Stress and Its Effects on Health Essay
Introduction, physical effects, psychological effects, behavioral effects.
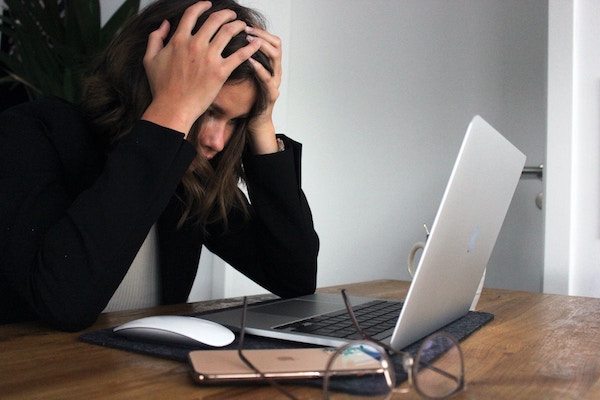
Stress is the emotional strain or tension experienced by an individual due to a reaction toward various demanding and influential situations. The challenging or compelling situations are termed stressors. Stressors can be internal or external and include life changes such as losing a significant figure, low socioeconomic status, relationship problems, occupational challenges, and familial or environmental factors. An individual’s response to stressors influences the outcome of their life. Health is a state of complete social, emotional, and physical well-being and not merely the absence of disease. Stress is a common risk factor for negative health status secondary to negative adaptation and coping with the stressors. Stressors can create a strain on one’s physical, psychological and behavioral well-being, leading to lasting effects that are detrimental to one’s health.
Stress is associated with various physical health impacts on an individual. In an online cross-sectional survey by Keech et al. (2020) to determine the association between stress and the physical and psychological health of police officers, the findings illustrate that stress negatively impacts physical and psychological well-being. One hundred and thirty-four police officers were involved in the study (Keech et al., 2020). The findings demonstrate that stress resulted in various short and long-term physical effects that included increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. In addition, stress resulted in the development of gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer and irritable bowel syndrome. Keech et al. (2020) note that stress’s associated physical health effects are explained by various mechanisms that include overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis.
Overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system results in increased sympathetic actions on the peripheral body organs leading to increased sweat production, heart rate, respiration rate, and urinary and bowel elimination. The study notes that chronic stress without positive adaptation measures results in the progressive development of hypertension, peptic ulcers, and irritable bowel syndrome as long-term effects (Keech et al., 2020). Within the gastrointestinal tract, chronic stress activity on the sympathetic nervous system results in increased parietal cell action. Overactivity of the parietal cells results in excessive gastric acid production, gradually eroding the mucosa, and ulceration occurs.
The effects of stress on the cardiovascular system are explained in a review by Kivimäki & Steptoe (2017) to determine the impact of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. In the review, stress is identified to cause cardiovascular conditions secondary to the effects of sustained sympathetic action on heart contractility and peripheral vascular resistance (Kivimäki & Steptoe, 2017). The sympathetic nervous system contributes to normal heart and blood vessel contractility. However, when the system is overstimulated, a surge in contractility above the normal limits ensues, leading to the progressive development of heart conditions.
Psychological well-being incorporates a positive mental health status evidenced by an individual’s satisfaction with life, happiness, rational thinking and decision-making, and positive mood patterns. Stress has been associated with alterations in an individual’s psychological wellness. An explanation for alteration in an individual’s psychological well-being secondary to stress is negative adaptation. Keech et al. (2020) note that an individual’s response to a stressor determines whether stress results in positive or negative effects. In the online cross-sectional survey by Keech et al. (2020), the findings illustrate that pressure resulted in the development of anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorders as long-term effects among the participants. Exposure to stressful situations resulted in progressively developing anxiety among the individual secondary to persistent worry over the issue. The anxiety results in other physical manifestations, including increased heart rate, palpitations, sweating, and altered mobility. Depression and bipolar conditions were also associated with chronic stress secondary to the impacts of stress on neurotransmitter function and nerves.
