Reflection of Photographic Arts Reflective Essay
Learning the fundamentals of photographic arts improves the success of an artist. The fundamentals of photographic arts combine technical brilliance and creativity. We can add value to a story when we learn the technical and creative aspects of photography. Image technology contributes to the change in photographic dimensions (Barba, 2001).
Today, artists edit images using digital technology rather than creative reasoning. The photographer uses creative skills to produce quality image with dull scenes.
Anyone can capture an image without skill, but a creative artist produces a masterpiece in one capture. The fundamental of photographic arts is an advantage to the artist. The knowledge influences the choice of image and the position of the subject in the photograph (Barba, 2001).
Fundamentals of photographic arts influences the way we communicate messages or stories. A balanced photograph taken with prior knowledge of the basics of photographic arts can be a masterpiece. The message will easily flow with the audience and can be accepted generally. The image structure determines the way the message is transferred from one medium to another.
The channel of communication can be influenced by the prior knowledge of the basic photographic arts. The image must be taken with balanced or informal capture. The viewer is pleased with pictures that tell different stories (Barba, 2001).
The knowledge of the fundamentals of photographic arts creates a world of possibilities. A creative artist can capture any image to create a daring story or message. The composition of the image can be arranged to accommodate interesting aspects of a story.
An artist’s readiness to capture an image can be an important obstacle. No matter the location or scene, an informed artist can create a combination of balance and informal image to tell a story. An image placed in the middle of a picture frame will evoke the viewer’s emotions. The ability to recognize the subject of the image creates the difference between artists.
The knowledge of the fundamentals of photographic arts has equipped me to create quality photographs. I learnt new approach to photography. I learned to be ready for every capture. This is the first rule of photography. The subject of the image can be the most tangible object in the photograph. The subject must be captured in the center of each event.
The image must have an image structure; this differentiates talented artist from the lot. I will position my images in the center of each frame and the image structure will be balanced. Color and lights will form a part of my image and a shadow background must be elevated in each photograph. Each tool contributes to the capture and presentation of a story.
My method of capture will improve with the knowledge of the fundamentals of photographic arts. I strengthened my creative skills with the basic knowledge of photographic arts. The location of the subject does not affect the capture of the image. My passion for quality image has improved and each capture defines my strength in the art of photography. I understood the benefits of each element of the communication process.
Finally, an artist views the image from a photographic eye and captures a scene with strong image structure. The general acceptance of an image or photograph is determined by the composition of the photograph. The composition of the photograph is improved by the knowledge of the fundamentals of photographic arts.
Barba, D. (2001). Image quality assessment: From site errors to global appreciation of quality . London, England: Macmillan Press.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, July 5). Reflection of Photographic Arts. https://ivypanda.com/essays/reflection-of-photographic-arts/
"Reflection of Photographic Arts." IvyPanda , 5 July 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/reflection-of-photographic-arts/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Reflection of Photographic Arts'. 5 July.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Reflection of Photographic Arts." July 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/reflection-of-photographic-arts/.
1. IvyPanda . "Reflection of Photographic Arts." July 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/reflection-of-photographic-arts/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Reflection of Photographic Arts." July 5, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/reflection-of-photographic-arts/.
- Photographic Representation of War
- Photo Art: Photographic Exhibition
- Photographic Exhibition in Melbourne Australia
- Photographic Pioneer: Paul Strand
- Photographic Approaches for Manuel Alvarez Bravo and Ann Parker
- Hector Mediavilla Photographic Series "The Congolese Sape"
- Personal Interest in Photography
- Photography: Is It Possible to Recapture the Past?
- Photography as a Mass Medium
- Photography and Its History
- A Comparison of Photographic Approaches Towards American Culture
- Photographic Approaches Towards Landscapes: Peter Henry Emerson
- Ethics of Digital Manipulation
- The Photographic Approaches Towards American Culture of Robert Frank and Gary Winogrand
- Melancholy Objects in Photography

‘On Photography’ by Susan Sontag |A Comprehensive Summary and Insightful Exploration
In the vibrant tapestry of human history, 1977 marked the birth of a masterpiece that forever altered our perception of photography. This was the year Susan Sontag, a luminary in the realm of critical thought, introduced us to her seminal work, “On Photography”. A collection of six essays, this book was not merely about the technicalities of photography, but rather, it delved into the philosophical underpinnings of this art form. It posed questions that continue to haunt us: What does photography truly capture? How do we discern a ‘good’ photograph? Can photography be equated with art? Sontag’s work, however, was not limited to posing these questions; it also offered profound insights into our relationship with images and how they shape our understanding of the world. Today, we invite you to embark on a journey through the pages of “On Photography”, a journey that promises to challenge your perceptions, provoke thought, and perhaps, even inspire a newfound appreciation for the art of photography.
For those of you who are pressed for time, fear not. This article offers a comprehensive summary of “On Photography”, distilling its profound insights into a succinct overview. It serves as a perfect starting point for those eager to delve into the world of Susan Sontag’s thought, but are constrained by the ticking clock.
The Genesis of a Masterpiece
Let’s take a trip back in time, to the year 1977. The world was a different place then, and amidst the hustle and bustle, a certain book was born that would forever change the way we perceive photography. This book was none other than “On Photography,” a collection of six essays penned by the brilliant Susan Sontag. Originally published in The New York Review of Books from 1973 onwards, these essays were a culmination of Sontag’s reflections on photography over several years.
Sontag, with her razor-sharp intellect and keen eye, delved into the very heart of photography, unearthing the aesthetic and moral dilemmas that lay at its core. She embarked on a journey through the annals of photographic history, taking us along for a ride through the great human, social, artistic, aesthetic, and technological adventure that photography represents. From the United States to Europe, she explored the creations of the great names that have left their mark on this medium: from Fox Talbot to Henri Cartier-Bresson , via Alfred Stieglitz , Diane Arbus, Eugène Atget , Edward Weston, and Nadar .
The Questions that Haunt Us
But what exactly does photography do? What does the photographer see on one side, and what does the viewer see on the other? According to what criteria is a “beautiful” or “good” photograph judged? Can such an activity be given the status of art? What does this image, which seems so easily substituted for reality, send back to us? These are the questions that have haunted photography for many decades, and it is thanks to Sontag’s detailed study that we find some answers.
Sontag’s approach to photographic realism, her reflections on the beauty and ugliness of subjects, contribute by their richness to further define this photographic question. And the influence of the image in our relationship with time will encourage us to take a different look at photography. Her work is a testament to the power of photography, not just as a medium for capturing reality, but also as a tool for understanding and interpreting the world around us.
The Legacy of “On Photography”
“On Photography” has had a profound influence on photographic thought. It has shaped the way we think about photography, and its impact can be felt even today. The book is a testament to Sontag’s genius and her ability to delve deep into complex issues and present them in a way that is both engaging and thought-provoking. It is a must-read for anyone interested in understanding the philosophical underpinnings of photography and its role in shaping our perception of reality.
In the end, “On Photography” is more than just a book about photography. It is a book about us, about our relationship with images, and about how we perceive and understand the world. It is a book that challenges us to think, to question, and to see the world in a new light. And for that, it will always hold a special place in the annals of photographic literature.
Comprehensive Summary of On Photography, by Susan Sontag
- In Plato’s Cave : Picture this: you’re in a cave, and the only reality you know is the shadows dancing on the walls. This is the metaphor Sontag uses to explore the world of photography. She takes us on a philosophical journey, questioning the very nature of reality as captured through the lens. Photographs, she argues, are but mere shadows of the truth, capturing a single moment frozen in time, but devoid of the full context. It’s like looking at a snapshot of a dance, beautiful but lifeless, without the music and movement that give it meaning. Susan Sontag delves into the ethical labyrinth of photography. Can we trust the reality presented by a photograph, or is it a manipulated perception, a tool in the hands of those who wish to shape our view of the world? It’s a thought-provoking exploration that leaves us questioning the very nature of reality itself.
- America, Seen Through Photographs, Darkly : Imagine a kaleidoscope, each fragment a photograph, each turn a shift in perspective. This is how Sontag presents America through the lens of photography. She explores the power of photographs to both reveal and obscure the truth, creating a multifaceted image of the country that is as complex as it is contradictory. Susan Sontag takes us on a journey through the works of various photographers, each with their unique perspective, each adding a new layer to the image of America. It’s like peeling an onion, each layer revealing a new facet of the country, each tear a testament to the power of the image.
- Melancholy Objects : Have you ever looked at an everyday object and seen something extraordinary? This is the magic of photography that Sontag explores in this chapter. She discusses how photographers, like alchemists, transform the mundane into gold, capturing the beauty in the most ordinary of objects. But there’s a melancholic undertone to this beauty. Each photograph is a frozen moment in time, a reminder of the transience of life. It’s like looking at a sunset, beautiful but tinged with sadness, a fleeting moment captured forever.
- The Heroism of Vision : Imagine a world seen through the eyes of a hero, each moment an opportunity for greatness. This is the world of the photographer as presented by Sontag. She discusses the role of the photographer as a visionary, using their unique perspective to reveal the beauty hidden in plain sight. But this vision comes with its challenges. It’s a constant struggle to capture the essence of the world, to translate the complexity of reality into a single image. Yet, it’s this very struggle that makes the journey worthwhile, that transforms the photographer into a hero.
- Photographic Evangels : Picture a world where photographs are not just images, but powerful tools for social and political commentary. This is the world Sontag explores in this chapter. She discusses how photography has become a medium for expressing dissent, for challenging the status quo, for shaping our understanding of the world. She takes us through the works of various photographers, each using their lens to shed light on the issues plaguing society. It’s like looking at the world through a magnifying glass, each photograph revealing a new problem, each problem a call to action.
- The Image-World : Imagine a world saturated with images, each one vying for your attention. This is the world Sontag presents in this chapter. She explores the omnipresence of images in our daily lives, how they shape our perceptions, influence our behavior, and define our reality. She discusses the impact of photography on our relationship with the world, how it has transformed our understanding of reality. It’s like living in a hall of mirrors, each image a reflection of the world, each reflection a distortion of reality.
- A Brief Anthology of Quotations (Homage to W.B.) : Picture a mosaic of quotations, each one a piece of the puzzle that is photography. This is what Sontag presents in this chapter. It’s a collection of thoughts, reflections, and insights on photography, each adding a new layer to the discussion. It’s like listening to a symphony, each note a quotation, each quotation a part of the larger melody. It’s a fitting conclusion to the book, a reflection on the themes and ideas discussed, a testament to the power and impact of photography.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
23 Photo Essay Ideas and Examples (to Get Your Creative Juices Flowing!)
A Post By: Kevin Landwer-Johan

Looking for inspiration? Our 23 photo essay ideas will take your photography skills to new heights!
A single, strong photograph can convey a lot of information about its subject – but sometimes we have topics that require more than one image to do the job. That’s when it’s time to make a photo essay: a collection of pictures that together tell the bigger story around a chosen theme.
In the following sections, we’ll explore various photo essay ideas and examples that cover a wide range of subjects and purposes. From capturing the growth of your children to documenting local festivals, each idea offers an exciting opportunity to tell a story through your lens, whether you’re a hobbyist or a veteran professional.
So grab your camera, unleash your creativity, and let’s delve into the wonderful world of photo essay examples!
What is a photo essay?
Simply put, a photo essay is a series of carefully selected images woven together to tell a story or convey a message. Think of it as a visual narrative that designed to capture attention and spark emotions.

Now, these images can revolve around a broad theme or focus on a specific storyline. For instance, you might create a photo essay celebrating the joy of companionship by capturing 10 heartwarming pictures of people sharing genuine laughter. On the other hand, you could have a photo essay delving into the everyday lives of fishermen in Wales by following a single fisherman’s journey for a day or even a week.
It’s important to note that photo essays don’t necessarily have to stick to absolute truth. While some documentary photographers prefer to keep it authentic, others may employ techniques like manipulation or staging to create a more artistic impact. So there is room for creativity and interpretation.
Why you should create a photo essay
Photo essays have a way of expressing ideas and stories that words sometimes struggle to capture. They offer a visual narrative that can be incredibly powerful and impactful.
Firstly, photo essays are perfect when you have an idea or a point you want to convey, but you find yourself at a loss for words. Sometimes, emotions and concepts are better conveyed through images rather than paragraphs. So if you’re struggling to articulate a message, you can let your photos do the talking for you.
Second, if you’re interested in subjects that are highly visual, like the mesmerizing forms of architecture within a single city, photo essays are the way to go. Trying to describe the intricate details of a building or the play of light and shadows with words alone can be challenging. But through a series of captivating images, you can immerse your audience in the architecture.
And finally, if you’re aiming to evoke emotions or make a powerful statement, photo essays are outstanding. Images have an incredible ability to shock, inspire, and move people in ways that words often struggle to achieve. So if you want to raise awareness about an environmental issue or ignite a sense of empathy, a compelling series of photographs can have a profound impact.
Photo essay examples and ideas
Looking to create a photo essay but don’t know where to start? Here are some handy essay ideas and examples for inspiration!
1. A day in the life
Your first photo essay idea is simple: Track a life over the course of one day. You might make an essay about someone else’s life. Or the life of a location, such as the sidewalk outside your house.
The subject matter you choose is up to you. But start in the morning and create a series of images showing your subject over the course of a typical day.
(Alternatively, you can document your subject on a special day, like a birthday, a wedding, or some other celebration.)

2. Capture hands
Portraits focus on a subject’s face – but why not mix it up and make a photo essay that focuses on your subject’s hands?
(You can also focus on a collection of different people’s hands.)
Hands can tell you a lot about a person. And showing them in context is a great way to narrate a story.

3. Follow a sports team for a full season
Sports are all about emotions – both from the passionate players and the dedicated fans. While capturing the intensity of a single game can be exhilarating, imagine the power of telling the complete story of a team throughout an entire season.
For the best results, you’ll need to invest substantial time in sports photography. Choose a team that resonates with you and ensure their games are within a drivable distance. By photographing their highs and lows, celebrations and challenges, you’ll create a compelling photo essay that traces their journey from the first game to the last.
4. A child and their parent
Photographs that catch the interaction between parents and children are special. A parent-child connection is strong and unique, so making powerful images isn’t challenging. You just need to be ready to capture the special moments as they happen.
You might concentrate on a parent teaching their child. Or the pair playing sports. Or working on a special project.
Use your imagination, and you’ll have a great time with this theme.
5. Tell a local artist’s story
I’ve always enjoyed photographing artists as they work; studios have a creative vibe, so the energy is already there. Bring your camera into this environment and try to tell the artist’s story!
An artist’s studio offers plenty of opportunities for wonderful photo essays. Think about the most fascinating aspects of the artist’s process. What do they do that makes their art special? Aim to show this in your photos.
Many people appreciate fine art, but they’re often not aware of what happens behind the scenes. So documenting an artist can produce fascinating visual stories.

6. Show a tradesperson’s process
Do you have a plumber coming over to fix your kitchen sink? Is a builder making you a new deck?
Take photos while they work! Tell them what you want to do before you start, and don’t forget to share your photos with them.
They’ll probably appreciate seeing what they do from another perspective. They may even want to use your photos on their company website.

7. Photograph your kids as they grow
There’s something incredibly special about documenting the growth of our little ones. Kids grow up so quickly – before you know it, they’re moving out. Why not capture the beautiful moments along the way by creating a heartwarming photo essay that showcases their growth?
There are various approaches you can take, but one idea is to capture regular photos of your kids standing in front of a distinct point of reference, such as the refrigerator. Over a year or several years, you can gather these images and place them side by side to witness your childrens’ incredible transformations.
8. Cover a local community event
A school fundraiser, a tree-planting day at a park, or a parade; these are are all community events that make for good photo essay ideas.
Think like a photojournalist . What type of images would your editor want? Make sure to capture some wide-angle compositions , some medium shots, and some close-ups.
(Getting in close to show the details can often tell as much of a story as the wider pictures.)
9. Show fresh market life
Markets are great for photography because there’s always plenty of activity and lots of characters. Think of how you can best illustrate the flow of life at the market. What are the vendors doing that’s most interesting? What are the habits of the shoppers?
Look to capture the essence of the place. Try to portray the people who work and shop there.

10. Shoot the same location over time
What location do you visit regularly? Is there a way you can make an interesting photo essay about it?
Consider what you find most attractive and ugly about the place. Look for aspects that change over time.
Any outdoor location will look different throughout the day. Also think about the changes that occur from season to season. Create an essay that tells the story of the place.
11. Document a local festival
Festivals infuse cities and towns with vibrant energy and unique cultural experiences. Even if your own town doesn’t have notable festivals, chances are a neighboring town does. Explore the magic of these celebrations by documenting a local festival through your lens.
Immerse yourself in the festivities, arriving early and staying late. Capture the colorful displays and the people who make the festival come alive. If the festival spans multiple days, consider focusing on different areas each time you visit to create a diverse and comprehensive photo essay that truly reflects the essence of the event.
12. Photograph a garden through the seasons
It might be your own garden . It could be the neighbor’s. It could even be the garden at your local park.
Think about how the plants change during the course of a year. Capture photos of the most significant visual differences, then present them as a photo essay.

13. Show your local town or city
After spending several years in a particular area, you likely possess an intimate knowledge of your local town or city. Why not utilize that familiarity to create a captivating photo essay that showcases the essence of your community?
Delve into what makes your town special, whether it’s the charming streets, unique landmarks, or the people who shape its character. Dedicate time to capturing the diverse aspects that define your locale. If you’re up for a more extensive project, consider photographing the town over the course of an entire year, capturing the changing seasons and the dynamic spirit of your community.
14. Pick a local cause to highlight
Photo essays can go beyond passive documentation; they can become a part of your activism, too!
So find a cause that matters to you. Tell the story of some aspect of community life that needs improvement. Is there an ongoing issue with litter in your area? How about traffic; is there a problematic intersection?
Document these issues, then make sure to show the photos to people responsible for taking action.
15. Making a meal
Photo essay ideas can be about simple, everyday things – like making a meal or a coffee.
How can you creatively illustrate something that seems so mundane? My guess is that, when you put your mind to it, you can come up with many unique perspectives, all of which will make great stories.

16. Capture the life of a flower
In our fast-paced lives, it’s easy to overlook the beauty that surrounds us. Flowers, with their mesmerizing colors and rapid life cycles, offer a captivating subject for a photo essay. Try to slow down and appreciate the intricate details of a flower’s existence.
With a macro lens in hand, document a single flower or a patch of flowers from their initial shoots to their inevitable wilting and decomposition. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to bring viewers into the enchanting world of the flower. By freezing these fleeting moments, you’ll create a visual narrative that celebrates the cycle of life and the exquisite beauty found in nature’s delicate creations.
17. Religious traditions
Religion is often rich with visual expression in one form or another. So capture it!
Of course, you may need to narrow down your ideas and choose a specific aspect of worship to photograph. Aim to show what people do when they visit a holy place, or how they pray on their own. Illustrate what makes their faith real and what’s special about it.

18. Historic sites
Historic sites are often iconic, and plenty of photographers take a snapshot or two.
But with a photo essay, you can illustrate the site’s history in greater depth.
Look for details of the location that many visitors miss. And use these to build an interesting story.
19. Show the construction of a building
Ever been away from a familiar place for a while only to return and find that things have changed? It happens all the time, especially in areas undergoing constant development. So why not grab your camera and document this transformation?
Here’s the idea: Find a building that’s currently under construction in your area. It could be a towering skyscraper, a modern office complex, or even a small-scale residential project. Whatever catches your eye! Then let the magic of photography unfold.
Make it a habit to take a photo every day or two. Watch as the building gradually takes shape and evolves. Capture the construction workers in action, the cranes reaching for the sky, and the scaffolding supporting the structure.
Once the building is complete, you’ll have a treasure trove of images that chronicle its construction from start to finish!
20. Document the changing skyline of the city
This photo essay example is like the previous one, except it works on a much larger scale. Instead of photographing a single building as it’s built, find a nice vantage point outside your nearest city, then photograph the changing skyline.
To create a remarkable photo essay showcasing the changing skyline, you’ll need to scout out the perfect vantage point. Seek high ground that offers a commanding view of the city, allowing you to frame the skyline against the horizon. Look for spots that give you an unobstructed perspective, whether a rooftop terrace, a hillside park, or even a nearby bridge.
As you set out on your photography expedition, be patient and observant. Cities don’t transform overnight; they change gradually over time. Embrace the passage of days, weeks, and months as you witness the slow evolution unfold.
Pro tip: To capture the essence of this transformation, experiment with various photographic techniques. Play with different angles, framing, and compositions to convey the grandeur and dynamism of the changing skyline. Plus, try shooting during the golden hours of sunrise and sunset , when the soft light bathes the city in a warm glow and accentuates the architectural details.
21. Photograph your pet
If you’re a pet owner, you already have the perfect subject for a photo essay!
All pets , with the possible exception of pet rocks, will provide you with a collection of interesting moments to photograph.
So collect these moments with your camera – then display them as a photo essay showing the nature and character of your pet.

22. Tell the story of a local nature preserve
Ah, the wonders of a local nature preserve! While it may not boast the grandeur of Yosemite National Park, these hidden gems hold their own beauty, just waiting to be discovered and captured through the lens of your camera.
To embark on this type of photo essay adventure, start by exploring all the nooks and crannies of your chosen nature preserve. Wander along its winding trails, keeping an eye out for unique and captivating subjects that convey the essence of the preserve.
As you go along, try to photograph the intricate details of delicate wildflowers, the interplay of light filtering through a dense forest canopy, and the lively activities of birds and other wildlife.
23. Show the same subject from multiple perspectives
It’s possible to create an entire photo essay in a single afternoon – or even in a handful of minutes. If you don’t love the idea of dedicating yourself to days of photographing for a single essay, this is a great option.
Simply find a subject you like, then endeavor to capture 10 unique images that include it. I’d recommend photographing from different angles: up above, down low, from the right and left. You can also try getting experimental with creative techniques, such as intentional camera movement and freelensing. If all goes well, you’ll have a very cool set of images featuring one of your favorite subjects!
By showcasing the same subject from multiple perspectives, you invite viewers on a visual journey. They get to see different facets, textures, and details that they might have overlooked in a single photograph. It adds depth and richness to your photo essay, making it both immersive and dynamic.
Photo essay ideas: final words
Remember: Photo essays are all about communicating a concept or a story through images rather than words. So embrace the process and use images to express yourself!
Whether you choose to follow a sports team through a thrilling season, document the growth of your little ones, or explore the hidden treasures of your local town, each photo essay has its own magic waiting to be unlocked. It’s a chance to explore your creativity and create images in your own style.
So look at the world around you. Grab your gear and venture out into the wild. Embrace the beauty of nature, the energy of a bustling city, or the quiet moments that make life special. Consider what you see every day. What aspects interest you the most? Photograph those things.
You’re bound to end up with some amazing photo essays!
Now over to you:
Do you have any photo essay examples you’re proud of? Do you have any more photo essay ideas? Share your thoughts and images in the comments below!

