Excel at Science
- Feb 16, 2021

AP Biology Past FRQs by Topic
Updated: Jan 31

**Updated on 1/31/24 to include the 2022-23 FRQ exams!**
If you are looking for past AP Biology free-response questions (FRQs) that are organized by topic, then you have come to the right place. In this post, we have linked every freely available past FRQ there is from College Board and organized it into the following major topics of AP Biology .
(Please note that we are not associated with College Board and are simply sharing the resources they have made available to students.)
Biochemistry
Metabolism & energetics.
Physiology (note that this topic will not be tested on the official AP Biology exam this year in 2021, although many questions about physiology could also cover concepts that will be tested)
Experiment design & data analysis
Need more AP-style practice problems?
Intensively doing and reviewing practice questions is proven to be much more effective than spending hours studying. Check out our AP Bio Practice Portal , which is an easy-to-use database of 300+ AP-style MCQ and FRQ practice questions. Students love the Practice Portal because it includes answers and explanations for every problem, tracks progress, and saves time from Googling practice problems.
Try the Practice Portal >
How to make the most of past frqs from college board.
As noted above, the diversity of organisms, plants, and physiology will not be on the 2021 AP Biology exam. However, the exam could include questions about topics or hypothetical situations that are related to those topics. One great example is cell communication, which is used in multiple systems inside our bodies. Let’s say an FRQ was to appear about the immune system and how the immune cells communicate. That would be fair game as long as the question focuses on the cell signaling part, not the details of the immune system. If the question requires some background knowledge about the immune system, it will be provided.
If you want to do a whole practice FRQ set just like the ones on the real exam (which we highly recommend), all the freely available past FRQs by year are available here on the College Board website. Tip: time yourself and take the practice FRQ set in an environment that mimics how you imagine your actual testing environment to be.
If you would like to focus on a particular topic, then the section coming up is for you. Some FRQs will show up under multiple topics because they truly do test students’ understanding of multiple different topics.
Tip : Whether you are doing individual free-response questions or doing a full problem set in one go, it is extremely important and effective to do test corrections! Don’t only consult the scoring guidelines and model responses when you have no clue how to answer a question. You should be checking them for all the FRQs you do. When you find a difference between your answer and the scoring guidelines, it is important that you pause and analyze why your response is incorrect. Take the time to understand your mistakes and see how your answer could have been better. This will help you boost your scores the most efficiently.
AP BIOLOGY FRQs BY TOPIC
Below are the linked FRQs organized by topic. The header for each topic will also lead you to the corresponding study guide that will help you review the unit in detail!
Basic and organic chemistry concepts do not come up often on the FRQs (but of course, it’s better to be prepared). The properties of water and macromolecules come up occasionally.
2017 #7 and 8
Includes cell structure and function, cell transport and the proteins involved.
2019 #3 and 8
2018 #2, 6, and 8
2006 #1, 3, and 4
2001 #1 and 4
(study guide coming soon!)
This unit includes enzymes, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis.
2023 #2 (cell respiration & photosynthesis)
2023 #4 (photosynthesis)
2022 #3 (enzymes)
2021 #3 (cell respiration)
2019 #3 (cell respiration)
2018 #2 (cell respiration)
2017 #7 (cell respiration)
2017 #5 (photosynthesis)
2015 #2 (cell respiration)
2013 #2 (photosynthesis) and 4 (cell respiration & photosynthesis)
2012 #2 (cell respiration) and 4 (cell respiration & photosynthesis)
2010 #2 (enzymes)
2007 #3 (photosynthesis)
2006 #4 (photosynthesis)
2005 #1 (cell respiration & photosynthesis)
2004 #3 (photosynthesis)
Cell cycle & cell signaling
This topic has shown up more frequently and in more difficult FRQs in recent years, especially cell communication. The trend will most likely continue so definitely prioritize reviewing and practicing this topic!
