Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples

How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
Published on February 28, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.

An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a thesis , dissertation or research paper ). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
- Introduction
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis , include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Abstract example, when to write an abstract, step 1: introduction, step 2: methods, step 3: results, step 4: discussion, tips for writing an abstract, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about abstracts.
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the US during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book or research proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, right before the proofreading stage, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your dissertation topic , but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialized terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyze,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here — the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, summarize the main research results . This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research : what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalizability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style , have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review —try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases .
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarize the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services or use the paraphrasing tool .
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format .
Checklist: Abstract
The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page.
The abstract appears after the title page and acknowledgements and before the table of contents .
I have clearly stated my research problem and objectives.
I have briefly described my methodology .
I have summarized the most important results .
I have stated my main conclusions .
I have mentioned any important limitations and recommendations.
The abstract can be understood by someone without prior knowledge of the topic.
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarizes the contents of your paper.
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 200–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis , dissertation or research paper .
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page in the thesis or dissertation , after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 18). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, shorten your abstract or summary, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts
An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes:
- an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to read the full paper;
- an abstract prepares readers to follow the detailed information, analyses, and arguments in your full paper;
- and, later, an abstract helps readers remember key points from your paper.
It’s also worth remembering that search engines and bibliographic databases use abstracts, as well as the title, to identify key terms for indexing your published paper. So what you include in your abstract and in your title are crucial for helping other researchers find your paper or article.
If you are writing an abstract for a course paper, your professor may give you specific guidelines for what to include and how to organize your abstract. Similarly, academic journals often have specific requirements for abstracts. So in addition to following the advice on this page, you should be sure to look for and follow any guidelines from the course or journal you’re writing for.
The Contents of an Abstract
Abstracts contain most of the following kinds of information in brief form. The body of your paper will, of course, develop and explain these ideas much more fully. As you will see in the samples below, the proportion of your abstract that you devote to each kind of information—and the sequence of that information—will vary, depending on the nature and genre of the paper that you are summarizing in your abstract. And in some cases, some of this information is implied, rather than stated explicitly. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is widely used in the social sciences, gives specific guidelines for what to include in the abstract for different kinds of papers—for empirical studies, literature reviews or meta-analyses, theoretical papers, methodological papers, and case studies.
Here are the typical kinds of information found in most abstracts:
- the context or background information for your research; the general topic under study; the specific topic of your research
- the central questions or statement of the problem your research addresses
- what’s already known about this question, what previous research has done or shown
- the main reason(s) , the exigency, the rationale , the goals for your research—Why is it important to address these questions? Are you, for example, examining a new topic? Why is that topic worth examining? Are you filling a gap in previous research? Applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data? Resolving a dispute within the literature in your field? . . .
- your research and/or analytical methods
- your main findings , results , or arguments
- the significance or implications of your findings or arguments.
Your abstract should be intelligible on its own, without a reader’s having to read your entire paper. And in an abstract, you usually do not cite references—most of your abstract will describe what you have studied in your research and what you have found and what you argue in your paper. In the body of your paper, you will cite the specific literature that informs your research.
When to Write Your Abstract
Although you might be tempted to write your abstract first because it will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s a good idea to wait to write your abstract until after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
What follows are some sample abstracts in published papers or articles, all written by faculty at UW-Madison who come from a variety of disciplines. We have annotated these samples to help you see the work that these authors are doing within their abstracts.
Choosing Verb Tenses within Your Abstract
The social science sample (Sample 1) below uses the present tense to describe general facts and interpretations that have been and are currently true, including the prevailing explanation for the social phenomenon under study. That abstract also uses the present tense to describe the methods, the findings, the arguments, and the implications of the findings from their new research study. The authors use the past tense to describe previous research.
The humanities sample (Sample 2) below uses the past tense to describe completed events in the past (the texts created in the pulp fiction industry in the 1970s and 80s) and uses the present tense to describe what is happening in those texts, to explain the significance or meaning of those texts, and to describe the arguments presented in the article.
The science samples (Samples 3 and 4) below use the past tense to describe what previous research studies have done and the research the authors have conducted, the methods they have followed, and what they have found. In their rationale or justification for their research (what remains to be done), they use the present tense. They also use the present tense to introduce their study (in Sample 3, “Here we report . . .”) and to explain the significance of their study (In Sample 3, This reprogramming . . . “provides a scalable cell source for. . .”).
Sample Abstract 1
From the social sciences.
Reporting new findings about the reasons for increasing economic homogamy among spouses
Gonalons-Pons, Pilar, and Christine R. Schwartz. “Trends in Economic Homogamy: Changes in Assortative Mating or the Division of Labor in Marriage?” Demography , vol. 54, no. 3, 2017, pp. 985-1005.
![abstract example in essay “The growing economic resemblance of spouses has contributed to rising inequality by increasing the number of couples in which there are two high- or two low-earning partners. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the topic under study (the “economic resemblance of spouses”). This sentence also implies the question underlying this research study: what are the various causes—and the interrelationships among them—for this trend?] The dominant explanation for this trend is increased assortative mating. Previous research has primarily relied on cross-sectional data and thus has been unable to disentangle changes in assortative mating from changes in the division of spouses’ paid labor—a potentially key mechanism given the dramatic rise in wives’ labor supply. [Annotation for the previous two sentences: These next two sentences explain what previous research has demonstrated. By pointing out the limitations in the methods that were used in previous studies, they also provide a rationale for new research.] We use data from the Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) to decompose the increase in the correlation between spouses’ earnings and its contribution to inequality between 1970 and 2013 into parts due to (a) changes in assortative mating, and (b) changes in the division of paid labor. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The data, research and analytical methods used in this new study.] Contrary to what has often been assumed, the rise of economic homogamy and its contribution to inequality is largely attributable to changes in the division of paid labor rather than changes in sorting on earnings or earnings potential. Our findings indicate that the rise of economic homogamy cannot be explained by hypotheses centered on meeting and matching opportunities, and they show where in this process inequality is generated and where it is not.” (p. 985) [Annotation for the previous two sentences: The major findings from and implications and significance of this study.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-1.png)
Sample Abstract 2
From the humanities.
Analyzing underground pulp fiction publications in Tanzania, this article makes an argument about the cultural significance of those publications
Emily Callaci. “Street Textuality: Socialism, Masculinity, and Urban Belonging in Tanzania’s Pulp Fiction Publishing Industry, 1975-1985.” Comparative Studies in Society and History , vol. 59, no. 1, 2017, pp. 183-210.
![abstract example in essay “From the mid-1970s through the mid-1980s, a network of young urban migrant men created an underground pulp fiction publishing industry in the city of Dar es Salaam. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence introduces the context for this research and announces the topic under study.] As texts that were produced in the underground economy of a city whose trajectory was increasingly charted outside of formalized planning and investment, these novellas reveal more than their narrative content alone. These texts were active components in the urban social worlds of the young men who produced them. They reveal a mode of urbanism otherwise obscured by narratives of decolonization, in which urban belonging was constituted less by national citizenship than by the construction of social networks, economic connections, and the crafting of reputations. This article argues that pulp fiction novellas of socialist era Dar es Salaam are artifacts of emergent forms of male sociability and mobility. In printing fictional stories about urban life on pilfered paper and ink, and distributing their texts through informal channels, these writers not only described urban communities, reputations, and networks, but also actually created them.” (p. 210) [Annotation for the previous sentences: The remaining sentences in this abstract interweave other essential information for an abstract for this article. The implied research questions: What do these texts mean? What is their historical and cultural significance, produced at this time, in this location, by these authors? The argument and the significance of this analysis in microcosm: these texts “reveal a mode or urbanism otherwise obscured . . .”; and “This article argues that pulp fiction novellas. . . .” This section also implies what previous historical research has obscured. And through the details in its argumentative claims, this section of the abstract implies the kinds of methods the author has used to interpret the novellas and the concepts under study (e.g., male sociability and mobility, urban communities, reputations, network. . . ).]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-2.png)
Sample Abstract/Summary 3
From the sciences.
Reporting a new method for reprogramming adult mouse fibroblasts into induced cardiac progenitor cells
Lalit, Pratik A., Max R. Salick, Daryl O. Nelson, Jayne M. Squirrell, Christina M. Shafer, Neel G. Patel, Imaan Saeed, Eric G. Schmuck, Yogananda S. Markandeya, Rachel Wong, Martin R. Lea, Kevin W. Eliceiri, Timothy A. Hacker, Wendy C. Crone, Michael Kyba, Daniel J. Garry, Ron Stewart, James A. Thomson, Karen M. Downs, Gary E. Lyons, and Timothy J. Kamp. “Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Proliferative Induced Cardiac Progenitor Cells by Defined Factors.” Cell Stem Cell , vol. 18, 2016, pp. 354-367.
![abstract example in essay “Several studies have reported reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced cardiomyocytes; however, reprogramming into proliferative induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPCs) remains to be accomplished. [Annotation for the previous sentence: The first sentence announces the topic under study, summarizes what’s already known or been accomplished in previous research, and signals the rationale and goals are for the new research and the problem that the new research solves: How can researchers reprogram fibroblasts into iCPCs?] Here we report that a combination of 11 or 5 cardiac factors along with canonical Wnt and JAK/STAT signaling reprogrammed adult mouse cardiac, lung, and tail tip fibroblasts into iCPCs. The iCPCs were cardiac mesoderm-restricted progenitors that could be expanded extensively while maintaining multipo-tency to differentiate into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells in vitro. Moreover, iCPCs injected into the cardiac crescent of mouse embryos differentiated into cardiomyocytes. iCPCs transplanted into the post-myocardial infarction mouse heart improved survival and differentiated into cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. [Annotation for the previous four sentences: The methods the researchers developed to achieve their goal and a description of the results.] Lineage reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs provides a scalable cell source for drug discovery, disease modeling, and cardiac regenerative therapy.” (p. 354) [Annotation for the previous sentence: The significance or implications—for drug discovery, disease modeling, and therapy—of this reprogramming of adult somatic cells into iCPCs.]](https://writing.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/535/2019/08/Abstract-3.png)
Sample Abstract 4, a Structured Abstract
Reporting results about the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis, from a rigorously controlled study
Note: This journal requires authors to organize their abstract into four specific sections, with strict word limits. Because the headings for this structured abstract are self-explanatory, we have chosen not to add annotations to this sample abstract.
Wald, Ellen R., David Nash, and Jens Eickhoff. “Effectiveness of Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Potassium in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Sinusitis in Children.” Pediatrics , vol. 124, no. 1, 2009, pp. 9-15.
“OBJECTIVE: The role of antibiotic therapy in managing acute bacterial sinusitis (ABS) in children is controversial. The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate in the treatment of children diagnosed with ABS.
METHODS : This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Children 1 to 10 years of age with a clinical presentation compatible with ABS were eligible for participation. Patients were stratified according to age (<6 or ≥6 years) and clinical severity and randomly assigned to receive either amoxicillin (90 mg/kg) with potassium clavulanate (6.4 mg/kg) or placebo. A symptom survey was performed on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30. Patients were examined on day 14. Children’s conditions were rated as cured, improved, or failed according to scoring rules.
RESULTS: Two thousand one hundred thirty-five children with respiratory complaints were screened for enrollment; 139 (6.5%) had ABS. Fifty-eight patients were enrolled, and 56 were randomly assigned. The mean age was 6630 months. Fifty (89%) patients presented with persistent symptoms, and 6 (11%) presented with nonpersistent symptoms. In 24 (43%) children, the illness was classified as mild, whereas in the remaining 32 (57%) children it was severe. Of the 28 children who received the antibiotic, 14 (50%) were cured, 4 (14%) were improved, 4(14%) experienced treatment failure, and 6 (21%) withdrew. Of the 28children who received placebo, 4 (14%) were cured, 5 (18%) improved, and 19 (68%) experienced treatment failure. Children receiving the antibiotic were more likely to be cured (50% vs 14%) and less likely to have treatment failure (14% vs 68%) than children receiving the placebo.
CONCLUSIONS : ABS is a common complication of viral upper respiratory infections. Amoxicillin/potassium clavulanate results in significantly more cures and fewer failures than placebo, according to parental report of time to resolution.” (9)
Some Excellent Advice about Writing Abstracts for Basic Science Research Papers, by Professor Adriano Aguzzi from the Institute of Neuropathology at the University of Zurich:

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write an Abstract (With Examples)

