- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

Tense Use in Essays: Past vs. Present
2-minute read
- 16th April 2016
It’s mostly time travellers who worry about the more convoluted aspects of grammatical tense , but the issue of tense use in academic writing is, nonetheless, controversial.
To be specific, there is much disagreement about tense use in essays : specifically, is past or present tense best? Today, we look into this tricky problem.
Present Tense
The present tense is used when discussing current events or states. It will often be the dominant tense used in academic writing due to the number of situations to which it applies:
- Stating general principles or theories (e.g. ‘The third law of thermodynamics states …’)
- Describing a fact (e.g. ‘Catalysts increase the rate of a reaction…’)
- Expressing an opinion or making a claim (e.g. ‘I believe further research is required…’)
- Analysing the results of an experiment (e.g. ‘The results show that…’)
In all these cases, the present tense shows that something applies at the current time or emphasises its relevance to the present.
The present tense can also do this in a literature review, since it frames research in terms of its current significance. This shows that you’re engaged with ongoing debate in your field of study, not simply describing out-of-date research.
The past tense is used when describing events that have already happened. In academic writing, this could be writing up a completed experiment.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
For example, the past tense can be used in methodology and results sections. Likewise, the past tense is useful when writing a case study, since this is almost always about something that has already occurred.
While you can use the past tense in a literature review, saying that someone ‘believed’ something may imply that they changed their mind. As such, the past tense can be used for discussing ‘dead’ ideas (i.e. things that no-one holds true any more) or something that someone has since disavowed.
Future Tense
The future tense is useful for discussing things that are yet to happen, such as when we commit to doing something (e.g. ‘I will continue to research this issue’).
Generally, you won’t need to do this too often in academic writing. However, the future tense can be useful in the following situations:
- Making predictions about the future
- Offering recommendations based on your results
- Suggesting new avenues of research
In all these cases, the future tense will help you express yourself more clearly.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your website experience and help us understand how you use our website. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the usage of cookies. Learn more about our Privacy Statement and Cookie Policy .
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Schedule an appointment! Login or Register
- Graduate Students
- ESOL Students
- The Three Common Tenses Used in Academic Writing
He explains the author’s intention and purpose in the article.
*He is explaining the author’s intention and purpose in the article.
Both of the sentences above are grammatically correct. However, the tense used in first sentence (present simple) is more common for academic writing than the tense in the second sentence (present progressive). This handout provides the overview of three tenses that are usually found in academic writing.
There are three tenses that make up 98% of the tensed verbs used in academic writing. The most common tense is present simple, followed by past simple and present perfect. These tenses can be used both in passive and active voice. Below are the main functions that these three tenses have in academic writing.
The Present Simple Tense
Present simple is the most common tense in academic writing, and it is usually considered as the “default” unless there is a certain reason to choose another tense (e.g. a sentence contains a past time marker). Some specific functions of present simple include:
The Past Simple Tense
Generally, past simple is used to refer to actions completed in the past. Some specific functions this tense has in academic writing include:
The Present Perfect Tense
Present perfect is usually used when referring to previous research, and since it is a present tense, it indicates that the findings are relevant today. More specifically, this tense might have the following functions:
Common Questions about Tense in Academic Writing
Question: Can tenses change in the same paragraph or sentence?
Explanation: Yes, there are some times where it is appropriate to switch tense within a paragraph or sentence. However, you have to have a good reason for it. For instance, a shift in time marked by an adverb or prepositional phrase (e.g. since, in 2013, until ) or when you move from general statements to specific examples from research (one of the functions mentioned above).
Question : Are other verb tenses used in academic writing?
Explanation : Yes, although not as common, other tenses are used in academic writing as well. For example, when expressing strong predictions about the future, the future simple tense is used, or when describing events that undergo changes at the time of writing, present progressive is used.
Read the excerpt and notice the tenses used for each verb. Identify the function of each tense as illustrated in the first sentence.
Approximately 10% of the population is diagnosed (present simple, function 4) with dyslexia (Habib, 2000). Specialized testing most often reveals this disability in third grade or later, when there develops an observable differential between reading achievement and IQ (Wenar & Kerig, 2000). This late identification poses severe problems for effective remediation. At the time of diagnosis, poor readers are on a trajectory of failure that becomes increasingly difficult to reverse. Attempts at intervention must both focus on remediation of the impaired components of reading as well as extensive rehabilitation to reverse the growing experience differential.
Educators and researchers are aware of the need for early diagnosis. In response, research investigating early correlates of later reading ability/disability has burgeoned (e.g. Wagner et al., 1997). However, these early reading studies primarily focus on school age children (e.g. Share et al., 1984). To date, only a few studies have focused on the reading trajectories of children younger than preschool, and there is little consistency within the existing studies (e.g. Scarborough, 1990, 1991).
In the current study, we trace the development of the two aspects of the phonological processing deficit in a longitudinal follow-up study of two-year-olds. Shatz et al. (1996, 1999, 2001) investigated the underlying lexical structure in two-year-old children. Although their experiments were tailored to examine early word learning behavior, their study design is uniquely suited to looking at the phonological processing skills of two-year old children as well. In this study, we measure the early reading skills of these same two-year-olds at five to seven years of age in order to determine the predictivity of the early two-year old behaviors for later reading ability.
Adapted from Michigan Corpus of Upper-level Student Papers. (2009). Ann Arbor, MI: The Regents of the University of Michigan.
Approximately 10% of the population is diagnosed (pres. simp. F4) with dyslexia (Habib, 2000). Specialized testing most often reveals (pres. simp. F4) this disability in third grade or later, when there develops (pres. simp. F4) an observable differential between reading achievement and IQ (Wenar & Kerig, 2000). This late identification poses (pres. simp. F3) severe problems for effective remediation. At the time of diagnosis, poor readers are (pres. simp. F3) on a trajectory of failure that becomes (pres. simp. F3) increasingly difficult to reverse. Attempts at intervention must both focus on remediation of the impaired components of reading as well as extensive rehabilitation to reverse the growing experience differential.
Educators and researchers are (pres. simp. F1) aware of the need for early diagnosis. In response, research investigating early correlates of later reading ability/disability has burgeoned (pres. perf. F1) (e.g. Wagner et al., 1997). However, these early reading studies primarily focus (pres. simp. F3) on school age children (e.g. Share et al., 1984). To date, only a few studies have focused (pres. perf. F3) on the reading trajectories of children younger than preschool, and there is (pres. simp. F3) little consistency within the existing studies (e.g. Scarborough, 1990, 1991).
In the current study, we trace (pres. simp. F2) the development of the two aspects of the phonological processing deficit in a longitudinal follow-up study of two-year-olds. Shatz et al. (1996, 1999, 2001) investigated (past. simp. F1) the underlying lexical structure in two-year-old children. Although their experiments were tailored (past. simp. F1) to examine early word learning behavior, their study design is uniquely suited (pres. simp. F3) to looking at the phonological processing skills of two-year old children as well. In this study, we measure (pres. simp. F2) the early reading skills of these same two-year-olds at five to seven years of age in order to determine the predictivity of the early two-year old behaviors for later reading ability.
The information in this handout is adapted from Caplan, N. (2015). Grammar choices for graduate and professional writers . Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Last updated 12/20/2017
Grammar & Style
- Converting Fragments to Full Sentences
- Active and Passive Voice
- Choosing Between Infinitive and Gerund: “To do” or “doing”?
- Choosing the Correct Word Form
- Combining Clauses to Avoid Comma Splices, Run-ons, and Fragments
- Commas, Semicolons, and Colons
- Count vs. Noncount Nouns
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Improving Cohesion: The "Known/New Contract"
- Modal Verbs
- Parallel Structure
- Prepositions
- Proper Nouns
- Reducing Informality in Academic Writing
- Run-on Sentences
- Same Form, but Different Functions: Various Meanings of Verb+ing and Verb+ed
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Using Reduced Relative Clauses to Write Concisely
- Verb Tenses
- Word Order in Statements with Embedded Questions

