- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students

UMGC Effective Writing Center The Introductory Paragraph
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
The paragraph that begins an essay causes students the most trouble, yet carries the most importance. Although its precise construction varies from genre to genre (and from essay to essay), good introductory paragraphs generally accomplish the same tasks and follow a few basic patterns. Some of them are listed below, but keep in mind that what follows are guidelines, not immutable templates.
Tasks: The introductory paragraph to a short essay usually attempts to do three things:
- Introduce the topic with some indication of its inherent interest or importance, and a clear definition of the boundaries of the subject area
- Indicate the structure and/or methodology of the essay , often with the major sections of the essay or its structural principle clearly stated
- State the thesis of the essay , preferably in a single, arguable statement with a clear main clause
Not every essay does all three in the first paragraph, and the degree to which an essay declares its structure or methodology may vary widely, depending on how necessary that information will be to the readers. Sometimes, the entire first paragraph will serve no other purpose than to generate interest in the subject or raise a question, leaving the other tasks for the second paragraph. However, this kind of opening requires a lot of skill, and you can lose your readers in the second and third paragraphs if do not make your purpose clear.
Patterns: The standard pattern for an introductory paragraph follows the order of the tasks outlined above. Below is an outline of that pattern, written as if it were the first section of a formal outline of the entire essay:
Introduction
- Its boundaries
- Why it is interesting
- The essay’s main sections (structure)
- Why they come in that order (structural principle)
- How the author plans to draw the necessary conclusions from the information available (methodology)
- Its premise (the general claim about the information available)
- Its conclusion (the consequences of the first claim)
Not every essay contains every element in precisely this order, but most good essays cover all of them, either explicitly or implicitly. In longer and more scholarly essays, the structure/methodology section should be longer, or can even be its own paragraph. It should also include some mention of the essay’s position within the field as a whole.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- The Writing Process
- Addressing the Prompt
- Writing Skill: Development
- Originality
- Timed Writing (Expectations)
- Integrated Writing (Writing Process)
- Introduction to Academic Essays
- Organization
Introduction Paragraphs
- Body Paragraphs
- Conclusion Paragraphs
- Example Essay 1
- Example Essay 2
- Timed Writing (The Prompt)
- Integrated Writing (TOEFL Task 1)
- Process Essays
- Process Essay Example 1
- Process Essay Example 2
- Writing Skill: Unity
- Revise A Process Essay
- Timed Writing (Choose a Position)
- Integrated Writing (TOEFL Task 2)
- Comparison Essays
- Comparison Essay Example 1
- Comparison Essay Example 2
- Writing Skill: Cohesion
- Revise A Comparison Essay
- Timed Writing (Plans & Problems)
- Integrated Writing (Word Choice)
- Problem/Solution Essays
- Problem/Solution Essay Example 1
- Problem/Solution Example Essay 2
- Writing Skill: Summary
- Revise A Problem/Solution Essay
- Timed Writing (Revising)
- Integrated Writing (Summary)
- More Writing Skills
- Punctuation
- Simple Sentences
- Compound Sentences
- Complex Sentences Part 1
- Complex Sentences Part 2
- Using Academic Vocabulary
- Translations
Choose a Sign-in Option
Tools and Settings
Questions and Tasks
Citation and Embed Code

The introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay. This paragraph helps your reader be ready to understand your main idea.
Your introduction paragraph should—
grab your reader’s attention introduce the topic of your essay present your thesis
You can visualize the ideas in your introduction paragraph by thinking about an inverted triangle. The ideas in the beginning of your introduction paragraph are general. Then you narrow down the topic to a specific idea.
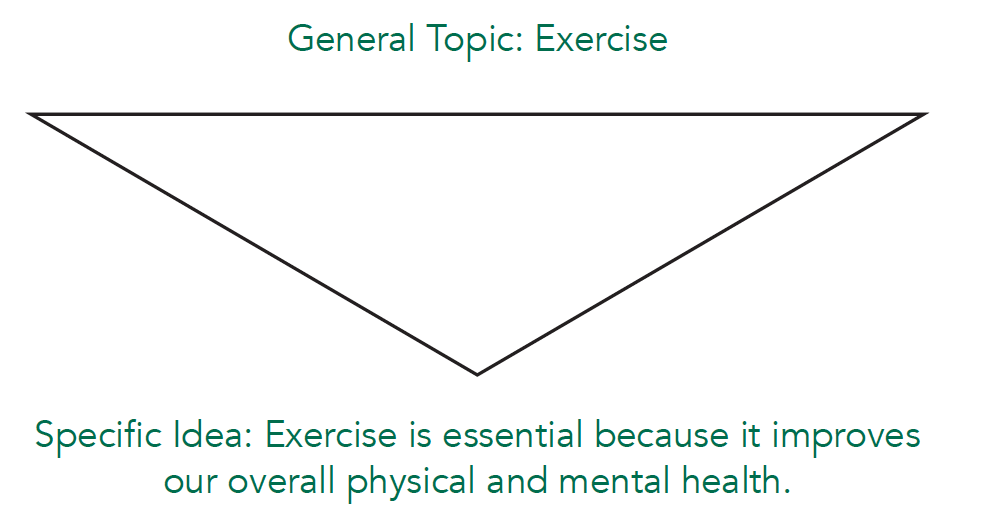
Grab the reader’s attention and introduce the topic
The very first sentence of your introduction should get your reader interested in your topic. The first sentence of an introduction is called a “hook.” There are many types of hooks: facts, questions, problems, descriptions, etc. There is not one “perfect” hook for each essay. Your hook can help you introduce the general topic of your essay.
As you introduce your topic, make sure to give the reader enough background information about the topic that the reader will be able to understand the thesis.
Present your thesis
The thesis states the main idea, or focus, of the essay. The rest of the essay will give evidence and explanations that show why or how your thesis is true. Your reader will expect to find the main idea in the introduction paragraph, rather than later in the essay.
An effective thesis—
- addresses the prompt if there is one* (i.e., answers the question).
- is usually at the end of the introduction paragraph.
- controls the content of all of the body paragraphs.
- is a complete sentence.
- does not announce the topic (e.g., “I’m going to talk about exercise.”).
- should not simply be a fact (e.g., “Many people exercise.”).
- should not be too general (e.g., “Exercise is good.”).
- should not be too specific (e.g., “Exercise decreases the chance of developing diabetes, heart disease, asthma, osteoporosis, depression, and anxiety.”).
- may state main points (e.g., “Exercise is essential because it improves overall physical and mental health.”).
- may imply main points (e.g., “Exercise is essential for improving our well-being.”)
*In some essays you write, you will not have a specific question to answer. Instead, you may need to choose your own topic. Your essay should still answer a question (e.g., how are typical Japanese and Chinese birthday celebrations similar or different?).
Exercise 1: Identify hooks and general topics.
Identify the type of hook used in each introduction paragraph as well as the general topic.
1. Working students deal with a lot of stress in their lives every day. Stress is very common for students while they are working because they have a lot of responsibiltities to balance. They have a list of tasks for school and work that can overwhelm their schedules. Feeling stress is normal when there is not enough time to finish all of your responsibilities, but it can have negative results. Instead of avoiding stress, students simply need to learn how to manage it. In order for students to manage stress better, they need to prioritize their tasks, eat well, and get enough sleep.
Type of hook: __________________ General topic of the paragraph: __________________
2. Many business owners find that running a business is a lot harder than they thought it was. How business owners decide to manage their business will determine their future success. They have to make important decisions about how to manage their business every day. These decisions include hiring employees, the hours of operation, the products and services that will be provided, and the way the business will be advertised. These decisions impact a lot of people. Successful business owners need to make wise decisions that satisfy employees, customers, and investors.
Exercise 2: Analyze a thesis.
Read the introduction paragraph below to complete this exercise.
Prompt: Why is exercise important?
Thesis: Exercise is essential because it improves overall physical and mental health.
Use this list of criteria to evaluate the thesis.
- Does the thesis address the prompt?
- Is the thesis a complete sentence?
- Does the thesis announce the topic?
- Is the thesis simply a fact?
- Is the thesis too general? Too specific?
- Are the main points stated or implied?
Exercise 3: Identify effective thesis statements.
For each prompt, identify which thesis statement is more effective. Write an X on the line next to the more effective thesis statement.
- _____Thesis #1 Let’s see all of the interesting things you can do in Rome.
- _____Thesis #2 Rome has a very unique cultural history.
- _____Thesis #1 An influential leader is open-minded and humble.
- _____Thesis #2 Some people are born to be leaders and influence the world.
- _____Thesis #1 There are some ways to solve feeling homesick.
- _____Thesis #2 Enjoying comforts from home can help combat homesickness.
- _____Thesis #1 Writing provides more time to plan and revise than speaking.
- _____Thesis #2 Many people around the world communicate through writing.
Exercise 4: Evaluate thesis statements.
Which sentences are effective thesis statements? Which sentences are not effective thesis statements? On a piece of paper, write “yes” if you think the thesis is effective or “no” if you think it is ineffective. Discuss why each thesis is (or is not) effective.
Exercise 5: Write a thesis.
On a piece of paper, write a thesis for each prompt. Make sure the thesis addresses the prompt clearly.
1. What are weddings like in your country? 2. What problems do smartphones cause in our lives? 3. What are qualities of a true friend? 4. Should video games be prohibited?
This content is provided to you freely by BYU Open Learning Network.
Access it online or download it at https://open.byu.edu/academic_a_writing/introduction_paragra .
The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
Begin with a great first sentence
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The introductory paragraph of any paper, long or short, should start with a sentence that piques the interest of your readers .
In a well-constructed first paragraph, that first sentence leads into three or four sentences that provide details about the subject you address in the body of your essay. These sentences should also set the stage for your thesis statement .
Writing a good thesis statement is the subject of much instruction and training, as it's the driver of your research and the subject of your paper. The entirety of your paper hangs on that sentence, which is generally the last sentence of your introductory paragraph and is refined throughout your research and drafting phases.
Writing an Intro Paragraph
It's often easier to write the introductory paragraph after you've written the first draft of the main part of the paper (or at least sketched out a detailed outline, section by section or paragraph by paragraph). After the drafting stage, your research and main points are fresh in your mind, and your thesis statement has been polished to gleaming. It's typically honed during the drafting stage, as research may have necessitated its adjustment.
At the start of a large writing project, it can also be intimidating to put those first words down, so it's often easier to begin composing in the middle of the paper and work on the introduction and conclusion after the meat of the report has been organized, compiled, and drafted.
Construct your introductory paragraph with the following:
- An attention-grabbing first sentence
- Informative sentences that build to your thesis
- The thesis statement, which makes a claim or states a view that you will support or build upon
Your First Sentence
As you researched your topic, you probably discovered some interesting anecdotes, quotes, or trivial facts. This is exactly the sort of thing you should use for an engaging introduction.
Consider these ideas for creating a strong beginning.
Surprising fact: The Pentagon has twice as many bathrooms as are necessary. The famous government building was constructed in the 1940s when segregation laws required that separate bathrooms be installed for people of African descent. This building isn’t the only American icon that harkens back to this embarrassing and hurtful time in our history. Across the United States, there are many examples of leftover laws and customs that reflect the racism that once permeated American society.
Humor: When my older brother substituted fresh eggs for our hard-boiled Easter eggs, he didn’t realize our father would take the first crack at hiding them. My brother’s holiday ended early that particular day in 1991, but the rest of the family enjoyed the warm April weather, outside on the lawn, until late into the evening. Perhaps it was the warmth of the day and the joy of eating Easter roast while Tommy contemplated his actions that make my memories of Easter so sweet. Whatever the true reason, the fact remains that my favorite holiday of the year is Easter Sunday.
Quotation: Hillary Rodham Clinton once said, “There cannot be true democracy unless women's voices are heard.” In 2006, when Nancy Pelosi became the nation’s first female Speaker of the House, one woman’s voice rang out clearly. With this development, democracy grew to its truest level ever in terms of women’s equality. The historical event also paved the way for Senator Clinton as she warmed her own vocal cords in preparation for a presidential race.