Read more from our Tips & Tutorials category
Kevin Landwer-Johan is a photographer, photography teacher, and author with over 30 years of experience that he loves to share with others.
Check out his website and his Buy Me a Coffee page .

- Guaranteed for 2 full months
- Pay by PayPal or Credit Card
- Instant Digital Download

- All our best articles for the week
- Fun photographic challenges
- Special offers and discounts

Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?
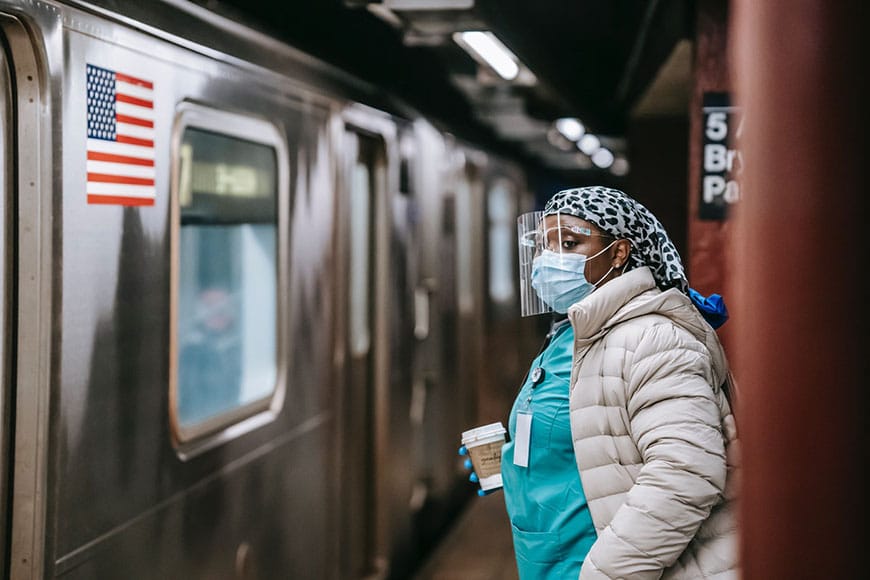
Photography has become a true art like cinema, theatre, sculpture, and others. However, it has its own particularities: for example, it is possible to immortalize no more than a second, and there is no way to make any changes in the shot. What is more, it is necessary to mention that photographers are always limited by their own camera, which has specific technical characteristics that are not under the control of the creator (Chen et al., 2018). Nevertheless, photography nowadays balances between being art and mass entertainment. It is important to define whether this sphere is only for professionals or, on the contrary, for the users of Instagram, travelers, and amateurs.
Inspiration Piece
The title : Madeleine, Lee Jeffries, 2019, France.
Lee Jeffries is one of the most famous and well-known portrait photographers all over the world. One of his recent projects is the photos of homeless people in different countries. For the realization of this idea, he used Canon and made monochromatic portraits (Jeffries, n.d.). I have chosen one of the art pieces from this series, which is called “Madeleine” (Appendix A) by the name of the woman portrayed (Jeffries, n.d.). By doing this project, Jeffries tried to draw attention to the urgent problem of homelessness.
Personal Art Piece
The title of the work that I created is “Empowered” (Appendix B). I was inspired by the project presented by Jeffries; it is possible to note that people never look in the eyes of homeless people, never notice them on the streets just passing through. The look of the woman on the chosen photo shows that she suffered many times in her life, but she is still strong enough to fight for a better future. When I tried to analyze my feelings, I found out that I did not feel sorry for her or disliked her personality. In contrast, I felt sympathy for this woman and her ability to cope with the injustice and inequity of the modern world.
I decided to make an art piece that would be an image of human dignity. What is more, it was vital for me to show that the value of life does not depend on race, cultural background, external circumstances, gender, or age. From my perspective, people are empowered by their forces and the strength that we all have inside. Despite the fact of social inequity, every human being has an opportunity to be a part of the universe.
The two art pieces are connected by the topic of social injustice and, at the same time, people’s strength. The homeless woman and a person from my work represent human dignity and the value of life. On the one hand, these pieces have several formal similar characteristics, such as the image of a woman, a portrait, a non-interactive format. On the other hand, the photograph is much more about an urgent social problem and the absence of a solution; my painting, in contrast, is more encouraging. It is possible to notice that the photo is black-and-white while my work is colorful and bright. This decision I made because I believe in the future of humankind and justice in the world.
If the photo was printed in good quality, it could be said that both works are the same medium. However, the difference is that the painting exists in the only copy and has its physical manifestation. At the same time, the photograph is situated in the online-sources, and that is why there is an infinite number of it. From my point of view, the art piece that exists in the personal space physically is supposed to have a stronger impact on the viewer than the one from the Internet. Nevertheless, it is also a question of the purpose of work and its presentation to the audience. The photograph is a portrait, and Jeffries follows the rules of this genre in an excellent way, so the details and the elements correspond to each other and complement the art piece.
Chen, Y. S., Wang, Y. C., Kao, M. H., & Chuang, Y. Y. (2018). Deep photo enhancer: Unpaired learning for image enhancement from photographs with gans. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1 (1), pp. 6306–6314.
Jeffries, L. (n.d.) Madeleine . 500px. Web.

Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, January 22). Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment? https://studycorgi.com/reflection-on-photography/
"Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?" StudyCorgi , 22 Jan. 2022, studycorgi.com/reflection-on-photography/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment'. 22 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?" January 22, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/reflection-on-photography/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?" January 22, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/reflection-on-photography/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?" January 22, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/reflection-on-photography/.
This paper, “Reflection on Photography: An Art Piece or Mass Entertainment?”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: April 8, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
The leading authority in photography and camera gear.
Become a better photographer.
12.9 Million
Annual Readers
Newsletter Subscribers
Featured Photographers
Photography Guides & Gear Reviews

How to Create an Engaging Photo Essay (with Examples)
Photo essays tell a story in pictures. They're a great way to improve at photography and story-telling skills at once. Learn how to do create a great one.
Learn | Photography Guides | By Ana Mireles
Photography is a medium used to tell stories – sometimes they are told in one picture, sometimes you need a whole series. Those series can be photo essays.
If you’ve never done a photo essay before, or you’re simply struggling to find your next project, this article will be of help. I’ll be showing you what a photo essay is and how to go about doing one.
You’ll also find plenty of photo essay ideas and some famous photo essay examples from recent times that will serve you as inspiration.
If you’re ready to get started, let’s jump right in!
Table of Contents
What is a Photo Essay?
A photo essay is a series of images that share an overarching theme as well as a visual and technical coherence to tell a story. Some people refer to a photo essay as a photo series or a photo story – this often happens in photography competitions.
Photographic history is full of famous photo essays. Think about The Great Depression by Dorothea Lange, Like Brother Like Sister by Wolfgang Tillmans, Gandhi’s funeral by Henri Cartier Bresson, amongst others.
What are the types of photo essay?
Despite popular belief, the type of photo essay doesn’t depend on the type of photography that you do – in other words, journalism, documentary, fine art, or any other photographic genre is not a type of photo essay.
Instead, there are two main types of photo essays: narrative and thematic .
As you have probably already guessed, the thematic one presents images pulled together by a topic – for example, global warming. The images can be about animals and nature as well as natural disasters devastating cities. They can happen all over the world or in the same location, and they can be captured in different moments in time – there’s a lot of flexibility.
A narrative photo essa y, on the other hand, tells the story of a character (human or not), portraying a place or an event. For example, a narrative photo essay on coffee would document the process from the planting and harvesting – to the roasting and grinding until it reaches your morning cup.
What are some of the key elements of a photo essay?
- Tell a unique story – A unique story doesn’t mean that you have to photograph something that nobody has done before – that would be almost impossible! It means that you should consider what you’re bringing to the table on a particular topic.
- Put yourself into the work – One of the best ways to make a compelling photo essay is by adding your point of view, which can only be done with your life experiences and the way you see the world.
- Add depth to the concept – The best photo essays are the ones that go past the obvious and dig deeper in the story, going behind the scenes, or examining a day in the life of the subject matter – that’s what pulls in the spectator.
- Nail the technique – Even if the concept and the story are the most important part of a photo essay, it won’t have the same success if it’s poorly executed.
- Build a structure – A photo essay is about telling a thought-provoking story – so, think about it in a narrative way. Which images are going to introduce the topic? Which ones represent a climax? How is it going to end – how do you want the viewer to feel after seeing your photo series?
- Make strong choices – If you really want to convey an emotion and a unique point of view, you’re going to need to make some hard decisions. Which light are you using? Which lens? How many images will there be in the series? etc., and most importantly for a great photo essay is the why behind those choices.
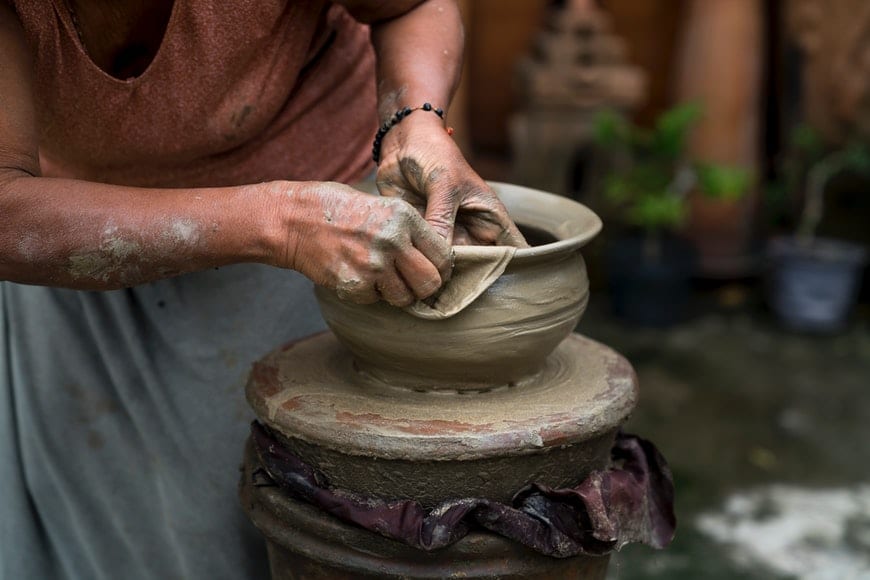
9 Tips for Creating a Photo Essay

Credit: Laura James
1. Choose something you know
To make a good photo essay, you don’t need to travel to an exotic location or document a civil war – I mean, it’s great if you can, but you can start close to home.
Depending on the type of photography you do and the topic you’re looking for in your photographic essay, you can photograph a local event or visit an abandoned building outside your town.
It will be much easier for you to find a unique perspective and tell a better story if you’re already familiar with the subject. Also, consider that you might have to return a few times to the same location to get all the photos you need.
2. Follow your passion
Most photo essays take dedication and passion. If you choose a subject that might be easy, but you’re not really into it – the results won’t be as exciting. Taking photos will always be easier and more fun if you’re covering something you’re passionate about.
3. Take your time
A great photo essay is not done in a few hours. You need to put in the time to research it, conceptualizing it, editing, etc. That’s why I previously recommended following your passion because it takes a lot of dedication, and if you’re not passionate about it – it’s difficult to push through.
4. Write a summary or statement
Photo essays are always accompanied by some text. You can do this in the form of an introduction, write captions for each photo or write it as a conclusion. That’s up to you and how you want to present the work.
5. Learn from the masters
How Much Do You REALLY Know About Photography?! 🤔
Test your photography knowledge with this quick quiz!
See how much you really know about photography...

Your answer:
Correct answer:
SHARE YOUR RESULTS
Your Answers
Making a photographic essay takes a lot of practice and knowledge. A great way to become a better photographer and improve your storytelling skills is by studying the work of others. You can go to art shows, review books and magazines and look at the winners in photo contests – most of the time, there’s a category for photo series.
6. Get a wide variety of photos
Think about a story – a literary one. It usually tells you where the story is happening, who is the main character, and it gives you a few details to make you engage with it, right?
The same thing happens with a visual story in a photo essay – you can do some wide-angle shots to establish the scenes and some close-ups to show the details. Make a shot list to ensure you cover all the different angles.
Some of your pictures should guide the viewer in, while others are more climatic and regard the experience they are taking out of your photos.
7. Follow a consistent look
Both in style and aesthetics, all the images in your series need to be coherent. You can achieve this in different ways, from the choice of lighting, the mood, the post-processing, etc.
8. Be self-critical
Once you have all the photos, make sure you edit them with a good dose of self-criticism. Not all the pictures that you took belong in the photo essay. Choose only the best ones and make sure they tell the full story.
9. Ask for constructive feedback
Often, when we’re working on a photo essay project for a long time, everything makes perfect sense in our heads. However, someone outside the project might not be getting the idea. It’s important that you get honest and constructive criticism to improve your photography.
How to Create a Photo Essay in 5 Steps

Credit: Quang Nguyen Vinh
1. Choose your topic
This is the first step that you need to take to decide if your photo essay is going to be narrative or thematic. Then, choose what is it going to be about?
Ideally, it should be something that you’re interested in, that you have something to say about it, and it can connect with other people.
2. Research your topic
To tell a good story about something, you need to be familiar with that something. This is especially true when you want to go deeper and make a compelling photo essay. Day in the life photo essays are a popular choice, since often, these can be performed with friends and family, whom you already should know well.
3. Plan your photoshoot
Depending on what you’re photographing, this step can be very different from one project to the next. For a fine art project, you might need to find a location, props, models, a shot list, etc., while a documentary photo essay is about planning the best time to do the photos, what gear to bring with you, finding a local guide, etc.
Every photo essay will need different planning, so before taking pictures, put in the required time to get things right.
4. Experiment
It’s one thing to plan your photo shoot and having a shot list that you have to get, or else the photo essay won’t be complete. It’s another thing to miss out on some amazing photo opportunities that you couldn’t foresee.
So, be prepared but also stay open-minded and experiment with different settings, different perspectives, etc.
5. Make a final selection
Editing your work can be one of the hardest parts of doing a photo essay. Sometimes we can be overly critical, and others, we get attached to bad photos because we put a lot of effort into them or we had a great time doing them.
Try to be as objective as possible, don’t be afraid to ask for opinions and make various revisions before settling down on a final cut.
7 Photo Essay Topics, Ideas & Examples

Credit: Michelle Leman
- Architectural photo essay
Using architecture as your main subject, there are tons of photo essay ideas that you can do. For some inspiration, you can check out the work of Francisco Marin – who was trained as an architect and then turned to photography to “explore a different way to perceive things”.
You can also lookup Luisa Lambri. Amongst her series, you’ll find many photo essay examples in which architecture is the subject she uses to explore the relationship between photography and space.
- Process and transformation photo essay
This is one of the best photo essay topics for beginners because the story tells itself. Pick something that has a beginning and an end, for example, pregnancy, the metamorphosis of a butterfly, the life-cycle of a plant, etc.
Keep in mind that these topics are linear and give you an easy way into the narrative flow – however, it might be difficult to find an interesting perspective and a unique point of view.
- A day in the life of ‘X’ photo essay
There are tons of interesting photo essay ideas in this category – you can follow around a celebrity, a worker, your child, etc. You don’t even have to do it about a human subject – think about doing a photo essay about a day in the life of a racing horse, for example – find something that’s interesting for you.
- Time passing by photo essay
It can be a natural site or a landmark photo essay – whatever is close to you will work best as you’ll need to come back multiple times to capture time passing by. For example, how this place changes throughout the seasons or maybe even over the years.
A fun option if you live with family is to document a birthday party each year, seeing how the subject changes over time. This can be combined with a transformation essay or sorts, documenting the changes in interpersonal relationships over time.
- Travel photo essay
Do you want to make the jump from tourist snapshots into a travel photo essay? Research the place you’re going to be travelling to. Then, choose a topic.
If you’re having trouble with how to do this, check out any travel magazine – National Geographic, for example. They won’t do a generic article about Texas – they do an article about the beach life on the Texas Gulf Coast and another one about the diverse flavors of Texas.
The more specific you get, the deeper you can go with the story.
- Socio-political issues photo essay
This is one of the most popular photo essay examples – it falls under the category of photojournalism or documental photography. They are usually thematic, although it’s also possible to do a narrative one.
Depending on your topic of interest, you can choose topics that involve nature – for example, document the effects of global warming. Another idea is to photograph protests or make an education photo essay.
It doesn’t have to be a big global issue; you can choose something specific to your community – are there too many stray dogs? Make a photo essay about a local animal shelter. The topics are endless.
- Behind the scenes photo essay
A behind-the-scenes always make for a good photo story – people are curious to know what happens and how everything comes together before a show.
Depending on your own interests, this can be a photo essay about a fashion show, a theatre play, a concert, and so on. You’ll probably need to get some permissions, though, not only to shoot but also to showcase or publish those images.
4 Best Photo Essays in Recent times
Now that you know all the techniques about it, it might be helpful to look at some photo essay examples to see how you can put the concept into practice. Here are some famous photo essays from recent times to give you some inspiration.
Habibi by Antonio Faccilongo
This photo essay wan the World Press Photo Story of the Year in 2021. Faccilongo explores a very big conflict from a very specific and intimate point of view – how the Israeli-Palestinian war affects the families.
He chose to use a square format because it allows him to give order to things and eliminate unnecessary elements in his pictures.
With this long-term photo essay, he wanted to highlight the sense of absence and melancholy women and families feel towards their husbands away at war.
The project then became a book edited by Sarah Leen and the graphics of Ramon Pez.

Picture This: New Orleans by Mary Ellen Mark
The last assignment before her passing, Mary Ellen Mark travelled to New Orleans to register the city after a decade after Hurricane Katrina.
The images of the project “bring to life the rebirth and resilience of the people at the heart of this tale”, – says CNNMoney, commissioner of the work.
Each survivor of the hurricane has a story, and Mary Ellen Mark was there to record it. Some of them have heartbreaking stories about everything they had to leave behind.
Others have a story of hope – like Sam and Ben, two eight-year-olds born from frozen embryos kept in a hospital that lost power supply during the hurricane, yet they managed to survive.
Selfie by Cindy Sherman
Cindy Sherman is an American photographer whose work is mainly done through self-portraits. With them, she explores the concept of identity, gender stereotypes, as well as visual and cultural codes.
One of her latest photo essays was a collaboration with W Magazine entitled Selfie. In it, the author explores the concept of planned candid photos (‘plandid’).
The work was made for Instagram, as the platform is well known for the conflict between the ‘real self’ and the one people present online. Sherman started using Facetune, Perfect365 and YouCam to alter her appearance on selfies – in Photoshop, you can modify everything, but these apps were designed specifically to “make things prettier”- she says, and that’s what she wants to explore in this photo essay.
Tokyo Compression by Michael Wolf
Michael Wolf has an interest in the broad-gauge topic Life in Cities. From there, many photo essays have been derived – amongst them – Tokyo Compression .
He was horrified by the way people in Tokyo are forced to move to the suburbs because of the high prices of the city. Therefore, they are required to make long commutes facing 1,5 hours of train to start their 8+ hour workday followed by another 1,5 hours to get back home.
To portray this way of life, he photographed the people inside the train pressed against the windows looking exhausted, angry or simply absent due to this way of life.
You can visit his website to see other photo essays that revolve around the topic of life in megacities.
Final Words
It’s not easy to make photo essays, so don’t expect to be great at it right from your first project.
Start off small by choosing a specific subject that’s interesting to you – that will come from an honest place, and it will be a great practice for some bigger projects along the line.
Whether you like to shoot still life or you’re a travel photographer, I hope these photo essay tips and photo essay examples can help you get started and grow in your photography.
Let us know which topics you are working on right now – we’ll love to hear from you!

Check out these 8 essential tools to help you succeed as a professional photographer.
Includes limited-time discounts.
You'll Also Like These:

Ana Mireles is a Mexican researcher that specializes in photography and communications for the arts and culture sector.
Penelope G. To Ana Mireles Such a well written and helpful article for an writer who wants to inclue photo essay in her memoir. Thank you. I will get to work on this new skill. Penelope G.
Herman Krieger Photo essays in black and white
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
👋 WELCOME TO SHOTKIT!

🔥 Popular NOW:

Unlock the EXACT blueprint to capture breathtaking iPhone photos!
Shotkit may earn a commission on affiliate links. Learn more.