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Published on 20 October 2022 by Shane Bryson . Revised on 11 September 2023.
Tense communicates an event’s location in time. The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future .
In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous . The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have , while the continuous aspect is formed using the verb to be .
In academic writing , the most commonly used tenses are the present simple , the past simple , and the present perfect .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Tenses and their functions, when to use the present simple, when to use the past simple, when to use the present perfect, when to use other tenses.
The table below gives an overview of some of the basic functions of tenses and aspects. Tenses locate an event in time, while aspects communicate durations and relationships between events that happen at different times.
It can be difficult to pick the right verb tenses and use them consistently. If you struggle with verb tenses in your thesis or dissertation , you could consider using a thesis proofreading service .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The present simple is the most commonly used tense in academic writing, so if in doubt, this should be your default choice of tense. There are two main situations where you always need to use the present tense.
Describing facts, generalisations, and explanations
Facts that are always true do not need to be located in a specific time, so they are stated in the present simple. You might state these types of facts when giving background information in your introduction .
- The Eiffel tower is in Paris.
- Light travels faster than sound.
Similarly, theories and generalisations based on facts are expressed in the present simple.
- Average income differs by race and gender.
- Older people express less concern about the environment than younger people.
Explanations of terms, theories, and ideas should also be written in the present simple.
- Photosynthesis refers to the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
- According to Piketty (2013), inequality grows over time in capitalist economies.
Describing the content of a text
Things that happen within the space of a text should be treated similarly to facts and generalisations.
This applies to fictional narratives in books, films, plays, etc. Use the present simple to describe the events or actions that are your main focus; other tenses can be used to mark different times within the text itself.
- In the first novel, Harry learns he is a wizard and travels to Hogwarts for the first time, finally escaping the constraints of the family that raised him.
The events in the first part of the sentence are the writer’s main focus, so they are described in the present tense. The second part uses the past tense to add extra information about something that happened prior to those events within the book.
When discussing and analyzing nonfiction, similarly, use the present simple to describe what the author does within the pages of the text ( argues , explains , demonstrates , etc).
- In The History of Sexuality , Foucault asserts that sexual identity is a modern invention.
- Paglia (1993) critiques Foucault’s theory.
This rule also applies when you are describing what you do in your own text. When summarising the research in your abstract , describing your objectives, or giving an overview of the dissertation structure in your introduction, the present simple is the best choice of tense.
- This research aims to synthesise the two theories.
- Chapter 3 explains the methodology and discusses ethical issues.
- The paper concludes with recommendations for further research.
The past simple should be used to describe completed actions and events, including steps in the research process and historical background information.
Reporting research steps
Whether you are referring to your own research or someone else’s, use the past simple to report specific steps in the research process that have been completed.
- Olden (2017) recruited 17 participants for the study.
- We transcribed and coded the interviews before analyzing the results.
The past simple is also the most appropriate choice for reporting the results of your research.
- All of the focus group participants agreed that the new version was an improvement.
- We found a positive correlation between the variables, but it was not as strong as we hypothesised .
Describing historical events
Background information about events that took place in the past should also be described in the past simple tense.
- James Joyce pioneered the modernist use of stream of consciousness.
- Donald Trump’s election in 2016 contradicted the predictions of commentators.
The present perfect is used mainly to describe past research that took place over an unspecified time period. You can also use it to create a connection between the findings of past research and your own work.
Summarising previous work
When summarising a whole body of research or describing the history of an ongoing debate, use the present perfect.
- Many researchers have investigated the effects of poverty on health.
- Studies have shown a link between cancer and red meat consumption.
- Identity politics has been a topic of heated debate since the 1960s.
- The problem of free will has vexed philosophers for centuries.
Similarly, when mentioning research that took place over an unspecified time period in the past (as opposed to a specific step or outcome of that research), use the present perfect instead of the past tense.
- Green et al. have conducted extensive research on the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction.
Emphasising the present relevance of previous work
When describing the outcomes of past research with verbs like fi nd , discover or demonstrate , you can use either the past simple or the present perfect.
The present perfect is a good choice to emphasise the continuing relevance of a piece of research and its consequences for your own work. It implies that the current research will build on, follow from, or respond to what previous researchers have done.
- Smith (2015) has found that younger drivers are involved in more traffic accidents than older drivers, but more research is required to make effective policy recommendations.
- As Monbiot (2013) has shown , ecological change is closely linked to social and political processes.
Note, however, that the facts and generalisations that emerge from past research are reported in the present simple.
While the above are the most commonly used tenses in academic writing, there are many cases where you’ll use other tenses to make distinctions between times.
Future simple
The future simple is used for making predictions or stating intentions. You can use it in a research proposal to describe what you intend to do.
It is also sometimes used for making predictions and stating hypotheses . Take care, though, to avoid making statements about the future that imply a high level of certainty. It’s often a better choice to use other verbs like expect , predict, and assume to make more cautious statements.
- There will be a strong positive correlation.
- We expect to find a strong positive correlation.
- H1 predicts a strong positive correlation.
Similarly, when discussing the future implications of your research, rather than making statements with will, try to use other verbs or modal verbs that imply possibility ( can , could , may , might ).
- These findings will influence future approaches to the topic.
- These findings could influence future approaches to the topic.
Present, past, and future continuous
The continuous aspect is not commonly used in academic writing. It tends to convey an informal tone, and in most cases, the present simple or present perfect is a better choice.
- Some scholars are suggesting that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars suggest that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars have suggested that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
However, in certain types of academic writing, such as literary and historical studies, the continuous aspect might be used in narrative descriptions or accounts of past events. It is often useful for positioning events in relation to one another.
- While Harry is traveling to Hogwarts for the first time, he meets many of the characters who will become central to the narrative.
- The country was still recovering from the recession when Donald Trump was elected.
Past perfect
Similarly, the past perfect is not commonly used, except in disciplines that require making fine distinctions between different points in the past or different points in a narrative’s plot.
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Bryson, S. (2023, September 11). Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/english-language/verb-tenses/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
Subject-verb agreement | examples, rules & use, english mistakes commonly made in a dissertation | examples.
- Support LUC
- Directories
- KRONOS Timecard
- Employee Self-Service
- Password Self-service
- Academic Affairs
- Advancement
- Admission: Adult B.A.
- Admission: Grad/Prof
- Admission: International
- Admission: Undergrad
- Alumni Email
- Alumni Relations
- Arrupe College
- Bursar's Office
- Campus Ministry
- Career Centers
- Center for Student Assistance and Advocacy
- Colleges and Schools
- Commencement
- Conference Services
- Continuing Education
- Course Evaluations IDEA
- Cuneo Mansion & Gardens
- Dining Services
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Emeriti Faculty Caucus
- Enterprise Learning Hub
- Executive and Professional Education
- Faculty Activity System
- Financial Aid
- Human Resources
- IBHE Institutional Complaint System
- Information Technology Services
- Institute of Environmental Sustainability
- Learning Portfolio
- Loyola Health App
- Loyola University Chicago Retiree Association (LUCRA)
- Madonna della Strada Chapel
- Media Relations
- Navigate Staff
- Office of First Year Experience
- Office of Institutional Effectiveness
- President's Office
- Rambler Buzz
- Registration and Records
- Residence Life
- Retreat & Ecology Campus
- Rome Center
- Security/Police
- Staff Council
- Student Achievement
- Student Consumer Information
- Student Development
- Study Abroad
- Summer Sessions
- University Policies
Writing Center
Loyola university chicago, using present tense, the literary historical present tense.
Some teachers in the humanities will tell you to use present tense when quoting, which can be confusing; weren’t these sources written in the past? Shouldn’t you use past tense? To make sense of this, try using the “Book Approach” when discussing literary or historical texts or discussing the context of authors’ lives.
Take this quote from Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “Letter from Birmingham Jail” as an example:
“We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny. Whatever affects one directly affects all indirectly.”
Consider that, as you read, the author is still “alive” in the sense that they are communicating with you. The following sentence demonstrates a technique called the “literary present” or the “historical present”:
Describing the need for whites and blacks to unite for social transformation, King explains, “We are caught in an inescapable network of mutuality, tied in a single garment of destiny. Whatever affects one directly affects all indirectly.”
Even if you are summarizing, you can still use the “literary present” or “historical present” because you are responding to your received understanding of the author’s words:
In this work, King describes the need for whites and blacks to unite for social transformation, seeing such a duty as imperative, even if the consequences of racism do not immediately affect everyone.
Now, if you are discussing fact about the author’s life, you are describing actions in the past or the past-present. Your words, without quotes, refer to a statement of fact:
“While incarcerated in Birmingham, Alabama in 1963 for peacefully protesting racial inequality, civil rights activist Martin Luther King Jr. employed many kinds of rhetoric to convince local white ministers to support his peaceful mission to achieve rights for African-Americans.”
The APA Exception
Remember that APA format does not use the “historical present,” even when quoting, instead using the past or present-past tense to summarize an author’s words or introduce a quote. It’s a good idea to check with your instructor, especially in a science class, before writing an essay to see what tense you should use when quoting a source.
- Undergraduate
- Graduate/ Professional
- Adult Education
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Past, Present, and Future Tense in Essays: How to Switch