Similar findings are noted in a cross-sectional study by Zhang et al. (2020) to compare the prevalence and severity of stress-associated mental health symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and insomnia among healthcare workers during the COVID pandemic. Five hundred and twenty-four healthcare workers were involved in the study. The study findings illustrate that 31.3% of the participants developed depression secondary to the stressful working environment, 41.2% reported anxiety, and 39.3% reported sleep disturbances (Zhang et al., 2020). The scientific explanation for the relationship between stress and depression was attributed to the effects of stressful periods on neurotransmitter homeostasis. Chronic stress results in the altered regulation of neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. Alterations in serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine resulted in the progressive development of depression and anxiety. Sleep disturbances reported by the participants are attributed to alterations in cortisol hormone homeostasis secondary to overstimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis.
Stressful situations can also lead to alterations in the behavioral patterns of an individual. The most common behavioral effects secondary to stress include the development of eating disorders, altered sleeping patterns, impaired concentration, and drug abuse especially alcohol. Alterations in sleep and eating patterns are linked to stress’s effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis (HPA). Exposure to stressful events leads to increased activation of the HPA axis with a net effect of increased catecholamine production (adrenaline and noradrenaline) (Moustafa et al., 2018). Increased adrenaline and noradrenaline production results in dysregulation in the eating and sleeping patterns. Sustained high levels of cortisol results in difficulty falling asleep and increased metabolic processes. The biological clock regulates the typical sleeping pattern that relies on producing the sleep hormone melatonin. Melatonin production by the pineal gland is regulated indirectly by the concentration of serum cortisol levels and directly by light perception. Imbalances in the serum concentration cycle secondary to stress results in imbalanced melatonin production and concentration with a net effect of sleeping difficulties.
The emotional strain caused by stress increases the risk of alcohol and other illicit drug use and dependence. Moustafa et al. (2018) conducted an integrative literature review to determine the relationship between childhood trauma, early-life stress, alcohol and drug use, addiction, and abuse. The review findings illustrate that stress increases the risk of alcohol and drug use, addiction, and abuse among the victims. An explanation for the increased risk is the individuals’ lack of identification and implementation of effective coping strategies (Moustafa et al., 2018). Lack of effective coping strategies results in maladaptive measures such as illicit drug use and alcohol consumption. Extensive use of the maladaptive measures results in progressive addiction and drug abuse among individuals with an increased predisposition to other health effects. Alcohol consumption and other illicit drug use over time increase the risk of developing cardiac, respiratory, and liver conditions.
Stress is the emotional strain or tension experienced by an individual due to a reaction toward various demanding and influential situations. Individual response to stressors influences their health. Maladaptive response to stress results in various physical, psychological, and behavioral negative effects. Negative effects of stress on physical health include increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. Psychological effects include the development of anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorders. The behavioral effects of stress on an individual include the development of eating disorders, altered sleeping patterns, impaired concentration, and abuse of alcohol and other drugs. Based on the research findings, it is essential for healthcare providers to identify strategic measures and health initiatives to educate and sensitize the community members on effective stress management approaches in all settings to aid in combating the health effects.
Keech, J. J., Cole, K. L., Hagger, M. S., & Hamilton, K. (2020). The association between stress mindset and physical and psychological well being: Testing a stress beliefs model in police officers . Psychology & Health , 35 (11), 1306-1325. Web.
Kivimäki, M., & Steptoe, A. (2017). Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease . Nature Reviews Cardiology , 15 (4), 215–229. Web.
Moustafa, A. A., Parkes, D., Fitzgerald, L., Underhill, D., Garami, J., Levy-Gigi, E., Stramecki, F., Valikhani, A., Frydecka, D., & Misiak, B. (2018). The relationship between childhood trauma, early-life stress, and alcohol and drug use, abuse, and addiction: An integrative review . Current Psychology , 40 (2), 579–584. Web.