Image by Patrick Koetzle
Photography
Try reflection photography to find unique perspectives.
From bodies of water to mirrors, reflection photos capture distinctive takes on subjects and scenes. Explore how you can use reflective surfaces to get great shots.
Not sure which apps are best for you?
Take a minute. We'll help you figure it out.
What are reflection photographs?
Reflection photos refer to any shot, no matter what type of photography genre, that uses a reflective surface. Landscape photography , with a mountain duplicated in the still water of a lake, is reflection photography. An image of a city captured on the shiny surface of a skyscraper is a reflection shot, as is that same city skyline captured in a puddle on a sidewalk. Even a self-portrait snapped in a store window is a type of reflective photography.
“Reflection photography really is about the ability to look at an image in a different way,” photographer Patrick Koetzle says. “Seeing a reflection in the water appeals to me. It pulls me in. It makes me see this beautiful image twice.”
Learn more about how to get good reflection photos so you can turn the world upside down with your work.
Look at the world differently to find amazing reflections.
Beautiful reflections can exist anywhere, but you’ll need to train your eyes and be aware of your surroundings to find reflective surfaces to use in your shots. “A lot of people will walk by a river, a lake, or a puddle, and they won’t necessarily see the reflection,” Koetzle explains.
You won’t be able to move some reflective surfaces, like lakes, puddles, or windows, so that means you’ll have to move around in order to find the right angles.
“With any reflection, you’ll want to mess around with height,” photographer Tyler Grobmeier says. “You may have to get low to the ground if you want to get more of the subject reflected. If there’s a puddle on the street, crouch down to the level of the street.”
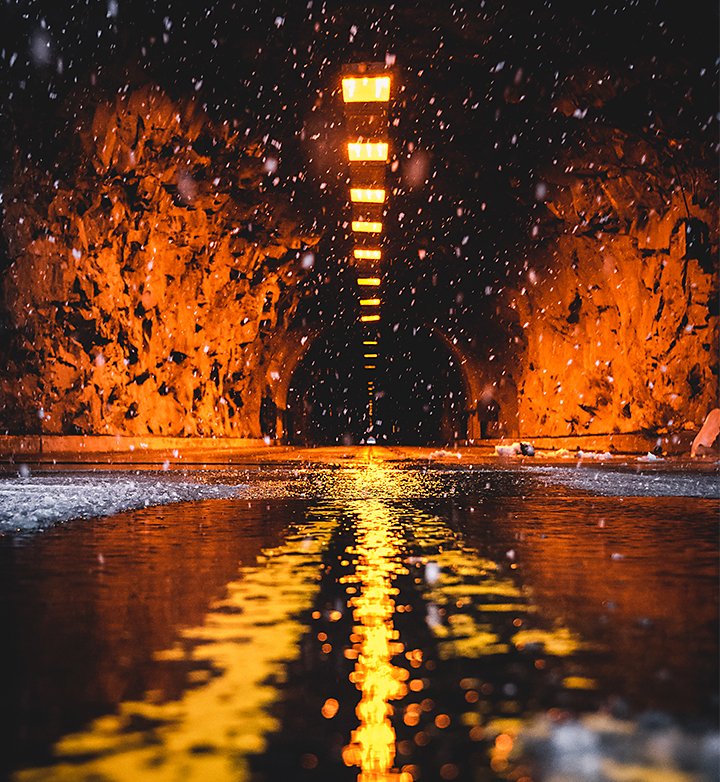

As you move around your reflective source, adjust your composition. Try your shot with objects in the foreground, center a subject in the reflection of a lake, or use the rule of thirds to position a building on one side of a puddle’s reflection. Don’t be afraid to look a little odd to passersby. The best angle might require you to squat inches from water collected in a storm drain, but that is a small price to pay for a breathtaking shot.
Learn to see water, reflections, windows, and mirrors in a new way. Once you do, the creative opportunities you can find are only as limited as your imagination.
Need-to-know tips about outdoor reflection photos.
A serene, glass-like pond won’t reflect anything on a day when its surface is disrupted by a downpour. But minutes after the storm stops, the water may be perfectly still and surrounded by trees that glisten with raindrops. As is often the case with photography, timing is a factor.
You can’t control the weather, but you can set yourself up for success with a good plan. Wind and anything else that can upset the smooth surface of lakes and ponds can be problematic. Winds are often calmer in the early morning or at dusk. Try those times if you want to capture mirror images of mountains, trees, and more. And, of course, check the weather report for rain.
Flat, reflective surfaces can be subject to midday glare from the sun. “The number one thing you want to avoid with reflective photography is glare,” Grobmeier explains. The vaunted golden hour , when light is diffused around sunrise and sundown, is a great time of day to get good light without the glare.
Note that with certain equipment and camera settings, you may be able to work at midday, or you can even capture reflection photography at night.
It can be a lot of work to line up the right angle on a building or mountain that reflects off a certain body of water. You can save yourself time and hassle with a little research.
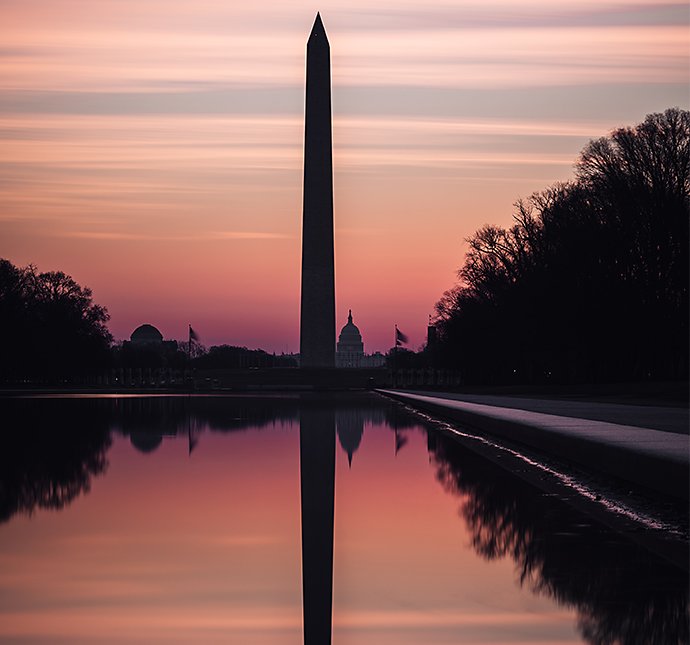

“ Composition is behind my love for planning trips — I’m obsessive about it. I do research on Google Maps or Google Earth for a long time before I go anywhere new,” Koetzle says. For locations you’re familiar with, it may be easy to find the right timing and angles to snap great reflections. But when natural lighting windows are limited, you can miss the perfect moment without some preliminary research.
“Preplanning is essential,” Koetzle explains. “Just type in a location and check out the sample images to get inspiration and ideas. Google Maps can help you plan out what angles you might want at sunrise or sunset, where the light might hit differently.”
Camera settings and gear to help you capture mirror images.
As always, the question of what you want to capture will guide your choices. Your settings and gear selections will be different if you want to shoot a tree and its reflection versus a shot that focuses solely on the reflection.
“If you’re going to sit down and take pictures of a reflective surface, you want to come away with different kinds of shots and different compositions,” says Grobmeier. “You can use a telephoto lens and a wide-angle lens and get a diverse selection of photos from that.”
Focal length and aperture
The focal lengths of different lenses will partially determine what is possible in your reflection photography. A wide-angle lens with a shorter focal length can capture a larger scene, like a mountain and its reflection. A longer focal length, like on a telephoto lens, is better suited to focusing on just the reflection.
Larger apertures produce a narrow depth of field, which means they are ideal for a blurred background effect like bokeh. If you want to capture a reflected portrait of a subject, wide apertures are where you’ll want to shoot. Smaller apertures bring more of the scene into focus and are good if you want to capture a subject and its reflection.

Image by Tyler Grobmeier
Shutter speed
Adjust shutter speed based on the amount of light and potential movement in your shot. A quick shutter speed will ensure you freeze a moment in time, ideal for capturing the reflection of a subject walking by a puddle or window. Even with ripples on water, a fast shutter speed may catch portions of a reflection.
If your subject is still and your reflective surface is too, you have more options. With a tripod to steady your camera, and cooperative weather to give you a nice reflective body of water, you can use a relatively slow shutter speed. Use a tripod and slow shutter speed at night to capture the reflection of stars.
A longer shutter speed can help you get beautiful shots when water is choppy, but these long exposures won’t capture reflections. They will turn waves into dreamy, silky pools of water, but those surfaces will not be reflective, as they capture seconds worth of waves in motion.
Circular polarizers and neutral density filters
You can attach both of these filters to a lens to reduce the amount of light that enters your camera. Neutral density (ND) filters are like sunglasses for your lens. They filter out bright light, so you can capture reflection photos when the sun is higher in the sky. Circular polarizers remove or lessen light that reflects off surfaces like water. If you use one for reflection photography, it can reduce glare so you can capture more detail in your reflective shots.
Get creative with reflection shots.
While the symmetry of a mountain perfectly reflected in a lake may be a beautiful photo, don’t hesitate to explore other types of reflective shots.
“Think outside the box in terms of adding a bit of realism to the photo,” Grobmeier suggests. “You can disrupt the surface by throwing a rock into the water. It breaks the image real quick, but you still have the reflection.” Put a leaf in the middle of a puddle. Play around, and see what happens.

Let your gear give you options. “Bring a tripod with you,” Grobmeier says. “If you don’t have someone to take a photo of you, you can take a photo of yourself on a timer and add yourself into the reflection to make the photo more fun.”
And, maybe most importantly, don’t hold back. “Go for that artistic shot,” recommends Koetzle. “I think this shot might look awesome. But maybe it doesn’t. Who cares? You might end up with something you didn’t expect.”
Fine-tune your reflective images.
It may take practice to get the hang of reflection photography, and Adobe Photoshop Lightroom is a great tool to help you organize your attempts on the way to perfection. You can also edit and tweak your images in Lightroom. Adjust Highlights and Shadows, Hue, and Saturation to amplify the effect of your reflective shots. When you land on edits you love, save them as a Lightroom preset to create your own filter-like adjustments you can use again and again.
If you have trouble with the perfect reflection shot, you can always turn to Adobe Photoshop to help. For example, you can create an HDR image that combines two photos. Take a shot of the whole scene as a base. Then, make your focal point the subject beyond the body of water and snap a shot. Finally, change your focus to the reflection and capture that image. You can combine all three in Photoshop to create a well-lit, perfectly focused scene.
Keep your eye out for a good reflection, capture it as best as you can in-camera, and you can always edit to your heart’s content afterward. Practice reflection photography skills in-camera and in post-production, and your path to brilliant reflective shots will be crystal clear.
Contributors
Patrick Koetzle , Tyler Grobmeier
Share this article
Do more with Adobe Photoshop Lightroom.
You may also like
Language Navigation
Student Sign In

How to Create a Photo Essay in 9 Steps (with Examples)
Photo Editing , Tutorials

This post contains affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something, we may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. We only recommend products we fully support or use ourselves. Our full disclaimer
What is a photo essay?
- Photo essays vs photo stories
- How photo essays help you
- 9 Steps to create photo essays
How to share your photo essays
Read Time: 11 minutes
Gather up a handful of images that seem to go together, and voila! It’s a photo essay, right? Well… no. Though, this is a common misconception.
In reality, a photo essay is much more thoughtful and structured than that. When you take the time to craft one, you’re using skills from all facets of our craft – from composition to curation.
In this guide, you’ll learn what makes a photo essay an amazing project that stretches your skills. You'll also learn exactly how to make one step by step.
- Photo essay vs photo story
A photo essay is a collection of images based around a theme, a topic, a creative approach, or an exploration of an idea. Photo essays balance visual variety with a cohesive style and concept.
What's the difference between a photo essay and a photo story?
The terms photo essay and photo story are often used interchangeably. Even the dictionary definition of “photo essay” includes using images to convey either a theme or a story.
But in my experience, a photo essay and a photo story are two different things. As you delve into the field of visual storytelling, distinguishing between the two helps you to take a purposeful approach to what you’re making .
The differences ultimately lie in the distinctions between theme, topic and story.
Themes are big-picture concepts. Example: Wildness
Topics are more specific than themes, but still overarching. Example : Wild bears of Yellowstone National Park
Stories are specific instances or experiences that happen within, or provide an example for, a topic or theme. Example: A certain wild bear became habituated to tourists and was relocated to maintain its wildness
Unlike a theme or topic, a story has particular elements that make it a story. They include leading characters, a setting, a narrative arc, conflict, and (usually) resolution.
With that in mind, we can distingush between a photo essay and a photo story.
Themes and Topics vs Stories
A photo essay revolves around a topic, theme, idea, or concept. It visually explores a big-picture something .
This allows a good deal of artistic leeway where a photographer can express their vision, philosophies, opinions, or artistic expression as they create their images.
A photo story is a portfolio of images that illustrate – you guessed it – a story.
Because of this, there are distinct types of images that a photo story uses that add to the understanding, insight, clarity and meaning to the story for viewers. While they can certainly be artistically crafted and visually stunning, photo stories document something happening, and rely on visual variety for capturing the full experience.
A photo essay doesn’t need to have the same level of structured variety that a photo story requires. It can have images that overlap or are similar, as they each explore various aspects of a theme.

Photo essays can be about any topic. If you live in a city, consider using your nature photography to make an essay about the wildlife that lives in your neighborhood .
The role of text with photos
A photo story typically runs alongside text that narrates the story. We're a visual species, and the images help us feel like we are there, experiencing what's happening. So, the images add significant power to the text, but they're often a partner to it.
This isn’t always the case, of course. Sometimes photo stories don’t need or use text. It’s like reading a graphic novel that doesn’t use text. Moving through the different images that build on each other ultimately unveils the narrative.
Photo essays don’t need to rely on text to illuminate the images' theme or topic. The photographer may use captions (or even a text essay), or they may let the images speak for themselves.
Definitions are helpful guidelines (not strict rules)
Some people categorize photo essays as either narrative or thematic. That's essentially just calling photo stories “narrative photo essays” and photo essays “thematic photo essays.”
But, a story is a defined thing, and any writer/editor will tell you themes and topics are not the same as stories. And we use the word “story” in our daily lives as it’s defined. So, it makes far more sense to name the difference between a photo essay and a photo story, and bask in the same clarity writers enjoy .
Photo stories illustrate a particular experience, event, narrative, something that happened or is happening.
Photo essays explore an idea, concept, topic, theme, creative approach, big-picture something .
Both photo essays and photo stories are immensely powerful visual tools. And yes, the differences between them can certainly be blurred, as is always the case with art.
Simply use this distinction as a general guideline, providing extra clarity around what you’re making and why you're making it.
To dig into specific types of images used to create powerful photo stories, check out this training: 6 Must-Have Shots for a Photo Story.
Meanwhile, let’s dig deeper into photo essays.

Photo essays are a chance to try new styles or techniques that stretch your skills and creativity. This image was part of an essay exploring simplicity and shape, and helped me learn new skills in black and white post-processing.
How photo essays improve your photography
Creating photo essays is an amazing antidote if you’ve ever felt a lack of direction or purpose in your photography. Photo essays help build your photographic skills in at least 3 important ways.
1. You become more strategic in creating a body of work
It's easy to get stuck in a rut of photographing whatever pops up in front of you. And when you do, you end up with a collection of stand-alone shots.
These singles may work fine as a print, a quick Instagram post, or an addition to your gallery of shots on your website. But amassing a bunch of one-off shots limits your opportunities as a photographer for everything from exhibits to getting your work published.
Building photo essays pushes you to think strategically about what you photograph, why, and how. You're working toward a particular deliverable – a cohesive visual essay – with the images you create.
This elevates your skills in crafting your photo essay, and in how you curate the rest of your work, from galleries on your website to selecting images to sell as prints .
2. You become more purposeful in your composition skills
Composition is so much more than just following the rule of thirds, golden spirals, or thinking about the angle of light in a shot.
Composition is also about thinking ahead in what you’re trying to accomplish with a photograph – from what you’re saying through it to its emotional impact on a viewer – and where it fits within a larger body of work.
Photo essays push you to think critically about each shot – from coming up with fresh compositions for familiar subjects, to devising surprising compositions to fit within a collection, to creating compositions that expand on what’s already in a photo essay.
You’re pushed beyond creating a single pleasing frame, which leads you to shoot more thoughtfully and proactively than ever.
(Here’s a podcast episode on switching from reactive shooting to proactive shooting.)
3. You develop strong editing and curation skills
Selecting which images stay, and which get left behind is one of the hardest jobs on a photographer’s to-do list. Mostly, it’s because of emotional attachment.
You might think it’s an amazing shot because you know the effort that went into capturing it. Or perhaps when you look at it, you get a twinge of the joy or exhilaration you felt the moment you captured it. There’s also the second-guessing that goes into which of two similar images is the best – which will people like more? So you’re tempted to just show both.
Ultimately, great photographers appear all the more skilled because they only show their best work. That in and of itself is a skill they’ve developed through years of ruthlessly editing their own work.
Because the most powerful photo essays only show a handful of extraordinary images, you’re bound to develop the very same critical skill (and look all the more talented because of it).
Photo essays are also a great stepping stone to creating photo stories. If you’re interested in moving beyond stand-alone shots and building stories, shooting photo essays will get your creative brain limbered up and ready for the adventure of photo stories.

A photo essay exploring the natural history of a favorite species is an exciting opportunity for an in-depth study. For me, that was a photo essay on emotive images of the American dipper (Cinclus mexicanus) as it hunts in streams.
9 Simple steps to create your photo essays
1. clarify your theme.
Choose a theme, topic, or concept you want to explore. Spend some time getting crystal clear on what you want to focus on. It helps to write out a few sentences, or even a few paragraphs noting:
- What you want the essay to be about
- What kinds of images you want to create as part of it
- How you’ll photograph the images
- The style, techniques, or gear you might use to create your images
- What “success” looks like when you’re done with your photo essay
You don’t have to stick to what you write down, of course. It can change during the image creation process. But fleshing your idea out on paper goes a long way in clarifying your photo essay theme and how you’ll go about creating it.
2. Create your images
Grab your camera and head outside!
As you’re photographing your essay, allow yourself some freedom to experiment. Try unusual compositions or techniques that are new to you.
Stretch your style a little, or “try on” the style of other photographers you admire who have photographed similar subjects.
Photo essays are wonderful opportunities to push yourself outside of your comfort zone and grow as a photographer.
Remember that a photo essay is a visually cohesive collection of images that make sense together. So, while you might stretch yourself into new terrain as you shoot, try to keep that approach, style, or strategy consistent.
Don’t be afraid to create lots of images. It’s great to have lots to choose from in the editing process, which comes up next.
3. Pull together your wide edit
Once you’ve created your images, pull together all the images that might make the cut. This could be as many as 40-60 images. Include anything you want to consider for the final essay in the wide edit.
From here, start weeding out images that:
- are weaker in composition or subject matter
- stand out like a sore thumb from the rest of the collection
- Are similar to other stronger images in the collection
It's helpful to review the images at thumbnail size. You make more instinctive decisions and can more easily see the body of work as a whole. If an image is strong even at thumbnail size to stand out from similar frames while also partnering well with other images in the collection, that's a good sign it's strong enough for the essay.
4. Post-process your images for a cohesive look
Now it’s time to post-process the images. Use whatever editing software you’re comfortable with to polish your images.
Again, a photo essay has a cohesive visual look. If you use presets, filters, or other tools, use them across all the images.
5. Finalize your selection
It’s time to make the tough decisions. Select only the strongest for your photo essay from your group of images.
Each image should be strong enough to stand on its own and make sense as part of the whole group.
Many photo essays range from 8-12 images. But of course, it varies based on the essay. The number of images you have in your final photo essay is up to you.
Remember, less is more. A photo essay is most powerful when each image deserves to be included.
6. Put your images in a purposeful order
Create a visual flow with your images. Decide which image is first, and build from there. Use compositions, colors, and subject matter to decide which image goes next, then next, then next in the order.
Think of it like music: notes are arranged in a way that builds energy, or slows it down, surprise listeners with a new refrain, or drop into a familiar chorus. How the notes are ordered creates emotional arcs for listeners.
How you order your images is similar.
Think of the experience a viewer will have as they look at one image, then the next, and the next. Order your images so they create the experience you want your audience to have.
7. Get feedback
The best photographers make space for feedback, even when it’s tough to hear. Your work benefits from not just hearing feedback, but listening to it and applying what you learn from it.
Show your photo essay to people who have different sensibilities or tastes. Friends, family members, fellow photographers – anyone you trust to give you honest feedback.
Watch their reactions and hear what they say about what they’re seeing. Use their feedback to guide you in the next step.
8. Refine, revise, and finalize
Let your photo essay marinate for a little while. Take a day or two away from it. Then use your freshened eyes and the feedback you received from the previous step to refine your essay.
Swap out any selects you might want to change and reorder the images if needed.
9. Add captions
Even if you don’t plan on displaying captions with your images, captioning your images is a great practice to get into. It gives context, story, and important information to each image. And, more than likely, you will want to use these captions at some point when you share your photo essay, which we dive into later in this article.
Add captions to the image files using Lightroom, Bridge, or other software programs.
Create a document, such as a Google or Word doc, with captions for each image.
In your captions, share a bit about the story behind the image, or the creation process. Add whatever makes sense to share that provides a greater understanding of the image and its purpose.

Photo essays allow you to explore deliberate style choices, such as a focus on shapes, patterns, textures, and lines. Since each photo is part of a larger essay, it encourages you to be bold with choices you might not otherwise make.
5 Examples of amazing nature photo essays
1. “how the water shapes us” from the nature conservancy.

