Essay Writing Guide
Essay Format

Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
10 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Are you having trouble making your essay look just right? Lots of students find formatting tricky, so you're not alone.
This guide is here to help you figure out how to format your essay. We've got examples of essays in APA, MLA, Chicago, and other styles to make it easier for you to learn.
So, keep reading – we've got you covered!
- 1. What is an Essay Format?
- 2. How To Format Essay in MLA Style
- 3. How to Format Essay in APA
- 4. How to Format Essay in Chicago Style
- 5. Formatting In-Text Citations: APA, MLA, and Chicago Styles
- 6. How to Determine What Format to Follow
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format refers to a set of guidelines that decides how the elements of your paper should be arranged. No matter what type of essay you’re writing, formatting is an essential step in the essay writing process.
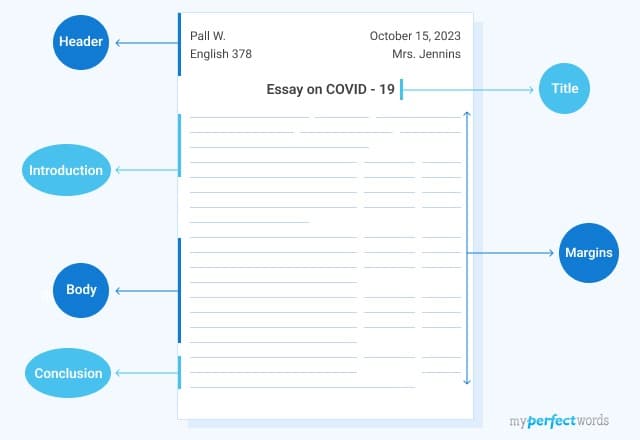
The format guidelines cover the essay structure, title, citations, and the basic outline of the essay.
When formatting a paper, there are certain things that you need to pay attention to. These include the structure of an essay, title page, works cited page, and citation styles .
Here is a basic essay format template:
How To Format Essay in MLA Style
Formatting an essay in MLA style is a common requirement in many academic settings, particularly in the humanities.
MLA provides guidelines for various aspects of your essay, from font and margins to citations and bibliography. Here’s an essay format MLA you can use as a reference:
MLA Essay Format Template
- Title Page: MLA does not typically require a separate title page. Instead, place your title at the top of the first page, centered, and do not use bold, italics, or underline for the title. Below the title, include your name, the instructor's name, the course name and number, and the due date, each on a separate line, left-aligned.
- Header and Page Numbers: Create a header with your last name and page number in the upper right corner of every page, half an inch from the top, and flush with the right margin. For example: Smith 1.
- Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch, and use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Font and Size: Use a legible font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12.
- Indentation: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches, which can be done automatically using the "Tab" key.
- Paragraphs: Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks within sentences.
- Title: Place the title of your essay (centered) at the top of the first page. Do not use bold, italics, or underlining for the title. Capitalize major words.
- Citations: MLA uses in-text citations to acknowledge sources. When quoting or paraphrasing, include the author's last name and the page number (e.g., Smith 45).
- Works Cited Page: At the end of your essay, include a separate page titled "Works Cited." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific MLA citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample MLA Essay

How to Format Essay in APA
Formatting an essay in APA style is commonly used in the social sciences and psychology.
APA provides a set of guidelines for various elements of your essay, including formatting, citations, and references. Here’s how to format essay in apa:
APA Essay Format Template
- Title Page: The title page in APA includes: Title of the Essay (centered, bold, and in title case) Your Name (centered) Institutional Affiliation (centered) Running head: [Shortened Title] (flush left, in uppercase) Page Number (flush right)
- Header and Page Numbers: Create a header with the title of your essay in all capital letters, followed by a colon and a shortened version of the title (up to 50 characters), in the upper left corner of every page. The page number should be in the upper right corner.
- Font and Size: Use a clear and readable font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12.
- Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Use a hanging indent for references on the reference page.
- Citations: Use in-text citations to acknowledge sources. Include the author's last name and the publication year (e.g., Smith, 2023) when quoting or paraphrasing.
- Title: Use bold and title case for the title of your essay on the title page. On subsequent pages, use a shortened version of the title (in uppercase) as the header.
- References Page: At the end of your essay, create a separate page titled "References." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific APA citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample APA Essay

How to Format Essay in Chicago Style
Formatting an essay in Chicago style, often used in history and some other humanities disciplines, requires specific guidelines for citations and formatting. Here are the guidelines to format your essay in Chicago style:
Chicago Essay Format Template
- Title Page: The title page in Chicago style includes: Title of the Essay (centered, in headline-style capitalization) Your Name (centered) Course Name and Number (centered) Instructor's Name (centered) Date (centered)
- Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch. Use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Page Numbers: Number pages in the upper right corner of each page, beginning with the first page of the main text (usually page 1). Page numbers should be in Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Use a block paragraph style with no extra space between paragraphs.
- Citations: In Chicago style, you have two citation options: footnotes and endnotes. In your text, place a superscript number (e.g., ^1) at the end of the sentence containing the cited information. Corresponding footnotes or endnotes should provide full citation details.
- Title: Use headline-style capitalization for the title of your essay (e.g., "The History of Ancient Civilizations").
- Bibliography: At the end of your essay, include a separate page titled "Bibliography." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific Chicago citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample Chicago Essay

Formatting In-Text Citations: APA, MLA, and Chicago Styles
An in-text citation is a brief reference within the body of your essay or research paper that indicates the source of information you have incorporated into your writing.
Each of the formatting style have a unique way for adding in-text citations:
In APA style, remember to include the author's last name, the publication date, and the page number (if applicable) within parentheses.
Example: "The impact of climate change on biodiversity is a growing concern (Smith, 2020, p. 27)."
In MLA style, provide the author's last name and the page number without any punctuation between them.
Example: "The impact of climate change on biodiversity is a growing concern (Jones 42)."
Chicago Style Format
The Chicago Manual of Style offers two distinct options for in-text citations:
- Author-Date Style: In this approach, you place your citations within parentheses directly within the text. This style involves citing the author's last name and the publication date within the body of your text. Example: (Smith 2021) or "According to Smith (2021),..."
- Notes and Bibliography Style: This style utilizes numbered footnotes or endnotes to provide citations. Instead of placing citations within the text, you include a superscript number at the end of the relevant sentence, which corresponds to a full citation located in a footnote at the bottom of the page (or endnotes at the end of the document). Example: Johnson argues that "the data is unconvincing."¹ Nevertheless, Smith contends that the study makes "a compelling case" for this plan of action.²
Each of these Chicago citation styles has its unique advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the assignment or the preferences of the writer.
How to Determine What Format to Follow
Selecting the appropriate citation format for your academic writing is essential to ensure that your work meets the expected standards. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
Subject and Discipline
- APA Style: Primarily used in the social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and education. It is also common in business and nursing disciplines.
- MLA Style: Commonly employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. It's widely used for papers related to literature and the arts.
- Chicago Style: Used in history, some social sciences, and certain humanities disciplines. Chicago offers both author-date and notes and bibliography styles, making it versatile for various subjects.
Professor's Instructions
Always adhere to your professor's specific instructions regarding citation style and writing convention . Professors may have preferences or requirements based on the nature of the course or assignment.
For instance, an English professor might prefer MLA for literary analysis, while a psychology professor may opt for APA to encourage familiarity with research norms. However, when formatting styles are not specified by the instructor, you can follow whatever is appropriate for your subject.
Institutional Guidelines
Your educational institution may have established guidelines or standards for citation formats.
Check your institution's style guide or consult with academic advisors to ensure compliance with their specific requirements.
By considering the subject matter, your professor's preferences, and your institution's guidelines, you can confidently choose the appropriate citation style to enhance the clarity and professionalism of your academic writing.
Now that you've gained a solid understanding of the basics for three major formatting styles, you're well-prepared to tackle your essay formatting with confidence.
Whether you're crafting an essay, a research paper, or any academic document, these formatting principles will help you present your ideas professionally.
If you find yourself in a time crunch, our expert writers are here to help you tackle your academic challenges in no time.
With our essay writing service , you get reliable help with any type of assignment, even with tight deadlines. Our writers are sure to deliver you 100% original papers that meet your requirements.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Format an Essay
Last Updated: August 26, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 85,290 times.
You’re opening your laptop to write an essay, knowing exactly what you want to write, but then it hits you—you don’t know how to format it! Using the correct format when writing an essay can help your paper look polished and professional while earning you full credit. There are 3 common essay formats—MLA, APA, and Chicago Style—and we’ll teach you the basics of properly formatting each in this article. So, before you shut your laptop in frustration, take a deep breath and keep reading because soon you’ll be formatting like a pro.
Setting Up Your Document

- If you can’t find information on the style guide you should be following, talk to your instructor after class to discuss the assignment or send them a quick email with your questions.
- If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts.

- Most word processors default to 1 inch (2.5 cm) margins.

- Do not change the font size, style, or color throughout your essay.

- Change the spacing on Google Docs by clicking on Format , and then selecting “Line spacing.”
- Click on Layout in Microsoft Word, and then click the arrow at the bottom left of the “paragraph” section.

- Using the page number function will create consecutive numbering.
- When using Chicago Style, don’t include a page number on your title page. The first page after the title page should be numbered starting at 2. [4] X Research source
- In APA format, a running heading may be required in the left-hand header. This is a maximum of 50 characters that’s the full or abbreviated version of your essay’s title. [5] X Research source

- For APA formatting, place the title in bold at the center of the page 3 to 4 lines down from the top. Insert one double-spaced line under the title and type your name. Under your name, in separate centered lines, type out the name of your school, course, instructor, and assignment due date. [6] X Research source
- For Chicago Style, set your cursor ⅓ of the way down the page, then type your title. In the very center of your page, put your name. Move your cursor ⅔ down the page, then write your course number, followed by your instructor’s name and paper due date on separate, double-spaced lines. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Double-space the heading like the rest of your paper.
Writing the Essay Body

- Use standard capitalization rules for your title.
- Do not underline, italicize, or put quotation marks around your title, unless you include other titles of referred texts.

- A good hook might include a quote, statistic, or rhetorical question.
- For example, you might write, “Every day in the United States, accidents caused by distracted drivers kill 9 people and injure more than 1,000 others.”

- "Action must be taken to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, including enacting laws against texting while driving, educating the public about the risks, and giving strong punishments to offenders."
- "Although passing and enforcing new laws can be challenging, the best way to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving is to enact a law against texting, educate the public about the new law, and levy strong penalties."

- Use transitions between paragraphs so your paper flows well. For example, say, “In addition to,” “Similarly,” or “On the other hand.” [12] X Research source

- A statement of impact might be, "Every day that distracted driving goes unaddressed, another 9 families must plan a funeral."
- A call to action might read, “Fewer distracted driving accidents are possible, but only if every driver keeps their focus on the road.”
Using References

- In MLA format, citations should include the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information. If the author's name appears in the sentence, use just the page number. [14] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For APA format, include the author’s last name and the publication year. If the author’s name appears in the sentence, use just the year. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- If you don’t use parenthetical or internal citations, your instructor may accuse you of plagiarizing.