2023 #1 (cell communication)
2022 #1 (cell communication)
2022 #2 (cell cycle, meiosis)
2021 #1 (cell communication)
2019 #4 (cell communication)
2018 #8 (cell communication)
2017 #8 (cell communication)
2016 # 7 (cell division)
2015 # 4 (cell division)
2015 #5 and 7 (cell communication)
2013 #8 (cell communication)
2011 #1B (cell division)
2010 #1 (cell communication)
2006 #1B (cell division)
2004 #1 (cell division)
Genetics, Gene Expression and Regulation
Genetics Pt 1 and Genetics Pt 2 Study Guides
This section includes the classic Mendelian genetics, with Punnett squares, crosses, and Mendel’s laws. It also includes DNA replication, protein synthesis, and gene expression regulation for both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
2023 #6 (gene expression)
2022 #6 (protein synthesis, gene expression)
2021 #6 (gene expression)
2021 #2 (heredity + pedigrees)
2020 #1 parts a-b
2019 #1 and 3
2018 #1, 4, and 7
2016 #4 and 7
2023 #5 (Cladistics)
2022 #4 (speciation)
2020 #1 parts f-j
2015 #3 and 6
2014 #2 and 4
2015 #2 (nervous system)
2014 #2 (immune system) and 6 (musculoskeletal system) and 7
2017 #2, 4, and 7b
2016 #3 and 5
2014 #3 and 4
Experimental design & analysis
This is an additional section that isn’t focused on any particular topic or has significant data analysis involved. While most FRQs do pertain to a specific topic(s), some are simply there to test your knowledge of experimental design and understanding of statistical concepts such as performing Chi-Square tests and interpreting error bars on graphs. These types of questions have become more and more common on the AP exam, so it is important to feel comfortable and confident with them.
2023 #6 (data analysis)
2022 #3 (experiment design)
2020 #1 parts c-e
2016 #2 , 6 and 8
2014 #1 and 5
2013 #1 and 7
Hope these organized FRQs saved you some time so you can focus more on actually doing them and practicing! You can easily share this post with friends who may find it helpful as well.
How to Improve AP Biology FRQ Scores, Fast
Do a lot of FRQ practice problems and review the answers! Practice is key, especially for a subject as dense as AP Bio. Check out the AP Bio Practice Portal , which is our popular vault of 300+ AP-style MCQ and FRQ problem sets with answers and explanations for every question. Don't waste any more time Googling practice problems or answers - try it out now!
Recent Posts
How to Study for AP Biology Finals: Tactical Strategies for Success
How to Interpret Diagrams and Graphs on AP Biology Exams
How to Get a 5 on the AP Biology Exam: A Comprehensive Study Guide
ความคิดเห็น

AP Biology Practice Test: Unit 2 — Cell Structure & Function
Congratulations - you have completed .
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Which structure-function pair is incorrectly matched?
Which of the following statements regarding the nucleus is false, which part of the cell allows the cell to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with its environment, which statement is true of both mitochondria and chloroplasts, which of the following is not part of the endomembrane system, which group of organelles works together to regulate protein traffic and performs metabolic functions of the cell, although animal cells lack cell walls, they have a complex network of glycoproteins that provide structure and strength to the cell, referred to as:, which group of cellular structures form the endomembrane system, white blood cells engulf invading bacterium in a process called:, which description best matches the diagram.
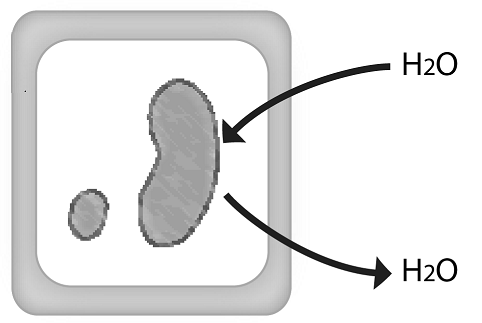
Which diagram below shows the correct order diffusion of solute in water across a membrane?
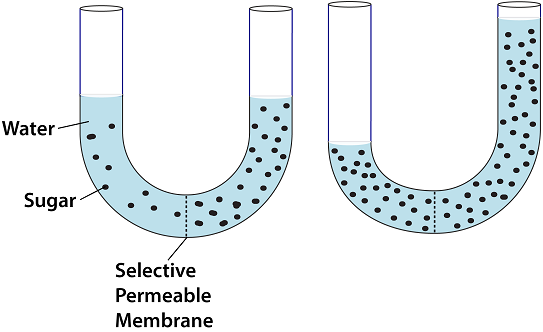
Which answer correctly describes what is happening in the following diagram.
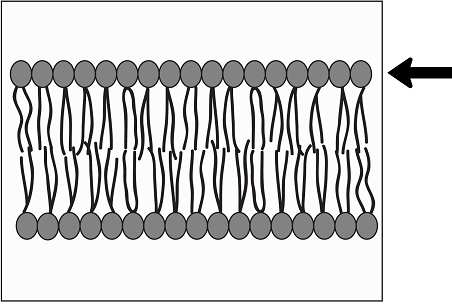
In the diagram below, what is the arrow pointing to?