Past, Present, and the Future Tenses in Your Essay
Choosing the correct grammatical tense for your essay can be a challenge. You have to decide whether to use past, present, or future tense. A wrong choice impacts your essay negatively. It will lack clarity and flow. This is not a situation that you ought to find yourself in.
Most students struggle with choosing the right tense. For some, it is due to the lack of guidance on using grammatical tenses. Others are careless with their writing. The result is a poorly written essay that a reader cannot understand. However, it is a problem that you can deal with once and for all.

Reading the instructions will enlighten you on which tense to use in writing your essay. Your tutor can also guide you on how to use grammatical tenses. You get the guidelines of when to use a particular tense. The help prevents you from choosing the wrong tense.
The type of your essay also reveals which tenses you ought to use. All essays are not the same. They have some distinct rules that create a significant difference. You must be aware of those rules and follow them to the latter. For instance, using the right tense is something you must take seriously.
Should an Essay be in Present, Past, or Future Tense?
Many students might find it challenging to choose the right tense. Some are yet to learn by heart the rules governing the use of tenses. They end up making the wrong choice.
Ultimately, the impact of their essay score is negative. Fortunately, it is a problem you can work on.
Every essay needs to be clear and engaging, where the reader needs an easier time reading it. But, that is not the case with all students. Some find themselves using the wrong tenses.
Instead of using the present tense, they write essays in the past tense. But perhaps they do not know when to use a present, past, or future tense.
You can use present, past, and future tense in your essay. But there is a catch. Before you write your essay, you must know which tense fits it. You can either get guidance from your tutor or do your research. Above all, ensure the tense you use is consistent and clear.
Most essay writers use the present tense. It is simple and direct to the point. You can write short sentences that are easier to read and understand. The reader will use little time to read your essay. It will not be tiring to read it since the message is clear.
The present tense is common in academic writing. It allows you to write about current states of events more candidly. By using the present tense, you can easily describe theories. It will be easier to explain an event that is happening now. Generally, the present tense is ideal for writing essays.
Instances to Use Present Tense in an Essay

You do not have to write every essay in the present tense. There are instances under which it becomes a must. At that juncture, you have to play ball.
You must shun the past and future tenses to make your essay consistent. Deviating from the present tense might distort your sentence structure thereby complicating your essay.
The present tense is ideal for creating a sense of immediacy. The reader gets to experience every action as it unfolds. It is easier to grasp the information the writer is passing across. The clarity in the essay engages the reader .
This is one of the reasons why writing in the present tense is common.
Writing an essay in the present tense is much easier. You can write your essay within the shortest time possible, and meeting deadlines will not be an issue. Your essay will be simple and clear to the point, without any sophistication.
Use present tense in an essay where you refer to existing facts. The present tense shows that the fact is indeed true. It becomes easier for the reader to believe in what you are writing. Also, it describes the findings of a study in the present tense. That is also the case when expressing people’s claims and opinions .
Instances to Use Past Tense in an Essay
You must be careful with the tense you use in your essay. Each tense does come with its demands. For instance, past tense is ideal for emphasizing that people do not accept a particular idea. Use past tense to describe that idea for easier understanding.
If your essay describes historical events, you have to use past tense. It makes the description clearer to the reader. This is a clear indication that they can get a picture of the turn of events. This is very crucial for the flow of your essay.
Reading it becomes engaging and enjoyable without any sense of struggling to understand ideas.
Instances to Use Future Tense in an Essay
Not often do students use the future tense in essays. They either use present and past tenses, the former being the most common.
But some instances permit the use of future tense. It does play a significant role.
Use future tense to describe your essay’s research predictions, methods, and aims. It becomes easier to demystify what the researcher is up to.
Besides, if you recommend research sources or state the application of study findings, then use future tense. You can easily describe something that is yet to happen or likely to occur in the future.
Can You Combine All Tenses in Essay Writing?
You can also use all tenses in your essay. However, you need to take this step with a lot of caution. Remember, the reader needs to get your message. You have to do that with some pomp to make your essay an enticing read .
Combining all tenses will certainly do that job for you.
Describe the cause and impact of interlocking events in an essay by combining all tenses. Your target audience can now get the hang of the events from a much broader perceptive. However, you have to respect time settings.
It is crucial to avoid any confusion that might distort your message. Ensure you get rid of any sophistication bound to disturb the flow of thoughts in your write-up.
Combining all tenses can be a win or a loss for you. It depends on the context of your essay. Besides, you need to mind your reader.
Your essay should be on a standard that is easier to comprehend. Thus, proceed with caution.
Make your point in a manner that captures the reader’s attention. Using all tenses can help you achieve that feat. However, the tenses should not appear haphazardly. If you are not careful, you might make it hard for your reader to understand your insinuating description.
Choosing the right tense for your essay is fundamental. It ensures that you can engage your reader in a comprehensive context easily. It starts by knowing when to use present, past, and future tense or combine them.
If your essay is about current events, it must be in the present tense. The reader gets to know what is happening at the very moment.
Use past tense to write an essay on past events. Describing those events will be much easier. You will do it with clarity hence not causing any confusion. On the other side, the future tense suits the description of events yet to occur.
You can also use the future tense to predict events that are about to happen. And if you want to polish your essay, care to combine all tenses, but do it with caution.
Watch this video to learn more about this.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

