

SWOT Analysis of Toyota (6 Key Strengths in 2023)

This Toyota SWOT analysis reveals how one of the most innovative automotive companies used its competitive advantages to become the dominant player in the automotive industry.
It identifies all the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats that affect the company the most. If you want to find out more about the SWOT of Toyota, you’re in the right place.
For more information on how to do a SWOT analysis please refer to our article.
Keep reading.
Company Overview
Toyota Motor Corporation (further Toyota) is the world’s leading automaker (often tied with Volkswagen for 1st-2nd place) based in Toyota City, Japan. In 2012, the company was the first automotive company to produce over 10 million vehicles in a single year.
The company operates 4 different brands: Daihatsu, Hino, Lexus and Toyota. Toyota’s brand is the world’s 7th most valuable brand in the world and the most valuable automotive brand, worth US$50.291 billion.
The main Toyota’s markets are Japan, United States and China, where the company sells over 50% of its vehicles. The company produces the best-selling hybrid vehicle Prius.
You can find more information about the business in Toyota’s official website or Wikipedia’s article .
Toyota SWOT analysis
1. strong focus on research and development (r&d) leading to some of the most innovative vehicles in the world.
Toyota is famous for its innovative culture. The company’s goal on being ahead of its competition by introducing some of the most innovative vehicles in the market has proven to be a successful strategy.
Toyota’s R&D initiatives, especially in producing environmentally friendly vehicle technologies, vehicle safety and information technology, provide it with some of the best strategic advantages.
The company operates one of the largest research facility network among the automotive companies to achieve the best possible results from its R&D expenditure. In total, 15 research facilities in 8 different countries, including Japan, United States, China, Thailand, Australia, Germany, France and Belgium, focus on 3 key R&D areas: [1]
- Basic research. This area researches basic vehicle technology.
- Forward-looking and leading-edge technology development. Development of newest technology and components that surpasses rivals’ technologies.
- Product development. New model development and upgrades for existing ones.
Toyota’s focus on innovation has resulted in one of the highest automotive R&D spending. Toyota’s R&D expenditures were approximately JP¥1.064.2 billion (US$9.613 billion) in fiscal 2018, ¥1,037.5 billion (US$9.579 billion) in fiscal 2017, and ¥1,055.6 billion (US$8.787 billion) in fiscal 2016. [1]
Figure 1. Toyota’s and its competitors R&D spending (US$ billions)
Among the automotive companies, only Volkswagen spends more on R&D than Toyota. Nonetheless, Toyota uses its R&D budget the most effectively, spending just 3.6% of its total revenue on R&D, while Volkswagen spends 6.7%.
This means that Toyota needs to spend less on R&D to generate the same amount of revenue than its key rivals.
Huge, efficient R&D spending has allowed Toyota to gain a competitive advantage over its competitors and to become one of the largest automotive manufacturers in the world by researching and introducing the leading-edge technology and vehicles to the consumers.
2. The most valuable and one of the most recognizable automotive brands in the world
Toyota Motor Corporation was incorporated in 1937 and since then, has become one of the most recognizable brands in the world.
According to Interbrand [5] and Forbes [6] , Toyota’s brand is the world’s 7th and 9th most valuable brand worth US$50.291 billion and US$44.7 billion, accordingly. In both lists, it is the most valuable brand out of all automotive companies.
Figure 2. Automotive brand ranking by Interbrand
Brand value is closely related to brand reputation and recognition. Toyota, which produced and sold 8.964 million vehicles in 190 countries in 2018 alone, has one of the widest consumer reach in the world.
Manufacturing, research and sales operations worldwide, combined with a huge number or vehicles sold, as well as advertising spending has helped the company to create one of the most recognizable brands in the world. Brand recognition helps the company to introduce new products to the market more easily and with fewer costs.
Toyota brand is also one of the most reputable brands in the automotive industry. Over its 75 years’ history, the company received hundreds of awards accolades in vehicle design, safety, environment-friendliness and manufacturing operations. [7]
In 2018 alone, the company has received 7 IIHS (Insurance Institute for Highway Safety) Top Safety Picks 2018 awards (more than any other automotive company) for its Toyota Corolla, Prius, Camry, Avalon, Highlander and RAV4 vehicle models as well as 4 other Top Safety awards for Lexus models. [8]
The company received more 2017 J.D. Power Vehicle Dependability Awards than any other brand. [9] In addition to the awards for its vehicles, the company ranks the 2nd on the Carbon Clean 200 List, which ranks the companies according to their efforts to transition to clean energy. [10]
Toyota’s brand and recognition provides the company with a competitive edge over competitors as few other automotive brands are so well-known and reputable.
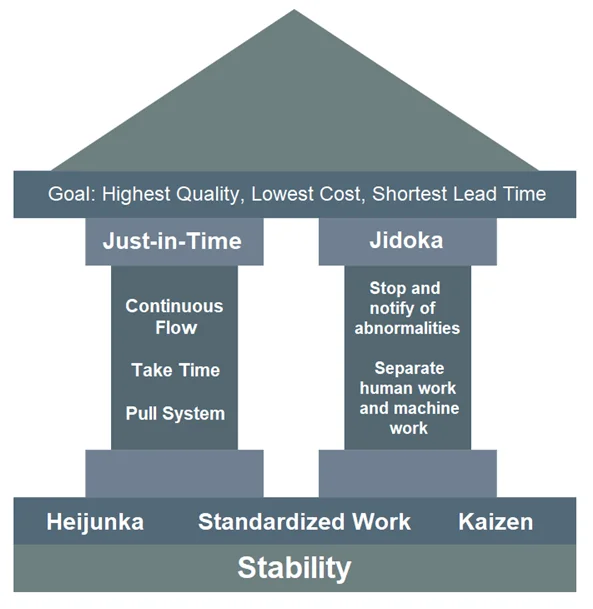
3. Toyota Production System
Toyota production system or TPS is a manufacturing system developed by Toyota. The system’s philosophy is to ‘eliminate all waste from manufacturing process’. The system was based on Just-in-Time concept. TPS has become very successful in allowing the company to increase production efficiency, decrease manufacturing time and simplify its processes. All of which resulted in lower costs and better quality vehicles.
Figure 3. Toyota Production System
Due to the TPS, Toyota’s operating profit margin of 8.2% is the highest when compared to its largest competitors Volkswagen’s operating profit margin of 6% or General Motors’ operating profit margin of 6.2% (in 2016).
Figure 4. Toyota and its largest competitors’ operating profit margin comparison (in percentages)
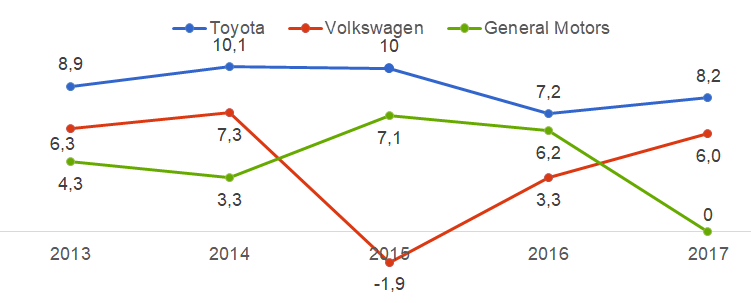
The graph shows that Toyota constantly enjoys higher operating profit margins than Volkswagen or General Motors. This means that costs of running the business are much lower for Toyota, which is most likely the result of the company’s production system.
Toyota’s production system is unique and is very hard to replicate. It is a strength few rivals can match.
4. Competence in electrified vehicle production
Toyota is heavily invested in its hybrid vehicle (HV) lineup and is betting its long-term future on HVs and electric HVs.
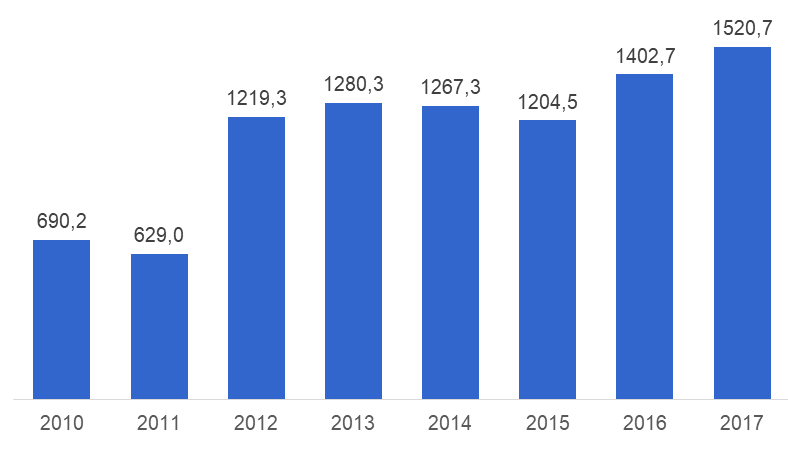
The company has introduced its first hybrid vehicle Toyota Prius in 1997. Prius became the first mass-produced hybrid vehicle and the most successful to date. By the end of 2017, the company has sold over 6.5 million Prius models, of which 457.4 thousand were sold in 2017 alone. Toyota’s total sales of electrified (mostly hybrid) vehicles were 1.521 million in 2017. Since 1997, the company has sold 11.471 million electrified vehicles, more than any other automotive company in the world. [12] The sales of Toyota’s electrified vehicles are growing faster every year.
Figure 5. Toyota’s sales of electrified vehicles in 2010-2017 (in thousands)
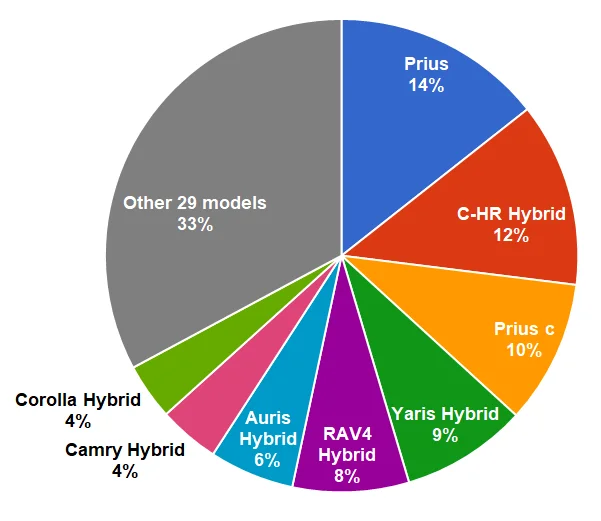
Currently, Toyota offers over 30 hybrid vehicles and plug-in hybrid vehicles under its four brands. Toyota’s HV technology is probably the best-in-class. It is proven by a 2017 Prius Eco model, which is the most fuel efficient car that doesn’t have a plug-in capability.
Figure 6. Toyota’s sales of electrified (mostly hybrid) vehicles by model in 2017
Toyota’s competence in hybrid vehicles is a long-term competitive advantage that its competitors will not be able to match in a near future.
5. Toyota environmental challenge 2050
In 2015, Toyota announced six environmental challenges that it hopes to achieve until 2050. Covering issues such as climate change and resource and water recycling, the challenges all involve formidable difficulties, but Toyota is committed to continuing with steady initiatives to achieve sustained development together with society. [1]
In its New Vehicle Zero CO2 Emissions Challenge, Toyota has set itself the target of achieving by 2050 a 90% reduction in new vehicle CO2 emissions compared to 2010. Towards this goal, Toyota will roll out the technology it has built up in the hybrid vehicle sector, adapting it to plug-in hybrid vehicles and to fuel cell and electric vehicles, which generate no CO2 emissions whatsoever. Toyota is committed to further accelerating its initiatives toward the development and widespread adoption of hybrid vehicles and other eco-cars.
The company’s clear strategy and past successes in achieving environmental challenges before the deadlines will help the company to strengthen its brand reputation, lower the environmental costs and will help to achieve compliance for government regulations earlier, which will ultimately result in more sales and higher profits.
6. Production of the most dependable cars in the industry
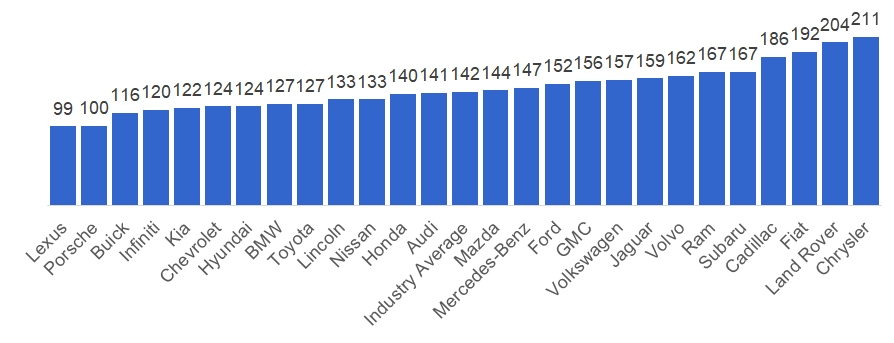
In 2018, a U.S. Vehicles Dependability Study (VDS) done by J.D. Power revealed that Toyota has some of the best industry’s ratings for vehicle dependability. The VDS measures the number of problems experienced per 100 vehicles during the past 12 months by original owners of 2015 model-year vehicles. The lower the score the better vehicle dependability.
Toyota’s Lexus was ranked as the most dependable brand among all automotive brands with only 99 problems per 100 vehicles. Toyota’s own brand ranked 9 th with only 127 problems per 100 vehicles. Toyota Motor Corporation also won 6 out of 19 category awards, two for Toyota Tacoma and Toyota Prius and four for Lexus various models, more than any other automotive company.
Figure 7. J.D. Power 2018 Vehicles Dependability Study (problems per 100 vehicles)
1. Lack of competence in autonomous vehicles
Toyota has long been reluctant to invest in autonomous vehicle technology. The company has been engaged in R&D aimed at contributing to the complete elimination of traffic casualties, but the company had no plans to introduce completely autonomous vehicles in the near-future. [1]
The company’s first attempt to developing such technology was in 2015, through the Team Mobility concept, which aims to facilitate the connection between the car and its surroundings and between the car and the driver to assure safe and efficient driving. These initiatives were far behind rivals’ efforts on autonomous vehicles and Toyota had to step up.
In 2017, Toyota Research Institute introduced the first Toyota autonomous vehicle trials on roads. [14] In 2018, the company announced that it will invest US$2.8 billion into the new Toyota Research Institute-Advanced development company. The company will focus on developing software for artificial intelligence, which will be used for autonomous vehicles. [15]
Nonetheless, Toyota still lags behind its main competitors like General Motors, Volkswagen and Ford. Ford and General Motors were testing their first autonomous cars back in 2013. [16] In 2018, these companies have made more progress and have better technologies in developing fully autonomous cars. According to the research done by Navigant Research, Toyota’s strategy and execution in developing autonomous vehicles is worse than most of its rivals. [17]
Figure 8. Assessment of Strategy and Execution for 19 Companies Developing Automated Driving Systems
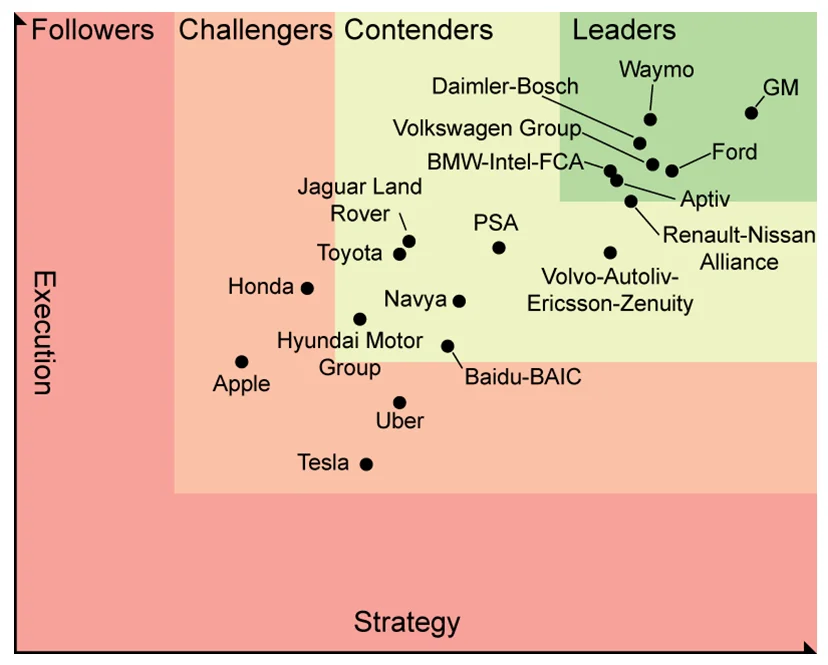