Zhang, X., Zhao, K., Zhang, G., Feng, R., Chen, J., Xu, D., Liu, X., Ngoubene-Italy, A. J., Huang, H., Liu, Y., Chen, L., & Wang, W. (2020). Occupational Stress and Mental Health: A comparison between frontline medical staff and non-frontline medical staff during the 2019 novel Coronavirus Disease outbreak . Frontiers in Psychiatry , 11 . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, December 19). Stress and Its Effects on Health. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/
"Stress and Its Effects on Health." IvyPanda , 19 Dec. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Stress and Its Effects on Health'. 19 December.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
1. IvyPanda . "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Stress and Its Effects on Health." December 19, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/stress-and-its-effects-on-health/.
- History and Concept of the Psychoneuroimmunology
- Insomnia: Cause and Effect
- Genes, Neurotransmitters, and Emotions
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Its Theories
- Effect of Stress Hormones on Brain Cells
- Pathophysiology of Stress, Processed Foods, and Risky Alcohol Consumption
- Coronary Heart Disease Caused by Stress
- Mood and Stress Psychology: Causes, Effects and Treatments
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Regulation
- Jessie as the Most Sympathetic Character of “Night, Mother” by Marsha Norman
- Intergenerational Trauma and Traumatic Memory
- The Lifespan Theory Applied to a Grieving Case
- Psychological Conditions in Addition to Highly Superior Autobiographical Memory
- Self-Control: Individual Development Plan
- Arachnophobia: Systematic Desensitization Project

Psychology Discussion
Essay on stress: it’s meaning, effects and coping with stress.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Stress: It’s Meaning, Effects and Coping with Stress!
Stress is a very common problem being faced today. Every individual will experience stress in one or the other time.
The term stress has many definitions, Lazarus and Folkman (1984) have defined stress as “an internal state which can be caused by physical demands of body or by environmental and social situations, which are evaluated as potentially harmful, uncontrollable, or exceeding our resources for coping”.
According to David Fontana “stress is a demand made upon the adaptive capacities of the mind and body”.
These definitions indicate that stress represents those conditions under which individuals have demand made upon them, that they cannot physically or psychologically meet, leading to breakdown at one or other of these levels.
Stress is usually thought of in negative terms. But ii can manifest itself in both positive and negative way. It is said to be positive when the situation offers an opportunity for one, to gain something.
Eustress (the Greek word ‘eu’ means good) is the term used to describe positive stress. It is often viewed as motivator, since in its absence the individual lacks the spirit necessary for peak performance. Distress is the term used to indicate negative stress.
Almost any change in the environment- even a pleasant change such as a joyful trip- demands some coping, and a little stress is useful in helping us to adapt. But beyond some point, stress becomes a ‘distress’.
What acts to produce distress varies from person to person, but some events seem to be stressors for every person.
Examples of stressors are:
1. Injury or infections of the body, dangers in environment, major changes or transitions in life which force us to cope in new ways.
2. Physical stressors like noise, pollutions, climatic changes, etc.
3. Hustles of everyday life centering on work, family, social activities, health and finances.
4. Frustrations and conflicts.
The physical, environmental and social causes of the stress state are termed stressors. Once induced by stressors the internal stress state can then lead to various responses. On the other hand, psychological responses such as anxiety, hopelessness, depression, irritability, and a general feeling of not being able to cope with the world, can result from the stress state.
Stress cycles:
Stress has a number of immediate effects. If the stressors are maintained, long-term behavioural, physiological, emotional and cognitive effects occur. If these effects hinder adaptation to the environment or create discomfort and distress, they themselves become stressors and, tend to perpetuate a ‘cycle’ of distress.
Example, a patient spends more money on treatment, may experience continued stress even after the cure of the disease, because repayment of debt cause stress for long time in him or a patient whose leg is amputated after accident may continue to worry about it.
On the other hand, many people have developed ways of coping with stressors, so that they are able to respond adaptively. This is the ‘wellness cycle’. Teaching people adaptive ways of handling stress, so as to promote the wellness cycle is an important part of the newly emerging field of behavioural medicine.