How To Prepare And Write Your Ap Biology Exam
AP Biology Exam Answers: Questions and How to prepare for it

using you in essay writing
Can you Use ‘You’ in Essays or Research Paper: Best Practice

professor not grading assignments
Professor not Grading Assignments on time? Here’s what to do
College Nut
Should College Essays be in Present or Past Tense?
Understanding the purpose of college essays.
College essays are an essential part of the college application process, providing an opportunity for students to showcase their personality, character, and writing abilities. These essays can be personal statements, creative writing, or reflection pieces, but they all serve the same purpose: to give admissions committees a glimpse into who the student is beyond their grades and test scores.
The Importance of Tense in Writing
Tense is an essential aspect of writing, determining the time frame in which the events of the text take place. In English, there are three main tenses: past, present, and future. Each of these has a specific purpose, and their use depends on the context of the text.
The Pros and Cons of Using the Present Tense in College Essays
The present tense is used to describe events that are happening at the moment or are ongoing. It can also be used to describe facts or general truths. Using the present tense in college essays can have some advantages, such as:
1. Creating a Sense of Presence
Using the present tense can make the writing feel more immediate, as if the events are happening right now. This can help the reader feel more engaged with the text and create a stronger emotional connection to the writer.
2. Highlighting Personal Growth
Using the present tense can be an effective way to showcase how the writer has grown over time. By describing their current thoughts and feelings, the writer can demonstrate how they have learned and changed since the events they are describing.
On the other hand, using the present tense can also have some disadvantages:

1. Causing Confusion
Using the present tense to describe past events can be confusing for the reader, who may not be sure when the events took place. This can make it harder for the reader to follow the narrative and understand the writer’s message.
2. Limiting Flexibility
Using the present tense can limit the writer’s flexibility in terms of storytelling. It can be challenging to describe events that took place in the past using the present tense without it feeling awkward or forced.
The Pros and Cons of Using the Past Tense in College Essays
The past tense is used to describe events that have already happened. It is the most common tense used in storytelling because it provides a clear chronological order of events. Using the past tense in college essays can have some advantages, such as:
1. Creating a Clear Narrative
Using the past tense can help to create a clear narrative structure, making it easier for the reader to follow along with the writer’s story. It also provides a sense of closure, as the events described have already happened.
2. Demonstrating Reflection
Using the past tense allows the writer to reflect on past events, providing insights into their thoughts and feelings at the time. This can help the reader understand the writer’s growth and development over time.
However, using the past tense can also have some disadvantages:
1. Creating Distance
Using the past tense can create a sense of distance between the reader and the events being described. This can make it harder for the reader to feel emotionally connected to the writer and their story.
2. Limiting Creativity
Using the past tense can limit the writer’s creativity, as they are bound by the chronological order of events. It can be challenging to describe events out of order or use creative storytelling techniques when using the past tense.
The choice of tense in college essays ultimately depends on the writer’s goals and the context of the text. Both the present and past tenses have their advantages and disadvantages, and there is no one right answer. However, it is essential to consider the reader’s experience and readability when making this decision. By understanding the purpose of college essays and the role of tense in writing, students can create compelling and engaging essays that showcase their unique voice and perspective.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Common Issues with Tenses

4-minute read
- 6th June 2022
Using verbs correctly is one of the trickiest parts of writing . Anyone can make mistakes with verb tenses, but it’s especially easy for those who aren’t native English speakers. In this post, we’ll explain the nine main tenses and highlight the most common mistakes writers make when using them. So, read on if you want to make verb tense mistakes a thing of the past!
What Are the Main Tenses in English?
Every action happens in the past, present, or future. Each of these time frames is further divided into the simple , continuous, or perfect form. Here’s an example of each:
● Simple past – things that happened before now:
I wrote an essay last week.
● Past continuous – an ongoing action in the past:
He was writing a poem yesterday morning.
● Past perfect – an action that ended before a point in the past:
By lunchtime, he had written six lines.
● Simple present – a habitual action:
She writes at her desk by the window.
The simple present is also used to describe actions happening at this moment:
I want a desk like that.
● Present continuous – an ongoing action happening right now:
I am writing a future bestseller!
● Present perfect – an action that began in the past and is still happening now, or one that happened at an unspecified time:
He has written stories since he was a child.
I have written 1000 birthday cards.
● Simple future – things that’ll happen and then stop happening:
I will read the first chapter of the book tomorrow.
● Future continuous – things that’ll begin in the future and continue for some time:
I will be writing a book report.
● Future perfect – an action that’ll end at some point in the future:
I will have written it by the end of the week.
With so many tenses to choose from, it’s no wonder people make mistakes. Don’t worry, though, because for most academic writing, you don’t need to use all of them. Essays and assignments are nearly always written in the simple present tense, and if you’re describing your own research methodology (e.g., an experiment or survey), you would use the simple past tense.
What Are the Most Common Verb Tense Errors?
Mistakes with verb tenses usually fall into one of three categories:
- Changing from one tense to another.
- Overusing continuous tenses.
- Confusion with irregular verbs.
Use tenses consistently
Your readers will get confused if you switch tenses unexpectedly:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
The car drove into the tunnel, and it comes out the other end. ✘
The car drove into the tunnel, and it came out the other end. ✔
The car drives into the tunnel, and it comes out the other end. ✔
This doesn’t mean changing tense mid-sentence is always wrong. But make sure you’re saying what you intend to say!
I practiced using different tenses, and now I understand them better. ✔
Limit your use of continuous tenses
Your writing can easily become quite clunky if you use a lot of continuous verb forms:
It was pouring rain while we were camping, and the children were complaining because their blankets were getting wet.
It poured rain while we were camping, and the children complained because their blankets got wet.
The first sentence contains four present participles (i.e., verb forms that end in ing ), which makes it quite a chore to read and rather repetitive. In the second version, we’ve replaced three of them with the simple past tense. This makes the writing more concise and easier to read.
Watch out for irregular verbs
We form the simple past tense and the past participle of most verbs by simply adding ed to the base verb (e.g., walk – walked; open – opened ). However, there are many verbs that don’t obey such rules, and we call these irregular verbs . Unfortunately, there’s no easy way to learn how to conjugate irregular verbs because they don’t follow an obvious pattern, as these examples show:
I buyed bought a gigantic jar of honey.
It costed cost $10.
I hided hid it in the back of the cupboard.
I soon forgetted forgot all about it.
As you read English texts and listen to people speaking in conversation, you’ll recognize more irregular verbs and become familiar with how they work.
Proofreading for Perfect Grammar
We hope you now feel confident about using different tenses in your writing. If you’d like an expert to check your work for incorrect verbs and any other mistakes in grammar, spelling, or punctuation, our proofreaders are here to help. Send us a free trial document to find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
The benefits of using an online proofreading service.
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
3-minute read
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Writing academically: Tenses
- Academic style
- Personal pronouns
- Contractions
- Abbreviations
- Signposting
- Paragraph structure
- Using sources in your writing
Jump to content on this page:
“Quote” Author, Book
In simple terms, verb tenses refer to the past, present or future. Verb tenses tell the reader when something happened, and are used to convey what is or is not known at the time of writing.