The company’s lack of technology and experience in building autonomous vehicles puts it at disadvantage against such competitors as General Motors, Ford and Volkswagen Group.
2. Negative publicity due to large vehicle recalls damages company’s brand and sales
Vehicle recalls affect every automaker. Toyota is no exception. While some automakers experience fewer recalls, other have to recall millions of vehicles each year. Toyota’s recall rates are very high and this draws more negative publicity than usual. In 2017 and 2018 (July) alone, the company has issued the following recalls:
- 2.9 million vehicles recalled in China, Japan and Oceania, due to faulty Takata airbags;
- 228,000 Tacoma vehicles recalled over an issue that could cause drivers to lose control of their cars;
- 300,000 Sienna vehicles sold in the U.S. were recalled because of safety concerns;
- 700,000 vehicles recalled in South Africa over faulty airbags;
- 74,000 pickups and SUVs were recalled over safety issues;
- 600,000 additional vehicles recalled in the U.S. over airbag issues;
- 115,000 Lexus cars recalled due to possible fuel leaks in engines.
These are only some of the biggest recalls issued by Toyota in 2017 and 2018. Large and frequent recalls negatively affect the company’s brand reputation and result in disappointed customers as well as fewer sales.
3. Weak presence in China lowers company’s future growth potential
China is the world’s largest automotive market and Toyota’s third largest market in terms of volume. The company currently sells 14.5% of its vehicles there. It isn’t the most profitable market for car manufacturers, but with 28.2 million vehicles sold in 2017, it dwarfs any other vehicle market, including the U.S. [1]
Toyota sold 1.3 million vehicles in China in 2017. The company sold 6% more units in 2017 when compared to 2016 (1.23 million units sold) and 16% more units when compared to 2015 (1.12 million units sold), but its market share increased only slightly from 4.5% in 2015 to 4.6% in 2017. [1]
Figure 9. Automotive companies’ market share in China
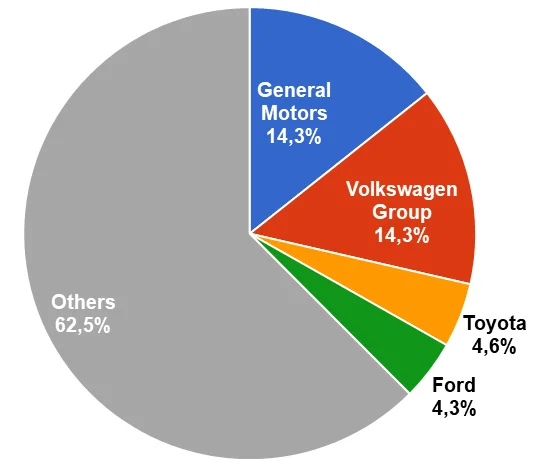
China is the largest vehicle market for the two main Toyota’s competitors, General Motors and Volkswagen where both companies sold 4.041 million vehicles and 4.020 million vehicles, and held 14.3% market share, respectively.
For any automotive company, China is a crucial market, if the company wants to succeed in the future. Toyota, which has a weak market share in China will find it hard to compete with General Motors and Volkswagen in the long run.
4. Poor brand portfolio
Toyota sells its vehicles under 4 different brands: Hino, Daihatsu, Lexus and Toyota. Toyota currently sells the majority of its vehicles under its own ‘Toyota’ brand, with top-end luxury cars being sold under its Lexus brand. [1] By comparison, some of its major competitors have a much larger brand portfolio, as illustrated below.
Figure 10. Brand portfolio of selected major Ford competitors
While Toyota’s branding strategy assists with brand awareness and recognition (Toyota is the most valuable automotive brand in the world), there are several potential disadvantages to this approach. Toyota’s competitors with brand diversification (i.e. multiple brands) can more easily create a hierarchy for their vehicles in consumers’ minds, facilitating product differentiation. A brand diversification strategy can also minimize the fallout from any controversies that a vehicle manufacturer may experience.
A company like Toyota with their minimalist branding strategy is unlikely to be able to negate the negative publicity associated with product recalls, advertising scandals or vehicle failures.
With only a few brands, Toyota cannot target many different consumer segments and satisfy their various needs as well as Volkswagen or General Motors with their many brands.
Opportunities
1. future markets for self-driving vehicles.
The global demand for autonomous vehicles is growing fast, mainly due to the need to improve road safety, ease the driving experience and minimize traffic congestion in big cities. There are five main levels of vehicle automation:
Figure 11. Levels of automation in vehicles
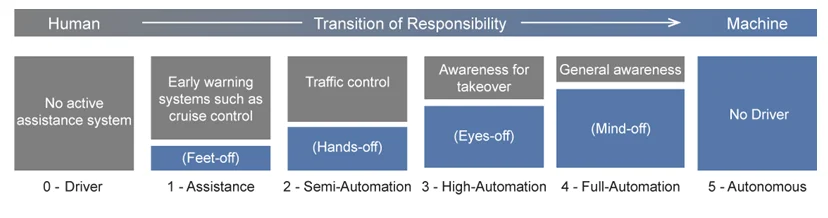
At the moment, companies offer only level 2 automation vehicles for general consumers. According to Markets & Markets research [19] , auto manufacturers produced only 2.73 million of these vehicles in 2016. Other research from Grand View Research reports that fully autonomous vehicles will be introduced to the market at a significant scale only in 2021-2022. [20]
In 2017, there were 44 companies working on autonomous vehicles, including Toyota. [21] While Toyota is one of the latest major automotive companies to start working on autonomous vehicles, the company expects to introduce vehicles with automated driving on highways by 2020 and vehicles with automated driving in urban areas in early 2020s. [1]
Even though the potential opportunity for autonomous vehicles is huge, there are still many challenges. It is yet to be determined what the potential market size would be, how effective the vehicles are, costs, and how they will be regulated in terms of safety concerns. For example, currently only 33 states in America permit driverless cars on the roads. [22] However, in terms of innovation and potential, the market for self-driving cars could potentially be very lucrative. It is an opportunity that automotive companies have no choice but to explore in the current competitive technological environment.
2. Significant untapped potential of Chinese, Indian and other Asian international markets
Along with many global automotive companies, Toyota has been capitalizing on China’s double digit economic growth for much of the past decade. Although this economic growth is slowing [23] , China still represents a country of tremendous opportunity for automotive manufacturers, including Toyota. China’s middle class is growing on the back of its economic growth, and demand for motor vehicles is increasing accordingly. [24] The Chinese motor vehicle industry is currently the largest in the world. Toyota however only has a 4.6% market share in it. [1]
Toyota’s strategy to increase market share in China is to focus on introducing more hybrid and electric vehicles to comply with strict Chinese quotas over production and sales for new energy vehicles. With its strong brand reputation and increasing focus on research and development, Toyota is well-positioned to capitalize on this opportunity.
In India, Toyota similarly has a minimal market share of just 5%. [25] However the market is forecast to be the world’s third largest by 2020 behind China and the United States, on the back of a rising middle class population, many of whom will be able to afford cars for the first time. [26]
By 2030, Asia’s share of the world’s middle class population is predicted to double, from 30% to 60%. Much of this growth will be in China and India, but also in Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand and Malaysia. In many of these countries, the average number of cars per household is well below the levels in Western countries. [27] These countries represent a significant opportunity for all automotive companies, including Toyota.
3. Improving U.S. economic conditions
North America is the largest Toyota’s geographic segment by vehicle unit sales. The company sells 31.3% of its vehicles in Mexico, Canada and the United States, combined. The company reveals that the U.S. accounts for 87% of the North America’s sales, which makes it the second most important Toyota’s market in terms of revenue, after Japan.
The outlook for the U.S. economy is positive [28] , which is an opportunity for Toyota to consolidate and increase its already significant market share. Toyota currently has the 3 rd largest market share in the U.S.
Figure 12. Market share of major competitors in the U.S. market
Unlike Ford or General Motors, Toyota does not rely as heavily on pickup trucks to generate the majority of its sales in the U.S., so the company has better opportunities grow its sales by offering smaller electrified passenger cars for the market.
4. Timing and frequency of new model releases
The market share of automotive companies is significantly impacted by the timing and frequency of new model releases, a fact that Toyota itself acknowledges. [1] Historically, new models have tended to have major upgrades every 4 or 5 years, with only minor modifications in between.
However, due to rising consumer expectations in relation to in-car technology and the competitive nature of the industry, there is an argument to release upgraded models more frequently. Toyota is well-positioned to be able to do this, with its current focus on R&D. The key will be its ability to cost effectively implement technology initiatives in order to maximize competitive advantage.
1. Increasing competition in the worldwide automotive market
The automotive industry is highly competitive, both in the Japan’s automotive market and in international markets around the world. Toyota’s international rivals such as Volkswagen and General Motors have aggressively taken market share from Toyota. Despite the fact that the worldwide automotive market is already highly competitive, the competition is further increasing due to the excess of vehicle production, rapid technological changes, new entrants and saturation of the largest markets. This competition may further increase with the potential future entry of Chinese and Indian rivals.
In international markets, particularly in growth regions such as China, there is a similar intensity of competition. This competition is fueled by the fact that global automotive production capacity far exceeds demand. In 2017, there was an estimated global excess production capacity of 35 million units. [2]
In addition to traditional automotive competitors, technology companies such as Google and Apple are showing interest in the automotive market, through initiatives such as the development of driverless vehicles and sophisticated in-car technology that is compatible with their devices and operating platforms. [30] This may give these organizations technological influence over future vehicle development, which automotive companies may not be able to control.
2. The automotive industry is subject to various governmental regulations
Increasing government regulations is one of the key threats affecting Toyota. The company has emphasized this issue in its financial report:
“The worldwide automotive industry is subject to various laws and governmental regulations including those related to environmental matters such as emission levels, fuel economy, noise and pollution. Toyota has incurred, and expects to incur in the future, significant costs in complying with these regulations.
Furthermore, new legislation or changes in existing legislation may also subject Toyota to additional expenses in the future. If Toyota incurs significant costs related to meeting laws and governmental regulations, Toyota’s financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.” [1]
3. Potential economic and political volatility in international markets
With Toyota currently generating 68.4% of its total revenue from outside of its home Japan market, the company is vulnerable to international economic and political conditions. Stricter local government regulations and/or import controls, rising interest rates as well as the outbreak of hostilities or acts of terrorism could all adversely affect Toyota’s operations internationally. Toyota acknowledges this risk in its most recent financial report:
“Each of the markets in which Toyota competes has been subject to considerable volatility in demand. Demand for vehicles depends to a large extent on economic, social and political conditions in a given market. As Toyota’s revenues are derived from sales in markets worldwide, economic conditions in such markets are particularly important to Toyota.”
“Toyota is subject to various risks associated with conducting business worldwide. These risks include natural calamities; political and economic instability. Should the major markets in which Toyota purchases materials, parts and components be affected by any of these events, it may result in disruptions and delays in the operations of Toyota’s business. Should significant or prolonged disruptions or delays related to Toyota’s business operations occur, it may adversely affect Toyota’s financial condition and results of operations.”[1]
4. Toyota may be adversely affected by natural disasters
Toyota and its suppliers have many manufacturing facilities in Japan, Thailand, China and Indonesia. These countries, are often affected by natural disasters, such as earthquakes, tsunamis and flooding. Every occurrence of such calamity may disrupt the manufacturing processes and result in supply shortages or an overall halt of the production.
In the past, Toyota’s operations have been significantly impacted by such disasters and resulted in huge losses. For as long as the company or its suppliers will continue to run their manufacturing in these or similarly affected countries, Toyota will be subject to further occurrences of natural disasters and huge losses.
Toyota has become one of the world’s largest automotive companies because of its innovative and quality vehicles that are also resonably priced. The company should further rely on its R&D capabilities, Toyota Production System and competence in electrified vehicles. These are the key Toyota’s strengths that should drive company’s growth in the future.
As for the weaknesses, Toyota has to really push forward on autonomous vehicles and increase its market share in China. Both weaknesses can significantly harm the company over the next 5-10 years.
Out of all the opportunities, future market growth of self-driving vehicles is the most significant one. Nonetheless, Toyota is behind its rivals in developing autonomous vehicles and the company may find it hard to get the most of this opportunity.
None of the threats immediatelly pose any danger for Toyota and the company is capable to prepare for them in the future or mitigate their potential damage.
Toyota will continue to successfully compete in the automotive market in the future.
- Toyota Motor Corporation (2018). Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31 st , 2018. Available at: http://www.toyota-global.com/pages/contents/investors/ir_library/sec/pdf/20-F_201803_final.pdf Accessed July 16, 2018
- Ford Motor Company (2018). Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31st, 2017. Available at: http://shareholder.ford.com/~/media/Files/F/Ford-IR-V2/events-and-presentations/2018/F-2017-10-K-report.pdf Accessed July 16, 2018
- General Motors Company (2018). Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31st, 2017. Available at: http://www.gm.com/company/investors/sec-filings.html Accessed July 16, 2018
- Volkswagen AG (2018). Annual Report 2017. Available at: https://www.volkswagenag.com/presence/investorrelation/publications/annual-reports/2018/volkswagen/en/Y_2017_e.pdf Accessed July 16, 2018
- Interbrand (2018). Best Global Brands 2017. Available at: http://interbrand.com/best-brands/best-global-brands/2017/ranking/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Forbes (2018). The World’s Most Valuable Brands. Available at: http://www.forbes.com/powerful-brands/list/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Toyota Motor Corporation (2018). Award History. Available at: https://www.toyota-global.com/company/history_of_toyota/75years/data/automotive_business/products_technology/technology_development/award/index.html Accessed July 16, 2018
- Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (2018). Top Safety Picks by year. Available at: http://www.iihs.org/iihs/ratings/TSP-List Accessed July 16, 2018
- Toyota (2018). Toyota Awards & Ratings. Available at: https://www.toyota.com/awards/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- As You Sow (2018). Carbon Clean 200: Investing In A Clean Energy Future. Available at: https://www.asyousow.org/report/clean200-2018-q1 Accessed July 16, 2018
- Lean Enterprise Institute (2018). Toyota Production System. Available at: http://www.lean.org/lexicon/toyota-production-system Accessed July 16, 2018
- Toyota (2018). Toyota sells 1.52 million electrified vehicles in 2017, three years ahead of 2020 target. Available at: https://newsroom.toyota.co.jp/en/corporate/20966057.html Accessed July 16, 2018
- J.D. Power (2018). Most Owners Still in Love with Their Three-Year-Old Vehicles, J.D. Power Finds. Available at: http://www.jdpower.com/press-releases/jd-power-2018-us-vehicle-dependability-study Accessed July 16, 2018
- Iliff, L. (2017). Toyota says its ‘in the game’ on autonomous technology. Available at: http://www.autonews.com/article/20171023/MOBILITY/171029940/toyota-autonomous-vehicle-testing-tri Accessed July 16, 2018
- O’Kane, S. (2018). Toyota starts a new $2.8 billion company to develop self-driving software. Available at: https://www.theverge.com/2018/3/2/17070828/toyota-research-institute-tri-ad-tokyo Accessed July 16, 2018
- Dormehl, L. and Edelstein, S. (2018). Sit back, relax, and enjoy a ride through the history of self-driving cars. Available at: https://www.digitaltrends.com/cars/history-of-self-driving-cars-milestones/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Navigant Research (2018). Navigant Research Leaderboard: Automated Driving Vehicles. Available at: https://www.navigantresearch.com/research/navigant-research-leaderboard-automated-driving-vehicles Accessed July 16, 2018
- BMW Group (2016). Annual Report 2016. Available at: https://www.bmwgroup.com/content/dam/bmw-group-websites/bmwgroup_com/ir/downloads/en/2015/12784_GB_2015_engl_Finanzbericht_Online.pdf Accessed July 16, 2018
- Research and Markets (2017). Global Autonomous Vehicles Market – Analysis & Forecast (2016-2025). Available at: http://www.researchandmarkets.com/research/wd2lrs/global_autonomous Accessed July 16, 2018
- Grand View Research (2017). Autonomous Cars/Driverless Cars Market Analysis and Segment Forecasts To 2024. Available at: http://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/driverless-cars-market Accessed July 16, 2018
- CB Insights (2017). 44 Corporations Working On Autonomous Vehicles. Available at: https://www.cbinsights.com/blog/autonomous-driverless-vehicles-corporations-list/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- National Conference of State Legislature (2018). Autonomous Vehicles | Self-Driving Vehicles Enacted. Available at: http://www.ncsl.org/research/transportation/autonomous-vehicles-self-driving-vehicles-enacted-legislation.aspx Accessed July 16, 2018
- Trading Economics (2018). China GDP Annual Growth Rate. Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/gdp-growth-annual Accessed July 16, 2018
- McCaffrey, C. R. and Peterson, E. R. (2018). The Rise of China’s Middle-Class Consumer. Available at: https://www.atkearney.com/diversity-and-inclusion/article/-/asset_publisher/O7EGSazwBWC9/content/the-rise-of-china-s-middle-class-consumer-article/236833 Accessed July 16, 2018
- Shah, R. (2018). Top-10 carmakers in India and their market share: Maruti Suzuki owns half of the Indian market. Available at: https://www.financialexpress.com/auto/car-news/top-10-carmakers-in-india-and-their-market-share-maruti-suzuki-owns-half-of-the-indian-market/1129193/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Karnik, M. (2016). 600 million people are now part of India’s middle class—including your local carpenter. Available at: https://qz.com/742986/600-million-people-are-now-part-of-indias-middle-class-including-your-local-carpenter/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Roughneen, S. and Asia, N. (2017) Booming Southeast Asian vehicle sales drive urban congestion. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/96608536-4204-11e7-9d56-25f963e998b2 Accessed July 16, 2018
- Trading Economics (2018). United States GDP Growth Rate. Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/united-states/gdp-growth Accessed July 16, 2018
- Matthews, J. (2018). U.S. Auto Sales Brand Rankings – December 2017 YTD. Available at: http://www.goodcarbadcar.net/2018/01/u-s-auto-sales-brand-rankings-december-2017-ytd/ Accessed July 16, 2018
- Greenough, J. (2017). How Tech Companies Will Win the Battle Over the Connected Car’s Digital Dashboard. Available at: http://www.businessinsider.com.au/how-tech-companies-will-win-the-battle-over-the-connected-cars-digital-dashboard-2015-12 Accessed July 16, 2018
- Toyota Mission Statement
- SWOT Analysis of Walmart (5 Key Strengths in 2023)
- SWOT Analysis of Starbucks (6 Key Strengths in 2023)
- SWOT Analysis of Samsung (6 Key Strengths in 2023)
- SWOT Analysis of Ford (5 Key Strengths in 2023)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Search 89500
- Search 8067
- Search 89366

Toyota SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: Toyota Motor Corporation President: Akio Toyoda Founder: Kiichiro Toyoda Year founded: 1937 Headquarter: Aichi, Japan Employees (2022): 372,817 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: TM Annual Revenue (FY 2022): JPY 31,379.5 billion Profit | Net income (FY 2022): JPY 2,850.1 billion
Products & Services: Automobile | Materials’ Handling Equipment | Textile Machinery | Financial Services | Biotechnology and Afforestation | Boats and Marine Engines | Housing Services Competitors: Nissan | Ford | Volkswagen | Hyundai | Honda | General Motors | Tesla | Mazda Motor | SOA | Chrysler | Mercedes Benz | BMW | Porsche | Audi | Jaguar | Tata Motors
Did you know ? Toyota was first founded in 1933 as an automated loom business . Founded from humble beginnings, Toyota grew gradually into a multinational automotive company and one of the world’s most profitable and valuable companies.
With a presence in over 170 countries , Toyota is a force to reckon with. We can learn a lot by assessing Toyota’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Table of Contents
Toyota’s Strengths
1. Global Dominance
Companies that dominate the market have leverage over competitors. From Asia to Europe, Africa, and America, Toyota cars are sold in over 170 countries in different regions and 10.5% of the global market .
2. Diversified Variety
Toyota offers a wide variety of vehicles , from Corolla to Prius, Camry, Land Cruiser, Scion, Hilux, Supra, and many more.
The cars are of different models , including sedans, pickup trucks, and off-road vehicles. They are powered by electric, hybrid, petrol, or diesel, allowing the company to cater to consumers across the entire auto market.
3. Effective Leadership
Toyota’s strong leadership and organizational structure have enabled the company to avoid friction and turmoil witnessed in other auto companies like Nissan.
Leadership and structure have enhanced the stability of the company.
4. Strong Brand
Having strong brand recognition and awareness enhances the value of the brand and contributes to the bottom line with higher sales.
Toyota is regarded as one of the most recognized brands globally and, according to reports , has continued to be the world’s most valuable car brand , with a brand value of $75.5 billion .
5. Technological Leadership
Apart from its title as one of the biggest automakers in the world, Toyota is an innovator , disruptor, and leader in technology.
From hybrid Prius to RAV4 and Corolla, Toyota has manufactured and sold over 20 million hybrids since 1997, with some competitors relying on its cutting-edge hybrid technology.
6. Extensive Supply Chain
Toyota has built an extensive and one of the best global supply chains in the industry.
From manufacturing factories to assembly plants, outlets, branches, and auto parts vendors, the company’s global supply enables resilience and minimizes market-based risk.
7. High Production Capability
With higher production capacity comes stability and flexibility in sales leading to higher profits. Toyota is giving serious competition to the competitors with its high production capacity of almost 10 million cars per year .
8. Strong Financial Position
Toyota has extra cash saved away compared to its competitors, offering it flexibility and long-term stability. In 2022, Toyota’s Issuer Default Ratings (IDR) rating by Fitch Ratings International was A+.
Toyota’s Weaknesses
1. Overdependence on Suppliers
To succeed, global auto manufacturers must rely on suppliers of cheaper raw materials like aluminum worldwide.
Toyota’s overdependence on suppliers exposes the company to a wide range of risks, including a shutdown of production in case suppliers declare a strike or fail to deliver vital materials in time.
2. Poor Marketing of Eco-friendly Cars
Although Toyota manufactures eco-friendly vehicles using advanced green vehicle technology, the company has failed to advertise and grab meaningful market share for these highly demanded technologies.
3. Manufacturing Defects
A high vehicle recall rate can immensely destroy an automaker’s reputation, forcing customers to mass-migrate to its competitors.
Toyota has a high recall rate and recalled about 3.9 million vehicles in 2020 due to fuel pump defects that can lead to stalling.
4. Ineffective Marketing
Apart from Toyota and Lexus cars, the company also owns Hino and Daihatsu car brands that are unrecognized by consumers due to Toyota’s ineffective marketing strategies .
Toyota’s Opportunities
1. Focus on Emerging Economies
The financial situation in developing countries has improved immensely over the past few decades.
Toyota can increase investment in emerging economies like China and take advantage of the ever-increasing demand for cars by the growing middle class.
2. Expand into Autonomous Vehicles
The demand for safe but cheaper self-driving vehicles is increasing astoundingly. Toyota can expand into this growing market and exploit readily available opportunities.
3. Expand into Medical Device Sector
The coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the importance of automakers engaging in other unrelated industries .
Toyota contributed to global efforts to combat COVID-19 by switching its factories to manufacture medical face shields . The company can expand further by manufacturing other medical devices, such as ventilators.
4. Increase Focus on Eco-friendly Vehicles
The number of eco-conscious consumers has increased over the past few years.
Toyota can exploit this opportunity by increasing its investment in and focusing on manufacturing eco-friendly vehicles, such as hybrid and electric cars. Toyota has set an internal goal to sell about 5.5 million electric vehicles by 2030.
5. Invest in Related Fields
Toyota has the expertise and resources to engage in other fields within the auto industry like motorcycle production or related to the industry, such as ridesharing apps and multi-modal mobility services .
Toyota’s Threats
1. Global Pandemic
Automotive is a capital-intensive industry that cannot operate effectively without stockpiles of parts and raw materials.
The coronavirus pandemic has revealed that Toyota and other automakers are highly vulnerable in case of worse global pandemics in the future.
2. Cut-throat Competition
Toyota faces increased global competition from ridesharing apps and traditional competitors like Nissan, Ford , Volkswagen, BMW, Mitsubishi, Hyundai, and many new entrants.
With increased competition comes slower growth in profitability and market share .
3. Negative Publicity
Consumers are constantly exposed to images of terror groups, rebels, and armies of rogue regimes riding Toyota’s off-road trucks .
Although it is a testament to effectiveness in all terrains, the association with terror, bloodshed, and war zones can affect sales. Also, car names like Toyota ISIS and Corona do not help.
4. Global Economic Turmoil
From the global recession due to the pandemic to Trump’s tariffs and isolationism, partaking in the global arena profitably will increasingly become a challenge for Toyota if these threats persist.
5. Technology Race
With the race to deliver electric and autonomous vehicles, auto manufacturers, including Toyota, are pushed to invest billions in partnerships and upcoming technologies to keep up with competitors .
Over-investing can undermine stability and even lead to bankruptcy.
6. Scarce and Expensive Raw Materials
For centuries, global consumption has diminished resources worldwide, leading to an increase in the prices of inputs.
Toyota’s operations, profitability, and sustainability can be negatively affected if the trend continues.
References & more information
- Featured Image by Joshua Yu
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
Brianna Parker
She is a creative writer, corporate storyteller and global brand consultant, who has a unique combination of a business and creative mindset.
Cancel reply
Thanks 😊 man
Glad you liked our analysis, Happy Reading!
Good information
You may also like

DoorDash SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: DoorDash Founders: Tony Xu, Andy Fang, Evan Moore, and Stanley Tang Year founded: 2013 CEO: Tony Xu Headquarter: San Francisco, California, United States Employees (2022): 8,600 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: DASH...
Volkswagen SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Volkswagen
Company: Volkswagen Group Founders: German Labor Front Year founded: May 28th, 1937 CEO: Herbert Diess Headquarters: Wolfsburg, Germany Employees (Dec 2019): 671,200 Type: Public Annual Revenue (Dec 2019):...

Verizon SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Verizon
Company: Verizon Communications Inc. CEO: Hans Erik Vestberg Year founded: October 7, 1983 Headquarters: Hans Erik Vestberg Employees (Dec 2019): 135,400 Ticker Symbol: VZ Type: Public Annual...

What does SWOT stand for ?
Model Name : SWOT Analysis Creator : Albert Humphrey Year : 1969 Purpose : Analysis tool | Identify strength | Identify Weakness | Discover Opportunities | Eliminate Threat | New...
Adidas SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Adidas
Company: Adidas Group Founder: Adolf (Adi) Dassler Year founded: 1924 (as Gebruder Dassler Schuhfabrik), 1949 (as Adidas) CEO: Kasper Bo Rorsted Headquarter: Herzogenaurach, Bavaria, Germany Type: Public Ticker...

HDFC Bank SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: HDFC CEO: Sashidhar Jagdishan Founder: HT Parekh Year founded: 1994 Headquarter: Mumbai, India Employees (2022): 141,579 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: HDFCBANK Annual Revenue (Mar 2022): 101,519 Crore Rupees...