- At the bottom of the page, include the source’s information from your bibliography page next to the footnote number. [16] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Each footnote should be numbered consecutively.

- If you’re using MLA format , this page will be titled “Works Cited.”
- In APA and Chicago Style, title the page “References.”

- If you have more than one work from the same author, list alphabetically following the title name for MLA and by earliest to latest publication year for APA and Chicago Style.
- Double-space the references page like the rest of your paper.
- Use a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) if your citations are longer than one line. Press Tab to indent any lines after the first. [17] X Research source
- Citations should include (when applicable) the author(s)’s name(s), title of the work, publication date and/or year, and page numbers.
- Sites like Grammarly , EasyBib , and MyBib can help generate citations if you get stuck.
Formatting Resources

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://www.une.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/392149/WE_Formatting-your-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalEnglish/unit10/Foundations/formatting-a-college-essay-mla-style.html
- ↑ https://camosun.libguides.com/Chicago-17thEd/titlePage
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/page-header
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/handouts/writing_process/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.deanza.edu/faculty/cruzmayra/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://library.menloschool.org/chicago
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maansi Richard
May 8, 2019
Did this article help you?

Jan 7, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 3 popular essay formats: which should you use.
General Education

Not sure which path your essay should follow? Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it’s an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we’ll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
For each, we’ll do a high-level overview of what your essay’s structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for each and whether they’re a proponent of the Oxford comma. We also include information on why essay formatting is important and what you should do if you’re not sure which style to use.
Why Is Your Essay Format Important?
Does it really matter which font size you use or exactly how you cite a source in your paper? It can! Style formats were developed as a way to standardize how pieces of writing and their works cited lists should look.
Why is this necessary? Imagine you’re a teacher, researcher, or publisher who reviews dozens of papers a week. If the papers didn’t follow the same formatting rules, you could waste a lot of time trying to figure out which sources were used, if certain information is a direct quote or paraphrased, even who the paper’s author is. Having essay formatting rules to follow makes things easier for everyone involved. Writers can follow a set of guidelines without trying to decide for themselves which formatting choices are best, and readers don’t need to go hunting for the information they’re trying to find.
Next, we’ll discuss the three most common style formats for essays.
MLA Essay Format
MLA style was designed by the Modern Language Association, and it has become the most popular college essay format for students writing papers for class. It was originally developed for students and researchers in the literature and language fields to have a standardized way of formatting their papers, but it is now used by people in all disciplines, particularly humanities. MLA is often the style teachers prefer their students to use because it has simple, clear rules to follow without extraneous inclusions often not needed for school papers. For example, unlike APA or Chicago styles, MLA doesn’t require a title page for a paper, only a header in the upper left-hand corner of the page.
MLA style doesn’t have any specific requirements for how to write your essay, but an MLA format essay will typically follow the standard essay format of an introduction (ending with a thesis statement), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
One of the nice things about creating your works cited for MLA is that all references are structured the same way, regardless of whether they’re a book, newspaper, etc. It’s the only essay format style that makes citing references this easy! Here is a guide on how to cite any source in MLA format. When typing up your works cited, here are a few MLA format essay rules to keep in mind:
- The works cited page should be the last paper of your paper.
- This page should still be double-spaced and include the running header of your last name and page number.
- It should begin with “Works Cited” at the top of the page, centered.
- Your works cited should be organized in alphabetical order, based on the first word of the citation.
APA Essay Format
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. This format type is most often used for research papers, specifically those in behavioral sciences (such as psychology and neuroscience) and social sciences (ranging from archeology to economics). Because APA is often used for more research-focused papers, they have a more specific format to follow compared to, say, MLA style.
All APA style papers begin with a title page, which contains the title of the paper (in capital letters), your name, and your institutional affiliation (if you’re a student, then this is simply the name of the school you attend). The APA recommends the title of your paper not be longer than 12 words.
After your title page, your paper begins with an abstract. The abstract is a single paragraph, typically between 150 to 250 words, that sums up your research. It should include the topic you’re researching, research questions, methods, results, analysis, and a conclusion that touches on the significance of the research. Many people find it easier to write the abstract last, after completing the paper.
After the abstract comes the paper itself. APA essay format recommends papers be short, direct, and make their point clearly and concisely. This isn’t the time to use flowery language or extraneous descriptions. Your paper should include all the sections mentioned in the abstract, each expanded upon.
Following the paper is the list of references used. Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an interview. Here’s a guide for how to reference different source types in APA format . Your references should begin on a new page that says “REFERENCES” at the top, centered. The references should be listed in alphabetical order.

Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style (sometimes referred to as “Turabian style”) was developed by the University of Chicago Press and is typically the least-used by students of the three major essay style formats. The Chicago Manual of Style (currently on its 17th edition) contains within its 1000+ pages every rule you need to know for this style. This is a very comprehensive style, with a rule for everything. It’s most often used in history-related fields, although many people refer to The Chicago Manual of Style for help with a tricky citation or essay format question. Many book authors use this style as well.
Like APA, Chicago style begins with a title page, and it has very specific format rules for doing this which are laid out in the chart below. After the title page may come an abstract, depending on whether you’re writing a research paper or not. Then comes the essay itself. The essay can either follow the introduction → body → conclusion format of MLA or the different sections included in the APA section. Again, this depends on whether you’re writing a paper on research you conducted or not.
Unlike MLA or APA, Chicago style typically uses footnotes or endnotes instead of in-text or parenthetical citations. You’ll place the superscript number at the end of the sentence (for a footnote) or end of the page (for an endnote), then have an abbreviated source reference at the bottom of the page. The sources will then be fully referenced at the end of the paper, in the order of their footnote/endnote numbers. The reference page should be titled “Bibliography” if you used footnotes/endnotes or “References” if you used parenthetical author/date in-text citations.
Comparison Chart
Below is a chart comparing different formatting rules for APA, Chicago, and MLA styles.
How Should You Format Your Essay If Your Teacher Hasn’t Specified a Format?
What if your teacher hasn’t specified which essay format they want you to use? The easiest way to solve this problem is simply to ask your teacher which essay format they prefer. However, if you can’t get ahold of them or they don’t have a preference, we recommend following MLA format. It’s the most commonly-used essay style for students writing papers that aren’t based on their own research, and its formatting rules are general enough that a teacher of any subject shouldn’t have a problem with an MLA format essay. The fact that this style has one of the simplest sets of rules for citing sources is an added bonus!

What's Next?
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Compound sentences are an importance sentence type to know. Read our guide on compound sentences for everything you need to know about compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Need ideas for a research paper topic? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
Writing Guides / Proper Essay Format Guide (Updated for 2021)
Proper Essay Format Guide (Updated for 2021)

Content is king. The substance of what you write is the most important thing in your essays and term papers .
However, you also have to nail the mechanics of academic writing. You need to master good grammar and sentence structure, and use appropriate vocabulary for your subject or assignment. Many instructors take points off for incorrect formatting.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
You also need to understand different types of essay format, and use the one that is appropriate to your assignment. This article introduces you to the basic elements of essay format, and helps you to improve your essay formatting.
What is Proper Essay Format?
The format of an essay refers to its basic structure , layout, and even its appearance on the page. Although it seems confusing at first, mastering the different essay formats is not that hard.
There are different formats you will use in different classes, but they share many elements in common. After you write enough essays, you will become familiar with the main essay formats used in typical college classes. Also, some subject areas have preferred essay formats or styles.
Standard College Essay Format
Technically, there is no “right” college essay format. Each teacher will have personal preferences for how they want their students’ papers to appear. Each class will have its own rules, and it is up to you to follow whatever rules your professor provides.
However, there are some basic elements in a college essay format including font or typeface, linen spacing, margins, and whether to include page numbers, headers, headings, and/or a title page. With a few possible variations, the common formatting elements in college essays include the following:
Standard college essays use standard fonts to create a uniform appearance. The most widely acceptable font used in college essays is Times New Roman, but Arial is sometimes acceptable too. Typically, you will be asked to standardize the size of your font to 12 point, but some instructors prefer 10. Read this article for more information on how to write an essay .
Line Spacing
Most of the time, you will be asked to use double spacing in your college essays. Occasionally you will be asked to use single spacing, or even 1.5 spacing.
The most common margin size is one inch all around.
Page Numbers and Title Page
Short essays usually do not take a title page, but some do. Likewise, you may be asked to include page numbers only for longer assignments.
First Line Indent
Your college essay will be formatted a lot like the books you read, with the first line of each paragraph being indented. Typically, the first line indent is .5 inch. Also, your college essay should be left aligned, as opposed to centering the text on the page.
Essay Format Headings vs. Headers
Some of your college professors may request that you use a heading, while others will ask that you use a header. Some may ask for both. What is the difference between a heading and a header ?
A heading appears only on the first page, and will typically include your name, your professor’s name, the name of the class, and the date of the assignment. For example, MLA style formatting frequently asks for a heading in addition to a running header.
A running header appears on all the pages of your college essay and typically includes only the title of the essay and the page number. Your pages will look like this:
Essay Format Outline
Essay outlines also have their own formats. If you have to create a formal outline for an academic essay, it is always best to check with your professor to see if there is a specific style you are supposed to follow. A typical college essay outline is as follows, using Roman numerals as the top level:
I. Introduction
A. Body section
1. Sub-section
2. Sub-section
B. Body section
III. Conclusion
Essay Format Templates
Scholarship essay format.
If you ever hope to earn a scholarship, now is the time to master the scholarship essay . A scholarship essay should be tailored to the specific fund you are applying for, and it is best to avoid a generalized essay. The main components of the scholarship essay format are similar to those in a standard college essay:
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- First line indent
- Double-spacing
- 1-inch margins
Unlike most college essays, a scholarship essay is going to be written in the first person, because it is about you. You are supposed to talk about yourself in a scholarship essay, whereas in a college essay, you should be writing in third person unless instructed otherwise. The scholarship essay will give you a chance to show how much work you have done to reach your goals, and why you stand out from the crowd.
Even for needs-based scholarships, you will want your reader to know that receiving financial aid is not the only reason you are worthy of receiving the scholarship. Talk at length about what motivates you and what makes you tick. Even if your future goals and career plans are not etched in stone, you can share information about your visions and dreams for the future and how you believe a college education will help you contribute to society.
College Application Essay Format
Like a scholarship essay, a college application essay should be written in the first person. Some college essays will be as short as 100 words, whereas others will be 1500 words or even more. Always follow the instructions, while also keeping in mind the standard rules for what the admissions committee wants:
If you are sincere about getting into a school, spend time on your admissions essay. Make sure the formatting is correct, that you answered the question or responded to the prompts, and that you use good grammar.
For many college application essays, you want to start with a powerful introduction. Telling a brief story about something that happened in your life to shape your character is a good start. Then, be honest and tell the admissions committee about who you are, and why you are interested in their institution. You should ideally share information about your interests and goals, and what courses you are interested in as well. Many college entrance essays have prompts that ask you to reflect on a personal experience that shaped who you are, a position of leadership that you held, or a story about how you overcame a challenge or defeated an obstacle. Because a college application essay is a high stakes situation, it is advisable to seek help from a professional writer or tutor to help you polish your prose. Remember, you are competing with hundreds of applicants and your essay needs to stand out.
Reflective Essay Format
A reflective essay is naturally less formal than an ordinary expository essay. However, there are still formats that you would be expected to follow when you prepare a reflective essay. Some reflective essays are written in the first person, whereas others are more formal like a typical college essay. The format of the reflective essay will include the basic rules of font, paragraph and line formatting, and page setting like margins.
Some reflective essays ask you to reflect on an event in your life or on your own personality. However, not all reflective essays are that personal. Many reflective essays ask you to comment on a specific text that you have been reading in class, a work of art or music, or a current event. When asked to write a more formal reflective essay like this, it helps to begin with an introduction to the object of reflection. If you are reflecting on a scholarly article, your introductory paragraph would include information about the author and title of the publication, and a brief summary of the main arguments. Then, you would begin the reflection as if you were having a conversation with the author.
A sample reflective essay outline is as follows:
A. Name, date, and title of the article, piece of music, or work of art.
B. Brief overview or summary of the object of reflection
C. Thesis: Your opinion or take on the article.
1. Do you agree or disagree with the author, or like or dislike the piece?
2. Introduce a new angle or line of thinking that adds to or challenges the original piece.
A. Focus on one element of the source, weaving in your own ideas or personal experiences.
B. Focus on another element of the source, weaving in your own ideas or personal experiences.
A. Wrap up the reflective essay with a brief summary
B. Suggestions for further research or reflection
Persuasive Essay Format
When you write a persuasive essay , your goal is to influence your reader. For example, you want to talk your reader into changing his or her voting habits, or you want your reader to stop eating meat. When you write a persuasive essay, you have the opportunity to use all the rhetorical strategies you have been learning, such as pathos, ethos, and logos. Use strong and emotionally powerful diction, tone, and imagery, but also rely on credible evidence to substantiate your claim.
A persuasive essay can be of almost any length, and is written in formal academic style. You will follow the structure and outline used for a standard academic essay with an introduction, body, and conclusion. Persuasive essays are also strongly driven by a thesis statement .
A. Hook your reader with a fun or controversial opening statement.
B. Lead into the main topic with background information.
C. State your case, persuade your reader with a strong thesis statement.
A. Reason one
B. Reason two
C. Reason three
D. Acknowledge the opposing or alternative points of view
E. Respond to and refute the opposing points of view
A. Restate your claim
B. Urge the audience to take action
Use the same essay format for standard college essays, with 12-point Times New Roman font throughout and double spacing.
APA Essay Format
The American Psychological Association (APA) offers one of the most widely used essay formats. It is unlikely you will get through college without having to write at least one essay using APA style citation . Psychology classes almost always rely on APA formatting, but APA formatting is standard in a range of other social science disciplines including criminal justice and nursing.
APA formatting follows the basic rules for a standard college essay:
- 12-point font (Times New Roman)
However, APA formatting also includes a title page, a running header with both title and page numbers, and in some cases, an abstract.
APA Title Page
A title page helps your completed essay look polished and presentable in class. On the APA formatted title page, you will include the title of your essay, centered on the page. On a line immediately below the title, also centered, you will write your name. You may also write the name of your class or institution below your name, as well as the date.
APA Running Header
A running header is what appears at the top of every page of the completed essay. In APA format, your essay header will include the TITLE OF THE ESSAY IN ALL CAPITAL LETTERS, and also the page numbers. An example of a title page with the running header in APA format is as follows:

APA Abstract
Longer research papers in APA format may include an abstract. An abstract is similar to a summary in that it includes the main points of your research. Especially if you are preparing the results of your own research, you will include an abstract that reviews the methods and results of your experiment. Not all papers require an abstract. Usually an abstract accompanies original research in which you want the reader to have a snapshot or overview of how you conducted the study and what the results indicate.
Some APA format papers follow the standard format of research publications, which include the following sections after the abstract:
Introduction or Background
- Review of Literature
Conclusions
Not all APA format papers are research reports, though. Some will be standard college essays, some will be article reviews, and others will be responses to essay questions or prompts.
In APA formatting, when you have a longer paper it helps to organize it with subheadings. The subheadings help draw the reader’s eye to the different sections of your paper. You can use bold font to identify the subheadings, as follows:
- Introduction
This is the introduction to your topic, and where you hook the audience into reading the rest of the paper.
The review of literature is where you describe some of the most important research studies that have already been done on this topic.
The methods section is where you describe the research participants and procedures of the experiment. If you did not conduct an experiment, then you would discuss how you went about compiling data, such as through a search of academic databases or through interviews.
This is the section where you list the raw data from your survey or experiment, or where you simply discuss the results without making inferences or analyses.
In the discussion section of an APA paper, you analyze the results of your research, placing those results into the context of prior literature. Talk about whether you proved your hypothesis. Also discuss limitations to the research, and suggestions for future research.
Wrap up all your research neatly, mentioning how your research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on the topic.
Always list the sources you used in the paper, but do not list any sources that you do not cite directly in the body of the essay using parenthetical citations.
Appendix or Appendices
Include the survey instrument you used, a list of interview questions, or important tables and charts.
MLA Essay Format
Another one of the common essay formats you will encounter in college is from the Modern Language Association (MLA). Used most commonly in the arts and literature classes, MLA format shares some elements in common with other college essays, such as:
Unlike APA formatting, MLA does not typically require a title page. However, you may be asked to put your name, professor’s name, class name, and date in the upper left corner of the first page of your essay instead. For example:

Another thing that differentiates MLA format from APA and other types of essay formats is how you cite your sources. In MLA, you always offer the page number even when you do not quote directly. This may seem problematic when you are paraphrasing an author’s main idea, but it is nevertheless standard practice. MLA papers tend to be discursive. You are expected to engage a work of art or literature in a sort of conversation, weaving in what other people have said on the topic.
Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style format is also common in college essays, particularly in classes in history, political science, and public policy. With Chicago style, you can stick to the basics:
Chicago style formatting also has a title page, similar to APA format. However, you will insert a lot of space between the title of the essay and your name and date as follows:
Another thing that differentiates Chicago style from other styles of essay formats is the citation style. Whereas APA and MLA style essays use in-text parenthetical citations, Chicago style usually takes footnotes.
Additional Elements of an Essay
Some types of essays, such as longer research papers or dissertations , also include other elements. A table of contents is one thing that is unnecessary in all shorter essays, but essential for long assignments like dissertations or Masters theses. Software like Microsoft Word can help you create a table of contents that takes into account the important headings or subheadings of your document.
Types of Essay Formats
The most common types of essay format you are likely to encounter in college include the following:
- APA essay format
- MLA essay format
- Chicago essay format
- Harvard essay format
- Persuasive essay format
- Argumentative essay format
- Research essay format
- Reflective essay format
- Expository essay format
- Compare and contrast essay format
- Cause and effect essay format
- Analytical essay format
Essay Format Example
The main elements of any standard college essay include the following:
- Running Header (Title and Page Number)
- Bibliography/References/Works Cited
The main elements of an APA format essay include the following:
- Introduction/Background
The format of an essay is important for its overall appearance and structure. When you master the different essay formats, you will find it much easier to complete your assignments. Each essay format has its own set of rules and guidelines, but all college essays share certain elements in common.
Almost all essays have an introduction, body, and a conclusion. In some cases, you will also need a title page, an abstract, and a running header. Each class and each instructor will give you specific instructions about the formatting of your essay.
After reading this article, you have a better understanding of the most common essay formats you will encounter during your academic career. You can apply what you have learned about standard college essays to any assignment you encounter. In addition to this guide, you can also consult with a writing coach or assistant to help you with your work.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips and Techniques

Why Using Chat-GPT for Writing Your College Essays is Not Smart

The Importance of an Outline in Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay

A Guide to Choosing the Perfect Compare and Contrast Essay Topic
Learn the Standard Essay Format: MLA, APA, Chicago Styles

Being able to write an essay is a vital part of any student's education. However, it's not just about linearly listing ideas. A lot of institutions will require a certain format that your paper must follow; prime examples would be one of a basic essay format like MLA, the APA, and the Chicago formats. This article will explain the differences between the MLA format, the APA format, and the Chicago format. The application of these could range from high school to college essays, and they stand as the standard of college essay formatting. EssayPro — dissertation services , that will help to make a difference!
What is an Essay Format: Structure
Be it an academic, informative or a specific extended essay - structure is essential. For example, the IB extended essay has very strict requirements that are followed by an assigned academic style of writing (primarily MLA, APA, or Chicago):
- Abstract: comprised of 3 paragraphs, totaling about 300 words, with 100 words in each.
- ~ Paragraph 1: must include a research question, thesis, and outline of the essay’s importance.
- ~ Paragraph 2: Key resources, scope and limits of research, etc.
- ~ Paragraph 3: Conclusion that you’ve already reached in your essay.
- Table of Contents (with page numbers)
- ~ Research question
- ~ Introduction
- ~ Arguments
- ~ Sub-headings
- ~ Conclusion
- ~ Works cited (bibliography)
- Introduction
- ~ The research question is required
- Bibliography (Works Cited)
This outline format for an extended essay is a great example to follow when writing a research essay, and sustaining a proper research essay format - especially if it is based on the MLA guidelines. It is vital to remember that the student must keep track of their resources to apply them to each step outlined above easily. And check out some tips on how to write an essay introduction .

Lost in the Labyrinth of Essay Formatting?
Navigate the complexities of essay structures with ease. Let our experts guide your paper to the format it deserves!
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format
To write an essay in MLA format, one must follow a basic set of guidelines and instructions. This is a step by step from our business essay writing service
- Font : 12pt Times New Roman
- ~ Double spaced everywhere
- ~ No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs
- Heading : Example of the heading on the first page of the essay (upper left corner)
- ~ Your name (John Smith)
- ~ Teacher’s / Professor’s name (Margot Robbie)
- ~ The class (Depends on course/class)
- ~ Date (20 April 2017)
- Margins : One-inch margin on the top, bottom, left and right.
- Page Numbers : Last name and page number must be put on every page of the essay as a “header”. Otherwise, it would go in place of the text.
- Title : There needs to be a proper essay title format, centered and above the first line of the essay of the same font and size as the essay itself.
- Indentation : Just press tab (1/2 inch, just in case)
- Align : Align to the left-hand side, and make sure it is aligned evenly.