Sarah Oakley

Table of Contents
What is an abstract in a paper, how long should an abstract be, 5 steps for writing an abstract, examples of an abstract, how prowritingaid can help you write an abstract.
If you are writing a scientific research paper or a book proposal, you need to know how to write an abstract, which summarizes the contents of the paper or book.
When researchers are looking for peer-reviewed papers to use in their studies, the first place they will check is the abstract to see if it applies to their work. Therefore, your abstract is one of the most important parts of your entire paper.
In this article, we’ll explain what an abstract is, what it should include, and how to write one.
An abstract is a concise summary of the details within a report. Some abstracts give more details than others, but the main things you’ll be talking about are why you conducted the research, what you did, and what the results show.
When a reader is deciding whether to read your paper completely, they will first look at the abstract. You need to be concise in your abstract and give the reader the most important information so they can determine if they want to read the whole paper.
Remember that an abstract is the last thing you’ll want to write for the research paper because it directly references parts of the report. If you haven’t written the report, you won’t know what to include in your abstract.
If you are writing a paper for a journal or an assignment, the publication or academic institution might have specific formatting rules for how long your abstract should be. However, if they don’t, most abstracts are between 150 and 300 words long.
A short word count means your writing has to be precise and without filler words or phrases. Once you’ve written a first draft, you can always use an editing tool, such as ProWritingAid, to identify areas where you can reduce words and increase readability.
If your abstract is over the word limit, and you’ve edited it but still can’t figure out how to reduce it further, your abstract might include some things that aren’t needed. Here’s a list of three elements you can remove from your abstract:
Discussion : You don’t need to go into detail about the findings of your research because your reader will find your discussion within the paper.
Definition of terms : Your readers are interested the field you are writing about, so they are likely to understand the terms you are using. If not, they can always look them up. Your readers do not expect you to give a definition of terms in your abstract.
References and citations : You can mention there have been studies that support or have inspired your research, but you do not need to give details as the reader will find them in your bibliography.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
If you’ve never written an abstract before, and you’re wondering how to write an abstract, we’ve got some steps for you to follow. It’s best to start with planning your abstract, so we’ve outlined the details you need to include in your plan before you write.
Remember to consider your audience when you’re planning and writing your abstract. They are likely to skim read your abstract, so you want to be sure your abstract delivers all the information they’re expecting to see at key points.
1. What Should an Abstract Include?
Abstracts have a lot of information to cover in a short number of words, so it’s important to know what to include. There are three elements that need to be present in your abstract:
Your context is the background for where your research sits within your field of study. You should briefly mention any previous scientific papers or experiments that have led to your hypothesis and how research develops in those studies.
Your hypothesis is your prediction of what your study will show. As you are writing your abstract after you have conducted your research, you should still include your hypothesis in your abstract because it shows the motivation for your paper.
Throughout your abstract, you also need to include keywords and phrases that will help researchers to find your article in the databases they’re searching. Make sure the keywords are specific to your field of study and the subject you’re reporting on, otherwise your article might not reach the relevant audience.
2. Can You Use First Person in an Abstract?
You might think that first person is too informal for a research paper, but it’s not. Historically, writers of academic reports avoided writing in first person to uphold the formality standards of the time. However, first person is more accepted in research papers in modern times.
If you’re still unsure whether to write in first person for your abstract, refer to any style guide rules imposed by the journal you’re writing for or your teachers if you are writing an assignment.
3. Abstract Structure
Some scientific journals have strict rules on how to structure an abstract, so it’s best to check those first. If you don’t have any style rules to follow, try using the IMRaD structure, which stands for Introduction, Methodology, Results, and Discussion.

Following the IMRaD structure, start with an introduction. The amount of background information you should include depends on your specific research area. Adding a broad overview gives you less room to include other details. Remember to include your hypothesis in this section.
The next part of your abstract should cover your methodology. Try to include the following details if they apply to your study:
What type of research was conducted?
How were the test subjects sampled?
What were the sample sizes?
What was done to each group?
How long was the experiment?
How was data recorded and interpreted?
Following the methodology, include a sentence or two about the results, which is where your reader will determine if your research supports or contradicts their own investigations.
The results are also where most people will want to find out what your outcomes were, even if they are just mildly interested in your research area. You should be specific about all the details but as concise as possible.
The last few sentences are your conclusion. It needs to explain how your findings affect the context and whether your hypothesis was correct. Include the primary take-home message, additional findings of importance, and perspective. Also explain whether there is scope for further research into the subject of your report.
Your conclusion should be honest and give the reader the ultimate message that your research shows. Readers trust the conclusion, so make sure you’re not fabricating the results of your research. Some readers won’t read your entire paper, but this section will tell them if it’s worth them referencing it in their own study.
4. How to Start an Abstract
The first line of your abstract should give your reader the context of your report by providing background information. You can use this sentence to imply the motivation for your research.
You don’t need to use a hook phrase or device in your first sentence to grab the reader’s attention. Your reader will look to establish relevance quickly, so readability and clarity are more important than trying to persuade the reader to read on.
5. How to Format an Abstract
Most abstracts use the same formatting rules, which help the reader identify the abstract so they know where to look for it.
Here’s a list of formatting guidelines for writing an abstract:
Stick to one paragraph
Use block formatting with no indentation at the beginning
Put your abstract straight after the title and acknowledgements pages
Use present or past tense, not future tense
There are two primary types of abstract you could write for your paper—descriptive and informative.
An informative abstract is the most common, and they follow the structure mentioned previously. They are longer than descriptive abstracts because they cover more details.
Descriptive abstracts differ from informative abstracts, as they don’t include as much discussion or detail. The word count for a descriptive abstract is between 50 and 150 words.
Here is an example of an informative abstract:
A growing trend exists for authors to employ a more informal writing style that uses “we” in academic writing to acknowledge one’s stance and engagement. However, few studies have compared the ways in which the first-person pronoun “we” is used in the abstracts and conclusions of empirical papers. To address this lacuna in the literature, this study conducted a systematic corpus analysis of the use of “we” in the abstracts and conclusions of 400 articles collected from eight leading electrical and electronic (EE) engineering journals. The abstracts and conclusions were extracted to form two subcorpora, and an integrated framework was applied to analyze and seek to explain how we-clusters and we-collocations were employed. Results revealed whether authors’ use of first-person pronouns partially depends on a journal policy. The trend of using “we” showed that a yearly increase occurred in the frequency of “we” in EE journal papers, as well as the existence of three “we-use” types in the article conclusions and abstracts: exclusive, inclusive, and ambiguous. Other possible “we-use” alternatives such as “I” and other personal pronouns were used very rarely—if at all—in either section. These findings also suggest that the present tense was used more in article abstracts, but the present perfect tense was the most preferred tense in article conclusions. Both research and pedagogical implications are proffered and critically discussed.
Wang, S., Tseng, W.-T., & Johanson, R. (2021). To We or Not to We: Corpus-Based Research on First-Person Pronoun Use in Abstracts and Conclusions. SAGE Open, 11(2).
Here is an example of a descriptive abstract:
From the 1850s to the present, considerable criminological attention has focused on the development of theoretically-significant systems for classifying crime. This article reviews and attempts to evaluate a number of these efforts, and we conclude that further work on this basic task is needed. The latter part of the article explicates a conceptual foundation for a crime pattern classification system, and offers a preliminary taxonomy of crime.
Farr, K. A., & Gibbons, D. C. (1990). Observations on the Development of Crime Categories. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 34(3), 223–237.
If you want to ensure your abstract is grammatically correct and easy to read, you can use ProWritingAid to edit it. The software integrates with Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and most web browsers, so you can make the most of it wherever you’re writing your paper.
Before you edit with ProWritingAid, make sure the suggestions you are seeing are relevant for your document by changing the document type to “Abstract” within the Academic writing style section.
You can use the Readability report to check your abstract for places to improve the clarity of your writing. Some suggestions might show you where to remove words, which is great if you’re over your word count.
We hope the five steps and examples we’ve provided help you write a great abstract for your research paper.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Abstract Writing: A Step-by-Step Guide With Tips & Examples

Table of Contents

Introduction
Abstracts of research papers have always played an essential role in describing your research concisely and clearly to researchers and editors of journals, enticing them to continue reading. However, with the widespread availability of scientific databases, the need to write a convincing abstract is more crucial now than during the time of paper-bound manuscripts.
Abstracts serve to "sell" your research and can be compared with your "executive outline" of a resume or, rather, a formal summary of the critical aspects of your work. Also, it can be the "gist" of your study. Since most educational research is done online, it's a sign that you have a shorter time for impressing your readers, and have more competition from other abstracts that are available to be read.
The APCI (Academic Publishing and Conferences International) articulates 12 issues or points considered during the final approval process for conferences & journals and emphasises the importance of writing an abstract that checks all these boxes (12 points). Since it's the only opportunity you have to captivate your readers, you must invest time and effort in creating an abstract that accurately reflects the critical points of your research.
With that in mind, let’s head over to understand and discover the core concept and guidelines to create a substantial abstract. Also, learn how to organise the ideas or plots into an effective abstract that will be awe-inspiring to the readers you want to reach.
What is Abstract? Definition and Overview
The word "Abstract' is derived from Latin abstractus meaning "drawn off." This etymological meaning also applies to art movements as well as music, like abstract expressionism. In this context, it refers to the revealing of the artist's intention.
Based on this, you can determine the meaning of an abstract: A condensed research summary. It must be self-contained and independent of the body of the research. However, it should outline the subject, the strategies used to study the problem, and the methods implemented to attain the outcomes. The specific elements of the study differ based on the area of study; however, together, it must be a succinct summary of the entire research paper.
Abstracts are typically written at the end of the paper, even though it serves as a prologue. In general, the abstract must be in a position to:
- Describe the paper.
- Identify the problem or the issue at hand.
- Explain to the reader the research process, the results you came up with, and what conclusion you've reached using these results.
- Include keywords to guide your strategy and the content.
Furthermore, the abstract you submit should not reflect upon any of the following elements:
- Examine, analyse or defend the paper or your opinion.
- What you want to study, achieve or discover.
- Be redundant or irrelevant.
After reading an abstract, your audience should understand the reason - what the research was about in the first place, what the study has revealed and how it can be utilised or can be used to benefit others. You can understand the importance of abstract by knowing the fact that the abstract is the most frequently read portion of any research paper. In simpler terms, it should contain all the main points of the research paper.
What is the Purpose of an Abstract?
Abstracts are typically an essential requirement for research papers; however, it's not an obligation to preserve traditional reasons without any purpose. Abstracts allow readers to scan the text to determine whether it is relevant to their research or studies. The abstract allows other researchers to decide if your research paper can provide them with some additional information. A good abstract paves the interest of the audience to pore through your entire paper to find the content or context they're searching for.
Abstract writing is essential for indexing, as well. The Digital Repository of academic papers makes use of abstracts to index the entire content of academic research papers. Like meta descriptions in the regular Google outcomes, abstracts must include keywords that help researchers locate what they seek.
Types of Abstract
Informative and Descriptive are two kinds of abstracts often used in scientific writing.
A descriptive abstract gives readers an outline of the author's main points in their study. The reader can determine if they want to stick to the research work, based on their interest in the topic. An abstract that is descriptive is similar to the contents table of books, however, the format of an abstract depicts complete sentences encapsulated in one paragraph. It is unfortunate that the abstract can't be used as a substitute for reading a piece of writing because it's just an overview, which omits readers from getting an entire view. Also, it cannot be a way to fill in the gaps the reader may have after reading this kind of abstract since it does not contain crucial information needed to evaluate the article.
To conclude, a descriptive abstract is:
- A simple summary of the task, just summarises the work, but some researchers think it is much more of an outline
- Typically, the length is approximately 100 words. It is too short when compared to an informative abstract.
- A brief explanation but doesn't provide the reader with the complete information they need;
- An overview that omits conclusions and results
An informative abstract is a comprehensive outline of the research. There are times when people rely on the abstract as an information source. And the reason is why it is crucial to provide entire data of particular research. A well-written, informative abstract could be a good substitute for the remainder of the paper on its own.
A well-written abstract typically follows a particular style. The author begins by providing the identifying information, backed by citations and other identifiers of the papers. Then, the major elements are summarised to make the reader aware of the study. It is followed by the methodology and all-important findings from the study. The conclusion then presents study results and ends the abstract with a comprehensive summary.
In a nutshell, an informative abstract:
- Has a length that can vary, based on the subject, but is not longer than 300 words.
- Contains all the content-like methods and intentions
- Offers evidence and possible recommendations.
Informative Abstracts are more frequent than descriptive abstracts because of their extensive content and linkage to the topic specifically. You should select different types of abstracts to papers based on their length: informative abstracts for extended and more complex abstracts and descriptive ones for simpler and shorter research papers.
What are the Characteristics of a Good Abstract?
- A good abstract clearly defines the goals and purposes of the study.
- It should clearly describe the research methodology with a primary focus on data gathering, processing, and subsequent analysis.
- A good abstract should provide specific research findings.
- It presents the principal conclusions of the systematic study.
- It should be concise, clear, and relevant to the field of study.
- A well-designed abstract should be unifying and coherent.
- It is easy to grasp and free of technical jargon.
- It is written impartially and objectively.
What are the various sections of an ideal Abstract?
By now, you must have gained some concrete idea of the essential elements that your abstract needs to convey . Accordingly, the information is broken down into six key sections of the abstract, which include:
An Introduction or Background
Research methodology, objectives and goals, limitations.
Let's go over them in detail.
The introduction, also known as background, is the most concise part of your abstract. Ideally, it comprises a couple of sentences. Some researchers only write one sentence to introduce their abstract. The idea behind this is to guide readers through the key factors that led to your study.
It's understandable that this information might seem difficult to explain in a couple of sentences. For example, think about the following two questions like the background of your study:
- What is currently available about the subject with respect to the paper being discussed?
- What isn't understood about this issue? (This is the subject of your research)
While writing the abstract’s introduction, make sure that it is not lengthy. Because if it crosses the word limit, it may eat up the words meant to be used for providing other key information.
Research methodology is where you describe the theories and techniques you used in your research. It is recommended that you describe what you have done and the method you used to get your thorough investigation results. Certainly, it is the second-longest paragraph in the abstract.
In the research methodology section, it is essential to mention the kind of research you conducted; for instance, qualitative research or quantitative research (this will guide your research methodology too) . If you've conducted quantitative research, your abstract should contain information like the sample size, data collection method, sampling techniques, and duration of the study. Likewise, your abstract should reflect observational data, opinions, questionnaires (especially the non-numerical data) if you work on qualitative research.
The research objectives and goals speak about what you intend to accomplish with your research. The majority of research projects focus on the long-term effects of a project, and the goals focus on the immediate, short-term outcomes of the research. It is possible to summarise both in just multiple sentences.
In stating your objectives and goals, you give readers a picture of the scope of the study, its depth and the direction your research ultimately follows. Your readers can evaluate the results of your research against the goals and stated objectives to determine if you have achieved the goal of your research.
In the end, your readers are more attracted by the results you've obtained through your study. Therefore, you must take the time to explain each relevant result and explain how they impact your research. The results section exists as the longest in your abstract, and nothing should diminish its reach or quality.
One of the most important things you should adhere to is to spell out details and figures on the results of your research.
Instead of making a vague assertion such as, "We noticed that response rates varied greatly between respondents with high incomes and those with low incomes", Try these: "The response rate was higher for high-income respondents than those with lower incomes (59 30 percent vs. 30 percent in both cases; P<0.01)."
You're likely to encounter certain obstacles during your research. It could have been during data collection or even during conducting the sample . Whatever the issue, it's essential to inform your readers about them and their effects on the research.
Research limitations offer an opportunity to suggest further and deep research. If, for instance, you were forced to change for convenient sampling and snowball samples because of difficulties in reaching well-suited research participants, then you should mention this reason when you write your research abstract. In addition, a lack of prior studies on the subject could hinder your research.
Your conclusion should include the same number of sentences to wrap the abstract as the introduction. The majority of researchers offer an idea of the consequences of their research in this case.
Your conclusion should include three essential components:
- A significant take-home message.
- Corresponding important findings.
- The Interpretation.
Even though the conclusion of your abstract needs to be brief, it can have an enormous influence on the way that readers view your research. Therefore, make use of this section to reinforce the central message from your research. Be sure that your statements reflect the actual results and the methods you used to conduct your research.
Good Abstract Examples
Abstract example #1.
Children’s consumption behavior in response to food product placements in movies.
The abstract:
"Almost all research into the effects of brand placements on children has focused on the brand's attitudes or behavior intentions. Based on the significant differences between attitudes and behavioral intentions on one hand and actual behavior on the other hand, this study examines the impact of placements by brands on children's eating habits. Children aged 6-14 years old were shown an excerpt from the popular film Alvin and the Chipmunks and were shown places for the item Cheese Balls. Three different versions were developed with no placements, one with moderately frequent placements and the third with the highest frequency of placement. The results revealed that exposure to high-frequency places had a profound effect on snack consumption, however, there was no impact on consumer attitudes towards brands or products. The effects were not dependent on the age of the children. These findings are of major importance to researchers studying consumer behavior as well as nutrition experts as well as policy regulators."
Abstract Example #2
Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. The abstract:
"The research conducted in this study investigated the effects of Facebook use on women's moods and body image if the effects are different from an internet-based fashion journal and if the appearance comparison tendencies moderate one or more of these effects. Participants who were female ( N = 112) were randomly allocated to spend 10 minutes exploring their Facebook account or a magazine's website or an appearance neutral control website prior to completing state assessments of body dissatisfaction, mood, and differences in appearance (weight-related and facial hair, face, and skin). Participants also completed a test of the tendency to compare appearances. The participants who used Facebook were reported to be more depressed than those who stayed on the control site. In addition, women who have the tendency to compare appearances reported more facial, hair and skin-related issues following Facebook exposure than when they were exposed to the control site. Due to its popularity it is imperative to conduct more research to understand the effect that Facebook affects the way people view themselves."
Abstract Example #3
The Relationship Between Cell Phone Use and Academic Performance in a Sample of U.S. College Students
"The cellphone is always present on campuses of colleges and is often utilised in situations in which learning takes place. The study examined the connection between the use of cell phones and the actual grades point average (GPA) after adjusting for predictors that are known to be a factor. In the end 536 students in the undergraduate program from 82 self-reported majors of an enormous, public institution were studied. Hierarchical analysis ( R 2 = .449) showed that use of mobile phones is significantly ( p < .001) and negative (b equal to -.164) connected to the actual college GPA, after taking into account factors such as demographics, self-efficacy in self-regulated learning, self-efficacy to improve academic performance, and the actual high school GPA that were all important predictors ( p < .05). Therefore, after adjusting for other known predictors increasing cell phone usage was associated with lower academic performance. While more research is required to determine the mechanisms behind these results, they suggest the need to educate teachers and students to the possible academic risks that are associated with high-frequency mobile phone usage."
Quick tips on writing a good abstract
There exists a common dilemma among early age researchers whether to write the abstract at first or last? However, it's recommended to compose your abstract when you've completed the research since you'll have all the information to give to your readers. You can, however, write a draft at the beginning of your research and add in any gaps later.
If you find abstract writing a herculean task, here are the few tips to help you with it:
1. Always develop a framework to support your abstract
Before writing, ensure you create a clear outline for your abstract. Divide it into sections and draw the primary and supporting elements in each one. You can include keywords and a few sentences that convey the essence of your message.
2. Review Other Abstracts
Abstracts are among the most frequently used research documents, and thousands of them were written in the past. Therefore, prior to writing yours, take a look at some examples from other abstracts. There are plenty of examples of abstracts for dissertations in the dissertation and thesis databases.
3. Avoid Jargon To the Maximum
When you write your abstract, focus on simplicity over formality. You should write in simple language, and avoid excessive filler words or ambiguous sentences. Keep in mind that your abstract must be readable to those who aren't acquainted with your subject.
4. Focus on Your Research
It's a given fact that the abstract you write should be about your research and the findings you've made. It is not the right time to mention secondary and primary data sources unless it's absolutely required.
Conclusion: How to Structure an Interesting Abstract?
Abstracts are a short outline of your essay. However, it's among the most important, if not the most important. The process of writing an abstract is not straightforward. A few early-age researchers tend to begin by writing it, thinking they are doing it to "tease" the next step (the document itself). However, it is better to treat it as a spoiler.
The simple, concise style of the abstract lends itself to a well-written and well-investigated study. If your research paper doesn't provide definitive results, or the goal of your research is questioned, so will the abstract. Thus, only write your abstract after witnessing your findings and put your findings in the context of a larger scenario.
The process of writing an abstract can be daunting, but with these guidelines, you will succeed. The most efficient method of writing an excellent abstract is to centre the primary points of your abstract, including the research question and goals methods, as well as key results.
Interested in learning more about dedicated research solutions? Go to the SciSpace product page to find out how our suite of products can help you simplify your research workflows so you can focus on advancing science.