Finding the Hook
In each example, the first sentence draws the reader in to find out how the interesting fact leads to a point. You can use many methods to capture your reader’s interest.
Curiosity: A duck’s quack doesn’t echo. Some people might find a deep and mysterious meaning in this fact…
Definition: A homograph is a word with two or more pronunciations. Produce is one example…
Anecdote: Yesterday morning I watched as my older sister left for school with a bright white glob of toothpaste gleaming on her chin. I felt no regret at all until she stepped onto the bus …
Supporting Sentences
The body of your introductory paragraph should fulfill two functions: It should explain your first sentence and should build up to your thesis statement. You'll find that this is much easier than it sounds. Just follow the pattern you see in the above examples.
During the revision stage for the paper as a whole, you can make further refinements to the introduction as needed.
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- How To Write an Essay
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- How to Structure an Essay
- How to Help Your 4th Grader Write a Biography
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- How to Write a Response Paper
- What Is Expository Writing?
- 6 Steps to Writing the Perfect Personal Essay
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.2: Opening Paragraphs
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 165696

- Ann Inoshita, Karyl Garland, Kate Sims, Jeanne K. Tsutsui Keuma, and Tasha Williams
- University of Hawaii via University of Hawaiʻi OER
An introduction exists as the first paragraph in a 5-page essay, and it serves the following purposes:
- Establishes reader interest.
- Introduces the general topic of the essay while establishing the writer’s voice, tone, or attitude, toward the subject.
- States the thesis that will be supported in the body paragraphs.
Establishing Reader Interest
Introductions should begin with an engaging lead or opener (sometimes called a “hook” in middle school or high school) that is devised to evoke readers’ interest. Capturing readers’ attention motivates them to continue reading. Writers can garner a reader’s interest by doing the following:
- Beginning by quoting an expert on the respective topic or an inspirational individual.
- Beginning by offering some statistical evidence that is both informative and intriguing.
- Opening with a striking mental image.
- Appealing to the reader’s emotions.
- Raising a question or series of questions.
- Presenting an explanation or rationalization for the essay.
- Including a personal anecdote.
- Stating in the middle of a story with the conclusion of the story existing as the first sentence in the conclusion paragraph.
Transition Sentences
After the opener or hook, writers need to add transition sentences that should introduce the readers to the topic by stating general facts or ideas about the subject. These important sentences help readers move or “transition” from the hook toward the thesis statement.
A Strong Thesis Statement
An introduction usually contains a thesis statement (i.e., the main point of the essay). A thesis statement is a promise to the reader about what the essay will be about. A thesis is not the topic itself, but rather the writer’s angle on the topic. For whatever topic a professor gives, writers must ask themselves, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful, and confident.
A thesis is usually one sentence long and appears toward the end of the introduction. It is specific, and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how the writer will organize the information.
Specificity
A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. The creation of a thesis statement begins when writers choose a broad subject and then narrow it down until they have pinpointed a specific aspect of that topic. For example, healthcare is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic and essentially answer the following question. “What are the options for individuals without healthcare coverage?”
A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic pertains to options for individuals without healthcare coverage, then the precise thesis statement must make an exact, related, claim, such as the following: “Limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers.” To elaborate on this topic further, the writer might discuss how limited options impact the lives of the uninsured.
Ability to be Argued
A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement is often not considered arguable. A thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
However, a wise way to think about a thesis statement within a persuasive or “argumentative” essay is to write one that strikes up or furthers a conversation versus creating an argument. Imagine someone reading only your thesis statement and the two of you, then, having a conversation in which you share your stance, your reader shares his or her stance, and you continue your discussion with the information from your body paragraphs.
Ability to be Demonstrated
For any claim in the thesis, the writer must be able to provide reasons and examples for this opinion. Personal observations can help, or the writer can consult outside sources to demonstrate validity. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
The demonstration of validity comes from incorporating the voices of the experts—those who have already had their work on your topic published, vetted, and added to the respective canon. Use the strategies of quoting, summarizing, or paraphrasing.
Remember that the only way to hit a word or page requirement when writers feel like they have already said everything is to add examples.
Forcefulness
A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that the writer is, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
That being said, college-level thesis statements would do well to not include the word “should,” as a means of trying to sound authoritative so as to make a solid argument.
In addition to using forcefulness in their thesis statement, writers must also be confident in their claims. Phrases such as “I feel” or “I believe” actually weaken the readers’ sense of confidence in what they are reading because these phrases imply that the writer may be the only person who feels this way.
Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades readers to have faith in the argument and to open their minds to the point of view of the writer. So, no thesis should contain phrases such as “in my opinion” or “I believe.” These statements reduce credibility and weaken the argument.
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the requirements: specificity, precision, ability to be argued, ability to be demonstrated, forcefulness, and confidence.
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the 1986 play Fences symbolize the challenges faced by black men who lived through segregation and integration in the United States, and their life stories can be considered as critical to understand the challenge black men continue to face over thirty years later.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one idea proposed so as to deal with illegal immigration; however, contemporary strategies regarding this issue do not address the essential human right for safety along with the essentials of food, clothing, and shelter.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused and somewhat rebellious young person who voices his disgust with “phonies.” Yet, in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions making him a complicated character within one of Salinger’s most celebrated novels.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, a no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown, although no divorce is easy since the issues involved extend well beyond the monetary and are usually based in an unfortunate undercurrent of misunderstandings and sorrow.
- Discussing the dangers of illegal drug use is with elementary and middle school students is one method that schools use to help dissuade young people from abusing drugs as they grow up. However, children learn a great deal from what they observe making it imperative that parents monitor what their children watch on tv, see in movies, and glean from their friends and family members.
- In today’s challenging professional world, a high school diploma is not a significant enough confirmation of one’s education so as to obtain a stable, lucrative, lifelong job. Therefore, many colleges and universities are offering more online courses making it possible for more individuals to work toward a college degree while still working to make a living.
Avoid Weak Thesis Statements
Here are some pitfalls to avoid when composing a thesis:
- A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of a subject or a description of what the writer will discuss in the essay. Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge. Remember, do not refer to your essay in your essay. By the time one enters college, such strategies for writing thesis statements have passed.
- A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side. Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
- A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end. Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies often use sexual or romantic appeal to sell their products.
- A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad. Weak thesis statement: The life and presidency of Abraham Lincoln was challenging.
This section is adapted from OER material from “Writing Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs” and “Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement” in Writing for Success v. 1.0 (2012). Writing for Success was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work’s original creator or licensor.
- Introduce the topic with some indication of its inherent interest or importance, and a clear definition of the boundaries of the subject area
- Indicate the structure and/or methodology of the essay , often with the major sections of the essay or its structural principle clearly stated
- State the thesis of the essay , preferably in a single, arguable statement with a clear main clause
- Its boundaries
- Why it is interesting
- Structure and/or Methodology
- The essays main sections (structure)
- Why they come in that order (structural principle)
- How the author plans to draw the necessary conclusions from the information available (methodology)
- The Thesis Statement (usually a single sentence)
- Its premise (the general claim about the information available)
- Its conclusion (the consequences of the first claim)
Writing Process: Organizing
Paragraph structure.
The manner in which your essay presents material is vital. As you know, an essay (or any academic text) is built up around paragraphs. These help the reader understand the organization of your essay and grasp its main points. A paragraph is a series of sentences that are organized and coherent, and are all related to a single topic. The main rule is:
One paragraph = one new point in your argument
Each paragraph typically contains a three-part structure:
1. Introduction : includes a topic sentence and transition words 2. Body : discusses the topic, using various forms of evidence 3. Conclusion : comments and draws connections
Paragraph Principles

- Each paragraph should be able to stand on its own and have its own internal structure.
- Each paragraph should state its purpose, in the form of a topic sentence.
Try extracting the first line from your essay paragraphs and see if you can follow your main line of argument. If you can’t, they your essay is not so easy to follow as you might want it to be. (Of course, not every argument has to be organized this way. But try to look up a few articles in some “serious” newspapers: you will find this structure widely used!)
The reason why paragraphs should be “headlined” with reference to the overall argument is to keep that argument in the reader’s mind, thereby making it easier for them to see the relevance of the rest of the paragraph. This way, the reader doesn’t lose track, and neither do you as you write.
Connecting Paragraphs Together
Ideally, paragraphs should be well connected to each other. Order paragraphs so that each one follows logically from the previous one. To make this logic more obvious, you can use transition words (or “connectors”), so that the paragraphs flow better and the reader is always kept on track.
As the author, you know why one paragraph relates to the next, because you’ve put a lot of effort, research, and thought into the planning of this document. Your reader isn’t as well-versed in the subject as you are, however. Adding transition words and phrases helps cue your reader into the connections between ideas you’ve already made for yourself.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Paragraph Structure. Provided by : Academic Writing. Located at : http://academicwriting.wikidot.com/paragraph-structure . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of paragraph. Authored by : JuanRax. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/4w1ReJ . License : CC BY: Attribution
11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)
How do you structure a paragraph in an essay?
If you’re like the majority of my students, you might be getting your basic essay paragraph structure wrong and getting lower grades than you could!
In this article, I outline the 11 key steps to writing a perfect paragraph. But, this isn’t your normal ‘how to write an essay’ article. Rather, I’ll try to give you some insight into exactly what teachers look out for when they’re grading essays and figuring out what grade to give them.
You can navigate each issue below, or scroll down to read them all:
1. Paragraphs must be at least four sentences long 2. But, at most seven sentences long 3. Your paragraph must be Left-Aligned 4. You need a topic sentence 5 . Next, you need an explanation sentence 6. You need to include an example 7. You need to include citations 8. All paragraphs need to be relevant to the marking criteria 9. Only include one key idea per paragraph 10. Keep sentences short 11. Keep quotes short
Paragraph structure is one of the most important elements of getting essay writing right .
As I cover in my Ultimate Guide to Writing an Essay Plan , paragraphs are the heart and soul of your essay.
However, I find most of my students have either:
- forgotten how to write paragraphs properly,
- gotten lazy, or
- never learned it in the first place!
Paragraphs in essay writing are different from paragraphs in other written genres .
In fact, the paragraphs that you are reading now would not help your grades in an essay.
That’s because I’m writing in journalistic style, where paragraph conventions are vastly different.
For those of you coming from journalism or creative writing, you might find you need to re-learn paragraph writing if you want to write well-structured essay paragraphs to get top grades.
Below are eleven reasons your paragraphs are losing marks, and what to do about it!

Essay Paragraph Structure Rules
1. your paragraphs must be at least 4 sentences long.
In journalism and blog writing, a one-sentence paragraph is great. It’s short, to-the-point, and helps guide your reader. For essay paragraph structure, one-sentence paragraphs suck.
A one-sentence essay paragraph sends an instant signal to your teacher that you don’t have much to say on an issue.
A short paragraph signifies that you know something – but not much about it. A one-sentence paragraph lacks detail, depth and insight.
Many students come to me and ask, “what does ‘add depth’ mean?” It’s one of the most common pieces of feedback you’ll see written on the margins of your essay.
Personally, I think ‘add depth’ is bad feedback because it’s a short and vague comment. But, here’s what it means: You’ve not explained your point enough!
If you’re writing one-, two- or three-sentence essay paragraphs, you’re costing yourself marks.
Always aim for at least four sentences per paragraph in your essays.
This doesn’t mean that you should add ‘fluff’ or ‘padding’ sentences.
Make sure you don’t:
a) repeat what you said in different words, or b) write something just because you need another sentence in there.
But, you need to do some research and find something insightful to add to that two-sentence paragraph if you want to ace your essay.
Check out Points 5 and 6 for some advice on what to add to that short paragraph to add ‘depth’ to your paragraph and start moving to the top of the class.
- How to Make an Essay Longer
- How to Make an Essay Shorter
2. Your Paragraphs must not be more than 7 Sentences Long
Okay, so I just told you to aim for at least four sentences per paragraph. So, what’s the longest your paragraph should be?