Effects of stress:
Stress is not always harmful. In fact, it is recognised that low levels of stress can even helps for better performance. For example, a student can prepare well for forthcoming examination only if he has some stress. However, excess level of stress is undoubtedly harmful.
The effects of stress are divided into three categories:
a. Physiological effects:
Commonly appearing stress related bodily disorders are-peptic ulcers, hypertension, chronic fatigue, hormonal changes, increased heart rate, difficulty in breathing, numbness of limbs, heart disease and reduction in immunity, etc.
b. Psychological effects:
Anxiety, depression, hopelessness, helplessness, anger, nervousness, irritability, tension and boredom may be experienced.
c. Behavioural changes:
Decreasing efficiency, making mistakes, inability to take decisions, under eating or overeating, sleeplessness, increased smoking, develop addiction to alcohol and drugs, forgetfulness, hypersensitivity or passiveness, accident proneness and interpersonal difficulties are seen.
Stress is linked to disorders such as cancer and heart disorders. There are several mediating variables that determine whether stress becomes dangerous or not. For example, good coping mechanisms which can help to reduce stress, having good social support, often help in reducing stress.
Perception of stress or how a person views stress is also very important. For example, a person may not perceive a situation as stressful whereas the same situation may be perceived as highly stressful by some other person.
People with personality type ‘A’ are more prone to be affected by stress related disorders like cardiovascular diseases. Personality character like hardiness or emotional stability helps to withstand effects of stress.
Hans Selye, a renowned biological scientist defines stress as the nonspecific response of the body to any demand upon it. He termed the body’s response to stressors the “General Adaptation Syndrome” (GAS).
The GAS consists of 3 stages:
1. Alarm reaction:
It is an emergency response of the body. In this stage prompt responses of the body, many of them mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, prepare us to cope with the stressor here and now.
2. Stage of resistance:
If the stressor continues to be present, the stage of resistance begins, wherein the body resists the effects of the continuous stressor. During this stage certain hormonal responses of the body are an important line of defence in resisting the effects of stressors (For example, release of ACTH).
3. Stage of exhaustion:
In this stage, the body’s capacity to respond to both continuous and new stressors has been seriously compromised. The person will no longer be able to face stressor and he will finally succumb to it. The person may develop psychosomatic illness.
The stress leads to many psychosomatic diseases. Treatment for such diseases involves medical help for the physical problems and, at the same time, attention to the psychological factors producing the stress.
Coping with Stress :
There are different ways of coping with stress such as: confronting (facing), distancing (remoteness), self-control, seeking social support, accepting responsibility, escape or avoid (from the stressor), plan a problem solving strategy and positive reappraisal.
Usually two broad type of coping types are seen- Instrumental coping and Emotional coping.
In instrumental coping, a person focuses on the problem and tries to solve it. In emotional coping, the focus is more on the feelings generated by the problem.
Today, self- help remedies, Do to yourself approaches, weight loss clinics and diets, health foods and physical exercise are being given much attention in mass media. People are actually taking more responsibility to maintain good health.
However, some specific techniques to eliminate or to manage more effectively the inevitable, prolonged stress are as follows:
Good physical exercise like walking, jogging, swimming, riding bicycle, playing soft ball, tennis are necessary to cope with stress.
Relaxation:
Whether a person simply takes it easy once in a while or uses specific relaxation techniques such as bio-feedback, or meditation, the intent is to eliminate the immediately stressful situation or manage a prolonged stressful situation more effectively.
Taking it easy may mean curling up with a good book on an easy chair or watching some light programme on television or listening to a light music. Meditation is scientifically proved to be very useful, both physically and mentally to cope with stress.
Behavioural self-control:
By deliberately managing the antecedents and the consequence of their own behaviour, people can achieve self-control. Besides managing their own behaviour to reduce stress, people can also become more aware of their limits and of ‘red flags’ that signal trouble ahead. They can avoid people or situations that they know will put them under stress.