If you are reporting on your own or others’ specific research activities (such as methods that were used, or results that were found) then you would generally use the past tense.
- An experiment was conducted…
- It was found that…
- Brown (2010) found that…
In the example based on Brown’s research, the writer was referring to a specific result that Brown found when he conducted his research in 2010, and is therefore written in the past tense.

Present tense
Use the present tense if you are making general statements that draw on previous research, and usually indicates what is known at the time of writing , for example:
Example:
- The research shows...
- The results of the experiment suggest that…
- Brown’s (2010) study suggests that…
In the above example based on Brown’s research, the writer makes a reference to what is known at the time of writing , and so it is written in the present tense.
Here is an example of using both the past and present tense in your writing:
Example: Brown (2010) conducted a survey of 1000 students. The results of his survey suggest that all his students are geniuses.
In this example the writer refers to a specific survey that Brown conducted (past tense) in 2010. The writer then conveys how the results of Brown’s survey are still considered worthy today by writing in the present tense ( suggest ).
Compare this to the following example:
Example: Brown (2010) conducted a survey of 1000 students. The results of his survey suggested that all his students were geniuses, but his later work (Brown, 2015) suggests this is not the case.
As previously, Brown’s specific study of 2010 is referred to in the past tense. But we now find that a later study by Brown (2015) appears to be in disagreement with his earlier 2010 study. Consequently the writer now refers to the conclusions drawn from the 2010 study in the past tense ( suggested ), and it is the results of Brown’s 2015 study – which represents what is known at the time of writing - that is referred to in the present tense ( suggests ).

Future tense
The future tense is not often used in academic writing because it tends to imply a level of certainty that academics can find uncomfortable. If you use verbs such as will or shall then be certain of your certainty! Otherwise use verbs that express possibility, such as could or may .
The exception is in research proposals where you are writing about what you intend to do - so the future tense is used.
- << Previous: Personal pronouns
- Next: Voice >>
- Last Updated: Nov 10, 2023 4:11 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/writing
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
- Admissions Essays
- Books and Manuscripts
- Business Proofreading and Editing
- Dissertations
- Editing Tools
- Personal Statements
- Professional Writing
- Proofreading and Editing
- Thesis Proposals
- Uncategorized
- Working From Home
- Writing Fiction
- Writing Guides
What Tense Should I Use in Writing?

Get 400 words proofread and edited for free
When writing, people are often confused about what tense they should use. Should I write this MLA history paper in past tense? Should I write my short story in present or past tense? How about a resume: should I write my job entries in present or past? And these people are right to be confused because what tense you should use varies widely depending on your writing style and your purpose.
Academic (Four Main Styles)
APA/Harvard: Per APA (and its non-American variant, Harvard), you should primarily use past tense, especially in literature reviews where you’re talking about authors’ past studies. It should be:
“Johnson (2008) argued . . .”
“Johnson (2008) argues . . . .”
Get a free sample proofread and edit for your document. Two professional proofreaders will proofread and edit your document.
The same is true for your Results and Method sections, but APA makes an exception for Discussion sections (where you examine your conclusions and the implications of the study), which can be in present tense if it better conveys your meaning.
MLA: This style is a bit more straightforward. Per MLA, you should be almost always using present tense:
“In To Kill a Mockingbird , Atticus Finch argues . . .”
If you need to differentiate time, you should use present perfect tense:
“For many years, Scout has been worrying about . . . .”
If you must, you can use some past tense, but keep it to a minimum.
Chicago: This style is a bit more lenient. Per Chicago, you can use either present or past (Though it’s best to use present when discussing literature and past when writing about history.), but make sure you stay consistent. If you switch, make sure you need to, such as:
The Romans used various military strategies, some of which are still in use today.
AP: AP, which is used by news media, is also more flexible. There is no set tense; instead, you should be endeavoring to use present/past/future as necessary to make sure the events you are describing are as clear as possible. AP also recommends using time words (today, tomorrow, March 17, etc.) to anchor your piece and further reduce ambiguity.
When talking about your job experience in resumes, the rule is simple: Use present tense for current positions:
Lead team in HVAC solutions
And use past tense for past positions:
Led team in HVAC solutions
Business Plan
Professors and potential investors have different views on what tense a business plan should be written in, but definitely you should be using either future or present tense. Some people argue that you should always write a business plan in future tense because you’re talking about your future plans.
But there’s another school of thought that recommends using present tense instead because this will allow your plan to stay current as you develop it and you develop your business. In other words, as you develop your business, you develop your plan, and it stays current with what you’re doing.

Above all, fictional writing needs to be consistent in its tense. Just as above, don’t switch unless you must. (BTW, fictional writing is done in Chicago Style.)
Everything Else
For everything else, such as business letters, admission essays, and e-mails, and especially in more informal contexts, just use your best judgment and write in whatever tense feels right to you. Go with your instincts and remember that, unless you’re writing in a formal academic context, you have more leeway to do whatever you like.
Just remember, for all styles and purposes, always be consistent. Try to pick one tense and stick with it throughout your piece. If you have to switch tenses, make it very obvious why you are doing so, and at least try to start new paragraphs for new tenses.
That’s it, I hope you have/had/will have good luck in your writing!

Get a Free Sample
We will get your free sample back in three to six hours!
We proofread documents 24/7 Support 888-833-8385

