) and seven-in-ten agnostics know Hitler became chancellor through a democratic political process, compared with 57% of Jews.
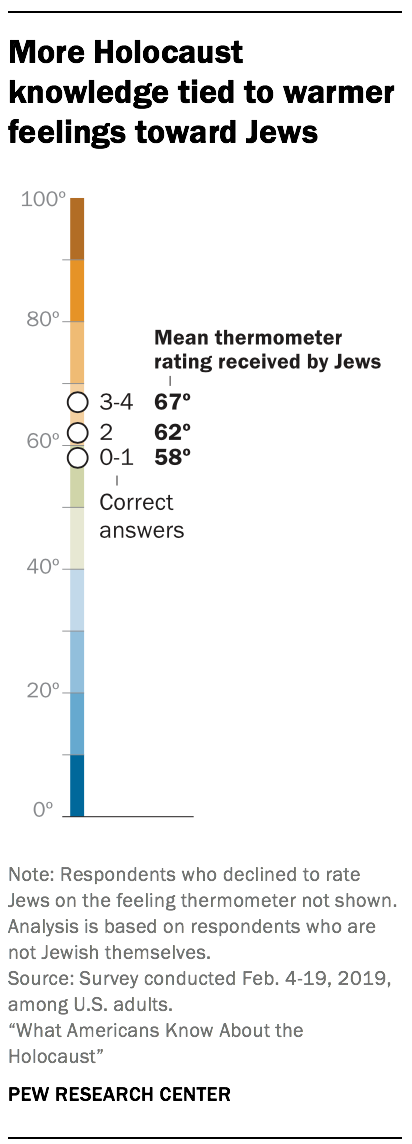
Education, visiting a Holocaust museum and knowing someone who is Jewish are strongly linked with Holocaust knowledge
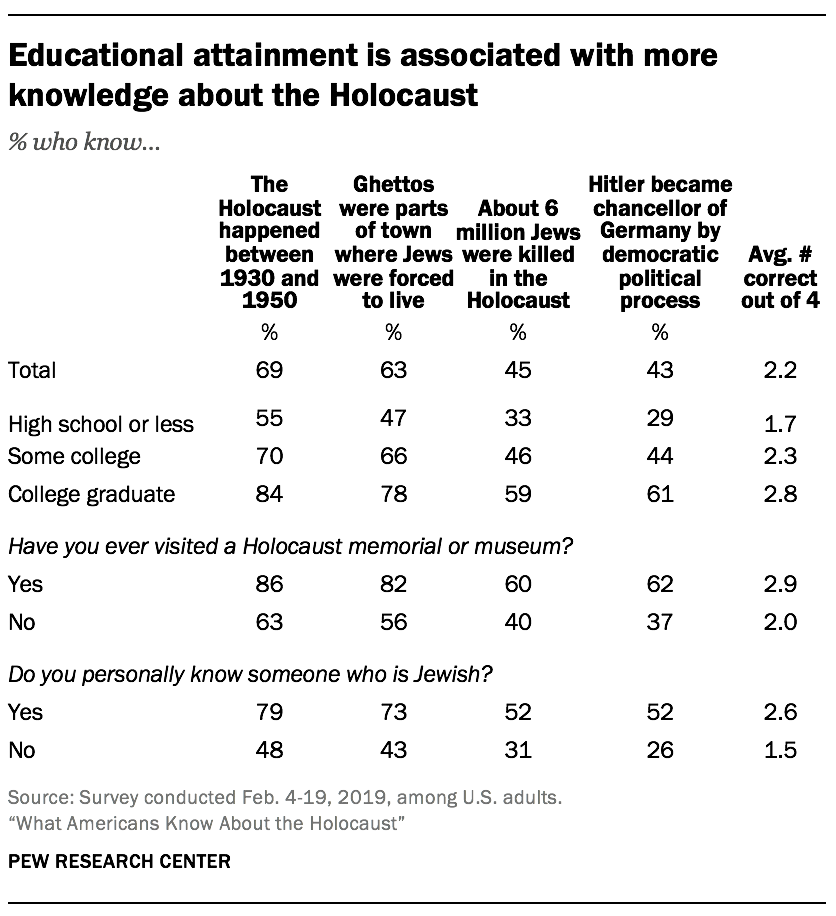
Another factor linked with how much Americans know about the Holocaust is whether respondents have ever visited a Holocaust memorial or museum. U.S. adults who say they have visited a Holocaust memorial or museum (27% of all respondents) correctly answer 2.9 questions right out of the four multiple-choice questions about the Holocaust. By comparison, those who have never visited a Holocaust memorial or museum answer 2.0 questions right, on average.
The survey included a question that asked respondents whether they personally know someone who is Jewish. Compared with those who say they do not know anyone who is Jewish, Americans who know a Jewish person answer about one additional question right, on average (2.6 vs. 1.5).