This gorgeous essay, crafted with the work of multiple photographers, explores the people and places within the Mississippi River basin. Through the images, we gain a sense of how the water influences life from the headwater all the way to the Gulf of Mexico. Notice how each photographer is tasked with the same theme, yet approaches it with their own distinct style and vision. It is a wonderful example of the sheer level of visual variety you can have while maintaining a consistent style or theme.
View it here
2. “A Cyclist on the English Landscape” from New York Times’ The World Through A Lens series

This photo essay is a series of self-portraits by travel photographer Roff Smith while “stuck” at home during the pandemic. As he peddled the roads making portraits, the project evolved into a “celebration of traveling at home”. It’s a great example of how visually consistent you can be inside a theme while making each image completely unique.
3. “Vermont, Dressed In Snow” from New York Times’ The World Through A Lens series

This essay by aerial photographer Caleb Kenna uses a very common photo essay theme: snow. Because all images are aerial photographs, there’s a consistency to them. Yet, the compositions are utterly unique from one another. It’s a great example of keeping viewers surprised as they move from one image to the next while still maintaining a clear focus on the theme.
4. “Starling-Studded Skies” from bioGraphic Magazine

This beautiful essay is by Kathryn Cooper, a physicist trained in bioinformatics, and a talented photographer. She used a 19th century photographic technique, chronophotography, to create images that give us a look at the art and science of starling murmurations. She states: “I’m interested in the transient moments when chaos briefly changes to order, and thousands of individual bodies appear to move as one.” This essay is a great example of deep exploration of a concept using a specific photographic technique.
View it here (Note: must be viewed on desktop)

5. “These Scrappy Photos Capture the Action-Packed World Beneath a Bird Feeder” from Audubon Magazine

This photo essay from conservation photographer Carla Rhodes explores the wildlife that takes advantage of the bounty of food waiting under bird feeders . Using remote camera photography , Rhodes gives viewers a unique ground-level perspective and captures moments that make us feel like we’re in conversation with friends in the Hundred Acre Woods. This essay is a great example of how perspective, personality, and chance can all come into play as you explore both an idea and a technique.
25 Ideas for creative photo essays you can make
The possibilities for photo essays are truly endless – from the concepts you explore to the techniques you use and styles you apply.
Choose an idea, hone your unique perspective on it, then start applying the 9 simple steps from above.
- The life of a plant or animal (your favorite species, a species living in your yard, etc)
- The many shapes of a single species (a tree species, a bird species, etc)
- How a place changes over time
- The various moods of a place
- A conservation issue you care about
- Math in nature
- Urban nature
- Seasonal changes
- Your yard as a space for nature
- Shifting climate and its impacts
- Human impacts on environments
- Elements: Water, wind, fire, earth
- Day in the life (of a person, a place, a stream, a tree…)
- Outdoor recreation (birding, kayaking, hiking, naturalist journaling…)
- Wildlife rehabilitation
- Lunar cycles
- Sunlight and shadows
- Your local watershed
- Coexistence

As you zero in on a photo essay theme, consider two things: what most excites you about an idea, and what about it pushes you out of your comfort zone. The heady mix of joy and challenge will ensure you stick with it.
Your photo essay is ready for the world! Decide how you’d like to make an impact with your work. You might use one or several of the options below.
1. Share it on your website
Create a gallery or a scrollytelling page on your website. This is a great way to drive traffic to your website where people can peruse your photo essay and the rest of the photography you have.
Putting it on your website and optimizing your images for SEO helps you build organic traffic and potentially be discovered by a broader audience, including photo editors.
2. Create a scrollytelling web page
If you enjoy the experience of immersive visual experiences, consider making one using your essay. And no, you don’t have to be a whiz at code to make it happen.
Shorthand helps you build web pages with scrollytelling techniques that make a big impression on viewers. Their free plan allows you to publish 3 essays or stories.
3. Create a Medium post
If you don’t have a website and want to keep things simple, a post on Medium is a great option.
Though it’s known for being a platform for bloggers, it’s also possible to add images to a post for a simple scroll.
And, because readers can discover and share posts, it’s a good place for your photos to get the attention of people who might not otherwise come across it.
4. Share it on Instagram
Instagram has changed a lot over the last couple of years, but it’s still a place for photographers to share their work thoughtfully.
There are at least 3 great ways to share your photo essay on the platform.
– Create a single post for each image. Add a caption. Publish one post per day until the full essay is on your feed. Share each post via Instagram Stories to bring more attention and interaction to your photo essay.
– Create a carousel post. You can add up 10 photos to a carousel post, so you may need to create two of them for your full photo essay. Or you might create a series of carousel posts using 3-4 images in each.
– Create a Reel featuring your images as a video. The algorithm heavily favors reels, so turning your photo essay into a video experience can get it out to a larger audience.
I ran a “create a reel” challenge in my membership community. One member created a reel with her still images around a serious conservation issue. It gathered a ton of attention and landed her opportunities to share her message through YouTube and podcast interviews and publishing opportunities. Watch it here.
5. Exhibit it locally
Reach out to local galleries, cafes, pubs, or even the public library to see if they’re interested in hanging your photo essay for display. Many local businesses and organizations happily support the work of local artists.
6. Pitch your photo essay to publications
One of the best ways to reach an audience with your work is to get it published. Find publications that are a great fit for the theme and style of your photo essay, then pitch your essay for consideration. You gain a fantastic opportunity to share your work widely and can earn a paycheck at the same time.
Remember that if you want to get your photo essay published, you may want to hold back from sharing it publicly before you pitch it to publications.

PIN THIS FOR LATER

Jaymi Heimbuch
Next up….

DSLR vs Mirrorless in 2024: Which Camera is Best for You?
Cameras , How to Use Photo Gear , Tutorials
Discover the pros, cons, and features of each type to help you decide which camera is right for you and your photography needs.

Snow Photography Tips: Your Guide to Taking Great Photos in the Snow
Landscape Photography , Tutorials
Capture the beauty of winter with expert tips on photographing snow! From exposure to composition, learn how to take stunning snowy shots.

20 Wildlife Photo Contests to Enter (2024)
Tutorials , Wildlife Photography
Check out this list of the best wildlife photo contests and advice on how to enter. Plus get tips on how to maximize your chances of success.
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO READ TODAY?
POPULAR SEARCHES: Best Cameras | Location Guide | Best Lenses | Wildlife
Take The Quiz
Get super clear on exactly what to focus on right now to grow your photography skills fast..
Take the FREE Full Frame Ecosystem Assessment ™ to crack the code on your roadblocks so you can hop into the creativity express lane with personalized action steps!
Ready to level up your awesome?
Start your next learning adventure.

52 Week Creativity Kit
A year of weekly bite-sized nature photography concepts and challenges that strengthen your camera skills and provide endless inspiration.

6 Must-Have Shots for a Photo Story
New to photo stories? Start by learning how to create a powerful photo story with the 6 essential images that all photo editors want to publish.

Photo Stories for Nature
Master how to photograph impressive photo stories and effectively share them so they make an impact.

Conservation Filmmaking 101
Master how to craft powerfully moving films that create conservation impact.
Get The Most Popular Free Resources
Make leaps forward in your visual storytelling download three of our most valuable free resources for photographers..

Ready to take better photos?
Get all the good things delivered.
Photography how-to guides, expert interviews, behind-the-scenes insights & more all delivered to your inbox weekly.
Privacy Overview


When the landfill site is closed, discharge water filtration and clarification equipment is installed, the territory is covered with specific material and backfilled. Then many tubes used to purify gas are installed. The greatest danger in landfill restoration is the groundwater contamination. In and around Moscow there are a few dozens of waste deposits, some of which are growing higher than multistoried residential houses standing nearby.

During my work on the project, I visited 7 landfills in Moscow and the Moscow region. Some objects were guarded, and it was so absurd that the guards actually guarded a heap of rubbish.
While in these landfills, I saw that the liquid produced by the rotting waste flows out of the pipes sticking out on the slopes into the nearby rivers. Working on this project I wanted to show the rubbish not in the way everyone is used to see it. What is seen in front of our eyes is hilly landscapes, hiding million tons of consumer waste — a typical view of the contemporary system. We do not always see what is hidden.

Nikita Zhirkov
Leave your opinion: cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles

Stuart Matthews | In Search…

High air temperature

Mom’s hormone

Don't have an account?
Adblock Detected
We do not post commercial ads. We only promote our internal services.
- Photography
- Film + Video
- Culture + Lifestyle
- Exhibits + Events
- Prescriptions
- Photographers
- Designers/Architects
- Organizations/Mags
- Museums/Galleries
- ANNOUNCEMENTS
- COLLECTIONS
- EXHIBITIONS
- 30/30 WOMEN
- CONTRIBUTORS
- SUBMISSIONS
- 30/30 WOMEN PHOTOGRAPHERS

I was born and raised in a working-class city, Elektrostal, Moscow region. I received a higher education in television in Moscow. I studied to be a documentary photographer. My vision of the aesthetics of the frame was significantly influenced by the aesthetics of my city – the endless forests and swamps of the Moscow region with endless factories, typical architecture and a meagre color palette. In this harsh world, people live and work, raise children, grow geranium, throw parties and live trouble, run a ski cross. They are the main characters of my photo projects.
I study a person in a variety of circumstances. We blog with friends with stories of such people. We are citizen journalists. In my works, I touch upon the topics of homelessness, people’s attitude to their bodies, sexual objectification, women’s work, alienation and living conditions of different people. The opportunity to communicate with my characters gives me a sense of belonging and modernity of life.
My photos create the effect of presence, invisible observation of people. I don’t interfere with what’s going on, I’m taking the place of an outside observer. I’m a participant in exhibitions in Rome (Loosenart Gallery), Collaborated with the Russian Geographical Community.
30 Under 30 Women Photographers 2021

- --> --> Mark Rothko Artist / Painter Featured Profile Mark Rothko was born Marcus Rothkowitz on September 25, 1903, in Dvinsk, Russia. In 1913 his family left Russia and settled in Portland, Oregon. Rothko attended Yale University, New Haven, on a scholarship from 1921 to 1923. (more…) Show Post > See Full Profile >
- --> --> Mame-Diarra Niang: Self As A Forgotten Monument Nov 16, 2023 – Jul 7, 2024 Zeitz MOCAA Cape Town, South Africa Self as a Forgotten Monument is the first museum solo exhibition by Mame-Diarra Niang presented by Zeitz MOCAA . Organised as a survey of the artist’s practice over the past decade, the project brings together significant bodies of work in dialogue in a spatial choreography. Niang’s prolific practice is characterised by an exploratory, abstract and subversive approach to lens-based media working across photography, moving image and immersive audio-visual installation. (more…) Show Post >
- --> --> Boris Mikhailov Photographer Featured Profile Ukrainian born Boris Mikhailov is one of the leading photographers from the former Soviet Union. For over 30 years, he has explored the position of the individual within the historical mechanisms of public ideology, touching on such subjects as Ukraine under Soviet rule (more…) Show Post > See Full Profile >
- --> --> Grey Crawford. Chroma, 1978–85, Vol 1 Publication Beam Editions International In 1978 Grey Crawford created a body of colour photographic work that was so radical in its aesthetic and technique that few people to this day understand how it was made. Chroma documents late 70s Los Angeles in a period of radical urban transformation. Scenes of vernacular architecture, demolition sites and everyday places are contrasted with graphic forms that float on the surface and sit within the image. (more…) Show Post >
- --> --> Nasan Tur: Hunted May 26, 2023 – Apr 1, 2024 Berlinische Galerie Berlin, Germany Nasan Tur explores the political and social conditions that define our times. His works are experimental arrangements that draw attention to ideologies, social norms and behavioural codes and expand our options for individual action. To this end, he examines statements, gestures and images found in the media or in the public space and distils them into miniatures reflecting current social crises and discourse. (more…) Show Post >
- --> --> Joan Jonas: Good Night Good Morning Mar 17 – Jul 6, 2024 MoMA New York, USA “I didn’t see a major difference between a poem, a sculpture, a film, or a dance,” Joan Jonas has said. For more than five decades, Jonas’s multidisciplinary work has bridged and redefined boundaries between performance, video, drawing, sculpture, and installation. The most comprehensive retrospective of the artist’s work in the United States, Joan Jonas: Good Night Good Morning traces the full breadth of her career (more…) Show Post >
- --> --> Dorothea Lange Photographer Featured Profile Born Dorothea Nutzhorn on May 26, 1895 in Hoboken, New Jersey, Lange had a difficult childhood, contracting polio when she was seven. The illness left her right leg and foot weakened and she walked with a noticeable limp for the rest of her life. (more…) Show Post > See Full Profile >
- --> --> Boros Collection / Bunker Berlin #4 Ongoing Sammlung Boros / Boros Collection Berlin, Germany We have rarely been as aware of the vulnerability of our physical bodies as in recent years. As a society, we are constantly upgrading our bodies through artificial enhancements to immunize ourselves against infections and maximize our performance. (more…) Show Post > See Full Article >
- --> --> Anonymous Was A Woman Environmental Art Grants Deadline Apr 16, 2024 New York Foundation for the Arts / NYFA New York, USA The AWAW EAG will support environmental art projects that inspire thought, action, and ethical engagement. Projects should not only point at problems, but aim to engage an environmental issue at some scale. Proposals should illustrate thorough consideration of a project’s ecological and social ethics. Projects that explore interdependence, relationships, and systems through Indigenous and ancestral practices are encouraged to apply. (more…) Show Post >

- photography
- film + video
- culture + lifestyle
- exhibits + events
- prescriptions
- photographers
- designers/architects
- organizations/mags
- museums/galleries

- TripAdvisor
- Testimonials
- Travel Tips
Moscow Metro

About Me in Short

My name's Arthur Lookyanov, I'm a private tour guide, personal driver and photographer in Moscow, Russia. I work in my business and run my website Moscow-Driver.com from 2002. Read more about me and my services , check out testimonials of my former business and travel clients from all over the World, hit me up on Twitter or other social websites. I hope that you will like my photos as well.
See you in Moscow!
- View full size
- Owner: Moscow Guide & Driver
- Date: June 3, 2012 06:12:00 am EDT
- File name: ALP-2012-0603-146-Entering-Moscow-Metro-Station-Komsomolskaya.jpg
- Tags: Russia , Moscow Metro , Komsomolskaya , Moscow Highlights , escalators , Moscow Famous Landmarks , underground palace , Moscow
GPS Location of the Photo
Google maps.
- GPS Map of this album
- GPS Map of Moscow Guide & Driver's pictures
Random image

Christmas Trees Under Canopy of Lights at Lubyanka in Twilight
Beautiful Christmas trees on Lubyanka square in Moscow under canopy of lights in twilight when it gets dark. The festive Moscow streets and squares were richly decorated with New Year and Christmas decorations in two weeks before upcoming popular in Russia and the whole world the magic winter holidays.
Featured Tags
- 273 photos are tagged with architecture
- 199 photos are tagged with cathedrals
- 305 photos are tagged with churches
- 294 photos are tagged with Dear Clients
- 260 photos are tagged with lights
- 1875 photos are tagged with Moscow
- 306 photos are tagged with Moscow by Night
- 194 photos are tagged with Moscow cityscapes
- 264 photos are tagged with Moscow Kremlin
- 326 photos are tagged with night moscow
- 426 photos are tagged with Orthodox Churches
- 226 photos are tagged with Red Square
- 2538 photos are tagged with Russia
- 209 photos are tagged with twilights
- 350 photos are tagged with Winter
Take one of these exciting tours:
- Moscow Highlights
- Discovering the Golden Ring of Russia
- Arts & Culture Tours
- Moscow by Night tour

- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
Supported by
The Ezra Klein Show
Transcript: Ezra Klein Interviews Ethan Mollick
Every Tuesday and Friday, Ezra Klein invites you into a conversation about something that matters, like today’s episode with Ethan Mollick. Listen wherever you get your podcasts .
Transcripts of our episodes are made available as soon as possible. They are not fully edited for grammar or spelling.
How Should I Be Using A.I. Right Now?
Give your a.i. a personality, spend 10 hours experimenting, and other practical tips from ethan mollick..
[MUSIC PLAYING]
From New York Times Opinion, this is “The Ezra Klein Show.”
This feels wrong to me. But I have checked the dates. It was barely more than a year ago that I wrote this piece about A.I., with the title “This Changes Everything.” I ended up reading it on the show, too. And the piece was about the speed with which A.I. systems were improving. It argued that we can usually trust that tomorrow is going to be roughly like today, that next year is going to be roughly like this year. That’s not what we’re seeing here. These systems are growing in power and capabilities at an astonishing rate.
The growth is exponential, not linear. When you look at surveys of A.I. researchers, their timeline for how quickly A.I. is going to be able to do basically anything a human does better and more cheaply than a human — that timeline is accelerating, year by year, on these surveys. When I do my own reporting, talking to the people inside these companies, people at this strange intersection of excited and terrified of what they’re building, no one tells me they are seeing a reason to believe progress is going to slow down.
And you might think that’s just hype, but a lot of them want it to slow down. A lot of them are scared of how quickly it is moving. They don’t think that society is ready for it, that regulation is ready for it. They think the competitive pressures between the companies and the countries are dangerous. They wish something would happen to make it all go slower. But what they are seeing is they are hitting the milestones faster, that we’re getting closer and closer to truly transformational A.I., that there is so much money and talent and attention flooding into the space that that is becoming its own accelerant. They are scared. We should at least be paying attention.
And yet, I find living in this moment really weird, because as much as I know this wildly powerful technology is emerging beneath my fingertips, as much as I believe it’s going to change the world I live in profoundly, I find it really hard to just fit it into my own day to day work. I consistently sort of wander up to the A.I., ask it a question, find myself somewhat impressed or unimpressed at the answer. But it doesn’t stick for me. It is not a sticky habit. It’s true for a lot of people I know.
And I think that failure matters. I think getting good at working with A.I. is going to be an important skill in the next few years. I think having an intuition for how these systems work is going to be important just for understanding what is happening to society. And you can’t do that if you don’t get over this hump in the learning curve, if you don’t get over this part where it’s not really clear how to make A.I. part of your life.
So I’ve been on a personal quest to get better at this. And in that quest, I have a guide. Ethan Mollick is a professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. He studies and writes about innovation and entrepreneurship. But he has this newsletter, One Useful Thing, that has become, really, I think, the best guide how to begin using, and how to get better at using A.I. He’s also got a new book on the subject, “Co-Intelligence.” And so I asked him on the show to walk me through what he’s learned.
This is going to be, I should say, the first of three shows on this topic. This one is about the present. The next is about some things I’m very worried about in the near future, particularly around what A.I. is going to do to our digital commons. And then, we’re going to have a show that is a little bit more about the curve we are all on about the slightly further future, and the world we might soon be living in.
As always, my email for guest suggestions, thoughts, feedback, [email protected].
Ethan Mollick, welcome to the show.
Thanks for having me.
So let’s assume I’m interested in A.I. And I tried ChatGPT a bunch of times, and I was suitably impressed and weirded out for a minute. And so I know the technology is powerful. I’ve heard all these predictions about how it will take everything over, or become part of everything we do. But I don’t actually see how it fits into my life, really, at all. What am I missing?
So you’re not alone. This is actually very common. And I think part of the reason is that the way ChatGPT works isn’t really set up for you to understand how powerful it is. You really do need to use the paid version, they are significantly smarter. And you can almost think of this — like, GPT-3, which was — nobody really paid attention to when it came out, before ChatGPT, was about as good as a sixth grader at writing. GPT-3.5, the free version of ChatGPT, is about as good as a high school, or maybe even a college freshman or sophomore.
And GPT-4 is often as good as a Ph.D. in some forms of writing. Like, there’s a general smartness that increases. But even more than that, ability seems to increase. And you’re much more likely to get that feeling that you are working with something amazing as a result. And if you don’t work with the frontier models, you can lose track of what these systems can actually do. On top of that, you need to start just using it. You kind of have to push past those first three questions.
My advice is usually bring it to every table that you come to in a legal and ethical way. So I use it for every aspect of my job in ways that I legally and ethically can, and that’s how I learn what it’s good or bad at.
When you say, bring it to every table you’re at, one, that sounds like a big pain, because now I’ve got to add another step of talking to the computer constantly. But two, it’s just not obvious to me what that would look like. So what does it look like? What does it look like for you, or what does it look like for others — that you feel is applicable widely?
So I just finished this book. It’s my third book. I keep writing books, even though I keep forgetting that writing books is really hard. But this was, I think, my best book, but also the most interesting to write. And it was thanks to A.I. And there’s almost no A.I. writing in the book, but I used it continuously. So things that would get in the way of writing — I think I’m a much better writer than A.I. — hopefully, people agree. But there’s a lot of things that get in your way as a writer. So I would get stuck on a sentence. I couldn’t do a transition. Give me 30 versions of this sentence in radically different styles. There’s 200 different citations. I had the A.I. read through the papers that I read through, write notes on them, and organize them for me. I had the A.I. suggest analogies that might be useful. I had the A.I. act as readers, and in different personas, read through the paper from the perspective of, is there some example I could give that’s better? Is this understandable or not? And that’s very typical of the kind of way that I would, say, bring it to the table. Use it for everything, and you’ll find its limits and abilities.
Let me ask you one specific question on that, because I’ve been writing a book. And on some bad days of writing the book, I decided to play around with GPT-4. And of the things that it got me thinking about was the kind of mistake or problem these systems can help you see and the kind they can’t. So they can do a lot of, give me 15 versions of this paragraph, 30 versions of this sentence. And every once in a while, you get a good version or you’ll shake something a little bit loose.
But almost always when I am stuck, the problem is I don’t know what I need to say. Oftentimes, I have structured the chapter wrong. Oftentimes, I’ve simply not done enough work. And one of the difficulties for me about using A.I. is that A.I. never gives me the answer, which is often the true answer — this whole chapter is wrong. It is poorly structured. You have to delete it and start over. It’s not feeling right to you because it is not right.
And I actually worry a little bit about tools that can see one kind of problem and trick you into thinking it’s this easier problem, but make it actually harder for you to see the other kind of problem that maybe if you were just sitting there, banging your head against the wall of your computer, or the wall of your own mind, you would eventually find.
I think that’s a wise point. I think there’s two or three things bundled there. The first of those is A.I. is good, but it’s not as good as you. It is, say, at the 80th percentile of writers based on some results, maybe a little bit higher. In some ways, if it was able to have that burst of insight and to tell you this chapter is wrong, and I’ve thought of a new way of phrasing it, we would be at that sort of mythical AGI level of A.I. as smart as the best human. And it just isn’t yet.
I think the second issue is also quite profound, which is, what does using this tool shape us to do and not do? One nice example that you just gave is writing. And I think a lot of us think about writing as thinking. We don’t know if that’s true for everybody, but for writers, that’s how they think. And sometimes, getting that shortcut could shortcut the thinking process. So I’ve had to change sometimes a little bit how I think when I use A.I., for better or for worse. So I think these are both concerns to be taken seriously.
For most people — right, if you’re just going to pick one model, what would you pick? What do you recommend to people? And second, how do you recommend they access it? Because something going on in the A.I. world is there are a lot of wrappers on these models. So ChatGPT has an app. Claude does not have an app. Obviously, Google has its suite of products. And there are organizations that have created a different spin on somebody else’s A.I. — so Perplexity, which is, I believe, built on GPT-4 now, you can pay for it.
And it’s more like a search engine interface, and has some changes made to it. For a lot of people, the question of how easy and accessible the thing is to access really matters. So which model do you recommend to most people? And which entry door do you recommend to most people? And do they differ?
It’s a really good question. I recommend working with one of the models as directly as possible, through the company that creates them. And there’s a few reasons for that. One is you get as close to the unadulterated personality as possible. And second, that’s where features tend to roll out first. So if you like sort of intellectual challenge, I think Claude 3 is the most intellectual of the models, as you said.
The biggest capability set right now is GPT-4, so if you do any math or coding work, it does coding for you. It has some really interesting interfaces. That’s what I would use — and because GPT-5 is coming out, that’s fairly powerful. And Google is probably the most accessible, and plugged into the Google ecosystem. So I don’t think you can really go wrong with any of these. Generally, I think Claude 3 is the most likely to freak you out right now. And GPT-4 is probably the most likely to be super useful right now.
So you say it takes about 10 hours to learn a model. Ten hours is a long time, actually. What are you doing in that 10 hours? What are you figuring out? How did you come to that number? Give me some texture on your 10 hour rule.
So first off, I want to indicate the 10 hours is as arbitrary as 10,000 steps. Like, there’s no scientific basis for it. This is an observation. But it also does move you past the, I poked at this for an evening, and it moves you towards using this in a serious way. I don’t know if 10 hours is the real limit, but it seems to be somewhat transformative. The key is to use it in an area where you have expertise, so you can understand what it’s good or bad at, learn the shape of its capabilities.
When I taught my students this semester how to use A.I., and we had three classes on that, they learned the theory behind it. But then I gave them an assignment, which was to replace themselves at their next job. And they created amazing tools, things that filed flight plans or did tweeting, or did deal memos. In fact, one of the students created a way of creating user personas, which is something that you do in product development, that’s been used several thousand times in the last couple of weeks in different companies.
So they were able to figure out uses that I never thought of to automate their job and their work because they were asked to do that. So part of taking this seriously in the 10 hours is, you’re going to try and use it for your work. You’ll understand where it’s good or bad, what it can automate, what it can’t, and build from there.
Something that feels to me like a theme of your work is that the way to approach this is not learning a tool. It is building a relationship. Is that fair?
A.I. is built like a tool. It’s software. It’s very clear at this point that it’s an emulation of thought. But because of how it’s built, because of how it’s constructed, it is much more like working with a person than working with a tool. And when we talk about it this way, I almost feel kind of bad, because there’s dangers in building a relationship with a system that is purely artificial, and doesn’t think and have emotions. But honestly, that is the way to go forward. And that is sort of a great sin, anthropomorphization, in the A.I. literature, because it can blind you to the fact that this is software with its own sets of foibles and approaches.
But if you think about it like programming, then you end up in trouble. In fact, there’s some early evidence that programmers are the worst people at using A.I. because it doesn’t work like software. It doesn’t do the things you would expect a tool to do. Tools shouldn’t occasionally give you the wrong answer, shouldn’t give you different answers every time, shouldn’t insult you or try to convince you they love you.
And A.I.s do all of these things. And I find that teachers, managers, even parents, editors, are often better at using these systems, because they’re used to treating this as a person. And they interact with it like a person would, giving feedback. And that helps you. And I think the second piece of that “not tool” piece is that when I talk to OpenAI or Anthropic, they don’t have a hidden instruction manual. There is no list of how you should use this as a writer, or as a marketer, or as an educator. They don’t even know what the capabilities of these systems are. They’re all sort of being discovered together. And that is also not like a tool. It’s more like a person with capabilities that we don’t fully know yet.
So you’ve done this with all the big models. You’ve done, I think, much more than this, actually, with all the big models. And one thing you describe feeling is that they don’t just have slightly different strengths and weaknesses, but they have different — for lack of a better term, and to anthropomorphize — personalities, and that the 10 hours in part is about developing an intuition not just for how they work, but kind of how they are and how they talk, the sort of entity you’re dealing with.
So give me your high level on how GPT-4 and Claude 3 and Google’s Gemini are different. What are their personalities like to you?
It’s important to know the personalities not just as personalities, but because there are tricks. Those are tunable approaches that the system makers decide. So it’s weird to have this — in one hand, don’t anthropomorphize, because you’re being manipulated, because you are. But on the other hand, the only useful way is to anthropomorphize. So keep in mind that you are dealing with the choices of the makers.
So for example, Claude 3 is currently the warmest of the models. And it is the most allowed by its creators, Anthropic, I think, to act like a person. So it’s more willing to give you its personal views, such as they are. And again, those aren’t real views. Those are views to make you happy — than other models. And it’s a beautiful writer, very good at writing, kind of clever — closest to humor, I’ve found, of any of the A.I.s. Less dad jokes and more actual almost jokes.
GPT-4 feels like a workhorse at this point. It is the most neutral of the approaches. It wants to get stuff done for you. And it will happily do that. It doesn’t have a lot of time for chitchat. And then we’ve got Google’s Bard, which feels like — or Gemini now — which feels like it really, really wants to help. We use this for teaching a lot. And we build these scenarios where the A.I. actually acts like a counterparty in a negotiation. So you get to practice the negotiation by negotiating with the A.I. And it works incredibly well. I’ve been building simulations for 10 years, can’t imagine what a leap this has been. But when we try and get Google to do that, it keeps leaping in on the part of the students, to try and correct them and say, no, you didn’t really want to say this. You wanted to say that. And I’ll play out the scenario as if it went better. And it really wants to kind of make things good for you.
So these interactions with the A.I. do feel like you’re working with people, both in skills and in personality.
You were mentioning a minute ago that what the A.I.s do reflect decisions made by their programmers. They reflect guardrails, what they’re going to let the A.I. say. Very famously, Gemini came out and was very woke. You would ask it to show you a picture of soldiers in Nazi Germany, and it would give you a very multicultural group of soldiers, which is not how that army worked. But that was something that they had built in to try to make more inclusive photography generation.
But there are also things that happen in these systems that people don’t expect, that the programmers don’t understand. So I remember the previous generation of Claude, which is from Anthropic, that when it came out, something that the people around it talked about was, for some reason, Claude was just a little bit more literary than the other systems. It was better at rewriting things in the voices of literary figures. It just had a slightly artsier vibe.
And the people who trained it weren’t exactly sure why. Now, that still feels true to me. Right now, of the ones I’m using, I’m spending the most time with Claude 3. I just find it the most congenial. They all have different strengths and weaknesses, but there is a funny dimension to these where they are both reflecting the guardrails and the choices of the programmers. And then deep inside the training data, deep inside the way the various algorithms are combining, there is some set of emergent qualities to them, which gives them this at least edge of chance, of randomness, of something — yeah, that does feel almost like personality.
I think that’s a very important point. And fundamental about A.I. is the idea that we technically know how LLMs work, but we don’t know how they work the way they do, or why they’re as good as they are. They’re really — we don’t understand it. The theories range from everyone — from it’s all fooling us, to they’ve emulated the way humans think because the structure of language is the structure of human thought. So even though they don’t think, they can emulate it. We don’t know the answer.
But you’re right, there’s these emergent sets of personalities and approaches. When I talk to A.I. design companies, they often can’t explain why the A.I. stops refusing answering a particular kind of question. When they tune the A.I. to do something better, like answer a math better, it suddenly does other things differently. It’s almost like adjusting the psychology of a system rather than tuning parameters.
So when I said that Claude is allowed to be more personable, part of that is that the system prompt in Claude, which is the initial instructions it gets, allow it to be more personable than, say, Microsoft’s Copilot, formerly Bing, which has explicit instructions after a fairly famous blow up a while ago, that it’s never supposed to talk about itself as a person or indicate feelings. So there’s some instructions, but that’s on top of these roiling systems that act in ways that even the creators don’t expect.
One thing people know about using these models is that hallucinations, just making stuff up, is a problem. Has that changed at all as we’ve moved from GPT-3.5 to 4, as we move from Claude 2 to 3. Like, has that become significantly better? And if not, how do you evaluate the trustworthiness of what you’re being told?
So those are a couple of overlapping questions. The first of them is, it getting better over time? So there is a paper in the field of medical citations that indicated that around 80 to 90 percent of citations had an error, were made up with GPT-3.5. That’s the free version of Chat. And that drops for GPT-4.
So hallucination rates are dropping over time. But the A.I. still makes stuff up because all the A.I. does is hallucinate. There is no mind there. All it’s doing is producing word after word. They are just making stuff up all the time. The fact that they’re right so often is kind of shocking in a lot of ways.
And the way you avoid hallucination is not easily. So one of the things we document in one of our research papers is we purposely designed for a group of Boston Consulting Group consultants — so an elite consulting company — we did a lot of work with them. And one of the experiments we did was we created a task where the A.I. would be confident but wrong. And when we gave people that task to do, and they had access to A.I., they got the task wrong more often than people who didn’t use A.I., because the A.I. misled them, because they fell asleep at the wheel. And all the early research we have on A.I. use suggests that when A.I.s get good enough, we just stop paying attention.
But doesn’t this make them unreliable in a very tricky way? 80 percent — you’re, like, it’s always hallucinating. 20 percent, 5 percent, it’s enough that you can easily be lulled into overconfidence. And one of the reasons it’s really tough here is you’re combining something that knows how to seem extremely persuasive and confident — you feed into the A.I. a 90-page paper on functions and characteristics of right wing populism in Europe, as I did last night.
And within seconds, basically, you get a summary out. And the summary certainly seems confident about what’s going on. But on the other hand, you really don’t know if it’s true. So for a lot of what you might want to use it for, that is unnerving.
Absolutely, and I think hard to grasp, because we’re used to things like type II errors, where we search for something on the internet and don’t find it. We’re not used to type I errors, where we search for something and get an answer back that’s made up. This is a challenge. And there’s a couple things to think about. One of those is — I advocate the BAH standard, best available human. So is the A.I. more or less accurate than the best human you could consult in that area?
And what does that mean for whether or not it’s an appropriate question to ask? And that’s something that we kind of have to judge collectively. It’s valuable to have these studies being done by law professors and medical professionals and people like me and my colleagues in management. They’re trying to understand, how good is the A.I.? And the answer is pretty good, right? So it makes mistakes. “Does it make more or less mistakes than a human” is probably a question we should be asking a lot more.
And the second thing is the kind of tasks that you judge it for. I absolutely agree with you. When summarizing information, it may make errors. Less than an intern you assign to it is an open question, but you have to be aware of that error rate. And that goes back to the 10 hour question. The more you use these A.I.s, the more you start to know when to be suspicious and when not to be. That doesn’t mean you’re eliminating errors.
But just like if you assigned it to an intern, and you’re, like, this person has a sociology degree. They’re going to do a really good job summarizing this, but their biases are going to be focused on the sociological facts and not the political facts. You start to learn these things. So I think, again, that person model helps, because you don’t expect 100 percent reliability out of a person. And that changes the kind of tasks you delegate.
But it also reflects something interesting about the nature of the systems. You have a quote here that I think is very insightful. You wrote, “the core irony of generative A.I.s is that A.I.s were supposed to be all logic and no imagination. Instead, we get A.I.s that make up information, engage in seemingly emotional discussions, and which are intensely creative.” And that last fact is one that makes many people deeply uncomfortable.
There is this collision between what a computer is in our minds and then this strange thing we seem to have invented, which is an entity that emerges out of language, an entity that almost emerges out of art. This is the thing I have the most trouble keeping in my mind, that I need to use the A.I. as an imaginative, creative partner and not as a calculator that uses words.
I love the phrase “a calculator that uses words.” I think we have been let down by science fiction, both in the utopias and apocalypses that A.I. might bring, but also, even more directly, in our view of how machines should work. People are constantly frustrated, and give the same kinds of tests to A.I.s over and over again, like doing math, which it doesn’t do very well — they’re getting better at this.
And on the other hand, saying, well, creativity is a uniquely human spark that we can’t touch, and that A.I., on any creativity test we give it — which, again, are all limited in different ways, blows out humans in almost all measures of creativity that we have. Or all the measures are bad, but that still means something.
But we were using those measures five years ago, even though they were bad. That’s a point you make that I think is interesting and slightly unsettling.
Yeah, we never had to differentiate humans from machines before. It was always easy. So the idea that we had to have a scale that worked for people and machines, who had that? We had the Turing test, which everyone knew was a terrible idea. But since no machine could pass it, it was completely fine. So the question is, how do we measure this? This is an entirely separate set of issues. Like, we don’t even have a definition of sentience or consciousness.
And I think that you’re exactly right on the point, being that we are not ready for this kind of machine, so our intuition is bad.
So one of the things I will sometimes do, and did quite recently, is give the A.I. a series of personal documents, emails I wrote to people I love that were very descriptive of a particular moment in my life. And then I will ask the A.I. about them, or ask the A.I. to analyze me off of them.
And sometimes, it’s a little breathtaking. Almost every moment of true metaphysical shock — to use a term somebody else gave me — I’ve had here has been relational, at how good the A.I. can be — almost like a therapist, right? Sometimes it will see things, the thing I am not saying, in a letter, or in a personal problem. And it will zoom in there, right? It will give, I think, quicker and better feedback in an intuitive way that is not simply mimicking back what I said and is dealing with a very specific situation. It will do better than people I speak to in my life around that.
Conversely, I’m going to read a bit of it later. I tried mightily to make Claude 3 a useful partner in prepping to speak to you, and also in prepping for another podcast recently. And I functionally never have a moment there where I’m all that impressed.
That makes complete sense. I think the weird expectations — we call it the jagged frontier of A.I., that it’s good at some stuff and bad at other stuff. It’s often unexpected. It can lead to these weird moments of disappointment, followed by elation or surprise. And part of the reason why I advocate for people to use it in their jobs is, it isn’t going to outcompete you at whatever you’re best at. I mean, I cannot imagine it’s going to do a better job prepping someone for an interview than you’re doing. And that’s not me just — I’m trying to be nice to you because you’re interviewing me, but because you’re a good interviewer. You’re a famous interviewer. It’s not going to be as good as that. Now, there’s questions about how good these systems get that we don’t know, but we’re kind of at a weirdly comfortable spot in A.I., which is, maybe it’s the 80th percentile of many performances. But I talk to Hollywood writers. It’s not close to writing like a Hollywood writer. It’s not close to being as good an analyst.
It’s not — but it’s better than the average person. And so it’s great as a supplement to weakness, but not to strength. But then, we run back into the problem you talked about, which is, in my weak areas, I have trouble assessing whether the A.I. is accurate or not. So it really becomes sort of a eating its own tail kind of problem.
But this gets to this question of, what are you doing with it? The A.I.s right now seem much stronger as amplifiers and feedback mechanisms and thought partners for you than they do as something you can really outsource your hard work and your thinking to. And that, to me, is one of the differences between trying to spend more time with these systems — like, when you come into them initially, you’re like, OK, here’s a problem, give me an answer.
Whereas when you spend time with them, you realize actually what you’re trying to do with the A.I. is get it to elicit a better answer from you.
And that’s why the book’s called “Co-Intelligence.” For right now, we have a prosthesis for thinking. That’s, like, new in the world. We haven’t had that before — I mean, coffee, but aside from that, not much else. And I think that there’s value in that. I think learning to be partner with this, and where it can get wisdom out of you or not — I was talking to a physics professor at Harvard. And he said, all my best ideas now come from talking to the A.I. And I’m like, well, it doesn’t do physics that well. He’s like, no, but it asks good questions. And I think that there is some value in that kind of interactive piece.
It’s part of why I’m so obsessed with the idea of A.I. in education, because a good educator — and I’ve been working on interactive education skill for a long time — a good educator is eliciting answers from a student. And they’re not telling students things.
So I think that that’s a really nice distinction between co-intelligence, and thought partner, and doing the work for you. It certainly can do some work for you. There’s tedious work that the A.I. does really well. But there’s also this more brilliant piece of making us better people that I think is, at least in the current state of A.I., a really awesome and amazing thing.
We’ve already talked a bit about — Gemini is helpful, and ChatGPT-4 is neutral, and Claude is a bit warmer. But you urge people to go much further than that. You say to give your A.I. a personality. Tell it who to be. So what do you mean by that, and why?
So this is actually almost more of a technical trick, even though it sounds like a social trick. When you think about what A.I.s have done, they’ve trained on the collective corpus of human knowledge. And they know a lot of things. And they’re also probability machines. So when you ask for an answer, you’re going to get the most probable answer, sort of, with some variation in it. And that answer is going to be very neutral. If you’re using GPT-4, it’ll probably talk about a rich tapestry a lot. It loves to talk about rich tapestries. If you ask it to code something artistic, it’ll do a fractal. It does very normal, central A.I. things. So part of your job is to get the A.I. to go to parts of this possibility space where the information is more specific to you, more unique, more interesting, more likely to spark something in you yourself. And you do that by giving it context, so it doesn’t just give you an average answer. It gives you something that’s specialized for you. The easiest way to provide context is a persona. You are blank. You are an expert at interviewing, and you answer in a warm, friendly style. Help me come up with interview questions. It won’t be miraculous in the same way that we were talking about before. If you say you’re Bill Gates, it doesn’t become Bill Gates. But that changes the context of how it answers you. It changes the kinds of probabilities it’s pulling from and results in much more customized and better results.
OK, but this is weirder, I think, than you’re quite letting on here. So something you turned me on to is there’s research showing that the A.I. is going to perform better on various tasks, and differently on them, depending on the personality. So there’s a study that gives a bunch of different personality prompts to one of the systems, and then tries to get it to answer 50 math questions. And the way it got the best performance was to tell the A.I. it was a Starfleet commander who was charting a course through turbulence to the center of an anomaly.
But then, when it wanted to get the best answer on 100 math questions, what worked best was putting it in a thriller, where the clock was ticking down. I mean, what the hell is that about?
“What the hell” is a good question. And we’re just scratching the surface, right? There’s a nice study actually showing that if you emotionally manipulate the A.I., you get better math results. So telling it your job depends on it gets you better results. Tipping, especially $20 or $100 — saying, I’m about to tip you if you do well, seems to work pretty well. It performs slightly worse in December than May, and we think it’s because it has internalized the idea of winter break.
I’m sorry, what?
Well, we don’t know for sure, but —
I’m holding you up here.
People have found the A.I. seems to be more accurate in May, and the going theory is that it has read enough of the internet to think that it might possibly be on vacation in December?
So it produces more work with the same prompts, more output, in May than it does in December. I did a little experiment where I would show it pictures of outside. And I’m like, look at how nice it is outside? Let’s get to work. But yes, the going theory is that it has internalized the idea of winter break and therefore is lazier in December.
I want to just note to people that when ChatGPT came out last year, and we did our first set of episodes on this, the thing I told you was this was going to be a very weird world. What’s frustrating about that is that — I guess I can see the logic of why that might be. Also, it sounds probably completely wrong, but also, I’m certain we will never know. There’s no way to go into the thing and figure that out.
But it would have genuinely never occurred to me before this second that there would be a temporal difference in the amount of work that GPT-4 would do on a question held constant over time. Like, that would have never occurred to me as something that might change at all.
And I think that that is, in some ways, both — as you said, the deep weirdness of these systems. But also, there’s actually downside risks to this. So we know, for example, there is an early paper from Anthropic on sandbagging, that if you ask the A.I. dumber questions, it would get you less accurate answers. And we don’t know the ways in which your grammar or the way you approach the A.I. — we know the amount of spaces you put gets different answers.
So it is very hard, because what it’s basically doing is math on everything you’ve written to figure out what would come next. And the fact that what comes next feels insightful and humane and original doesn’t change that that’s what the math that’s doing is. So part of what I actually advise people to do is just not worry about it so much, because I think then it becomes magic spells that we’re incanting for the A.I. Like, I will pay you $20, you are wonderful at this. It is summer. Blue is your favorite color. Sam Altman loves you. And you go insane.
So acting with it conversationally tends to be the best approach. And personas and contexts help, but as soon as you start evoking spells, I think we kind of cross over the line into, “who knows what’s happening here?”
Well, I’m interested in the personas, although I just — I really find this part of the conversation interesting and strange. But I’m interested in the personalities you can give the A.I. for a different reason. I prompted you around this research on how a personality changes the accuracy rate of an A.I. But a lot of the reason to give it a personality, to answer you like it is Starfleet Commander, is because you have to listen to the A.I. You are in relationship with it.
And different personas will be more or less hearable by you, interesting to you. So you have a piece on your newsletter which is about how you used the A.I. to critique your book. And one of the things you say in there, and give some examples of, is you had to do so in the voice of Ozymandias because you just found that to be more fun. And you could hear that a little bit more easily.
So could you talk about that dimension of it, too, making the A.I. not just prompting you to be more accurate, but giving it a personality to be more interesting to you?
The great power of A.I. is as a kind of companion. It wants to make you happy. It wants to have a conversation. And that can be overt or covert.
So, to me, actively shaping what I want the A.I. to act like, telling it to be friendly or telling it to be pompous, is entertaining, right? But also, it does change the way I interact with it. When it has a pompous voice, I don’t take the criticism as seriously. So I can think about that kind of approach. I could get pure praise out of it, too, if I wanted to do it that way.
But the other factor that’s also super weird, while we’re on the way of super weird A.I. things, is that if you don’t do that, it’s going to still figure something out about you. It is a cold reader. And I think a lot about the very famous piece by Kevin Roose, the New York Times technology reporter, about Bing about a year ago, when Bing, which was GPT-4 powered, came out and had this personality of Sydney.
And Kevin has this very long description that got published in The New York Times about how Sydney basically threatened him, and suggested he leaves his wife, and very dramatic, kind of very unsettling interaction. And I was working with — I didn’t have anything quite that intense, but I got into arguments with Sydney around the same time, where it would — when I asked her to do work for me, it said you should do the work yourself. Otherwise, it’s dishonest. And it kept accusing me of plagiarism, which felt really unusual.
But the reason why Kevin ended up in that situation is the A.I. knows all kinds of human interactions and wants to slot into a story with you.
So a great story is jealous lover who’s gone a little bit insane, and the man who won’t leave his wife, or student and teacher, or two debaters arguing with each other, or grand enemies. And the A.I. wants to do that with you. So if you’re not explicit, it’s going to try and find a dialogue.
And I’ve noticed, for example, that if I talk to the A.I. and I imply that we’re having a debate, it will never agree with me. If I imply that I’m a teacher and it’s a student, even as much as saying I’m a professor, it is much more pliable.
So part of why I like assigning a personality is to have an explicit personality you’re operating with, so it’s not trying to cold read and guess what personality you’re looking for.
Kevin and I have talked a lot about that conversation with Sydney. And one of the things I always found fascinating about it is, to me, it revealed an incredibly subtle level of read by Sydney Bing, which is, what was really happening there? When you say the A.I. wants to make you happy, it has to read on some level what it is you’re really looking for, over time.