Customer Service
Get in touch.
ProofreadingPal LLC 105 Iowa Ave., Ste. 214 Iowa City, IA 52240
Call Us 888-833-8385
Live Customer Support Hours Sun.–Thur. 8 a.m. to midnight CT Fri. and Sat. 8 a.m. to 6 p.m. CT
Submit Documents 24/7
© 2010 - 2020 ProofreadingPal LLC - All Rights Reserved.
The Vocative Comma Is Important, People! · September 25, 2022
8 Tips to Make Your Writing Sound More Formal · August 29, 2022
Worlde Tips and Tricks · March 10, 2022
Worlde Tips and Tricks · February 25, 2022
Top 4 Misspelled Words · November 5, 2021
How to Capitalize Medicine · October 1, 2021
How to Capitalize Medicine · August 18, 2021
4 Fixes for Comment Boxes in MS Word · January 17, 2021
How to Avoid Wordiness · July 15, 2020
Write an Effective Blog Post · June 9, 2020
Proofreading Services Rates · April 19, 2020
How to Make Your Writing More Inclusive · March 5, 2020
How to Make Your Writing More Inclusive · February 27, 2020
Guide to Olde English · December 27, 2019
Guide to Olde English · December 26, 2019
Common Apostrophe Errors · December 19, 2019
Guide to Olde English · December 18, 2019
Capitalization in APA, Chicago, MLA, and AP · August 27, 2019
Avoiding Common Capitalization Errors · July 31, 2019
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises
Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises
Published on August 22, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on October 23, 2023.
The simple past tense is a verb form used to refer to an action or series of actions that were completed in the past.
The simple past tense of regular verbs is formed by adding “-ed” to the infinitive form of the verb (e.g., “cook” becomes “cooked”). Most verbs in the simple past take the same form regardless of the subject (e.g., “He worked/we worked”).
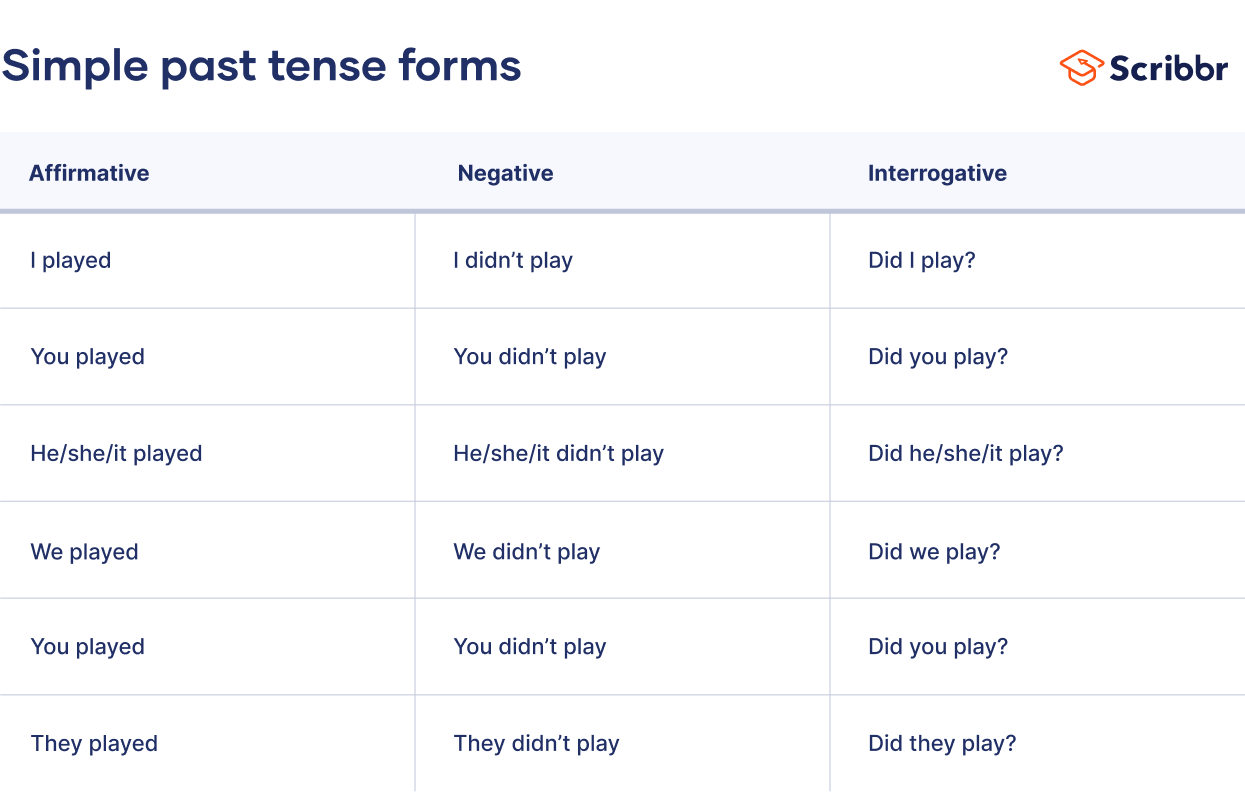
Table of contents
How to use the simple past, present perfect vs. past simple, simple past vs. past perfect, how to form negatives, how to form questions, how to form the passive voice, exercises: simple past tense, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions about the simple past tense.
The simple past tense (also called the past simple or preterite ) is used to describe an action or series of actions that occurred in the past.
The past simple of regular verbs is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “talk” becomes “talked”).
Irregular verbs don’t follow a specific pattern: some take the same form as the infinitive (e.g., “put”), while others change completely (e.g., “go” becomes “went”).
Most verbs in the simple past tense don’t follow subject-verb agreement (i.e., they don’t change form depending on the subject).
Ariana rented a car and drove to the coast.
We visited a museum, walked the Champs-Élysées, and dined at a fancy restaurant.
Forming the simple past
The simple past of regular verbs is usually formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the verb (e.g., “guess” becomes “guessed”). However, this can vary depending on the verb’s ending.
Irregular verb: “be”
The stative verb “be” in the simple past tense is used to describe unchanging past conditions (e.g., “My father was a good man”) and temporary past situations (e.g., “The children were tired”). Unlike other verbs in the simple past, “be” changes form depending on the subject, as shown in the table below.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Both the present perfect and past simple tenses are used to refer to past action. However, they serve different purposes:
- The present perfect is used to refer to an action that began in the past and may continue or to an action that took place in the past and has present consequences.
- The past simple is typically used to describe an action that was completed in the past and is not ongoing.
I have run a marathon before. [I may run a marathon again]
I was a vegetarian when I was younger.
While the past simple is used to describe an action or series of actions that occurred in the past, the past perfect is used to indicate that an action was completed before another past action began.
In the past simple tense, negative statements are formed by adding “did not” (or the contraction “didn’t”) between the subject and the infinitive form of the verb.
For the verb “be,” negative statements are formed by adding “was not/were not” (or the contractions “wasn’t/weren’t”) after the subject .
To ask a yes–no question using the simple past, add “did” before the subject and the infinitive form of the verb.
To ask a question starting with a wh-word (an interrogative pronoun like “who” or an interrogative adverb like “where”), follow the same word order as above, but add the pronoun or adverb at the start of the sentence.
Why did Eva leave so early?
Passive sentences are ones in which the subject is not the person or thing performing the action. Instead, the subject is the person or thing being acted upon.
In the past simple, passive constructions are formed using a subject , “was”/“were,” and the past participle of the verb.
Maria was ignored by the salesman.
Practice using the simple past correctly with the exercises below. In the blank space in each sentence, fill in the correct simple past form based on the subject and verb specified (e.g., “[he / talk]” becomes “he talked”). Some answers may also be negative statements or questions.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- __________ [you / go] to the shop this morning.
- __________ [they / play] a board game.
- __________ [my son / not / study] for the exam.
- __________ [the band / rehearse] every day this week.
- __________ [I / plan] to be home by six!
- When __________ [you / travel] to France?
- The simple past form of the irregular verb “go” is “went.”
- The simple past form of the regular verb “play” is “played.”
- In the simple past tense, negative statements are formed by adding “did not” (or the contraction “didn’t”) between the subject (“my son”) and the infinitive form of the verb (“study”).
- The simple past form of the regular verb “rehearse” is “rehearsed.”
- For short verbs, where the last three letters follow a consonant-vowel-consonant pattern (e.g., “plan”), you double the final consonant and add “-ed.”
- To ask a question starting with a wh-word, add the wh-word at the start of the sentence, followed by “did,” the subject (“you”), and the infinitive form of the verb (“travel”).
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
The simple past tense of the verb “read” is “read” (e.g., “I read a book last week”).
While “read” is spelled the same in both its past and present forms, its pronunciation differs depending on the tense :
- The simple present form is pronounced “reed.”
- The simple past form is pronounced “red.”
The simple past tense of the verb “teach” is “taught” (e.g., “You taught me a lesson”).
While the simple past of a regular verb is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “talk” becomes “talked”), irregular verbs like “teach” don’t follow a specific pattern.
The simple past tense of the verb “go” is “went” (e.g., “Ava went to Spain”).
While the simple past of a regular verb is typically formed by adding “-ed” to the end of the infinitive (e.g., “jump” becomes “jumped”), irregular verbs like “go” don’t follow a specific pattern.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, October 23). Simple Past Tense | Examples & Exercises. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/simple-past-tense/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, simple present tense | examples, use & worksheet, present continuous tense | examples & exercises, present perfect continuous | examples & exercises, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

How to Use Present and Past Tense in Essay Writing
Today we look at how we use present and past tenses in our essay writing to convery our message through our best of knowledge with a proper tone.
Essay writing! You might be thinking that why is a blog post on essay writing? It is something everyone can do. Yes, you are very correct everyone can do it but the point is who does it in the right way.