Seven sentences. That’s a maximum.
So, here’s the rule:
Between four and seven sentences is the sweet spot that you need to aim for in every single paragraph.
Here’s why your paragraphs shouldn’t be longer than seven sentences:
1. It shows you can organize your thoughts. You need to show your teacher that you’ve broken up your key ideas into manageable segments of text (see point 10)
2. It makes your work easier to read. You need your writing to be easily readable to make it easy for your teacher to give you good grades. Make your essay easy to read and you’ll get higher marks every time.
One of the most important ways you can make your work easier to read is by writing paragraphs that are less than six sentences long.
3. It prevents teacher frustration. Teachers are just like you. When they see a big block of text their eyes glaze over. They get frustrated, lost, their mind wanders … and you lose marks.
To prevent teacher frustration, you need to ensure there’s plenty of white space in your essay. It’s about showing them that the piece is clearly structured into one key idea per ‘chunk’ of text.
Often, you might find that your writing contains tautologies and other turns of phrase that can be shortened for clarity.
3. Your Paragraph must be Left-Aligned
Turn off ‘Justified’ text and: Never. Turn. It. On. Again.
Justified text is where the words are stretched out to make the paragraph look like a square. It turns the writing into a block. Don’t do it. You will lose marks, I promise you! Win the psychological game with your teacher: left-align your text.
A good essay paragraph is never ‘justified’.
I’m going to repeat this, because it’s important: to prevent your essay from looking like a big block of muddy, hard-to-read text align your text to the left margin only.
You want white space on your page – and lots of it. White space helps your reader scan through your work. It also prevents it from looking like big blocks of text.
You want your reader reading vertically as much as possible: scanning, browsing, and quickly looking through for evidence you’ve engaged with the big ideas.
The justified text doesn’t help you do that. Justified text makes your writing look like a big, lumpy block of text that your reader doesn’t want to read.
What’s wrong with Center-Aligned Text?
While I’m at it, never, ever, center-align your text either. Center-aligned text is impossible to skim-read. Your teacher wants to be able to quickly scan down the left margin to get the headline information in your paragraph.
Not many people center-align text, but it’s worth repeating: never, ever center-align your essays.

Don’t annoy your reader. Left align your text.
4. Your paragraphs must have a Topic Sentence
The first sentence of an essay paragraph is called the topic sentence. This is one of the most important sentences in the correct essay paragraph structure style.
The topic sentence should convey exactly what key idea you’re going to cover in your paragraph.
Too often, students don’t let their reader know what the key idea of the paragraph is until several sentences in.
You must show what the paragraph is about in the first sentence.
You never, ever want to keep your reader in suspense. Essays are not like creative writing. Tell them straight away what the paragraph is about. In fact, if you can, do it in the first half of the first sentence .
I’ll remind you again: make it easy to grade your work. Your teacher is reading through your work trying to determine what grade to give you. They’re probably going to mark 20 assignments in one sitting. They have no interest in storytelling or creativity. They just want to know how much you know! State what the paragraph is about immediately and move on.
Suggested: Best Words to Start a Paragraph
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing a Topic Sentence If your paragraph is about how climate change is endangering polar bears, say it immediately : “Climate change is endangering polar bears.” should be your first sentence in your paragraph. Take a look at first sentence of each of the four paragraphs above this one. You can see from the first sentence of each paragraph that the paragraphs discuss:
When editing your work, read each paragraph and try to distil what the one key idea is in your paragraph. Ensure that this key idea is mentioned in the first sentence .
(Note: if there’s more than one key idea in the paragraph, you may have a problem. See Point 9 below .)
The topic sentence is the most important sentence for getting your essay paragraph structure right. So, get your topic sentences right and you’re on the right track to a good essay paragraph.
5. You need an Explanation Sentence
All topic sentences need a follow-up explanation. The very first point on this page was that too often students write paragraphs that are too short. To add what is called ‘depth’ to a paragraph, you can come up with two types of follow-up sentences: explanations and examples.
Let’s take explanation sentences first.
Explanation sentences give additional detail. They often provide one of the following services:
Let’s go back to our example of a paragraph on Climate change endangering polar bears. If your topic sentence is “Climate change is endangering polar bears.”, then your follow-up explanation sentence is likely to explain how, why, where, or when. You could say:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing Explanation Sentences 1. How: “The warming atmosphere is melting the polar ice caps.” 2. Why: “The polar bears’ habitats are shrinking every single year.” 3. Where: “This is happening in the Antarctic ice caps near Greenland.” 4. When: “Scientists first noticed the ice caps were shrinking in 1978.”
You don’t have to provide all four of these options each time.
But, if you’re struggling to think of what to add to your paragraph to add depth, consider one of these four options for a good quality explanation sentence.
>>>RELATED ARTICLE: SHOULD YOU USE RHETORICAL QUESTIONS IN ESSAYS ?
6. Your need to Include an Example
Examples matter! They add detail. They also help to show that you genuinely understand the issue. They show that you don’t just understand a concept in the abstract; you also understand how things work in real life.
Example sentences have the added benefit of personalising an issue. For example, after saying “Polar bears’ habitats are shrinking”, you could note specific habitats, facts and figures, or even a specific story about a bear who was impacted.
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: Writing an ‘Example’ Sentence “For example, 770,000 square miles of Arctic Sea Ice has melted in the past four decades, leading Polar Bear populations to dwindle ( National Geographic, 2018 )
In fact, one of the most effective politicians of our times – Barrack Obama – was an expert at this technique. He would often provide examples of people who got sick because they didn’t have healthcare to sell Obamacare.
What effect did this have? It showed the real-world impact of his ideas. It humanised him, and got him elected president – twice!
Be like Obama. Provide examples. Often.
7. All Paragraphs need Citations
Provide a reference to an academic source in every single body paragraph in the essay. The only two paragraphs where you don’t need a reference is the introduction and conclusion .
Let me repeat: Paragraphs need at least one reference to a quality scholarly source .
Let me go even further:
Students who get the best marks provide two references to two different academic sources in every paragraph.
Two references in a paragraph show you’ve read widely, cross-checked your sources, and given the paragraph real thought.
It’s really important that these references link to academic sources, not random websites, blogs or YouTube videos. Check out our Seven Best types of Sources to Cite in Essays post to get advice on what sources to cite. Number 6 w ill surprise you!
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: In-Text Referencing in Paragraphs Usually, in-text referencing takes the format: (Author, YEAR), but check your school’s referencing formatting requirements carefully. The ‘Author’ section is the author’s last name only. Not their initials. Not their first name. Just their last name . My name is Chris Drew. First name Chris, last name Drew. If you were going to reference an academic article I wrote in 2019, you would reference it like this: (Drew, 2019).
Where do you place those two references?
Place the first reference at the end of the first half of the paragraph. Place the second reference at the end of the second half of the paragraph.
This spreads the references out and makes it look like all the points throughout the paragraph are backed up by your sources. The goal is to make it look like you’ve reference regularly when your teacher scans through your work.
Remember, teachers can look out for signposts that indicate you’ve followed academic conventions and mentioned the right key ideas.
Spreading your referencing through the paragraph helps to make it look like you’ve followed the academic convention of referencing sources regularly.
Here are some examples of how to reference twice in a paragraph:
- If your paragraph was six sentences long, you would place your first reference at the end of the third sentence and your second reference at the end of the sixth sentence.
- If your paragraph was five sentences long, I would recommend placing one at the end of the second sentence and one at the end of the fifth sentence.
You’ve just read one of the key secrets to winning top marks.

8. Every Paragraph must be relevant to the Marking Criteria
Every paragraph must win you marks. When you’re editing your work, check through the piece to see if every paragraph is relevant to the marking criteria.
For the British: In the British university system (I’m including Australia and New Zealand here – I’ve taught at universities in all three countries), you’ll usually have a ‘marking criteria’. It’s usually a list of between two and six key learning outcomes your teacher needs to use to come up with your score. Sometimes it’s called a:
- Marking criteria
- Marking rubric
- (Key) learning outcome
- Indicative content
Check your assignment guidance to see if this is present. If so, use this list of learning outcomes to guide what you write. If your paragraphs are irrelevant to these key points, delete the paragraph .
Paragraphs that don’t link to the marking criteria are pointless. They won’t win you marks.
For the Americans: If you don’t have a marking criteria / rubric / outcomes list, you’ll need to stick closely to the essay question or topic. This goes out to those of you in the North American system. North America (including USA and Canada here) is often less structured and the professor might just give you a topic to base your essay on.
If all you’ve got is the essay question / topic, go through each paragraph and make sure each paragraph is relevant to the topic.
For example, if your essay question / topic is on “The Effects of Climate Change on Polar Bears”,
- Don’t talk about anything that doesn’t have some connection to climate change and polar bears;
- Don’t talk about the environmental impact of oil spills in the Gulf of Carpentaria;
- Don’t talk about black bear habitats in British Columbia.
- Do talk about the effects of climate change on polar bears (and relevant related topics) in every single paragraph .
You may think ‘stay relevant’ is obvious advice, but at least 20% of all essays I mark go off on tangents and waste words.
Stay on topic in Every. Single. Paragraph. If you want to learn more about how to stay on topic, check out our essay planning guide .
9. Only have one Key Idea per Paragraph
One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph. One key idea for each paragraph.
Don’t forget!
Too often, a student starts a paragraph talking about one thing and ends it talking about something totally different. Don’t be that student.
To ensure you’re focussing on one key idea in your paragraph, make sure you know what that key idea is. It should be mentioned in your topic sentence (see Point 3 ). Every other sentence in the paragraph adds depth to that one key idea.
If you’ve got sentences in your paragraph that are not relevant to the key idea in the paragraph, they don’t fit. They belong in another paragraph.
Go through all your paragraphs when editing your work and check to see if you’ve veered away from your paragraph’s key idea. If so, you might have two or even three key ideas in the one paragraph.
You’re going to have to get those additional key ideas, rip them out, and give them paragraphs of their own.
If you have more than one key idea in a paragraph you will lose marks. I promise you that.
The paragraphs will be too hard to read, your reader will get bogged down reading rather than scanning, and you’ll have lost grades.
10. Keep Sentences Short
If a sentence is too long it gets confusing. When the sentence is confusing, your reader will stop reading your work. They will stop reading the paragraph and move to the next one. They’ll have given up on your paragraph.
Short, snappy sentences are best.
Shorter sentences are easier to read and they make more sense. Too often, students think they have to use big, long, academic words to get the best marks. Wrong. Aim for clarity in every sentence in the paragraph. Your teacher will thank you for it.
The students who get the best marks write clear, short sentences.
When editing your draft, go through your essay and see if you can shorten your longest five sentences.
(To learn more about how to write the best quality sentences, see our page on Seven ways to Write Amazing Sentences .)
11. Keep Quotes Short
Eighty percent of university teachers hate quotes. That’s not an official figure. It’s my guestimate based on my many interactions in faculty lounges. Twenty percent don’t mind them, but chances are your teacher is one of the eight out of ten who hate quotes.
Teachers tend to be turned off by quotes because it makes it look like you don’t know how to say something on your own words.
Now that I’ve warned you, here’s how to use quotes properly:
Ideal Essay Paragraph Structure Example: How To Use Quotes in University-Level Essay Paragraphs 1. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 2. Your quote should be less than one sentence long. 3. You should never start a sentence with a quote. 4. You should never end a paragraph with a quote. 5 . You should never use more than five quotes per essay. 6. Your quote should never be longer than one line in a paragraph.
The minute your teacher sees that your quote takes up a large chunk of your paragraph, you’ll have lost marks.
Your teacher will circle the quote, write a snarky comment in the margin, and not even bother to give you points for the key idea in the paragraph.
Avoid quotes, but if you really want to use them, follow those five rules above.
I’ve also provided additional pages outlining Seven tips on how to use Quotes if you want to delve deeper into how, when and where to use quotes in essays. Be warned: quoting in essays is harder than you thought.