TikTok SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: TikTok Founders: Zhang Yiming Year founded: 2016 CEO: Shou Zi Chew Headquarter: Culver City, Calif Employees (2021): 10,000 Annual Revenue (FY 2021): $4.6 Billion Products & Services: Video sharing | Mobile...

COSTCO SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of COSTCO
Company: Costco Wholesale Corporation CEO: W. Craig Jelinek Founders: James Sinegal, Jeffrey Brotman, Sol Price Year founded: July 12, 1976 (as Price Club), September 15, 1983 (as Costco)...

Cadbury SWOT Analysis (2024)
Company: Cadbury CEO: Anand Kripalu Founder: John Cadbury Year founded: 1824 Headquarter: Uxbridge, United Kingdom Employees (2022): 140,000 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: Revenue (2021): 572.80 Rupees Profit | Net...
Disney SWOT 2024 | SWOT Analysis of Disney
Company: Walt Disney CEO: Robert Chapek Year founded: 1923 Headquarter: Burbank, California, USA Number of Employees (2022): 220,000 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: DIS Market Cap (Feb...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns TracFone
- Who Owns Rolex?
- Who Owns Bellagio?
- Who Owns Skechers?
- Who Owns JetBlue?
- Who Owns Ciroc?
- Who owns Aston Martin?
- Top 10 Bed Bath and Beyond Competitors and Alternatives
- Who Owns Sheraton?
- Who owns Volkswagen?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Buy us Coffee
If you like our work and would like to show appreciation to our team, buy us coffee!
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
- Buy Us Coffee!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
PESTLE Analysis
The Latest and Best Analysis Online
Toyota SWOT Analysis 2021: Quick Reference Guide
Last Updated: Dec 1, 2022 by Amrith Sudhakaran Filed Under: SWOT Analysis , SWOT Examples
In this Toyota SWOT analysis, you will learn about the triumphs and struggles of Toyota, one of the top 10 largest companies in the world. Specifically, we will use the SWOT analysis tool to dive into the following:
- Toyota’s Strengths
- Toyota’s Weaknesses
- Toyota’s Opportunities
- Toyota’s Threats
If you’re new to SWOT analysis, the way we look at strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats while performing a SWOT analysis is different from the way we traditionally view these words. But don’t worry, each section explains what these words mean in the context of SWOT analysis. Now, before we dive in, let’s look at three main ways the article will help you:
- Improve Critical Thinking : Learning to use the SWOT analysis framework through this example will help you develop your critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
- Develop Business Knowledge : A business operates in a complex environment of many parts that interact and integrate in subtle and obvious ways. SWOT analysis helps you understand these intricacies; thus, developing your business knowledge.
- Decision Making : Making decisions is a core skill people in management must possess. However, personal bias influences decision making. A tool like SWOT analysis, which forces you to look at all dimensions, negates this bias and leads to better decisions.
So, if you’re interested in honing your critical thinking, business knowledge, and decision-making skills, you’ll want to read our SWOT analysis for Toyota. Let’s get started.
What are Toyota’s major strengths?
In the SWOT analysis scheme, Toyota’s strengths are internal factors that help Toyota maintain its success in the auto industry. These are the reasons why Toyota is so successful today:
- The Toyota Way : Toyota’s operations follow the principles of continuous improvement and respect for people. These principles boost productivity and foster innovation . They also inspired the concept of lean management. For many decades, these principles have formed the core strength of Toyota.
- Fuel Cell Patents : Automobile companies are pursuing the vision of zero-emission vehicles through two main technologies – hydrogen fuel cells and electric vehicles. Toyota owns around 5,680 global patents related to hydrogen fuel cells. These patents put Toyota in a strong position in the zero-emission vehicles market.
- Solid-State Battery Pack : In addition to fuel cells, Toyota is also actively researching and developing technology for electric vehicles. Toyota is unveiling its revolutionary solid-state battery in 2021 . The company claims the new battery pack will extend the maximum EV range to 500 km on a single charge. Plus, it charges from 0 to 100% in 10 minutes. What’s even more impressive – Toyota developed the technology four years ahead of schedule.
- Hybrids : While Toyota develops competencies in clean energy vehicles, it’s consolidating its position in hybrid vehicles. Toyota makes some of the most reliable green cars in the market. Until the reliance on fossil fuels can be eliminated, Toyota’s hybrids will be an attractive option for environmentally conscious buyers.
- Strong Stock Performance : The pandemic-triggered economic slowdown hit automakers hard. Despite this, Toyota’s stocks fared better than most car manufacturers. While General Motors ’ stocks fell 64% from peak to trough, Toyota’s stocks showed only a 15% fall. This shows the company’s resilience.
Among these strengths, the prime reason why Toyota is so successful is the company’s commitment to continuous improvement. All the other strengths stem from this core strength.
What are some of Toyota’s weaknesses?
As a tool, SWOT analysis looks at weaknesses as internal factors that prevent or slow down growth. Here are some of Toyota’s weaknesses:
- Recalls : Although Toyota sets the standards for quality control, its design and production aren’t flawless. For instance, early this year, Toyota recalled 700,000 vehicles because of a faulty fuel pump. Such situations devalue the people’s trust in the brand and can undo decades of goodwill.
- Strikes : Adhering to strict quality control standards while maintaining high productivity and profitability at times puts the management at odds with the labor. Recently, the workers at a Toyota manufacturing plant in India went on strike due to labor problems . Such issues debilitate the company’s ability to meet market demands.
- Rigid Hierarchy : Toyota follows a rigid hierarchy where the orders flow in one direction – top to bottom. The rigid hierarchy allows better control, it does stifle creativity and flexibility .
- Partial Global Presence : Toyota has strong sales in the US, Europe, and Japan . However, it doesn’t boast similar sales figures in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. For Toyota to be a truly global company, it cannot leave these regions unexplored.
- Technology Gap : As far as future-tech goes, Toyota is playing catch up with Tesla. In a teardown of the Tesla Model 3, engineers found Tesla’s technology 6 years ahead of Toyota and Volkswagen .
What’s unique about Toyota is its ability to learn from weaknesses and become stronger than ever. In that regard, the weaknesses presented above could give Toyota a great edge if they’re able to overcome them.
What are some opportunities for Toyota?
When conducting a SWOT analysis, all external factors enabling Toyota’s growth are considered Toyota’s opportunities. Some of these opportunities are:
- Flying Car Project : Japanese startup SkyDrive successfully conducted the first manned test flight of its flying car. Toyota is one of the companies backing SkyDrive. Although SkyDrive has to overcome many technological and regulatory hurdles, Toyota believes its investment in the company would pay off.
- Smart Cars : Toyota is working on self-driving systems such as the Guardian and the Chauffeur . These systems aim to make driving safe and convenient for people not experienced enough to drive (Guardian) or able to drive due to old age (Chauffeur). Toyota is still unsure how the markets would react to its self-driving options. But, with technology in every area moving towards enabling convenience and ease, Toyota’s plan for autonomous vehicles is a smart one.
- Nanomaterials : Toyota AI ventures recently invested in Carbice, an Atlanta-based nanotech developer . Nanomaterials have a wide range of applications ranging from making vehicles lighter, stronger, more durable, quieter, cooler, and safer. For example, Toyota has invested in Carbice to help solve issues that high temperatures cause in the car’s electronics. Toyota should continue making such investments.
- Cloud and AI Technology : Many sectors are leveraging the combination of cloud-based and AI technology to improve ways in which it serves its customers. Automotive-based cloud technology is growing at 19.88% and is projected to touch nearly $70 billion by 2022 . So, cloud and AI are important opportunities Toyota should seek to leverage.
- Big Data : Automakers are using vehicle-generated data in interesting ways such as predictive maintenance, use-based insurance , and autonomous driving. As one of the largest car manufacturers in the world, Toyota is sitting on a goldmine of data.
Toyota’s biggest advantage is its budget for research and development. This year, Toyota plans to spend $13 billion on R&D . This budget allows for Toyota to invest in future technologies that will give the company an edge in the world of clean technology.
What are the biggest threats to Toyota?
Although a threat can mean many things, in SWOT analysis a threat is an external circumstance that stops progress. Some of Toyota’s threats are as follows:
- Brexit : With just days for the UK to negotiate a trade deal with the EU, a no-deal Brexit would add 10% to the cost of imported cars. Also, increased tariffs will negatively impact Toyota’s car factories in the UK.
- Trailing Tesla : Toyota may be one of the largest car manufacturers in the world. But, it isn’t the most valued; Tesla is the most valued automaker . At the time of this writing, Tesla’s market cap is 175% higher than Toyota’s. Although the President of Toyota dismissed Tesla for not being a “real” car company , Tesla sure is giving Toyota stiff competition in the post-fossil fuel tech.
- COVID-19 Restrictions : Japan, the USA, and Europe account for 66% of Toyota’s sales . The pandemic has severely impacted these regions. Measures to prevent the spread of the virus have caused economic recession and unemployment. Until the governments administer the vaccine on a large scale, COVID-19 would continue to threaten Toyota’s growth.
- Economic Crisis : In the second quarter, Toyota’s profits dropped by 74% . In a statement Toyota issued, the company expects the weakness to continue impacting performance in the foreseeable future.
- Competition : Toyota’s rivals Tesla and Volkswagen are matching Toyota’s stride for stride. Toyota can’t afford to slip. Falling back now would be a critical hit. For instance, a venture capitalist investor says Tesla’s evaluation could soar to $2 trillion in the next three years. What would Toyota do to match this growth?
Among these threats, the most significant one is the threat the competitors pose. Issues arising from the pandemic will resolve in a couple of years. But Toyota’s biggest competitors – Tesla and Volkswagen – are here to stay. If anything, the competition will intensify.
Toyota SWOT Analysis: Conclusion
90 years of dedicated pursuit of excellence has propelled Toyota to the forefront of the auto industry. A leader in production, sales, and research, Toyota plays a vital role in bridging the gap between the fossil-fuel era and the clean-energy era.
The company’s operation philosophy – The Toyota Way – is its biggest strength. And the promise of a cleaner future is its biggest opportunity.
However, a traditional organization at its core, will Toyota’s rigid hierarchy enable it to adapt to a new future? Also, how will Toyota handle the rapid rise of Tesla ? Time will tell whether Toyota overcomes these weaknesses and threats.
If you would like to improve your business knowledge and sharpen your problem-solving skills, look at other SWOT analysis examples . And if you would like to learn what is a SWOT analysis , check out our SWOT analysis templates and how-to guide .
Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis
Introduction: toyota’s strategic management.
SWOT analysis can be used for strategic planning for almost any kind of companies (Simerson, 2011). In this paper, it is going to be applied to the current situation of the Toyota Company that is still recovering from the major crisis that began in 2007. Although SWOT analysis cannot be used to provide a detailed description of the company’s expected strategies, it can offer a generalized interpretation of the current situation along with the possible opportunities for future business growth.
Toyota Motor Corporation: Case Study
The Toyota Motor Company (Toyota) was established in 1933 when it used to create trucks for military purposes (Heller & Darling, 2012, p. 157). Since the end of WWII, Toyota started to produce non-military cars, both cheap and elite versions. It entered the world market in the mid-1950s and by the end of the 1960s it possessed manufacturing facilities in the USA, Brazil, South Africa, Thailand, and Malaysia (Heller & Darling, 2012, p. 157). Apart from that Toyota started to acquire car manufacturing companies back in Japan (for example, Hino) as it expanded rapidly.
The key points of Toyota’s international marketing included adapting its products to suit the needs of the local customers and paying particular attention to the suppliers. It was the chain of suppliers and its effective management that allowed the rapid growth of the company. Still, in the end it was the mismanagement of the chain that led to the infamous Toyota crisis of 2007 (Andrews, Simon, Tian & Zhao, 2011).
Toyota Supply Management
One of the most prominent Toyota’s achievements is the supply chain it has established. There are four tiers of suppliers in Toyota, the fourth including more than 40,000 entrepreneurs (Andrews et al., 2011, p. 1068). Toyota’s supplier association was the tool used by the company to unite the partners and encourage knowledge sharing between them, to coordinate, supervise them, and to ensure the high quality of the supply. Toyota has always aimed at a long-term partnership, and the association aided achieving this.
Fast Growth
In 2000, the program named the “Construction of Cost Competitiveness in the 21st century” (CCC21) was launched by Toyota (Andrews et al., 2011, p. 1069). It was aimed at decreasing the price of the products by 30 % which was achieved through the expansion of the chain of suppliers (among other improvements). This lead to the increase in sales and Toyota started to grow rapidly. In April 2007, Toyota excelled General Motors and became the largest car manufacturer in the world (Heller & Darling, 2012, p. 159).
Toyota Crisis
The fast pace at which Toyota developed did have its drawbacks. As the chain of suppliers was increasing, it was becoming harder to control. New suppliers were not supervised enough and as the result the quality of the product decreased.
This problem was officially admitted to the public in 2006, but it was not fixed. Since 2007 Toyota car owners started to report having accelerating problems (Andrews et al., 2011, p. 1070). Still, even then Toyota did not appear to direct enough efforts at changing the situation. The displeasure of customers increased, and in 2007 Toyota had to recall 55,000 automobiles, but the problem persisted (Heller and Darling, 2012, p. 159).
It should be pointed out that other large car manufacturers, including the main Toyota rival General Motors, have also recalled their vehicles (Rankin, 2014). Still, the 2007 Toyota recall cost the company more than 2 billion dollars along with its reputation (Andrews et al., 2011, p. 1065).
Toyota was admittedly slow to respond to the crisis and became notorious for it. The first significant effort at rectifying the situation was made in 2010 when the Automotive Center of Quality Excellence was created (Heller and Darling, 2012, p. 166). However, the damage to the company’s reputation was immense, and part of it was caused by the company’s neglect of customers’ needs and its failure to meet its own promises.
The Toyota Way is the code of conduct that the company adopted in 2001 (Heller & Darling, 2012, p. 157). It consists of a number of philosophical guidelines that included, for example, an instruction to continuously improve the quality of the product, to thoroughly test new technology before implementing it, to learn by reflecting on the past experience, to make decisions slowly but implement them rapidly, to respect the stakeholders. In general, the Toyota Way includes 14 principles that appear most reasonable and, above all, ethical.
The problem lies in the fact that Toyota seems to have failed to implement these principles, and the 2007 crisis proved it. The quality of the products was obviously deficient; the company kept denying its responsibility and, therefore, failed to analyze its actions and learn from its experience (Heller & Darling, 2012; Andrews et al., 2011). The way the company neglected the safety of its customers aggravated the damage dealt to Toyota’s reputation.
In general, one may say that the company is still struggling with the crisis which is not over but instead is in its chronic stage. In order to create a sound strategy for the growth of the business, this fact must be taken into account.
Current Positioning in the Market
According to Andrews et al. (2011) the car manufacturing industry is an oligopoly, and Toyota is one of its most influential participants along with other giants like General Motors, Ford, and Honda. The survival on the market depends on the price, the quality of the products, and the brand loyalty. Apart from that, fuel pricing and local or worldwide economic situations also have their impact on the market (Andrews et al., 2011).
Since the beginning of the century, Toyota’s cars had stayed competitive due to their quality combined with relative low costs; however, the crisis situation has severely damaged the image of the product. Apart from that, it appears that Toyota has had a significant impact on the market in general by setting off the trend of developing cheaper cars. As a result, other car manufacturers have also faced the problem of quality standards as they kept searching for inexpensive materials (Rankin, 2014).
SWOT Analysis for Toyota
The SWOT analysis is a tool of strategic planning that involves characterizing the strengths, weaknesses opportunities and threats of the company; apart from that, the trends existing in the market are described in order to define the possible directions of development.
Therefore, SWOT is devoted to a short summary of the external and internal factors that may determine the future growth of the business (Simerson, 2011). The previous sections include a detailed description of the internal and external factors influencing the company. An attempt at classifying the factors and integrating them in the process of strategic planning will be made in the following section.
Toyota’s Strengths
Among the main Toyota’s strength are its size, power, and impressive market share. Apart from that, the suppliers’ chain that was so extensively investigated in the previous sections is another significant advantage. The company has spent more than fifty years in the market, and it had time to create proper relationships with its partners including other car manufacturers. The experience its managers possess can also be considered an advantage, especially in case the company proves that it is able to learn from its mistakes.
Toyota’s Weaknesses
It is apparent from the information given above that the main weaknesses of Toyota are the persisting quality problems, the difficulties connected with faulty crisis management, and the reputation issues. As it has been mentioned, Toyota is still struggling with the crisis and this point is proved by the fact that last year the company performed another massive recall due to the variety of problems detected in the models that were built before 2010 (Rankin, 2014). While attempts at rectifying the situation are apparently being made, the problem is far from solved.
Market Opportunities
Many of Toyota’s opportunities stem from its advantages. For example, the size of the company results in a better access to all the necessary resources which in turn opens up the opportunities for further development. The relationships with other firms have been used by Toyota, for example, to conduct collaborative research (Agence France-Presse in Tokyo, 2015). Apart from that, a number of opportunities that Toyota may use could be better described as the modern market trends.
Market Trends
Technically, market trends or tendencies can be parts of both the opportunities and the threats existing in the market. It is obvious that adopting the technologies or strategies that have become a trend in the market may allow the company to develop, but any innovation is at least partially a risk. At the same time, a neglected trend very often ends up adopted by a competitor firm and provides it with an advantage.
Therefore, it is not surprising that trends are regarded as an opportunity that has to be taken. Apart from that, trends can also be “trendy”, popular, and adopting those means attracting customers. An example of such a trend is the “green” technology which has been extensively researched by Toyota on its own and in collaboration with other manufacturers, for instance, Mazda (Agence France-Presse in Tokyo, 2015).
This kind of technology is supposed to be both more efficient and less harmful to the environment. Given the growing public concern with the future of the planet and the environmental issues along with the economic crisis that makes cost-saving technologies particularly alluring, participating in this trend should be beneficial for Toyota.
At the same time, the trend of attempting to create cheaper cars that was described above can be less beneficial. This is a challenge that can hardly be turned down since it is already typical for the market; at the same time, with the quality is a priority for Toyota nowadays, which means that the company may follow this trend only to a limit. This particular market tendency can become a threat for Toyota’s future.
Market Threats
The greatest threat existing in the oligopolistic market is the competition. While Toyota’s size and power are an advantage, the fact that several other competitors have equally big market shares and similarly famous brands is much less helpful. At the same time, one should take into account that the competitors are also capable of making mistakes.
For example, General Motors’ faulty ignition switches may have caused 13 deaths and resulted in a massive recall in 2014 (Rankin, 2014). While the reputation of Toyota has been damaged by the 2007 crisis, it is still a competitive and powerful player in the market.
The Essential Areas of the Strategic Plan
It is hard to deny the fact that the company’s weaknesses are crucial. The crisis of both quality and reputation demands consistent efforts aimed at eliminating them. At the same time, the company’s strengths are providing it with enough resources that may assist in fighting the company’s weaknesses. Finally, the trends existing in the market are extremely hard to ignore.
Being one of the major competitions, Toyota cannot help but respond to the challenges offered by other market players and create challenges of its own.
Toyota’s Strategy Analysis: Method and Evaluation
The strategic plan of the future development of Toyota must be based on the fact that the current state of the company needs to be improved. This may be achieved by increasing the quality of the products (with the help of the Automotive Center of Quality Excellence) which will slowly lead to improving the company’s reputation.
It is obvious that the company has all the resources needed to improve its production process. However, restoring the reputation of the business is going to be a more challenging task. It could be completed by a more extensive and aggressive promotion of the Toyota Way which it includes most ethical and reasonable suggestions (Andrews et al., 2011).
Unfortunately, it is impossible for the company to stabilize first and then proceed to grow the business. The competitiveness of the market would not allow it, which means that in addition to eliminating its flaws, the company should continue to develop new products and implement new technologies in order to keep expanding the business. The existing trends should be used to the company’s advantage albeit carefully since the current issues Toyota has should not be aggravated.
It could be useful to point out that SWOT is a truly widespread but extremely criticized methodology. For example, throughout its existence the method has been characterized as vague, oversimplified, elusive, superficial, non-prioritized, and generalized (Helms & Nixon, 2010).
At the same time, all these drawbacks can be used for the benefit of the strategic planning. As such, the generalized and simplified character of the method allows concentrating on the big picture and general view on the positive and negative factors and their potential interaction. As a result, it cannot provide detailed information about the company’s future but it may be useful for preliminary analysis and may give insights regarding the future of the business which was the aim of this paper.
Conclusion: Toyota’s Future Strategic Plans
Toyota’s SWOT analysis has allowed us a glimpse into the main factors that may affect its further development. Despite the fact that the methodology can only provide generalized results, we have found out that one of the main Toyota’s concerns is its current weaknesses caused by the 2007 crisis.
Apart from that, Toyota seems to be using the current trends existing in the market in order to keep expanding and developing. The possible plan for the future growth of the business should be aimed at restoring the position of the company after the crisis along with responding to the market’s challenges in order to keep up with the competitors. Despite the fact that Toyota is experiencing a crisis, it cannot afford any kind of respite.
Agence France-Presse in Tokyo. (2015, May 9). Toyota and Mazda reportedly cooperating on green car technology . The Guardian.
Andrews, A., Simon, J., Tian, F., & Zhao, J. (2011). The Toyota crisis: an economic, operational and strategic analysis of the massive recall. Management Research Review, 34 (10), 1064-1077. doi:10.1108/01409171111171474
Heller, V., & Darling, J. (2012). Anatomy of crisis management: lessons from the infamous Toyota Case. European Business Review , 24 (2), 151-168. doi:10.1108/09555341211204017
Helms, M., & Nixon, J. (2010). Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now?. Journal Of Strategy And Mgt , 3 (3), 215-251. doi:10.1108/17554251011064837
Rankin, J. (2014, April 9). Toyota recalls more than 6.5m cars over steering and seat problems . The Guardian .
Simerson, B. (2011). Strategic planning . Santa Barbara, Calif.: Praeger.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, February 18). Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/toyota-companys-strategic-plan-and-swot-analysis/
"Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis." IvyPanda , 18 Feb. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/toyota-companys-strategic-plan-and-swot-analysis/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis'. 18 February.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis." February 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/toyota-companys-strategic-plan-and-swot-analysis/.
1. IvyPanda . "Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis." February 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/toyota-companys-strategic-plan-and-swot-analysis/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Toyota’s Strategic Plan & SWOT Analysis." February 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/toyota-companys-strategic-plan-and-swot-analysis/.
- Toyota Motor Corporation's Strategic Planning Tools
- Marketing Audit: Toyota
- Strategic Management: Internal Analysis and SWOT
- Toyota Company: Keeping Up With the Challenge
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Major Global Corporation: Toyota
- Strategic Management: Toyota Japan
- Toyota Production System: Crisis and Adjustments
- Strategic Implementation at Toyota Company in 2011
- Walt Disney Company Analysis: Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Chevron Corporation Analysis
- Dubai Autism Center' Quality Management
- Cardinal Health Company Global Issues
- Airbnb: Company Challenges Analysis