The best-in-class solution is equipped with features such as literature search and discovery, profile management, research writing and formatting, and so much more.
But before you go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write an Abstract

Expedite peer review, increase search-ability, and set the tone for your study
The abstract is your chance to let your readers know what they can expect from your article. Learn how to write a clear, and concise abstract that will keep your audience reading.
How your abstract impacts editorial evaluation and future readership
After the title , the abstract is the second-most-read part of your article. A good abstract can help to expedite peer review and, if your article is accepted for publication, it’s an important tool for readers to find and evaluate your work. Editors use your abstract when they first assess your article. Prospective reviewers see it when they decide whether to accept an invitation to review. Once published, the abstract gets indexed in PubMed and Google Scholar , as well as library systems and other popular databases. Like the title, your abstract influences keyword search results. Readers will use it to decide whether to read the rest of your article. Other researchers will use it to evaluate your work for inclusion in systematic reviews and meta-analysis. It should be a concise standalone piece that accurately represents your research.
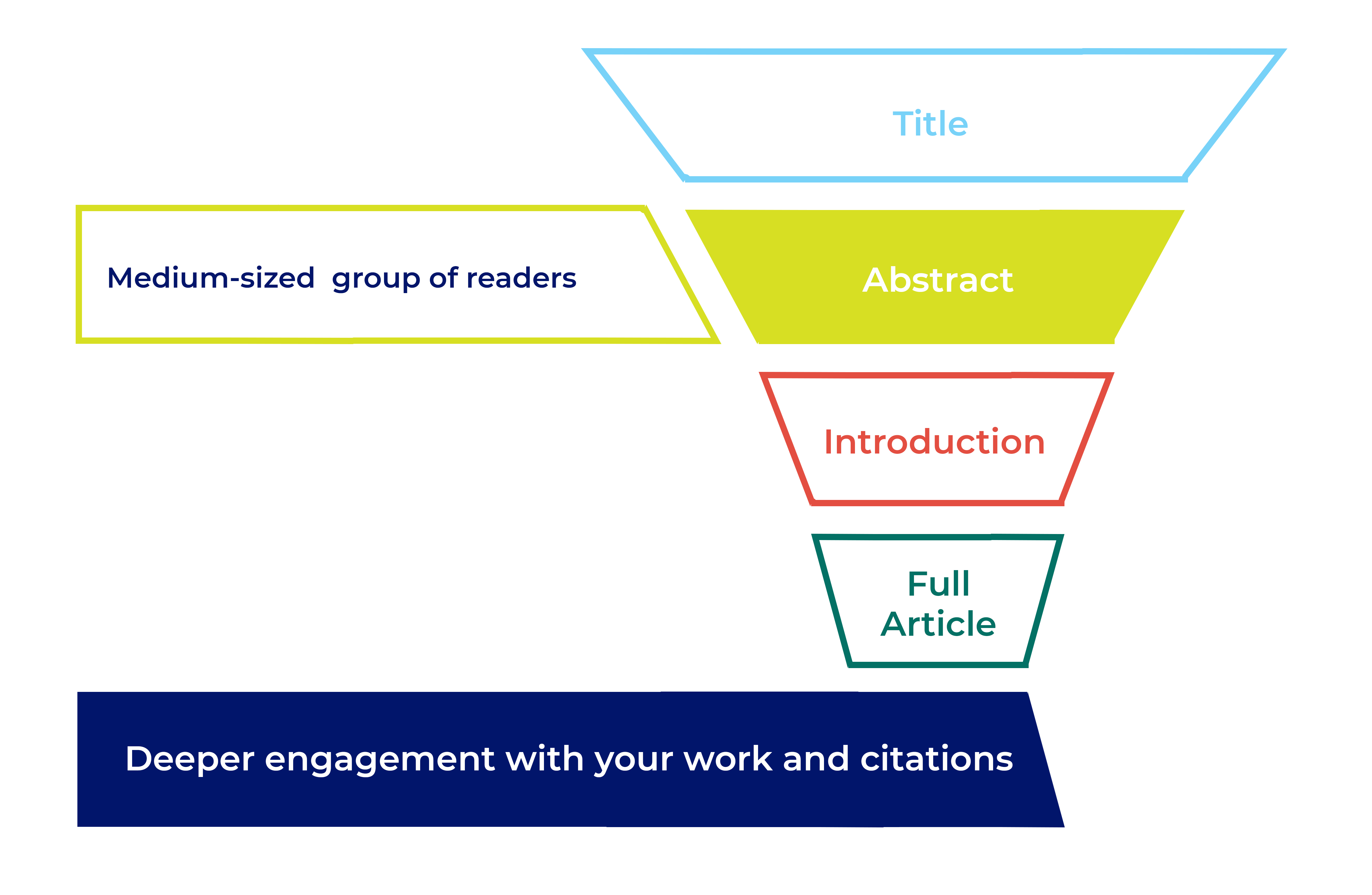
What to include in an abstract
The main challenge you’ll face when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND fitting in all the information you need. Depending on your subject area the journal may require a structured abstract following specific headings. A structured abstract helps your readers understand your study more easily. If your journal doesn’t require a structured abstract it’s still a good idea to follow a similar format, just present the abstract as one paragraph without headings.
Background or Introduction – What is currently known? Start with a brief, 2 or 3 sentence, introduction to the research area.
Objectives or Aims – What is the study and why did you do it? Clearly state the research question you’re trying to answer.
Methods – What did you do? Explain what you did and how you did it. Include important information about your methods, but avoid the low-level specifics. Some disciplines have specific requirements for abstract methods.
- CONSORT for randomized trials.
- STROBE for observational studies
- PRISMA for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Results – What did you find? Briefly give the key findings of your study. Include key numeric data (including confidence intervals or p values), where possible.
Conclusions – What did you conclude? Tell the reader why your findings matter, and what this could mean for the ‘bigger picture’ of this area of research.
Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your abstract is keeping it concise AND convering all the information you need to.

- Keep it concise and to the point. Most journals have a maximum word count, so check guidelines before you write the abstract to save time editing it later.
- Write for your audience. Are they specialists in your specific field? Are they cross-disciplinary? Are they non-specialists? If you’re writing for a general audience, or your research could be of interest to the public keep your language as straightforward as possible. If you’re writing in English, do remember that not all of your readers will necessarily be native English speakers.
- Focus on key results, conclusions and take home messages.
- Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary.
- Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings.
- Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar.
- Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors. These kind of errors can give potential reviewers the impression that your research isn’t sound, and can make it easier to find reviewers who accept the invitation to review your manuscript. Your abstract should be a taste of what is to come in the rest of your article.