Older adults display slightly higher levels of Holocaust knowledge
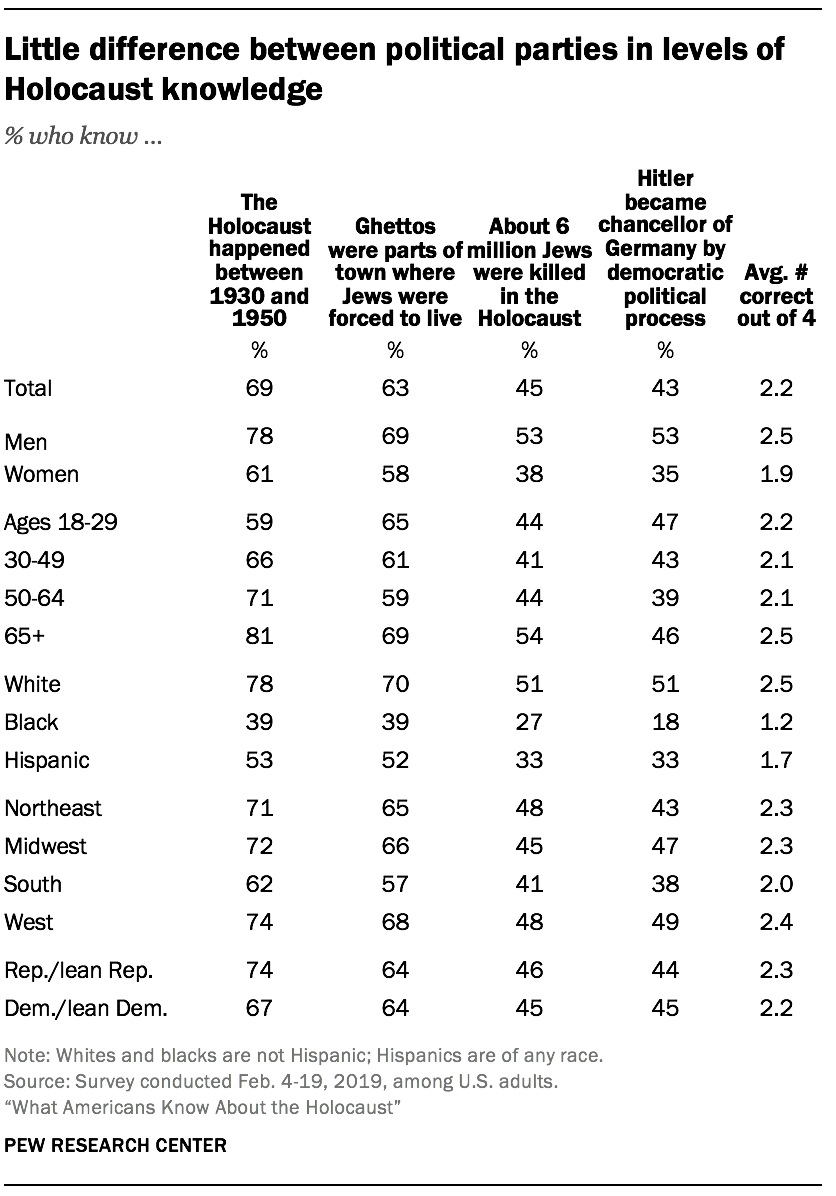
In addition, Americans ages 65 and older correctly answer an average of 2.5 questions about the Holocaust, compared with 2.2 right answers among those under the age of 65. And U.S. adults who live in the West, Northeast and Midwest perform slightly better than those who live in the South.
Politically, Republicans and those who lean toward the Republican Party (2.3) correctly answer about as many Holocaust knowledge questions as Democrats and Democratic leaners do (2.2).
U.S. teens’ levels of Holocaust knowledge similar to those of adults without post-secondary education
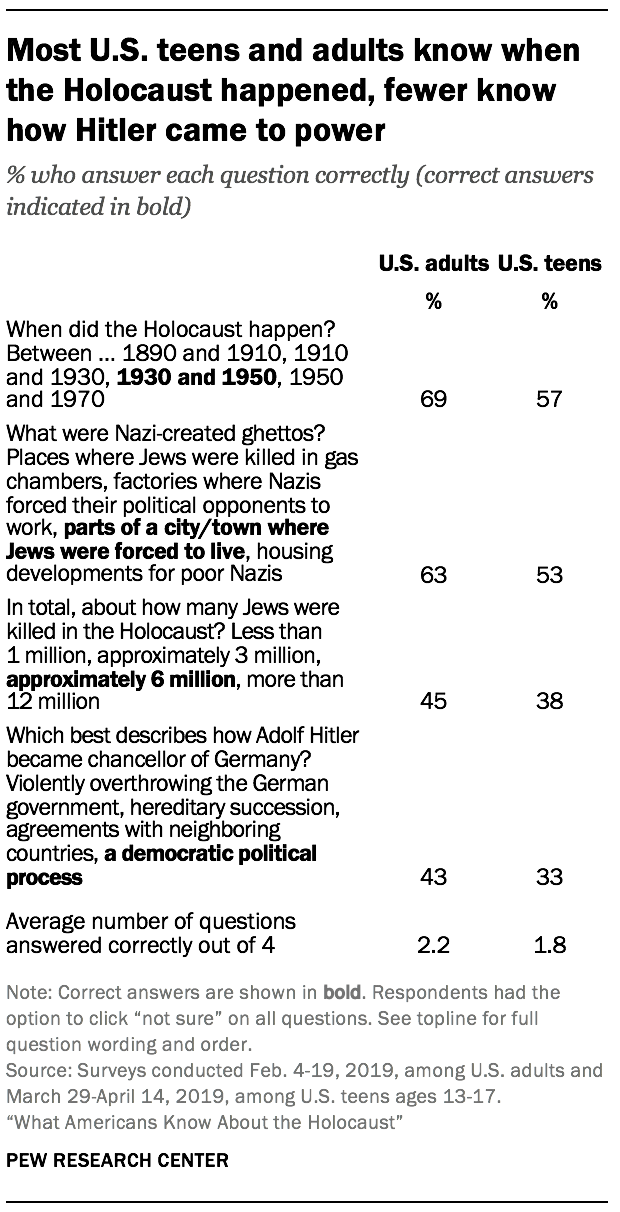
Like adults, more teens know when the Holocaust occurred (57%) and what Nazi-created ghettos were (53%) than know how many Jews were killed during the Holocaust (38%) or how Hitler became chancellor of Germany (33%).
On average, teens correctly answer slightly fewer questions than U.S. adults do (1.8 vs. 2.2, on average). This may reflect disparities in education. Among adults, those with a college degree correctly answer about one question more than those with a high school degree or less. Of course, teens between the ages of 13 and 17 have not yet had a chance to pursue post-secondary education. Overall, U.S. teens correctly answer about the same number of questions (1.8, on average) as adults whose formal education ended with high school (1.7).
However, one difference between teens and adults is the relationship between gender and Holocaust knowledge. While adult men answer slightly more questions right than women, teen boys and girls correctly answer a similar number of questions about the Holocaust (1.8 each, on average).
Previous Holocaust knowledge surveys
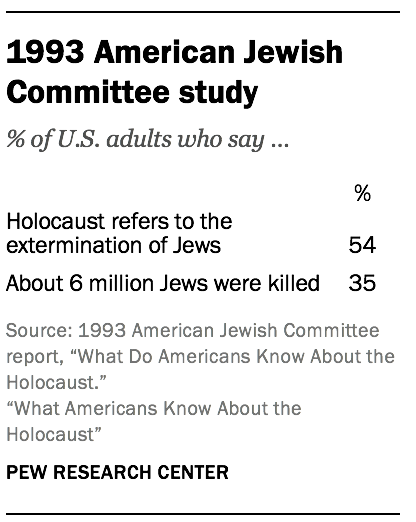
There are several important differences between Pew Research Center’s 2019 Holocaust knowledge questions and the other two surveys that make it so that they are not directly comparable (and thus unable to gauge whether levels of knowledge about the Holocaust have changed over time).
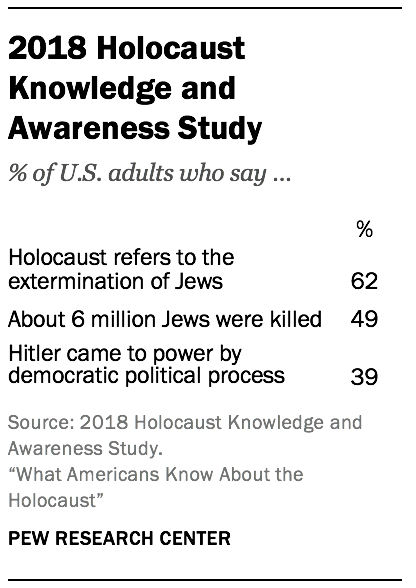