Toyota SWOT Analysis

Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let us get the business overview of Toyota. Toyota Motor Corporation is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan.
It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda in 1937 as a spinoff from his father’s company, Toyota Industries, to create automobiles. Over the years, Toyota has become one of the world’s largest automakers, renowned for its reliability, quality, and innovation.
Key aspects of Toyota’s business overview include:
- Product Portfolio: Toyota has a diverse product lineup, ranging from compact cars to luxury vehicles, trucks, and buses. The company also offers hybrid, electric, and fuel-cell vehicles. Some of the popular Toyota brands include Toyota, Lexus, Hino, and Daihatsu.
- Global Presence: Toyota has a strong international presence, with manufacturing facilities and distribution networks in multiple countries. The company operates in North America, Europe, Asia, and Oceania. Toyota’s global strategy allows it to benefit from economies of scale and adapt to local market needs.
- Research & Development: Toyota invests heavily in research and development (R&D) to maintain its competitive edge. The company focuses on fuel-efficient technologies, alternative energy vehicles, autonomous driving, and artificial intelligence. Toyota’s commitment to innovation has led to the development of pioneering technologies such as the Toyota Hybrid System and the fuel cell-powered Mirai.
- Environmental Initiatives: Toyota is dedicated to reducing its environmental footprint and promoting sustainable mobility solutions. The company has set ambitious targets to reduce CO2 emissions from its vehicles and manufacturing processes. Toyota is a leader in developing hybrid and electric vehicles and is actively working on fuel cell technology.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Toyota has forged strategic partnerships and collaborations with various companies, suppliers, and governments to further its goals. These collaborations help Toyota develop new technologies, expand its product lineup, and enter new markets. Notable partnerships include those with Mazda, Subaru, and Suzuki and technology companies such as Panasonic and NVIDIA.
- Financial Performance: Toyota has consistently demonstrated strong financial performance, with stable revenue growth and profitability. The company’s financial strength enables it to invest in R&D, expand its global footprint, and withstand economic downturns.
Financial Performance : In FY22, Toyota generated 31.4 Trillion Yen (~$23.7 billion) with an operating income of ~3 trillion Yen ($2.2 billion).
Here is a SWOT analysis for Toyota :
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Toyota.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
- Brand Reputation : Toyota is known for its reliability, quality, and durability. This strong brand reputation has helped the company establish customer loyalty and attract new buyers. Toyota had a brand value of $33 bn in 2022 .
- Diverse Product Portfolio : Toyota offers a wide range of vehicles catering to different customer segments, including sedans, hatchbacks, SUVs, trucks, and luxury vehicles under brands like Toyota, Lexus, Hino, and Daihatsu. This diverse product lineup helps Toyota reach a broader customer base and adapt to changing market trends.
- Technological Innovation : Toyota’s commitment to research and development has resulted in groundbreaking technologies, such as the Toyota Hybrid System, fuel cell vehicles, and advanced safety features. This focus on innovation helps the company maintain a competitive edge and meet evolving customer needs.
- Strong Global Presence : Toyota has an extensive global presence, with manufacturing facilities and distribution networks in multiple countries. This enables the company to benefit from economies of scale, adapt to local market needs, and manage risks associated with fluctuations in currency and regional demand.
- Environmental Leadership : Toyota is a pioneer in developing hybrid, electric, and fuel cell vehicles, essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable mobility. The company’s environmental initiatives demonstrate its commitment to social responsibility and long-term sustainability.
- Efficient Production System : The Toyota Production System (TPS) is a renowned management philosophy emphasizing continuous improvement, waste reduction, and just-in-time inventory management. The TPS has enabled Toyota to achieve operational efficiency and maintain high-quality standards across its production facilities.
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations : Toyota has formed numerous strategic alliances with other automakers, technology companies, and governments. These partnerships help Toyota access new markets, share resources and knowledge, and accelerate the development of new technologies.
- Financial Stability : Toyota’s strong financial performance, marked by consistent revenue growth and profitability, allows it to invest in research and development, expand its global footprint, and withstand economic downturns.
- Dependence on Certain Markets : Toyota relies heavily on specific markets like North America and Japan, which account for a significant portion of its sales. This dependence can expose the company to regional economic fluctuations, changes in consumer preferences, and potential geopolitical risks.
- Slow Adaptation to Electric Vehicles (EVs) : Although Toyota has pioneered hybrid technology, it has been relatively slow in embracing fully electric vehicles compared to competitors like Tesla and Nissan. This delay in EV development may limit Toyota’s ability to capitalize on the growing demand for electric vehicles and meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations.
- Product Recalls : Toyota has faced several high-profile product recalls over the years due to safety concerns and manufacturing defects. These recalls can harm the company’s brand reputation, lead to financial losses, and erode customer trust.
- Intense Competition : The automotive industry is highly competitive, with numerous well-established players such as General Motors, Volkswagen, Ford, and Honda. This fierce competition can pressure Toyota’s market share, pricing power, and profit margins.
- Supply Chain Disruptions : Toyota’s global supply chain is susceptible to disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and other unforeseen events. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic and semiconductor shortages have highlighted the vulnerability of the automotive industry’s supply chain, impacting production and sales for several manufacturers, including Toyota.
- Currency Fluctuations : As a global company, Toyota is exposed to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. Changes in currency values can impact the company’s financial performance, mainly when revenues generated in foreign markets are converted back to the Japanese yen.
Opportunities
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Market : The global demand for electric vehicles is growing rapidly, driven by environmental concerns, government incentives, and advancements in battery technology. Toyota can leverage its expertise in hybrid technology and invest in developing a more comprehensive range of EV models to capture a larger share of this growing market.
- Autonomous Driving Technology : The development of autonomous vehicles is accelerating, with potential benefits such as increased safety, reduced traffic congestion, and enhanced mobility for the elderly and disabled. Toyota can invest in research and development of autonomous driving technologies and forge partnerships with technology companies to stay ahead in this emerging market.
- Expanding in Emerging Markets : Developing economies, such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia, offer significant growth potential due to increasing disposable income and automobile demand. Toyota can focus on expanding its presence in these markets by offering affordable and locally tailored vehicle models.
- Shared Mobility and Ride-Hailing Services : The rise of shared mobility and ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft is changing how people use and own vehicles. Toyota can explore opportunities in this space by partnering with ride-hailing companies, offering vehicle leasing options, or developing purpose-built vehicles for shared mobility services.
- Enhancing Connectivity and Digital Services : As vehicles become more connected, there is a growing demand for advanced infotainment systems, vehicle-to-vehicle communication, and over-the-air software updates. Toyota can invest in developing innovative connected car technologies and digital services to enhance the driving experience and generate new revenue streams.
- Sustainable Manufacturing and Supply Chain : Consumers and governments are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. Toyota can strengthen its commitment to sustainability by implementing more environmentally friendly production methods, sourcing materials responsibly, and working to reduce its carbon footprint further.
- Strategic Partnerships and Mergers : Toyota can continue to forge strategic partnerships, collaborations, and mergers with other automakers, technology companies, and suppliers to share resources, reduce costs, and accelerate the development of new technologies and products.
Threats
- Intense Competition : The automotive industry is highly competitive, with established players such as General Motors, Volkswagen, Ford, and Honda, as well as emerging companies like Tesla and Chinese automakers. Increased competition can impact Toyota’s market share, pricing power, and profitability.
- Rapid Technological Changes : The automotive industry is transforming rapidly with the development of electric vehicles, autonomous driving technology, and connected car services. If Toyota fails to keep pace with these technological advancements, it risks losing its competitive edge and market share.
- Regulatory and Emissions Standards : Governments worldwide are imposing stricter emissions standards and regulations to combat climate change and promote sustainable mobility. Toyota must continue to invest in the development of fuel-efficient and zero-emission vehicles to comply with these regulations and maintain its market position.
- Global Economic Fluctuations : Economic downturns or slowdowns in key markets can lead to reduced consumer spending and lower automobile demand. Toyota’s reliance on certain markets, such as North America and Japan, makes it vulnerable to regional economic fluctuations.
- Supply Chain Disruptions : Toyota’s global supply chain is susceptible to disruptions caused by natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and other unforeseen events, impacting production and sales. Examples include the COVID-19 pandemic, semiconductor shortages, and Japan’s 2011 earthquake and tsunami.
- Currency Fluctuations : As a global company, Toyota is exposed to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates, which can impact its financial performance and competitiveness when revenues generated in foreign markets are converted back to the Japanese yen.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy : As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches increases. Toyota must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and ensure data privacy to protect its customers and maintain trust in its brand.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences : Changes in consumer preferences, such as a growing demand for SUVs or a decline in sedan sales, can impact Toyota’s product lineup and sales performance. The company must continuously monitor market trends and adapt its product offerings to meet evolving customer needs.
Check out the SWOT Analysis of Global Businesses
Related posts.

T Mobile SWOT Analysis
Robinhood SWOT Analysis

Revlon SWOT Analysis

Rebisco SWOT Analysis

Razer SWOT Analysis

Revolut SWOT Analysis

Tencent SWOT Analysis

Telus SWOT Analysis
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Toyota SWOT Analysis & Recommendations

This SWOT analysis of Toyota enumerates the internal and external strategic factors relevant to the automotive business and its industry. The SWOT framework pinpoints the most significant opportunities, threats, and organizational weaknesses that Toyota must address using its strengths. As a global leader in the automotive industry, the company effectively addresses such factors. This SWOT analysis provides insights into the factors influencing the business and the realization of Toyota’s mission statement and vision statement . The automaker’s high performance serves as an indicator of its ability to address the issues enumerated in this SWOT analysis.
This SWOT analysis shows that Toyota remains strong in the global automobile market, although issues related to competition, organizational structure, and corporate culture must be addressed. The success of Toyota’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies depends on business effectiveness in addressing the challenges and opportunities included in this SWOT analysis.
Toyota’s Strengths (Internal Factors)
The company’s strengths indicate the ability to keep the position as one of the top auto manufacturers in the world. This element of the SWOT analysis model identifies the internal strategic factors that serve as capabilities of the firm. Toyota’s strengths are as follows:
- Strong brand image
- Control of an expansive global supply chain
- Rapid innovation capabilities
Toyota is one of the strongest brands in the global automotive industry. The company’s control of its global supply chain is also a strength that enables resilience and market-based risk minimization. Furthermore, Toyota has an organizational culture (company culture) that facilitates rapid innovation , which is crucial for long-term competitive advantages. This SWOT analysis shows that Toyota’s strengths support its position as one of the biggest automobile manufacturers in the world.
Toyota’s Weaknesses (Internal Factors)
The company’s weaknesses point to barriers and challenges in the automotive business organization. This element of the SWOT analysis model determines the internal strategic factors that serve as obstacles to business growth. Toyota’s main weaknesses are as follows:
- Rigidity of the hierarchical organizational structure
- Secrecy in the organizational culture
- Effects of product recalls
Along with strict quality standards and efficiency measures for operations, the global hierarchy of Toyota’s organizational structure (company structure) prevents maximum flexibility of regional operations. Also, the company’s culture of secrecy is a weakness that reduces response times in addressing emerging problems. In addition, the company’s product recalls weaken the automotive business because the recall processes consume business capacity that could be used for product distribution instead. Also, these recalls have a negative effect on the automaker’s brand strength. This SWOT analysis shows that Toyota can improve its performance through adjustments to reduce the weaknesses based on its organizational structure and culture.
Opportunities for Toyota (External Factors)
The company’s opportunities are mainly based on technological and economic trends relevant to the automotive industry and the transportation market. This element of the SWOT analysis identifies the external strategic factors that the firm can use to improve its business. Toyota’s most significant opportunities are as follows:
- Growing markets in developing countries
- Rising demand for fuel-efficient and electric automobiles
- Growing interest in advanced electronics in vehicles
- Advantages based on the weak Japanese Yen vs. U.S. Dollar
Developing markets present the opportunity for Toyota to increase revenues by further penetrating these markets. Also, the current trends of the increasing demand and interest for higher fuel efficiency, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics present opportunities for Toyota to focus its innovation on these directions. In addition, the weaker Japanese Yen versus the U.S. Dollar means higher competitiveness of products and components exported from Japan to the U.S. This SWOT analysis of Toyota shows that the automotive business must emphasize market penetration and innovation to exploit its opportunities.
Threats to Toyota (External Factors)
The threats to the car manufacturing business are based mainly on the competitive landscape. This element of the SWOT analysis determines the external strategic factors that can reduce the firm’s performance. In Toyota’s case, the main threats are as follows:
- Growing market presence of low-cost competitors
- Rapid innovation of competitors
Toyota faces the threat of competition with low-cost automobiles from Korean, Chinese, and Indian manufacturers, which have been increasing their presence in foreign markets. The company also experiences the threat of rapid innovation among competitors, like General Motors , Tesla , Ford , BMW , Nissan, and Honda, as well as Hyundai, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz. The Five Forces analysis of Toyota demonstrates that these competitors are responsible for strong competitive pressures in the industry. This part of the SWOT analysis shows that Toyota must ensure competitive advantages, such as through innovation.
Recommendations – SWOT Analysis of Toyota
This SWOT analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation identifies key issues, such as the effects of competition and the company’s weaknesses based on its organizational structure and culture. To address the threats based on competition, the company needs to maximize its competitive advantage based on its innovative capabilities to support competitive mobility solutions. Toyota can also further adjust its culture and structure to optimize its flexibility in decision-making and problem-solving processes. Strategies addressing the opportunities and threats in this SWOT analysis can also account for other external factors, like the ones identified in the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis of Toyota .
- Benzaghta, M. A., Elwalda, A., Mousa, M. M., Erkan, I., & Rahman, M. (2021). SWOT analysis applications: An integrative literature review. Journal of Global Business Insights, 6 (1), 55-73.
- Pacheco, D. A. D. J., & Librelato, T. P. (2023). Optimising process and product performance in complex systems: A study in the automotive industry. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 40 (4), 922-941.
- Palazzo, M., & Micozzi, A. (2024). The SWOT Analysis: An Evolving Decision-Making Model. In Rethinking Decision-Making Strategies and Tools: Emerging Research and Opportunities (pp. 53-70). Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Toyota Motor Corporation – Form 20-F .
- Toyota Motor Corporation – TMC Strengthens Battery Production Capabilities .
- Toyota Motor Corporation – Our Story .
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Automotive Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.

- Calculators
- Swot Analysis
- Pestle Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Organizational Structure
- Copywriting
- Research Topics
- Student Resources
Services We Provide

Resources We Provide

Login / Register

- An Exclusive and Elucidated SWOT Analysis of Toyota
- Toyota Overview
Toyota is a Japanese automobile manufacturer. The company has its presence throughout the world with current operations in more than 170 countries. The company employs more than 360,000 personnel in its facilities worldwide (Carlier, 2021). It earned a revenue of $245 billion in 2021 and more than 90% of its revenue is generated through automotive sales. The highest selling vehicles of Toyota include Toyota Corolla with more than 1 million sales annually. Other models include RAV-4 which occupied the third position in overall vehicle sales in 2020 (Ashraf, 2022).
This Toyota SWOT analysis article would analyze the internal strengths and weaknesses of Toyota along with highlighting the opportunities that it can capitalize on and the threats that it faces because of the external environment. In case you wish to learn about conducting a SWOT analysis in detail, you should definitely go through our meticulous Swot Analysis guide .
Table of Contents
- Toyota Strengths
- Toyota Weaknesses
- Opportunities for Toyota
- Threats for Toyota
A delineated SWOT analysis of Toyota
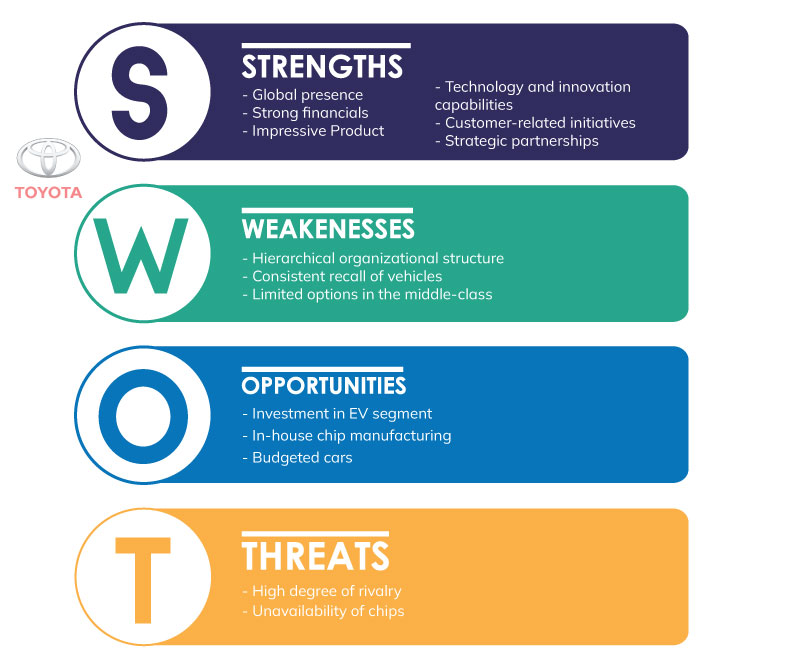
Toyota’s Strengths
- Global presence- Toyota sells its cars in more than 170 countries and sells more than 9 million vehicles every year. The strong foothold over the market can provide it with a competitive edge.
- Strong financials- Toyota group generated $245 billion in revenue in 2021. It has a free cash flow of 10, 40,783 yen and it has an excellent debt to equity ratio of 1.007, meaning that the company is not much in debt. The financial power can benefit a company while overcoming market threats and exploring new opportunities.
- Impressive Product range- Toyota has a full range of vehicles including hatchbacks, sedans, SUVs, and pick-up trucks. Its most popular hatchback is Corolla with more than 1.1 million units sold worldwide in 2021 while Camry is most sold in the Sedan category with more than 300,000 units sold annually and RAV-4 is the most sold SUV with more than 1.1 million units sold annually and it occupies more than 3% market share in the pick-up segment. Toyota also owns a luxury vehicle brand named Lexus.
- Technology and innovation capabilities- Toyota is innovating with its products and has recently launched two new models of Lexus and Mirai that are equipped with autonomous driver technology wherein the car would automatically be able to maintain a safe distance from the vehicles ahead by detecting the traffic through sensors that would help in the reduction of accidents (Reuters, 2021).
- Customer-related initiatives- Toyota engages in continuous improvement of its vehicles by implementing Kaizen and PDCA business processes. Further, the company has an excellent after-sales service wherein it has implemented the 3S model that relates to Seikaku, Shinsetsu, and Shinrai which in simple terms means accuracy, care, and trust (Toyota, 2019).
- Strategic partnerships- Effective and beneficial partnerships with other brands have helped Toyota broaden its customer base in emerging markets. For instance, the strategic partnership of the company with Maruti Suzuki to jointly develop successful cars for the Indian market has proved highly beneficial to the company. Such partnerships will help Toyota in greater market penetration across developing countries like India.
Toyota’s Weaknesses
- Strategic partnerships- Toyota has a hierarchical structure and decision making is fully centralized wherein the top bosses are responsible for decision making and the employees are just required to follow the order. This can lead to less employee engagement levels which would affect their motivation and work performance.
- Consistent recall of vehicles- Toyota has recalled a large number of vehicles over the years. Recently, it announced 227,000 recalls of its 2019 model Camry and 41,544 Venza Hybrid models (Toyota, 2021). The frequent recalls can hamper the trust of the customers and this can have a direct impact on the sales of the vehicles.
- Limited options in the middle-class segment- In emerging markets like India, Toyota offers limited options in budget-friendly cars including light utility vehicle and hatchbacks. This proves to be a major inability of the company to capture markets in developing countries through effective change management .
Toyota’s Opportunities
- Investment in EV segment- Toyota can enhance its investment in the EV segment, especially in emerging markets like India where the government is offering financial assistance on a large scale and the market is expected to grow by a huge margin of 94.4% from 2021-2030.
- In-house chip manufacturing- Toyota can utilize its expertise in engineering and start production of the semiconductor chips. This would enable the company to have more control over the quality and the company would be able to overcome the supply chain barriers to some extent.
- Budgeted cars- Toyota can launch more budget-friendly options with more fuel efficiency, especially in the market of India where 72% of people prefer low-priced cars (Gupta, 2020).
Toyota’s Threats
- High degree of rivalry- The top competitors of Toyota include Hyundai, Volkswagen, and General Motors along with many others. General Motors occupies a 15.5% market share in the US and its global revenue increased by 3.7% in 2021 to $127 billion. Hyundai occupies a 5.4% market share globally in the automobile segment while it is gaining dominance in the Indian market with its share being 12.70% (Cain, 2022). Furthermore, Tesla has the ability to provide stiff competition to Toyota if it decides to expand its electric vehicle segment worldwide as it is the global leader with a 14% market share (ET, 2022).
- Unavailability of chips- The disruption in production and supply of chips, an important component in the manufacturing of vehicles because of the shortage in raw material due to the Russia-Ukraine war can pose a threat to its protection level.
To encapsulate, Toyota has the advantage of being present worldwide in more than 170 countries. Because of its high presence, it is able to sell more vehicles, it sold around 9 million vehicles in 2021. Further, Toyota has effectively maintained its debt and its debt to equity ratio is 1.007 which is considered to be excellent. Toyota needs to build its cars with more efficiency to avoid recalling the vehicles on a frequent basis and it is an expert in high-end models but it can capture more market if it launches more affordable and fuel-efficient options. The company faces threats in the form of a shortage of ships globally and even the competitiveness in the market is also high with General Motors occupying a 15% market share in the US and the expansion of the EV segment can be a hurdle as the company would have to compete with Tesla, that is already a dominant market player with 14% market share in the EV segment. Besides, to understand how external factors can affect the company, you can go through our well-crafted Toyota PESTLE Analysis .
Recommended Readings
SWOT Analysis of General Motors
SWOT Analysis of Kia
SWOT Analysis of Ford
SWOT Analysis of BMW
Ashraf, Y. (2022). The world’s best-selling cars. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.autoexpress.co.uk/best-cars-vans/33872/worlds-best-selling-cars
CAIN, T. (2022). HYUNDAI SALES FIGURES – US MARKET. www.goodcarbadcar.net. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.goodcarbadcar.net/hyundai-us-sales-figures/
Daniels, P. (2022). Car Market Share Dec 2021 – Maruti, Tata, Hyundai, Mahindra, Honda, Kia Copyright (C) 'RUSH LANE' Read more at. https://www.rushlane.com/car-market-share-dec-2021-maruti-tata-hyundai-12422089.html
www.rushlane.com Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.rushlane.com/car-market-share-dec-2021-maruti-tata-hyundai-12422089.html#:~:text=Hyundai%20Motor%20India%20at%20No,percent%20held%20in%20December%202020
Hyatt, K. (2022). Toyota recalls 41K 2021 Venza Hybrids over short-circuiting rear turn signals. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.cnet.com/roadshow/news/toyota-venza-hybrid-recall-2021-rear-turn-signals/#:~:text=Toyota%20is%20recalling%2041%2C544%20Venza,and%2C%20consequently%2C%20hazard%20lights.
Reuters. (2021). Toyota unveils new models in advanced driver-assist technology push. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.reuters.com/article/us-toyota-autonomous-idUSKBN2BV0F1
Toyota. (2019). Annual Report 2019. www.annualreports.com. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.annualreports.com/HostedData/AnnualReports/PDF/NYSE_TM_2019.pdf.
Sign up for our Newsletters
Enter your email address to register to our newsletter subscription delivered on a regular basis!
Copyright © 2023 CrowJack. All Rights Reserved