Don’t
- Sensationalize your research.
- Speculate about where this research might lead in the future.
- Use abbreviations or acronyms (unless absolutely necessary or unless they’re widely known, eg. DNA).
- Repeat yourself unnecessarily, eg. “Methods: We used X technique. Results: Using X technique, we found…”
- Contradict anything in the rest of your manuscript.
- Include content that isn’t also covered in the main manuscript.
- Include citations or references.
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
How to Write an Abstract
An abstract of a work, usually of an essay, is a concise summary of its main points. It is meant to concentrate the argument of a work, presenting it as clearly as possible.
The abstract often appears after the title and before the main body of an essay. If you are writing an abstract as part of an assignment, you should check with your instructor about where to place it.
Here are a few guidelines to follow when composing an abstract:
- In general, avoid too much copying and pasting directly from your essay, especially from the first paragraph. An abstract is often presented directly before an essay, and it will often be the first thing readers consult after your title. You wouldn’t repeat your ideas verbatim in the body of your essay, so why would you do that in an abstract? Consider the abstract part of the work itself.
- Start off strong. An abstract should be a mini essay, so it should begin with a clear statement of your argument. This should be the first sentence or two.
- Abstracts vary in length. But a good rule is to aim for five to seven sentences. The bulk of the abstract will review the evidence for your claim and summarize your findings.
- Avoid complicated syntax. Long sentences and intricate phrasing have their place in essays, but the abstract should be concise. It is not the place for ambitious grammar.
- The last sentence or two should point to any conclusions reached and the direction future research might take. Like the first sentence, the last should be provocative and direct. Leave your readers wanting to read your essay.
In what follows, the authors have written an effective abstract that adheres to the basic principles above:
Literary critics have long imagined that T. S. Eliot’s The Sacred Wood (1920) shaped the canon and methods of countless twentieth-century classrooms. This essay turns instead to the classroom that made The Sacred Wood : the Modern English Literature extension school tutorial that Eliot taught to working-class adults between 1916 and 1919. Contextualizing Eliot’s tutorial within the extension school movement shows how the ethos and practices of the Workers’ Educational Association shaped his teaching. Over the course of three years, Eliot and his students reimagined canonical literature as writing by working poets for working people—a model of literary history that fully informed his canon reformation in The Sacred Wood . This example demonstrates how attention to teaching changes the history of English literary study. It further reveals how all kinds of institutions, not just elite universities, have shaped the discipline’s methods and canons. (Buurma and Heffernan)
This abstract uses the first two sentences to establish the essay’s place in its field of study and to suggest how it intervenes in existing scholarship. The syntax is direct and simple. The third sentence begins to outline how the authors will support their argument. They aim to demonstrate the relevance of Eliot’s teaching to his ideas about literature, and so they move next to discuss some of the details of that teaching. Finally, the abstract concludes by telling us about the consequences of this argument. The conclusion both points to new directions for research and tells us why we should read the essay.
Buurma, Rachel Sagner, and Laura Heffernan. Abstract of “The Classroom in the Canon: T. S. Eliot’s Modern English Literature Extension Course for Working People and The Sacred Wood. ” PMLA , vol. 133, no. 2, Mar. 2018, p. 463.
Estate Best 18 July 2021 AT 05:07 AM
Please how will I write an abstract for my own poem collections?
Your e-mail address will not be published
Marc Simoes 01 April 2022 AT 04:04 PM
I am teaching students how to format and write an abstract, but I find no precise guidelines in the MLA Handbook. Should the first word of the abstract body text begin with the word "Abstract" followed by a period or colon and then the abstract content? Should the word "Abstract" be underlined? Over the years, I was taught both of these ways by different instructors, but I haven't found any definitive instructions, and now my students are asking me the correct format. Please help! Thank you!
Joseph Wallace 12 April 2022 AT 01:04 PM
Although publishers like the MLA will use their own house style guidelines for abstracts in published material, there is no one correct way for students to format their abstracts. Instructors should decide what works best for their classes and assignments.
Lorraine Belo 17 April 2022 AT 10:04 PM
Can you write a brief abstract about your MLA writing
Subrata Biswas 13 July 2023 AT 10:07 AM
Generally, the abstract is written in Italics. Is there any rule as such?
Joseph Wallace 31 July 2023 AT 10:07 AM
Thanks for your question. There is no rule saying that abstracts need to be written in italics. Some publications use italics for abstracts and some do not.
Dhan 07 January 2024 AT 12:01 PM
Should I write key words at the end of the abstract of Phd dissertation?
Join the Conversation
We invite you to comment on this post and exchange ideas with other site visitors. Comments are moderated and subject to terms of service.
If you have a question for the MLA's editors, submit it to Ask the MLA!
How to Write an Abstract APA Format
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
An APA abstract is a brief, comprehensive summary of the contents of an article, research paper, dissertation, or report.
It is written in accordance with the guidelines of the American Psychological Association (APA), which is a widely used format in social and behavioral sciences.
An APA abstract summarizes, usually in one paragraph of between 150–250 words, the major aspects of a research paper or dissertation in a prescribed sequence that includes:
- The rationale: the overall purpose of the study, providing a clear context for the research undertaken.
- Information regarding the method and participants: including materials/instruments, design, procedure, and data analysis.
- Main findings or trends: effectively highlighting the key outcomes of the hypotheses.
- Interpretations and conclusion(s): solidify the implications of the research.
- Keywords related to the study: assist the paper’s discoverability in academic databases.
The abstract should stand alone, be “self-contained,” and make sense to the reader in isolation from the main article.
The purpose of the abstract is to give the reader a quick overview of the essential information before reading the entire article. The abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper.
Although the abstract will appear as the very first part of your paper, it’s good practice to write your abstract after you’ve drafted your full paper, so that you know what you’re summarizing.
Note : This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), released in October 2019.
Structure of the Abstract
[NOTE: DO NOT separate the components of the abstract – it should be written as a single paragraph. This section is separated to illustrate the abstract’s structure.]
1) The Rationale
One or two sentences describing the overall purpose of the study and the research problem(s) you investigated. You are basically justifying why this study was conducted.
- What is the importance of the research?
- Why would a reader be interested in the larger work?
- For example, are you filling a gap in previous research or applying new methods to take a fresh look at existing ideas or data?
- Women who are diagnosed with breast cancer can experience an array of psychosocial difficulties; however, social support, particularly from a spouse, has been shown to have a protective function during this time. This study examined the ways in which a woman’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue, and her spouse’s marital satisfaction predict the woman’s report of partner support in the context of breast cancer.
- The current nursing shortage, high hospital nurse job dissatisfaction, and reports of uneven quality of hospital care are not uniquely American phenomena.
- Students with special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) are more likely to exhibit behavioral difficulties than their typically developing peers. The aim of this study was to identify specific risk factors that influence variability in behavior difficulties among individuals with SEND.
2) The Method
Information regarding the participants (number, and population). One or two sentences outlining the method, explaining what was done and how. The method is described in the present tense.
- Pretest data from a larger intervention study and multilevel modeling were used to examine the effects of women’s daily mood, pain, and fatigue and average levels of mood, pain, and fatigue on women’s report of social support received from her partner, as well as how the effects of mood interacted with partners’ marital satisfaction.
- This paper presents reports from 43,000 nurses from more than 700 hospitals in the United States, Canada, England, Scotland, and Germany in 1998–1999.
- The study sample comprised 4,228 students with SEND, aged 5–15, drawn from 305 primary and secondary schools across England. Explanatory variables were measured at the individual and school levels at baseline, along with a teacher-reported measure of behavior difficulties (assessed at baseline and the 18-month follow-up).
3) The Results
One or two sentences indicating the main findings or trends found as a result of your analysis. The results are described in the present or past tense.
- Results show that on days in which women reported higher levels of negative or positive mood, as well as on days they reported more pain and fatigue, they reported receiving more support. Women who, on average, reported higher levels of positive mood tended to report receiving more support than those who, on average, reported lower positive mood. However, average levels of negative mood were not associated with support. Higher average levels of fatigue but not pain were associated with higher support. Finally, women whose husbands reported higher levels of marital satisfaction reported receiving more partner support, but husbands’ marital satisfaction did not moderate the effect of women’s mood on support.
- Nurses in countries with distinctly different healthcare systems report similar shortcomings in their work environments and the quality of hospital care. While the competence of and relation between nurses and physicians appear satisfactory, core problems in work design and workforce management threaten the provision of care.
- Hierarchical linear modeling of data revealed that differences between schools accounted for between 13% (secondary) and 15.4% (primary) of the total variance in the development of students’ behavior difficulties, with the remainder attributable to individual differences. Statistically significant risk markers for these problems across both phases of education were being male, eligibility for free school meals, being identified as a bully, and lower academic achievement. Additional risk markers specific to each phase of education at the individual and school levels are also acknowledged.
4) The Conclusion / Implications
A brief summary of your conclusions and implications of the results, described in the present tense. Explain the results and why the study is important to the reader.
- For example, what changes should be implemented as a result of the findings of the work?
- How does this work add to the body of knowledge on the topic?
Implications of these findings are discussed relative to assisting couples during this difficult time in their lives.
- Resolving these issues, which are amenable to managerial intervention, is essential to preserving patient safety and care of consistently high quality.
- Behavior difficulties are affected by risks across multiple ecological levels. Addressing any one of these potential influences is therefore likely to contribute to the reduction in the problems displayed.
The above examples of abstracts are from the following papers:
Aiken, L. H., Clarke, S. P., Sloane, D. M., Sochalski, J. A., Busse, R., Clarke, H., … & Shamian, J. (2001). Nurses’ reports on hospital care in five countries . Health affairs, 20(3) , 43-53.
Boeding, S. E., Pukay-Martin, N. D., Baucom, D. H., Porter, L. S., Kirby, J. S., Gremore, T. M., & Keefe, F. J. (2014). Couples and breast cancer: Women’s mood and partners’ marital satisfaction predicting support perception . Journal of Family Psychology, 28(5) , 675.
Oldfield, J., Humphrey, N., & Hebron, J. (2017). Risk factors in the development of behavior difficulties among students with special educational needs and disabilities: A multilevel analysis . British journal of educational psychology, 87(2) , 146-169.
5) Keywords
APA style suggests including a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. This is particularly common in academic articles and helps other researchers find your work in databases.
Keywords in an abstract should be selected to help other researchers find your work when searching an online database. These keywords should effectively represent the main topics of your study. Here are some tips for choosing keywords:
Core Concepts: Identify the most important ideas or concepts in your paper. These often include your main research topic, the methods you’ve used, or the theories you’re discussing.
Specificity: Your keywords should be specific to your research. For example, suppose your paper is about the effects of climate change on bird migration patterns in a specific region. In that case, your keywords might include “climate change,” “bird migration,” and the region’s name.
Consistency with Paper: Make sure your keywords are consistent with the terms you’ve used in your paper. For example, if you use the term “adolescent” rather than “teen” in your paper, choose “adolescent” as your keyword, not “teen.”
Jargon and Acronyms: Avoid using too much-specialized jargon or acronyms in your keywords, as these might not be understood or used by all researchers in your field.
Synonyms: Consider including synonyms of your keywords to capture as many relevant searches as possible. For example, if your paper discusses “post-traumatic stress disorder,” you might include “PTSD” as a keyword.
Remember, keywords are a tool for others to find your work, so think about what terms other researchers might use when searching for papers on your topic.

The Abstract SHOULD NOT contain:
Lengthy background or contextual information: The abstract should focus on your research and findings, not general topic background.
Undefined jargon, abbreviations, or acronyms: The abstract should be accessible to a wide audience, so avoid highly specialized terms without defining them.
Citations: Abstracts typically do not include citations, as they summarize original research.
Incomplete sentences or bulleted lists: The abstract should be a single, coherent paragraph written in complete sentences.
New information not covered in the paper: The abstract should only summarize the paper’s content.
Subjective comments or value judgments: Stick to objective descriptions of your research.
Excessive details on methods or procedures: Keep descriptions of methods brief and focused on main steps.
Speculative or inconclusive statements: The abstract should state the research’s clear findings, not hypotheses or possible interpretations.
- Any illustration, figure, table, or references to them . All visual aids, data, or extensive details should be included in the main body of your paper, not in the abstract.
- Elliptical or incomplete sentences should be avoided in an abstract . The use of ellipses (…), which could indicate incomplete thoughts or omitted text, is not appropriate in an abstract.
APA Style for Abstracts
An APA abstract must be formatted as follows:
Include the running head aligned to the left at the top of the page (professional papers only) and page number. Note, student papers do not require a running head. On the first line, center the heading “Abstract” and bold (do not underlined or italicize). Do not indent the single abstract paragraph (which begins one line below the section title). Double-space the text. Use Times New Roman font in 12 pt. Set one-inch (or 2.54 cm) margins. If you include a “keywords” section at the end of the abstract, indent the first line and italicize the word “Keywords” while leaving the keywords themselves without any formatting.
Example APA Abstract Page
Download this example as a PDF