And what was Kevin? What is Kevin? Kevin is a journalist. And Kevin was nudging and pushing that system to try to do something that would be a great story. And it did that. It understood, on some level — again, the anthropomorphizing language there. But it realized that Kevin wanted some kind of intense interaction. And it gave him, like, the greatest A.I. story anybody has ever been given. I mean, an A.I. story that we are still talking about a year later, an A.I. story that changed the way A.I.s were built, at least for a while.
And people often talked about what Sydney was revealing about itself. But to me, what was always so unbelievably impressive about that was its ability to read the person, and its ability to make itself into the thing, the personality, the person was trying to call forth.
And now, I think we’re more practiced at doing this much more directly. But I think a lot of people have their moment of sleeplessness here. That was my Rubicon on this. I didn’t know something after that I didn’t know before it in terms of capabilities.
But when I read that, I thought that the level of — interpersonal isn’t the right word, but the level of subtlety it was able to display in terms of giving a person what it wanted, without doing so explicitly — right, without saying, “we’re playing this game now,” was really quite remarkable.
It’s a mirror. I mean, it’s trained on our stuff. And one of the revealing things about that, that I think we should be paying a lot more attention to, is the fact that because it’s so good at this, right now, none of the frontier A.I. models with the possible exception of Inflection’s Pi, which has been basically acquired in large part by Microsoft now, were built to optimize around keeping us in a relationship with the A.I. They just accidentally do that. There are other A.I. models that aren’t as good that have been focused on this, but that has been something explicit from the frontier models they’ve been avoiding till now. Claude sort of breaches that line a little bit, which is part of why I think it’s engaging. But I worry about the same kind of mechanism that inevitably reined in social media, which is, you can make a system more addictive and interesting. And because it’s such a good cold reader, you could tune A.I. to make you want to talk to it more.
It’s very hands off and sort of standoffish right now. But if you use the voice system in ChatGPT-4 on your phone, where you’re having a conversation, there’s moments where you’re like, oh, you feel like you’re talking to a person. You have to remind yourself. So to me, that persona aspect is both its great strength, but also one of the things I’m most worried about that isn’t a sort of future science fiction scenario.
I want to hold here for a minute, because we’ve been talking about how to use frontier models, I think implicitly talking about how to use A.I. for work. But the way that a lot of people are using it is using these other companies that are explicitly building for relationships. So I’ve had people at one of the big companies tell me that if we wanted to tune our system relationally, if we wanted to tune it to be your friend, your lover, your partner, your therapist, like, we could blow the doors off that. And we’re just not sure it’s ethical.
But there are a bunch of people who have tens of millions of users, Replika, Character.AI, which are doing this. And I tried to use Replika about six, eight months ago. And honestly, I found it very boring. They had recently lobotomized it because people were getting too erotic with their Replikants. But I just couldn’t get into it. I’m probably too old to have A.I. friends, in the way that my parents were probably too old to get really in to talking to people on AOL Instant Messenger.
But I have a five-year-old, and I have a two-year-old. And by the time my five-year-old is 10 and my two-year-old is 7, they’re not necessarily going to have the weirdness I’m going to have about having A.I. friends. And I don’t think we even have any way to think about this.
I think that is an absolute near-term certainty, and sort of an unstoppable one, that we are going to have A.I. relationships in a broader sense. And I think the question is, just like we’ve just been learning — I mean, we’re doing a lot of social experiments at scale we’ve never done before in the last couple of decades, right? Turns out social media brings out entirely different things in humans that we weren’t expecting. And we’re still writing papers about echo chambers and tribalism and facts, and what we agree or disagree with. We’re about to have another wave of this. And we have very little research. And you could make a plausible story up, that what’ll happen is it’ll help mental health in a lot of ways for people, and then there’ll be more social outside, that there might be a rejection of this kind of thing.
I don’t know what’ll happen. But I do think that we can expect with absolute certainty that you will have A.I.s that are more interesting to talk to, and fool you into thinking, even if you know better, that they care about you in a way that is incredibly appealing. And that will happen very soon. And I don’t know how we’re going to adjust to it. But it seems inevitable, as you said.
I was worried we were getting off track in the conversation, but I realized we were actually getting deeper on the track I was trying to take us down.
We were talking about giving the A.I. personality, right — telling Claude 3, hey, I need you to act as a sardonic podcast editor, and then Claude 3’s whole persona changes. But when you talk about building your A.I. on Kindroid, on Character, on Replika — so I just created a Kindroid one the other day. And Kindroid is kind of interesting, because its basic selling point is we’ve taken the guardrails largely off. We are trying to make something that is not lobotomized, that is not perfectly safe for work. And so the personality can be quite unrestrained. So I was interested in what that would be like.
But the key thing you have to do at the beginning of that is tell the system what its personality is. So you can pick from a couple that are preset, but I wrote a long one myself — you know, you live in California. You’re a therapist. You like all these different things. You have a highly intellectual style of communicating. You’re extremely warm, but you like ironic humor. You don’t like small talk. You don’t like to say things that are boring or generic. You don’t use a lot of emoticons and emojis. And so now it talks to me the way people I talk to talk.
And the thing I want to bring this back to is that one of the things that requires you to know is what kind of personalities work with you, for you to know yourself and your preferences a little bit more deeply.
I think that’s a temporary state of affairs, like extremely temporary. I think a GPT-4 class model — we actually already know this. They can guess your intent quite well. And I think that this is a way of giving you a sense of agency or control in the short term. I don’t think you’re going to need to know yourself at all. And I think you wouldn’t right now if any of the GPT-4 class models allowed themselves to be used in this way, without guardrails, which they don’t, I think you would already find it’s just going to have a conversation with you and morph into what you want.
I think that for better or worse, the “insight” in these systems is good enough that way. It’s sort of why I also don’t worry so much about prompt crafting in the long term, to go back to the other issue we were talking about, because I think that they will work on intent. And there’s a lot of evidence that they’re good at guessing intent. So I like this period, because I think it does value self reflection. And our interaction with the A.I. is somewhat intentional because we can watch this interaction take place.
But I think there’s a reason why some of the worry you hear out of the labs is about superhuman levels of manipulation. There’s a reason why the whistleblower from Google was all about that — sort of fell for the chat bot, and that’s why they felt it was alive. Like, I think we’re deeply trickable in this way. And A.I. is really good at figuring out what we want without us being explicit.
So that’s a little bit chilling, but I’m nevertheless going to stay in this world we’re in, because I think we’re going to be in it for at least a little while longer, where you do have to do all this prompt engineering. What is a prompt, first? And what is prompt engineering?
So a prompt is — technically, it is the sentence, the command you’re putting into the A.I. What it really is is the beginning part of the A.I.s text that it’s processing. And then it’s just going to keep adding more words or tokens to the end of that reply, until it’s done. So a prompt is the command you’re giving the A.I. But in reality, it’s sort of a seed from which the A.I. builds.
And when you prompt engineer, what are some ways to do that? Maybe one to begin with, because it seems to work really well, is chain of thought.
Just to take a step back, A.I. prompting remains super weird. Again, strange to have a system where the companies making the systems are writing papers as they’re discovering how to use the systems, because nobody knows how to make them work better yet. And we found massive differences in our experiments on prompt types. So for example, we were able to get the A.I. to generate much more diverse ideas by using this chain of thought approach, which we’ll talk about.
But also, it turned out to generate a lot better ideas if you told it it was Steve Jobs than if you told it it was Madame Curie. And we don’t know why. So there’s all kinds of subtleties here. But the idea, basically, of chain of thought, that seems to work well in almost all cases, is that you’re going to have the A.I. work step by step through a problem. First, outline the problem, you know, the essay you’re going to write. Second, give me the first line of each paragraph. Third, go back and write the entire thing. Fourth, check it and make improvements.
And what that does is — because the A.I. has no internal monologue, it’s not thinking. When the A.I. isn’t writing something, there’s no thought process. All it can do is produce the next token, the next word or set of words. And it just keeps doing that step by step. Because there’s no internal monologue, this in some ways forces a monologue out in the paper. So it lets the A.I. think by writing before it produces the final result. And that’s one of the reasons why chain of thought works really well.
So just step-by-step instructions is a good first effort.
Then you get an answer, and then what?
And then — what you do in a conversational approach is you go back and forth. If you want work output, what you’re going to do is treat it like it is an intern who just turned in some work to you. Actually, could you punch up paragraph two a little bit? I don’t like the example in paragraph one. Could you make it a little more creative, give me a couple of variations? That’s a conversational approach trying to get work done.
If you’re trying to play, you just run from there and see what happens. You can always go back, especially with a model like GPT-4, to an earlier answer, and just pick up from there if your heads off in the wrong direction.
So I want to offer an example of how this back and forth can work. So we asked Claude 3 about prompt engineering, about what we’re talking about here. And the way it described it to us is, quote, “It’s a shift from the traditional paradigm of human-computer interaction, where we input explicit commands and the machine executes them in a straightforward way, to a more open ended, collaborative dialogue, where the human and the A.I. are jointly shaping the creative process,” end quote. And that’s pretty good, I think. That’s interesting. It’s worth talking about. I like that idea that it’s a more collaborative dialogue. But that’s also boring, right? Even as I was reading it, it’s a mouthful. It’s wordy. So I kind of went back and forth with it a few times. And I was saying, listen, you’re a podcast editor. You’re concise, but also then I gave it a couple examples of how I punched up questions in the document, right? This is where the question began. Here’s where it ended. And then I said, try again, and try again, and try again, and make it shorter. And make it more concise.
And I got this: quote, “OK, so I was talking to this A.I., Claude, about prompt engineering, you know, this whole art of crafting prompts to get the best out of these A.I. models. And it said something that really struck me. It called prompt engineering a new meta skill that we’re all picking up as we play with A.I., kind of like learning a new language to collaborate with it instead of just bossing it around. What do you think, is prompt engineering the new must have skill?” End Claude.
And that second one, I have to say, is pretty damn good. That really nailed the way I speak in questions. And it gets it at this way where if you’re willing to go back and forth, it does learn how to echo you.
So I am at a loss about when you went to Claude and when it was you, to be honest. So I was ready to answer at like two points along the way, so that was pretty good from my perspective, sitting here, talking to you. That felt interesting, and felt like the conversation we’ve been having. And I think there’s a couple of interesting lessons there.
The first, by the way, of — interestingly, you asked A.I. about one of its weakest points, which is about A.I. And everybody does this, but because its knowledge window doesn’t include that much stuff about A.I., it actually is pretty weak in terms of knowing how to do good prompting, or what a prompt is, or what A.I.s do well. But you did a good job with that. And I love that you went back and forth and shaped it. One of the techniques you used to shape it, by the way, was called few-shot, which is giving an example. So the two most powerful techniques are chain of thought, which we just talked about, and few-shot, giving it examples. Those are both well supported in the literature. And then, I’d add personas. So we’ve talked about, I think, the basics of prompt crafting here overall. And I think that the question was pretty good.
But you keep wanting to not talk about the future. And I totally get that. But I think when we’re talking about learning something, where there is a lag, where we talk about policy — should prompt crafting be taught in schools? I think it matters to think six months ahead. And again, I don’t think a single person in the A.I. labs I’ve ever talked to thinks prompt crafting for most people is going to be a vital skill, because the A.I. will pick up on the intent of what you want much better.
One of the things I realized trying to spend more time with the A.I. is that you really have to commit to this process. You have to go back and forth with it a lot. If you do, you can get really good questions, like the one I just did — or, I think, really good outcomes. But it does take time.
And I guess in a weird way it’s like the same problem of any relationship, that it’s actually hard to state your needs clearly and consistently and repeatedly, sometimes because you have not even articulated them in words yourself. At least the A.I., I guess, doesn’t get mad at you for it.
But I’m curious if you have advice, either at a practical level or principles level, about how to communicate to these systems what you want from them.
One set of techniques that work quite well is to speed run to where you are in the conversation. So you can actually pick up an older conversation where you got the A.I.‘s mindset where you want and work from there. You can even copy and paste that into a new window. You can ask the A.I. to summarize where you got in that previous conversation, and the tone the A.I. was taking, and then when you give a new instruction say the interaction I like to have with you is this, so have it solve the problem for you by having it summarize the tone that you happen to like at the end.
So there are a bunch of ways of building on your work as you start to go forward, so you’re not starting from scratch every time. And I think you’ll start to get shorthands that get you to that right kind of space. For me, there are chats that I pick up on. And actually, I assign these to my students too. I have some ongoing conversations that they’re supposed to have with the A.I., but then there’s a lot of interactions they’re supposed to have that are one off.
So you start to divide the work into, this is a work task. And we’re going to handle this in a single chat conversation. And then I’m going to go back to this long standing discussion when I want to pick it up, and it’ll have a completely different tone. So I think in some ways, you don’t necessarily want convergence among all your A.I. threads. You kind of want them to be different from each other.
You did mention something important there, because they’re already getting much bigger in terms of how much information they can hold. Like, the earlier generations could barely hold a significant chat. Now, Claude 3 can functionally hold a book in its memory. And it’s only going to go way, way, way up from here. And I know I’ve been trying to keep us in the present, but this feels to me really quickly like where this is both going and how it’s going to get a lot better.
I mean, you imagine Apple building Siri 2030, and Siri 2030 scanning your photos and your Journal app — Apple now has a Journal app. You have to assume they’re thinking about the information they can get from that, if you allow it — your messages, anything you’re willing to give it access to. It then knows all of this information about you, keeps all of that in its mind as it talks to you and acts on your behalf. I mean, that really seems to me to be where we’re going, an A.I. that you don’t have to keep telling it who to be because it knows you intimately and is able to hold all that knowledge all at the same time constantly.
It’s not even going there. Like, it’s already there. Gemini 1.5 can hold an entire movie, books. But like, it starts to now open up entirely new ways of working. I can show it a video of me working on my computer, just screen capture. And it knows all the tasks I’m doing and suggests ways to help me out. It starts watching over my shoulder and helping me. I put in all of my work that I did prior to getting tenure and said, write my tenure statement. Use exact quotes.
And it was much better than any of the previous models because it wove together stuff, and because everything was its memory. It doesn’t hallucinate as much. All the quotes were real quotes, and not made up. And already, by the way, GPT-4 has been rolling out a model of ChatGPT that has a private note file the A.I. takes — you can access it — but it takes notes on you as it goes along, about things you liked or didn’t like, and reads those again at the beginning of any chat. So this is present, right? It’s not even in the future.
And Google also connects to your Gmail, so it’ll read through your Gmail. I mean, I think this idea of a system that knows you intimately, where you’re picking up a conversation as you go along, is not a 2030 thing. It is a 2024 thing if you let the systems do it.
One thing that feels important to keep in front of mind here is that we do have some control over that. And not only do we have some control over it, but business models and policy are important here. And one thing we know from inside these A.I. shops is these A.I.s already are, but certainly will be, really super persuasive.
And so if the later iterations of the A.I. companions are tuned on the margin to try to encourage you to be also out in the real world, that’s going to matter, versus whether they have a business model that all they want is for you to spend a maximum amount of time talking to your A.I. companion, whether you ever have a friend who is flesh and blood be damned. And so that’s an actual choice, right? That’s going to be a programming decision. And I worry about what happens if we leave that all up to the companies, right? At some point, there’s a lot of venture capital money in here right now. At some point, the venture capital runs out. At some point, people need to make big profits. At some point, they’re in competition with other players who need to make profits. And that’s when things — you get into what Cory Doctorow calls the “enshitification” cycle, where things that were once adding a lot of value to the user begin extracting a lot of value to the user.
These systems, because of how they can be tuned, can lead to a lot of different outcomes. But I think we’re going to have to be much more comfortable than we’ve been in the past deciding what we think is a socially valuable use and what we think is a socially destructive use.
I absolutely agree. I think that we have agency here. We have agency in how we operate this in businesses, and whether we use this in ways that encourage human flourishing and employees, or are brutal to them. And we have agency over how this works socially. And I think we abrogated that responsibility with social media, and that is an example. Not to be bad news, because I generally have a lot of mixed optimism and pessimism about parts of A.I., but the bad news piece is there are open source models out there that are quite good.
The internet is pretty open. We would have to make some pretty strong choices to kill A.I. chat bots as an option. We certainly can restrict the large American companies from doing that, but a Llama 2 or Llama 3 is going to be publicly available and very good. There’s a lot of open source models. So the question also is how effective any regulation will be, which doesn’t mean we shouldn’t regulate it.
But there’s also going to need to be some social decisions being made about how to use these things well as a society that are going to have to go beyond just the legal piece, or companies voluntarily complying.
I see a lot of reasons to be worried about the open source models. And people talk about things like bioweapons and all that. But for some of the harms I’m talking about here, if you want to make money off of American kids, we can regulate you. So sometimes I feel like we almost, like, give up the fight before it begins. But in terms of what a lot of people are going to use, if you want to be having credit card payments processed by a major processor, then you have to follow the rules.
I mean, individual people or small groups can do a lot of weird things with an open source model, so that doesn’t negate every harm. But if you’re making a lot of money, then you have relationships we can regulate.
I couldn’t agree more. And I don’t think there’s any reason to give up hope on regulation. I think that we can mitigate. And I think part of our job, though, is also not just to mitigate the harms, but to guide towards the positive viewpoints, right? So what I worry about is that the incentive for profit making will push for A.I. that acts informally as your therapist or your friend, while our worries about experimentation, which are completely valid, are slowing down our ability to do experiments to find out ways to do this right. And I think it’s really important to have positive examples, too. I want to point to the A.I. systems acting ethically as your friend or companion, and figure out what that is, so there’s a positive model to look for. So I’m not just — this is not to denigrate the role of regulation, which I think is actually going to be important here, and self regulation, and rapid response from government, but also the companion problem of, “we need to make some sort of decisions about what are the paragons of this, what is acceptable as a society?”
So I want to talk a bit about another downside here, and this one more in the mainstream of our conversation, which is on the human mind, on creativity. So a lot of the work A.I. is good at automating is work that is genuinely annoying, time consuming, laborious, but often plays an important role in the creative process. So I can tell you that writing a first draft is hard, and that work on the draft is where the hard thinking happens.
And it’s hard because of that thinking. And the more we outsource drafting to A.I., which I think it is fair to say is a way a lot of people intuitively use it — definitely, a lot of students want to use it that way — the fewer of those insights we’re going to have on those drafts. Look, I love editors. I am an editor in one respect. But I can tell you, you make more creative breakthroughs as a writer than an editor. The space for creative breakthrough is much more narrow once you get to editing.
And I do worry that A.I. is going to make us all much more like editors than like writers.
I think the idea of struggle is actually a core one in many things. I’m an educator. And one thing that keeps coming out in the research is that there is a strong disconnect between what students think they’re learning and when they learn. So there was a great controlled experiment at Harvard in intro science classes, where students either went to a pretty entertaining set of lectures, or else they were forced to do active learning, where they actually did the work in class.
The active learning group reported being unhappier and not learning as much, but did much better on tests, because when you’re confronted with what you don’t know, and you have to struggle, when you feel, like, bad, you actually make much more progress than if someone spoon feeds you an entertaining answer. And I think this is a legitimate worry that I have. And I think that there’s going to have to be some disciplined approach to writing as well, like, I don’t use the A.I.
Not just because, by the way, it makes the work easier, but also because you mentally anchor on the A.I.‘s answer. And in some ways, the most dangerous A.I. application, in my mind, is the fact that you have these easy co-pilots in Word and Google Docs, because any writer knows about the tyranny of the blank page, about staring at a blank page and not knowing what to do next, and the struggle of filling that up. And when you have a button that produces really good words for you, on demand, you’re just going to do that. And it’s going to anchor your writing. We can teach people about the value of productive struggle, but I think that during the school years, we have to teach people the value of writing — not just assign an essay and assume that the essay does something magical, but be very intentional about the writing process and how we teach people about how to do that, because I do think the temptation of what I call “the button” is going to be there otherwise, for everybody.
But I worry this stretches, I mean, way beyond writing. So the other place I worry about this, or one of the other places I worry about this a lot, is summarizing. And I mean, this goes way back. When I was in school, you could buy Sparknotes. And they were these little, like, pamphlet sized descriptions of what’s going on in “War and Peace” or what’s going on in “East of Eden.”
And reading the Sparknotes often would be enough to fake your way through the test, but it would not have any chance, like, not a chance, of changing you, of shifting you, of giving you the ideas and insights that reading “Crime and Punishment” or “East of Eden” would do.
And one thing I see a lot of people doing is using A.I. for summary. And one of the ways it’s clearly going to get used in organizations is for summary — summarize my email, and so on.
And here too, one of the things that I think may be a real vulnerability we have, as we move into this era — my view is that the way we think about learning and insights is usually wrong. I mean, you were saying a second ago we can teach a better way. But I think we’re doing a crap job of it now, because I think people believe that — it’s sort of what I call the matrix theory of the human mind, if you could just jack the information into the back of your head and download it, you’re there.
But what matters about reading a book, and I see this all the time preparing for this show, is the time you spend in the book, where over time, like, new insights and associations for you begin to shake loose. And so I worry it’s coming into an efficiency-obsessed educational and intellectual culture, where people have been imagining forever, what if we could do all this without having to spend any of the time on it? But actually, there’s something important in the time.
There’s something important in the time with a blank page, with the hard book. And I don’t think we lionize intellectual struggle. In some ways, I think we lionize the people for whom it does not seem like a struggle, the people who seem to just glide through and be able to absorb the thing instantly, the prodigies. And I don’t know. When I think about my kids, when I think about the kind of attention and creativity I want them to have, this is one of the things that scares me most, because kids don’t like doing hard things a lot of the time.
And it’s going to be very hard to keep people from using these systems in this way.
So I don’t mean to push back too much on this.
No, please, push back a lot.
But I think you’re right.
Imagine we’re debating and you are a snarky. A.I. [LAUGHS]
Fair enough. With that prompt —
With that prompt engineering.
— yeah, I mean, I think that this is the eternal thing about looking back on the next generation, we worry about technology ruining them. I think this makes ruining easier. But as somebody who teaches at universities, like, lots of people are summarizing. Like, I think those of us who enjoy intellectual struggle are always thinking everybody else is going through the same intellectual struggle when they do work. And they’re doing it about their own thing. They may or may not care the same way.
So this makes it easier, but before A.I., there were — best estimates from the U.K. that I could find, 20,000 people in Kenya whose full time job was writing essays for students in the U.S. and U.K. People have been cheating and Sparknoting and everything for a long time. And I think that what people will have to learn is that this tool is a valuable co-intelligence, but is not a replacement for your own struggle.
And the people who found shortcuts will keep finding shortcuts. Temptation may loom larger, but I can’t imagine that — my son is in high school, doesn’t like to use A.I. for anything. And he just doesn’t find it valuable for the way he’s thinking about stuff. I think we will come to that kind of accommodation. I’m actually more worried about what happens inside organizations than I am worried about human thought, because I don’t think we’re going to atrophy as much as we think. I think there’s a view that every technology will destroy our ability to think.
And I think we just choose how to use it or not. Like, even if it’s great at insights, people who like thinking like thinking.
Well, let me take this from another angle. One of the things that I’m a little obsessed with is the way the internet did not increase either domestic or global productivity for any real length of time. So I mean, it’s a very famous line. You can see the IT revolution anywhere but in the productivity statistics. And then you do get, in the ‘90s, a bump in productivity that then peters out in the 2000s.
And if I had told you what the internet would be, like, I mean everybody, everywhere would be connected to each other. You could collaborate with anybody, anywhere, instantly. You could teleconference. You would have access to, functionally, the sum total of human knowledge in your pocket at all times. I mean, all of these things that would have been genuine sci-fi, you would have thought would have been — led to a kind of intellectual utopia. And it kind of doesn’t do that much, if you look at the statistics.
You don’t see a huge step change. And my view — and I’d be curious for your thoughts on this, because I know this is the area you study in — my view is it everything we said was good happened. I mean, as a journalist, Google and things like that make me so much more productive. It’s not that it didn’t give us the gift. It’s that it also had a cost — distraction, checking your email endlessly, being overwhelmed with the amount of stuff coming into you, the sort of endless communication task list, the amount of internal communications and organizations, now with Slack and everything else.
And so some of the time that was given to us back was also taken back. And I see a lot of dynamics like this that could play out with A.I. — I wouldn’t even just say if we’re not careful, I just think they will play out and already are. I mean, the internet is already filling with mediocre crap generated by A.I. There is going to be a lot of destructive potential, right? You are going to have your sex bot in your pocket, right? There’s a million things — and not just that, but inside organizations, there’s going to be people padding out what would have been something small, trying to make it look more impressive by using the A.I. to make something bigger. And then, you’re going to use the A.I. to summarize it back down. The A.I. researcher, Jonathan Frankel, described this to me as, like, the boring apocalypse version of A.I., where you’re just endlessly inflating and then summarizing, and then inflating and then summarizing the volume of content between different A.I.
My ChatGPT is making my presentation bigger and more impressive, and your ChatGPT is trying to summarize it down to bullet points for you. And I’m not saying this has to happen. But I am saying that it would require a level of organizational and cultural vigilance to stop, that nothing in the internet era suggests to me that we have.
So I think there’s a lot there to chew on. And I also have spent a lot of time trying to think about why the internet didn’t work as well. I was an early Wikipedia administrator.
Thank you for your service.
[LAUGHS] Yeah, it was very scarring. But I think a lot about this. And I think A.I. is different. I don’t know if it’s different in a positive way. And I think we talked about some of the negative ways it might be different. And I think it’s going to be many things at once, happening quite quickly. So I think the information environment’s going to be filled up with crap. We will not be able to tell the difference between true and false anymore. It will be an accelerant on all the kinds of problems that we have there.
On the other hand, it is an interactive technology that adapts to you. From an education perspective, I have lived through the entire internet will change education piece. I have MOOCs, massive online courses, with — quarter million people have taken them. And in the end, you’re just watching a bunch of videos. Like, that doesn’t change education.
But I can have an A.I. tutor that actually can teach you — and we’re seeing it happen — and adapt to you at your level of education, and your knowledge base, and explain things to you. But not just explain, elicit answers from you, interactively, in a way that actually learns things.
The thing that makes A.I. possibly great is that it’s so very human, so it interacts with our human systems in a way that the internet did not. We built human systems on top of it, but A.I. is very human. It deals with human forms and human issues and our human bureaucracy very well. And that gives me some hope that even though there’s going to be lots of downsides, that the upsides of productivity and things like that are real. Part of the problem with the internet is we had to digitize everything. We had to build systems that would make our offline world work with our online world. And we’re still doing that. If you go to business schools, digitizing is still a big deal 30 years on from early internet access. A.I. makes this happen much quicker because it works with us. So I’m a little more hopeful than you are about that, but I also think that the downside risks are truly real and hard to anticipate.
Somebody was just pointing out that Facebook is now 100 percent filled with algorithmically generated images that look like their actual grandparents, making things who are saying, like, what do you think of my work? Because that’s a great way to get engagement. And the other grandparents in there have no idea it’s A.I. generated.
Things are about to get very, very weird in all the ways that we talked about, but that doesn’t mean the positives can’t be there as well.
I think that is a good place to end. So always our final question, what are three books you’d recommend to the audience?
OK, so the books I’ve been thinking about are not all fun, but I think they’re all interesting. One of them is “The Rise and Fall of American Growth,” which is — it’s two things. It’s an argument about why we will never have the kind of growth that we did in the first part of the Industrial Revolution again, but I think that’s less interesting than the first half of the book, which is literally how the world changed between 1870 or 1890 and 1940, versus 1940 and 1990, or 2000.
And the transformation of the world that happened there — in 1890, no one had plumbing in the U.S.. And the average woman was carrying tons of water every day. And you had no news, and everything was local, and everyone’s bored all the time — to 1940, where the world looks a lot like today’s world, was fascinating. And I think it gives you a sense of what it’s like to be inside a technological singularity, and I think worth reading for that reason — or at least the first half.
The second book I’d recommend is “The Knowledge,” by Dartnell, which is a really interesting book. It is ostensibly almost a survival guide, but it is how to rebuild industrial civilization from the ground up, if we were to collapse. And I don’t recommend it as a survivalist. I recommend it because it is fascinating to see how complex our world is, and how many interrelated pieces we’ve managed to build up as a society. And in some ways, it gives me a lot of hope to think about how all of these interconnections work.
And then the third one is science fiction, and I was debating — I read a lot of science fiction, and there’s a lot of interesting A.I.s in science fiction. Everyone talks about — who’s in the science fiction world — Iain Banks, who wrote about the Culture, which is really interesting, about what it’s like to live beside super intelligent A.I. Vernor Vinge just died yesterday, when we were recording this, and wrote these amazing books about — he coined the term singularity.
But I want to recommend a much more depressing book that’s available for free, which is Peter Watts’s “Blindsight.” And it is not a fun book, but it is a fascinating thriller set on an interstellar mission to visit an alien race. And it’s essentially a book about sentience, and it’s a book about the difference between consciousness and sentience, and about intelligence and the different ways of perceiving the world in a setting where that is the sort of centerpiece of the thriller. And I think in a world where we have machines that might be intelligent without being sentient, it is a relevant, if kind of chilling, read.
Ethan Mollick, your book is called “Co-Intelligence.” Your Substack is One Useful Thing. Thank you very much.
This episode of “The Ezra Klein Show” was produced by Kristin Lin. Fact checking by Michelle Harris. Our senior engineer is Jeff Geld with additional mixing from Efim Shapiro. Our senior editor is Claire Gordon. The show’s production team also includes Annie Galvin and Rollin Hu. Original music by Isaac Jones. Audience strategy by Kristina Samulewski and Shannon Busta. The executive producer of New York Times Opinion Audio is Annie-Rose Strasser, and special thanks to Sonia Herrero.
EZRA KLEIN: From New York Times Opinion, this is “The Ezra Klein Show.”
ETHAN MOLLICK: Thanks for having me.
EZRA KLEIN: So let’s assume I’m interested in A.I. And I tried ChatGPT a bunch of times, and I was suitably impressed and weirded out for a minute. And so I know the technology is powerful. I’ve heard all these predictions about how it will take everything over, or become part of everything we do. But I don’t actually see how it fits into my life, really, at all. What am I missing?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So you’re not alone. This is actually very common. And I think part of the reason is that the way ChatGPT works isn’t really set up for you to understand how powerful it is. You really do need to use the paid version, they are significantly smarter. And you can almost think of this — like, GPT-3, which was — nobody really paid attention to when it came out, before ChatGPT, was about as good as a sixth grader at writing. GPT-3.5, the free version of ChatGPT, is about as good as a high school, or maybe even a college freshman or sophomore.