Follow the advice above and you’ll be well on your way to getting top marks at university.
Writing essay paragraphs that are well structured takes time and practice. Don’t be too hard on yourself and keep on trying!
Below is a summary of our 11 key mistakes for structuring essay paragraphs and tips on how to avoid them.
I’ve also provided an easy-to-share infographic below that you can share on your favorite social networking site. Please share it if this article has helped you out!
11 Biggest Essay Paragraph Structure Mistakes you’re probably Making
1. Your paragraphs are too short 2. Your paragraphs are too long 3. Your paragraph alignment is ‘Justified’ 4. Your paragraphs are missing a topic sentence 5 . Your paragraphs are missing an explanation sentence 6. Your paragraphs are missing an example 7. Your paragraphs are missing references 8. Your paragraphs are not relevant to the marking criteria 9. You’re trying to fit too many ideas into the one paragraph 10. Your sentences are too long 11. Your quotes are too long

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
4 thoughts on “11 Rules for Essay Paragraph Structure (with Examples)”
Hello there. I noticed that throughout this article on Essay Writing, you keep on saying that the teacher won’t have time to go through the entire essay. Don’t you think this is a bit discouraging that with all the hard work and time put into your writing, to know that the teacher will not read through the entire paper?

Hi Clarence,
Thanks so much for your comment! I love to hear from readers on their thoughts.
Yes, I agree that it’s incredibly disheartening.
But, I also think students would appreciate hearing the truth.
Behind closed doors many / most university teachers are very open about the fact they ‘only have time to skim-read papers’. They regularly bring this up during heated faculty meetings about contract negotiations! I.e. in one university I worked at, we were allocated 45 minutes per 10,000 words – that’s just over 4 minutes per 1,000 word essay, and that’d include writing the feedback, too!
If students know the truth, they can better write their essays in a way that will get across the key points even from a ‘skim-read’.
I hope to write candidly on this website – i.e. some of this info will never be written on university blogs because universities want to hide these unfortunate truths from students.
Thanks so much for stopping by!
Regards, Chris
This is wonderful and helpful, all I say is thank you very much. Because I learned a lot from this site, own by chris thank you Sir.
Thank you. This helped a lot.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.2 Effective Means for Writing a Paragraph
Learning objectives.
- Identify characteristics of a good topic sentence.
- Identify the three parts of a developed paragraph.
- Apply knowledge of topic sentences and parts of a developed paragraph in an assignment.
Now that you have identified common purposes for writing and learned how to select appropriate content for a particular audience, you can think about the structure of a paragraph in greater detail. Composing an effective paragraph requires a method similar to building a house. You may have the finest content, or materials, but if you do not arrange them in the correct order, then the final product will not hold together very well.
A strong paragraph contains three distinct components:
- Topic sentence . The topic sentence is the main idea of the paragraph.
- Body . The body is composed of the supporting sentences that develop the main point.
- Conclusion . The conclusion is the final sentence that summarizes the main point.
The foundation of a good paragraph is the topic sentence, which expresses the main idea of the paragraph. The topic sentence relates to the thesis, or main point, of the essay (see Chapter 9 “Writing Essays: From Start to Finish” for more information about thesis statements) and guides the reader by signposting what the paragraph is about. All the sentences in the rest of the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
This section covers the major components of a paragraph and examines how to develop an effective topic sentence.
Developing a Topic Sentence
Pick up any newspaper or magazine and read the first sentence of an article. Are you fairly confident that you know what the rest of the article is about? If so, you have likely read the topic sentence. An effective topic sentence combines a main idea with the writer’s personal attitude or opinion. It serves to orient the reader and provides an indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph. Read the following example.
Creating a national set of standards for math and English education will improve student learning in many states.
This topic sentence declares a favorable position for standardizing math and English education. After reading this sentence, a reader might reasonably expect the writer to provide supporting details and facts as to why standardizing math and English education might improve student learning in many states. If the purpose of the essay is actually to evaluate education in only one particular state, or to discuss math or English education specifically, then the topic sentence is misleading.
When writing a draft of an essay, allow a friend or colleague to read the opening line of your first paragraph. Ask your reader to predict what your paper will be about. If he or she is unable to guess your topic accurately, you should consider revising your topic sentence so that it clearly defines your purpose in writing.
Main Idea versus Controlling Idea
Topic sentences contain both a main idea (the subject, or topic that the writer is discussing) and a controlling idea (the writer’s specific stance on that subject). Just as a thesis statement includes an idea that controls a document’s focus (as you will read about in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” ), a topic sentence must also contain a controlling idea to direct the paragraph. Different writers may use the same main idea but can steer their paragraph in a number of different directions according to their stance on the subject. Read the following examples.
- Marijuana is a destructive influence on teens and causes long-term brain damage.
- The antinausea properties in marijuana are a lifeline for many cancer patients.
- Legalizing marijuana would create a higher demand for Class A and Class B drugs.
Although the main idea—marijuana—is the same in all three topic sentences, the controlling idea differs depending on the writer’s viewpoint.
Circle the main idea and underline the controlling idea in each of the following topic sentences.
- Exercising three times a week is the only way to maintain good physical health.
- Sexism and racism are still rampant in today’s workplace.
- Raising the legal driving age to twenty-one would decrease road traffic accidents.
- Owning a business is the only way to achieve financial success.
- Dog owners should be prohibited from taking their pets on public beaches.
Characteristics of a Good Topic Sentence
Five characteristics define a good topic sentence:
A good topic sentence provides an accurate indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph.
Weak example. People rarely give firefighters the credit they deserve for such a physically and emotionally demanding job. (The paragraph is about a specific incident that involved firefighters; therefore, this topic sentence is too general.)
Stronger example. During the October riots, Unit 3B went beyond the call of duty. (This topic sentence is more specific and indicates that the paragraph will contain information about a particular incident involving Unit 3B.)
A good topic sentence contains both a topic and a controlling idea or opinion.
Weak example. In this paper, I am going to discuss the rising suicide rate among young professionals. (This topic sentence provides a main idea, but it does not present a controlling idea, or thesis.)
Stronger example. The rising suicide rate among young professionals is a cause for immediate concern. (This topic sentence presents the writer’s opinion on the subject of rising suicide rates among young professionals.)
A good topic sentence is clear and easy to follow.
Weak example. In general, writing an essay, thesis, or other academic or nonacademic document is considerably easier and of much higher quality if you first construct an outline, of which there are many different types. (This topic sentence includes a main idea and a controlling thesis, but both are buried beneath the confusing sentence structure and unnecessary vocabulary. These obstacles make it difficult for the reader to follow.)
Stronger example. Most forms of writing can be improved by first creating an outline. (This topic sentence cuts out unnecessary verbiage and simplifies the previous statement, making it easier for the reader to follow.)
A good topic sentence does not include supporting details.
Weak example. Salaries should be capped in baseball for many reasons, most importantly so we don’t allow the same team to win year after year. (This topic sentence includes a supporting detail that should be included later in the paragraph to back up the main point.)
Stronger example. Introducing a salary cap would improve the game of baseball for many reasons. (This topic sentence omits the additional supporting detail so that it can be expanded upon later in the paragraph.)
A good topic sentence engages the reader by using interesting vocabulary.
Weak example. The military deserves better equipment. (This topic sentence includes a main idea and a controlling thesis, but the language is bland and unexciting.)
Stronger example. The appalling lack of resources provided to the military is outrageous and requires our immediate attention. (This topic sentence reiterates the same idea and controlling thesis, but adjectives such as appalling and immediate better engage the reader. These words also indicate the writer’s tone.)
Choose the most effective topic sentence from the following sentence pairs.
a. This paper will discuss the likelihood of the Democrats winning the next election.
b. To boost their chances of winning the next election, the Democrats need to listen to public opinion.
a. The unrealistic demands of union workers are crippling the economy for three main reasons.
b. Union workers are crippling the economy because companies are unable to remain competitive as a result of added financial pressure.
a. Authors are losing money as a result of technological advances.
b. The introduction of new technology will devastate the literary world.
a. Rap music is produced by untalented individuals with oversized egos.
b. This essay will consider whether talent is required in the rap music industry.
Using the tips on developing effective topic sentences in this section, create a topic sentence on each of the following subjects. Remember to include a controlling idea as well as a main idea. Write your responses on your own sheet of paper.
An endangered species
____________________________________________
The cost of fuel
The legal drinking age
A controversial film or novel
Writing at Work
When creating a workplace document, use the “top-down” approach—keep the topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph so that readers immediately understand the gist of the message. This method saves busy colleagues precious time and effort trying to figure out the main points and relevant details.
Headings are another helpful tool. In a text-heavy document, break up each paragraph with individual headings. These serve as useful navigation aids, enabling colleagues to skim through the document and locate paragraphs that are relevant to them.
Developing Paragraphs That Use Topic Sentences, Supporting Ideas, and Transitions Effectively
Learning how to develop a good topic sentence is the first step toward writing a solid paragraph. Once you have composed your topic sentence, you have a guideline for the rest of the paragraph. To complete the paragraph, a writer must support the topic sentence with additional information and summarize the main point with a concluding sentence.
This section identifies the three major structural parts of a paragraph and covers how to develop a paragraph using transitional words and phrases.
Identifying Parts of a Paragraph
An effective paragraph contains three main parts: a topic sentence, the body, and the concluding sentence. A topic sentence is often the first sentence of a paragraph. This chapter has already discussed its purpose—to express a main idea combined with the writer’s attitude about the subject. The body of the paragraph usually follows, containing supporting details. Supporting sentences help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence. The concluding sentence is the last sentence in the paragraph. It reminds the reader of the main point by restating it in different words.
Figure 6.2 Paragraph Structure Graphic Organizer

Read the following paragraph. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
After reading the new TV guide this week I had just one thought—why are we still being bombarded with reality shows? This season, the plague of reality television continues to darken our airwaves. Along with the return of viewer favorites, we are to be cursed with yet another mindless creation. Prisoner follows the daily lives of eight suburban housewives who have chosen to be put in jail for the purposes of this fake psychological experiment. A preview for the first episode shows the usual tears and tantrums associated with reality television. I dread to think what producers will come up with next season, but if any of them are reading this blog—stop it! We’ve had enough reality television to last us a lifetime!
The first sentence of this paragraph is the topic sentence. It tells the reader that the paragraph will be about reality television shows, and it expresses the writer’s distaste for these shows through the use of the word bombarded .
Each of the following sentences in the paragraph supports the topic sentence by providing further information about a specific reality television show. The final sentence is the concluding sentence. It reiterates the main point that viewers are bored with reality television shows by using different words from the topic sentence.
Paragraphs that begin with the topic sentence move from the general to the specific. They open with a general statement about a subject (reality shows) and then discuss specific examples (the reality show Prisoner ). Most academic essays contain the topic sentence at the beginning of the first paragraph.
Now take a look at the following paragraph. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
Last year, a cat traveled 130 miles to reach its family, who had moved to another state and had left their pet behind. Even though it had never been to their new home, the cat was able to track down its former owners. A dog in my neighborhood can predict when its master is about to have a seizure. It makes sure that he does not hurt himself during an epileptic fit. Compared to many animals, our own senses are almost dull.
The last sentence of this paragraph is the topic sentence. It draws on specific examples (a cat that tracked down its owners and a dog that can predict seizures) and then makes a general statement that draws a conclusion from these examples (animals’ senses are better than humans’). In this case, the supporting sentences are placed before the topic sentence and the concluding sentence is the same as the topic sentence.
This technique is frequently used in persuasive writing. The writer produces detailed examples as evidence to back up his or her point, preparing the reader to accept the concluding topic sentence as the truth.