Maladaptive strategies, rigid strategies or relying on one type of coping method lead to increase in the stress. Social support helps reduce the effect of stress. People may provide help, advice, material support or moral support that helps to reduce stress.
In addition to the above, psychotherapy (Beck’s cognitive therapy, Ellis’s rational emotive therapy and Meichenbaum’s stress- inoculation training), skill training, environmental changes, Bio-feedback (control of physical signs such as Blood pressure, headache, etc), family therapy, group therapy, hypnosis, yoga, are found to be very useful. Finally, uses of drugs are some of the other strategies adopted in coping with stress.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Tension: Meaning, Causes and Effects
- Stress: Meaning, Causes and Suggestions to Manage It
- Essay on Stress: Top 7 Essays | Human Behaviour | Psychology
- Emotions in Children: Meaning, Effects and Hints | Term Paper | Psychology
Essays About Stress: 5 Examples and 7 Helpful Prompts
Stress deals with various sensitive matters and is a popular topic. See our top examples of essays about stress and prompts to assist in your writing.
Stress is a poison that gradually affects a person’s mental and physical health. It’s a common problem in all aspects of life, with money being the top stressor. There’s also a spectrum of stress, but chronic stress is the most dangerous of all types and levels. It can lead to health problems such as high blood pressure, anxiety disorders, heart disease, and more.

5 Essay Examples
1. post-traumatic stress disorder and substance use disorders by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 2. coping up with stress by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 3. stress management: how stress can cause mental illness and how to treat it by anonymous on papersowl.com, 4. assessing the personal stress levels by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 5. sources of stress in youths by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 1. what is stress, 2. good stress vs. bad stress, 3. how stress can affect our daily lives, 4. the impact of stress on children, 5. what is financial stress, 6. the importance of stress management, 7. stress and health problems.
“…the self-medication hypothesis… is supportive to healthcare as it offers a clear pathway to sufferers from existing addiction, which, in turn, enhances the bond between specialists and victims, it improves access to dosages, and it may also decrease the cost of a prescribed drug.”
In this essay, the writer investigates the leading causes of stress and substance abuse resulting from a disorder. They note that stress, anxiety, and depression often develop after divorce, widowhood, disasters, and other traumatic events.
To show the relationship between post-traumatic stress disorder and substance use, the author adds statistics and situations in which people who have gone through a separation or sexual abuse utilize self-medication, drugs, and alcohol to forget what happened to them. However, this brief escapes lead to addiction. Ultimately, the writer believes that developing stress, anxiety, and depression coping alternatives will reduce the number of people addicted to substances.
Do you want to write about depression? Check out our guide on how to write essays about depression .
“Stress coping and management is essential to have a healthy life. We need to manage stress effectively to avoid the side effects that can arise if not managed effectively. Let’s prioritize on our tasks, manage a healthy lifestyle, have time for fun and for one another, and practice the 4A’s of stress management to have a stress free life.”
This essay shares that stress can be beneficial as it teaches a person to handle difficult situations. However, stress becomes dangerous when it starts to control someone’s life. That’s why it’s vital to manage stress depending on its severity.
To effectively cope with stress, the author suggests having a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and writing in journals. They also mention the importance of talking to a professional and identifying and avoiding the primary source of stress.
“When people get stressed out, they try many coping mechanisms, and that usually helps a decent amount, however for some, the stress can be too overwhelming. That being said, stress is seen to have a very significant link to mental illness, more specifically, schizophrenia.”
In this essay, the author contends that stress is the root cause of some mental illnesses like schizophrenia. To support the claim, the author uses a real-life situation and shows the development of the disease, originating from the simple stress of moving and working in the city.
The essay presents the different levels of schizophrenia and its symptoms. Then, after offering various sources, the author concludes that the most common way to treat stress and schizophrenia is having someone to spend time with and get therapy. You might also be interested in these essays about leadership .
“… A proper assessment of an individual’s stress levels is a critical factor in their well-being. Physiological and psychological aspects of intense pressure should be carefully studied and checked. Using corresponding methods and tools can be of significant help for the person, providing them with a clear understanding of the problems encountered.”