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Toyota SWOT analysis
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 2 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 9 March 2021*
- File format: Text
- Words: 485 (approx)
- Number of pages: 2 (approx)
- Tags: SWOT analysis examples
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 485 words. Download the full version above.
Toyota Motor Corporation
- Global organization, with a strong international position in 170 countries worldwide.
- High financial strength (1997, sales turnover, £131,511 million), sales growth of 29.3%[1]
- Strong brand image based on quality, environmental friendly (greener), customized range.
- Industry leader in manufacturing and production. Maximizes profit through efficient lean manufacturing approaches (e.g. Total Quality Management) and JIT (Just in Time) manufacturing and first mover in car research and development[2].
- Excellent penetration in key markets (US, China, EMEA) and now the second largest car manufacturer in the world, surpassing Ford.
- Japanese car manufacturer – seen as a foreign importer.
- Production capacity. Toyota produces most of its cars in US and Japan whereas competitors may be more strategically located worldwide to take advantage of global efficiency gains.
- Some criticism has been made due to large-scale re-call made in 2005, quality issues.
Opportunities
- Innovation -first to develop commercial mass-produced hybrid gas-electric vehicles (gas and electric), e.g. Prius model. Based on advanced technologies and R&D activity. With oil prices at an all time high – this investment and widening of product portfolio fits consumers looking to alternative sources of fuels away from gas guzzling cars[3].
- To expand more aggressively into new segments of the market. The launch of Aygo model by Toyota is intended to take market share in youth market.
- To produce cars which are more fuel efficient, have greater performance and less impact on the environment.
- To develop new cars which respond to social and institutional needs and wants. The development of electric cars, hybrid fuels, and components reduces the impact on the environment. Toyota’s Eco-Vehicle Assessment System (Eco-VAS) has helped in production, usage, and disposal[4].
- Continued global expansion – especially in the emerging markets e.g. China and India, Russia, where population and demand is accelerating.
- Saturation and increased competition, intense marketing campaigns increasing competitive pressures[5].
- Shifts in the exchange rates affecting profits and cost of raw materials.
- Predictions of a downturn in the economy e.g. recession, will affect car purchases (especially new cars). As household budgets tighten – this could lead a decline in new car sales and possible rationalization of dealerships.
- Changing demographics e.g. number of large families is declining. Undermining the demand for large family cars[6].
- Changing usage – families using the car less for taking children to schools. Home deliveries. Businesses – restricting business travel (tele-conferencing). Governments encouraging alternative forms of transport – cycling and incentives to use public transport across Europe.
- Rising oil prices (fuel costs) and the costs of maintaining cars. Increase in families who have chosen not to own a car, or decided to use their car less.[7]
[1] Hoovers & Toyota Corporation, 2007, Annual Report [2] International Business 6e by Charles W. L. Hill, Mcgraw Hill [3] Toyota Corporation, 2007, Annual Report [4] www.toyota.com [5] http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/6346325.stm [6] CD Rom, Census Data 1990 (Age Structure and Issues) [7] http://www.marketresearchworld.net/index.php?option=content&task=view&id=1263&Itemid
Related Pages:
- Starbucks SWOT Analysis
...(download the rest of the essay above)
Discover more:
- SWOT analysis examples
Recommended for you
- Musahamat Farms (Bananas) SWOT & PESTLE analysis
- Panera Bread marketing analysis (SWOT, marketing mix, Ansoff’s matrix)
- Johnson and Johnson SWOT analysis
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Toyota SWOT analysis . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/toyota-swot-analysis/> [Accessed 06-04-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays

Toyota SWOT Analysis

1. Background of Toyota
1.1. general overview of toyota, 1.2. introduction to toyota.
For the Toyota SWOT analysis , it is crucial to know about its past and future planning. The Toyota Motor Corporation is a multinational automaker company founded in Toyota, Aichi, Japan. It started its journey back in 1937, and by 2017, it had 364,445 employees worldwide. As of 2019, it is the 10th largest company in the world by revenue. After Volkswagen, Toyota is the second-largest automotive manufacturer in the world. It is the largest listed company by revenue and market capitalization in Japan, as of 2014.
1.3. Development Timeline of Toyota
2. swot analysis of toyota.
The Toyota's SWOT analysis can find out the strategies that can help the company to strengthen its position and maximize revenue. It identifies the effects of competition and weaknesses as per the culture and organizational structure. The company can take decisions for its betterment by considering opportunities. At the same time, the company can look for business diversification to earn long-term stability in the market.
2.1. SWOT Analysis of Toyota in Detail
Analyzing the strength of any company is a very significant part of their SWOT analysis. The company must be well aware of its strengths as those features have helped them earn its name in the market. The company must keep in mind that they must not neglect their strengths when working on their weaknesses and new opportunities. Like most other brands, The Toyota Market also has some strengths:
- Toyota's biggest strength is to indicate that the firm is capable of retaining its reputation and good name as one of the top-notch auto manufacturers in the world;
- No doubt, Toyota has a strong brand image;
- The brand has one of the most extended global supply chains, which enable market-based risk minimization and resilience;
- ➢Toyota has its ambition for development and research. The brand’s core strategy and organizational culture are to build rapid innovation capabilities.
For any company, it is pretty common to have some weaknesses. The companies need to find strategies that can remove those weaknesses. When a company is in a competitive market, any weakness can impact its growth against its competitors. The company can plan some long-term plans to change those weaknesses into their strengths. Toyota also has some weaknesses. For example:
- The weakness point of Toyota is to possible inefficiencies within the organization. By pointing weaknesses, the company can determine the internal strategic factors that stand as obstacles to business growth;
- Toyota has its global hierarchical organizational structure that stands as the impediment of regional operations' maximum flexibility;
- It maintains secrecy in its corporate culture, and as an effect, it shortens the response times to address the emerging problems. The recall of Toyota in 2009 consumed its business capacity, which could save instead for product distribution;
Opportunities:
A company must consider the opportunities that they can get to survive the high market competition. They must set their policies as per those opportunities to ensure their growth in the future. They should also consider the condition of the market while working on their opportunities. Here are some opportunities for Toyota:
- Toyota’s opportunities are based on economic and technological trends. The opportunities part includes various external strategic factors based on its economic and technological trends;
- Toyota's Smart Car, flying car project, nanomaterial, big DATA, A.I. technology, and Cloud are its assets;
- Toyota has large growing markets in developing countries that showcase that it can further increase its revenue by penetrating the markets;
- The world is witnessing a rising interest and demand for higher fuel-efficient automobiles. Toyota can work on this trait and focus on innovative techniques;
- There is a trend of growing interest worldwide in advanced electronic vehicles;
- Japanese Yen is weaker than the U.S. Dollar. It can lead to higher competitiveness of components and products and a rise in Japan's export to the U.S.A.
All the companies that survive in a competitive market must have some threats that can stop their growth. Other competent opponents' market conditions change of taste of the customers can be prevalent threats. Similarly, a famous brand like Toyota also has some threats:
- The threats of Toyota are there in its competitive landscape. The SWOT analysis model can assess the potential hazards;
- The company has quite a few competitors, making it challenging for Toyota to make strong feet in the automotive market;
- The raw materials are expensive, and they increase the cost of the end product;
- The Dollar-Yen exchange rates are a crucial factor. The profit becomes lower when sent to Japan in comparison to other countries;
- A no-deal Brexit and COVID-19 are factors to take into account for the potential economic crisis.
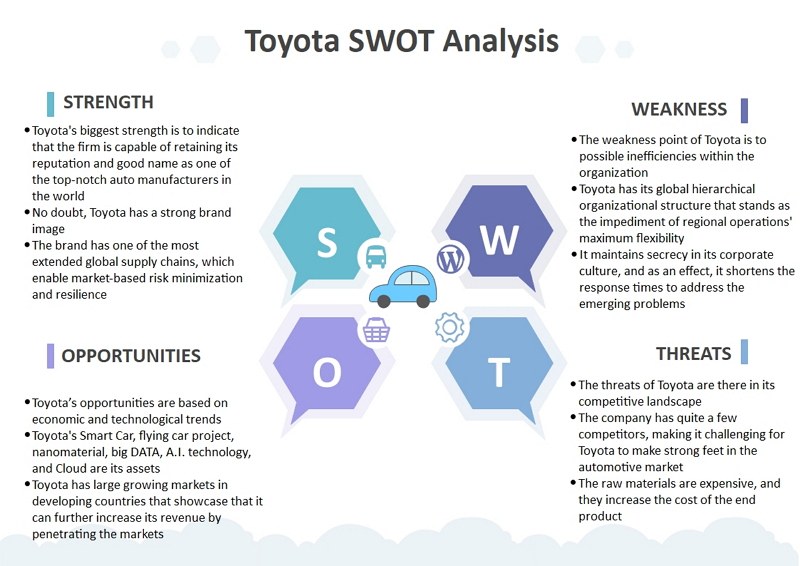
3. Key Takeaways
The Toyota SWOT analysis points out the fact that the company has numerous scopes to perform better. No doubt, the brand is one of the most desired brands in the automotive industry, but by adopting a few measures, Toyota can maintain its success in the auto industry.
- Toyota needs to maximize the competitive advantage based on its innovative capabilities;
- The Toyota Company can also adjust its structure and culture to optimize its flexibility in problem-solving and decision-making procedures;
- Toyota has scope to improve through minor adjustments;
- There is room for Toyota to emphasize innovation and market penetration.
Use EdrawMax Online to create a SWOT analysis diagram, or create any other diagram with ease! There are massive SWOT templates and symbols to choose from, and creating a SWOT analysis diagram could be really simple. Also, you can find substantial SWOT templates in our template community to have a quick start.

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Wells Fargo

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Johnson & Johnson

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Whole Foods

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Home Depot

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of FedEx

An In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Fitbit

- Privacy Policy
- Affiliate Disclosure

The Strategy Watch
To be the Best Source of Business Strategy & Analysis
SWOT Analysis of Toyota
Toyota Motor was founded by Kichiro Toyota in the year of 1937 as a spinoff from his father’s company Toyota Industries to manufacture automobiles.
It is a Japanese automotive company, headquarter is in Toyota , Aichi, Japan. It’s a multinational automotive company, and by March 2014 it consisted of more than 338,875 employees worldwide (Wikipedia). It is the first company that manufactured 10 million cars per year from 2012. In that year, Toyota announced it had manufactured its 200 millionth car.
The STRENGTHS of Toyota
The strengths of Toyota indicates the internal power of its resources and strategies which are behind the glorified success of this brand.
- Brand Image: Toyota has a strong and sustainable brand value all over the world. It’s one of the leading companies around the in terms of its sales, profit margin and market share. Over the years, this Japanese automobile manufacturer company has created its distinct identity with world-class designs, product quality and superior customer services.
- Large Product Portfolio: Toyota has an extended product line for almost all kinds of target market. This brand offers vehicles such as sedans, SUV’s, racing cars , trucks, busses, minivans, station wagons etc. From personal to professional transport needs, all can be met with Toyota. It’s one of the top automobile company in terms of producing hybrid cars. This brand also has a segment or premium cars called Lexus.
- Kaizen Philosophy: Toyota is known as the pioneer of Kaizen philosophy through which it has been proving itself on the improvement of performance and operations. Through this strategy, Toyota has been successful in beating its competitors as the process concentrates on the higher production speed and decreasing the amount of waste. The process has included the employees as well to make the decision about what will be best for the company.
- Investment in Research & Development: Every year Toyota invests approximately 9 million dollars on its research and development sector, which is higher than any other company’s R&D cost. And there’s no scope of doubt about the efficiency of the outcomes. The brand is continuously growing in terms of new and innovative products worldwide with massive popularity and acceptance.
- Green Branding: Toyota is not only known for its quality, innovation and superior designs; it’s also equally recognized for its green branding image. It has the tagline of Leading Global Green Brand. The focus on hybrid car production to reduce pollution has been a massive success for this brand. In the first few years, this brand sold nearly 8.5 million hybrid cars all over the world.
The WEAKNESSES of Toyota
The weaknesses of Toyota indicates the factors that are absent in this company and making it slower than other business.
- Recalling Products: Since 2016, Toyota has recalled millions of cars because of many technical issues. In 2016, it announced a recalling of 3.37 million vehicles worldwide because of the problems malfunctioning of airbags, fuel control unit etc. Also in 2018, the company again recalled almost 2.4 million hybrid cars that had the potential of crashing due to technical and safety problems. All these things have caused damage to this brand’s image globally.
- Not All Designs got praised: Although Toyota is famous for its world-class unique designs, some of its new production lines didn’t get the acknowledgement. Automobiles named Master Ace was criticized as the worst looking car. Also, there was Yaris that is considered as the biggest downfall of Toyota’s history. These incidents have caused this company tremendous loss.
- Weak Position in Asian Market: Toyota has a more vulnerable position and less market share compared to its other competitors in the Asian market. Though this brand is very popular in other parts of the world, still it couldn’t capture a good market in India and China which are the biggest markets in Asia. As a result, this brand is losing its competitive advantages there.
The OPPORTUNITIES for Toyota
The opportunities of Toyota indicates the market situation and analysis that can help it to overcome the weaknesses and become more influential in the upcoming future.
- Extending Market with Hybrid & Electric cars: The craze of hybrid and electric cars are growing day by day due to the environmental concern and reducing the consumption of fuel resources. As Toyota has already proved itself in terms of superior quality and production of hybrid and electric cars, it can be a good competition in the automobile industry among other brands.
- Balance the Price & Production to capture the Asian market: The Asian market is growing in terms of standard of living and consumption of luxury items. These countries can be a good target market for Toyota. Its other competitors like Ford, Honda, Volkswagen, Mitsubishi, Maruti Suzuki etc. has already captured the market and growing day by day. Toyota should grab the chance as well.
- Concentration on Making Autonomous cars: The next step of the automobile car will be autonomous cars, which is being expected by the researchers. And already many automobile brands have started to focus on this sector and working on it. Toyota, with its intense research and development area, can work in this product line as well to tackle the new emerging demands of the market.
- Growing concern for Environment pollution: people are becoming more concern for the environment; as a result, there is a possible boom in the sale of environment-friendly cars.
The THREATS for Toyota
Threats refers to the facts that can cause issues for Toyota in Near future depending on the market situation,
- Competitive Pressure: Toyota is facing substantial competitive pressure by both existing competitors and new entrants based on innovation and price. This company is also lagging on the Asian market. As a result, it’s losing its potential there. Also recalling of products has given its competitors to win the market against this company.
- Effects of Global recession and pandemics: Toyota has already faced massive disruptions and loses due to Japanese tsunamis, earthquake, nuclear crisis etc. And recently this Covid-19 situation has made the things worse for every company especially for automobile industries due to the discouragements of transportation. This pandemic situation has created a challenge for companies like Toyota to come up with new ideas at present and after the pandemic.
- Increasing Operating Cost: The cost of labor and raw materials are increasing worldwide day by day. And because of Toyota’s broad product range and large productions, it’s becoming challenging to maintain a balance with the production cost and market price. And if this company doesn’t find any solution to solve this problem, it’ll be a huge problem for it.
- Lower Exchange Rates: Toyota is a Japanese company, and that’s why all of their profit gets exchanged into Japanese Yen. But due to the lower exchanging rate and fluctuations of Yen, this company is facing lower profits, in contrast to other currencies.
Recommendation
As the Toyota SWOT Analysis discussed, Toyota Motor has great strength internationally. But to address the threats based on competition, it must increase the competitive advantages by offering more environment-friendly cars.
- SWOT Analysis of Volkswagen
- SWOT Analysis of Mazda
- Best Calculators for CFP Exam
- https://www.mbaskool.com/brandguide/automobiles/2261-toyota-motor-corporation.html
- http://www.marketingteacher.com/toyota-swot/
- http://study-aids.co.uk/dissertation-blog/swot-analysis-toyota/
- https://www.cayenneapps.com/blog/2015/11/13/toyota-swot-analysis/
- http://heartofcodes.com/swot-analysis-of-toyota/
- http://www.toyota-global.com/company/profile/overview/
- Toyota Wiki
- Toyota Body
- “INSIDE THE MIND OF TOYOTA: MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR ENDURING GROWTH” by Satoshi Hino

The Strategy Watch (TWS) is a fast-growing multi-author blog on Strategic management, Business Planning, Investment, & Analysis. It provides useful resource of knowledge to business starters, researchers, strategists, and students.
The TWS team consists of 4 (four) members who are know as the prime team of the blog. The purpose of the team are to provide valuable contents on B usiness Strategy and Management .
To know effective business strategies, please follow our Facebook and Twitter
Home Essay Examples Business Toyota
Toyota: Case Study And Swot Analysis
- Category Business
- Subcategory Corporation
- Topic Toyota