The respondents also took the surveys in different ways. The 2019 Pew Research Center survey was administered online on the American Trends Panel, a nationally representative panel of randomly selected U.S. adults. By contrast, the survey discussed in the 1993 AJC report was administered by interviewers in respondents’ homes. The 2018 Holocaust Knowledge and Awareness Study was administered mostly by interviewers over the phone, but also included some interviews administered online. Sometimes when the same question is asked in different modes, such as over the phone and online, there is a difference in results that is attributable to what survey methodologists call a mode effect . In other words, the presence of a live interviewer may encourage people to answer questions differently than they would if no one was observing their (self-recorded) responses.
- For more information, see United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. “ Holocaust deniers and public misinformation .” Holocaust Encyclopedia. ↩
- Responses to this question were coded to prioritize knowledge of the mass murder of Jews during the Holocaust. For example, if a respondent said that the Holocaust refers to the attempted elimination of Jews by Hitler and his followers during World War II, that answer was coded into the “annihilation of Jews” category but not the Hitler or World War II categories. If the respondent did not mention Jews or the killing of Jews, the answer was coded to reflect any other aspects of the Holocaust that were mentioned (such as Nazis, Hitler or concentration camps) or the context in which the Holocaust occurred (for example, World War II). If a respondent mentioned more than one of these other aspects of the Holocaust (for example, “Hitler and the Nazis”), the first one mentioned was coded (in this example, Hitler). ↩
- Men get more questions right, even after controlling for religious affiliation, education level, race and ethnicity, age, region, and marital status. One possible reason that men correctly answer more religious knowledge questions than women do is that men tend to be more likely to guess , even when they are unsure about the correct answer to knowledge questions. ↩
- Golub, Jennifer, and Renae Cohen. 1993. “What Do Americans Know About the Holocaust?” American Jewish Committee. ↩
Sign up for our Religion newsletter
Sent weekly on Wednesday
Report Materials
Table of contents, rising numbers of americans say jews and muslims face a lot of discrimination, how u.s. muslims are experiencing the israel-hamas war, how u.s. jews are experiencing the israel-hamas war, striking findings from 2023, americans’ views of the israel-hamas war, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
The importance of teaching and learning about the Holocaust