In this essay, the author discusses tools that help assess stress levels and effective strategies for combating stress. They use the “Symptoms of Stress Methodology” from Stress Management for Life: A Research-Based Experiential Approach and the “Ardell Wellness Stress Test” to determine stress levels and evaluate physiological symptoms. These symptoms assist in constructing effective ways to release stress, including participating in PTSD therapies and getting a service dog.
“Early exposure to stress not only affects children’s social and mental development during their formative years, it also can increase the risk of alcoholism, illicit drug use, adult depression, anxiety, and even heart disease much later in life.”
In this essay, the writer proves that stress can affect people of all ages and genders. However, the author focuses on young people and how quickly it appears in their adult life. According to the author, technostress, the fear of missing out, lack of personal space, and high expectations are the common causes of stress in youths.
The author strongly discourages using drugs, cigarettes, and alcohol to relieve stress. Instead, they recommend reducing stress by taking regular breaks, replacing big life goals with smaller, more attainable goals, being open and sharing problems with others, and getting professional help.
7 Writing Prompts for Essays About Stress

Stress is a person’s emotional response to pressure to meet standards, commitments, and responsibilities. It usually occurs in a situation or an outcome we fail to manage or control. In your essay, explain what stress is all about and why it’s essential to understand this reaction. Use this prompt to help your readers know the early signs of stress. Then, add ways stress can be managed and avoided, so it doesn’t interfere with daily activities.
Although stress is often connected with bad instances, there’s also “good stress,” or eustress. Eustress pertains to a positive response to a stressor. For example, it happens when one is excited or ecstatic. Meanwhile, bad stress, or “distress,” negatively affects your mental and physical well-being.
Consider using this prompt to compare and contrast the good and bad stress that people usually experience. Then, give real-life examples and suggest how your readers can effectively handle both eustress and distress.
The effects of stress vary in degree and duration. For example, stress can prevent us from functioning properly at work, home, or anywhere else. It can also affect our relationships with others and with ourselves.
To make your essay relatable, share a personal experience on how stress affects your life. You can also interview others in various professions and statuses to demonstrate the range of which stress affects different individuals.
Stress does not only occur among adults or teenagers. Children can also experience stress at a young age. For instance, a child can succumb to the pressure of adapting to a new environment, getting bullied, and sometimes being separated from loved ones. These can lead to anxiety, trust issues, and depression.
Identify and discuss these factors and why it affects young children. Include recent statistics that show the number of children experiencing stress and additional relevant citations to make your essay credible.
The most recent survey found that 65% of Americans worry about money and the economy’s decline. Pick this prompt to make your essay relevant and informative. Delve into what financial stress is and discuss its typical causes and effects. Then, add the latest percentage of people who experience financial stress and address why it’s a pressing issue.
Stress management offers various strategies to battle stress. First, explain to your readers the importance and effectiveness of proper stress management. Then, include proven and tested methods commonly used to treat stress. You can also share the strategies that have worked for you to persuade your readers that stress management is effective.

Stress causes several physical and mental health problems. Use this prompt to show the importance of treating stress before it worsens and affects a person’s welfare. Include research findings from reliable sources and real-life experiences where someone has damaged their health because of stress. If you’re looking for more ideas, check out our essays about bullying topic guide !

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
- Signs of Burnout
- Stress and Weight Gain
- Stress Reduction Tips
- Self-Care Practices
- Mindful Living
What Is Stress?
Your Body's Response to a Situation That Requires Attention or Action
Elizabeth Scott, PhD is an author, workshop leader, educator, and award-winning blogger on stress management, positive psychology, relationships, and emotional wellbeing.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Elizabeth-Scott-MS-660-695e2294b1844efda01d7a29da7b64c7.jpg)
- Identifying
- Next in How Stress Impacts Your Health Guide How to Recognize Burnout Symptoms
Stress can be defined as any type of change that causes physical , emotional, or psychological strain. Stress is your body's response to anything that requires attention or action.