It’s important to remember that the essay format of MLA is usually used in humanities, which differs from other types of academic writing that we’ll go into detail later. For now, feast your eyes upon an MLA format essay example:
Essay in MLA Format Example
Mla format digital technology and health, mla vs. apa.
Before we move on to the APA essay format, it is important to distinguish the two types of formatting. Let’s go through the similarities first:
- The formatting styles are similar: spacing, citation, indentation.
- All of the information that is used within the essay must be present within the works cited page (in APA, that’s called a reference page)
- Both use the parenthetical citations within the body of the paper, usually to show a certain quote or calculation.
- Citations are listed alphabetically on the works cited / reference page.
What you need to know about the differences is not extensive, thankfully:
- MLA style is mostly used in humanities, while APA style is focused more on social sciences. The list of sources has a different name (works cited - MLA / references - APA)
- Works cited differ on the way they display the name of the original content (MLA -> Yorke, Thom / APA -> Yorke T.)
- When using an in-text citation, and the author’s name is listed within the sentence, place the page number found at the end: “Yorke believes that Creep was Radiohead’s worst song. (4).” APA, on the other hand, requires that a year is to be inserted: “According to Yorke (2013), Creep was a mess.”
Alright, let’s carry over to the APA style specifics.
Order an Essay Now & and We Will Cite and Format It For Free :
How to write an essay in apa format.
The APA scheme is one of the most common college essay formats, so being familiar with its requirements is crucial. In a basic APA format structure, we can apply a similar list of guidelines as we did in the MLA section:
- Spacing : Double-space that bad boy.
- Margins : One Inch margins on all sides.
- Page Numbers : Insert a header at the top left of every page that includes a shortened title of your essay, below 50 characters including punctuation. Slap a number in there too (top right corner).
- Title Page : Title of the paper, author’s name, institutional affiliation. Additional information may be required, such as course title, instructor name and date.
- Headings: All headings should be written in bold and titlecase. Different heading levels have different additional criteria to apply.
You can also ask us to write or rewrite essay in APA format if you find it difficult or don't have time.
Note that some teachers and professors may request deviations from some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.

Note that some teachers and professors maybe have deviations to some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.
If you think: 'I want someone write a research paper for me ', you can do it at Essaypro.
Essay in APA Format Example
Apa format chronobiology, chicago style.
The usage of Chicago style is prevalent in academic writing that focuses on the source of origin. This means that precise citations and footnotes are key to a successful paper.
Chicago Style Essay Format
The same bullet point structure can be applied to the Chicago essay format.
- ~ Chicago style title page is all about spacing.
- ~ Down the page should be the title, with regular text. If longer than one line, double-spaced.
- ~ Next, in the very middle, center your full name.
- ~ Down the page - course number, instructor’s name and the date in separate double-spaced lines.
- Margins : Use one-inch margins apart from the right side.
- ~ Double spaced everywhere.
- ~ No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs.
- Font : Times New Roman is the best choice (12pt)
- Page Numbers
- ~ Last name, page number in the heading of every page on the top right
- ~ Do not number the title page. The first page of the text should start with a 2.
- Footnotes : The Chicago format requires footnotes on paraphrased or quoted passages.
- Bibliography : The bibliography is very similar to that of MLA. Gather the proper information and input it into a specialized citation site.

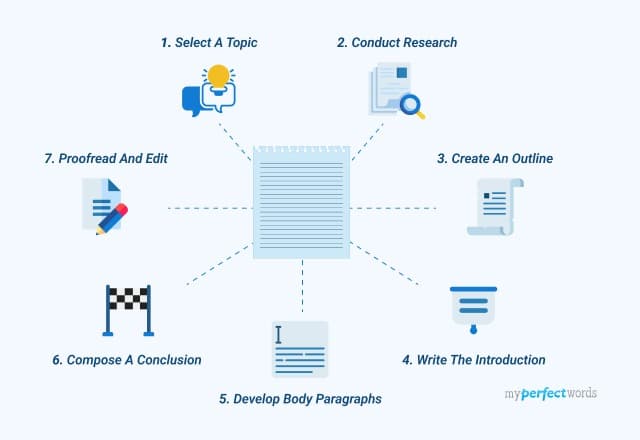
Tips for Writing an Academic Paper
There isn’t one proper way of writing a paper, but there are solid guidelines to sustain a consistent workflow. Be it a college application essay, a research paper, informative essay, etc. There is a standard essay format that you should follow. For easier access, the following outline will be divided into steps:
Choose a Good Topic
A lot of students struggle with picking a good topic for their essays. The topic you choose should be specific enough so you can explore it in its entirety and hit your word limit if that’s a variable you worry about. With a good topic that should not be a problem. On the other hand, it should not be so broad that some resources would outweigh the information you could squeeze into one paper. Don’t be too specific, or you will find that there is a shortage of information, but don’t be too broad or you will feel overwhelmed. Don’t hesitate to ask your instructor for help with your essay writing.
Start Research as Soon as Possible
Before you even begin writing, make sure that you are acquainted with the information that you are working with. Find compelling arguments and counterpoints, trivia, facts, etc. The sky is the limit when it comes to gathering information.
Pick out Specific, Compelling Resources
When you feel acquainted with the subject, you should be able to have a basic conversation on the matter. Pick out resources that have been bookmarked, saved or are very informative and start extracting information. You will need all you can get to put into the citations at the end of your paper. Stash books, websites, articles and have them ready to cite. See if you can subtract or expand your scope of research.
Create an Outline
Always have a plan. This might be the most important phase of the process. If you have a strong essay outline and you have a particular goal in mind, it’ll be easy to refer to it when you might get stuck somewhere in the middle of the paper. And since you have direct links from the research you’ve done beforehand, the progress is guaranteed to be swift. Having a list of keywords, if applicable, will surely boost the informational scope. With keywords specific to the subject matter of each section, it should be much easier to identify its direction and possible informational criteria.
Write a Draft
Before you jot anything down into the body of your essay, make sure that the outline has enough information to back up whatever statement you choose to explore. Do not be afraid of letting creativity into your paper (within reason, of course) and explore the possibilities. Start with a standard 5 paragraph structure, and the content will come with time.
Ask for a Peer Review of Your Academic Paper
Before you know it, the draft is done, and it’s ready to be sent out for peer review. Ask a classmate, a relative or even a specialist if they are willing to contribute. Get as much feedback as you possibly can and work on it.
Final Draft
Before handing in the final draft, go over it at least one more time, focusing on smaller mistakes like grammar and punctuation. Make sure that what you wrote follows proper essay structure. Learn more about argumentative essay structure on our blog. If you need a second pair of eyes, get help from our service.
Read also our movie review example and try to determine the format in which it is written.
Want Your Essay to Stand Out in Structure and Style?
Don't let poor formatting dim your ideas. Our professional writers are here to give your paper the polished look it needs!
Related Articles
.webp)
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Essay in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
What Is APA Format?
Apa essay format basics.
- Steps to Follow
Frequently Asked Questions
If your instructor has asked you to write an APA format essay, it might at first seem like a daunting task, especially if you are accustomed to using another style such as MLA or Chicago. But you can master the rules of APA essay format, too.
An essay is one type of paper that can be written in APA format; others include lab reports, experimental reports, and case studies. Before you begin, familiarize yourself with some of the basic guidelines for writing a paper in APA format. Of course, it will also be important to follow any other formatting instructions that are part of your assignment.
How do you write an essay in APA format? The basic elements you need to include are:
- A title page
- An abstract
- An introduction, main body, and conclusion
- A reference section
- Proper APA formatting with regard to margins, layout, spacing, titles, and indentations
This article discusses how to write an essay in APA format, including the basic steps you should follow and tips for how to get started.
Whether you’re taking an introductory or graduate-level psychology class, chances are strong that you will have to write at least one paper during the course of the semester. In almost every case, you will need to write your paper in APA format, the official publication style of the American Psychological Association . It is also used for academic journals.
Such rules are generally the same whether you are writing a high school essay, college essay, or professional essay for publication.
APA format is used in a range of disciplines including psychology , education, and other social sciences. The format dictates presentation elements of your paper including spacing, margins, and how the content is structured.
Most instructors and publication editors have strict guidelines when it comes to how your format your writing. Not only does adhering to APA format allow readers to know what to expect from your paper, but it also means that your work will not lose critical points over minor formatting errors.
While the formatting requirements for your paper might vary depending on your instructor's directions, writing APA essay format means you will most likely need to include a title page, abstract, introduction, body, conclusion, and reference sections.
Your APA format essay should have a title page . This title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your school affiliation. In some instances, your teacher might require additional information such as the course title, instructor name, and the date.
- The title of your paper should be concise and clearly describe what your paper is about.
- Your title can extend to two lines, but it should be no longer than 12 words.
An abstract is a brief summary of your paper that immediately follows the title page. It is not required for student papers, according to APA style. However, your instructor may request one.
If you include an abstract , it should be no more than 100 to 200 words, although this may vary depending upon the instructor requirements.
Your essay should also include a reference list with all of the sources that were cited in your essay,
- The reference section is located at the end of your paper.
- References should be listed alphabetically by the last name of the author.
- References should be double-spaced.
- Any source that is cited in your paper should be included in your reference section.
When writing in APA essay format, the text will include the actual essay itself: The introduction, body, and conclusion.
- There should be uniform margins of at least one inch at the top, bottom, left, and right sides of your essay.
- The text should be in Times New Roman size 12 font or another serif typeface that is easily readable.
- Your paper should be double-spaced.
- Every page should include a page number in the top right corner.
- The first word of each paragraph in your paper should be indented one-half inch.
For professional papers (usually not student papers), every page of the essay also includes a running head at the top left. The running head is a shortened form of the title, often the first few words, and should be no more than 50 characters (including spaces).
Steps to a Successful APA Format Essay
In addition to ensuring that you cite your sources properly and present information according to the rules of APA style, there are a number of things you can do to make the writing process a little bit easier.
Choose a Topic
Start by choosing a good topic to write about. Ideally, you want to select a subject that is specific enough to let you fully research and explore the topic, but not so specific that you have a hard time finding sources of information.
If you choose something too specific, you may find yourself with not enough to write about. If you choose something too general, you might find yourself overwhelmed with information.
Research Your Topic
Start doing research as early as possible. Begin by looking at some basic books and articles on your topic to help develop it further. What is the question you are going to answer with your essay? What approach will you take to the topic?
Once you are more familiar with the subject, create a preliminary source list of potential books, articles, essays, and studies that you may end up using in your essay.
Remember, any source used in your essay must be included in your reference section. Conversely, any source listed in your references must be cited somewhere in the body of your paper.
Write Your Rough Draft
With research in hand, you are ready to begin. Some people like to create an outline to organize their argument prior to drafting. You may want to start with a very rough outline, and then add details.
Once you have a detailed outline, the next step is to translate it from notes to complete sentences and paragraphs. Remember, this is a first draft. It doesn't have to be perfect.
As you write your paper in APA essay format, be sure to keep careful track of the sources that you cite.
How do you start an APA paper? Your paper should begin with an introduction that includes a thesis statement that presents your main ideas, points, or arguments. Your introduction should start on the third page of your paper (after the title page and abstract). The title of your paper should be centered, bolded, and typed in title case at the top of the page.
Review and Revise
After you have prepared a rough draft of your essay, it's time to revise, review, and prepare your final draft. In addition to making sure that your writing is cohesive and supported by your sources, you should also check carefully for typos, grammar errors, and possible formatting mistakes.
When citing information or quotations taken from an interview, APA format requires that you cite the source, how the information was collected, and the date of the interview. They should not be included in the reference section, however, because they are not something that can be located by a reader in any published source or searchable database.
Instead, the information should be cited parenthetically in the main body of the text. For example: “There was an increase in the number of college students who screened positive for depression/anxiety” (R. Heathfield, personal communication, May 9, 2021).
If the essay is in a chapter of a book, edited collection, or anthology, APA format states that you should cite the last name, first name, title of essay, title of collection, publisher, year, and page range. For example: Smith, John, "The Light House," A Book of Poems , editing by Peter Roberts, Allworth Press, 2005, pp. 20-25.
According to APA format, a two-part essay is formatted the same as an essay, however, you'll need to create two title pages.
If you're including a short direct quote in your APA-format essay, you will need to cite the author, year of publication, and page number (p.) or page number span (pp.). Quotations longer than 40 words should omit the quotation marks and be put in the text using block quotation formatting, on its own line and indented 1/2 inch from the left margin.
The cover page or "title page" in APA essay format should always include the title of your paper, your name, and school affiliation as well as the course title, instructor name, and date, if requested by your teacher.
Nagda S. How to write a scientific abstract. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013;13(3):382-383. doi:10.1007/s13191-013-0299-x
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How To Write An Essay
Essay Format

Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
10 min read
Published on: Nov 14, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
Drafting a perfect college essay is very important for students' academics. And to write a perfect essay, its formatting is important.
An essay is a formal piece of writing. Any formal writing requires proper structure and formatting. You can not just jumble up information and expect your essay to be effective. Its clarity depends on the format you choose.
This blog is written to give a better understanding of an essay format and the general guidelines of each type of format to present the gathered information in a disciplined way.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format is a way in which the information is organized for your essay. The format of an essay has a lot to do with the presentation of the text. If your essay is poorly structured or lacks a format, your readers will have difficulty understanding the main argument and the idea.
Readers will never continue reading something that is confusing or gives the impression that a writer is sloppy.
A standard format to write your essay or paper is the linear approach. In this, each idea is presented to make it easier for the readers to understand. If you know how to structure an essay, you are halfway through.
Types of Essay Formats
There are 3 basic formatting styles or types in which all essays and papers are formatted. They are:
Whether you are writing a research paper or a general academic essay, you have to choose a format to draft it. Students are often assigned a format by their instructors, so they should read the guidelines carefully.
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format?
MLA format style is quite common in the humanities world. Papers and essays that are to be written in this format should fulfill the following requirements.
- The font you are using should be Times New Roman in 12pt.
- Double spacing.
- No extra space between the new paragraphs
- One inch margin on both sides of the paper
- Page number in the header.
- Essay title in the center of the page.
- Sources mentioned in âwork citedâ
MLA vs. APA
Before we move to another common essay format APA, you should know that MLA and APA are different from each other.
Look at the table below and know their differences and similarities.
How to Write an Essay in APA Format?
Unlike MLA format, the APA format is used for scientific papers and essays. Essays are written for behavioral or social sciences follow this format. Following are the guidelines for the American Psychological Association format:
- Font or Text in Times New Roman 12pt
- One inch margin (both sides)
- Double spacing in the text
- A short title on the upper left-hand corner in the header
- The page number on the right in the header
- A title page with the information, including the writerâs name, institution, instructor, and date.
- Reference page (for the citation)
APA Format Essay Example
Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style essay format is a bit similar to the other format style guides. This format includes;
- Double spacing
- Margins (one inch both left margin and right margin)
- Times New Roman 12pt font size
- Page number in the header
- Footnotes on quoted and paraphrased passages
- An alphabetical arrangement of citations on the bibliography page.
Chicago Format Essay Example
Basic Parts of an Essay Format
A typical and general format that an essay uses is simple. Every type of essay can be written in that format. Following are the parts that an essay format is based on:
In order to make sure that your academic essay is effective, each of the parts should be drafted professionally.
Here is an essay structure!
Continue reading to understand each part in detail.
1. Cover Or Title Page
The cover or title page is the first page on which the topic of your paper or essay is presented. Along with this, the title page includes other information such as the name of the writer, instructor, institution, course, and the submission date. 2. An Abstract
An abstract is a brief summary of your essay or research paper. It is usually a 300-word long paragraph and precisely presents the purpose of the essay, the main thesis statement, and the studyâs design.
3. Table Of Contents
When you are drafting a long essay or paper, a table of content is developed. In this table, headings and subheadings are presented along with their page numbers. The reader navigates your work using this table of content.
4. Introduction
An introduction is the first section of your essay. When writing a short essay of about 300 - 1000 words, a writer directly starts with an introduction after stating the essay topic.
An introduction of an essay is as important as the body of it. The essay introduction discloses the main idea of the essay and attempts to motivate readers to read the essay. Apart from the presentation of the main idea, it also contains background information about the topic.
A writer then forms a thesis statement which is the main argument of an essay. A thesis statement is the essence of the essay, and all other information provided in the body of an essay justifies it and proves it.
5. Main Body
The main body is the soul of an essay. Without it, the thesis statement will just be meaningless. The information you gather on the topic is presented in the body, which acts as evidence to prove the argument right or wrong depending on the writer.
A format helps the body give a logical flow that walks the reader towards the end. The point to prove your argument is to persuade the reader that your thesis statement is right. Make sure you give a topic sentence to all your body paragraphs.
6. Conclusion
Then comes the conclusion part of the essay. This is the final verdict of an essay writer. In this, a writer avoids giving new ideas to the readers and tries to sum up the whole conversation. This is done by restating the thesis statement in different words and summarizing the key ideas.
7. Appendix
An appendix is formulated when a writer uses unusual terms, phrases, and words in the document. This is a list prepared to describe those unordinary words for the readers.
8. Bibliography
When gathering information for your essay or paper, a writer has to consult different sources. Therefore, when using such sources and information in your content, a bibliography is created to provide their references.
A bibliography is a reference list presented at the end of the essay where all the cited sources are given along with the details.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Formatting an Essay
Formatting an essay means working on the essay structure. When writing an academic essay, make sure that every part is drafted according to format. Your title page, in-text citation, essay outline, and reference list should be following the chosen format.
To understand the formatting of the different parts better, continue reading.
- Title Page Format
According to the MLA style, the title page of an essay should be written in the following way:
- Writing the name of the writer, course, instructor, and date.
- Double spacing between paragraphs
- Instituteâs name in the top center of a page
- Title of your essay or paper
- Font Times New Roman (12pt)
If you are using an APA style formatting for your essay, make sure to format your title page in the following way:
- Title written in all caps
- The margin on both sides (1 inch)
- 12pt font Times New Roman
- Name of writer and institute
A title page is the first thing that an instructor sees in your assignment. Therefore, it is very important to form it in a neat format.
- First Page of an Essay
Before you start writing your essay, format your first page. To do this, add a header in which you give your last name and the page number. Place the header on the right-hand corner of your page.
Follow this for every page of your essay except the last page; the âwork citedâ page.
On the left upper corner, write your name, instructorâs, courseâs, and the date. Put the title in the center and use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Cite According to Essay Format
When you are conducting research for your essay, you will come across a lot of text which will complement your essay topic. Without knowing the consequences, people take the text from the internet and add it to the essay.
Citing the source properly is essential. If you do not cite the sources properly, you will be accused of plagiarism, a crime in the writing world. Therefore, even if you are using otherâs words in the form of quotation marks or rephrasing it, it needs to be cited to avoid plagiarism.
Get to know which style of the in-text citations is recommended by your instructor and follow that. In APA format, the citation is done in the following way:
- Give the authorâs name (last name), followed by the publication date and the paragraph number of the original work.
The other way is to cite in MLA style:
- Give the authorâs last name and the page number of the publication you are taking words from.
Therefore, cite your sources according to the essay format and make your essay writing phase easy.
- Format The Bibliography
The last page of your essay is the âworks citedâ page. This page is written in the way presented below:
- Sources are alphabetically arranged
- Double spacing is used on the entire page
- Hanging indention is also used.
Essay Format Examples
There are several types of academic essays that students get assigned. No matter which type the essay is, it has to be properly formatted. Carefully examine the formats provided below for the different essay types:
Argumentative Essay Format
College Essay Format
Narrative Essay Format
Descriptive Essay Format
Scholarship Essay Format
Persuasive Essay Format
Essay Format for University
Expository Essay Format
Essay Format Template
Essay Format Outline
Writing a good essay includes the proper representation of the text. For this purpose, formatting is done. Unfortunately, when students rush to finish their assignments, they often end up with poorly formatted content.
Looking for an exceptional essay writing service for students ? You've found it!
We specialize in essay writing for students, providing top-notch assistance tailored to your academic needs.
You can also supercharge your writing with our AI essay writing tool !
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
How to Format a College Essay: Step-by-Step Guide