Which of the following statements is not true of a plasma membrane protein:
Which of the following is an example of active transport used by the cell to maintain internal concentrations of small solutes different form concentrations in the environment, how do large particles, such as proteins and polysaccharides, generally cross the plasma membrane into cells, what cellular structure is responsible for its selective permeability, the pumping of substances across a membrane against the direction of spontaneous movement is which type of work, which of the following is not a type of intracellular junction in animal cells.
Next Practice Test: Cellular Energetics >> AP Biology Main Menu >>
AP® Biology
Unit 1 | chemistry of life, long free response, on fertile ground, unit 2 | cell structure and function, short answer free response, osmoregulation in fish, properties of the cell membrane, salty celery, structure vs. function in the fluid mosaic model, urine for a surprise, water potential, bacteria, and osmosis, compartmentalizing of eukaryotic cells, why it's separate, transpiration with changing environmental conditions, unit 3 | cellular energetics, determining pigment activity, mechanisms of cellular respiration, the effects of kelp on the $\text{ph}$ of disko bay, the evolution of energy, factors affecting the rate of enzyme function, intricacies of mitochondria and aerobic respiration, photosynthetic rate, common chemiosmolarity, energy in systems, factors affecting transpiration, the respiration of peas, unit 4 | cell communication and cell cycle, analyzing hormone signaling in cells, investigating the cell cycle, cell communication, pcb exposure as a selective pressure, from one to the next, unit 5 | heredity, familial hypercholesterolemia, huntington's disease, deer of a different color, pedigree: it's more than a dog food, genetic variation, ironing out the mechanics of genetic disorders, unit 6 | gene expression and regulation, analysis of data for chlamydomonas reinhardtii, bacterial restriction map analysis, polymerase chain reaction, everybody's shuffling, levels of control, pass it down, genetic engineering using bacteria, controlling hiv, methods of bacterial transformation, paternal dna identification, thermosensitivity and sex determination, a tale of two regulation types, there is more than denim in your genes, maternal care and acth level in rats, unit 7 | natural selection, evolution of the horse, mouse evolution, rounding up unwanted plants, common ground among cells, evolution of the arctic hare, allele frequencies and effects of mutation on hiv resistance | 1 of 2, allele frequencies and effects of mutation on hiv resistance | 2 of 2, explain evolution in a population of galapagos finches, exploring hardy-weinberg equilibrium, in defense of evolution, evolutionary comparisons using myoglobin dna sequencing, cat evolution and ancestry, unit 8 | ecology, crazy ants and ecosystem disruption, creeping of the kudzu, garlic mustard invasion, it's all connected, the new species in town, determining energy consumption based on metabolic lifestyle, 24 days of growth, fruit fly kinetics, symbiotic gut microbes and digestion, the trophic cascade and ecological change, energy transfer in deep sea communities, rise of the lichens, directional selection and body mass of white-tailed deer.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Unit 1: chemistry of life, unit 2: cell structure and function, unit 3: cellular energetics, unit 4: cell communication and cell cycle, unit 5: heredity, unit 6: gene expression and regulation, unit 7: natural selection, unit 8: ecology, unit 9: worked examples of ap®︎ biology free response questions, unit 10: ap®︎ biology standards mappings.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 4 top tips to make ap biology frqs a breeze.
Advanced Placement (AP)

AP Biology is known for being one of the tougher AP exams , and, for most students, the free-response section is the hardest part of the test. In 2021 , the average score for every free-response question was less than a 50%! However, knowing what to expect can make it easier to get a great score on AP Biology FRQ. And in this guide, we explain everything you need to know to ace this section. Read on to learn the format of AP Biology FRQ, what graders are looking for, what the questions will look like, and what you can do to be well-prepared on exam day.
What's the Format of the AP Biology Free Response Section?
The AP Biology exam has two sections: multiple choice and free response. The free-section comes second and contains six questions:
- Two long-response questions , both with a focus on analyzing experimental results. The second long question will require you to create a graph.
- Four short-answer questions on the following topics in this order:
- Scientific Investigation
- Conceptual Analysis
- Analysis of Model or Visual Representation
- Analysis of Data
Additionally:
- The free-response section is 90 minutes long
- It's worth 50% of your total score
- You're able to use the AP Biology formula sheet for the entire section
Long questions are worth 8-10 points each, whereas short-answer questions are each worth 4 points. It's recommended that you spend about 25 minutes on each long question and about 10 minutes on each short question (although you'll decide yourself how long you spend on each question).