Everyone experiences stress to some degree. The way you respond to stress, however, makes a big difference to your overall well-being.
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
Sometimes, the best way to manage your stress involves changing your situation. At other times, the best strategy involves changing the way you respond to the situation.
Developing a clear understanding of how stress impacts your physical and mental health is important. It's also important to recognize how your mental and physical health affects your stress level.
Watch Now: 5 Ways Stress Can Cause Weight Gain
Signs of stress.
Stress can be short-term or long-term. Both can lead to a variety of symptoms, but chronic stress can take a serious toll on the body over time and have long-lasting health effects.
Some common signs of stress include:
- Changes in mood
- Clammy or sweaty palms
- Decreased sex drive
- Difficulty sleeping
- Digestive problems
- Feeling anxious
- Frequent sickness
- Grinding teeth
- Muscle tension, especially in the neck and shoulders
- Physical aches and pains
- Racing heartbeat
Identifying Stress
What does stress feel like? What does stress feel like? It often contributes to irritability, fear, overwork, and frustration. You may feel physically exhausted, worn out, and unable to cope.
Stress is not always easy to recognize, but there are some ways to identify some signs that you might be experiencing too much pressure. Sometimes stress can come from an obvious source, but sometimes even small daily stresses from work, school, family, and friends can take a toll on your mind and body.
If you think stress might be affecting you, there are a few things you can watch for:
- Psychological signs such as difficulty concentrating, worrying, anxiety, and trouble remembering
- Emotional signs such as being angry, irritated, moody, or frustrated
- Physical signs such as high blood pressure, changes in weight, frequent colds or infections, and changes in the menstrual cycle and libido
- Behavioral signs such as poor self-care, not having time for the things you enjoy, or relying on drugs and alcohol to cope
Stress vs. Anxiety
Stress can sometimes be mistaken for anxiety, and experiencing a great deal of stress can contribute to feelings of anxiety. Experiencing anxiety can make it more difficult to cope with stress and may contribute to other health issues, including increased depression, susceptibility to illness, and digestive problems.
Stress and anxiety contribute to nervousness, poor sleep, high blood pressure , muscle tension, and excess worry. In most cases, stress is caused by external events, while anxiety is caused by your internal reaction to stress. Stress may go away once the threat or the situation resolves, whereas anxiety may persist even after the original stressor is gone.
Causes of Stress
There are many different things in life that can cause stress. Some of the main sources of stress include work, finances, relationships, parenting, and day-to-day inconveniences.
Stress can trigger the body’s response to a perceived threat or danger, known as the fight-or-flight response . During this reaction, certain hormones like adrenaline and cortisol are released. This speeds the heart rate, slows digestion, shunts blood flow to major muscle groups, and changes various other autonomic nervous functions, giving the body a burst of energy and strength.
Originally named for its ability to enable us to physically fight or run away when faced with danger, the fight-or-flight response is now activated in situations where neither response is appropriate—like in traffic or during a stressful day at work.
When the perceived threat is gone, systems are designed to return to normal function via the relaxation response . But in cases of chronic stress, the relaxation response doesn't occur often enough, and being in a near-constant state of fight-or-flight can cause damage to the body.
Stress can also lead to some unhealthy habits that have a negative impact on your health. For example, many people cope with stress by eating too much or by smoking. These unhealthy habits damage the body and create bigger problems in the long-term.
Mental Health in the Workplace Webinar
On May 19, 2022, Verywell Mind hosted a virtual Mental Health in the Workplace webinar, hosted by Amy Morin, LCSW. If you missed it, check out this recap to learn ways to foster supportive work environments and helpful strategies to improve your well-being on the job.
Types of Stress
Not all types of stress are harmful or even negative. Some of the different types of stress that you might experience include:
- Acute stress : Acute stress is a very short-term type of stress that can either be positive or more distressing; this is the type of stress we most often encounter in day-to-day life.