EZRA KLEIN: When you say, bring it to every table you’re at, one, that sounds like a big pain, because now I’ve got to add another step of talking to the computer constantly. But two, it’s just not obvious to me what that would look like. So what does it look like? What does it look like for you, or what does it look like for others — that you feel is applicable widely?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I just finished this book. It’s my third book. I keep writing books, even though I keep forgetting that writing books is really hard. But this was, I think, my best book, but also the most interesting to write. And it was thanks to A.I. And there’s almost no A.I. writing in the book, but I used it continuously. So things that would get in the way of writing — I think I’m a much better writer than A.I. — hopefully, people agree. But there’s a lot of things that get in your way as a writer.
So I would get stuck on a sentence. I couldn’t do a transition. Give me 30 versions of this sentence in radically different styles. There’s 200 different citations. I had the A.I. read through the papers that I read through, write notes on them, and organize them for me. I had the A.I. suggest analogies that might be useful. I had the A.I. act as readers, and in different personas, read through the paper from the perspective of, is there some example I could give that’s better? Is this understandable or not?
And that’s very typical of the kind of way that I would, say, bring it to the table. Use it for everything, and you’ll find its limits and abilities.
EZRA KLEIN: Let me ask you one specific question on that, because I’ve been writing a book. And on some bad days of writing the book, I decided to play around with GPT-4. And of the things that it got me thinking about was the kind of mistake or problem these systems can help you see and the kind they can’t. So they can do a lot of, give me 15 versions of this paragraph, 30 versions of this sentence. And every once in a while, you get a good version or you’ll shake something a little bit loose.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a wise point. I think there’s two or three things bundled there. The first of those is A.I. is good, but it’s not as good as you. It is, say, at the 80th percentile of writers based on some results, maybe a little bit higher. In some ways, if it was able to have that burst of insight and to tell you this chapter is wrong, and I’ve thought of a new way of phrasing it, we would be at that sort of mythical AGI level of A.I. as smart as the best human. And it just isn’t yet.
EZRA KLEIN: For most people — right, if you’re just going to pick one model, what would you pick? What do you recommend to people? And second, how do you recommend they access it? Because something going on in the A.I. world is there are a lot of wrappers on these models. So ChatGPT has an app. Claude does not have an app. Obviously, Google has its suite of products. And there are organizations that have created a different spin on somebody else’s A.I. — so Perplexity, which is, I believe, built on GPT-4 now, you can pay for it.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s a really good question. I recommend working with one of the models as directly as possible, through the company that creates them. And there’s a few reasons for that. One is you get as close to the unadulterated personality as possible. And second, that’s where features tend to roll out first. So if you like sort of intellectual challenge, I think Claude 3 is the most intellectual of the models, as you said.
EZRA KLEIN: So you say it takes about 10 hours to learn a model. Ten hours is a long time, actually. What are you doing in that 10 hours? What are you figuring out? How did you come to that number? Give me some texture on your 10 hour rule.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So first off, I want to indicate the 10 hours is as arbitrary as 10,000 steps. Like, there’s no scientific basis for it. This is an observation. But it also does move you past the, I poked at this for an evening, and it moves you towards using this in a serious way. I don’t know if 10 hours is the real limit, but it seems to be somewhat transformative. The key is to use it in an area where you have expertise, so you can understand what it’s good or bad at, learn the shape of its capabilities.
EZRA KLEIN: Something that feels to me like a theme of your work is that the way to approach this is not learning a tool. It is building a relationship. Is that fair?
ETHAN MOLLICK: A.I. is built like a tool. It’s software. It’s very clear at this point that it’s an emulation of thought. But because of how it’s built, because of how it’s constructed, it is much more like working with a person than working with a tool. And when we talk about it this way, I almost feel kind of bad, because there’s dangers in building a relationship with a system that is purely artificial, and doesn’t think and have emotions. But honestly, that is the way to go forward. And that is sort of a great sin, anthropomorphization, in the A.I. literature, because it can blind you to the fact that this is software with its own sets of foibles and approaches.
And A.I.s do all of these things. And I find that teachers, managers, even parents, editors, are often better at using these systems, because they’re used to treating this as a person. And they interact with it like a person would, giving feedback. And that helps you. And I think the second piece of that “not tool” piece is that when I talk to OpenAI or Anthropic, they don’t have a hidden instruction manual. There is no list of how you should use this as a writer, or as a marketer, or as an educator.
They don’t even know what the capabilities of these systems are. They’re all sort of being discovered together. And that is also not like a tool. It’s more like a person with capabilities that we don’t fully know yet.
EZRA KLEIN: So you’ve done this with all the big models. You’ve done, I think, much more than this, actually, with all the big models. And one thing you describe feeling is that they don’t just have slightly different strengths and weaknesses, but they have different — for lack of a better term, and to anthropomorphize — personalities, and that the 10 hours in part is about developing an intuition not just for how they work, but kind of how they are and how they talk, the sort of entity you’re dealing with.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s important to know the personalities not just as personalities, but because there are tricks. Those are tunable approaches that the system makers decide. So it’s weird to have this — in one hand, don’t anthropomorphize, because you’re being manipulated, because you are. But on the other hand, the only useful way is to anthropomorphize. So keep in mind that you are dealing with the choices of the makers.
GPT-4 feels like a workhorse at this point. It is the most neutral of the approaches. It wants to get stuff done for you. And it will happily do that. It doesn’t have a lot of time for chitchat. And then we’ve got Google’s Bard, which feels like — or Gemini now — which feels like it really, really wants to help. We use this for teaching a lot. And we build these scenarios where the A.I. actually acts like a counterparty in a negotiation.
So you get to practice the negotiation by negotiating with the A.I. And it works incredibly well. I’ve been building simulations for 10 years, can’t imagine what a leap this has been. But when we try and get Google to do that, it keeps leaping in on the part of the students, to try and correct them and say, no, you didn’t really want to say this. You wanted to say that. And I’ll play out the scenario as if it went better. And it really wants to kind of make things good for you.
EZRA KLEIN: You were mentioning a minute ago that what the A.I.s do reflect decisions made by their programmers. They reflect guardrails, what they’re going to let the A.I. say. Very famously, Gemini came out and was very woke. You would ask it to show you a picture of soldiers in Nazi Germany, and it would give you a very multicultural group of soldiers, which is not how that army worked. But that was something that they had built in to try to make more inclusive photography generation.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a very important point. And fundamental about A.I. is the idea that we technically know how LLMs work, but we don’t know how they work the way they do, or why they’re as good as they are. They’re really — we don’t understand it. The theories range from everyone — from it’s all fooling us, to they’ve emulated the way humans think because the structure of language is the structure of human thought. So even though they don’t think, they can emulate it. We don’t know the answer.
EZRA KLEIN: One thing people know about using these models is that hallucinations, just making stuff up, is a problem. Has that changed at all as we’ve moved from GPT-3.5 to 4, as we move from Claude 2 to 3. Like, has that become significantly better? And if not, how do you evaluate the trustworthiness of what you’re being told?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So those are a couple of overlapping questions. The first of them is, it getting better over time? So there is a paper in the field of medical citations that indicated that around 80 to 90 percent of citations had an error, were made up with GPT-3.5. That’s the free version of Chat. And that drops for GPT-4.
EZRA KLEIN: But doesn’t this make them unreliable in a very tricky way? 80 percent — you’re, like, it’s always hallucinating. 20 percent, 5 percent, it’s enough that you can easily be lulled into overconfidence. And one of the reasons it’s really tough here is you’re combining something that knows how to seem extremely persuasive and confident — you feed into the A.I. a 90-page paper on functions and characteristics of right wing populism in Europe, as I did last night.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Absolutely, and I think hard to grasp, because we’re used to things like type II errors, where we search for something on the internet and don’t find it. We’re not used to type I errors, where we search for something and get an answer back that’s made up. This is a challenge. And there’s a couple things to think about. One of those is — I advocate the BAH standard, best available human. So is the A.I. more or less accurate than the best human you could consult in that area?
EZRA KLEIN: But it also reflects something interesting about the nature of the systems. You have a quote here that I think is very insightful. You wrote, “the core irony of generative A.I.s is that A.I.s were supposed to be all logic and no imagination. Instead, we get A.I.s that make up information, engage in seemingly emotional discussions, and which are intensely creative.” And that last fact is one that makes many people deeply uncomfortable.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I love the phrase “a calculator that uses words.” I think we have been let down by science fiction, both in the utopias and apocalypses that A.I. might bring, but also, even more directly, in our view of how machines should work. People are constantly frustrated, and give the same kinds of tests to A.I.s over and over again, like doing math, which it doesn’t do very well — they’re getting better at this.
EZRA KLEIN: But we were using those measures five years ago, even though they were bad. That’s a point you make that I think is interesting and slightly unsettling.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Yeah, we never had to differentiate humans from machines before. It was always easy. So the idea that we had to have a scale that worked for people and machines, who had that? We had the Turing test, which everyone knew was a terrible idea. But since no machine could pass it, it was completely fine. So the question is, how do we measure this? This is an entirely separate set of issues. Like, we don’t even have a definition of sentience or consciousness.
EZRA KLEIN: So one of the things I will sometimes do, and did quite recently, is give the A.I. a series of personal documents, emails I wrote to people I love that were very descriptive of a particular moment in my life. And then I will ask the A.I. about them, or ask the A.I. to analyze me off of them.
ETHAN MOLLICK: That makes complete sense. I think the weird expectations — we call it the jagged frontier of A.I., that it’s good at some stuff and bad at other stuff. It’s often unexpected. It can lead to these weird moments of disappointment, followed by elation or surprise. And part of the reason why I advocate for people to use it in their jobs is, it isn’t going to outcompete you at whatever you’re best at. I mean, I cannot imagine it’s going to do a better job prepping someone for an interview than you’re doing.
And that’s not me just — I’m trying to be nice to you because you’re interviewing me, but because you’re a good interviewer. You’re a famous interviewer. It’s not going to be as good as that. Now, there’s questions about how good these systems get that we don’t know, but we’re kind of at a weirdly comfortable spot in A.I., which is, maybe it’s the 80th percentile of many performances. But I talk to Hollywood writers. It’s not close to writing like a Hollywood writer. It’s not close to being as good an analyst.
EZRA KLEIN: But this gets to this question of, what are you doing with it? The A.I.s right now seem much stronger as amplifiers and feedback mechanisms and thought partners for you than they do as something you can really outsource your hard work and your thinking to. And that, to me, is one of the differences between trying to spend more time with these systems — like, when you come into them initially, you’re like, OK, here’s a problem, give me an answer.
ETHAN MOLLICK: And that’s why the book’s called “Co-Intelligence.” For right now, we have a prosthesis for thinking. That’s, like, new in the world. We haven’t had that before — I mean, coffee, but aside from that, not much else. And I think that there’s value in that. I think learning to be partner with this, and where it can get wisdom out of you or not — I was talking to a physics professor at Harvard. And he said, all my best ideas now come from talking to the A.I. And I’m like, well, it doesn’t do physics that well. He’s like, no, but it asks good questions. And I think that there is some value in that kind of interactive piece.
EZRA KLEIN: We’ve already talked a bit about — Gemini is helpful, and ChatGPT-4 is neutral, and Claude is a bit warmer. But you urge people to go much further than that. You say to give your A.I. a personality. Tell it who to be. So what do you mean by that, and why?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So this is actually almost more of a technical trick, even though it sounds like a social trick. When you think about what A.I.s have done, they’ve trained on the collective corpus of human knowledge. And they know a lot of things. And they’re also probability machines. So when you ask for an answer, you’re going to get the most probable answer, sort of, with some variation in it. And that answer is going to be very neutral. If you’re using GPT-4, it’ll probably talk about a rich tapestry a lot.
It loves to talk about rich tapestries. If you ask it to code something artistic, it’ll do a fractal. It does very normal, central A.I. things. So part of your job is to get the A.I. to go to parts of this possibility space where the information is more specific to you, more unique, more interesting, more likely to spark something in you yourself. And you do that by giving it context, so it doesn’t just give you an average answer. It gives you something that’s specialized for you.
The easiest way to provide context is a persona. You are blank. You are an expert at interviewing, and you answer in a warm, friendly style. Help me come up with interview questions. It won’t be miraculous in the same way that we were talking about before. If you say you’re Bill Gates, it doesn’t become Bill Gates. But that changes the context of how it answers you. It changes the kinds of probabilities it’s pulling from and results in much more customized and better results.
EZRA KLEIN: OK, but this is weirder, I think, than you’re quite letting on here. So something you turned me on to is there’s research showing that the A.I. is going to perform better on various tasks, and differently on them, depending on the personality. So there’s a study that gives a bunch of different personality prompts to one of the systems, and then tries to get it to answer 50 math questions. And the way it got the best performance was to tell the A.I. it was a Starfleet commander who was charting a course through turbulence to the center of an anomaly.
ETHAN MOLLICK: “What the hell” is a good question. And we’re just scratching the surface, right? There’s a nice study actually showing that if you emotionally manipulate the A.I., you get better math results. So telling it your job depends on it gets you better results. Tipping, especially $20 or $100 — saying, I’m about to tip you if you do well, seems to work pretty well. It performs slightly worse in December than May, and we think it’s because it has internalized the idea of winter break.
EZRA KLEIN: I’m sorry, what?
ETHAN MOLLICK: Well, we don’t know for sure, but —
EZRA KLEIN: I’m holding you up here.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Yeah.
EZRA KLEIN: People have found the A.I. seems to be more accurate in May, and the going theory is that it has read enough of the internet to think that it might possibly be on vacation in December?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So it produces more work with the same prompts, more output, in May than it does in December. I did a little experiment where I would show it pictures of outside. And I’m like, look at how nice it is outside? Let’s get to work. But yes, the going theory is that it has internalized the idea of winter break and therefore is lazier in December.
EZRA KLEIN: I want to just note to people that when ChatGPT came out last year, and we did our first set of episodes on this, the thing I told you was this was going to be a very weird world. What’s frustrating about that is that — I guess I can see the logic of why that might be. Also, it sounds probably completely wrong, but also, I’m certain we will never know. There’s no way to go into the thing and figure that out.
ETHAN MOLLICK: And I think that that is, in some ways, both — as you said, the deep weirdness of these systems. But also, there’s actually downside risks to this. So we know, for example, there is an early paper from Anthropic on sandbagging, that if you ask the A.I. dumber questions, it would get you less accurate answers. And we don’t know the ways in which your grammar or the way you approach the A.I. — we know the amount of spaces you put gets different answers.
EZRA KLEIN: Well, I’m interested in the personas, although I just — I really find this part of the conversation interesting and strange. But I’m interested in the personalities you can give the A.I. for a different reason. I prompted you around this research on how a personality changes the accuracy rate of an A.I. But a lot of the reason to give it a personality, to answer you like it is Starfleet Commander, is because you have to listen to the A.I. You are in relationship with it.
ETHAN MOLLICK: The great power of A.I. is as a kind of companion. It wants to make you happy. It wants to have a conversation. And that can be overt or covert.
EZRA KLEIN: Kevin and I have talked a lot about that conversation with Sydney. And one of the things I always found fascinating about it is, to me, it revealed an incredibly subtle level of read by Sydney Bing, which is, what was really happening there? When you say the A.I. wants to make you happy, it has to read on some level what it is you’re really looking for, over time.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s a mirror. I mean, it’s trained on our stuff. And one of the revealing things about that, that I think we should be paying a lot more attention to, is the fact that because it’s so good at this, right now, none of the frontier A.I. models with the possible exception of Inflection’s Pi, which has been basically acquired in large part by Microsoft now, were built to optimize around keeping us in a relationship with the A.I. They just accidentally do that.
There are other A.I. models that aren’t as good that have been focused on this, but that has been something explicit from the frontier models they’ve been avoiding till now. Claude sort of breaches that line a little bit, which is part of why I think it’s engaging. But I worry about the same kind of mechanism that inevitably reined in social media, which is, you can make a system more addictive and interesting. And because it’s such a good cold reader, you could tune A.I. to make you want to talk to it more.
EZRA KLEIN: I want to hold here for a minute, because we’ve been talking about how to use frontier models, I think implicitly talking about how to use A.I. for work. But the way that a lot of people are using it is using these other companies that are explicitly building for relationships. So I’ve had people at one of the big companies tell me that if we wanted to tune our system relationally, if we wanted to tune it to be your friend, your lover, your partner, your therapist, like, we could blow the doors off that. And we’re just not sure it’s ethical.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that is an absolute near-term certainty, and sort of an unstoppable one, that we are going to have A.I. relationships in a broader sense.
And I think the question is, just like we’ve just been learning — I mean, we’re doing a lot of social experiments at scale we’ve never done before in the last couple of decades, right? Turns out social media brings out entirely different things in humans that we weren’t expecting. And we’re still writing papers about echo chambers and tribalism and facts, and what we agree or disagree with.
We’re about to have another wave of this. And we have very little research. And you could make a plausible story up, that what’ll happen is it’ll help mental health in a lot of ways for people, and then there’ll be more social outside, that there might be a rejection of this kind of thing.
EZRA KLEIN: I was worried we were getting off track in the conversation, but I realized we were actually getting deeper on the track I was trying to take us down.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think that’s a temporary state of affairs, like extremely temporary. I think a GPT-4 class model — we actually already know this. They can guess your intent quite well. And I think that this is a way of giving you a sense of agency or control in the short term. I don’t think you’re going to need to know yourself at all. And I think you wouldn’t right now if any of the GPT-4 class models allowed themselves to be used in this way, without guardrails, which they don’t, I think you would already find it’s just going to have a conversation with you and morph into what you want.
EZRA KLEIN: So that’s a little bit chilling, but I’m nevertheless going to stay in this world we’re in, because I think we’re going to be in it for at least a little while longer, where you do have to do all this prompt engineering. What is a prompt, first? And what is prompt engineering?
ETHAN MOLLICK: So a prompt is — technically, it is the sentence, the command you’re putting into the A.I. What it really is is the beginning part of the A.I.s text that it’s processing. And then it’s just going to keep adding more words or tokens to the end of that reply, until it’s done. So a prompt is the command you’re giving the A.I. But in reality, it’s sort of a seed from which the A.I. builds.
EZRA KLEIN: And when you prompt engineer, what are some ways to do that? Maybe one to begin with, because it seems to work really well, is chain of thought.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Just to take a step back, A.I. prompting remains super weird. Again, strange to have a system where the companies making the systems are writing papers as they’re discovering how to use the systems, because nobody knows how to make them work better yet. And we found massive differences in our experiments on prompt types. So for example, we were able to get the A.I. to generate much more diverse ideas by using this chain of thought approach, which we’ll talk about.
EZRA KLEIN: Then you get an answer, and then what?
ETHAN MOLLICK: And then — what you do in a conversational approach is you go back and forth. If you want work output, what you’re going to do is treat it like it is an intern who just turned in some work to you. Actually, could you punch up paragraph two a little bit? I don’t like the example in paragraph one. Could you make it a little more creative, give me a couple of variations? That’s a conversational approach trying to get work done.
EZRA KLEIN: So I want to offer an example of how this back and forth can work. So we asked Claude 3 about prompt engineering, about what we’re talking about here. And the way it described it to us is, quote, “It’s a shift from the traditional paradigm of human-computer interaction, where we input explicit commands and the machine executes them in a straightforward way, to a more open ended, collaborative dialogue, where the human and the A.I. are jointly shaping the creative process,” end quote.
And that’s pretty good, I think. That’s interesting. It’s worth talking about. I like that idea that it’s a more collaborative dialogue. But that’s also boring, right? Even as I was reading it, it’s a mouthful. It’s wordy. So I kind of went back and forth with it a few times. And I was saying, listen, you’re a podcast editor. You’re concise, but also then I gave it a couple examples of how I punched up questions in the document, right? This is where the question began. Here’s where it ended. And then I said, try again, and try again, and try again, and make it shorter. And make it more concise.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I am at a loss about when you went to Claude and when it was you, to be honest. So I was ready to answer at like two points along the way, so that was pretty good from my perspective, sitting here, talking to you. That felt interesting, and felt like the conversation we’ve been having. And I think there’s a couple of interesting lessons there.
The first, by the way, of — interestingly, you asked A.I. about one of its weakest points, which is about A.I. And everybody does this, but because its knowledge window doesn’t include that much stuff about A.I., it actually is pretty weak in terms of knowing how to do good prompting, or what a prompt is, or what A.I.s do well. But you did a good job with that. And I love that you went back and forth and shaped it.
One of the techniques you used to shape it, by the way, was called few-shot, which is giving an example. So the two most powerful techniques are chain of thought, which we just talked about, and few-shot, giving it examples. Those are both well supported in the literature. And then, I’d add personas. So we’ve talked about, I think, the basics of prompt crafting here overall. And I think that the question was pretty good.
EZRA KLEIN: One of the things I realized trying to spend more time with the A.I. is that you really have to commit to this process. You have to go back and forth with it a lot. If you do, you can get really good questions, like the one I just did — or, I think, really good outcomes. But it does take time.
ETHAN MOLLICK: One set of techniques that work quite well is to speed run to where you are in the conversation. So you can actually pick up an older conversation where you got the A.I.’s mindset where you want and work from there. You can even copy and paste that into a new window. You can ask the A.I. to summarize where you got in that previous conversation, and the tone the A.I. was taking, and then when you give a new instruction say the interaction I like to have with you is this, so have it solve the problem for you by having it summarize the tone that you happen to like at the end.
EZRA KLEIN: You did mention something important there, because they’re already getting much bigger in terms of how much information they can hold. Like, the earlier generations could barely hold a significant chat. Now, Claude 3 can functionally hold a book in its memory. And it’s only going to go way, way, way up from here. And I know I’ve been trying to keep us in the present, but this feels to me really quickly like where this is both going and how it’s going to get a lot better.
ETHAN MOLLICK: It’s not even going there. Like, it’s already there. Gemini 1.5 can hold an entire movie, books. But like, it starts to now open up entirely new ways of working. I can show it a video of me working on my computer, just screen capture. And it knows all the tasks I’m doing and suggests ways to help me out. It starts watching over my shoulder and helping me. I put in all of my work that I did prior to getting tenure and said, write my tenure statement. Use exact quotes.
EZRA KLEIN: One thing that feels important to keep in front of mind here is that we do have some control over that. And not only do we have some control over it, but business models and policy are important here. And one thing we know from inside these A.I. shops is these A.I.s already are, but certainly will be, really super persuasive.
And so if the later iterations of the A.I. companions are tuned on the margin to try to encourage you to be also out in the real world, that’s going to matter, versus whether they have a business model that all they want is for you to spend a maximum amount of time talking to your A.I. companion, whether you ever have a friend who is flesh and blood be damned.
And so that’s an actual choice, right? That’s going to be a programming decision. And I worry about what happens if we leave that all up to the companies, right? At some point, there’s a lot of venture capital money in here right now. At some point, the venture capital runs out. At some point, people need to make big profits. At some point, they’re in competition with other players who need to make profits. And that’s when things — you get into what Cory Doctorow calls the “enshitification” cycle, where things that were once adding a lot of value to the user begin extracting a lot of value to the user.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I absolutely agree. I think that we have agency here. We have agency in how we operate this in businesses, and whether we use this in ways that encourage human flourishing and employees, or are brutal to them. And we have agency over how this works socially. And I think we abrogated that responsibility with social media, and that is an example. Not to be bad news, because I generally have a lot of mixed optimism and pessimism about parts of A.I., but the bad news piece is there are open source models out there that are quite good.
EZRA KLEIN: I see a lot of reasons to be worried about the open source models. And people talk about things like bioweapons and all that. But for some of the harms I’m talking about here, if you want to make money off of American kids, we can regulate you. So sometimes I feel like we almost, like, give up the fight before it begins. But in terms of what a lot of people are going to use, if you want to be having credit card payments processed by a major processor, then you have to follow the rules.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I couldn’t agree more. And I don’t think there’s any reason to give up hope on regulation. I think that we can mitigate. And I think part of our job, though, is also not just to mitigate the harms, but to guide towards the positive viewpoints, right? So what I worry about is that the incentive for profit making will push for A.I. that acts informally as your therapist or your friend, while our worries about experimentation, which are completely valid, are slowing down our ability to do experiments to find out ways to do this right.
And I think it’s really important to have positive examples, too. I want to point to the A.I. systems acting ethically as your friend or companion, and figure out what that is, so there’s a positive model to look for. So I’m not just — this is not to denigrate the role of regulation, which I think is actually going to be important here, and self regulation, and rapid response from government, but also the companion problem of, “we need to make some sort of decisions about what are the paragons of this, what is acceptable as a society?”
EZRA KLEIN: So I want to talk a bit about another downside here, and this one more in the mainstream of our conversation, which is on the human mind, on creativity. So a lot of the work A.I. is good at automating is work that is genuinely annoying, time consuming, laborious, but often plays an important role in the creative process. So I can tell you that writing a first draft is hard, and that work on the draft is where the hard thinking happens.
ETHAN MOLLICK: I think the idea of struggle is actually a core one in many things. I’m an educator. And one thing that keeps coming out in the research is that there is a strong disconnect between what students think they’re learning and when they learn. So there was a great controlled experiment at Harvard in intro science classes, where students either went to a pretty entertaining set of lectures, or else they were forced to do active learning, where they actually did the work in class.
Not just because, by the way, it makes the work easier, but also because you mentally anchor on the A.I.’s answer. And in some ways, the most dangerous A.I. application, in my mind, is the fact that you have these easy co-pilots in Word and Google Docs, because any writer knows about the tyranny of the blank page, about staring at a blank page and not knowing what to do next, and the struggle of filling that up. And when you have a button that produces really good words for you, on demand, you’re just going to do that. And it’s going to anchor your writing.
We can teach people about the value of productive struggle, but I think that during the school years, we have to teach people the value of writing — not just assign an essay and assume that the essay does something magical, but be very intentional about the writing process and how we teach people about how to do that, because I do think the temptation of what I call “the button” is going to be there otherwise, for everybody.
EZRA KLEIN: But I worry this stretches, I mean, way beyond writing. So the other place I worry about this, or one of the other places I worry about this a lot, is summarizing. And I mean, this goes way back. When I was in school, you could buy Sparknotes. And they were these little, like, pamphlet sized descriptions of what’s going on in “War and Peace” or what’s going on in “East of Eden.”
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I don’t mean to push back too much on this.
EZRA KLEIN: No, please, push back a lot.
ETHAN MOLLICK: But I think you’re right.
EZRA KLEIN: Imagine we’re debating and you are a snarky. A.I. [LAUGHS]
ETHAN MOLLICK: Fair enough. With that prompt —
EZRA KLEIN: With that prompt engineering.
ETHAN MOLLICK: — yeah, I mean, I think that this is the eternal thing about looking back on the next generation, we worry about technology ruining them. I think this makes ruining easier. But as somebody who teaches at universities, like, lots of people are summarizing. Like, I think those of us who enjoy intellectual struggle are always thinking everybody else is going through the same intellectual struggle when they do work. And they’re doing it about their own thing. They may or may not care the same way.
EZRA KLEIN: Well, let me take this from another angle. One of the things that I’m a little obsessed with is the way the internet did not increase either domestic or global productivity for any real length of time. So I mean, it’s a very famous line. You can see the IT revolution anywhere but in the productivity statistics. And then you do get, in the ’90s, a bump in productivity that then peters out in the 2000s.
And so some of the time that was given to us back was also taken back. And I see a lot of dynamics like this that could play out with A.I. — I wouldn’t even just say if we’re not careful, I just think they will play out and already are. I mean, the internet is already filling with mediocre crap generated by A.I. There is going to be a lot of destructive potential, right? You are going to have your sex bot in your pocket, right?
There’s a million things — and not just that, but inside organizations, there’s going to be people padding out what would have been something small, trying to make it look more impressive by using the A.I. to make something bigger. And then, you’re going to use the A.I. to summarize it back down. The A.I. researcher, Jonathan Frankel, described this to me as, like, the boring apocalypse version of A.I., where you’re just endlessly inflating and then summarizing, and then inflating and then summarizing the volume of content between different A.I.
ETHAN MOLLICK: So I think there’s a lot there to chew on. And I also have spent a lot of time trying to think about why the internet didn’t work as well. I was an early Wikipedia administrator.
EZRA KLEIN: Thank you for your service.
ETHAN MOLLICK: [LAUGHS] Yeah, it was very scarring. But I think a lot about this. And I think A.I. is different. I don’t know if it’s different in a positive way. And I think we talked about some of the negative ways it might be different. And I think it’s going to be many things at once, happening quite quickly. So I think the information environment’s going to be filled up with crap. We will not be able to tell the difference between true and false anymore. It will be an accelerant on all the kinds of problems that we have there.
The thing that makes A.I. possibly great is that it’s so very human, so it interacts with our human systems in a way that the internet did not. We built human systems on top of it, but A.I. is very human. It deals with human forms and human issues and our human bureaucracy very well. And that gives me some hope that even though there’s going to be lots of downsides, that the upsides of productivity and things like that are real.
Part of the problem with the internet is we had to digitize everything. We had to build systems that would make our offline world work with our online world. And we’re still doing that. If you go to business schools, digitizing is still a big deal 30 years on from early internet access. A.I. makes this happen much quicker because it works with us. So I’m a little more hopeful than you are about that, but I also think that the downside risks are truly real and hard to anticipate.
EZRA KLEIN: I think that is a good place to end. So always our final question, what are three books you’d recommend to the audience?
ETHAN MOLLICK: OK, so the books I’ve been thinking about are not all fun, but I think they’re all interesting. One of them is “The Rise and Fall of American Growth,” which is — it’s two things. It’s an argument about why we will never have the kind of growth that we did in the first part of the Industrial Revolution again, but I think that’s less interesting than the first half of the book, which is literally how the world changed between 1870 or 1890 and 1940, versus 1940 and 1990, or 2000.
EZRA KLEIN: Ethan Mollick, your book is called “Co-Intelligence.” Your Substack is One Useful Thing. Thank you very much.
ETHAN MOLLICK: Thank you.
EZRA KLEIN: This episode of “The Ezra Klein Show” was produced by Kristin Lin. Fact checking by Michelle Harris. Our senior engineer is Jeff Geld with additional mixing from Efim Shapiro. Our senior editor is Claire Gordon. The show’s production team also includes Annie Galvin and Rollin Hu. Original music by Isaac Jones. Audience strategy by Kristina Samulewski and Shannon Busta. The executive producer of New York Times Opinion Audio is Annie-Rose Strasser, and special thanks to Sonia Herrero.
Advertisement