On the occasion of International Holocaust Remembrance Day , commemorated each year on 27 January, UNESCO pays tribute to the memory of the victims of the Holocaust and reaffirms its commitment to counter antisemitism, racism, and other forms of intolerance.
In 2017, UNESCO released a policy guide on Education about the Holocaust and preventing genocide , to provide effective responses and a wealth of recommendations for education stakeholders.
What is education about the Holocaust?
Education about the Holocaust is primarily the historical study of the systematic, bureaucratic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by Nazi Germany and its collaborators.
It also provides a starting point to examine warning signs that can indicate the potential for mass atrocity. This study raises questions about human behaviour and our capacity to succumb to scapegoating or simple answers to complex problems in the face of vexing societal challenges. The Holocaust illustrates the dangers of prejudice, discrimination, antisemitism and dehumanization. It also reveals the full range of human responses - raising important considerations about societal and individual motivations and pressures that lead people to act as they do - or to not act at all.
Why teach about the Holocaust?
Education stakeholders can build on a series of rationales when engaging with this subject, in ways that can relate to a variety of contexts and histories throughout the world. The guide lists some of the main reasons why it is universally relevant to engage with such education.
Teaching and learning about the Holocaust:
- Demonstrates the fragility of all societies and of the institutions that are supposed to protect the security and rights of all. It shows how these institutions can be turned against a segment of society. This emphasizes the need for all, especially those in leadership positions, to reinforce humanistic values that protect and preserve free and just societies.
- Highlights aspects of human behaviour that affect all societies, such as the susceptibility to scapegoating and the desire for simple answers to complex problems; the potential for extreme violence and the abuse of power; and the roles that fear, peer pressure, indifference, greed and resentment can play in social and political relations.
- Demonstrates the dangers of prejudice, discrimination and dehumanization, be it the antisemitism that fueled the Holocaust or other forms of racism and intolerance.
- Deepens reflection about contemporary issues that affect societies around the world, such as the power of extremist ideologies, propaganda, the abuse of official power, and group-targeted hate and violence.
- Teaches about human possibilities in extreme and desperate situations, by considering the actions of perpetrators and victims as well as other people who, due to various motivations, may tolerate, ignore or act against hatred and violence. This can develop an awareness not only of how hate and violence take hold but also of the power of resistance, resilience and solidarity in local, national, and global contexts.
- Draws attention to the international institutions and norms developed in reaction to the Second World War and the Holocaust. This includes the United Nations and its international agreements for promoting and encouraging respect for human rights; promoting individual rights and equal treatment under the law; protecting civilians in any form of armed conflict; and protecting individuals who have fled countries because of a fear of persecution. This can help build a culture of respect for these institutions and norms, as well as national constitutional norms that are drawn from them.
- Highlights the efforts of the international community to respond to modern genocide. The Military Tribunal at Nuremberg was the first tribunal to prosecute “crimes against humanity”, and it laid the foundations of modern international criminal justice. The Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, under which countries agree to prevent and punish the crime of genocide, is another example of direct response to crimes perpetrated by Nazi Germany. Educating about the Holocaust can lead to a reflection on the recurrence of such crimes and the role of the international community.
What are the teaching and learning goals?
Understanding how and why the Holocaust occurred can inform broader understandings of mass violence globally, as well as highlight the value of promoting human rights, ethics, and civic engagement that bolsters human solidarity. Studying this history can prompt discussion of the societal contexts that enable exclusionary policies to divide communities and promote environments that make genocide possible. It is a powerful tool to engage learners on discussions pertaining to the emergence and the promotion of human rights; on the nature and dynamics of atrocity crimes and how they can be prevented; as well as on how to deal with traumatic pasts through education.
Such education creates multiple opportunities for learners to reflect on their role as global citizens. The guide explores for example how education about the Holocaust can advance the learning objectives sought by Global Citizenship Education (GCED), a pillar of the Education 2030 Agenda. It proposes topics and activities that can help develop students to be informed and critically literate; socially connected, respectful of diversity; and ethically responsible and engaged.
What are the main areas of implementation?
Every country has a distinct context and different capacities. The guide covers all the areas policy-makers should take into consideration when engaging with education about the Holocaust and, possibly, education about genocide and mass atrocities. It also provides precise guidelines for each of these areas. This comprises for example curricula and textbooks, including how the Holocaust can be integrated across different subjects, for what ages, and how to make sure textbooks and curricula are historically accurate. The guide also covers teacher training, classroom practices and appropriate pedagogies, higher learning institutions. It also provides important recommendations on how to improve interactions with the non-formal sector of education, through adult education, partnerships with museums and memorials, study-trips, and the implementation of international remembrance days.
Learn more about UNESCO’s on Education about the Holocaust .