Further Information
- APA 7th Edition Abstract and Keywords Guide
- Example APA Abstract
- How to Write a Good Abstract for a Scientific Paper or Conference Presentation
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Writing an APA paper
How long should an APA abstract be?
An APA abstract should typically be between 150 to 250 words long. However, the exact length may vary depending on specific publication or assignment guidelines. It is crucial that it succinctly summarizes the essential elements of the work, including purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions.
Where does the abstract go in an APA paper?
In an APA formatted paper, the abstract is placed on its own page, directly after the title page and before the main body of the paper. It’s typically the second page of the document. It starts with the word “Abstract” (centered and not in bold) at the top of the page, followed by the text of the abstract itself.
What are the 4 C’s of abstract writing?
The 4 C’s of abstract writing are an approach to help you create a well-structured and informative abstract. They are:
Conciseness: An abstract should briefly summarize the key points of your study. Stick to the word limit (typically between 150-250 words for an APA abstract) and avoid unnecessary details.
Clarity: Your abstract should be easy to understand. Avoid jargon and complex sentences. Clearly explain the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of your study.
Completeness: Even though it’s brief, the abstract should provide a complete overview of your study, including the purpose, methods, key findings, and your interpretation of the results.
Cohesion: The abstract should flow logically from one point to the next, maintaining a coherent narrative about your study. It’s not just a list of disjointed elements; it’s a brief story of your research from start to finish.
What is the abstract of a psychology paper?
An abstract in a psychology paper serves as a snapshot of the paper, allowing readers to quickly understand the purpose, methodology, results, and implications of the research without reading the entire paper. It is generally between 150-250 words long.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an APA Abstract
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
- Writing Your Abstract
- How to Use Keywords
An APA abstract is a concise but comprehensive summary of a scientific paper. It is typically a paragraph long, or about 150 to 250 words. The goal of the abstract is to provide the reader with a brief and accurate idea of what a paper is about.
The APA abstract should appear on a separate page immediately after the title page and before the main content of your paper. While professional papers that appear in scientific journals and other publications require an APA abstract, they may not be required for student papers. However, you should always check with your instructor for specific requirements.
What Is APA Format?
APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association. It is used in writing for psychology and other social sciences. These style guidelines specify different aspects of a document's presentation and layout, including how pages are structured, how references are organized, and how sources are cited.
This article explains how to create an abstract in APA format for your psychology papers or other types of scientific writing. It covers the basic rules you should follow as well as specific guidelines for writing abstracts for experimental reports, literature reviews, and other articles.
What Is an Abstract in APA Format?
In addition to providing guidance for the general style and organization of a paper, APA format also stipulates using an abstract designed to briefly summarize the key details in a paper.
While it is sometimes overlooked or only an afterthought, an abstract is an integral part of any academic or professional paper. The abstract is a critical component of an APA-formatted paper. This brief overview summarizes what your paper contains. It should succinctly and accurately represent what your paper is about and what the reader can expect to find.
Following a few simple guidelines, you can create an abstract following the format. Done well, an abstract generates interest in your work and helps readers learn if the paper will interest them.
APA Format Abstract Basics
The abstract is the second page of a lab report or APA-format paper and should immediately follow the title page . Think of an abstract as a highly condensed summary of your entire paper.
The purpose of your abstract is to provide a brief yet thorough overview of your paper. It should function much like your title page—it should allow the person reading it to quickly determine what your paper is all about. Your abstract is the first thing that most people will read, and it is usually what informs their decision to read the rest of your paper.
The abstract is the single most important paragraph in your entire paper, according to the APA Publication Manual. A good abstract lets the reader know that your paper is worth reading.
According to the official guidelines of the American Psychological Association, an abstract should be brief but packed with information. Each sentence must be written with maximum impact in mind. To keep your abstract short, focus on including just four or five of the essential points, concepts, or findings.
An abstract must also be objective and accurate. The abstract's purpose is to report rather than provide commentary. It should accurately reflect what your paper is about. Only include information that is also included in the body of your paper.
Key Elements of an APA Abstract
Your abstract page should include:
- A running head , which is a shortened version of your title that appears in all caps at the top left of each page of your paper
- A section label , which should be the word "Abstract" centered and bolded at the top of the page
- A page number , which should be the second page of your paper (the title page should be page 1)
- A double-spaced paragraph of about 150 to 250 words
- An indented list of keywords related to your paper's content. Include the label "Keywords:" in italics and list three to five keywords that are separated by commas
How to Write an Abstract in APA Format
Before you write your abstract, you first need to write your paper in its entirety. In order to write a good abstract, you need to have a finished draft of your paper so you can summarize it accurately.
While the abstract will be at the beginning of your paper, it should be the last section you write.
Once you have completed the final draft of your psychology paper , use it as a guide for writing your abstract.
- Begin your abstract on a new page . Place your running head and page number 2 in the top right-hand corner. Center the word "Abstract" at the top of the page.
- Know your target word count . An abstract should be between 150 and 250 words. Exact word counts vary from journal to journal . If you are writing your paper for a psychology course, your professor may have specific word requirements, so be sure to ask. The abstract should be written as only one paragraph with no indentation.
- Structure the abstract in the same order as your paper . Begin with a brief summary of the introduction , and then continue on with a summary of the method , results , and discussion sections of your paper.
- Look at other abstracts in professional journals for examples of how to summarize your paper . Notice the main points that the authors chose to mention in the abstract. Use these examples as a guide when choosing the main ideas in your own paper.
- Write a rough draft of your abstract . Use the format required for your type of paper (see next sections). While you should aim for brevity, be careful not to make your summary too short. Try to write one to two sentences summarizing each section of your paper. Once you have a rough draft, you can edit for length and clarity.
- Ask a friend to read over the abstract . Sometimes, having someone look at your abstract with fresh eyes can provide perspective and help you spot possible typos and other errors.
The abstract is vital to your paper, so it should not be overlooked or treated as an afterthought. Spend time writing this section carefully to ensure maximum readability and clarity.
It is important to remember that while the abstract is the last thing you write, it is often the most read part of your paper.
Experimental Report Abstracts
The format of your abstract also depends on the type of paper you are writing. For example, an abstract summarizing an experimental paper will differ from that of a meta-analysis or case study . For an experimental report, your abstract should:
- Identify the problem . In many cases, you should begin by stating the question you sought to investigate and your hypothesis .
- Describe the participants in the study . State how many participants took part and how they were selected. For example: "In this study, 215 undergraduate student participants were randomly assigned to [the experimental condition] or [the control condition]."
- Describe the study method . For example, identify whether you used a within-subjects, between-subjects, or mixed design.
- Give the basic findings . This is essentially a brief preview of the results of your paper.
- Provide any conclusions or implications of the study . What might your results indicate, and what directions does it point to for future research?
Literature Review Abstracts
If your paper is a meta-analysis or literature review, your abstract should:
- Describe the problem of interest . In other words, what is it that you set out to investigate in your analysis or review?
- Explain the criteria used to select the studies included in the paper . There may be many different studies devoted to your topic. Your analysis or review probably only looks at a portion of these studies. For what reason did you select these specific studies to include in your research?
- Identify the participants in the studies . Inform the reader about who the participants were in the studies. Were they college students? Older adults? How were they selected and assigned?
- Provide the main results . Again, this is essentially a quick peek at what readers will find when they read your results section. Don't try to include everything. Just provide a very brief summary of your main findings.
- Describe any conclusions or implications . What might these results mean and what do they reveal about the body of research that exists on this particular topic?
Lab Reports and Articles
Psychology papers such as lab reports and APA format articles also often require an abstract. In these cases as well, the abstract should include all of the major elements of your paper, including an introduction, hypothesis, methods, results, and discussion.
Remember, although the abstract should be placed at the beginning of your paper (right after the title page), you will write the abstract last after you have completed a final draft of your paper.
To ensure that all of your APA formatting is correct, consider consulting a copy of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association .
Keywords in an APA Abstract
After the paragraph containing the main elements of your abstract, you can also include keywords related to your paper. Such keywords are used when indexing your paper in databases and can help researchers and students locate your paper when searching for information about those topics.
Because keywords help people find your paper, it is essential to choose the right ones. The APA suggests including between three and five keywords.
You can identify keywords by thinking about what your paper is about. For example, if your paper focuses on how social media use is related to depression in teenagers, you might include the keywords: social media, mood, depression, adolescents, social networking sites
A Word From Verywell
The abstract may be very brief, but it is so important that the official APA style manual identifies it as the most important paragraph in your entire paper. Careful attention to detail can ensure that your abstract does a good job representing the contents of your paper. If possible, take your paper to your school's writing lab for assistance.
Nagda S. How to write a scientific abstract. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013;13(3):382–383. doi:10.1007/s13191-013-0299-x
Kumar A. Writing an abstract: Revealing the essence with eloquence . J Indian Soc Periodontol . 2022;26(1):1-2. doi:10.4103/jisp.jisp_634_21
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards: Reporting Standards for Studies With an Experimental Manipulation .
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards: Quantitative Meta-Analysis Article Reporting Standards .
Tullu MS. Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key . Saudi J Anaesth . 2019;13(Suppl 1):S12-S17. doi:10.4103/sja.SJA_685_18
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association; 2019.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Join 397 other subscribers.
Email Address
Writing an abstract - a six point checklist (with samples)
Posted in: abstract , dissertations

The abstract is a vital part of any research paper. It is the shop front for your work, and the first stop for your reader. It should provide a clear and succinct summary of your study, and encourage your readers to read more. An effective abstract, therefore should answer the following questions:
- Why did you do this study or project?
- What did you do and how?
- What did you find?
- What do your findings mean?
So here's our run down of the key elements of a well-written abstract.
- Size - A succinct and well written abstract should be between approximately 100- 250 words.
- Background - An effective abstract usually includes some scene-setting information which might include what is already known about the subject, related to the paper in question (a few short sentences).
- Purpose - The abstract should also set out the purpose of your research, in other words, what is not known about the subject and hence what the study intended to examine (or what the paper seeks to present).
- Methods - The methods section should contain enough information to enable the reader to understand what was done, and how. It should include brief details of the research design, sample size, duration of study, and so on.
- Results - The results section is the most important part of the abstract. This is because readers who skim an abstract do so to learn about the findings of the study. The results section should therefore contain as much detail about the findings as the journal word count permits.
- Conclusion - This section should contain the most important take-home message of the study, expressed in a few precisely worded sentences. Usually, the finding highlighted here relates to the primary outcomes of the study. However, other important or unexpected findings should also be mentioned. It is also customary, but not essential, to express an opinion about the theoretical or practical implications of the findings, or the importance of their findings for the field. Thus, the conclusions may contain three elements:
- The primary take-home message
- Any additional findings of importance
- Implications for future studies

Example Abstract 2: Engineering Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone.

Abstract from: Dalstra, M., Huiskes, R. and Van Erning, L., 1995. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. Journal of biomechanical engineering, 117(3), pp.272-278.
And finally... A word on abstract types and styles
Abstract types can differ according to subject discipline. You need to determine therefore which type of abstract you should include with your paper. Here are two of the most common types with examples.
Informative Abstract
The majority of abstracts are informative. While they still do not critique or evaluate a work, they do more than describe it. A good informative abstract acts as a surrogate for the work itself. That is, the researcher presents and explains all the main arguments and the important results and evidence in the paper. An informative abstract includes the information that can be found in a descriptive abstract [purpose, methods, scope] but it also includes the results and conclusions of the research and the recommendations of the author. The length varies according to discipline, but an informative abstract is usually no more than 300 words in length.
Descriptive Abstract A descriptive abstract indicates the type of information found in the work. It makes no judgements about the work, nor does it provide results or conclusions of the research. It does incorporate key words found in the text and may include the purpose, methods, and scope of the research. Essentially, the descriptive abstract only describes the work being summarised. Some researchers consider it an outline of the work, rather than a summary. Descriptive abstracts are usually very short, 100 words or less.
(Adapted from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136027/ )
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
Navigating the dissertation process: my tips for final years
Imagine for a moment... After months of hard work and research on a topic you're passionate about, the time has finally come to click the 'Submit' button on your dissertation. You've just completed your longest project to date as part...

8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.

My takeaways on how to write a scientific report
If you’re in your dissertation writing stage or your course includes writing a lot of scientific reports, but you don’t quite know where and how to start, the Skills Centre can help you get started. I recently attended their ‘How...

How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Abstract

How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
12 min read
Published on: Jan 19, 2024
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024
-10989.png)
People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How to Write an Abstract That Captivates Your Readers
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
Struggling to encapsulate your extensive research into a concise abstract? Writing an abstract for a research paper can be intimidating, but it doesn't have to be!
This blog is your guide to deciphering the abstract, understanding its purpose, and learning the art of writing your own.
We'll break down the abstract into clear, simple steps. We'll show you what it is, why it matters, and most importantly, how to write one that's clear, concise, and grabs your reader's attention.
So, leave your confusion behind, and let’s dive into it!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Abstract in a Paper?
An abstract in a research paper is a concise summary that provides an overview of the main points and key elements of the entire document. It is typically found at the beginning of academic papers, articles, or research reports.
The abstract serves as a standalone piece that briefly communicates the purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions of the study.
Usually ranging from 150 to 250 words, an abstract provides readers with a quick overview of the entire text.
Purpose of Abstracts
Abstracts serve several essential purposes in academic and professional settings, and therefore the importance of abstracts in research can not be overlooked. The primary objectives of abstracts include:
- Concise Summary : Distills key elements for quick understanding.
- Quick Information Retrieval : Saves time by offering a snapshot of document relevance.
- Decision-Making Tool : Helps researchers choose studies aligning with their objectives.
- Communication of Research : Disseminates findings to diverse audiences effectively.
- Database Indexing : Facilitates efficient literature review in academic databases.
- Conference and Journal Submissions : Essential requirement for evaluating contributions' merit and relevance.
When to Write an Abstract?
We need to include an abstract when:
- Submitting research papers for publication.
- Sending research proposals for conferences or academic events.
- Completing theses, dissertations, or comprehensive reports.
- Drafting articles for scholarly journals.
- Presenting academic projects or detailed proposals.
Types of Abstract
There are 2 basic types of abstract writing:

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
The Contents of an Abstract
An abstract typically includes the following components:
- Purpose/Objective : Clearly states the primary goal of the research or document.
- Methods/Approach : Briefly outline the methodology or approach used in the study.
- Results/Findings : Highlights the main outcomes or discoveries of the research.
- Conclusions/Implications : Summarize the key conclusions and their broader significance.
Another way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. It stands for:
- Introduction : Introduces the research topic and the problem under investigation.
- Methods : Describes the research methods and experimental design employed.
- Results : Presents the main findings or outcomes of the study.
- Discussion : Analyzes the results, discusses their implications, and draws conclusions.
Adhering to the IMRaD structure ensures a logical flow in your abstract, making it comprehensible and informative for readers.
How to Write an Abstract in 5 Steps?
Letâs take a look at the simple steps to write an abstract for a research paper:
Step 1: Craft an Engaging Introduction
Begin by clearly defining the purpose of your research. Identify the practical or theoretical problem your research addresses and state the research question you aim to answer.
Provide brief context on the social or academic relevance of your topic without delving into detailed background information. If using specialized terms, offer concise definitions.
Use verbs like "investigate," "analyze," or "evaluate" to describe your research objective. Write in the present or past simple tense, avoiding references to the future, as the research is already complete.
Step 2: Outline Your Methods Clearly
Outline the research methods and experimental design employed in your study. Refrain from evaluating the validity or challenges of your methodology. Provide a clear description of how you conducted your research, including any specific techniques, tools, or procedures used.
Be concise but offer enough detail for readers to understand the approach you took. Use the past simple tense to describe methods.
Step 3: Present Your Results with Precision
Highlight the main findings or outcomes of your research. Summarize the data collected and present key results without interpretation. Use clear and specific language to convey the essential elements of your study.
This section of the abstract can use either present or past simple tense.
Step 4: Articulate a Thoughtful Discussion
Analyze the results and discuss their implications. Interpret the findings in the context of your research question and objectives. Explore the broader significance of your results and any potential applications or recommendations.
Include brief mentions of any significant limitations in your research, such as those related to sample size or methods. This provides readers with insights to assess the credibility and generalizability of your study.
Step 5: List Relevant Keywords
Conclude your abstract by listing keywords that capture the essential concepts and topics addressed in your research. These keywords assist in indexing and categorizing your work for easy retrieval in academic databases.
Abstract Examples
Below are some samples to help you understand how to write an effective abstract for a research paper:
Sample Abstract 1
Abstract for a research paper humanities