Toyota Case Study
The history of “TOYOTA” goes as far as February of 1867. Surprisingly, it all started from looms. In a wood makers family by the name of Toyoda, firstborn with the name of Sakichi was born. According to the Japanese laws back then, the firstborn was called to be the head of the house. Along with obligations, the baby has inherited his father’s profession. Instead, Sakichi decided to become the creator, the creator of a loom. Although he was not the first one to create it in general, he was the first one to construct one in Japan. At the age of 30, Sakichi Toyoda sold his first hand-assembled mechanical loom. After 10 years, Japan started to buy machines exclusively of local production. Moreover, through the export of his product to Europe, Toyoda became a very famous and wealthy man. Yet he did not stop there, in 1924, he created automated looms and patent rights for them were sold 5 years late to one English company. With the capital received from the company, he decided to expand his business and went into the development of auto production in Japan. Sakichi Toyoda’s plans were crossed out by his sudden death due to meningitis, yet he still managed to pass his ideas to his eldest son- Kiichirō. Having a diploma in mechanical engineering, He considered these ideas as his duty to fulfill.
Kiichirō Toyoda assembled his first car in 1931. Given the fact that he did not have either the necessary experience or the appropriate technology, it was not difficult to predict different defects; poor handling, poor engine, etc. Yet Kiichirō was not giving up and assembled a group of engineers to work on a new car.
Our writers can write you a new plagiarism-free essay on any topic
In 1935, A1 model was made. It featured a four-door saloon, with a six-cylinder engine with a capacity of 62 horsepower, which would allow the car to speed up to 100 kmh. This engine was copied from Chevrolet Six motors. The A1 model also had some obvious features appearing from Chrysler Airflow. The reason behind choosing these two companies is the fact that Americans were not favouring the streamline body of a car, instead they preferred box-like cars. This allowed Kiichiro to capitalise and produce somewhat a unique vehicle in Japan. It was much easier with motor engines as Chevrolet was the most common company so the parts were easier to find respectively.
In general, the car was quite durable and most importantly much cheaper than most of the competitors who entered the Japanese car market. Yet such vehicle was still a luxury for the locals.
As a result, Kiichirō Toyoda only managed to sell around 20 cars. In 1936, Toyoda made its first export delivery: China ordered four G1 trucks. However, the looming shadow of bankruptcy nullified any bright prospects for Toyoda.
The situation was rectified by the outbreak of war. General Sanjuro Hayashii, having hardly come to power, hastened to issue a decree ‘On the production of vehicles’, which in particular indicated that all companies producing self-propelled crews were required to register with the War Ministry. The contract with the army promised generous turnover, intransigence could have ended in complete collapse of Toyoda . Toyoda took the ideas of the Dodge brothers as the basis for the construction of the trucks. His trucks with wooden seats, brakes only on the rear wheels and one front headlight had a carrying capacity of up to two and a half tons. Out of the 7600 trucks ordered by the state from Japanese manufacturers, 3000 accounted for Toyota. In 1937, the car department was budded into a separate independent enterprise and the name TOYOTA Motor Company Ltd. began to appear in the company’s official documents. If you notice, the letter D was replaced with the letter T, among other things for mystical reasons. As it turned out, when writing the word TOYODA with hieroglyphs, you have to make as many brush strokes as are considered unlucky in Japan. So why take the risk if you can sacrifice one letter without sacrificing family honor?
In 1939, TMS (Toyota Motor Company Ltd) began production of the AE model. It was even smaller than the AA and was equipped with a 48-hp four-cylinder engine. Over the next five years, several more cars were produced. Among them is the ‘VA’ saloon, the design of which resonated strongly with one of the VOLVO models. However, despite the rather large size, this car was not so heavy, and this was explained by the fact that most of the parts (including the body and partially the suspension) were made of wood. There was a seven-seater limousine ‘Tour B’. It was equipped with a 3.4 liter engine of 85 hp, developed a speed of 20 km / h and had a very original design. A saloon ‘BE’ was popular in the highest circles of bureaucratic ratification and among representatives of the army general. In the same period, the company allocated significant funds for the construction of a research and development center and created several subsidiaries: steel, metal and component manufacturing. The war ended not in favor of Japan. Moreover, the occupiers(who occupied Japan) banned the production of cars for personal use. So, Toyota began to face issues again as initially that was the target clients for Toyoda himself.
However, by 1947, their production was still able to be restored again.
Yet, even a small car of the S series, inspired by the Toyota, probably the Porsche alike, was far from affordable for many people in the post-war years.
Soon the war with Korea stabilised the financial position in Toyota, yet again, during which Toyota simultaneously increased production capacity through orders from the US Army. At the same time, a new management policy was introduced at the enterprises of the company, which included a system of ‘proposals’. It consisted in the fact that any employee could make a proposal, which, in his opinion, could improve the production process. For this, cash bonuses were even paid. In addition, Kiichiro even then given the local limited space and resources, undertook to develop a Japanese production system. Namely: not a single element of any part should have been produced before the need arose.
From here came the slogan – just in time ‘(or’ just on time ‘). And the system was called “toyodaism”.
So, TMS has taken a firm approach in the production of its own models without a need of acquiring a license from Western companies, as many other Japanese companies did. The ‘death’ of the Japanese aircraft industry played a significant role in the development of the aerodynamic vehicles of Toyota. A number of scientists in the aircraft industry got to Toyota’s factory, and with them came their knowledge, with military secrets as well, in particular, the methods that improve the aerodynamics of car bodies. As a result, in 1948 TMS was the first among the automakers of the country of the rising sun tested its model in a wind tunnel, and a year later a bus was offered, many of the body parts of which were made of aluminum, commonly referred to as “winged metal”. The engine in this bus was located at the rear, and the rear wheels were also driving. This was a huge step forward to the great success Toyota is currently experiencing, this is without touching towards the hydric and electric vehicles.
The first Corona appeared in 1957 (then it was just a small sedan with a liter engine), and in 1961 the small-sized Publica model with a two-cylinder air-cooled engine saw the light of day. The next year was marked for Toyota with the release of a millionth car. As you can see, in order to achieve this level, the company needed as much as a quarter of a century, but already in 1972 Toyota crossed the 10-million mark. In 1964, the TMS decided that it was time to thoroughly tackle the segment of sports cars. A 45-cylinder twin-cylinder engine was installed on the Crown Sport 800. The maximum speed of this car was 155 km / h, while fuel consumption was a little more than three liters per 100 km of track. The following year, a prototype ‘2000GT’ appeared, which got on the conveyor in 1967. A 6-cylinder engine was installed on this model, which, with a power of 150 ‘horses’, accelerated the car to 220 km / h. In 1966, the Corolla, still popular today, was born (initially it was just a two-door sedan), and in 1967 – on the centenary of the birthday of Sakisha Toyoda – they released the Japanese Rolls-Royce – the Century model. Cressida appeared in 1969. In the 70s, the range of Toyota cars was replenished with models Starlet (successor of the Publica series), Tercel (the first Japanese front-wheel drive car), Carina, Celica, Mark II. And Corsa, Terser, Camry, 4Runner and MR2 were already in the 80s. In the same period, and to be more precise, in 1988, the Lexus brand was born. In fact, this is the same Toyota, only in a more comfortable design. Today Toyota Motor is the third largest global automaker. She owns 4 brands: Toyota, Lexus, Hino and Daihatsu, 12 factories in Japan and 46 foreign companies (which produce components), three research and development centers and one design center. More than five million cars produced per year are exported to 170 countries. The production program of the company has 125 models, which cover almost all classes and types of cars. Toyota’s range includes not only families of cars, four-wheel drive and sports cars, but also minibuses, pickups, vans, trucks and city buses. Each model is sometimes offered up to ten modifications: with various types of bodies, several engine options and interior trim. Moreover, in the standard configuration, Toyota cars often have more than in the options. In addition, Toyota Motor also owns the world’s first car with a hybrid engine. The power unit of the Prius model includes an electric motor-generator and a gasoline engine, as well as a universal planetary gear linking both engines to the drive wheels. This car is characterized by rather low toxicity of exhaust gases and high fuel economy. Toyota is the undisputed leader in Japan. It accounts for more than 40% of all cars produced in the country. So it would not be an exaggeration to name these very vehicles of the 21st century as the hallmark of the land of the rising sun.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis allows you to identify and structure the strengths and weaknesses of the company, as well as potential opportunities and threats. Table below summarizes the SWOT analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation.
- Strong market position and brand recognition
- Extensive production and distribution network
- The company is engaged in research and development
- Poor allocation of resources compared to competitors
- Decrease in sales in key geographical segments
- Weak presence in the Chinese market
Opportunities
- Global automotive industry growth
- Demand for vehicles
- Timing and frequency of release of new models
- Toyota can capitalize on growing partnership with BMW
- Increasing competition in the global automotive market
- Japanese yen appreciation
- Natural disasters can affect production patterns
- The automotive industry is subject to various government regulations.
Pair “Opportunities – Strengths”
- · The growth of the global automotive industry is a strong market position and brand recognition.
- · Timing and frequency of release of new models – the company is engaged in research and development.
Pair “Opportunities – Weaknesses”
- · Demand for vehicles – sales decline in key geographical segments
Pair “Threats – Strengths”
- · Increasing competition in the global automotive market – strong market position and brand recognition
- · Natural disasters can affect production structure – extensive distribution network
Pair “Threats – Weaknesses”
- · Increasing competition in the global automotive market – poor allocation of resources compared to competitors
Formation of company goals
The goal tree is a structured, built on a hierarchical principle (distributed by level, ranked) set of goals of the economic system, program, plan, in which are highlighted:
- · General goal (‘top of the tree’);
- · Subgoals of the first, second and subsequent levels subordinate to it (“tree branches”).
Toyota Motor Corporation Target Tree
Strategic goals and objectives of the company
International relationships
Expand your presence in key geographical segments
- · Increase its presence in the Chinese market by 2019 by 8%
- · Increase the amount of advertising in developed countries by 2020 by 25%
Increase in car sales by 12% by 2020
- · 11% increase in demand for manufactured products by 2019
15% increase in financial stability by 2020
- · Increase in the authorized capital of the company by 9% by 2020
Increase the company’s solvency by 13% by 2020
- · Strengthening control over suppliers (reduce receivables by 3% by 2019)
- · Cost reduction of 15% by 2020
10% increase in output by 2020
- · Improve staff qualifications by 2019 (reach 20% of employees)
- · Optimization of technological processes (Introduction of new developments by 2020)
Reduce staff turnover by 5% per year
- · Increase in wages by 5% by 2020
Nature of Toyota’s Business-Level Strategy
Toyota aims to combine cost leadership strategy with product and business innovation
An example of product innovation was the introduction of the Toyota Prius in 1997, which was a full hybrid electric car that attracted consumers who were concerned with environmental sustainability – being the first mass-produced hybrid vehicle (product innovation)
Toyota looks to give consumers high-quality motor vehicles at affordable prices, not being concerned about gaining the targeted profit return they initially estimate but aiming to reduce prices to the lowest possible point whilst keeping quality at its highest
This is the Toyota Production System manufacturing method (TPS), which aims to reduce waste, inventory cost and response time to gain maximum business efficiency
This has allowed Toyota to be a highly reputable multinational corporation to consumers across the world
In Toyota’s Business-Level Strategy, they aim to combine cost leadership strategy and with high product and business innovation, with cost leadership meaning that by reducing the cost of production for Toyota enables them to reduce prices of their goods and services (Thompson, 2017). They will then couple these low prices with goods that are highly innovative. Toyota attempt to provide consumers high quality, innovative motor vehicles at affordable prices, choosing to not solely be concerned about making large profit returns instead aiming to keep prices as low as possible whilst keeping quality at its highest (UKEssays, 2017). Toyota’s cost leadership strategy is displayed through the Toyota Production System (TPS) manufacturing method, which aims to reduce waste, inventory cost and response time to consumers in order to gain maximum business efficiency (Thompson, 2017). Toyota’s product and business innovation are conveyed through the introduction of the Toyota Prius in 1997, which was a full hybrid electric car that attracted new consumers to Toyota who were concerned about environmental sustainability as it was the first mass-produced hybrid vehicle. By using these two strategies together, Toyota achieves its business-level strategy and allows it to be a highly reputable multinational corporation to consumers across the world.
Key Functional Level Strategies
Toyota’s Functional Level Strategy aims to enhance the effectiveness of the firm’s operation to gain superior product quality and innovation in order to gain competitive advantages in the automobile industry over its competitors in the market
- Introduction of the Toyota Prius in 1997
- Innovative as it was the first mass-produced hybrid vehicle
- The vehicle has been given numerous quality awards
The United States Environmental Protection Agency and the California Air Resources Board but the Prius as one of the cleanest automobiles sold in the US
Newer models of the vehicle (2018 model) has also been ranked as the second most fuel-efficient gasoline-powered car
The high product quality and innovation leads to a greater reputation for Toyota to consumers in the automobile industry leading to a competitive advantage over its competitors
Toyota’s Functional Level Strategy aims to enhance the effectiveness of the firm’s operation to gain superior product quality and innovation in order to gain competitive advantages in the automobile industry than its competitors in the market (Wade, 2018), with the best example of this being the introduction of the Toyota Prius in 1997 as previously mentioned. The gaining of superior product quality and innovation gained by Toyota is made apparent through the numerous vehicle quality accolades awarded to the Toyota Prius; both the United States Environmental Protection Agency and California Air Resources Board named the Prius as one of the cleanest automobiles sold in the United States (Voelcker, 2015) as well the 2018 model of the Prius being ranked as the second most fuel-efficient gasoline-powered car (Fuel Economy, 2018). Through this, the high product quality and innovation leads to a greater reputation for Toyota to consumers in the automobile industry leading to a competitive advantage over its competitors.
Toyota Business Structure
Toyota’s brand image was negatively affected by numerous recalls that had been made in the recent past. For instance, in 2011, Toyota recalled 111,000 models of Toyota and Lexus brands’ cars due to the damage to parts of the substrate. Therefore, in 2013 the company’s organizational business structure was altered. This was a response to inefficient communication between individual business units, which was caused by a centralized hierarchy, with the Japanese headquarters making all the major decisions.
After the change in 2013, Toyota gave more decision-making power to its regional heads, thus making the decision-making process less centralized. However, all business unit heads still had to report to the central headquarters in Japan.
The change to the organizational business structure further led to the development of geographic divisions. The new organizational structure has 8 international divisions. Each head of region reports to the headquarters. By having such regional divisions, Toyota can adapt and improve its services according to each region’s requirement and wants. Furthermore, there were four product-based divisions created which allow the development of brands and product lines. Such reorganization allowed the company to get rid of diseconomies of scale that occurred before.
Even though there used to be poor communication between the branches, Toyota was always respected and recognized for Kaizen. The Kaizen business strategy is one of the most core values at Toyota, which translates to ‘Continuous Improvement’. The company believes that there is always room for improvement and that no production process can be deemed to be perfect. Thus, every worker at every level of the hierarchy is carefully listened to in order to correct errors at every stage of production.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
Toyota Swot Analysis: SWOT Analysis Of Toyota
SWOT Analysis Strengths: 1. Brand recognition and strong position in the market – the market position of Toyota is strong and in different geographies across continents. In 2012, the market share is 45.5% for Toyota and Lexus brands in Japan. In Asia on the other hand has market share of 13.4% and 12.2% in North America, 4.3% in Europe while 7% of the market in China as well as considerable market shares in Central and South America, Africa and Oceania (Store.marketline.com, 2015). Toyota has been allowed by such strong market position to gain competitive advantage and also expansion in the international markets. A portfolio is held by Toyota for strong brands in the automotive industry. The strong market awards a competitive advantage and …show more content…
Strong focus on research and development – the focus for research and development of Toyota is strong in the enhancement of functionality, safety, quality functionality, safety concerns, quality features and environmental compatibility and environmental compatibility as well as expanding its portfolio of products. There are 14 facilities around the globe where R&D is performed. The strong concentration on this allow Toyota in integrating the latest feature towards the current range of products and bringing out various technologies. It also pave the way for leadership in technology in most of its segments and making it a company driven by innovation (Store.marketline.com, 2015). 3. Extensive networks of production and distribution – The production and distribution network of Toyota is extensive. Automobiles and related parts are affiliated by Toyota through more than 27 countries in 50 manufacturing companies outside of Japan. 3.5 million cars were produced in Japan, almost 3.5 million cars were manufactured outside Japan while internally it is almost 3.9 million. The extensive distribution network of Japan provides a wide reach while its production base diversifies the risks of business that allows for revenue (Store.marketline.com, …show more content…
Intensifying competition – the competition in the automotive industry is intense. The competition faced by Toyota is very strong in various markets among other automotive manufacturers(Store.marketline.com, 2015) . In the light of the growing globalization and the worldwide automotive industry consolidation, the competition will become stiffer and may be affected by different factors such as features and product quality pricing, the amount of time required for innovation and development, safety, fuel economy. This will result to large inventory and lower vehicle unit which forces the prices to go downward thus in the long run may affect the profit generation of Toyota (Store.marketline.com, 2015). 2. Japanese Yen appreciation – the fluctuations in both the value of the Yen and other foreign currency makes Toyota vulnerable. Adverse effects can be impacted by the strengthening of the Yen versus the US dollar which would affect the operating results of Toyota that would impact the valuation of the company (Store.marketline.com, 2015). 3. Natural disasters – due to natural disasters such as earthquakes which is common in Japan, Toyota could face disruptions. Such as in the previous years, the country had been experiencing devastating quakes, such as the Tohoku 2011 earthquake which has a serious disruption of the economy and a halt at Toyota productions in the tune of 15000 cars. Such devastating phenomenon could impact the production and capacity of
Triangle Factory Fire Essay
To fully understand how this disaster was possible it is important to understand the historical background of the time period
Psy/270 Week 1 Reflection
This would lead to conflicts for resources and possible shortages that would harm the population. Finally, the increase in heat waves and droughts would have a huge impact on agriculture and water availability as it will be difficult to produce crop and clean water to meet the demand of the population. This would also lead to shortages of food and water, affecting many
Ted Steinberg Acts Of God Analysis
In chapter one, there is much emphasis on the economic impact of natural disasters. For
Allegro Automotive Case Analysis
The current state of the automotive industry is one of shrinking margins, changing consumer expectations and demands, as well as pressure from the government to increase fuel efficiency. There is increased competition in the American market as foreign companies challenge the “Big Two” automotive manufacturers. Costs increase while the price for their products has remained stagnant. One way that manufacturers have managed to stay profitable is actively working to decrease costs while needing to keep the selling price the same in order to be competitive. The most successful ones have changed their relationships with suppliers to a partnership between the two companies.
Hunger In Ethiopia Essay
These include floods and droughts. However, the most concrete impact recently has been by drought. The government and the people have not been able to provide enough food supply for themselves. Due to the growth
Five Forces Auto Insurance Industry
3. Threat of new entrants High barriers to entry in the industry. Licensing requirements are high. There is a minimum size requirement to achieve profitability and the initial investment is required and fixed costs of operating. How much of the control is in the hands of existing players of the market or key resources?
Toyota General Environment Analysis
Toyota Motor Corporation is a car organization working Worldwide (Multinational) with base camp in Japan, with US as the biggest business sector for
Ansoff Swot Analysis
SWOT ANALYSIS 4 3. ANSOFF MATRIX 5 3.1 Market Penetration 6 3.2 Product development 6 4. SEGMENTATION 6 4.1 Market Segmentation 6 4.2 Target Market Strategy 8 5. POSITIONING 8 5.1.1 Product 8 5.1.2 Place 8 5.1.3 Promotion 8 5.1.4 Price 9 5.1.5 People 9 5.1.6 Process 9 5.1.7 Physical evidence 9 6. MARKETING STRATEGY 10 6.1 The Product Plan 10 6.1.1 Competitors 10 6.2 Advertising 11 7.
Rolls Royce Pest Analysis
These factors have great impact on the way we think and act (PESTLE Analysis, 2015). For Rolls Royce, its operation was greatly affected by SARS virus in year 2002. Damage from the SARS have been done to an already ramshackling aviation division. For example, Singapore Airlines cut down 13% of its capacity due to SARS.
The Pros And Cons Of The Automobile Industry
The United States has one of the largest automotive markets in the world, and is home to many global vehicle and auto parts manufactures. In 2016 year alone, vehicle production reached almost 17.5 million passenger vehicles. Automobile industry involves many industries in it. It includes original equipment, manufacture, and adverting industry as well as oil and natural gases industry. Main players of the Automobile industry are Toyota, General motors, Volkswagen, Honda, Ford and more.
Impact Of External Business Environment On Automobile Industry
The Automobile business is a blend of organizations and companies engaged with the plan, advancement, assembling, promoting, and offering of vehicles. External environment is outside influences which has an effect on the industry. The environment factors help the industry to go through vast changes. Emergence of new competition have huge impact on vehicle development and design. Advancement of technology has helped the industry to use more high-tech driving capabilities.
Volkswagen Positioning Strategy
However, Toyota still sells more vehicles each year but the gap has narrowed down to less than 1.5 million cars. Though Toyotas reputation is going down after a series of recalls, low quality for Volkswagen remains an issue in the U.S market. Volkswagen needs to strengthen its market in the United States to expand its market share. Stefan Jacoby, VWs U.S chief persuaded the board to build a U.S plant. The board later approved the plant and allocated $1 billion for the construction of the plant scheduled to open in 2011.
Write An Essay About The Tohoku Earthquake
The Tohoku Earthquake was the most powerful earthquake recorded to have hit Japan. The earthquake was a magnitude 9.0 off the coasts of Japan that occurred at 2:46pm on Friday 11 March 2011, which triggered a powerful tsunami that reached the height up to 10.4 meters. A Japanese National Police Agency reported 15,889 deaths, 6,152 injured, and 2,601 people missing, 127,290 buildings totally collapse, 272,788 buildings half collapse, and another 747,989 buildings partially damaged. The Tohoku earthquake and tsunami caused severe structural damage in northeastern Japan, including heavy damage to roads, railways and dams, not to mention fires in many areas. It was the toughest and the most difficult crisis in Japan after the World War 2 leaving
Toyota Business Level Strategy Analysis
The Business Level of Toyota Toyota Motor Corporation is a Japanese company that is involved in the design, assembly, manufacture and sale of a wide range of motor vehicles such as minivans, passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and assorted accessories and parts (Nkomo, 3). Examples of brands under the Toyota portfolio include, but are not limited to; Lexus, Toyota, Hino and Daihatsu. Toyota was founded in 1937 by Kiichiro Toyoda and has grown to not only be the world’s leading auto manufacturer in the automotive industry, but also the world’s eighth largest company with operations in virtually every corner of the world (Nkomo, 3). This growth has been fueled by two key aspects of Toyota’s business; its ability to lower costs and concise
Literature Review On Unethical Behavior
Although many customers are disappointed in the way Toyota has dealt with these issues, it is obvious that their demand has dropped, however Toyota is still a popular brand and people are continuing to purchase their vehicles, some of which know the circumstances. Therefore Toyota’s unethical practice hasn’t affected their brand power. I have included some statistics of their market share and how sales decreased because of these unethical issues with the
More about Toyota Swot Analysis: SWOT Analysis Of Toyota
Related topics.
- Organizational structure
- Decision making
- Human resource policies
- Human resource management

- Management / Organizations
Toyota SWOT Analysis Organizational SWOT
Pages: 8 (2427 words) · Bibliography Sources: ≈ 8 · File: .docx · Topic: Business - Management
TOPIC: SWOT on Toyota SWOT Analysis Organizational Analysis of the Assignment
Two Ordering Options:

- To download this paper immediately , it takes only 2 minutes to subscribe. You can individually download any of our 2,000,000+ private & exclusive papers, 24/7! You'll also receive a permanent, 10% discount on custom writing. (After you pay and log-in, the "Download Full Paper" link will instantly download any paper(s) that you wish!)
- One of our highly experienced experts will write a brand new, 100% unique paper matching the exact specifications and topic that you provide! You'll be the only person on the planet to receive the one-of-a-kind paper that we write for you! Use code "Save10" to save 10% on your 1st order!
Download the perfectly formatted MS Word file!
We'll follow your exact instructions! Chat with the writer 24/7.
Related SWOTs:
Importance of a SWOT Analysis SWOT …
¶ … SWOT Analysis Over the last several decades the world of business has been affected, by the changes from globalization. Where, a business must use creative strategies to be…
Pages: 2 (710 words) · Type: SWOT · Bibliography Sources: 2
Toyota Organizational Assessment Research Proposal …
Toyota Organizational Assessment Company Overview As a Japanese-based company Toyota is a major international car retailer and automotive specialist. The company offers a wide variety of vehicles, from small sedans…
Pages: 15 (4095 words) · Type: Research Proposal · Bibliography Sources: ≈ 7
Nintendo SWOT Analysis Nintendo Co. Ltd Research Proposal …
Nintendo SWOT Analysis Nintendo Co. Ltd. was founded in 1889 in Kyoto, Japan. The software manufacturer is very influential in its industry, being Japan's third most valuable company with a…
Pages: 11 (3156 words) · Type: Research Proposal · Style: APA · Bibliography Sources: 6
SWOT Analysis on Honda Motor Company SWOT …
Honda Motor Company is one of the world's premier manufacturers. Over the past three decades it has taken up a dominant niche market within several industries and competes with other…
Pages: 4 (1239 words) · Type: SWOT · Bibliography Sources: 0
Accounting Function for a Chosen Organization Thesis …
Accounting Function for a chosen organization This paper will be aimed at providing a full background of the financial situation at General Motors, focusing on the role of the accounting…
Pages: 23 (6160 words) · Type: Thesis · Style: Harvard · Bibliography Sources: 5
View other related papers >>
View 200+ other related papers >>
How to Cite "Toyota SWOT Analysis Organizational" SWOT in a Bibliography:
Chicago Style
Sat, Apr 6, 2024
- 5-Day Trial for $8.97
- Write a Paper for Me!
- Download 175K Essays
- Paper Topics
- Paper Editing Service
- Writing Samples
- Essay Writing Tutorials
- Info / FAQ / Guarantee
- Beware of Copycats!
- Listen to our radio ad!
- 1-866-7O7-27З7
- Text (super fast):
- 1-65O-585-OOO5
EssayTown.com © and ™ 2001–2024. All Rights Reserved. Terms & Privacy
- TEXT: 1-65O-585-OOO5
- Avoid Copycats!
- Listen to our radio music ad
Toyota SWOT & PESTLE Analysis
Why toyota swot & pestle analysis.
Toyota SWOT & PESTLE Analysis are widely used tools in business strategy to evaluate the external and internal environment of the organization. Toyota is one of the largest manufacturers of automobiles in the world, offering a wide range of vehicles such as trucks, buses, and cars. It has a strong brand reputation that makes it maintain its competitive edge in the world market. The successful journey of Toyota of more than 80 years has made other key players and businesses in the market want to work on Toyota SWOT & PESTLE Analysis.
Toyota Company Overview
Toyota is a leading multinational organization that designs, manufactures, and distributes commercial vehicles, automobiles, and other products. Toyota has a rich history of more than 80 years, and it’s headquartered in Toyota city Japan. Toyota is currently under the leadership of Akio Toyoda since 2009.
Toyota was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda in 1937. Since then, Toyota has grown into a global brand in more than 170 countries. Toyota has more than 370,000 workers globally and is considered one of the largest automotive manufacturers globally.
Toyota is a public firm traded on the New York and Tokyo Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “TM.” The market cap of Toyota as of March 2023 was about $240 billion, making it one of the leading automobile manufacturers globally. In addition, the firm generates a significant annual revenue of about $275 billion.
Toyota products.
Toyota provides its customers with various products and services, including trucks, buses, cars, and other commercial vehicles. Some famous Toyota brands include Toyota Camry, Prius, Corolla, and Lexus. In addition, Toyota produces hybrid and electric vehicles and invests in autonomous driving cars.
Toyota Competitors
In terms of competition, the automotive manufacturing industry has many players and constantly competes for market share and dominance. For instance, Toyota faces fierce competition from its rivals like General Motors, Ford, and Volkswagen. However, Toyota has been able to uphold its market position due to its high-quality products, strong brand image, and innovative strategy. Toyota’s investments in market research and product development enable it to be ahead of its rivals in technological advancement.
Toyota SWOT Analysis
The first analysis in Toyota SWOT & PESTEL Analysis is the SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis is crucial strategic tool firms use to evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Toyota Strengths
- Strong brand reputation: Toyota is among the most popular and valued car brands globally. Its strong brand reputation is based on producing high-quality, durable, and reliable vehicles.
- Diverse product portfolio: Toyota presents its large customer base with a wide range of vehicles that caters to the needs of various customers and markets. The company has a diversified product portfolio like SUVs, Hybrids, trucks, and sedans.
- Research and Development: Toyota is globally popular due to its innovation and progressive improvement. The firm invests heavily in research and development to manufacture more efficient and environmentally friendly products.
- Strong global presence: the presence of the Toyota firm globally is very strong, with operations in more than 170 countries worldwide. Toyota has manufacturing plants in various regions to cater to local demands, making its presence felt almost everywhere.
Toyota Weaknesses
- High production cost: Toyota’s production cost is higher than some of its competitors due to its increased focus on quality and innovation. In this case, the firm’s profitability and competitiveness may be affected, especially in price-sensitive regions.
- High dependence on suppliers: Toyota depends mainly on its suppliers for raw materials and components. Any disruptions to the supply chain could negatively impact production and sales.
- High dependence on the Japanese Market: The sales of Toyota products heavily rely on the Japanese market. For instance, Toyota generates a considerable portion of its revenue from the domestic market. Thus, it becomes vulnerable due to economic changes in Japan.
- Limited to electric Vehicles Portfolio: compared to some of the Toyota rivals that have adopted electric vehicles, Toyota has been slow in embracing this technological advancement. Toyota largely depends on gasoline-powered vehicles, making it vulnerable to changing consumer preferences and environmental sustainability/regulations.
Toyota Opportunities
- Autonomous driving technology: The market trend is shifting towards this technology which is becoming more advanced daily and provides Toyota with an opportunity to develop its technology or partner with other key players in this sector to develop this new technology.
- Increasing demand for Electric Vehicles: Due to the increasing consumer consciousness about environmental sustainability, there is an increasing demand for electric vehicles. Toyota’s expertise in hybrid technology puts it in the best position to capitalize on this new market trend.
- Emerging Markets: Emerging markets like Africa and India allow Toyota to increase its presence. These emerging markets are expected to experience significant growth in the automotive industry.
Toyota Threats
- Intense competition: Toyota, the leader in the automotive industry, faces stiff competition from other key manufacturers like Ford, General Motors, and Volkswagen. These companies reduce the market share f Toyota and affect its pricing power by providing similar products in the same market.
- Economic downturns: The sales and profitability of Toyota can be significantly impacted by economic downturns in the global markets.
- Government regulations: Government policies on safety, emissions, and other factors may increase production costs and lower the company’s competitiveness.
- Changing consumer preferences: Changing consumer preferences and market trends can potentially impact Toyota products and market demand for the vehicles. For instance, shifting towards crossovers and SUVs may negatively affect sedan demand.
Toyota PESTLE Analysis
The other framework in Toyota SWOT & PESTEL Analysis is the PESTLE Analysis. A PESTLE analysis is a crucial strategic tool that firms use to analyze various external factors affecting their business operations. Conducting Toyota’s PESTLE analysis of external factors could go a long way to help identify opportunities and threats to help create appropriate strategies.
Political Factors
Political factors can be attributed to the impact of government regulations and policies on a business. The following are political factors that affect the operations of Toyota.
- Government policies: The governments in the world are becoming more conscious about environmental sustainability and climate change. In this case, most are implementing policies to minimize carbon emissions and encourage sustainable transportation. In response to environmental sustainability, Toyota is developing electric and hybrid vehicles making it maintain its position as the world leader in the automotive industry.
- Trade policies: Trade barriers and tariffs can impact the importation and export of Toyota products. For instance, the existing tension between China and US has led to higher taxes on vehicles imported from China and affects the operations of Toyota in this country.
- Political instability: Toyota operates in more than 170 countries worldwide, and political instability in any host country may affect its manufacturing, sales, and supply chain.
- Taxation policies: Increased taxation on vehicles can potentially lower the demand, while tax incentives on electric and hybrid cars can increase the demand.
Economic Factors
This refers to the economic conditions of Toyota’s operations. For instance:
- Economic growth: economic growth in any country increases demand for automobiles. Economic growth raises disposable income to spend on cars, and the need for Toyota automobiles grows.
- Exchange rates: The exchange rate in the market can significantly affect the production cost and the company’s profitability.
- Inflation rates: Inflation significantly impacts the cost of labor and raw materials, which can affect Toyota’s cost of production.
Social Factors
This refers to social and cultural impacts on business operations. For instance, Toyota faces the following social factors.
- Consumer preferences: The preferences for fuel efficiency, eco-friendly, and safety affect the demand for Toyota’s automobiles.
- Lifestyle changes: Changes in consumer lifestyle may affect the demand for Toyota products. For instance, urbanization has resulted in increased demand for small cars.
- Demographics: Gender, age, and income of the consumers affect their demand for Toyota automobiles. Young consumers will likely buy sports cars, while families may prefer SUVs or minivans.
Technological Factors
This refers to the impact of technology on the operations of the organization. For instance, the following affect Toyota’s operations:
- Innovation: This is very critical for Toyota. Toyota invests extensively in research and development to produce new automobiles and technologies that meet consumer demands.
- Automation: this new technology has the potential to enhance efficiency and minimize Toyota’s product cost.
- Connectivity: Technologies like vehicle-to-vehicle communication and in-car infotainment systems are increasingly becoming significant among consumers. Toyota is responding to this demand by integrating these new technologies into its products.
- Autonomous and electric cars: The future of automotive industries is autonomous and electric cars. Toyota has launched electric and hybrid cars and is developing autonomous vehicles. Toyota’s investment in this new technology is critical for its long-term success.
Legal Factors
This refers to the effects of government laws and regulations on an organization. The following laws and regulations have a potential impact on the operations of Toyota:
- Product safety regulation: different governments worldwide have strict regulations regarding the safety of automobiles. Non-compliance with these regulations may attract fines and damage the brand’s reputation.
- Intellectual property protection: Intellectual property theft can result in significant losses and damage to its reputation. Toyota invests heavily in research and development; therefore, it is significant to protect its intellectual property.
- Environmental regulations: this impacts the operations of Toyota as its dedicated to minimizing its environmental effects. Compliance with environmental regulations helps the organization maintain its environmentally conscious reputation.
- Labor laws: Compliance with a country’s labor laws is significant in upholding the company’s reputation. Toyota encourages fair and safe working conditions for its workers.
Environmental Factors
This is associated with the impact of the natural environment on business operations. For instance:
- Climate change: This is a significant concern for Toyota because it affects its operations and product demand. In response to environmental sustainability, Toyota is developing more environmentally friendly automobiles like electric and hybrid cars to reduce its carbon footprint.
- Resource depletion: This can adversely impact Toyota’s operations as it primarily relies on natural resources like minerals and oil. In response, Toyota is reducing its reliance on non-renewable sources.
- Sustainable manufacturing: Toyota is concerned with sustainable manufacturing and is committed to minimizing its environmental impacts. Toyota has implemented practices aimed at minimizing energy consumption and reducing waste.
Toyota is a leading multinational company with a strong brand reputation and diverse product portfolio. However, it faces challenges like intense competition, dependence on the Japanese market, and vulnerability to government policies. Toyota’s SWOT & PESTLE analysis provides significant insights into the firm’s strengths, weaknesses and potential external factors impacting future business operations.
Welcome to ESSAY FOR ALL
Select an option that suits you best

Toyota Swot Analysis Essay

Show More Some companies are not always perfect, for example Toyota. Toyota is world-renowned company manufacturing in vehicle making.Their cars are the most used cars in the world today, but it has its flaws. Toyota conducted a SWOT analysis to audit its company and its environment in order to make marketing decisions to maintain the value of its products. Toyota ’s strength is valued to show how strong of a corporation it is. Their rapid growth is a remarkable one as well, showing they are a valued customer in the market. As shown in Document E Toyota posted an extraordinary amount of money around 611.7 billion yen. Their growth is visible by the great growth it has achieved. Equally as important as their growth Toyota is considerably the most known car brand to this day. On the graph on Document D Toyota is third in market sales and is making around 150,000 in sales as of November 2015. The staff that Toyota is a well-trained staff to create their vehicles. The staff is known for their “teamwork, continuous improvement through learning,quality, and secretly.” It has shown their company is efficient through their staff. Moreover their staff consists of 364,445 employees. Their strengths have taken them to newer heights, as well …show more content… Toyota has a lot of competition in car making such as Google and Nissan. “Testing driverless cars, Japanese rival Nissan”. (Document A). Notably that Google is working on driverless cars, Toyota has a lot of competition for majority of all projects the company(Toyota) comes up with. In addition with competition, the value of yen is also decreasing. “ weaker yen that continues to buoy its gains.”(Document E) The yen value is majority of Toyota’s money and the decline of the yen value can hurt their sales. Ironically with the yen decreasing in value market sales have dropped for Toyota in Southeast
Related Documents
Boeing swot analysis essay.
This proves to be Boeing’s downfall as they have forgotten a critical component to TPS that was highlighted in the previous section of this paper, oversight. The problem breaks down into two issues that their TPS hybrid created and left out in the final model. This method only works when the father company, so to speak, is overseeing the entire operation and has to intervene when necessary. For example if the supplier is unable to meet a quota or needs help with something, the father company needs to then take the role of a supplier and then fix the problem together as well as ground their understanding of what goes into the final product so they are not left in the dark(Hartman 2015, pg 8).…
Chevy Swot Analysis
History of Chevys! Freshman technology Chevrolet was introduced by William C.durant and louis chevrolet. By 1980 they were selling around 50,000 horse-drawn vehicles. They started shared the company with the Durant-Dort Carriage Company. In 1909 William Durant asked Louis Chevrolet a famous race car driver to help design and promote a new car.…
Swot Analysis Paper
The community of Hermitage is located in eastern Davidson County, just minutes away from downtown Nashville. The neighborhood is named for its most famous home, The Hermitage. Once the home of Andrew Jackson, today the historical section of eastern Nashville is home to a dynamic and growing community. Despite its inclusion as part of Metropolitan Nashville, the Hermitage maintains a separate identity as its own residential and commercial suburban area.…
Treasury Casino Executive Summary
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Treasury Casino is embraced by ECHO, a major association (Echo Entertainment bunch, 2015). The principle present and future contenders are different clubhouse and excitement organizations compose by ECHO in Australia and different canter will likewise be on online contenders doing e-business. The Jupiter's, which is another greater gambling club of the ECHO excitement gathering, is pretty nearly eighty five km from the Treasury Casino. It can likewise affect the weekend guests of the Treasury Casino. Financial elements can be enhanced by drawing in the sponsorships for the occasions from the neighbourhood organizations and agents for advancement.…
Target Swot Analysis Essay
a) Mission Statement (Current)- Target’s mission is to make Target the preferred shopping destination for their guests by delivering outstanding value, continuous innovation and an exceptional guest experience by consistently fulfilling our Expect More. Pay Less. ® brand promise." b) New or Revised Mission Statement- Provide our guest with innovative solutions to enhance their shopping experience through easy and convenient channels while delivering exceptional service, outstanding value, and quality products and services that consistently fulfills the Expect More. Pay Less.…
General Motors Bailout
Setting their goal high on making more than $10 billion a year, the General Motors Co. had to be bailed out by the federal government (Kinicki & Williams, 2013). In 2011, the GM made the highest profit a year reporting on Feb. 16, 2012, of making about $8 billion, this is almost twice as much as, in 2010. With the growth in China and profits in North America, $4.7 billion of the strong profit was from them. This gave them the opportunity to “shed billions of dollars of costs and raise prices higher on their products” (Kinicki & Williams, 2013, 150).…
Rolls Royce
The two US competitors, Pratt & Whitney Aircraft Group and General Electric’s aerospace division, dominates this market. Rolls Royce will be having less competitive advantage or edge if the selling price of engines is more or less similar to two US competitors. The revenue of the Company will fall if the British pound gets strengthened and become more valuable because the company’s operating costs are measured or calculated in British pound. In this kind of situation, if the company decides to increase the selling price of engines then the company will lose its competitive advantage or edge and if the company decides to maintain the price then it will be incurring…
Causes Of Toyota's Rehearsal Crisis
Toyota Motor Corporation has been a well know car maker for over 30 years. Toyota vehicles are sold around the world. In the Toyota Motor Corp, there are several brands: Toyota, Lexus, Daihatsu, Ranz, Scion and Hino. Toyota, known as one of the world’s largest automakers, manufactures trucks, cars, parts, and motorcycles in 27 countries around the world including the United States. Toyota is known by the consumer for producing high quality, reliable vehicles.…
Subaru Swot Analysis
The company that I shall be working for, theoretically, is Subaru – Subaru is a renown Japanese car manufacturer whose emphasizes on creating cars prepared for any road condition. In Western markets, the Subaru brand has traditionally been popular among a dedicated core of buyers. Marketing is targeted towards specific niches centered on those who desire the company's signature drive train engine, all-wheel/rough-road capabilities or affordable sports car markets. Which means that the pistons and the cylinders in the engine fire left to right instead of up and down or at an angle to create a more balanced. Subaru has also had an extremely successful run in the world of Rally Championships, having won over 50 individual events and Slowly Subaru has built a reputation as a durable, affordable and reliable car, a people’s car that you can’t describe any other way apart from love.…
The Toyota Way Summary
So, it can give us the reason why they perform so well in the car manufacturing industry, because the Toyota company also pay a lot attention to their company’s culture construction instead of just targeting on making money. They focus a lot on the relationship between the managers and employees, workers and their working environment. These all became their most precious things for them to move on in the future,…
Examples Of Marketing Segmentation Of Toyota
With growing and changing world company change their strategy and plan to satisfy customers needs. However with huge competition company faces variety of problems and crisis. To be on the top of car market Toyota chooses the lowest price and the highest quality to be always number one. They provide different aspects to solve drivers gaps in their vehicles and improve it with new coming car. They focus on comfort and safety to be known as a smart innovative and modern company.…
Marketing Case Study: Dacia Renault
5.6 Dacia Renault company strategy The Renault Group is presenting in 118 countries and functioning in five major regions: Europe, Euromed, Russia, Asia, Africa and the Americas. The Renault Group now has more than 129,000 employees, who are working in 139 industrial sites. With regards to the environmental protection, all those industrial sites have ISO 14001 certification. Renault owns three brands: Renault, Samsung and Dacia, the Group design and produce personal vehicles and commercial vehicles.…
Toyota Case Study
Throughout all these years, Toyota had built a strong image in Malaysian customers’ mind. Based on a comment by UMW Toyota (Local Distributor of Toyota Motor in Malaysia) president Kuah Kock Heng, he said that UMW Toyota had the biggest share of the non-national makes in 2009, selling 81,785 units. It outsold its nearest competitor by over 40,000 units. Although the mass recall crisis not affecting Malaysia’s consumers “UMW Toyota would like to emphasize that we have received confirmation from our principal, Toyota Motor Corp, Japan that all Toyota and Lexus models sold by UMW Toyota are not affected by this recall exercise,” a statement by UMW Toyota. However, Toyota’s mass recall crisis affects many of its constituencies.…
Swot Analysis: SWOT Analysis Of F & N.
Question 2 SWOT Analysis SWOT analysis aims to identify the internal strengths and weaknesses involved an organization and the firm’s capability and resources to deal with changes. Besides, it is useful in assisting risk management by analyzing the opportunities and threats arising from external business environment. It is useful to assist the firm in providing specific insights that can be used to develop the appropriate marketing strategy by summarizing the key favorable and unfavorable issues from the business environment (Wheelen & Hunger 2002, p. 109). 2.1 Strengths In term of the beverages and diaries business, F&N has gained itself a strong and reputable brand name over the years with various brand awards (Awards 2014).…
SWOT Analysis Of Bank Islam
3.0 SWOT ANALYSIS A SWOT analysis is defined as an overall evaluation of the company’s strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O) and threats (T). Strength Strength is the internal capabilities that may help a company reach its objectives. Strength include internal capabilities, resources and positive situational factors that may help the company serve its customers and achieve its objectives. Bank Islam Trust company set their vision as fully client-focused in their operation.…
Related Topics
- Automotive industry
- General Motors
Ready To Get Started?
- Create Flashcards
- Mobile apps
- Cookie Settings
SWOT Analysis: Toyota, Starbucks,
In the business world is a real advantage to have some valuable case studies to work on.
SWOT Analysis of Toyota
Order custom essay SWOT Analysis: Toyota, Starbucks, with free plagiarism report
- New investment by Toyota in factories in the US and China saw 2005 profits rise, against the worldwide motor industry trend. Net profits rose 0.8% to 1.17 trillion yen ($11bn; .85bn), while sales were 7.3% higher at 18.55 trillion yen. Commentators argue that this is because the company has the right mix of products for the markets that it serves. This is an example of very focused segmentation, targeting and positioning in a number of countries.
- In 2003 Toyota knocked its rivals Ford into third spot, to become the World's second largest carmaker with 6.78 million units. The company is still behind rivals General Motors with 8.59 million units in the same period. Its strong industry position is based upon a number of factors including a diversified product range, highly targeted marketing and a commitment to lean manufacturing and quality.
- The company makes a large range of vehicles for both private customers and commercial organisations, from the small Yaris to large trucks. The company uses marketing techniques to identify and satisfy customer needs. Its brand is a household name. The company also maximizes profit through efficient manufacturing approaches (e.g. Total Quality Management).
- Being big has its own problems. The World market for cars is in a condition of over supply and so car manufacturers need to make sure that it is their models that consumers want. Toyota markets most of its products in the US and in Japan. Therefore it is exposed to fluctuating economic and political conditions those markets. Perhaps that is why the company is beginning to shift its attentions to the emerging Chinese market. Movements in exchange rates could see the already narrow margins in the car market being reduced.
- The company needs to keep producing cars in order to retain its operational efficiency. Car plants represent a huge investment in expensive fixed costs, as well as the high costs of training and retaining labour. So if the car market experiences a down turn, the company could see over capapacity. If on the other hand the car market experiences an upturn, then the company may miss out on potential sales due to under capacity i.e. it takes time to accommodate. This is a typical problem with high volume car manufacturing.
Opportunities
- Lexus and Toyota now have a reputation for manufacturing environmentally friendly vehicles. Lexus has RX 400h hybrid, and Toyota has it Prius. Both are based upon advance technologies developed by the organisation. Rocketing oil prices have seen sales of the new hybrid vehicles increase. Toyota has also sold on its technology to other motor manufacturers, for example Ford has bought into the technology for its new Explorer SUV Hybrid. Such moves can only firm up Toyota's interest and investment in hybrid R&D.
- Toyota is to target the 'urban youth' market. The company has launched its new Aygo, which is targeted at the streetwise youth market and captures (or attempts to the nature of dance and DJ culture in a very competitive segment. The vehicle itself is a unique convertible, with models extending at their rear! The narrow segment is notorious for it narrow margins and difficulties for branding.
- Product recalls are always a problem for vehicle manufacturers. In 2005 the company had to recall 880,00 sports utility vehicles and pick up trucks due to faulty front suspension systems. Toyota did not give details of how much the recall would cost. The majority of affected vehicles were sold in the US, while the rest were sold in Japan, Europe and Australia.
- As with any car manufacturer, Toyota faces tremendous competitive rivalry in the car market. Competition is increasing almost daily, with new entrants coming into the market from China, South Korea and new plants in Eastern Europe. The company is also exposed to any movement in the price of raw materials such as rubber, steel and fuel. The key economies in the Pacific, the US and Europe also experience slow downs. These economic factors are potential threats for Toyota.
SWOT Analysis Starbucks
- Starbucks Corporation is a very profitable organisation, earning in excess of $600 million in 2004. The company generated revenue of more than $5000 million in the same year.
- It is a global coffee brand built upon a reputation for fine products and services. It has almost 9000 cafes in almost 40 countries.
- Starbucks was one of the Fortune Top 100 Companies to Work For in 2005. The company is a respected employer that values its workforce.
- The organisation has strong ethical values and an ethical mission statement as follows, 'Starbucks is committed to a role of environmental leadership in all facets of our business.
- Starbucks has a reputation for new product development and creativity. However, they remain vulnerable to the possibility that their innovation may falter over time.
- The organisation has a strong presence in the United States of America with more than three quarters of their cafes located in the home market. It is often argued that they need to look for a portfolio of countries, in order to spread business risk.
- The organisation is dependant on a main competitive advantage, the retail of coffee. This could make them slow to diversify into other sectors should the need arise.
- Starbucks are very good at taking advantage of opportunties.
- In 2004 the company created a CD-burning service in their Santa Monica (California USA) cafe with Hewlett Packard, where customers create their own music CD.
- New products and services that can be retailed in their cafes, such as Fair Trade products.
- The company has the opportunity to expand its global operations. New markets for coffee such as India and the Pacific Rim nations are beginning to emerge.
- Co-branding with other manufacturers of food and drink, and brand franchising to manufacturers of other goods and services both have potential.
- Who knows if the market for coffee will grow and stay in favour with customers, or whether another type of beverage or leisure activity will replace coffee in the future?
- Starbucks are exposed to rises in the cost of coffee and dairy products.
- Since its conception in Pike Place Market, Seattle in 1971, Starbucks' success has lead to the market entry of many competitors and copy cat brands that pose potential threats.
'Starbucks' mission statement is 'Establish Starbucks as the premier purveyor of the finest coffee in the world while maintaining our uncompromising principles while we grow.' The following six guiding principles will help us measure the appropriateness of our decisions' more? Then go to Starbucks.
SWOT Analysis Dell
- Dell is the World's largest PC maker. Profits for the 3 months to July 2005 were in excess of $1 billion US, representing a growth of around 28%. For the last couple of years it has held its position as market leader (it took it from rivals Hewlett-Packard). The Dell brand is one of the best known and renowned computer brands in the World.
- Dell cuts out the retailer and supplies directly to the customers. It uses information technology, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) approaches to capture data on its loyal consumers. So a customer selects a generic PC model, and then adds items and upgrades until the PC is kitted out to the customer's own specification. Components are made by suppliers, never by Dell. PC's are assembled using relatively cheap labour. You can even keep track of your delivery by contacting customer services, based in India. The finished goods are then dropped off with the customer by courier. Dell has total command of the supply chain.
- The company has such a huge range of products and components from many suppliers from a plethora of countries, that there is the occasional product recall that can cause Dell some embarrassment. In 2004 Dell had to recall 4.4 million laptop adapters because of a fear that they could overheat, causing electric shocks or fires. *
- Whilst this is a tremendous advantage in terms of business operations, allowing Dell to focus on marketing and logistics, the company is reliant on a few large suppliers, and to an extent is locked in for periods of time (i.e. unable to switch supply dues to the lack of large suppliers in the World).
- Kevin Rollins replaced Michael Dell in 2004 as Dell's Chief Executive Officer. Dell remained the company's Chairman. Despite founder Dell's massive success, new blood and a change in management thinking could lead the company into a new, even more profitable period. Dell was born in 1965, and founded Dell in 1984 with $1000 whilst studying at the University of Texas. He became the youngest Fortune 500 CEO in 1992, and will be a tough act to follow.
- Dell is pursuing a diversification strategy by introducing many new products to its range. This initially has meant good such as peripherals including printers and toners, but now also included LCD televisions and other non-computing goods. So Dell compete against iPod and other consumer electronics brands.
- Dell is making and selling low-cost, low-price computers to PC retailers in the United States. The PC's are unbranded and should not be recognised as being Dell when the consumer makes a purchase. Rebranding and rebadging for retailers, although a departure for Dell, gives the company new market segments to attack with the associated marketing costs.
- The single biggest problem for Dell is the competitive rivalry that exists in the PC market globally. As with all profitable brands, retaliation from competitors and new entrants to the market pose potential threats. Dell sources from Far Eastern nations where labour costs remain low, but there is nothing stopping competitors doing the same - even sourcing the same or similar components from the same or similar suppliers. Remember, Dell is a PC maker, not a PC manufacturer.
- Dell, being global in its marketing and operations, is exposed to fluctuations in the World currency markets. Although it is a very lean organisation, orders do have to be placed some time ahead due to their size or value. Changes in exchange rates could leave the company exposed to potential loses in parts of its supply chain.
- Dell's commitment to customer value, to our team, to being direct, to operating responsibly and, ultimately, to winning continues to differentiate us from other companies. The Background section provides critical information and history about Dell's business world.
- SWOT Analysis Nike , Inc.
- Nike is a very competitive organisation. Phil Knight (Founder and CEO) is often quoted as saying that 'Business is war without bullets.' Nike has a healthy dislike of is competitors. At the Atlanta Olympics, Reebok went to the expense of sponsoring the games. Nike did not. However Nike sponsored the top athletes and gained valuable coverage.
- Nike has no factories. It does not tie up cash in buildings and manufacturing workers. This makes a very lean organisation. Nike is strong at research and development, as is evidenced by its evolving and innovative product range. They then manufacture wherever they can produce high quality product at the lowest possible price. If prices rise, and products can be made more cheaply elsewhere (to the same or better specification), Nike will move production.
- Nike is a global brand. It is the number one sports brand in the World. Its famous 'Swoosh' is instantly recognisable, and Phil Knight even has it tattooed on his ankle.
- The organisation does have a diversified range of sports products. However, the income of the business is still heavily dependent upon its share of the footwear market. This may leave it vulnerable if for any reason its market share erodes.
- The retail sector is very price sensitive. Nike does have its own retailer in Nike Town. However, most of its income is derived from selling into retailers. Retailers tend to offer a very similar experience to the consumer. Can you tell one sports retailer from another? So margins tend to get squeezed as retailers try to pass some of the low price competition pressure onto Nike.
- Product development offers Nike many opportunities. The brand is fiercely defended by its owners whom truly believe that Nike is not a fashion brand. However, like it or not, consumers that wear Nike product do not always buy it to participate in sport. Some would argue that in youth culture especially, Nike is a fashion brand. This creates its own opportunities, since product could become unfashionable before it wears out i.e. consumers need to replace shoes.
- There is also the opportunity to develop products such as sport wear, sunglasses and jewellery. Such high value items do tend to have associated with them, high profits.
- The business could also be developed internationally, building upon its strong global brand recognition. There are many markets that have the disposable income to spend on high value sports goods. For example, emerging markets such as China and India have a new richer generation of consumers. There are also global marketing events that can be utilised to support the brand such as the World Cup (soccer) and The Olympics.
- Nike is exposed to the international nature of trade. It buys and sells in different currencies and so costs and margins are not stable over long periods of time. Such an exposure could mean that Nike may be manufacturing and/or selling at a loss. This is an issue that faces all global brands.
- The market for sports shoes and garments is very competitive. The model developed by Phil Knight in his Stamford Business School days (high value branded product manufactured at a low cost) is now commonly used and to an extent is no longer a basis for sustainable competitive advantage. Competitors are developing alternative brands to take away Nike's market share.
- As discussed above in weaknesses, the retail sector is becoming price competitive. This ultimately means that consumers are shopping around for a better deal. So if one store charges a price for a pair of sports shoes, the consumer could go to the store along the street to compare prices for the exactly the same item, and buy the cheaper of the two. Such consumer price sensitivity is a potential external threat to Nike.
Cite this Page
SWOT Analysis: Toyota, Starbucks,. (2020, May 14). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/swot-analysis-toyota-starbucks/
Run a free check or have your essay done for you