The AP Biology test expects you to know how to:
- Understand how graphical and mathematical models can be used to explain biological principles and concepts
- Make predictions and justify events based on biological principles
- Implement your knowledge of proper experimental design
- Interpret data
AP Biology Sample Free Response Questions
Now we'll go through two AP Biology free response example questions: one long question and one short question. These questions both were used for the 2021 AP Biology exam . You can see answers and scoring for each of the 2021 AP Biology FRQs here .
Long Question
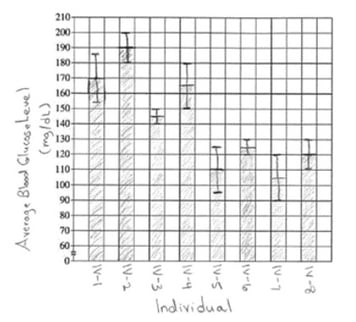
First let's look at one of the long questions. This is Question 2, so remember you'll need to create a graph for at least one part of it. The entire question is worth 8 points.
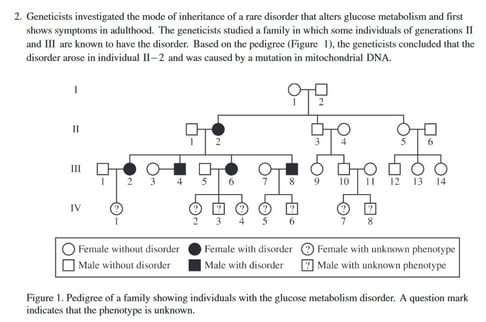
Part A (1 point)
Part B (4 points)
First, you need to create a graph based on the data in Table 1. The graph is worth 3 points: 1 for axis labels, 1 for the correct plotting in the bar graph, and 1 for the error bars. Here's an example of a graph that would get full points:
Part C (1 point)
Part D (2 points)
- The data do not support the claim because females III-2 and III-6 have the disorder and, if inheritance was X-linked recessive, they'd only have the disorder if their father II-1 had the disorder, which he does not.
- The data supports mitochondrial inheritance because all of the offspring of individual II-2 , not just the sons, have the disorder.
Giving one of those answers is worth one point.


Short Question
Next is a short question. It's question 3 in the free-response section which means it will focus on scientific investigation. It's worth a total of four points.

Part B (1 point)
- The researchers must run the experiment without adding resveratrol.
- The researchers must treat the cells with DMSO alone.
There are two potential answers; you only need to include one:
- No ATP production
- Reduced ATP production
Part D (1 point)
For Part D, you must state that more electrons can be transferred so that more oxygen is required as the final electron acceptor.
Where to Find AP Biology FRQs
Taking practice tests and answering practice questions is one of the best ways to prepare for any AP exam, including AP Biology FRQs. Fortunately, the College Board, who creates and administers AP courses and exams, has made dozens of old AP Bio FRQs available for free online. Because there are so many official FRQs available, we recommend only using them instead of looking online for unofficial questions (those not created by the College Board), which can be hit or miss in terms of quality. However, if you're using an AP Biology prep book, they often have solid FRQs. For advice on which prep book to get, check out our guide on the best AP Biology prep books.
Here are links to the FRQs:
Additionally, the AP Biology Course and Exam Description includes two up-to-date FRQs, beginning on page 206.
Note that, until 2020, the AP Bio exam had six short-answer questions instead of the current four. This means that questions from 2019 and earlier will have a different format and slightly different content. They can still be useful to study, but be aware of the differences between them and the current free-response section.

4 Tips for AP Biology FRQs
When you're studying for AP Bio FRQs and actually taking the exam, there are a lot of things to remember to ensure you do your absolute best. Keep these four tips in mind throughout the year and on exam day.
#1: Know Your 13 Required Labs
There are 13 labs you're required to complete during the AP Biology course. Questions that relate at least in part to these labs make up 25% of the AP Biology exam. It’s important to understand how these labs are conducted and how the principles behind them relate to the main ideas of the course. This will help in answering both free-response and multiple-choice questions that deal with lab scenarios on the test. There's a nice overview of each of the 13 labs on this site that can refresh your memory, and we link to in-depth explanations of each of the labs in our AP Biology study guide .
You should also know general lab skills. Many free-response questions ask you to identify the components of a proposed experiment (dependent and independent variables) or to design a lab to test a certain hypothesis. You might have forgotten about the labs you did toward the beginning of the year, so take extra care to go over them. Make sure that you understand just how they were conducted and what the results mean.