Other recent news
Search the Holocaust Encyclopedia
- Animated Map
- Discussion Question
- Media Essay
- Oral History
- Timeline Event
- Clear Selections
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Português do Brasil
Featured Content
Find topics of interest and explore encyclopedia content related to those topics
Find articles, photos, maps, films, and more listed alphabetically
For Teachers
Recommended resources and topics if you have limited time to teach about the Holocaust
Explore the ID Cards to learn more about personal experiences during the Holocaust
Timeline of Events
Explore a timeline of events that occurred before, during, and after the Holocaust.
- Introduction to the Holocaust
- Liberation of Nazi Camps
- Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
- Boycott of Jewish Businesses
- Axis Invasion of Yugoslavia
- Antisemitism
- How Many People did the Nazis Murder?
- The Rwanda Genocide
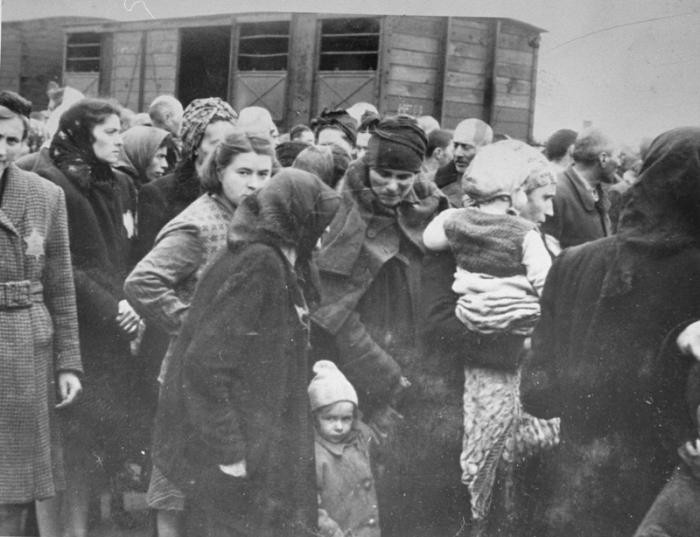