Mark Twain once said, “I like a good story well told. That’s the reason I am sometimes forced to tell them myself.”
At College Essay Guy, we too like good stories well told.
The problem is that sometimes students have really good stories … that just aren’t well told.
They have the seed of an idea and the makings of a great story, but the essay formatting or structure is all over the place.
Which can lead a college admissions reader to see you as disorganized. And your essay doesn’t make as much of an impact as it could.
So, if you’re here, you’re probably wondering:
Is there any kind of required format for a college essay? How do I structure my essay?
And maybe what’s the difference?
Good news: That’s what this post answers.
First, let’s go over a few basic questions students often have when trying to figure out how to format their essay.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- College essay format guidelines
- How to brainstorm and structure a college essay topic
- Recommended brainstorming examples
- Example college essay: The “Burying Grandma” essay
College Essay Format Guidelines
Should I title my college essay?
You don’t need one. In the vast majority of cases, students we work with don’t use titles. The handful of times they have, they’ve done so because the title allows for a subtle play on words or reframing of the essay as a whole. So don’t feel any pressure to include one—they’re purely optional.
Should I indent or us paragraph breaks in my college essay?
Either. Just be consistent. The exception here is if you’re pasting into a box that screws up your formatting—for example, if, when you copy your essay into the box, your indentations are removed, go with paragraph breaks. (And when you get to college, be sure to check what style guide you should be following: Chicago, APA, MLA, etc., can all take different approaches to formatting, and different fields have different standards.)
How many paragraphs should a college essay be?
Personal statements are not English essays. They don’t need to be 5 paragraphs with a clear, argumentative thesis in the beginning and a conclusion that sums everything up. So feel free to break from that. How many paragraphs are appropriate for a college essay? Within reason, it’s up to you. We’ve seen some great personal statements that use 4 paragraphs, and some that use 8 or more (especially if you have dialogue—yes, dialogue is OK too!).
How long should my college essay be?
The good news is that colleges and the application systems they use will usually give you specific word count maximums. The most popular college application systems, like the Common Application and Coalition Application, will give you a maximum of 650 words for your main personal statement, and typically less than that for school-specific supplemental essays . Other systems will usually specify the maximum word count—the UC PIQs are 350 max, for example. If they don’t specify this clearly in the application systems or on their website (and be sure to do some research), you can email them to ask! They don’t bite.
So should you use all that space? We generally recommend it. You likely have lots to share about your life, so we think that not using all the space they offer to tell your story might be a missed opportunity. While you don’t have to use every last word, aim to use most of the words they give you. But don’t just fill the space if what you’re sharing doesn’t add to the overall story you’re telling.
There are also some applications or supplementals with recommended word counts or lengths. For example, Georgetown says things like “approx. 1 page,” and UChicago doesn’t have a limit, but recommends aiming for 650ish for the extended essay, and 250-500 for the “Why us?”
You can generally apply UChicago’s recommendations to other schools that don’t give you a limit: If it’s a “Why Major” supplement, 650 is probably plenty, and for other supplements, 250-500 is a good target to shoot for. If you go over those, that can be fine, just be sure you’re earning that word count (as in, not rambling or being overly verbose). Your readers are humans. If you send them a tome, their attention could drift.
Regarding things like italics and bold
Keep in mind that if you’re pasting text into a box, it may wipe out your formatting. So if you were hoping to rely on italics or bold for some kind of emphasis, double check if you’ll be able to. (And in general, try to use sentence structure and phrasing to create that kind of emphasis anyway, rather than relying on bold or italics—doing so will make you a better writer.)
Regarding font type, size, and color
Keep it simple and standard. Regarding font type, things like Times New Roman or Georgia (what this is written in) won’t fail you. Just avoid things like Comic Sans or other informal/casual fonts.
Size? 11- or 12-point is fine.
Color? Black.
Going with something else with the above could be a risk, possibly a big one, for fairly little gain. Things like a wacky font or text color could easily feel gimmicky to a reader.
To stand out with your writing, take some risks in what you write about and the connections and insights you make.
If you’re attaching a doc (rather than pasting)
If you are attaching a document rather than pasting into a text box, all the above still applies. Again, we’d recommend sticking with standard fonts and sizes—Times New Roman, 12-point is a standard workhorse. You can probably go with 1.5 or double spacing. Standard margins.
Basically, show them you’re ready to write in college by using the formatting you’ll normally use in college.
Is there a college essay template I can use?
Depends on what you’re asking for. If, by “template,” you’re referring to formatting … see above.
But if you mean a structural template ... not exactly. There is no one college essay template to follow. And that’s a good thing.
That said, we’ve found that there are two basic structural approaches to writing college essays that can work for every single prompt we’ve seen. (Except for lists. Because … they’re lists.)
Below we’ll cover those two essay structures we love, but you’ll see how flexible these are—they can lead to vastly different essays. You can also check out a few sample essays to get a sense of structure and format (though we’d recommend doing some brainstorming and outlining to think of possible topics before you look at too many samples, since they can poison the well for some people).
Let’s dig in.
STEP 1: HOW TO BRAINSTORM AN AMAZING ESSAY TOPIC
We’ll talk about structure and topic together. Why? Because one informs the other.
(And to clarify: When we say, “topic,” we mean the theme or focus of your essay that you use to show who you are and what you value. The “topic” of your college essay is always ultimately you.)
We think there are two basic structural approaches that can work for any college essay. Not that these are the only two options—rather, that these can work for any and every prompt you’ll have to write for.
Which structural approach you use depends on your answer to this question (and its addendum): Do you feel like you’ve faced significant challenges in your life … or not so much? (And do you want to write about them?)
If yes (to both), you’ll most likely want to use Narrative Structure . If no (to either), you’ll probably want to try Montage Structure .
So … what are those structures? And how do they influence your topic?
Narrative Structure is classic storytelling structure. You’ve seen this thousands of times—assuming you read, and watch movies and TV, and tell stories with friends and family. If you don’t do any of these things, this might be new. Otherwise, you already know this. You may just not know you know it. Narrative revolves around a character or characters (for a college essay, that’s you) working to overcome certain challenges, learning and growing, and gaining insight. For a college essay using Narrative Structure, you’ll focus the word count roughly equally on a) Challenges You Faced, b) What You Did About Them, and c) What You Learned (caveat that those sections can be somewhat interwoven, especially b and c). Paragraphs and events are connected causally.
You’ve also seen montages before. But again, you may not know you know. So: A montage is a series of thematically connected things, frequently images. You’ve likely seen montages in dozens and dozens of films before—in romantic comedies, the “here’s the couple meeting and dating and falling in love” montage; in action movies, the classic “training” montage. A few images tell a larger story. In a college essay, you could build a montage by using a thematic thread to write about five different pairs of pants that connect to different sides of who you are and what you value. Or different but connected things that you love and know a lot about (like animals, or games). Or entries in your Happiness Spreadsheet .
How does structure play into a great topic?
We believe a montage essay (i.e., an essay NOT about challenges) is more likely to stand out if the topic or theme of the essay is:
X. Elastic (i.e., something you can connect to variety of examples, moments, or values) Y. Uncommon (i.e., something other students probably aren’t writing about)
We believe that a narrative essay is more likely to stand out if it contains:
X. Difficult or compelling challenges Y. Insight
These aren’t binary—rather, each exists on a spectrum.
“Elastic” will vary from person to person. I might be able to connect mountain climbing to family, history, literature, science, social justice, environmentalism, growth, insight … and someone else might not connect it to much of anything. Maybe trees?
“Uncommon” —every year, thousands of students write about mission trips, sports, or music. It’s not that you can’t write about these things, but it’s a lot harder to stand out.
“Difficult or compelling challenges” can be put on a spectrum, with things like getting a bad grade or not making a sports team on the weaker end, and things like escaping war or living homeless for three years on the stronger side. While you can possibly write a strong essay about a weaker challenge, it’s really hard to do so.
“Insight” is the answer to the question “so what?” A great insight is likely to surprise the reader a bit, while a so-so insight likely won’t. (Insight is something you’ll develop in an essay through the writing process, rather than something you’ll generally know ahead of time for a topic, but it’s useful to understand that some topics are probably easier to pull insights from than others.)
To clarify, you can still write a great montage with a very common topic, or a narrative that offers so-so insights. But the degree of difficulty goes up. Probably way up.
With that in mind, how do you brainstorm possible topics that are on the easier-to-stand-out-with side of the spectrum?