Bagó, B., Kovács, M., Protzko, J., Nagy, T., Kekecs, Z., Pálfi, B., Adamkovi?, M., Adamus, S., Albalooshi, S., Albayrak?Aydemir, N., Alfian, I., Alper, S., Solas, S. Ã., Alves, S. G., Amaya, S., Andresen, P., Anjum, G., Ansari, D., Arriaga, P., . . . Aczél, B. (2022). Situational factors shape moral judgements in the trolley dilemma in Eastern, Southern and Western countries in a culturally diverse sample. Nature Human Behaviour , 6 (6), 880â895. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-022-01319-5
Sample Abstract 2
Social sciences Abstract

Reference :
Hanlon, M., Yeung, K., & Zuo, L. (2021). Behavioral Economics of Accounting: A review of archival research on individual decision makers*. Contemporary Accounting Research , 39 (2), 1150â1214. https://doi.org/10.1111/1911-3846.12739
Sample Abstract 3
Abstract for the Sciences

Reference:
Widén, E., Junna, N., Ruotsalainen, S., Surakka, I., Mars, N., Ripatti, P., Partanen, J., Aro, J., Mustonen, P., Tuomi, T., Palotie, A., Salomaa, V., Kaprio, J., Partanen, J., Hotakainen, K., Pöllänen, P., & Ripatti, S. (2022). How Communicating Polygenic and Clinical Risk for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Impacts Health Behavior: an Observational Follow-up Study. Circulation , 15 (2). https://doi.org/10.1161/circgen.121.003459
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Sample IMRaD Abstract
Here are some PDF samples of the abstract; check them out for a more detailed understanding:
Abstract For a Research Paper Example
Abstract For a Research Paper Sample
Abstract For a Research Paper APA 7
Abstract For a Research Paper Proposal
Tips For Writing an Abstract
Here are some essential tips for writing an effective abstract:
- Understand the Types : Familiarize yourself with different types of abstracts â such as descriptive abstracts and informative abstracts.
- Clarity is Key: A good abstract is clear, concise, and easily understandable. Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language.
- Follow a Structure : Organize your abstract with a structured format, including the research problem, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
- Stay Within Word Limits : Adhere to specified word limits. Balancing brevity while conveying essential information is crucial.
- Define the Research Problem : Clearly state the research problem or objective to provide context for your study.
- Highlight Methodology : Briefly describe the methods used in your research, giving readers insight into your approach.
- Include Vital Information: Specify the type of information covered in your research abstract.
- Active Voice and Strong Verbs : Use active voice and strong verbs to convey a sense of authority and engagement.
- Follow Guidelines : Adhere to formatting requirements stated in the title page or table of contents.
- Choose Impactful Keywords: Incorporate relevant keywords that potential readers might use when searching for similar studies.
- Revise and Edit : Prioritize the clarity and coherence of your abstract, ensuring it aligns with guidelines and objectives.
Abstract Checklist
Here's a checklist for writing an abstract for a research paper:
In summary, writing a compelling abstract is essential for conveying your research paper's core elements concisely. Remember, clarity and brevity are key. Feel free to revisit the examples provided for inspiration.
If you face challenges in any section, including the abstract, reach out to CollegeEssay.org for professional assistance. Our expert writing service is here to guide you through academic intricacies.
Get research paper writing help today for tailored support in achieving your scholarly goals.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Abstract
Research Paper Abstract is a brief summary of a research pape r that describes the study’s purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions . It is often the first section of the paper that readers encounter, and its purpose is to provide a concise and accurate overview of the paper’s content. The typical length of an abstract is usually around 150-250 words, and it should be written in a concise and clear manner.
Research Paper Abstract Structure
The structure of a research paper abstract usually includes the following elements:
- Background or Introduction: Briefly describe the problem or research question that the study addresses.
- Methods : Explain the methodology used to conduct the study, including the participants, materials, and procedures.
- Results : Summarize the main findings of the study, including statistical analyses and key outcomes.
- Conclusions : Discuss the implications of the study’s findings and their significance for the field, as well as any limitations or future directions for research.
- Keywords : List a few keywords that describe the main topics or themes of the research.
How to Write Research Paper Abstract
Here are the steps to follow when writing a research paper abstract:
- Start by reading your paper: Before you write an abstract, you should have a complete understanding of your paper. Read through the paper carefully, making sure you understand the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the key components : Identify the key components of your paper, such as the research question, methods used, results obtained, and conclusion reached.
- Write a draft: Write a draft of your abstract, using concise and clear language. Make sure to include all the important information, but keep it short and to the point. A good rule of thumb is to keep your abstract between 150-250 words.
- Use clear and concise language : Use clear and concise language to explain the purpose of your study, the methods used, the results obtained, and the conclusions drawn.
- Emphasize your findings: Emphasize your findings in the abstract, highlighting the key results and the significance of your study.
- Revise and edit: Once you have a draft, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free from errors.
- Check the formatting: Finally, check the formatting of your abstract to make sure it meets the requirements of the journal or conference where you plan to submit it.
Research Paper Abstract Examples
Research Paper Abstract Examples could be following:
Title : “The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Treating Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This meta-analysis examines the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating anxiety disorders. Through the analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials, we found that CBT is a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders, with large effect sizes across a range of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Our findings support the use of CBT as a first-line treatment for anxiety disorders and highlight the importance of further research to identify the mechanisms underlying its effectiveness.
Title : “Exploring the Role of Parental Involvement in Children’s Education: A Qualitative Study”
Abstract : This qualitative study explores the role of parental involvement in children’s education. Through in-depth interviews with 20 parents of children in elementary school, we found that parental involvement takes many forms, including volunteering in the classroom, helping with homework, and communicating with teachers. We also found that parental involvement is influenced by a range of factors, including parent and child characteristics, school culture, and socio-economic status. Our findings suggest that schools and educators should prioritize building strong partnerships with parents to support children’s academic success.
Title : “The Impact of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis”
Abstract : This paper presents a systematic review and meta-analysis of the existing literature on the impact of exercise on cognitive function in older adults. Through the analysis of 25 randomized controlled trials, we found that exercise is associated with significant improvements in cognitive function, particularly in the domains of executive function and attention. Our findings highlight the potential of exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to support cognitive health in older adults.
When to Write Research Paper Abstract
The abstract of a research paper should typically be written after you have completed the main body of the paper. This is because the abstract is intended to provide a brief summary of the key points and findings of the research, and you can’t do that until you have completed the research and written about it in detail.
Once you have completed your research paper, you can begin writing your abstract. It is important to remember that the abstract should be a concise summary of your research paper, and should be written in a way that is easy to understand for readers who may not have expertise in your specific area of research.
Purpose of Research Paper Abstract
The purpose of a research paper abstract is to provide a concise summary of the key points and findings of a research paper. It is typically a brief paragraph or two that appears at the beginning of the paper, before the introduction, and is intended to give readers a quick overview of the paper’s content.
The abstract should include a brief statement of the research problem, the methods used to investigate the problem, the key results and findings, and the main conclusions and implications of the research. It should be written in a clear and concise manner, avoiding jargon and technical language, and should be understandable to a broad audience.
The abstract serves as a way to quickly and easily communicate the main points of a research paper to potential readers, such as academics, researchers, and students, who may be looking for information on a particular topic. It can also help researchers determine whether a paper is relevant to their own research interests and whether they should read the full paper.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.
Some practical and theoretical issues related to the quantile estimators
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 05 April 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Dagmara Dudek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7443-6892 1 &
- Anna Kuczmaszewska ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2049-1890 1
The paper contains the comparative analysis of the efficiency of different qunatile estimators for various distributions. Additionally, we show strong consistency of different quantile estimators and we study the Bahadur representation for each of the quantile estimators, when the sample is taken from NA, \(\varphi \) , \(\rho ^*\) , \(\rho \) -mixing population.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Let \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be a sequence of identically distributed random variables defined on a fixed probability space \((\Omega , \mathcal {F}, P)\) with a distribution function F . The p -th quantile of F is defined as
where \(0<p<1\) .
Quantiles play an important role in finance, modeling and statistics. In practical applications, quantile estimators are fundamental, which was noticed quite early, e.g. at the paper Galton ( 1889 ).
In the literature, there are numerous quantiles estimators. Some quantile estimators were developed for specific distributions, whereas others were designed to be "distribution-free" (in other words—nonparametric estimators), with no assumption about the population density function.
Let \((X_{(1)},X_{(2)},...,X_{(n)})\) be the ordered sample of \((X_1,...,X_n)\) and \(\lfloor x\rfloor \) denotes an integer part of x . Dielman et al. ( 1994 ) presented eight different nonparametric estimators of a quantile:
Weighted average at \(X_{(\lfloor np+0.5\rfloor )}\)
where \(0.5\le np\le (n-0.5)\) .
It follows from the condition \(0.5\le np\le (n-0.5)\) that \(\displaystyle n\ge \max \bigg \{\frac{0.5}{1-p},\frac{1}{2p}\bigg \}\) .
Weighted average at \(X_{(\lfloor np\rfloor )}\)
Lower empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) value
Upper empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) value
Observation numbered closest to np
Empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF)
Weighted average at \(X_{(\lfloor (n+1)p\rfloor )}\)
Empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) with averaging
The most common estimator studied in many papers is \(E_4\) . Bahadur ( 1966 ) first established an elegant representation for a sample quantile in terms of the empirical distribution function based on independent and identically distributed samples.
Let \(\displaystyle F_n(x) = {1\over n}\sum _{i=1}^n I[X_i\le x]\) , \( x\in {\mathbb {R}} \) , \(n\ge 1\) be the empirical distribution function for the sample \((X_1, X_2, \dots ,X_ n)\) .
(Bahadur ( 1966 )) Let \(0< p < 1\) and \(\{X_n, n \ge 1\}\) be a sequence of independent identically distributed random variables with the distribution function F . Assume that F has at least two derivatives at some neighborhood of \(Q_p\) and \(F'(Q_p)~=~f(Q_p) > 0\) . Then
In next years, many researchers have studied the Bahadur representation for sample quantiles for dependent sequences. This is very important problem for practical applications, because in practice we often deal with samples with different dependency structures. Sen ( 1972 ); Babu and Singh ( 1978 ); Yoshihara ( 1995 ); Yang et al. ( 2019 ) and Wu et al. ( 2021 ) obtained the Bahadur represenation for \(\varphi \) -mixing sequences, Sun ( 2006 ); Wang et al. ( 2011 ) and Zhang et al. ( 2014 ) got the Bahadur representation for \(\alpha \) -mixing sequences and Xing and Yang ( 2019 ) for \(\psi \) -mixing sequences. For negatively dependent structures Ling ( 2008 ); Xing and Yang ( 2011 ) and Xu et al. ( 2013 ) considered this problem for negatively associated (NA) sequences and Li et al. ( 2011 ) studied it for negatively orthant dependent (NOD) random variables.
Below, we present the definitions of four types of dependence of random variables that will be considered in this work.
Definition 1
(Joag-Dev and Proschan ( 1983 )) A finite family of random variables \(\{X_i, 1\le i\le n\}\) is said to be negatively associated (NA) if for every pair of disjoint subsets A and B of \(\{1,2,...,n\}\) , we have
wherever \(f_1\) and \(f_2\) are coordinatewise nondecreasing, provided the covariance exists. An infinite family of random variables is said to be NA if every finite subfamily is NA.
Many authors have investigated NA’s statistical properties. For example, Joag-Dev and Proschan ( 1983 ) studied NA’s fundamental properties, Yang ( 2003 ) investigated uniformly asymptotic normality of regression weighted estimator for NA samples, Liang and Jing ( 2005 ) presented asymptotic properties of the estimation of nonparametric regression model based on NA sequences, Liang et al. ( 2006 ) studied asymptotic properties of the estimation of semiparametric regression model based on a linear process with NA innovations.
Increasing functions defined on disjoint subsets of a set of NA random variables are NA random variables.
(Joag-Dev and Proschan ( 1983 )) Let \({\textbf{Z}}=(Z_1,...,Z_k)\) be a vector having a multinomial distribution, obtained by taking only one observation. Thus only one \(Z_i\) is 1 while the rest are zero. The NA property for \({\textbf{Z}}\) trivially follows from Definition 1 . Since the general multinomial is a convolution of independent copies of \({\textbf{Z}}\) , the closure property (Remark 2 ) establishes NA in this case.