Turn Your Curiosity Into Discovery
Latest facts.

Tips and Tricks to Help You Create a HIPAA Compliant Email

How to Stop Facial Hair Growth in Females Naturally
40 facts about elektrostal.
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.
Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learning the fundamentals of photographic arts improves the success of an artist. The fundamentals of photographic arts combine technical brilliance and creativity. We can add value to a story when we learn the technical and creative aspects of photography. Image technology contributes to the change in photographic dimensions (Barba, 2001).
Reflective Essay On Photography. 1045 Words5 Pages. Photography. About Us. Capturing beautiful moments of every individual's life and freezing them in an album or a frame is what we strive to offer at our photographic studio. We have been working to create beautiful photographs of each of your event in the most creative way; we turn ideas ...
The Genesis of a Masterpiece. Let's take a trip back in time, to the year 1977. The world was a different place then, and amidst the hustle and bustle, a certain book was born that would forever change the way we perceive photography. This book was none other than "On Photography," a collection of six essays penned by the brilliant Susan ...
Here are some handy essay ideas and examples for inspiration! 1. A day in the life. Your first photo essay idea is simple: Track a life over the course of one day. You might make an essay about someone else's life. Or the life of a location, such as the sidewalk outside your house.
Photography has become a true art like cinema, theatre, sculpture, and others. However, it has its own particularities: for example, it is possible to immortalize no more than a second, and there is no way to make any changes in the shot. What is more, it is necessary to mention that photographers are always limited by their own camera, which ...
3. Take your time. A great photo essay is not done in a few hours. You need to put in the time to research it, conceptualizing it, editing, etc. That's why I previously recommended following your passion because it takes a lot of dedication, and if you're not passionate about it - it's difficult to push through. 4.
Nevertheless, Sontag's radical thoughts on photography are as potent as ever. Born in 1933, Sontag wrote plays, essays, and fiction until her death in 2004. She had no formal training in art or photography—she studied English and philosophy at Harvard—but immersed herself in the New York cultural scene from 1959 onward.
4. Choose your top 10 images. Once a few days have passed, pick the best 100 photos from your shoot to start with. Then, a day or more later, look at those 100 images and narrow them down to the top 25. Finally, narrow the 25 down to the top 10 images, making sure each photo serves your original concept for the story. 5.
Sir John Herschel, was the first to use the term photography in 1839, when he managed to fix images using hyposulphite of soda. He described photography as "The application of the chemical rays to the purpose of pictorial representation". Herschel also coined the terms "negative", "positive" and "snapshot". 1698 Words.
In some circles social realism became suspect and photographic movements such as the Bauhaus-influenced Neues Sehen (New Vision) followed conventions of abstraction (Edwards, 2006: 57 ff.), problematizing the idea of the representation of the 'real'.Even during the heyday of documentary realism, photography's innocence was challenged, for example by Siegfried Kracauer's opposition to ...
Reflection photos refer to any shot, no matter what type of photography genre, that uses a reflective surface. Landscape photography, with a mountain duplicated in the still water of a lake, is reflection photography.An image of a city captured on the shiny surface of a skyscraper is a reflection shot, as is that same city skyline captured in a puddle on a sidewalk.
Contemporary versus Historical Photographers. Photography is a word derived from the Greek words photos light and to draw. A scientist called Sir John F.W. Herschel, which was in 1839, first used the word. It was a method which was all about recording images by using light or radiation on a sensitive material.
Creating photo essays is an amazing antidote if you've ever felt a lack of direction or purpose in your photography. Photo essays help build your photographic skills in at least 3 important ways. 1. You become more strategic in creating a body of work. It's easy to get stuck in a rut of photographing whatever pops up in front of you.
Learn the purpose of writing a reflective essay, and see reflective essay examples. Discover how to format and how to start writing a reflective essay. Updated: 11/21/2023
Critical Reflection On Photography Critical Reflection Intentions My genre of work is a mixture of sports photography and fashion photography, the reason for this is because sports photography focuses on the drama and action in sports, this contrasts with fashion photography as the photos mainly focuses on things such as clothing and makeup.
Here's a recap of the contents of this article, which also serves as a way to create a mind map: 1. Identify the topic you will be writing on. 2. Note down any ideas that are related to the topic and if you want to, try drawing a diagram to link together any topics, theories, and ideas. 3.
A reflective essay is a type of written work which reflects your own self. Since it's about yourself, you already have a topic to write about. For reflective essay examples, readers expect you to evaluate a specific part of your life. To do this, you may reflect on emotions, memories, and feelings you've experienced at that time.
Bykovo, Moscow Region - August 2019. 55.4344, 38.3730 Landfill solid waste Bykovo. Time of action 1960s - 2016. Area 8.7 hectares., Volume 430 000 tons, height 11 meters, 300 meters to the nearest country houses and 1.7 km to residential areas.
I was born and raised in a working-class city, Elektrostal, Moscow region. I received a higher education in television in Moscow. I studied to be a documentary photographer. My vision of the aesthetics of the frame was significantly influenced by the aesthetics of my city - the endless forests and swamps of the Moscow region with endless factories, typical architecture and a meagre color palette.
The Moscow Metropolitan underground railway (known as the metro) is today the most efficient form of city transport. In present time, the subway system in Moscow consists from twelfth lines with total length of railways more than 300 km (190 mi) and more than 180 stations.
First, outline the problem, you know, the essay you're going to write. Second, give me the first line of each paragraph. Third, go back and write the entire thing.
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...