Brainstorming exercises
Spend about 10 minutes (minimum) on each of these exercises.
Values Exercise
Essence Objects Exercise
21 Details Exercise
Everything I Want Colleges To Know About Me Exercise
Feelings and Needs Exercise
If you feel like you already have your topic, and you just want to know how to make it better…
Still do those exercises.
Maybe what you have is the best topic for you. And if you are incredibly super sure, you can skip ahead. But if you’re not sure this topic helps you communicate your deepest stories, spend a little time on the exercises above. As a bonus, even if you end up going with what you already had (though please be wary of the sunk cost fallacy ), all that brainstorming will be useful when you write your supplemental essays .
The Feelings and Needs Exercise in particular is great for brainstorming Narrative Structure, connecting story events in a causal way (X led to Y led to Z). The Essence Objects, 21 Details, Everything I Want Colleges to Know exercises can lead to interesting thematic threads for Montage Structure (P, Q, and R are all connected because, for example, they’re all qualities of a great endodontist). But all of them are useful for both structural approaches. Essence objects can help a narrative come to life. One paragraph in a montage could focus on a challenge and how you overcame it.
The Values Exercise is a cornerstone of both—regardless of whether you use narrative or montage, we should get a sense of some of your core values through your essays.
How (and why) to outline your college essay to use a good structure
While not every professional writer knows exactly how a story will end when they start writing, they also have months (or years) to craft it, and they may throw major chunks or whole drafts away. You probably don’t want to throw away major chunks or whole drafts. So you should outline.
Use the brainstorming exercises from earlier to decide on your most powerful topics and what structure (narrative or montage) will help you best tell your story.
Then, outline.
For a narrative, use the Feelings and Needs Exercise, and build clear bullet points for the Challenges + Effects, What I Did About It, and What I Learned. Those become your outline.
Yeah, that simple.
For a montage, outline 4-7 ways your thread connects to different values through different experiences, and if you can think of them, different lessons and insights (though these you might have to develop later, during the writing process). For example, how auto repair connects to family, literature, curiosity, adventure, and personal growth (through different details and experiences).
Here are some good example outlines:
Narrative outline (developed from the Feelings and Needs Exercise)
Challenges:
Domestic abuse (physical and verbal)
Controlling father/lack of freedom
Sexism/bias
Prevented from pursuing opportunities
Cut off from world/family
Lack of sense of freedom/independence
Faced discrimination
What I Did About It:
Pursued my dreams
Traveled to Egypt, London, and Paris alone
Challenged stereotypes
Explored new places and cultures
Developed self-confidence, independence, and courage
Grew as a leader
Planned events
What I Learned:
Inspired to help others a lot more
Learned about oppression, and how to challenge oppressive norms
Became closer with mother, somewhat healed relationship with father
Need to feel free
And here’s the essay that became: “ Easter ”
Montage outline:
Thread: Home
Values: Family, tradition, literature
Ex: “Tailgate Special,” discussions w/family, reading Nancy Drew
Perception, connection to family
Chinese sword dance
Values: Culture/heritage, meticulousness, dedication, creativity
Ex: Notebook, formations/choreography
Nuances of culture, power of connection
Values: Science/chemistry, curiosity
Synthesizing plat nanoparticles
Joy of discovery, redefining expectations
Governor’s School
Values: Exploration, personal growth
Knitting, physics, politics, etc.
Importance of exploring beyond what I know/am used to, taking risks
And here’s the essay that became: “ Home ”
When to scrap what you have and start over
Ultimately, you can’t know for sure if a topic will work until you try a draft or two. And maybe it’ll be great. But keep that sunk cost fallacy in mind, and be open to trying other things.
If you’re down the rabbit hole with a personal statement topic and just aren’t sure about it, the first step you should take is to ask for feedback. Find a partner who can help you examine it without the attachment to all the emotion (anxiety, worry, or fear) you might have built up around it.
Have them help you walk through The Great College Essay Test to make sure your essay is doing its job. If it isn’t yet, does it seem like this topic has the potential to? Or would other topics allow you to more fully show a college who you are and what you bring to the table?
Because that’s your goal. Format and structure are just tools to get you there.
Down the Road
Before we analyze some sample essays, bookmark this page, so that once you’ve gone through several drafts of your own essay, come back and take The Great College Essay Test to make sure your essay is doing its job. The job of the essay, simply put, is to demonstrate to a college that you’ll make valuable contributions in college and beyond. We believe these four qualities are essential to a great essay:
Core values (showing who you are through what you value)
Vulnerability (helps a reader feel connected to you)
Insight (aka “so what” moments)
Craft (clear structure, refined language, intentional choices)
To test what values are coming through, read your essay aloud to someone who knows you and ask:
Which values are clearly coming through the essay?
Which values are kind of there but could be coming through more clearly?
Which values could be coming through and were opportunities missed?
To know if you’re being vulnerable in your essay, ask:
Now that you’ve heard my story, do you feel closer to me?
What did you learn about me that you didn’t already know?
To search for “so what” moments of insight, review the claims you’re making in your essay. Are you reflecting on what these moments and experiences taught you? How have they changed you? Are you making common or (hopefully) uncommon connections? The uncommon connections are often made up of insights that are unusual or unexpected. (For more on how to test for this, click The Great College Essay Test link above.)
Craft comes through the sense that each paragraph, each sentence, each word is a carefully considered choice. That the author has spent time revising and refining. That the essay is interesting and succinct. How do you test this? For each paragraph, each sentence, each word, ask: Do I need this? (Huge caveat: Please avoid neurotic perfectionism here. We’re just asking you to be intentional with your language.)
Still feeling you haven’t found your topic? Here’s a list of 100 Brave and Interesting Questions . Read these and try freewriting on a few. See where they lead.
Finally, here’s an ...
Example College Essay Format Analysis: The “Burying Grandma” Essay
To see how the Narrative Essay structure works, check out the essay below, which was written for the Common App "Topic of your choice" prompt. You might try reading it here first before reading the paragraph-by-paragraph breakdown below.
They covered the precious mahogany coffin with a brown amalgam of rocks, decomposed organisms, and weeds. It was my turn to take the shovel, but I felt too ashamed to dutifully send her off when I had not properly said goodbye. I refused to throw dirt on her. I refused to let go of my grandmother, to accept a death I had not seen coming, to believe that an illness could not only interrupt, but steal a beloved life.
The author begins by setting up the Challenges + Effects (you’ve maybe heard of this referred to in narrative as the Inciting Incident). This moment also sets up some of her needs: growth and emotional closure, to deal with it and let go/move on. Notice the way objects like the shovel help bring an essay to life, and can be used for symbolic meaning. That object will also come back later.
When my parents finally revealed to me that my grandmother had been battling liver cancer, I was twelve and I was angry--mostly with myself. They had wanted to protect me--only six years old at the time--from the complex and morose concept of death. However, when the end inevitably arrived, I wasn’t trying to comprehend what dying was; I was trying to understand how I had been able to abandon my sick grandmother in favor of playing with friends and watching TV. Hurt that my parents had deceived me and resentful of my own oblivion, I committed myself to preventing such blindness from resurfacing.
In the second paragraph, she flashes back to give us some context of what things were like leading up to these challenges (i.e., the Status Quo), which helps us understand her world. It also helps us to better understand the impact of her grandmother’s death and raises a question: How will she prevent such blindness from resurfacing?
I became desperately devoted to my education because I saw knowledge as the key to freeing myself from the chains of ignorance. While learning about cancer in school I promised myself that I would memorize every fact and absorb every detail in textbooks and online medical journals. And as I began to consider my future, I realized that what I learned in school would allow me to silence that which had silenced my grandmother. However, I was focused not with learning itself, but with good grades and high test scores. I started to believe that academic perfection would be the only way to redeem myself in her eyes--to make up for what I had not done as a granddaughter.
In the third paragraph, she starts shifting into the What I Did About It aspect, and takes off at a hundred miles an hour … but not quite in the right direction yet. What does that mean? She pursues things that, while useful and important in their own right, won’t actually help her resolve her conflict. This is important in narrative—while it can be difficult, or maybe even scary, to share ways we did things wrong, that generally makes for a stronger story. Think of it this way: You aren’t really interested in watching a movie in which a character faces a challenge, knows what to do the whole time, so does it, the end. We want to see how people learn and change and grow.
Here, the author “Raises the Stakes” because we as readers sense intuitively (and she is giving us hints) that this is not the way to get over her grandmother’s death.
However, a simple walk on a hiking trail behind my house made me open my own eyes to the truth. Over the years, everything--even honoring my grandmother--had become second to school and grades. As my shoes humbly tapped against the Earth, the towering trees blackened by the forest fire a few years ago, the faintly colorful pebbles embedded in the sidewalk, and the wispy white clouds hanging in the sky reminded me of my small though nonetheless significant part in a larger whole that is humankind and this Earth. Before I could resolve my guilt, I had to broaden my perspective of the world as well as my responsibilities to my fellow humans.
There’s some nice evocative detail in here that helps draw us into her world and experience.
Structurally, there are elements of What I Did About It and What I Learned in here (again, they will often be somewhat interwoven). This paragraph gives us the Turning Point/Moment of Truth. She begins to understand how she was wrong. She realizes she needs perspective. But how? See next paragraph ...
Volunteering at a cancer treatment center has helped me discover my path. When I see patients trapped in not only the hospital but also a moment in time by their diseases, I talk to them. For six hours a day, three times a week, Ivana is surrounded by IV stands, empty walls, and busy nurses that quietly yet constantly remind her of her breast cancer. Her face is pale and tired, yet kind--not unlike my grandmother’s. I need only to smile and say hello to see her brighten up as life returns to her face. Upon our first meeting, she opened up about her two sons, her hometown, and her knitting group--no mention of her disease. Without even standing up, the three of us—Ivana, me, and my grandmother--had taken a walk together.
In the second-to-last paragraph, we see how she takes further action, and some of what she learns from her experiences: Volunteering at the local hospital helps her see her larger place in the world.
Cancer, as powerful and invincible as it may seem, is a mere fraction of a person’s life. It’s easy to forget when one’s mind and body are so weak and vulnerable. I want to be there as an oncologist to remind them to take a walk once in a while, to remember that there’s so much more to life than a disease. While I physically treat their cancer, I want to lend patients emotional support and mental strength to escape the interruption and continue living. Through my work, I can accept the shovel without burying my grandmother’s memory.
The final paragraph uses what we call the “bookend” technique by bringing us back to the beginning, but with a change—she’s a different, slightly wiser person than she was. This helps us put a frame around her growth.
… A good story well told . That’s your goal.
Hopefully, you now have a better sense of how to make that happen.
For more resources, check out our College Application Hub .

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Essay Writing

Introduction
In the simplest terms, an essay is a short piece of writing which is set around a specific topic or subject. The piece of writing will give information surrounding the topic but will also display the opinions and thoughts of the author. Oftentimes, an essay is used in an academic sense by way of examination to determine whether a student has understood their studies and as a way of testing their knowledge on a specific subject. An essay is also used in education as a way of encouraging a student to develop their writing skills.
Moreover; an essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essays, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At the university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
Types of Essay Writing
When it comes to writing an essay, there is not simply one type, there are, quite a few types of essay, and each of them has its purpose and function which are as follows:
Narrative Essays
A narrative essay details a story, oftentimes from a particular point of view. When writing a narrative essay, you should include a set of characters, a location, a good plot, and a climax to the story. It is vital that when writing this type of essay you use fine details which will allow the reader to feel the emotion and use their senses but also give the story the chance to make a point.
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay will describe something in great detail. The subject can be anything from people and places to objects and events but the main point is to go into depth. You might describe the item’s color, where it came from, what it looks like, smells like, tastes like, or how it feels. It is very important to allow the reader to sense what you are writing about and allow them to feel some sort of emotion whilst reading. That being said, the information should be concise and easy to understand, the use of imagery is widely used in this style of essay.
Expository Essay
An expository essay is used as a way to look into a problem and therefore compare it and explore it. For the expository essay, there is a little bit of storytelling involved but this type of essay goes beyond that. The main idea is that it should explain an idea giving information and explanation. Your expository essay should be simple and easy to understand as well as give a variety of viewpoints on the subject that is being discussed. Often this type of essay is used as a way to detail a subject which is usually more difficult for people to understand, clearly and concisely.
Argumentative Essay
When writing an argumentative essay, you will be attempting to convince your reader about an opinion or point of view. The idea is to show the reader whether the topic is true or false along with giving your own opinion. You must use facts and data to back up any claims made within the essay.
Format of Essay Writing
Now there is no rigid format of an essay. It is a creative process so it should not be confined within boundaries. However, there is a basic structure that is generally followed while writing essays.
This is the first paragraph of your essay. This is where the writer introduces his topic for the very first time. You can give a very brief synopsis of your essay in the introductory paragraph. Generally, it is not very long, about 4-6 lines.
This is the main crux of your essays. The body is the meat of your essay sandwiched between the introduction and the conclusion. So the most vital content of the essay will be here. This need not be confined to one paragraph. It can extend to two or more paragraphs according to the content.
This is the last paragraph of the essay. Sometimes a conclusion will just mirror the introductory paragraph but make sure the words and syntax are different. A conclusion is also a great place, to sum up, a story or an argument. You can round up your essay by providing some morals or wrapping up a story. Make sure you complete your essays with the conclusion, leave no hanging threads.
Writing Tips
Give your essays an interesting and appropriate title. It will help draw the attention of the reader and pique their curiosity
Keep it between 300-500 words. This is the ideal length, you can take creative license to increase or decrease it
Keep your language simple and crisp. Unnecessary complicated and difficult words break the flow of the sentence.
Do not make grammar mistakes, use correct punctuation and spelling five-paragraph. If this is not done it will distract the reader from the content
Before beginning the essay, organize your thoughts and plot a rough draft. This way you can ensure the story will flow and not be an unorganized mess.
Understand the Topic Thoroughly-Sometimes we jump to a conclusion just by reading the topic once and later we realize that the topic was different than what we wrote about. Read the topic as many times as it takes for you to align your opinion and understanding about the topic.
Make Pointers-It is a daunting task to write an essay inflow as sometimes we tend to lose our way of explaining and get off-topic, missing important details. Thinking about all points you want to discuss and then writing them down somewhere helps in covering everything you hoped to convey in your essay.
Develop a Plan and Do The Math-Essays have word limits and you have to plan your content in such a way that it is accurate, well-described, and meets the word limit given. Keep a track of your words while writing so that you always have an idea of how much to write more or less.
Essays are the most important means of learning the structure of writing and presenting them to the reader.