Discussion Questions
More details.
Organized by theme, these discussion questions examine how and why the Holocaust happened. They are designed to help teachers, students, and all citizens create discussion and encourage reflection about the Holocaust.
Browse all Discussion Questions
What made it possible.

Discussion Question How and why did ordinary people across Europe contribute to the persecution of their Jewish neighbors?

Discussion Question How did German professionals and civil leaders contribute to the persecution of Jews and other groups?

Discussion Question What conditions, ideologies, and ideas made the Holocaust possible?

Discussion Question How did the Nazis and their collaborators implement the Holocaust?

Discussion Question What does war make possible?

Discussion Question Which organizations and individuals aided and protected Jews from persecution between 1933 and 1945?

Discussion Question How did leaders, diplomats, and citizens around the world respond to the events of the Holocaust?

Discussion Question How did the United States government and American people respond to Nazism?
After the war.

Discussion Question What have we learned about the risk factors and warning signs of genocide?

Discussion Question How did postwar trials shape approaches to international justice?
Other topics.

Discussion Question How did the shared foundational element of eugenics contribute to the growth of racism in Europe and the United States?

Discussion Question What were some similarities between racism in Nazi Germany and in the United States, 1920s-1940s?

Discussion Question How did different goals and political systems shape racism in Nazi Germany and the United States?
Thank you for supporting our work.
We would like to thank Crown Family Philanthropies and the Abe and Ida Cooper Foundation for supporting the ongoing work to create content and resources for the Holocaust Encyclopedia. View the list of all donors .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Select one of the titles to work on. Some of the Holocaust essay topics include: Concentration camps in today's Europe. Lessons from the Holocaust: Fostering tolerance. The consequences of the Holocaust. Present and future of the Holocaust research. The causes of the Holocaust and discrimination against Jewish people.
The Holocaust is one of the most tragic events in world history, and writing an essay about it can help you understand it better. Among these Holocaust essay topics, you can find ideas for different types of middle school or college essays. Use them as the Holocaust essay titles or as a starting point for your dissertation research.
The Holocaust. Updated: April 11, 2023 | Original: October 14, 2009. The Holocaust was the state-sponsored persecution and mass murder of millions of European Jews, Romani people, the ...
10 Holocaust Essay Topics for Middle School Students. Anne Frank: A Young Voice in the Holocaust - Discuss the life and impact of Anne Frank and her diary. The Rise of Nazi Germany: Causes and Consequences - Explore the factors that led to the rise of the Nazi regime and its impact on the Holocaust.
The topic of the Holocaust is of utmost importance to write an essay about due to its profound historical significance and the lessons it teaches us about humanity. By exploring the Holocaust, we delve into one of the darkest periods in human history, where millions of innocent lives were brutally extinguished.
Holocaust Argumentative Essay Topics. These holocaust research questions present two perspectives of a given topic. They focus on the concentration research camp paper, as well as, the papers on arts and science during the holocaust. The argumentative holocaust paper topics give you a lot of scope for research.
Holocaust and Human Behavior, 2017 edition Facing History and Ourselves uses lessons of history to challenge teachers and their students ... Argumentative essays typically have one central argument (the thesis or central claim) and multiple smaller arguments in which the author presents a claim or reason, cites evidence, and
This resource provides writing prompts and strategies that align Holocaust and Human Behavior with the ... writing prompts and teaching strategies in this guide ask students to use evidence as they craft a formal argumentative essay. This guide also features effective writing strategies for general use in the social studies or English classroom ...
When asked to describe in their own words what the Holocaust was, more than eight-in-ten Americans mention the attempted annihilation of the Jewish people or other related topics, such as concentration or death camps, Hitler, or the Nazis. Seven-in-ten know that the Holocaust happened between 1930 and 1950.