Sometimes, the topic sentence appears in the middle of a paragraph. Read the following example. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
For many years, I suffered from severe anxiety every time I took an exam. Hours before the exam, my heart would begin pounding, my legs would shake, and sometimes I would become physically unable to move. Last year, I was referred to a specialist and finally found a way to control my anxiety—breathing exercises. It seems so simple, but by doing just a few breathing exercises a couple of hours before an exam, I gradually got my anxiety under control. The exercises help slow my heart rate and make me feel less anxious. Better yet, they require no pills, no equipment, and very little time. It’s amazing how just breathing correctly has helped me learn to manage my anxiety symptoms.
In this paragraph, the underlined sentence is the topic sentence. It expresses the main idea—that breathing exercises can help control anxiety. The preceding sentences enable the writer to build up to his main point (breathing exercises can help control anxiety) by using a personal anecdote (how he used to suffer from anxiety). The supporting sentences then expand on how breathing exercises help the writer by providing additional information. The last sentence is the concluding sentence and restates how breathing can help manage anxiety.
Placing a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph is often used in creative writing. If you notice that you have used a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph in an academic essay, read through the paragraph carefully to make sure that it contains only one major topic. To read more about topic sentences and where they appear in paragraphs, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Implied Topic Sentences
Some well-organized paragraphs do not contain a topic sentence at all. Instead of being directly stated, the main idea is implied in the content of the paragraph. Read the following example:
Heaving herself up the stairs, Luella had to pause for breath several times. She let out a wheeze as she sat down heavily in the wooden rocking chair. Tao approached her cautiously, as if she might crumble at the slightest touch. He studied her face, like parchment; stretched across the bones so finely he could almost see right through the skin to the decaying muscle underneath. Luella smiled a toothless grin.
Although no single sentence in this paragraph states the main idea, the entire paragraph focuses on one concept—that Luella is extremely old. The topic sentence is thus implied rather than stated. This technique is often used in descriptive or narrative writing. Implied topic sentences work well if the writer has a firm idea of what he or she intends to say in the paragraph and sticks to it. However, a paragraph loses its effectiveness if an implied topic sentence is too subtle or the writer loses focus.
Avoid using implied topic sentences in an informational document. Readers often lose patience if they are unable to quickly grasp what the writer is trying to say. The clearest and most efficient way to communicate in an informational document is to position the topic sentence at the beginning of the paragraph.
Identify the topic sentence, supporting sentences, and concluding sentence in the following paragraph.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Supporting Sentences
If you think of a paragraph as a hamburger, the supporting sentences are the meat inside the bun. They make up the body of the paragraph by explaining, proving, or enhancing the controlling idea in the topic sentence. Most paragraphs contain three to six supporting sentences depending on the audience and purpose for writing. A supporting sentence usually offers one of the following:
Sentence: The refusal of the baby boom generation to retire is contributing to the current lack of available jobs.
Sentence: Many families now rely on older relatives to support them financially.
Sentence: Nearly 10 percent of adults are currently unemployed in the United States.
Sentence: “We will not allow this situation to continue,” stated Senator Johns.
Sentence: Last year, Bill was asked to retire at the age of fifty-five.
The type of supporting sentence you choose will depend on what you are writing and why you are writing. For example, if you are attempting to persuade your audience to take a particular position you should rely on facts, statistics, and concrete examples, rather than personal opinions. Read the following example:
There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car. (Topic sentence)
First, they get 20 percent to 35 percent more miles to the gallon than a fuel-efficient gas-powered vehicle. (Supporting sentence 1: statistic)
Second, they produce very few emissions during low speed city driving. (Supporting sentence 2: fact)
Because they do not require gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump. (Supporting sentence 3: reason)
Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance. (Supporting sentence 4: example)
“It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas powered vehicles I’ve owned.” (Supporting sentence 5: quotation)
Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future. (Concluding sentence)
To find information for your supporting sentences, you might consider using one of the following sources:
- Reference book
- Encyclopedia
- Biography/autobiography
- Newspaper/magazine
- Previous experience
- Personal research
To read more about sources and research, see Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” .
When searching for information on the Internet, remember that some websites are more reliable than others. websites ending in .gov or .edu are generally more reliable than websites ending in .com or .org. Wikis and blogs are not reliable sources of information because they are subject to inaccuracies.
Concluding Sentences
An effective concluding sentence draws together all the ideas you have raised in your paragraph. It reminds readers of the main point—the topic sentence—without restating it in exactly the same words. Using the hamburger example, the top bun (the topic sentence) and the bottom bun (the concluding sentence) are very similar. They frame the “meat” or body of the paragraph. Compare the topic sentence and concluding sentence from the previous example:
Topic sentence: There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car.
Concluding sentence: Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Notice the use of the synonyms advantages and benefits . The concluding sentence reiterates the idea that owning a hybrid is advantageous without using the exact same words. It also summarizes two examples of the advantages covered in the supporting sentences: low running costs and environmental benefits.
You should avoid introducing any new ideas into your concluding sentence. A conclusion is intended to provide the reader with a sense of completion. Introducing a subject that is not covered in the paragraph will confuse the reader and weaken your writing.
A concluding sentence may do any of the following:
Restate the main idea.
Example: Childhood obesity is a growing problem in the United States.
Summarize the key points in the paragraph.
Example: A lack of healthy choices, poor parenting, and an addiction to video games are among the many factors contributing to childhood obesity.
Draw a conclusion based on the information in the paragraph.
Example: These statistics indicate that unless we take action, childhood obesity rates will continue to rise.
Make a prediction, suggestion, or recommendation about the information in the paragraph.
Example: Based on this research, more than 60 percent of children in the United States will be morbidly obese by the year 2030 unless we take evasive action.
Offer an additional observation about the controlling idea.
Example: Childhood obesity is an entirely preventable tragedy.
On your own paper, write one example of each type of concluding sentence based on a topic of your choice.
Transitions
A strong paragraph moves seamlessly from the topic sentence into the supporting sentences and on to the concluding sentence. To help organize a paragraph and ensure that ideas logically connect to one another, writers use transitional words and phrases. A transition is a connecting word that describes a relationship between ideas. Take another look at the earlier example:
There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car. First , they get 20 percent to 35 percent more miles to the gallon than a fuel-efficient gas-powered vehicle. Second , they produce very few emissions during low speed city driving. Because they do not require gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump. Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance. “It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas-powered vehicles I’ve owned.” Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Each of the underlined words is a transition word. Words such as first and second are transition words that show sequence or clarify order. They help organize the writer’s ideas by showing that he or she has another point to make in support of the topic sentence. Other transition words that show order include third , also , and furthermore .
The transition word because is a transition word of consequence that continues a line of thought. It indicates that the writer will provide an explanation of a result. In this sentence, the writer explains why hybrid cars will reduce dependency on fossil fuels (because they do not require gas). Other transition words of consequence include as a result , so that , since , or for this reason .
To include a summarizing transition in her concluding sentence, the writer could rewrite the final sentence as follows:
In conclusion, given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
The following chart provides some useful transition words to connect supporting sentences and concluding sentences. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for a more comprehensive look at transitional words and phrases.
Table 6.1 Useful Transitional Words and Phrases
Using your own paper, write a paragraph on a topic of your choice. Be sure to include a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a concluding sentence and to use transitional words and phrases to link your ideas together.
Transitional words and phrases are useful tools to incorporate into workplace documents. They guide the reader through the document, clarifying relationships between sentences and paragraphs so that the reader understands why they have been written in that particular order.
For example, when writing an instructional memo, it may be helpful to consider the following transitional words and phrases: before you begin , first , next , then , finally , after you have completed . Using these transitions as a template to write your memo will provide readers with clear, logical instructions about a particular process and the order in which steps are supposed to be completed.
Key Takeaways
- A good paragraph contains three distinct components: a topic sentence, body, and concluding sentence.
- The topic sentence expresses the main idea of the paragraph combined with the writer’s attitude or opinion about the topic.
- Good topic sentences contain both a main idea and a controlling idea, are clear and easy to follow, use engaging vocabulary, and provide an accurate indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph.
- Topic sentences may be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a paragraph. In most academic essays, the topic sentence is placed at the beginning of a paragraph.
- Supporting sentences help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence by offering facts, reasons, statistics, quotations, or examples.
- Concluding sentences summarize the key points in a paragraph and reiterate the main idea without repeating it word for word.
- Transitional words and phrases help organize ideas in a paragraph and show how these ideas relate to one another.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Pasco-Hernando State College
- The Writing Process
Parts of an Academic Essay
Rhetorical modes as types of essays, stylistic considerations.
- Literary Analysis Essay - Close Reading
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Test Yourself
- Essay Organization Quiz
- Sample Essay - Fairies
- Sample Essay - Modern Technology
Essay Organization – Overview
There are various types of writing assignments an instructor may give such as journals, reaction papers, questions to be answered, paragraphs on topics or questions, essays, and research papers.
An essay is a writing on a specific question or topic. Instructors may vary in what they are expecting when they assign an essay . It’s important to always ask your instructor if you are not sure. Some may simply want a discussion on a topic or question and are not asking for formal organization.
Others may be expecting a formal academic essay, also called a thesis-and-support paper, organized with an introduction, body, and conclusion that includes the following parts:
an introductory paragraph which gives a background and states the thesis (the point of the essay
a concluding paragraph which sums up the proof and restates the thesis.
body paragraphs which contain proof, also called supporting ideas, of the thesis statement
While some instructors may have slight variations about formal academic essay organization, you won’t have a problem if your paper has the following three components:
a thesis statement at the end of the introductory (opening) paragraph
body paragraphs contain only proof of the thesis, and
a concluding paragraph which contains a review of the proof and restatement of the thesis. Some instructors also ask for some general prediction or observation instead of or in addition to a restatement of thesis.
Always check with your instructor if you are not sure about what is expected. The discussion here is for a formal academic essay (thesis-and-support paper).
What is an academic essay and how should it look?
An essay is a collection of paragraphs that fit around one idea or position on an issue. This is usually called the thesis or main idea .
The sentence that contains the main idea is called the Thesis Statement. The Thesis Statement must take a position and not just state a fact. While some instructors vary on where a thesis statement may appear, it is safe to place it as th last sentence of the first paragraph.
An academic essay must have at least three paragraphs: an introduction, a body paragraph, and a concluding paragraph. Since there should be a separate body paragraph for each proof point, the more substantial the proof, the more paragraphs there will be. A typical essay of about five hundred words will usually have at least two or three proof paragraphs making the essay four to five paragraphs.
Instructors often require a specific page format (margins, line spacing, and so on). Page formatting is part of the requirements of a style system. Both MLA and APA styles have similar formatting requirements. Unless your instructor states otherwise, it use MLA page format.
In a way, these academic essays are like a court trial. The attorney, whether prosecuting the case or defending it, begins with an opening statement explaining the background and telling the jury what he or she intends to prove (the thesis statement). Then, the attorney presents witnesses for proof (the body of the paragraphs). Lastly, the attorney presents the closing argument (concluding paragraph).
The Introduction and Thesis
There are a variety of approaches regarding the content of the introduction paragraph such as a brief outline of the proof, an anecdote, explaining key ideas, and asking a question. In addition, some textbooks say that an introduction can be more than one paragraph. The placement of the thesis statement is another variable depending on the instructor and/or text. The approach used in this lesson is that an introduction paragraph gives background information leading into the thesis which is the main idea of the paper, which is stated at the end.
The background in the introductory paragraph consists of information about the circumstances of the thesis. This background information often starts in the introductory paragraph with a general statement which is then refined to the most specific sentence of the essay, the thesis. It is important to note that in this approach, the proof for the thesis is not found in the introduction except, possibly, as part of a thesis statement which includes the key elements of the proof. Proof is presented and expanded on in the body.
The thesis is the position statement. It must contain a subject and a verb and express a complete thought. It must also be defensible. This means it should be an arguable point with which people could reasonably disagree. The more focused and narrow the thesis statement, the better a paper will generally be.
If you are given a question in the instructions for your paper, the thesis statement is a one-sentence answer taking a position on the question.