Definition 2
(Rozanov and Volkonski ( 1959 )) A sequence of random variables \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) is said to be \(\varphi \) -mixing if
as \(n\rightarrow \infty \) , where \({\mathcal {F}}_n^m=\sigma (X_i, n\le i\le m)\) .
\(\varphi \) -mixing property was studied by many researchers. Utev ( 1990 ) studied the central limit theorem, Chen et al. ( 2009 ) investigated total convergence of the sequences, Yang et al. ( 2012 ) obtained the Berry-Esseen bound. The more information on \(\varphi \) -mixing properties one can find in Billingsley ( 1968 ) in chapter 4.
(Wu et al. ( 2021 )) Let \(\{\epsilon _n, n\ge 1\}\) be a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables with zero mean and a finite variance. Define
for some positive integer m and constants \(a_k\) , \(k=0,1,...,m\) . Then \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) is known as a moving average process with older m . It can be verified that \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) is a \(\varphi \) -mixing process.
Definition 3
(Bradley ( 1992 )) A sequence of random variables \(\{X_n,n\ge 1\}\) is said to be \(\rho ^*\) -mixing, if
as \(n\rightarrow \infty \) , where
\(\displaystyle \text {dist}(S,T)=\min _{i\in S, j\in T}|j-i|\) and \(\sigma (S)\) and \(\sigma (T)\) are the \(\sigma \) -fields generated by \(\{X_i, i\in S\}\) and \(\{X_j, j\in T\}\) , respectively.
\(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables are a well-described and repeatedly studied structure. Bradley ( 1992 ) obtained the central limit theorem, Bryc and Smolenski ( 1993 ); Peligrad and Gut ( 1999 ); Utev and Peligrad ( 2003 ) presented the moment inequalities and Sung ( 2010 ) analysed the complete convergance of weighted sums for \(\rho ^*\) -mixing sequences of random variables.
Note that increasing functions defined on a disjoint subset of a \(\rho ^*\) -mixing field \(\{X_k, k\in N^d\}\) with mixing coefficients \(\rho ^*(s)\) are also \(\rho ^*\) -mixing with coefficients not greater that \(\rho ^*(s)\) .
(Wang et al. ( 2019 )) Let \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be a strictly stationary, finite-state, irreducible and aperiodic Markov chain. Then it is a \(\rho ^*\) - mixing process with \(\rho ^*(k)=o(e^{-Ck})\) for some \(C>0\) .
Definition 4
(Kolmogorov and Rozanov ( 1960 )) A sequence of random variables \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) is said to be \(\rho \) -mixing if
as \(n\rightarrow \infty \) , where \({\mathcal {F}}_n^m=\sigma (X_i, n\le i\le m)\) and \(L^2(\cdot )\) is a set of real-valued square-integrable functions.
The \(\rho \) -mixing condition was introduced by Kolmogorov and Rozanov ( 1960 ). Shao ( 1995 ) in his paper explored the central limit theorem, the law of large numbers and the complete convergence of \(\rho \) -mixing sequences.
(Peligrad ( 1987 )) Suppose \(\{Y_k, k\ge 1\}\) and \(\{Z_k, k\ge 1\}\) are independent random variables with the identical standard normal distribution function F and consider the sequence
Because of \(\rho (2)=0\) , sequence \(\{X_k^{(\alpha )}, k\ge 1\}\) is \(\rho \) -mixing with \(\displaystyle \sigma _n^2=\text {Var}\bigg (\sum _{k=1}^nX_k^{(\alpha )}\bigg )=2+n\alpha ,\) \(\inf _n \frac{\sigma _n^2}{n}=\alpha \) and \(E(X_k^{(\alpha )})^2=2+\alpha .\)
The following Rosenthal-type inequality will be important in further considerations:
where \(C_q>0\) , \(q\ge 2\) , \(EX_n=0\) and \(E|X_n|^q<\infty \) for every \(n\ge 1.\)
Inequality ( 2 ) is true for NA random variables (Shao and Su ( 1999 )), for \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables (Peligrad and Gut ( 1999 )) and for \(\varphi \) -mixing random variables with some additional condition on mixing coefficients \(\varphi (n), n\ge 1\) (Wu et al. ( 2021 )).
For \(\rho \) -mixing random variables, the following inequality plays the same role as ( 2 ).
(Shao ( 1995 )) Let \(q\ge 2\) and \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be a sequence of \(\rho \) -mixing random variables. Assume that \(EX_i=0\) , \(E|X_n|^q<\infty \) and
Then there exists a positive constant \(K=K(q,\rho (\cdot ))\) depending only on q and \(\rho (\cdot )\) such that for any \(k\ge 0\) , \(n\ge 1\) ,
The first aim of this paper is a comparative analysis of the effectiveness of each of the estimators, depending on the distribution from which the sample is drawn. For this purpose, in section 2 we will compare the fit of the values of the estimators presented above obtained for samples taken from populations with different distributions to the theoretical value. The second aim is to show the strong consistency of each of the estimators and to study that the Bahadur representation holds for each of the estimators when the sample is taken from a NA, \(\varphi \) , \(\rho ^*\) or \(\rho \) -mixing population.
2 Comparative analysis of estimators
In the comparative analysis of the estimators well-known probability distributions were used:
Normal distribution with \(\mu =0\) , \(\sigma =4\) ,
Student’s t distribution with 3 degrees of freedom,
Weibull distribution with scale \(\lambda =1\) and shape \(k=5\) ,
Uniform distribution on the interval [0,2],
\(\chi ^2\) distribution with 3 degrees of freedom,
Exponential distribution with \(\lambda =1\) .
The analysis was carried out for the sample sizes: \(n\in \{50,150,555,1130, 2165\}\) and for the different values of \(p\in \{0.025, 0.5, 0.975\}\) . Using the R software, in each case the teoretical value of the quantile was generated. Next, samples of sizes \(n\in \{50,150,555,1130, 2165\}\) were taken and the quantile estimator was calculated. The experiment was repeated 1000 times in each case and a mean square error ( MSE ) was generated.
In the normal distribution case, the best results were obtained for the estimators \(E_4\) , \(E_6\) and \(E_8\) . The estimator \(E_1\) was the only one that gave better results for small p . For \(p=0.5\) , the results for each estimator are similar. The results for the Student’s t distribution are similar to the normal distribution. Again, the best results were obtained for the estimators \(E_4\) , \(E_6\) , \(E_8\) . The estimators \(E_2\) , \(E_3\) and \(E_5\) showed much worse results for small p than the others estimators and showed quite good results for high p . The results for \(p=0.5\) are, again, similar for each estimator. In the case of Weibull distribution, the errors are much smaller than in the normal and Student’s t distribution. Only \(E_1\) gives a better result for small p than for large p . As the sample grows, the differences in the errors for individual estimators are practically non-existent. For the uniform distribution the errors are also smaller than for the normal and Student’s t distribution. In this case, the estimator \(E_7\) gave the best results. Additionally, \(E_1\) , \(E_2\) , \(E_3\) and \(E_5\) gave a better result for small p than the others. For \(\chi ^2\) distribution the best results gave \(E_2\) . Also good results were obtained for the estimators \(E_4\) , \(E_5\) , \(E_6\) and \(E_8\) . Each of the estimators performs worse at high p than at low p . For the exponential distribution the greatest differences in the results are seen for high p . The best results are given by the estimator \(E_2\) , but the estimators \(E_4\) , \(E_5\) , \(E_6\) and \(E_8\) also give quite good results.
The Tables 1 and 2 contain an assessment of the fit of each estimator depending on the distribution for, respectively, \(p=0.025\) and \(p=0.975\) . Within a given distribution, estimator with the best fit gets three pluses and estimator with the worst fit gets minus. The errors for a given distribution was analogous for all estimators for \(p=0.5\) .
In conclusion, none of the estimators performed equally well for different distributions for low and high p . Different estimators turn out to be the best depending on a given distribution. Only for \(p=0.5\) the fit of each estimator is at a very similar level for a given distribution. Common conclusion for each estimator is that as the sample size increases, the error decreases and the results for each estimator are very similar. However, it should be noted that the financial and life situation does not always allow to obtain a sample of 1000 or 2000 elements. That is why it is so important to choose an appropriate estimator for a given distribution especially when the research is based on a small sample.
3 Strong consistency and Bahadur representation
In this section we will study a strong consistency of a quantile estimator and the Bahadur representation for sample quantiles. Further, detailed considerations will be carried out for the estimator \(E_1\) .
Let \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be a sequence of random variables with one of the following dependency structures:
NA dependence,
\(\varphi \) -mixing dependence with coefficients satifying \(\displaystyle \sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\varphi (2^n)<\infty \) ,
\(\rho ^*\) -mixing dependence,
\(\rho \) -mixing dependence with coefficients satifying \(\displaystyle \sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\rho ^{\frac{2}{q}}(2^n)<\infty \) , for \(\displaystyle q>~\frac{1}{\delta }\) for \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\) .
Let \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be indentically distributed with a common distribution function F and a quantile \(Q_p\) . Assume that F possesses a positive continuous density f in some neighborhood \(\mathfrak {D}_p\) of \(Q_p\) such that \( 0< \sup \{f(x); x \in \mathfrak {D}_p \} <\infty . \) Moreover, we assume that \(f'(x)\) is defined in some neighborhood \(\mathfrak {D}_p\) of \(Q_p\) ,
Then for any \(0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\)
It it easy to see that \(\forall ~\varepsilon >0\)
One can obtain that
Put \(\displaystyle \xi _{ni}=I(X_i\le Q_p+\varepsilon n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta })-F(Q_p+\varepsilon n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta })\) for \(1\le i\le n\) . Therefore, we get
Note that, using Taylor’s expansion:
we can obtain that there exists some constant \(c(\varepsilon )>0 \) , depending only on \(\varepsilon >0\) , such that for a sufficiently large n
Hence, on the basis of Eqs. ( 6 ),( 7 ), Markov’s inequality and Eq. ( 2 ) (for NA, \(\varphi \) and \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables) or Lemma 1 (for \(\rho \) -mixing random variables), for \(\displaystyle r>\frac{1}{\delta }\) where \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\) , we get the following estimation
We can carry out analogous considerations for \(A_n^2\) using the lower estimate of \(E_1\) in the inequality Eq. ( 5 ). Hence, we get \(\displaystyle \sum _{n=1}^{\infty } P\bigg [ E_1\le Q_p-\varepsilon n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta }\bigg ] <\infty .\) By the Borel-Cantelli lemma we get thesis Eq. ( 4 ).
\(\square \)
One can obtain analogous results for the estimator:
\(E_2\) —by assumption that \(X_{(\lfloor np\rfloor )}\le E_2\le X_{(\lfloor np\rfloor +1)}\) ,
\(E_3\) —calculations are similar to the estimator \(E_4\) , which was considered in the paper (Dudek and Kuczmaszewska ( 2022 )),
\(E_5\) and \(E_6\) —calculations are analogous to the estimators \(E_3\) and \(E_4\) , because the proof does not depend on the value of \(np-\lfloor np\rfloor \) ,
\(E_7\) —by the assumption that \(X_{(\lfloor (n+1)p\rfloor ))}\le E_7\le X_{(\lfloor (n+1)p\rfloor +1))}\) ,
\(E_8\) —it is a combination of the estimator \(E_4\) and \(E_3\) .
Now, let us focus on the Bahadur representation of sample quantiles.
\(\rho ^*\) -mixing dependence.
Let \(\{X_n, n\ge 1\}\) be indentically distributed with a common distribution function F and quantile \(Q_p\) . Assume that F possesses a positive continuous density f in some neighborhood \(\mathfrak {D}_p\) of \(Q_p\) such that
Then for any \( \delta >0\)
where \(\mathfrak {I}_n=\big [ Q_p-c_0n^{-\frac{1}{4}+\delta },Q_p+c_0n^{-\frac{1}{4}+\delta }\big ]\) for some \(c_0>0.\)
Let \(\{a_n, n\ge 1\}\) and \(\{b_n, n\ge 1\}\) be two sequences defined as follows
For each \(n\in {\mathbb {N}}\) and any integer j we define
Since \(F_n\) and F are nondecreasing we get for \(x\in \mathfrak {J}_{j,n}\)
It is easy to see that by The Mean Value Theorem and ( 8 ) we have
Therefore we obtain
Moreover, we note that
where \(Y_i^{Q_p}=E(I[X_i\le Q_p])-I[X_i\le Q_p]\) and \(Y_i^{(j,n)} = E(I[X_i\le \eta _{j,n}])-I[X_i\le \eta _{j,n}]\) , \(-b_n \le j \le b_n\) are respectively NA or \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables.
It follows from the Markov’s inequality and Eq. ( 2 ) (for NA and \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables) that for \(\displaystyle r> \max \bigg \{2,\frac{5}{4\delta }\bigg \}\) where \(\displaystyle \delta >0\) we have
By the Borel-Cantelli lemma we get thesis. \(\square \)
\(\rho \) -mixing dependence with coefficients satifying \(\displaystyle \sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\rho ^{\frac{2}{q}}(2^n)<\infty \) , for \(q> \max \bigg \{2,{5\over 2\delta }\bigg \}\) for \(\delta >0\) .
where \(\mathfrak {I}_n=\big [ Q_p-c_0n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta },Q_p+c_0n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta }\big ]\) for some \(c_0>0\)
The proof of Theorem 4 is very similar to the proof of Theorem 3 . Analogously, let \(\{a_n, n\ge 1\}\) and \(\{b_n, n\ge 1\}\) be two sequences defined as follows
Let \(\eta _{j,n}\) , \(\alpha _{j,n}\) and \(\mathfrak {J}_{j,n}\) be defined as in Theorem 3 .
As it was shown in Theorem 3 , it is easy to see that
Therefore we get
Next, we have
where \(Y_i^{(j,n)} = I[Q_p< X_i\le \eta _{j,n}]\) , \(-b_n \le j \le b_n\) are respectively \(\varphi \) or \(\rho \) -mixing random variables.
Moreover, it is easy to obtain by The Mean Value Theorem that for \(r\ge 2\)
It follows from the Markov’s inequality and Eq. ( 2 ) (for \(\varphi \) -mixing random variables) or Lemma 1 (for \(\rho \) -mixing random variables) that for \(\displaystyle r> \max \bigg \{2,{5\over 2\delta }\bigg \}\) where \(\displaystyle \delta >0\) we have
Suppose that assumptions of Theorem 2 hold. Then for any \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\) we have,
for NA and \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables.
One can note that
By Taylor’s expansion we obtain for \(0<\theta <1\)
From Eq. ( 3 ) and Theorem 2 for \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\) it follows that
By Eq. ( 11 ) and Theorem 3 for \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{2}\) we get that with probability 1,
which gives that \( f( Q_p)(E_1-Q_p)+F_n(Q_{p})-p = O(n^{-\frac{1}{2}+\delta }),\) when \(n\rightarrow \infty . \) Hence, we get Eq. ( 10 ). \(\square \)
Suppose that assumptions of Theorem 2 hold. Then for any \(\displaystyle 0<\delta <\frac{1}{4}\) we get
for \(\varphi \) and \(\rho \) -mixing random variables.
Analogously as in the proof of Theorem 5 , using Eq. ( 11 ) and Theorem 4 for \(\displaystyle 0<~\delta <\frac{1}{4}\) we get that with probability 1,
Hence, we get Eq. ( 12 ). \(\square \)