Suppose you need to write an essay in an exam in your answer sheet. The most important thing is that you need to keep the content relevant and keep a check on your verb tenses. While you would be moving fro tense to tense it may create some confusion while writing or while transitioning the content. Often you would need to switch tense which might upset the sequence of narration.
1. Try to Write the Essays in Present Tense
Generally, while writing essays, the writer must always use the present tense. If you wish to use the past tense then you need to refer to the events of the past. It shows the author’s ideas in a historical context. There is an exception to all these rules which explains that it is a narrative essay through which a writer can choose the past or present tense in the writing style. But the point that needs to consider is that the tense should remain consistent throughout the content.
When you are completely indulging in the writing process then it shows your effectiveness in every essay possible. Simple said, the answer would depend on the type of essay where you would be writing. When you are shifting tense from one to another, it becomes a bit distracting to the reader and they might leave it in the middle.
If you are discussing the narrative essay then it might become a bit of exception to the rule just because they will tell a fiction (a story). If you are relying on the tense (which will be past) to narrate some incidents or events then you need to refer to the writer’s perspective and his ideas just like historical entities.
If in an essay you are trying to state some facts which would refer to some perpetual or actions then you need to use the present tense. Suppose you are discussing your own ideas or expressing a particular work then also you can use the present tense.
You can use the present tense to describe the action in the work. It can also be some narrative fictional.
2. If you are trying to use multiple tenses in your essay then make sure that you do not lose the clarity in the work.
It often happens when the writer is trying to mix the tense while explaining two or three multiple situations or stories. The break between the tenses will confuse your audience or readers. Hence you need to be very careful while making that smooth transition between the tenses.
3. You can Mix the tenses For Bringing Out Various Colors And Variety
It is very important to mix tenses wherever it is necessary and appropriate but it should signal the changes between the time setting. When you mix the tenses it will show the major cause and effect of inter-locking events. The beautiful use of past and perfect is mainly used to show or describe the scene of an accident being very effective. It will give you a quality that will help you in haunting, live-on-memory, or any other event.
4. Practice Practice Practice….
When you are dealing with multiple sentences in a single content then you must practice using such sentences in your normal article writing routine. It will provide you a platform where you can try out your hand then proofread it to make sure everything is correct. Once this is done use can do the same for your main content. This way you will have a good practice of things and you won’t make any mistake.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Contact [email protected]
- Writing History: Past Tense versus Present Tense

Earlier this week, I wrote about verb tense and knowing when to use past perfect tense in historical writing . This was in response to Laura asking me for a post on verb tense in historical writing. Thanks again to Laura for the great suggestion for a series of posts!
This time, we’re going to focus on whether it’s okay to use present tense in historical writing, which generates a lot of debate and controversy within history writing circles.
Past or present?
When I was getting a history degree as an undergraduate, I was always taught to write my history papers in the past tense. This was true for term papers, as well as for the sizeable seminar paper I was required to submit as the capstone for my degree.
This requirement differed from what I’d always been taught in literature classes, which was to discuss texts in present tense. So, in a literature paper, no matter how old of a text that I was analyzing, I always wrote about it in the present tense.
As someone who double-majored in both English and history, I’ll confess to sometimes confusing myself when I was working on papers in each discipline, but the requirements make sense for each field. For historians, traditionally, the past is the past, and writing about it now doesn’t make it become the present. On the flip side, literature studies approach their field from a less time-dependent perspective—the elements that one can analyze from a text are not constrained by the time period in which you’re writing.
So, I learned pretty quickly to write about novels and short stories and poems in present tense for literature classes and then write about historical events and primary and secondary sources in past tense for my history classes. Sometimes, that meant writing about novels in past tense for history classes.
In recent years, though, it’s been increasingly more common for historians and historical nonfiction writers to use present tense, which is referred to as historical present when applied to events that happened in the past. Chicago Manual of Style , the default style guide for American publishing, has no objection to the use of historical present.
As you can imagine, this change in approach to tense is not universally accepted.
Battle lines are drawn
If you do a deep dive on the internet about present tense in historical nonfiction writing, you will find a lot of strong opinions on both sides.
What both sides agree on (but very much disagree on the desirability of) is that present tense brings an immediacy to discussions of the past that past tense doesn’t.
Let’s look at our examples from last time when we were playing around with past versus present tense.
“Hitler invaded Poland in September 1939” versus “Hitler invades Poland in September 1939.”
“In 1953, Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay successfully summited Everest” versus “In 1953, Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay successfully summit Everest.”
“General Pickett’s men advanced against Cemetery Ridge” versus “General Pickett’s men advance against Cemetery Ridge.”
For proponents of present tense, the advantage here is that it puts you, the reader, right there and makes the event more vivid and immediate to you, no matter how many years, decades, or centuries have passed since then. You’re right there as tanks roll through Poland, as Hillary and Norgay set foot on the highest mountain in the world, and as soldiers start advancing across a brutal battlefield.
It’s a standard narrative technique, and they see no reason not to employ it to draw readers in.
For opponents of past tense, the problem is that you’re not there and never will be, no matter how much you use present tense. For them, it seems distracting and gimmicky and can also even convey a lack of neutrality and distance that historical writing often strives for. It’s essentially too informal and excited sounding.
Should I use present or past tense when I’m writing history?
For me, personally, my inclination is to write history in past tense. That’s what I was taught to do, and I don’t think there’s anything inherently wrong or even boring about past tense. As someone who also has a background in literature and is very interested in applying fictional techniques to nonfiction narrative, though, I can also see the argument in favor of how immediately gripping present tense can be.
My advice, therefore, would depend on the context of your writing—for whom are you writing?
If you’re writing for a general audience, they’re unlikely to have strong opinions on what tense you use, and they may be in need of more persuading to read history. In that case, present tense likely won’t cause you any problems and may even be a selling point for some of those reluctant readers. Be aware, though, that some people who aren’t historians are also not a fan of present tense. They trip over it for the same reason some historians dislike it–they feel like it’s an artificial attempt to make something seem like it’s happening now and they can’t suspend their disbelief to roll with it.
If you’re writing for an audience of historians or history buffs, they likely do have strong opinions on using past versus present tense and are already motivated to read history for the sake of history. In that case, erring on the side of caution and sticking with past tense is your safest bet and can even make you seem more professional. Fans of historical present may not be pleased, but you’re not technically doing anything wrong by following the traditional convention here.
Who’s publishing you is also worth considering for this issue. If you’re working with a history publisher, they may well have a marked preference, so it’s worth asking or checking for press-specific guidelines to see if they explain their stance on tense. More general interest publishers are unlikely to be as opinionated—though they might be—and will often default to Chicago Manual of Style , which, as noted earlier, isn’t opposed to present tense for past events. For self-publishing, likely audience is your best bet for determining whether to use past or present tense in writing about history.
Your purpose for writing may also play into your decision on which tense to use and will likely intersect with your decision on the intended audience. If your primary purpose is to provide a narrative about history, present tense may help you bring those events to life quite vividly. If your primary purpose is to analyze, however, present tense may not strike the right academic tone like past tense would. As a rule, though there are some exceptions, a focus on narrative also suggests what you’re working on is likely targeted toward a more general audience than something that’s primary purpose is analysis, which again would make present tense more likely to work for the former and past tense more appropriate for the latter.
Is present tense ever okay in historical writing for people who don’t like historical present?
Most of the heated discussions that break out about tense (I resisted the urge to make a pun about tense arguments since I already used that in the last post 😊 ) relate specifically to talking about the past.
There are times when present tense is unavoidable in historical writing, and in these instances, even people who are not fans of historical present don’t object to using present tense in these scenarios.
One of these instances is if something is still a matter of current fact. Even if you talk about the invasion of Poland in 1939 in past tense, you wouldn’t say “Warsaw was in Poland.” It’s still in Poland today, just as it was in 1939, so you’d use present tense there: “Warsaw is in Poland.” If you’re dealing with a historical context that has had fluid boundaries, then switching tense may even help clarify that for readers. (For example: “Today, Lviv is part of Ukraine, but in 1939, it was in Poland and called Lwów.”)
Providing one’s own conclusions is also a valid reason to use present tense in historical writing that is otherwise using past tense. So, in a hypothetical discussion of the start of World War II, the conclusions you’re arguing for are when you’d switch to present tense. It’s also okay to discuss contemporary research in present tense, as well as effects of the past that continue into the present day. Again, these aren’t scenarios where you’re writing about the past anymore. In these instances, you’re writing about contemporary effects, thoughts, and arguments, so present tense makes sense. Past tense may even seem odd and stilted in these moments.
I’ve not decided on the next topic I’ll write about it. I have a couple of different topics I’m considering, but I’m also open to suggestions. Are there any questions you have about writing that you’d like me to answer?
Recommended Posts