If you are given a topic instead of a question, then in order to create a thesis statement, you must narrow your analysis of the topic to a specific controversial issue about the topic to take a stand. If it is not a research paper, some brainstorming (jotting down what comes to mind on the issue) should help determine a specific question.
If it is a research paper, the process begins with exploratory research which should show the various issues and controversies which should lead to the specific question. Then, the research becomes focused on the question which in turn should lead to taking a position on the question.
These methods of determining a thesis are still answering a question. It’s just that you pose a question to answer for the thesis. Here is an example.
Suppose, one of the topics you are given to write about is America’s National Parks. Books have been written about this subject. In fact, books have been written just about a single park. As you are thinking about it, you may realize how there is an issue about balancing between preserving the wilderness and allowing visitors. The question would then be Should visitors to America’s National Parks be regulated in order to preserve the wilderness?
One thesis might be There is no need for regulations for visiting America’s National Parks to preserve the wilderness.
Another might be There should be reasonable regulations for visiting America’s National Parks in order to preserve the wilderness.
Finally, avoid using expressions that announce, “Now I will prove…” or “This essay is about …” Instead of telling the reader what the paper is about, a good paper simply proves the thesis in the body. Generally, you shouldn’t refer to your paper in your paper.
Here is an example of a good introduction with the thesis in red:
Not too long ago, everyday life was filled with burdensome, time-consuming chores that left little time for much more than completing these tasks. People generally worked from their homes or within walking distance to their homes and rarely traveled far from them. People were limited to whatever their physical capacities were. All this changed dramatically as new technologies developed. Modern technology has most improved our lives through convenience, efficiency, and accessibility.
Note how the background is general and leads up to the thesis. No proof is given in the background sentences about how technology has improved lives.
Moreover, notice that the thesis in red is the last sentence of the introduction. It is a defensible statement.
A reasonable person could argue the opposite position: Although modern technology has provided easier ways of completing some tasks, it has diminished the quality of life since people have to work too many hours to acquire these gadgets, have developed health problems as a result of excess use, and have lost focus on what is really valuable in life.
Quick Tips:
The introduction opens the essay and gives background information about the thesis.
Do not introduce your supporting points (proof) in the introduction unless they are part of the thesis; save these for the body.
The thesis is placed at the end of the introductory paragraph.
Don’t use expressions like “this paper will be about” or “I intend to show…”
For more information on body paragraphs and supporting evidence, see Proving a Thesis – Evidence and Proving a Thesis – Logic, and Logical Fallacies and Appeals in Related Pages on the right sidebar.
Body paragraphs give proof for the thesis. They should have one proof point per paragraph expressed in a topic sentence. The topic sentence is usually found at the beginning of each body paragraph and, like a thesis, must be a complete sentence. Each topic sentence must be directly related to and support the argument made by the thesis.
After the topic sentence, the rest of the paragraph should go on to support this one proof with examples and explanation. It is the details that support the topic sentences in the body paragraphs that make the arguments strong. Proof may include discussion of an opposing view, but it must include a rebuttal explaining why that opposing view does not make sense or otherwise not be considered valid.
If the thesis statement stated that technology improved the quality of life, each body paragraph should begin with a reason why it has improved the quality of life. This reason is called a topic sentence . Following are three examples of body paragraphs that provide support for the thesis that modern technology has improved our lives through convenience, efficiency, and accessibility:
Almost every aspect of our lives has been improved through convenience provided by modern technology. From the sound of music from an alarm clock in the morning to the end of the day being entertained in the convenience of our living room, our lives are improved. The automatic coffee maker has the coffee ready at a certain time. Cars or public transportation bring people to work where computers operate at the push of a button. At home, there’s the convenience of washing machines and dryers, dishwashers, air conditioners, and power lawn mowers. Some may say the conveniences are not worth the extra cost and effort keeping these devices working, but, overwhelmingly, people opt to use them. Modern technology has made life better with many conveniences.
Not only has technology improved our lives through convenience, it has improved our lives through efficiency. The time saved by machines doing most of the work leaves more time for people to develop their personal goals or to just relax. Years ago, when doing laundry could take all day, there wasn’t time left over to read or go to school or even just to take a leisurely walk. The opposing view might argue that people misuse their increased free time sitting around and watching television. While some people have health problems as a result of technology, by far, lives are improved. Nowadays, people have more time and energy than ever to simply enjoy their lives and pursue their goals thanks to the efficiency of modern technology.
Accessibility to a wide range of options has been expanded through modern technology. Never before could people cross a continent or an ocean in an afternoon. Travel is not the only way technology has created accessibility. Software which types from voice commands has made using computers more accessible for school or work. People with special needs have many new options thanks to modern technology such as special chairs or text readers. Actually, those people who need hearing aids as a result of normal aging have access to continued communication and enjoyment of entertainment they did not previously have. There are many ways technology has improved lives through increased accessibility.
Notice how these proof paragraphs stick to one proof point introduced in the topic sentences in red. These three paragraphs, not only support the original thesis, but go on to give details and explanations which explain the proof point in the topic sentence.
Some instructors would like a rebuttal paragraph which raises the opposing arguments and explains why they are not valid instead of addressing opposition within the paragraphs as appropriate as shown in the above essay. In that case, the rebuttal should go before the conclusion.
Quick Tips on Body Paragraphs
- The body of your essay is where you give your main support for the thesis.
- Each body paragraph should start with a Topic Sentence that is directly related to and supports the thesis statement.
- Each body paragraph should also give details and explanations that further support the poof point for that paragraph.
- Don’t use enumeration such as first, second, and third. The reader will know by the topic sentence that it is a new proof point.
See Proving the Thesis in Related Pages on the right sidebar for more information on proof.
The Conclusion
Instructors vary of what they expect in the conclusion; however, there is general agreement that conclusions should not introduce any new proof points, should include a restatement of the thesis, and should not contain any words such as “In conclusion.”
Some instructors want only a summary of the proof and a restatement of the thesis. Some instructors ask for a general prediction or implication of the information presented without a restatement of thesis. Still others may want to include a restatement along with a general prediction or implication of the information presents. Be sure to review assignment instructions or check with instructor. If your assignment instructions don’t specify, just sum up the proof and restate the thesis.
Example which sums up proof and restates thesis :
Modern technology has created many conveniences in everyday from waking up to music to having coffee ready to getting to work and doing a day’s work. The efficiency provided by technology gives people more time to enjoy life and pursue personal development, and the accessibility has broadened options for travel, school, and work. Modern technology has improved our lives through convenience, efficiency, and accessibility.
See how the thesis statement was restated in red. The two major arguments about the possible locations proven to be incorrect were also included to remind the reader of the major proof points made in the paper.
Example which makes a general prediction or implication of the information presented:
Modern technology has created many conveniences in everyday life from waking up to music to having coffee ready to getting to work and doing a day’s work. The efficiency provided by technology gives people more time to enjoy life and pursue personal development, and the accessibility has broadened options for travel, school, and work. Without it, everyday life would be filled with burdensome tasks and be limited to our neighborhood and our physical capacity. Here’s an example of a conclusion with a general prediction or implication statement with a restatement of thesis.
Modern technology has created many conveniences in everyday life from waking up to music to having coffee ready to getting to work and doing a day’s work. The efficiency provided by technology gives people more time to enjoy life and pursue personal development, and the accessibility has broadened options for travel, school, and work. Without it, everyday life would be filled with burdensome tasks and be limited to our neighborhood and our physical capacity. Modern technology has improved our lives through convenience, efficiency, and accessibility.
Quick Tips for Conclusions
- The conclusion brings the essay to an end and is typically the shortest paragraph.
- It is important to not introduce new ideas or information here.
- Unless otherwise specified in your assignment, just sum up the proof and restate the conclusion.
- Some instructors may want the concluding paragraph to contain a general prediction or observation implied from the information presented.
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. Rhetorical modes are ways of using language with a specific focus. Narration, for example, tells a story or a sequence of events. A narrative essay tells a story.
Other rhetorical modes focus on describing, defining, using examples (exemplification), or classifying as the primary purpose. Comparing and contrasting simply compares one thing to another showing the differences as well as the similarities.
In a cause and/or effect paper, the causes and/or effects of a situation are the focus.
A persuasive or argumentative paper proves a position on a controversial issue.
Sometimes, instructors assign essays requiring a specific mode such as defining something or discussing the causes of a problem. These are considered useful ways to develop the particular skill such as looking closely at something to describe it or finding ways to define an object or situation.
More commonly, however, a writing assignment does not require a specific mode; these strategies are used as appropriate within an essay or other writing. For example, a paper arguing that pesticides are harmful might include information defining and describing various pesticides. It could include classifying them by potential harm and use examples of the types of pesticides. It could have information on the effects of particular pesticides.
It can be argued that all papers, regardless of the primary rhetorical strategy used, are persuasive or argumentative since all writing ultimately is to prove something – even if it is only the legitimacy of one’s feelings such as in a reaction paper or creative writing. Most writing blend the uses of rhetorical styles.
Unity and Coherence
Like all effective writing, essays must have unity. They must clearly stay focused on one purpose: proving the thesis. All the sentences in each paragraph and each paragraph must work together to achieve that purpose. It is critical for each sentence in each paragraph to start with a topic sentence that states a reason why the thesis is right and that the rest of the sentences in the paragraph support that topic sentence.
Essays must have coherence. Each sentence must flow smoothly and logically into the next. Each paragraph must flow smoothly and logically into the next. Words and word groups called transitions must be used to link one sentence to the next and one paragraph to the next.
See Unity and Coherence in Essays in Related Pages on the right side bar for more information.
Word Use (Appropriate Language)
Generally speaking, use of Standard English vocabulary and grammar is expected. These types of papers should not sound as though you were talking casually to a friend. Don’t use slang, for example, such as ok. Also, while we use second person (you, your) in informal speech, formal academic writing should not use second person since the reference is not specific. Here’s an example. You should know where your children are. The reader may not have young children or any children at all. Here’s an example with clear reference. Parents of young children should know where their children are.
Instructors will vary about accepting the use of first person (I, me, my, we, us, our) in essay writing. While first person may be appropriate in journal writing or reaction papers, typically, instructors will require third person (not first or second) in formal essays and research essays. Be aware of requirements for any particular assignment.
Formal academic essays should not include sentences that refer to yourself or the paper. Don’t use statements such as “In the opinion of this writer (referring to yourself)….” or “This paper will show….”
For more information on language use, see Appropriate Language in Related Pages on the right sidebar.
Literary Analysis Essay - Close Reading
The purpose of a literary analysis essay is to carefully examine and sometimes evaluate a work of literature or an aspect of a work of literature. Examining the different elements of a pieces of literature including plot, character, setting, point of view, irony, symbolism, and style to see how the author develops theme is not an end in itself but rather a process to help you better appreciate and understand the work of literature as a whole. The focus of a literary analysis essay is as expansive as the writers’ interests. For example, a short story analysis might include identifying a particular theme and then showing how the writer suggests that theme through the point of view of the story. It is important to remember that literary analysis does not merely demonstrate a particularly literary element. The focus is explaining how that element is meaningful or significant to the work as a whole. See Essay Organization and Elements of Fiction for more information.
Close reading is deep analysis of how a literary text function; it is both a reading process and something you include in a literary analysis paper. When you read a text paying specific attention to certain literary elements, looking for particular patters, or following the development of a particular character, you are practicing close reading. Likewise, when you watch a film with particular emphasis on a certain element, you are doing a close reading. Of course, when one writes an essay that teases out a certain element, this is the beginning of a close reading. Like literary analysis more generally, close reading is not a means in and of itself. Close reading helps inform the larger meaning or import of a work.
Literary analysis involves examining the components of a literary text, which allows us to focus on small parts of the text, clues to help us understand the work as a whole. The process of close reading should produce questions. When you begin to answer these questions, you are ready to participate thoughtfully in class discussion or write a literary analysis paper. Close reading is a process of finding as much information as you can in order form to as many questions as you can.