FAQs on Essay Writing
1. Writing an Essay in a format is important?
Yes, it is important because it makes your content more streamlined and understandable by the reader. A set format gives a reader a clear picture of what you are trying to explain. It also organises your own thoughts while composing an essay as we tend to think and write in a haphazard manner. The format gives a structure to the writeup.
2. How does Essay writing improve our English?
Essay writing is a very important part of your English earning curriculum, as you understand how to describe anything in your words or how to put your point of view without losing its meaning
3. How do you write a good essay?
Start by writing a thorough plan. Ensure your essay has a clear structure and overall argument. Try to back up each point you make with a quotation. Answer the question in your introduction and conclusion but remember to be creative too.
4. What is the format of writing an essay?
A basic essay consists of three main parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. This basic essay format will help you to write and organize an essay. However, flexibility is important. While keeping this basic essay format in mind, let the topic and specific assignment guide the writing and organization.
5. How many paragraphs does an essay have?
The basic format for an essay is known as the five paragraph essay – but an essay may have as many paragraphs as needed. A five-paragraph essay contains five paragraphs. However, the essay itself consists of three sections: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Below we'll explore the basics of writing an essay.
6. Can you use the word you in an essay?
In academic or college writing, most formal essays and research reports use third-person pronouns and do not use “I” or “you.” An essay is the writer's analysis of a topic. “You” has no place in an essay since the essay is the writer's thoughts and not the reader's thoughts.
7. What does bridge mean in an essay?
A bridge sentence is a special kind of topic sentence. In addition to signaling what the new paragraph is about, it shows how that follows from what the old paragraph said. The key to constructing good bridges is briefly pointing back to what you just finished saying.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability to their source material. Most importantly, the use of MLA style can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the purposeful or accidental uncredited use of source material produced by other writers.
If you are asked to use MLA format, be sure to consult the MLA Handbook (9th edition). Publishing scholars and graduate students should also consult the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3rd edition). The MLA Handbook is available in most writing centers and reference libraries. It is also widely available in bookstores, libraries, and at the MLA web site. See the Additional Resources section of this page for a list of helpful books and sites about using MLA Style.
Paper Format
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA Style is covered in part four of the MLA Style Manual . Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA Style :
General Guidelines
- Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another. The font size should be 12 pt.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks (unless otherwise prompted by your instructor).
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. MLA recommends that you use the “Tab” key as opposed to pushing the space bar five times.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor may ask that you omit the number on your first page. Always follow your instructor's guidelines.)
- Use italics throughout your essay to indicate the titles of longer works and, only when absolutely necessary, provide emphasis.
- If you have any endnotes, include them on a separate page before your Works Cited page. Entitle the section Notes (centered, unformatted).
Formatting the First Page of Your Paper
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically requested or the paper is assigned as a group project. In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the course, and the date. Again, be sure to use double-spaced text.
- Double space again and center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
- Use quotation marks and/or italics when referring to other works in your title, just as you would in your text. For example: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas as Morality Play; Human Weariness in "After Apple Picking"
- Double space between the title and the first line of the text.
- Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space with a page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor or other readers may ask that you omit the last name/page number header on your first page. Always follow instructor guidelines.)
Here is a sample of the first page of a paper in MLA style:

The First Page of an MLA Paper
Section Headings
Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document’s readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay.
MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
MLA does not have a prescribed system of headings for books (for more information on headings, please see page 146 in the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , 3rd edition). If you are only using one level of headings, meaning that all of the sections are distinct and parallel and have no additional sections that fit within them, MLA recommends that these sections resemble one another grammatically. For instance, if your headings are typically short phrases, make all of the headings short phrases (and not, for example, full sentences). Otherwise, the formatting is up to you. It should, however, be consistent throughout the document.
If you employ multiple levels of headings (some of your sections have sections within sections), you may want to provide a key of your chosen level headings and their formatting to your instructor or editor.
Sample Section Headings
The following sample headings are meant to be used only as a reference. You may employ whatever system of formatting that works best for you so long as it remains consistent throughout the document.
Formatted, unnumbered:
Level 1 Heading: bold, flush left
Level 2 Heading: italics, flush left
Level 3 Heading: centered, bold
Level 4 Heading: centered, italics
Level 5 Heading: underlined, flush left
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples
Published on August 14, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph , giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Organizing your material, presentation of the outline, examples of essay outlines, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay outlines.
At the stage where you’re writing an essay outline, your ideas are probably still not fully formed. You should know your topic and have already done some preliminary research to find relevant sources , but now you need to shape your ideas into a structured argument.
Creating categories
Look over any information, quotes and ideas you’ve noted down from your research and consider the central point you want to make in the essay—this will be the basis of your thesis statement . Once you have an idea of your overall argument, you can begin to organize your material in a way that serves that argument.
Try to arrange your material into categories related to different aspects of your argument. If you’re writing about a literary text, you might group your ideas into themes; in a history essay, it might be several key trends or turning points from the period you’re discussing.
Three main themes or subjects is a common structure for essays. Depending on the length of the essay, you could split the themes into three body paragraphs, or three longer sections with several paragraphs covering each theme.
As you create the outline, look critically at your categories and points: Are any of them irrelevant or redundant? Make sure every topic you cover is clearly related to your thesis statement.
Order of information
When you have your material organized into several categories, consider what order they should appear in.
Your essay will always begin and end with an introduction and conclusion , but the organization of the body is up to you.
Consider these questions to order your material:
- Is there an obvious starting point for your argument?
- Is there one subject that provides an easy transition into another?
- Do some points need to be set up by discussing other points first?
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Within each paragraph, you’ll discuss a single idea related to your overall topic or argument, using several points of evidence or analysis to do so.
In your outline, you present these points as a few short numbered sentences or phrases.They can be split into sub-points when more detail is needed.
The template below shows how you might structure an outline for a five-paragraph essay.
- Thesis statement
- First piece of evidence
- Second piece of evidence
- Summary/synthesis
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
You can choose whether to write your outline in full sentences or short phrases. Be consistent in your choice; don’t randomly write some points as full sentences and others as short phrases.
Examples of outlines for different types of essays are presented below: an argumentative, expository, and literary analysis essay.
Argumentative essay outline
This outline is for a short argumentative essay evaluating the internet’s impact on education. It uses short phrases to summarize each point.
Its body is split into three paragraphs, each presenting arguments about a different aspect of the internet’s effects on education.
- Importance of the internet
- Concerns about internet use
- Thesis statement: Internet use a net positive
- Data exploring this effect
- Analysis indicating it is overstated
- Students’ reading levels over time
- Why this data is questionable
- Video media
- Interactive media
- Speed and simplicity of online research
- Questions about reliability (transitioning into next topic)
- Evidence indicating its ubiquity
- Claims that it discourages engagement with academic writing
- Evidence that Wikipedia warns students not to cite it
- Argument that it introduces students to citation
- Summary of key points
- Value of digital education for students
- Need for optimism to embrace advantages of the internet
Expository essay outline
This is the outline for an expository essay describing how the invention of the printing press affected life and politics in Europe.
The paragraphs are still summarized in short phrases here, but individual points are described with full sentences.
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages.
- Provide background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press.
- Present the thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation.
- Discuss the very high levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe.
- Describe how literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites.
- Indicate how this discouraged political and religious change.
- Describe the invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg.
- Show the implications of the new technology for book production.
- Describe the rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible.
- Link to the Reformation.
- Discuss the trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention.
- Describe Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation.
- Sketch out the large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics.
- Summarize the history described.
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period.
Literary analysis essay outline
The literary analysis essay outlined below discusses the role of theater in Jane Austen’s novel Mansfield Park .
The body of the essay is divided into three different themes, each of which is explored through examples from the book.
- Describe the theatricality of Austen’s works
- Outline the role theater plays in Mansfield Park
- Introduce the research question : How does Austen use theater to express the characters’ morality in Mansfield Park ?
- Discuss Austen’s depiction of the performance at the end of the first volume
- Discuss how Sir Bertram reacts to the acting scheme
- Introduce Austen’s use of stage direction–like details during dialogue
- Explore how these are deployed to show the characters’ self-absorption
- Discuss Austen’s description of Maria and Julia’s relationship as polite but affectionless
- Compare Mrs. Norris’s self-conceit as charitable despite her idleness
- Summarize the three themes: The acting scheme, stage directions, and the performance of morals
- Answer the research question
- Indicate areas for further study
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
You will sometimes be asked to hand in an essay outline before you start writing your essay . Your supervisor wants to see that you have a clear idea of your structure so that writing will go smoothly.
Even when you do not have to hand it in, writing an essay outline is an important part of the writing process . It’s a good idea to write one (as informally as you like) to clarify your structure for yourself whenever you are working on an essay.
If you have to hand in your essay outline , you may be given specific guidelines stating whether you have to use full sentences. If you’re not sure, ask your supervisor.
When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is yours. Some students find it helpful to write out their ideas in full sentences, while others prefer to summarize them in short phrases.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Essay Outline | Guidelines & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-outline/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to create a structured research paper outline | example, a step-by-step guide to the writing process, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The page number should be in the upper right corner. Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch, and use double-spacing throughout the essay. Font and Size: Use a clear and readable font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12. Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
2. Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) for all styles. Whether you're writing in MLA, APA, or Chicago Style, always use a 0.5 in (1.3 cm) indent. This signals to the reader that a new paragraph is beginning. The easiest way to indent your essay is to press the tab key. 3.
Standard American argumentative essays begin with an introduction that gives a main point (thesis). The thesis is supported by a series of body paragraphs with sub-points, and the essay ends with a conclusion. Below is a visual representation of this structure, adapted from the Seattle University Writing Center; on the back is an example of the ...
Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it's an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
A scholarship essay should be tailored to the specific fund you are applying for, and it is best to avoid a generalized essay. The main components of the scholarship essay format are similar to those in a standard college essay: 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial) First line indent. Double-spacing. 1-inch margins.
Abstract: comprised of 3 paragraphs, totaling about 300 words, with 100 words in each. Paragraph 1: must include a research question, thesis, and outline of the essay's importance. Paragraph 2: Key resources, scope and limits of research, etc. Paragraph 3: Conclusion that you've already reached in your essay.
Essay Writing. This resource begins with a general description of essay writing and moves to a discussion of common essay genres students may encounter across the curriculum. The four genres of essays (description, narration, exposition, and argumentation) are common paper assignments you may encounter in your writing classes.
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
There are no set rules for how to structure a college application essay, but you should carefully plan and outline to make sure your essay flows smoothly and logically. Typical structural choices include. a series of vignettes with a common theme. a single story that demonstrates your positive qualities. Although many structures can work, there ...
If the essay is in a chapter of a book, edited collection, or anthology, APA format states that you should cite the last name, first name, title of essay, title of collection, publisher, year, and page range. For example: Smith, John, "The Light House," A Book of Poems, editing by Peter Roberts, Allworth Press, 2005, pp. 20-25.
One inch margin (both sides) Double spacing in the text. A short title on the upper left-hand corner in the header. The page number on the right in the header. A title page with the information, including the writerâ s name, institution, instructor, and date. Reference page (for the citation) APA Format Essay Example.
Again, we'd recommend sticking with standard fonts and sizes—Times New Roman, 12-point is a standard workhorse. You can probably go with 1.5 or double spacing. Standard margins. Basically, show them you're ready to write in college by using the formatting you'll normally use in college.
The basic format for an essay is known as the five paragraph essay - but an essay may have as many paragraphs as needed. A five-paragraph essay contains five paragraphs. However, the essay itself consists of three sections: an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Below we'll explore the basics of writing an essay.
A basic essay consists of three main parts: introduction, body, and conclusion. Following this format will help you write and organize an essay. However, flexibility is important. While keeping this basic essay format in mind, let the topic and specific assignment guide the writing and organization.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
MLA General Format. MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages. Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability ...
Revised on July 23, 2023. An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate ...
By outlining all these components in advance, you will write your essay faster and ensure that you haven't missed any critical points when drafting. Argumentative Essay Format. Things are more complicated with an argumentative essay format. Two rules are here: Choose a Model. It's okay to use a basic essay structure you already know.