#2: Eliminate Irrelevant Information
Free-response AP Biology questions (especially the long questions) include lots of scientific terminology and visual aids, and this kind of format might be intimidating if you’re not used to it. It’s important to practice sorting through this jumble of information so that you can quickly get to the root of the question rather than obsessing over small details you don’t understand.
Try underlining important words and phrases in the question to help you stay focused on the main points and avoid misleading distractions.
You should also practice responding to free-response questions in a straightforward way without any unnecessary fluff. Remember, this isn’t an English test; the graders are just looking for clear facts and analysis. Make it easy for them to give you points!
#3: Draw During Studying
If you're feeling shaky on your knowledge of a process or system in AP Biology, one helpful strategy is to draw it. This will both reinforce what you know and highlight what you still need to work on learning. Once you're able to draw an accurate diagram of a system or process without looking at your notes, you can feel confident that you know exactly how it works.
For example, you could challenge yourself to draw a diagram of a cell membrane, label its different components, and explain their significance. You could also draw a process like mitosis that happens in clear visual stages, or a more complex process like cellular respiration where you might focus on one aspect at a time (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain). You can also apply this tip during the exam, if you need help visualizing part of an AP Bio FRQ.
#4: Pay Attention to the Clock
Time is always tight on AP exams. For the AP Biology free response section, you get 90 minutes to answer six questions. It can be easy to get caught up on one question and suddenly realize you're nearly out of time but haven't had a chance to look at some of the questions, let alone answer them. Don't let this happen to you! We recommend spending 25 minutes on each of the two long questions and 10 minutes on each of the four short questions. You don't need to keep perfectly to that plan, but don't get too far off it, either.
At the very least, make note of where you are halfway through the free-response section (that's 45 minutes in). If you're roughly halfway finished with the section (taking into account that long questions take about twice as much time to complete as short questions), you're doing well. If you're significantly behind that, you know you need to pick up the pace.
Also, don't feel you need to answer the FRQ in the order they're listed. We recommend skimming through each of the questions at the start of the section, then tackling the questions that seem easiest first so you can spend more time on trickier questions.
Summary: Acing the AP Biology Free Response Section
The AP Biology free-response section can be tough, but if you prepare well for it, you can go into exam day confident and knowing what to expect. The section consists of two long questions and four short questions, lasts 90 minutes, and is worth half of your total score. You'll need to create a graph for the second AP biology FRQ. Old exam questions are a great study resource and, when you're preparing for the free-response section, keep these four tips in mind:
- Know your labs
- Eliminate irrelevant information
- Make drawings while studying
- Stay aware of time
What's Next?
How should you study for the AP Biology exam? Our expert article goes over all 5 steps to take during your AP Biology review.
What is the rest of the AP Biology exam like? Our article on the AP Biology exam goes over every question type you can expect to see as well as tips for answering them.
Looking for an easier AP class than Biology? Learn which AP classes tend to be the least challenging for students .
Looking for help studying for your AP exam?
Our one-on-one online AP tutoring services can help you prepare for your AP exams. Get matched with a top tutor who got a high score on the exam you're studying for!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Find what you need to study
Unit 2 Overview: Cell Structure and Function
6 min read • december 31, 2022
Tejas Bhartiya
Jed Quiaoit
This unit is all about the cell and parts of the cell!
Image from howstuffworks
Subcellular and Organelle Components
Subcellular and organelle components are especially important to know because they pop up throughout the year. All organelles are essential, and students must understand all of them. However, the most critical organelles are: 🍿
Ribosomes: composed of ribosomal RNA and protein. They help to synthesize proteins. All forms of life have ribosomes, which demonstrates common ancestry 👨👩👧👦.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): provides mechanical support and plays a role in intracellular transport. There are two kinds of ER, rough and smooth. 🚕
Rough ER: helps to compartmentalize the cell and helps to carry out protein synthesis in the ribosomes.
Smooth ER: helps in detoxification and lipid production, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Golgi Complex: a membrane-bound organelle that is composed of several flattened membrane sacs called cisternae. The Golgi is vital in the final stages of preparing a protein. A newly made protein will get help in correctly folding and modifying as needed. The Golgi also helps in packaging proteins and sorting them before transport. 📦
Mitochondria: helps with ATP production. It has a small set of its own DNA 🧬 and is a double membrane organelle. The outer membrane is a smooth phospholipid bilayer. The inner membrane is highly convoluted, meaning it is highly folded, which increases the surface area for a growing number of electron transport chains. The increase in surface area facilitates the production of ATP.