An outline includes the thesis and proof points. It is the skeleton of an academic essay. Starting with an outline can be extremely helpful in writing an essay. Once an outline is completed, it is a matter of developing the proof points (body paragraphs),adding a background before the thesis for an introduction paragraph, and adding a concluding paragraph. See Outlining in Related Pages on the right sidebar for more information.
The important thing in essay writing is to have a point, thereby knowing what you are trying to prove, and stick to that point. Keep it simple and focused.
This format is the basis for writing a research paper as well. If you can get the idea in a simple essay, writing research papers will be much easier.
- Printer-friendly version


TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
V. Process and Organization
5.2 Writing Paragraphs
Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; Kirk Swenson; and Terri Pantuso
Once you decide on a method for organizing your essay, you’ll want to start drafting your paragraphs. Think of your paragraphs as links in a chain where coherence and continuity are key. Imagine reading one long block of text, with each idea blurring into the next. You are likely to lose interest in a piece of writing that is disorganized and spans many pages without breaks. Paragraphs separate ideas into logical, manageable chunks, each paragraph focusing on only one main idea and presenting coherent sentences to support that one point. Because all the sentences in one paragraph support the same point, a paragraph may stand on its own. For most types of informative or persuasive academic writing, writers find it helpful to think of the paragraph analogous to an essay, as each is controlled by a main idea or point, and that idea is developed by an organized group of more specific ideas. Thus, the thesis of the essay is analogous to the topic sentence of a paragraph, just as the supporting sentences in a paragraph are analogous to the supporting paragraphs in an essay.
In essays, each supporting paragraph adds another related main idea to support the writer’s thesis, or controlling idea. Each related supporting idea is developed with facts, examples, and other details that explain it. By exploring and refining one idea at a time, writers build a strong case for their thesis. Effective paragraphing makes the difference between a satisfying essay that readers can easily process and one that requires readers to mentally organize the piece themselves. Thoughtful organization and development of each body paragraph leads to an effectively focused, developed, and coherent essay.
An effective paragraph contains three main parts:
- a topic sentence
- body, supporting sentences
- a concluding sentence
In informative and persuasive writing, the topic sentence is usually the first or second sentence of a paragraph and expresses its main idea, followed by supporting sentences that help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence. In narrative and descriptive paragraphs, however, topic sentences may be implied rather than explicitly stated, with all supporting sentences working to create the main idea. If the paragraph contains a concluding sentence, it is the last sentence in the paragraph and reminds the reader of the main point by restating it in different words.
Creating Focused Paragraphs with Topic Sentences
The foundation of a paragraph is the topic sentence which expresses the main idea or point of the paragraph. A topic sentence functions in two ways: it clearly refers to and supports the essay’s thesis, and it indicates what will follow in the rest of the paragraph. As the unifying sentence for the paragraph, it is the most general sentence, whereas all supporting sentences provide different types of more specific information such as facts, details, or examples.
An effective topic sentence has the following characteristics:
- A topic sentence provides an accurate indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph.
Weak Example
First, we need a better way to educate students.
Explanation: The claim is vague because it does not provide enough information about what will follow and it is too broad to be covered effectively in one paragraph.
Stronger Example
Creating a national set of standards for math and English education will improve student learning in many states.
Explanation: The sentence replaces the vague phrase “a better way” and leads readers to expect supporting facts and examples as to why standardizing education in these subjects might improve student learning in many states.
- A good topic sentence is the most general sentence in the paragraph and thus does not include supporting details.
Salaries should be capped in baseball for many reasons, most importantly so we don’t allow the same team to win year after year.
Explanation: This topic sentence includes a supporting detail that should be included later in the paragraph to back up the main point.
Introducing a salary cap would improve the game of baseball for many reasons.
Explanation: This topic sentence omits the additional supporting detail so that it can be expanded upon later in the paragraph, yet the sentence still makes a claim about salary caps – improvement of the game.
- A good topic sentence is clear and easy to follow.
In general, writing an essay, thesis, or other academic or nonacademic document is considerably easier and of much higher quality if you first construct an outline, of which there are many different types.
Explanation: The confusing sentence structure and unnecessary vocabulary bury the main idea, making it difficult for the reader to follow the topic sentence.
Most forms of writing can be improved by first creating an outline.
Explanation: This topic sentence cuts out unnecessary verbiage and simplifies the previous statement, making it easier for the reader to follow. The writer can include examples of what kinds of writing can benefit from outlining in the supporting sentences.
Location of Topic Sentences
As previously discussed, a topic sentence can appear anywhere within a paragraph depending upon the mode of writing, or it can be implied such as in narrative or descriptive writing. In college-level expository or persuasive writing, placing an explicit topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph (the first or second sentence) makes it easier for readers to follow the essay and for writers to stay on topic, but writers should be aware of variations and maintain the flexibility to adapt to different writing projects. The following examples illustrate varying locations for the topic sentence. In each example, the topic sentence is underlined.
Topic Sentence Begins the Paragraph (General to Specific)
After reading the new TV guide this week I wondered why we are still being bombarded with reality shows, a plague that continues to darken our airwaves. Along with the return of viewer favorites, we are to be cursed with yet another mindless creation. Prisoner follows the daily lives of eight suburban housewives who have chosen to be put in jail for the purposes of this fake psychological experiment. A preview for the first episode shows the usual tears and tantrums associated with reality television. I dread to think what producers will come up with next season and hope that other viewers will express their criticism. These producers must stop the constant stream of meaningless shows without plotlines. We’ve had enough reality television to last us a lifetime.
The first sentence tells readers that the paragraph will be about reality television shows, and it expresses the writer’s distaste for these shows through the use of the word bombarded . Each of the following sentences in the paragraph supports the topic sentence by providing further information about a specific reality television show and why the writer finds it unappealing. The final sentence is the concluding sentence. It reiterates the main point that viewers are bored with reality television shows by using different words from the topic sentence.
Paragraphs that begin with the topic sentence move from the general to the specific. They open with a general statement about a subject (reality shows) and then discuss specific examples (the reality show Prisoner ). Most academic essays contain the topic sentence at the beginning of the first paragraph. However, when utilizing a specific to general method, the topic sentence may be located later in the paragraph.
Topic Sentence Ends the Paragraph (Specific to General)
Last year, a cat traveled 130 miles to reach its family who had moved to another state and had left their pet behind. Even though it had never been to their new home, the cat was able to track down its former owners. A dog in my neighborhood can predict when its master is about to have a seizure. It makes sure that he does not hurt himself during an epileptic fit. Compared to many animals, our own senses are almost dull.
The last sentence of this paragraph is the topic sentence. It draws on specific examples (a cat that tracked down its owners and a dog that can predict seizures) and then makes a general statement that draws a conclusion from these examples (animals’ senses are better than humans’). In this case, the supporting sentences are placed before the topic sentence, and the concluding sentence is the same as the topic sentence. This technique is frequently used in persuasive writing. The writer produces detailed examples as evidence to back up his or her point, preparing the reader to accept the concluding topic sentence as the truth.
When the Topic Sentence Appears in the Middle of the Paragraph
For many years, I suffered from severe anxiety every time I took an exam. Hours before the exam, my heart would begin pounding, my legs would shake, and sometimes I would become physically unable to move. Last year, I was referred to a specialist and finally found a way to control my anxiety—breathing exercises. It seems so simple, but by doing just a few breathing exercises a couple of hours before an exam, I gradually got my anxiety under control. The exercises help slow my heart rate and make me feel less anxious. Better yet, they require no pills, no equipment, and very little time. It’s amazing how just breathing correctly has helped me learn to manage my anxiety symptoms.
In this paragraph, the underlined sentence is the topic sentence. It expresses the main idea—that breathing exercises can help control anxiety. The preceding sentences enable the writer to build up to his main point (breathing exercises can help control anxiety) by using a personal anecdote (how he used to suffer from anxiety). The supporting sentences then expand on how breathing exercises help the writer by providing additional information. The last sentence is the concluding sentence and restates how breathing can help manage anxiety. Placing a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph is often used in creative writing. If you notice that you have used a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph in an academic essay, read through the paragraph carefully to make sure that it contains only one major topic.
Implied Topic Sentences
Some well-organized paragraphs do not contain a topic sentence at all, a technique often used in descriptive and narrative writing. Instead of being directly stated, the main idea is implied in the content of the paragraph, as in the following narrative paragraph.
Example of Implied Topic Sentence
Heaving herself up the stairs, Luella had to pause for breath several times. She let out a wheeze as she sat down heavily in the wooden rocking chair. Tao approached her cautiously, as if she might crumble at the slightest touch. He studied her face, like parchment, stretched across the bones so finely he could almost see right through the skin to the decaying muscle underneath. Luella smiled a toothless grin.
Although no single sentence in this paragraph states the main idea, the entire paragraph focuses on one concept—that Luella is extremely old. The topic sentence is thus implied rather than stated so that all the details in the paragraph can work together to convey the dominant impression of Luella’s age. In a paragraph such as this one, an explicit topic sentence would seem awkward and heavy-handed. Implied topic sentences work well if the writer has a firm idea of what he or she intends to say in the paragraph and sticks to it. However, a paragraph loses its effectiveness if an implied topic sentence is too subtle or the writer loses focus.
Developing Paragraphs
If you think of a paragraph as a sandwich, the supporting sentences are the filling between the bread. They make up the body of the paragraph by explaining, proving, or enhancing the controlling idea in the topic sentence. The overall method of development for paragraphs depends upon the essay as a whole and the purpose of each paragraph; thus paragraphs may be developed by using examples, description, narration, comparison and contrast, definition, cause and effect, classification and division. A writer may use one method or combine several methods.
Writers often want to know how many words a paragraph should contain, and the answer is that a paragraph should develop the idea, point, or impression completely enough to satisfy the writer and readers. Depending on their function, paragraphs can vary in length from one or two sentences, to over a page; however, in most college assignments, successfully developed paragraphs usually contain approximately one hundred to two hundred and fifty words and span one-fourth to two-thirds of a typed page. A series of short paragraphs in an academic essay can seem choppy and unfocused, whereas paragraphs that are one page or longer can tire readers. Giving readers a paragraph break on each page helps them maintain focus.
This advice does not mean, of course, that composing a paragraph of a particular number of words or sentences guarantees an effective paragraph. Writers must provide enough supporting sentences within paragraphs to develop the topic sentence and simultaneously carry forward the essay’s main idea.
For example, in a descriptive paragraph about a room in the writer’s childhood home, a length of two or three sentences is unlikely to contain enough details to create a picture of the room in the reader’s mind, and it will not contribute in conveying the meaning of the place. In contrast, a half page paragraph, full of carefully selected vivid, specific details and comparisons, provides a fuller impression and engages the reader’s interest and imagination. In descriptive or narrative paragraphs, supporting sentences present details and actions in vivid, specific language in objective or subjective ways, appealing to the readers’ senses to make them see and experience the subject. In addition, some sentences writers use make comparisons that bring together or substitute the familiar with the unfamiliar, thus enhancing and adding depth to the description of the incident, place, person, or idea.
In a persuasive essay about raising the wage for certified nursing assistants, a paragraph might focus on the expectations and duties of the job, comparing them to that of a registered nurse. Needless to say, a few sentences that simply list the certified nurse’s duties will not give readers a complete enough idea of what these healthcare professionals do. If readers do not have plenty of information about the duties and the writer’s experience in performing them for what she considers inadequate pay, the paragraph fails to do its part in convincing readers that the pay is inadequate and should be increased.
In informative or persuasive writing, a supporting sentence usually offers one of the following:
- Reason: The refusal of the baby boom generation to retire is contributing to the current lack of available jobs.
- Fact: Many families now rely on older relatives to support them financially.
- Statistic: Nearly 10 percent of adults are currently unemployed in the United States.
- Quotation: “We will not allow this situation to continue,” stated Senator Johns.
- Example: Last year, Bill was asked to retire at the age of fifty-five.