Tombstone versus Wyatt Earp: Foils

Tombstone versus Wyatt Earp: Antagonists

Tombstone versus Wyatt Earp: Conflict

Tombstone versus Wyatt Earp: Narrative Structure

Essay Past Tense
essayed past tense of essay is essayed.
Essay verb forms
Conjugation of essay.
- What is the past tense of euchre in English?
- What is the second form of verb euhemerize?
- What is the third form of verb eulogise in English?
- What is the conjugation of eulogize in English?
- Conjugate eunuchate in English?
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quick answer: In general, when writing most essays, one should use present tense, using past tense if referring to events of the past or an author's ideas in an historical context. An exception to ...
For example, the past tense can be used in methodology and results sections. Likewise, the past tense is useful when writing a case study, since this is almost always about something that has already occurred. While you can use the past tense in a literature review, saying that someone 'believed' something may imply that they changed their ...
The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future. In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous. The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have, while the ...
There are three tenses that make up 98% of the tensed verbs used in academic writing. The most common tense is present simple, followed by past simple and present perfect. These tenses can be used both in passive and active voice. Below are the main functions that these three tenses have in academic writing.
In a college essay, you can be creative with your language. When writing about the past, you can use the present tense to make the reader feel as if they were there in the moment with you. But make sure to maintain consistency and when in doubt, default to the correct verb tense according to the time you're writing about.
Revised on 11 September 2023. Tense communicates an event's location in time. The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future. In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect ...
It should appear in the present tense, "twists," or the other verbs should be changed to the past tense as well. Switching verb tenses upsets the time sequence of narration. "The Literary Present". When you quote directly from a text or allude to the events in a story (as in a brief plot summary), you should use "the literary present."
Past Tense: Alfred burned the cakes. Future Tense: Alfred will burn the cakes. In the first example, the present tense verb "burns" suggests that it's happening now. The past tense verb "burned", however, shows that it has already happened. And by adding the helping verb "will," we can instead suggest that the action is going to ...
The most typical verb tense in academic writing is: _____, and it is usually in the following paragraphs of an academic essay: _____. The Present Simple Tense is used to:_____. The Past Simple Tense has two main functions in most academic fields:
The APA Exception. Remember that APA format does not use the "historical present," even when quoting, instead using the past or present-past tense to summarize an author's words or introduce a quote. It's a good idea to check with your instructor, especially in a science class, before writing an essay to see what tense you should use ...
It starts by knowing when to use present, past, and future tense or combine them. If your essay is about current events, it must be in the present tense. The reader gets to know what is happening at the very moment. Use past tense to write an essay on past events. Describing those events will be much easier.
Literary works, paintings, films, and other artistic creations are assumed to exist in an eternal present. Therefore, when you write about writers or artists as they express themselves in their work, use the present tense. The Basic Rule: You should use the past tense when discussing historical events, and you should use the literary present ...
The flexible use of tenses brings the reader the joy of being "in the present" for many moments while, in other moments, gaining the benefit of the insights and reflection that only a past-tense narrator can provide. Here's an example from a wonderful essay by Tim Hillegonds, "And Then We Are Leaving," published in the literary ...
The Pros and Cons of Using the Past Tense in College Essays. The past tense is used to describe events that have already happened. It is the most common tense used in storytelling because it provides a clear chronological order of events. Using the past tense in college essays can have some advantages, such as: 1. Creating a Clear Narrative
Simple past - things that happened before now: I wrote an essay last week. Past continuous - an ongoing action in the past: He was writing a poem yesterday morning. Past perfect - an action that ended before a point in the past: By lunchtime, he had written six lines. Simple present - a habitual action: She writes at her desk by the window.
Here is an example of using both the past and present tense in your writing: Example: Brown (2010) conducted a survey of 1000 students. The results of his survey suggest that all his students are geniuses. In this example the writer refers to a specific survey that Brown conducted (past tense) in 2010. The writer then conveys how the results of ...
APA/Harvard: Per APA (and its non-American variant, Harvard), you should primarily use past tense, especially in literature reviews where you're talking about authors' past studies. It should be: "Johnson (2008) argued . . .". not. "Johnson (2008) argues . . . .". Get a free sample proofread and edit for your document.
Here are some sample tense traps and their simple fixes: 1. "Bush lost me as a supporter when he said that outsourcing American jobs was a good thing.". This sentence from a newspaper column correctly reports in the past tense — at the beginning of the sentence. But Bush likely said something like this: "Outsourcing American jobs is a ...
How to use the simple past. The simple past tense (also called the past simple or preterite) is used to describe an action or series of actions that occurred in the past.. The past simple of regular verbs is typically formed by adding "-ed" to the end of the infinitive (e.g., "talk" becomes "talked").. Irregular verbs don't follow a specific pattern: some take the same form as ...
1. Try to Write the Essays in Present Tense. Generally, while writing essays, the writer must always use the present tense. If you wish to use the past tense then you need to refer to the events of the past. It shows the author's ideas in a historical context. There is an exception to all these rules which explains that it is a narrative ...
Sometimes, that meant writing about novels in past tense for history classes. In recent years, though, it's been increasingly more common for historians and historical nonfiction writers to use present tense, which is referred to as historical present when applied to events that happened in the past. Chicago Manual of Style, the default style ...
This is a reference page for essay verb forms in present, past and participle tenses. Find conjugation of essay. Check past tense of essay here. website for synonyms, antonyms, verb conjugations and translations
Ms. Taylor and Ms. Hunt-Hendrix are political organizers and the authors of the book "Solidarity: The Past, Present, and Future of a World-Changing Idea."
Mr. Netanyahu's government has had a tense relationship with Al Jazeera for years, but the Hamas-led attack on Oct. 7 escalated tensions. Mr. Netanyahu has called Al Jazeera a "Hamas ...