More related essays
Introduction Starbucks is a famous coffeehouse. Until the mid-1980s it was only a provider of coffee to fine restaurants. Thereafter Howard Schultz, director of retail operations and marketing, was impressed.
In 1971, Starbuck’s opened its first location in the touristy Pikes Place Market in Seattle. The Starbucks name is derived from the coffee-loving first mate in the novel, Moby Dick..
When you think of a company that has been very successful what company comes to mind? In particular one chain that is available all over the world that has deemed.
Starbucks has a strong brand name and its known international. Starbucks was the first coffee shop whereby high quality coffee and products at accessible locationsand affordable prices, provided a community.
SOOT Struck A politicized margin indicates efficient cost management or a strong pricing strategy by the company. Overall, such a rise in the operating margin under tight consumer spending reflects Starboard's.
SWOT Analysis is the most renowned tool for audit and analysis of the overall strategic position of the business and its environment. Its key purpose is to identify the strategies.
Identification According to our analysis, Toyota is lacking corporate identity in its host country. Toyota is experiencing difficulty bridging the gap between its Japanese collectivist culture and the individualist culture of.
Purchasing & Materials Management| | Strategic Procurement & Supply Chain Management| Introduction The topic selected is (Strategic Procurement & Supply Chain Management). For this study, we have selected Toyota Motor.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy
Save time and let our verified experts help you.
Ohio State nav bar
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Change & Scanning Our Ecosystems with PESTLE Analysis

“We cannot change what we are not aware of, and once we are aware, we cannot help but change. ” Sheryl Sandberg
Our ability to change with intention requires well-informed awareness. This applies to change ranging from personal to organizational to societal. Intentionality requires us to pause, scan and be aware of the ecosystem surrounding us whether as:
- an individual in our personal lives, or
- a collective such as in our families, schools, workplaces, extra-curricular and faith-based organizations, communities or even broader as in state-wide, nationally or multi-nationally.
An individual or group pause to assess occurrences beyond our immediate, metaphorical walls are too often overlooked apart from high stake undertakings with sizable financial, social or human capital risk. When pause does occur, it may be heavily informed by our most recent or immediate experiences including emotion. We can become so immersed in daily routines and operations, and their related aches, that we place energy where it provides maximum near-term relief. While we must act for immediate relief during extenuating circumstances, like during crises, our actions can risk being premature or suboptimal in their impression.
When we pause with intention, it opens our awareness to what is impacting or even disrupting our circumstances. We can then thoughtfully contribute to action and resulting change that is more well-informed, effective and sustainable. Examples of where this change applies in the business environment is with strategy, business and operating plans.
The PESTLE Analysis tool is one of my favorites to leverage for a well-rounded pause and resulting analysis. It helps elevate the daily boots-on-the-ground experience to a more macro-level view of our current and emerging circumstances. While there is not agreement on who is fully responsible for this tool which evolved over decades, its roots are often credited to author and former Harvard Business School Professor Frank Agular .
While PESTLE Analysis is typically associated with business, its scalability extends its relevance from personal to multi-national application. That is, it can be used to assess contributors impacting change from those in our personal lives to our business organizations to the state or province in which we reside to our country and beyond.
So, what’s a PESTLE Analysis? A PESTLE is an analysis tool that guides assessment from an outside-in perspective across six dimensions including:
- P olitical,
- S ociocultural,
- T echnological,
- L egal, and
- E nvironmental.

While there are six dimensions, these can be considered in any order and change contributors may fluctuate. Each use captures a moment in time. During especially volatile or disruptive periods, more frequent pauses and resulting analyses may be merited to capture newly surfacing change disruptors.
A hypothetical example of change contributors within each dimension is below for business pertinence yet can be adapted to meet other application needs. For example, if one was using this to assess personal change disrupters at a macro level during or following the COVID pandemic, a marital divorce or separation, or during personal illness, the change contributors could be modified for personal relevance.

To take this a step further, PESTLE Analysis tool application can be as simple or complex as you desire and needs merit. For example, within each of the six PESTLE dimensions, you might focus on change contributors of greatest priority. You might also dive even deeper into each dimension and its related change contributor(s) by asking SWOT Analysis related questions like in the example below using the PESTLE dimension, Economic.

Applying SWOT Analysis as a next-level analysis tool essentially results in what is good or bad, or desired or undesirable, about today (i.e., the current state) and tomorrow (i.e., the future state). In considering resulting change and action, this can inform what we:
- leverage, continue, continuously improve or capitalize via identified S trength impacts;
- develop, remedy or continuously improve via identified W eakness impacts;
- pursue or reprioritize for greater investment via identified O pportunity impacts; and
- mitigate via identified T hreat impacts.
However you leverage PESTLE Analysis, adding it to your toolbox can offer practical, content-rich output so that we not merely react to change from awareness and necessity, but we respond to change through intention and thoughtful strategy.
Interested in learning more about this framework? Michelle Leedy will host a dynamic panel conversation with thought-provoking and experienced leaders from JPMorgan Chase, AEP, Grange Insurance, and Bath & Body Works at the COE Summit 2024.
The Ohio State University Center for Operational Excellence Summit, now in its 11th year, is a 3-day event dedicated to connecting diverse industries and organizations to the latest best practices in leadership and problem-solving. With 4 engaging keynotes, 20 breakout sessions, and exclusive opportunities for networking and hands-on learning, the COE Summit is a high-value opportunity to equip your team with tools and tactics to spark sustainable transformation.
Learn more and register for the COE Summit 2024

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- No HTML tags allowed.
- Lines and paragraphs break automatically.
- Web page addresses and email addresses turn into links automatically.
Related Posts

©2024 Fisher College of Business
2100 Neil Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 43210
If you have a disability and experience difficulty accessing this site, please contact us for assistance .
OpenID Connect login

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Toyota SWOT analysis. Strengths. Weaknesses. 1. Strong focus on research and development (R&D) leading to some of the most innovative vehicles in the world. 2. The most valuable and one of the most recognizable automotive brands. 3. Toyota Production System.
3. Manufacturing Defects. A high vehicle recall rate can immensely destroy an automaker's reputation, forcing customers to mass-migrate to its competitors. Toyota has a high recall rate and recalled about 3.9 million vehicles in 2020 due to fuel pump defects that can lead to stalling. 4.
Toyota is unveiling its revolutionary solid-state battery in 2021. The company claims the new battery pack will extend the maximum EV range to 500 km on a single charge. Plus, it charges from 0 to 100% in 10 minutes. What's even more impressive - Toyota developed the technology four years ahead of schedule.
Toyota a sustainable brand name and a market leader position. 7 3.3. SWOT Analysis Strengths: Strong market position and brand recognition: Toyota has a strong market position in different geographies across the world. The company's market share for Toyota and Lexus brands, (excluding mini vehicles) in Japan was 45.5% in FY2012.
Toyota SWOT Analysis. Posted on June 20, 2023 June 20, 2023 by Daniel Pereira. 20 Jun. Toyota, known worldwide, is a big shot in the automobile industry. The company has been around since 1937, growing from a small entity to an industry titan. Today, Toyota isn't just a name; it's a brand representing quality, reliability, and value for money.
SWOT analysis can be used for strategic planning for almost any kind of companies (Simerson, 2011). In this paper, it is going to be applied to the current situation of the Toyota Company that is still recovering from the major crisis that began in 2007. Although SWOT analysis cannot be used to provide a detailed description of the company's ...
Here is a SWOT analysis for Toyota: A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture's success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan.
Introduction. This SWOT analysis looks at Toyota, an automobile maker that now operates in nearly 200 countries around the world and is known for making fuel-efficient, economical vehicles, including cars, trucks, people carriers and sports utility vehicles. It is often viewed as being at the forefront of alternative fuel vehicles but has also ...
This SWOT analysis provides insights into the factors influencing the business and the realization of Toyota's mission statement and vision statement. The automaker's high performance serves as an indicator of its ability to address the issues enumerated in this SWOT analysis. This SWOT analysis shows that Toyota remains strong in the ...
Toyota's Strengths. Global presence- Toyota sells its cars in more than 170 countries and sells more than 9 million vehicles every year. The strong foothold over the market can provide it with a competitive edge. Strong financials- Toyota group generated $245 billion in revenue in 2021. It has a free cash flow of 10, 40,783 yen and it has an ...
Toyota Motor Corporation Strengths Global organization, with a strong international position in 170 countries worldwide. High financial strength (1997, sales turnover, £131,511 million), sales growth of 29.3%[1] Strong brand image based on quality, environmental friendly (greener), customized range. Industry leader in manufacturing and production. Maximizes profit through efficient lean ...
1.2. Introduction to Toyota For the Toyota SWOT analysis, it is crucial to know about its past and future planning.The Toyota Motor Corporation is a multinational automaker company founded in Toyota, Aichi, Japan. It started its journey back in 1937, and by 2017, it had 364,445 employees worldwide.
SWOT Analysis of Toyota. Toyota Motor was founded by Kichiro Toyota in the year of 1937 as a spinoff from his father's company Toyota Industries to manufacture automobiles. It is a Japanese automotive company, headquarter is in Toyota, Aichi, Japan. It's a multinational automotive company, and by March 2014 it consisted of more than 338,875 ...
1. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite This Essay. Download. Toyota Motor Corporation tends to the inward and outer key factors in the business, as distinguished in this SWOT analysis. The SWOT structure pinpoints the most critical ...
Toyota: SWOT Analysis, BCG Matrix and Porter's Five. Toyota is a Japan based company which was established in 1937 by Sakichi Toyoda and is the world biggest automobile manufacturers, Toyota has achieved a record sale of 9 million cars in five continents. Toyota is also ranked in the top ten 500² companies.
This SWOT analysis of Toyota offers a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of this popular brand. ... Toyota SWOT Analysis Essay. 2022/05/04 by Simon White Free SWOT Analysis. Last modified on May 6th, 2022. This is a free Toyota SWOT analysis available for all students. You should use it only as a reference.
Toyota's brand image was negatively affected by numerous recalls that had been made in the recent past. For instance, in 2011, Toyota recalled 111,000 models of Toyota and Lexus brands' cars due to the damage to parts of the substrate. Therefore, in 2013 the company's organizational business structure was altered.
Toyota Swot Analysis: SWOT Analysis Of Toyota. 1327 Words6 Pages. SWOT Analysis Strengths: 1. Brand recognition and strong position in the market - the market position of Toyota is strong and in different geographies across continents. In 2012, the market share is 45.5% for Toyota and Lexus brands in Japan. In Asia on the other hand has ...
Toyota SWOT Analysis. Organizational Analysis of the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats of Toyota Motor Corporation. Toyota Motor Corporation is one of the largest and most diversified auto manufacturers globally today, with supply chains and production systems that span across over 70 nations with sourcing, procurement and ...
The other framework in Toyota SWOT & PESTEL Analysis is the PESTLE Analysis. A PESTLE analysis is a crucial strategic tool that firms use to analyze various external factors affecting their business operations. Conducting Toyota's PESTLE analysis of external factors could go a long way to help identify opportunities and threats to help create ...
Toyota is world-renowned company manufacturing in vehicle making.Their cars are the most used cars in the world today, but it has its flaws. Toyota conducted a SWOT analysis to audit its company and its environment in order to make marketing decisions to maintain the value of its products. Toyota 's strength is valued to show how strong of a ...
Order custom essay SWOT Analysis: Toyota, Starbucks, with free plagiarism report. New investment by Toyota in factories in the US and China saw 2005 profits rise, against the worldwide motor industry trend. Net profits rose 0.8% to 1.17 trillion yen ($11bn; .85bn), while sales were 7.3% higher at 18.55 trillion yen.
Toyota-Strengths. Published 2022/05/04 at 1920 × 1080 in Toyota SWOT Analysis Essay.
A PESTLE is an analysis tool that guides assessment from an outside-in perspective across six dimensions including: P olitical, E conomic, S ociocultural, T echnological, L egal, and. E nvironmental. While there are six dimensions, these can be considered in any order and change contributors may fluctuate. Each use captures a moment in time.