The type of supporting sentence you choose will depend on what you are writing and why you are writing. For example, if you are attempting to persuade your audience to take a particular position, you should rely on facts, statistics, and concrete examples, rather than personal opinions. Personal testimony in the form of an extended example can be used in conjunction with the other types of support.
Consider the elements in the following paragraph.
Example Persuasive Paragraph
Topic sentence: There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car.
Sentence 1 (statistic): First, they get 20 percent to 35 percent more miles to the gallon than a fuel- efficient gas-powered vehicle.
Sentence 2 (fact): Second, they produce very few emissions during low speed city driving.
Sentence 3 (reason): Because they do not require gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump.
Sentence 4 (example): Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance.
Sentence 5 (quotation): “It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas powered vehicles I’ve owned.”
Concluding sentence: Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Sometimes the writing situation does not allow for research to add specific facts or other supporting information, but paragraphs can be developed easily with examples from the writer’s own experience.
Farheya, a student in a freshman English Composition class, quickly drafted an essay during a timed writing assignment in class. To practice improving paragraph development, she selected the body paragraph below to add support:
Example of Original Body Paragraph
Topic: Would you be better off if you didn’t own a television? Discuss.
Lack of ownership of a television set is also a way to preserve innocence, and keep the exposure towards anything inappropriate at bay. From simply watching a movie, I have seen things I shouldn’t have, no matter how fast I switch the channel. Television shows not only display physical indecency, but also verbal. Many times movies do voice-overs of profane words, but they also leave a few words uncensored. Seeing how all ages can flip through and see or hear such things make t.v. toxic for the mind, and without it I wouldn’t have to worry about what I may accidentally see or hear.
The original paragraph identifies two categories of indecent material, and there is mention of profanity to provide a clue as to what the student thinks is indecent. However, the paragraph could use some examples to make the idea of inappropriate material clearer. Farheya considered some of the television shows she had seen and made a few changes.
Example of Revised Body Paragraph
Not owning a television set would also be a way to preserve innocence and keep my exposure to anything inappropriate at bay. While searching for a program to view, I have seen things I shouldn’t have, no matter how fast I switched the channel. The synopsis of Euro Trip, which describes high school friends traveling across Europe, leads viewers to think that the film is an innocent adventure; however; it is filled with indecency, especially when the students reach Amsterdam. The movie Fast and Furious has the same problem since the women are all half-naked in half tops and mini-skirts or short- shorts. Television shows not only display physical indecency, but also verbal. Many television shows have no filters, and the characters say profane words freely. On Empire, the main characters Cookie and Lucious Lyon use profane words during their fights throughout entire episodes. Because The Big Bang Theory is a show about a group of science geeks and their cute neighbor, viewers might think that these science geniuses’ conversations would be about their current research or other science topics. Instead, their characters regularly engage in conversations about their personal lives that should be kept private. The ease of flipping through channels and seeing or hearing such things makes t.v. toxic for the mind, and without a television I wouldn’t have to worry about what I may accidentally see or hear.
Farheya’s addition of a few examples helps to convey why she thinks she would be better off without a television.
Concluding Sentences
An effective concluding sentence draws together all the ideas raised in your paragraph. It reminds readers of the main point—the topic sentence—without restating it in exactly the same words. Using the hamburger example, the top bun (the topic sentence) and the bottom bun (the concluding sentence) are very similar. They frame the “meat” or body of the paragraph.
Compare the topic sentence and concluding sentence from the first example on hybrid cars:
Topic Sentence: There are many advantages to owning a hybrid car.
Concluding Sentence: Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Notice the use of the synonyms advantages and benefits . The concluding sentence reiterates the idea that owning a hybrid is advantageous without using the exact same words. It also summarizes two examples of the advantages covered in the supporting sentences: low running costs and environmental benefits.
Writers should avoid introducing any new ideas into a concluding sentence because a conclusion is intended to provide the reader with a sense of completion. Introducing a subject that is not covered in the paragraph will confuse readers and weaken the writing.
A concluding sentence may do any of the following:
- Restate the main idea.
Childhood obesity is a growing problem in the United States.
- Summarize the key points in the paragraph
A lack of healthy choices, poor parenting, and an addiction to video games are among the many factors contributing to childhood obesity.
- Draw a conclusion based on the information in the paragraph.
These statistics indicate that unless we take action, childhood obesity rates will continue to rise.
- Make a prediction, suggestion, or recommendation about the information in the paragraph.
Based on this research, more than 60 percent of children in the United States will be morbidly obese by the year 2030 unless we take evasive action.
- Offer an additional observation about the controlling idea.
Childhood obesity is an entirely preventable tragedy.
Paragraph Length
Although paragraph length is discussed in the section on developing paragraphs with supporting sentences, some additional reminders about when to start a new paragraph may prove helpful to writers:
- If a paragraph is over a page long, consider providing a paragraph break for readers. Look for a logical place to divide the paragraph; then revise the opening sentence of the second paragraph to maintain coherence.
- A series of short paragraphs can be confusing and choppy. Examine the content of the paragraphs and combine ones with related ideas or develop each one further.
- When dialogue is used, begin a new paragraph each time the speaker changes.
- Begin a new paragraph to indicate a shift in subject, tone, or time and place.
Improving Paragraph Coherence
A strong paragraph holds together well, flowing seamlessly from the topic sentence into the supporting sentences and on to the concluding sentence. To help organize a paragraph and ensure that ideas logically connect to one another, writers use a combination of elements:
- A clear organizational pattern: chronological (for narrative writing and describing processes), spatial (for descriptions of people or places), order of importance, general to specific (deductive), specific to general (inductive)
- Transitional words and phrases: These connecting words describe a relationship between ideas.
- Repetition of ideas: This element helps keep the parts of the paragraph together by maintaining focus on the main idea, so this element reinforces both paragraph coherence and unity.
In the following example, notice the use of transitions ( bolded ) and key words ( underlined ):
Example of Transition Words
Owning a hybrid car benefits both the owner and the environment . First , these cars get 20 percent to 35 percent more miles to the gallon than a fuel-efficient gas-powered vehicle. Second , they produce very few emissions during low speed city driving. Because they do not require gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump. Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance. “It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas-powered vehicles I’ve owned.” Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car , it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Words such as first and second are transition words that show sequence or clarify order. They help organize the writer’s ideas by showing that he or she has another point to make in support of the topic sentence. The transition word because is a transition word of consequence that continues a line of thought. It indicates that the writer will provide an explanation of a result. In this sentence, the writer explains why hybrid cars will reduce dependency on fossil fuels (because they do not require gas).
In addition to transition words, the writer repeats the word hybrid (and other references such as these cars , and they ), and ideas related to benefits to keep the paragraph focused on the topic and hold it together.
To include a summarizing transition for the concluding sentence, the writer could rewrite the final sentence as follows:
In conclusion, given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Although the phrase “in conclusion” certainly reinforces the idea of summary and closure, it is not necessary in this case and seems redundant, as the sentence without the phrase already repeats and summarizes the benefits presented in the topic sentence and flows smoothly from the preceding quotation. The second half of the sentence, in making a prediction about the future, signals a conclusion, also making the phrase “in conclusion” unnecessary. The original version of the concluding sentence also illustrates how varying sentence openings can improve paragraph coherence. As writers continue to practice and develop their style, they more easily make these decisions between using standard transitional phrases and combining the repetition of key ideas with varied sentence openings.
Table 5.2.1 provides some useful transition words and phrases to connect sentences within paragraphs as well as to connect body paragraphs:
Table 5.2.1. Common Transitional Words and Phrases
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition . 2nd edition. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8 . Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Corresponding or related to two ideas. An analogy refers to a comparison made to the similarity between two items, ideas, events, and phenomena. Forrest Gump’s famous saying that “life is like a box of chocolates—you never know what you are going to get” is an example of an analogy.
A statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes an argument that will later be explained, expanded upon, and developed in a longer essay or research paper. In undergraduate writing, a thesis statement is often found in the introductory paragraph of an essay. The plural of thesis is theses .
Use of words, particularly referring to the overuse or redundancy of them.
Repeat, rehash, or restate something that has already been conveyed; to echo a sentiment or idea that was stated earlier in a different way or manner.
A short account or telling of an incident or story, either personal or historical; anecdotal evidence is frequently found in the form of a personal experience rather than objective data or widespread occurrence.
5.2 Writing Paragraphs Copyright © 2022 by Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; Kirk Swenson; and Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis. The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way. The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Not every essay does all three in the first paragraph, and the degree to which an essay declares its structure or methodology may vary widely, depending on how necessary that information will be to the readers. ... Its conclusion (the consequences of the first claim) Not every essay contains every element in precisely this order, but most good ...
Paragraphs that begin with the topic sentence move from the general to the specific. They open with a general statement about a subject (reality shows) and then discuss specific examples (the reality show Prisoner). Most academic essays contain the topic sentence at the beginning of the first paragraph.
Your introduction paragraph should—. grab your reader's attention. introduce the topic of your essay. present your thesis. You can visualize the ideas in your introduction paragraph by thinking about an inverted triangle. The ideas in the beginning of your introduction paragraph are general. Then you narrow down the topic to a specific idea.
Begin with a great first sentence. The introductory paragraph of any paper, long or short, should start with a sentence that piques the interest of your readers . In a well-constructed first paragraph, that first sentence leads into three or four sentences that provide details about the subject you address in the body of your essay.
An introduction exists as the first paragraph in a 5-page essay, and it serves the following purposes: (1) Establishes reader interest, (2) Introduces the general topic of the essay while ... An introduction usually contains a thesis statement (i.e., the main point of the essay). A thesis statement is a promise to the reader about what the ...
The Introductory Paragraph. The paragraph that begins an essay causes students the most trouble, yet carries the most importance. ... Its conclusion (the consequences of the first claim) Not every essay contains every element in precisely this order, but most good essays cover all of them, either explicitly or implicitly. In longer and more ...
Each paragraph typically contains a three-part structure: 1. Introduction: includes a topic sentence and transition words 2. Body: discusses the topic, using various forms of evidence 3. Conclusion: comments and draws connections. Paragraph Principles. Each paragraph should contain one new point related to the essay's overall thesis.
8. All paragraphs need to be relevant to the marking criteria. 9. Only include one key idea per paragraph. 10. Keep sentences short. 11. Keep quotes short. Paragraph structure is one of the most important elements of getting essay writing right.
A paragraph is a series of sentences on a specific point or topic. A well written paragraph must have a topic sentence which states the main idea: what the paragraph is about. While some say the topic sentence can be anywhere in the paragraph, it is best to put it as the first sentence in a paragraph. The rest of the sentences in the paragraph ...
An effective paragraph contains three main parts: a topic sentence, the body, and the concluding sentence. A topic sentence is often the first sentence of a paragraph. This chapter has already discussed its purpose—to express a main idea combined with the writer's attitude about the subject.
An academic essay must have at least three paragraphs: an introduction, a body paragraph, and a concluding paragraph. Since there should be a separate body paragraph for each proof point, the more substantial the proof, the more paragraphs there will be. A typical essay of about five hundred words will usually have at least two or three proof ...
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
A series of short paragraphs can be confusing and choppy. Examine the content of the paragraphs and combine ones with related ideas or develop each one further. When dialogue is used, begin a new paragraph each time the speaker changes. Begin a new paragraph to indicate a shift in subject, tone, or time and place.
Generally, essays should have between three and seven paragraphs, depending on the length of the essay. For shorter essays, three paragraphs is usually enough, while for longer ones, seven is the maximum. In addition, each paragraph should be focused on a particular idea or topic and should have a clear beginning, middle, and end.
The introduction is the _____ paragraph of an essay and contains the main idea of the essay. first. A _____ statement should summarize all of the ideas in the essay. thesis. After writing a draft of an essay, the writer may find out that the thesis statement needs to be _____. changed.
If you want your order to be completed by one of the best writers from our essay writing service with superb feedback, choose this option. Your preferred writer. You can indicate a specific writer's ID if you have already received a paper from him/her and are satisfied with it. Also, our clients choose this option when they have a series of ...