The mitochondria is the site where cellular respiration occurs. Glycolysis is the first step in cell respiration and occurs with or without oxygen present and shows common ancestry. After the completion of glycolysis, the rest of cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria, given that oxygen is present. The Citric Acid/Kreb’s Cycle happens in the matrix of the mitochondria, and oxidative phosphorylation, with the help of the electron transport chain, occurs in the inner membrane. 💨
Image from Micromagnet
Lysosomes: membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes. These enzymes are digestive enzymes that help to break down excess or worn-out cell parts. The lysosomes also help with programmed cell death, known as apoptosis. 🚮☠️
Vacuole: a membrane-bound sac that has many different roles, including storage and release of macromolecules and waste . Plants have a specialized large central vacuole that also serves many functions. The primary function of the large central vacuole is water retention. Water retention is important in turgor pressure, which helps to maintain the rigidity and function of plant cells. 🌱
Chloroplasts : photosynthetic algae and plants contain these specialized organelles that can photosynthesize (capture, store, and use solar energy ⚡️) and make simple sugars. Chloroplasts have a double membrane and thylakoids that are flattened sacs with a phospholipid bilayer.
Chloroplasts are the site where photosynthesis occurs. The two stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent ☀️reaction and the light-independent reaction. The light-dependent reaction occurs in the grana and produces the ATP and NADPH necessary for the light-independent reaction. The light-independent reaction is where the Calvin-Benson cycle takes place and carbon is fixed to make simple sugars. 🌓
🎥 Watch: AP Bio - Cell Structure: Cellular Components
Image from biologydictionary .
Cell size is a concern because surface area-to-volume ratios affect the ability of a biological system to obtain necessary resources, eliminate wastes, pull in or remove heat energy, and exchange materials with the environment. 🤲
🎥 Watch: AP Bio - Cell Size
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer, composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules, with the hydrophobic tails facing inward and the hydrophilic heads facing outward. The arrangement of the phospholipids in the bilayer creates a semi-permeable barrier that selectively allows certain molecules to pass through while preventing others from entering or leaving the cell.
The plasma membrane is not a static structure and is constantly undergoing changes in response to various signals and stimuli. Many proteins are embedded in the membrane, and these proteins play a number of important roles in the cell. Some proteins are involved in cell recognition, helping the cell to communicate and interact with other cells. Others act as channels or pumps, allowing specific molecules to pass through the membrane. Others help to maintain the structural integrity of the membrane, providing rigidity and support.
The movement of molecules across the plasma membrane is regulated by the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of the phospholipids. Small, nonpolar molecules like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide can freely pass through the membrane, while larger, polar molecules and ions need the help of proteins to cross the membrane. Water is a small, polar molecule that can move across the membrane in small quantities, but it needs the help of aquaporins and other proteins to cross the membrane in larger amounts.
Image from Biology Dictionary .
🎥 Watch: AP Bio - Plasma Membrane
Membrane Transport
In order for a cell to function properly, it's important for the internal environment to be maintained in a way that is conducive to the life and function of the cell. To do this, materials must be able to move in and out of the cell as needed, and this movement is facilitated by the plasma membrane. The movement of molecules across the plasma membrane occurs through a process called membrane transport.
Depending on the type of molecule being transported, the cell may need the help of a transport protein to facilitate its movement across the membrane. Transport proteins are specialized proteins that are embedded in the plasma membrane and are responsible for the movement of specific molecules across the membrane. There are different types of transport proteins, including channels, pumps, and carriers, which work to transport molecules in different ways. There are several different types of membrane transport:
Passive Transport means that the molecules are moving from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Energy is not required in passive transport. ⚡️
Active Transport means that the molecules are moving from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration and will require energy use.
Endocytosis is the process of taking bulk material into the cell.
Exocytosis is the process of removing bulk material out of the cell.
Image from Wikibooks
🎥Watch: AP Bio - Membrane Transport
Tonicity and Osmoregulation
Water moves by osmosis from high water potential (low osmolarity, low solute concentrations) to low water potential (high osmolarity, high solute concentrations.) Osmoregulation maintains water balance and allows organisms to control the internal environment. Remember, the movement of water in osmosis will always occur in a way that brings the concentration of solute to equilibrium! More on this below. 💦
Image from wikipedia .
🎥 Watch: AP Bio - Tonicity and Osmoregulation
Image from LibreTexts .