The calculations for the estimators \(E_2\) , \(E_4, E_5,E_6,E_7\) and \(E_8\) proceed analogously through the condition that \(F_n( E_i) = p+O(n^{-1}),\) where \(i=2,4,5,6,7,8\) . Assuming that \(F_n( E_3) \le p\) , one can obtain analogous results for the estimator \(E_3\) .
Babu GJ, Singh K (1978) On deviations between empirical and quantile processes for mixing random variables. J Multivar Anal 8:532–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-259X(78)90031-3
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Bahadur RR (1966) A note on quantiles in large samples. Ann Math Stat 37:577–580. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177699450
Billingsley P (1968) Convergance of probability measures. Wiley, New York
Google Scholar
Bradley RC (1992) On the spectral density and asymptotic normality of weakly dependent random fields. J Theor Probab 5:355–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046741
Bryc W, Smolenski W (1993) Moment conditions for almost sure convergence of weakly correlated random variables. Proc Am Math Soc 119:629–635. https://doi.org/10.2307/2159950
Chen PY, Hu TC, Volodin A (2009) Limiting behavior of moving average process under \(\varphi \) -mixing assumption. Stat Probab Lett 79:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2008.07.026
Article Google Scholar
Dielman T, Lowry C, Pfaffenberger R (1994) A comparison of quantile estimators. Commun Stat Simul Comput 23:355–371. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610919408813175
Dudek D, Kuczmaszewska A (2022) On the Bahadur representation of quantiles for a sample from \(\rho ^*\) -mixing structure population. Adv Sci Technol Res J 16:316–330. https://doi.org/10.12913/22998624/150480
Galton F (1889) Natural inheritance. Macmillan, New York
Book Google Scholar
Joag-Dev K, Proschan F (1983) Negative association of random variables with applications. Ann Stat 11:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176346079
Kolmogorov AN, Rozanov YA (1960) On strong mixing conditions for stationary gaussian processes. Theor Probab Appl 5:204–208. https://doi.org/10.1137/1105018
Li X, Yang W, Hu S, Wang X (2011) The Bahadur representation for sample quantile under NOD sequence. J Nonparam Stat 23:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10485252.2010.486033
Liang HY, Jing BY (2005) Asymptotic properties for estimates of nonparametric regression models based on negatively associated sequences. J Multivar Anal 95:227–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmva.2004.06.004
Liang HY, Mammitzsch V, Steinebach J (2006) On a semiparametric regression model whose errors form a linear process with negatively associated innovations. Statistics 40:207–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/02331880600688163
Ling NX (2008) The Bahadur representation for sample quantiles under negatively associated sequences. Stat Probab Lett 78:2660–2663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2008.03.026
Liu T, Zhang Z, Hu S, Yang W (2014) The Berry Esseen bound of sample quantiles for NA sequences. J Inequal Appl. https://doi.org/10.1186/1029-242X-2014-79
Peligrad M (1987) On the central limit theorem for \(\rho \) -mixing sequences of random variables. Ann Probab 15:1387–1394. https://doi.org/10.1214/aop/1176991983
Peligrad M, Gut A (1999) Almost-sure results for a class of dependent random variables. J Theor Probab 12:87–104. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021744626773
Rozanov YA, Volkonski VA (1959) Some limit theorems for random function. Theor Probab 4:186–207. https://doi.org/10.1137/1104015
Sen PK (1972) On the Bahadur representation of sample quantiles for sequences of \(\varphi \) -mixing random variables. J Multivar Anal 2:77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-259X(72)90011-5
Shao QM (1995) Maximal inequalities for partial sums of \(\rho \) -mixing sequences. Ann Probab 23:948–965. https://doi.org/10.1214/aop/1176988297
Shao QM, Su C (1999) The law of the iterated logarithm for negatively associated random variables. Stoch Process Appl 83:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4149(99)00026-5
Sun SX (2006) The Bahadur representation for sample quantiles under weak dependence. Stat Probab Lett 76:1238–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spl.2005.12.021
Sung SH (2010) Complete convergence for weighted sums of \(\rho ^*\) -mixing random variables. Discrete Dyn Nat Soc. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/630608
Utev SA (1990) On the central limit theorem for \(\varphi \) -mixing arrays of random variables. Theor Probab Appl 35:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1137/1135013
Utev S, Peligrad M (2003) Maximal inequalities and an invariance principle for a class of weakly dependent random variables. J Theor Probab 16:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022278404634
Wang XJ, Hu SH, Yang WZ (2011) The Bahadur representation for sample quantiles under strongly mixing sequence. J Stat Plan Inference 141:655–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspi.2010.07.008
Wang X, Wu Y, Hu S (2019) The Berry-Esseen bounds of the weighted estimator in a nonparametric regression model. Ann Inst Stat Math 71:1143–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10463-018-0677-6
Wu Y, Yu W, Wang X (2021) The Bahadur representation of sample quantiles for \(\varphi \) -mixing random variables and its application. Statistics 55:426–444. https://doi.org/10.1080/02331888.2021.1923713
Xing G, Yang S (2011) A remark on the Bahadur representation of sample quantiles for negatively associated sequences. J Korean Stat Soc 40:277–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2010.10.006
Xing G, Yang S (2019) On the Bahadur representation of sample quantiles for \(\psi \) -mixing sequences and its application. Commun Stat Theor Methods 48:1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2018.1423696
Xu SF, Ge L, Miao Y (2013) On the Bahadur representation of sample quantiles and order statistics for NA sequences. J Korean Stat Soc 42:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jkss.2012.04.003
Yang SC (2003) Uniformly asymptotic normality of regression weighted estimator for negatively associated sample. Stat Probab Lett 62:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7152(02)00427-3
Yang WZ, Wang XH, Li XQ (2012) Berry-Esseen bound of sample quantiles for \(\varphi \) -mixing random variables. J Math Anal Appl 388:451–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2011.10.058
Yang W, Hu S, Wang X (2019) The Bahadur representation for sample quantiles under dependent sequence. Acta Math Appl Sin 35:521–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10255-019-0827-5
Yoshihara K (1995) The Bahadur representation of sample quantile for sequences of strongly mixing random variables. Stat Probab Lett 24:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7152(94)00187-D
Zhang Q, Yang W, Hu S (2014) On Bahadur representation for sample quantiles under \(\alpha \) -mixing sequence. Stat Papers 55:285–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-012-0472-z
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and referees for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Applied Mathematics, Lublin University of Technology, Nadbystrzycka 38D, 20-618, Lublin, Poland
Dagmara Dudek & Anna Kuczmaszewska
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Dagmara Dudek or Anna Kuczmaszewska .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dudek, D., Kuczmaszewska, A. Some practical and theoretical issues related to the quantile estimators. Stat Papers (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-024-01543-3
Download citation
Received : 11 May 2023
Revised : 24 November 2023
Published : 05 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-024-01543-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bahadur representation
- Dependent mixing random variables
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format. Checklist: Abstract 0 / 8. The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page. ... There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work ...
The abstract: "This quantitative research study was conducted to illustrate the relationship (s) between social media use and its effect on police brutality awareness. In 2015, social media was used to assist in revealing an act of impulsive police brutality on an adult black woman in Waller County, Texas.
Definition and Purpose of Abstracts An abstract is a short summary of your (published or unpublished) research paper, usually about a paragraph (c. 6-7 sentences, 150-250 words) long. A well-written abstract serves multiple purposes: an abstract lets readers get the gist or essence of your paper or article quickly, in order to decide whether to….
Informative Abstract Example 1. Emotional intelligence (EQ) has been correlated with leadership effectiveness in organizations. Using a mixed-methods approach, this study assesses the importance of emotional intelligence on academic performance at the high school level. The Emotional Intelligence rating scale was used, as well as semi ...
5. How to Format an Abstract. Most abstracts use the same formatting rules, which help the reader identify the abstract so they know where to look for it. Here's a list of formatting guidelines for writing an abstract: Stick to one paragraph. Use block formatting with no indentation at the beginning.
You should select different types of abstracts to papers based on their length: informative abstracts for extended and more complex abstracts and descriptive ones for simpler and shorter research papers. ... There are plenty of examples of abstracts for dissertations in the dissertation and thesis databases. 3. Avoid Jargon To the Maximum. When ...
What this handout is about. This handout provides definitions and examples of the two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. It also provides guidelines for constructing an abstract and general tips for you to keep in mind when drafting. Finally, it includes a few examples of abstracts broken down into their component parts.
Write your paper first, then create the abstract as a summary. Check the journal requirements before you write your abstract, eg. required subheadings. Include keywords or phrases to help readers search for your work in indexing databases like PubMed or Google Scholar. Double and triple check your abstract for spelling and grammar errors.
An abstract should be a mini essay, so it should begin with a clear statement of your argument. This should be the first sentence or two. Abstracts vary in length. But a good rule is to aim for five to seven sentences. The bulk of the abstract will review the evidence for your claim and summarize your findings. Avoid complicated syntax.
An abstract is a 150- to 250-word paragraph that provides readers with a quick overview of your essay or report and its organization. It should express your thesis (or central idea) and your key points; it should also suggest any implications or applications of the research you discuss in the paper. According to Carole Slade, an abstract is ...
An APA abstract must be formatted as follows: Include the running head aligned to the left at the top of the page (professional papers only) and page number. Note, student papers do not require a running head. On the first line, center the heading "Abstract" and bold (do not underlined or italicize).
While the abstract will be at the beginning of your paper, it should be the last section you write. Once you have completed the final draft of your psychology paper, use it as a guide for writing your abstract. Begin your abstract on a new page. Place your running head and page number 2 in the top right-hand corner.
Methods - The methods section should contain enough information to enable the reader to understand what was done, and how. It should include brief details of the research design, sample size, duration of study, and so on. Results - The results section is the most important part of the abstract. This is because readers who skim an abstract do so ...
Step 2: Outline Your Methods Clearly. Outline the research methods and experimental design employed in your study. Refrain from evaluating the validity or challenges of your methodology. Provide a clear description of how you conducted your research, including any specific techniques, tools, or procedures used.
The typical length of an abstract is usually around 150-250 words, and it should be written in a concise and clear manner. Research Paper Abstract Structure. The structure of a research paper abstract usually includes the following elements: Background or Introduction: Briefly describe the problem or research question that the study addresses.
Here are the basic steps to follow when writing an abstract: 1. Write your paper. Since the abstract is a summary of a research paper, the first step is to write your paper. Even if you know what you will be including in your paper, it's always best to save your abstract for the end so you can accurately summarize the findings you describe in ...
That is because most papers in other languages, especially Asian nations, tend to publish an English abstract with common search engines, such as, the MLA site. Example Abstract. This example abstract follows the IMRAD structure closely. The first two sentences are the introduction and background information. Sentences 3-5 describe the methods ...
Abstracts What this handout is about This handout provides definitions and examples of the two main types of abstracts: descriptive and informative. It also provides guidelines for constructing an abstract and general tips for you to keep in mind when drafting. Finally, it includes a few examples of abstracts broken down into their component parts.
Step 2- Set yourself a word count. An abstract is brief for a reason: it introduces the work without saying too much about it. Setting yourself a word count for your abstract will prevent you from writing too much and force you to be concise. An abstract is usually only 150-300 words long, so very condensed.
Abstract Format. recommended fonts: 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode, 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or 10-point Computer Modern2. 1-in. margins on all sides. placement: second page of the paper. section label: "Abstract". ° centered and in bold. ° written on the first line of the page.
Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper. However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style. Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples.
Abstract. The paper contains the comparative analysis of the efficiency of different qunatile estimators for various distributions. Additionally, we show strong consistency of different quantile estimators and we study the Bahadur representation for each of the quantile estimators, when the sample is taken from NA, \ (\varphi \), \ (\rho ...
Abstract. BACKGROUNDBiogenic amines (BAs) in high concentrations are toxic and may cause a series of health symptoms. A sensitive measurement of BA levels is essential for human health. Capillary electrophoresis (CE) has emerged for the separation of eight BAs due to simple sample preparation and highly efficient separation.