Microsoft Word - Holocaust History is Relevant to Our Lives Today by Sara J. Bloomfield.docx. This paper is based on remarks delivered by Ms. Sara J. Bloomfield at the at United Nations ...
Education about the Holocaust is primarily the historical study of the systematic, bureaucratic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by Nazi Germany and its collaborators. It also provides a starting point to examine warning signs that can indicate the potential for mass atrocity. This study raises questions about human ...
The Holocaust was a repulsive time where many Jews suffered miserably from Hitler's concentration camps and millions died. I researched this topic because I had learned about the Holocaust a little bit over the years, but I wanted to focus primarily on the United States and if Roosevelt helped the Jews who were suffering or if he only focused on the needs of his own country.
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was a genocide that occurred during World War II, resulting in the systematic extermination of six million Jews, as well as millions of other victims, including Romani people, Poles, Soviet prisoners of war, disabled individuals, and political dissidents.This dark chapter in human history was orchestrated by the Nazi regime led by Adolf Hitler, and it ...
The fruit of their ration, The Holocaust and The Crisis of Human Behavior, is a. toward a psycho-social understanding of the Holocaust. What is novel about their effort is their attempt to. various insights arrived at by certain of the preceding scholars, those of Arendt and Rubenstein.
The Holocaust teaches us that everybody has a capacity to be sadistic and horrible to other people, and that the destructiveness exists in all of us. People are born neither good nor bad, and the badness is something that is the way someone is treated as a child. One of the greatest forces in life is the ability to forgive.
The Path to Nazi Genocide provides general background information on the Holocaust for the instructor and for classroom use. This 38-minute film examines the Nazis' rise and consolidation of power in Germany. Using rare footage, the film explores their ideology, propaganda, and persecution of Jews and other victims.
At the start of the holocaust, only Jewish men were murdered in front of the community. The motive behind this was to make sure the barbarous behavior wasn't going to ruin Hitler's reputation by being seen shooting women but eventually, it didn't seem to matter to him. If they were Jewish they were dead (Nux).
Introduction to the Holocaust. The Holocaust was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million European Jews by the Nazi German regime and its allies and collaborators. The Holocaust was an evolving process that took place throughout Europe between 1933 and 1945. Antisemitism was at the foundation of the Holocaust.
It took place between 1938-1945 while Adolf Hitler and his group of Nazis were ruling Germany. Over the years, they were the reason for over 11 million total deaths, 6 million of them being Jewish. Anne Frank, a young Jewish girl who lived during the Holocaust, hid from the Nazis with her family for over two years until her capture.
Organized by theme, this learning site presents an overview of the Holocaust through historical photographs, maps, images of artifacts, and testimony clips. It is a resource for middle and secondary level students and teachers, with content that reflects the history as it is presented in the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum's Permanent ...
Many feared to return to their former homes. Key Facts. 1. Following the liberation of Nazi camps, many survivors found themselves living in displaced persons camps where they often had to wait years before emigrating to new homes. 2. Many feared returning to their former homes due to postwar violence and antisemitism. 3.
Individuals with mental and physical disabilities deemed hereditary were targeted by the Nazis. The Nazis viewed these individuals as biologically "defective" and a drain on national resources. Nazi propaganda depicted them as "useless eaters.". A 1933 law aimed to prevent the birth of children with genetic "defects.".
Media Essay Oral History Photo Series Song ... Find topics of interest and explore encyclopedia content related to those topics. Browse A-Z. Find articles, photos, maps, films, and more listed alphabetically ... these discussion questions examine how and why the Holocaust happened. They are designed to help teachers, students, and all citizens ...