Image from apcentral .
Water potential is the tendency for water to move in one direction or another. In this case, osmoregulation allows cells to maintain their internal solute balance. These two equations are used to find the solute concentration inside a cell and the tendency that water will leave the cell. As evolution has occurred, cells have changed and have been altered. One thing that helps cells to be able to take care of different processes inside the cell is the membrane and organelles that have membranes as well. The endosymbiotic theory is where organelles that were once free-living prokaryotic cells became engulfed and serve a purpose now inside the cell. The endosymbiotic theory is summarized below. (Click on the image to see a larger version)
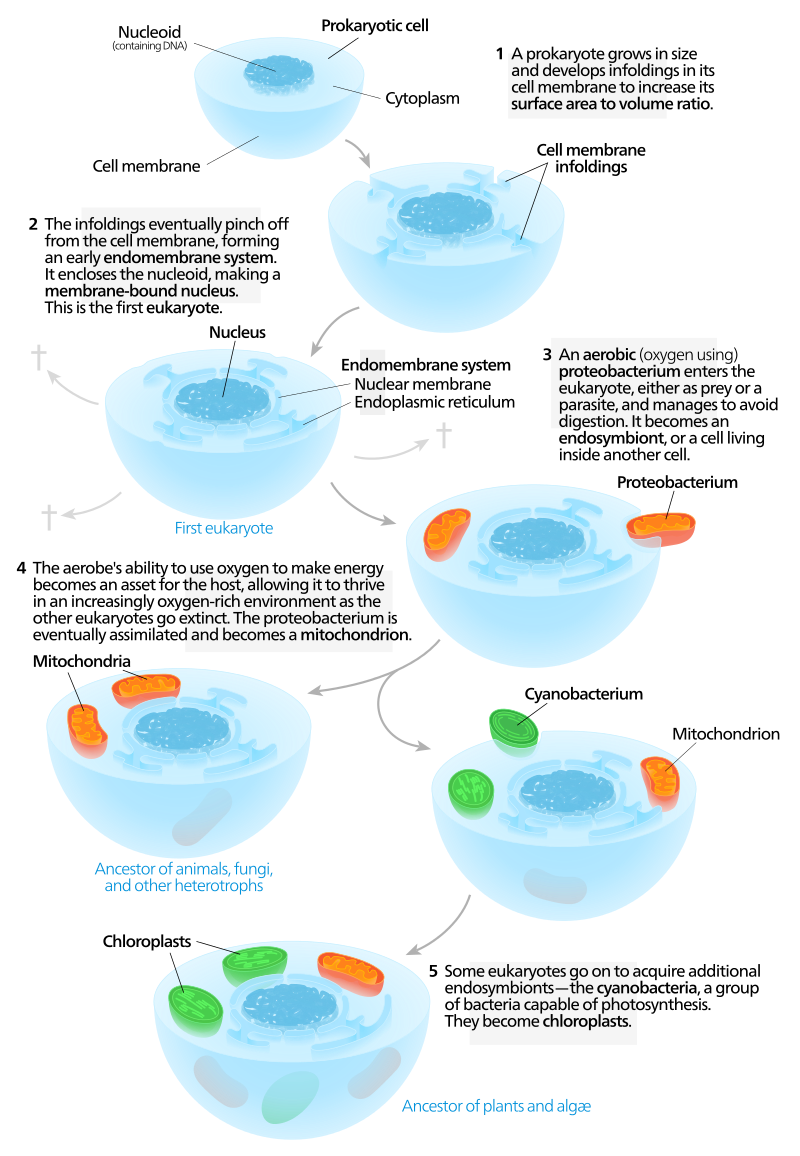
Image from Wikimedia

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.

COMMENTS
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. Organisms obtain nutrients and eliminate waste products efficiently by maintaining high surface area to volume ratios at the cellular level. Explain this statement using mathematical evidence and describe ONE specific example in a plant OR animal structure that increases the surface area of a cell., 2. Eukaryotic cells are ...
Question 1 During an investigation of a freshwater lake, an AP Biology student discovers a previously unknown microscopic organism. Further study shows that the unicellular organism is eukaryotic (a) Identify FOUR organelles that should be present in the eukaryotic organism and describe the function of each organelle.
Directions: Questions 1 and 2 are long free-response questions that require about 25 minutes each to answer. Questions 3 through 6 are short free-response questions that require about 10 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and completely. Answers must be written out in paragraph form.
Free-Response Questions. Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at ssd@info ...
Directions: Questions 1 and 2 are long free-response questions that require about 25 minutes each to answer. Questions 3 through 6 are short free-response questions that require about 10 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and completely. Answers must be written out in paragraph form.
AP Bio Free Response Question Answers for Intercellular Transport. 👋 Welcome to the AP Bio Unit 2 FRQ (Intercellular Transport) Answers. Have your responses handy as you go through the rubrics to see how you did! ⏱ Remember, the AP Biology exam has 6 free-response questions, and you will be given 90 minutes to complete the FRQ section ...
After you finish, you can see how you did with Unit 2 FRQ (Intercellular Transport) Answers . ⏱ The AP Biology exam has 6 free-response questions, and you will be given 90 minutes to complete the FRQ section. (This means you should give yourself ~15 minutes to go through each practice FRQ.)
Free Response Practice Submission 1. a) The K+/H+ transport protein is responsible for the increase in the pH of the vacuole during flower opening. It changes the pH of the vacuole by moving the H+ ions in and out of it, and pH is a measure of the concentration of H+ ions (inverse relationship). b) The changing concentrations of the K+ and H+ ...
**Updated on 1/31/24 to include the 2022-23 FRQ exams!**If you are looking for past AP Biology free-response questions (FRQs) that are organized by topic, then you have come to the right place. ... This unit includes enzymes, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis. 2023 #2 (cell respiration & photosynthesis) 2023 #4 (photosynthesis)
Directions: Questions 1 and 2 are long free-response questions that require about 25 minutes each to answer. Questions 3 through 6 are short free-response questions that require about 10 minutes each to answer. Read each question carefully and completely. Answers must be written out in paragraph form.
A. May aid in the transport of materials from one side of the membrane to the other. B. Membrane proteins of adjacent cells may hook together in various kinds of junctions. C. May be an enzyme or series of enzymes involved in metabolic pathways. D. May be a membrane carbohydrate used for cell-to-cell recognition.
AP BIO Unit 2 Released FRQs. 2017 BIOLOGY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 8. Estrogens are small hydrophobic lipid hormones that promote cell division and the development of reproductive structures in mammals. Estrogens passively diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to their receptor proteins in the cytoplasm of target cells.
Original free-response prompts for AP® Biology that mimic the questions found on the real exam. Our expert authors also provide an exemplary response for each AP free response question so students can better understand what AP graders look for. ... Unit 4 | Cell Communication and Cell Cycle. Short Answer Free Response. 2 questions. Analyzing ...
Study guides & practice questions for 11 key topics in AP Bio Unit 2 - Cell Structure & Function ... Unit 2 FRQ (Intercellular Transport) Answers. 2 min read. ... AP Biology Cram Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function. slides by Kari Parnin. 🌶️ AP Bio Cram Review: Unit 3: Cellular Energetics ...
Learn AP Biology using videos, articles, and AP-aligned multiple choice question practice. Review the fundamentals of biochemistry, cell biology, genetics, evolution, and ecology, and develop scientific thinking skills as you explore the study of life.
Pedigree of a family showing individuals with the glucose metabolism disorder. A question mark indicates that the phenotype is unknown. TABLE 1. AVERAGE BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS OF INDIVIDUALS IN GENERATION IV. Individual − − 12. Average Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL 170 190 ± 145 ± 15 ± 2SEX ) IV. 10. IV − 3.
AP Biology is known for being one of the tougher AP exams, and, for most students, the free-response section is the hardest part of the test.In 2021, the average score for every free-response question was less than a 50%! However, knowing what to expect can make it easier to get a great score on AP Biology FRQ. And in this guide, we explain everything you need to know to ace this section.
AP Bio Unit 2 Free Response. (1Q1a) Role of PHOTORECEPTOR IN RETINA OF EYE in responding to light-dark stimuli. Click the card to flip 👆. detects light/dark stimuli and intiates/transmits signal. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 12.
Some proteins are involved in cell recognition, helping the cell to communicate and interact with other cells. Others act as channels or pumps, allowing specific molecules to pass through the membrane. Others help to maintain the structural integrity of the membrane, providing rigidity and support.
AP Classroom AP Biology Unit 2 Progress Check MCQ Questions with Answer Key and Explanations Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. ... Biology Unit 2 Progress Check: FRQ. 8 terms. Seb1282. Preview. AP Bio Unit 3 MCQ. 20 terms. N111ancy. Preview. Gene Expression and Regulation. 12 terms. hannabordage. Preview. Bio1020 Lab Exam.