- Chronic stress : Chronic stress is stress that seems never-ending and inescapable, like the stress of a bad marriage or an extremely taxing job; chronic stress can also stem from traumatic experiences and childhood trauma.
- Episodic acute stress : Episodic acute stress is acute stress that seems to run rampant and be a way of life, creating a life of ongoing distress.
- Eustress : Eustress is fun and exciting. It's known as a positive type of stress that can keep you energized. It's associated with surges of adrenaline, such as when you are skiing or racing to meet a deadline.
4 Main Types of Stress:
The main harmful types of stress are acute stress, chronic stress, and episodic acute stress. Acute stress is usually brief, chronic stress is prolonged, and episodic acute stress is short-term but frequent. Positive stress, known as eustress, can be fun and exciting, but it can also take a toll.
Impact of Stress
Stress can have several effects on your health and well-being. It can make it more challenging to deal with life's daily hassles, affect your interpersonal relationships, and have detrimental effects on your health. The connection between your mind and body is apparent when you examine stress's impact on your life.
Feeling stressed over a relationship, money, or living situation can create physical health issues. The inverse is also true. Health problems, whether you're dealing with high blood pressure or diabetes , will also affect your stress level and mental health. When your brain experiences high degrees of stress , your body reacts accordingly.
Serious acute stress, like being involved in a natural disaster or getting into a verbal altercation, can trigger heart attacks, arrhythmias, and even sudden death. However, this happens mostly in individuals who already have heart disease.
Stress also takes an emotional toll. While some stress may produce feelings of mild anxiety or frustration, prolonged stress can also lead to burnout , anxiety disorders , and depression.
Chronic stress can have a serious impact on your health as well. If you experience chronic stress, your autonomic nervous system will be overactive, which is likely to damage your body.
Stress-Influenced Conditions
- Heart disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Sexual dysfunction
- Tooth and gum disease
Treatments for Stress
Stress is not a distinct medical diagnosis and there is no single, specific treatment for it. Treatment for stress focuses on changing the situation, developing stress coping skills , implementing relaxation techniques, and treating symptoms or conditions that may have been caused by chronic stress.
Some interventions that may be helpful include therapy, medication, and complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
Press Play for Advice On Managing Stress
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast featuring professor Elissa Epel, shares ways to manage stress. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts / Amazon Music
Psychotherapy
Some forms of therapy that may be particularly helpful in addressing symptoms of stress including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) . CBT focuses on helping people identify and change negative thinking patterns, while MBSR utilizes meditation and mindfulness to help reduce stress levels.
Medication may sometimes be prescribed to address some specific symptoms that are related to stress. Such medications may include sleep aids, antacids, antidepressants, and anti-anxiety medications.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Some complementary approaches that may also be helpful for reducing stress include acupuncture, aromatherapy, massage, yoga, and meditation .
Coping With Stress
Although stress is inevitable, it can be manageable. When you understand the toll it takes on you and the steps to combat stress, you can take charge of your health and reduce the impact stress has on your life.
- Learn to recognize the signs of burnout. High levels of stress may place you at a high risk of burnout. Burnout can leave you feeling exhausted and apathetic about your job. When you start to feel symptoms of emotional exhaustion, it's a sign that you need to find a way to get a handle on your stress.
- Try to get regular exercise. Physical activity has a big impact on your brain and your body . Whether you enjoy Tai Chi or you want to begin jogging, exercise reduces stress and improves many symptoms associated with mental illness.
- Take care of yourself. Incorporating regular self-care activities into your daily life is essential to stress management. Learn how to take care of your mind, body, and spirit and discover how to equip yourself to live your best life.
- Practice mindfulness in your life. Mindfulness isn't just something you practice for 10 minutes each day. It can also be a way of life. Discover how to live more mindfully throughout your day so you can become more awake and conscious throughout your life.
If you or a loved one are struggling with stress, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for information on support and treatment facilities in your area.
For more mental health resources, see our National Helpline Database .
Cleveland Clinic. Stress .
National institute of Mental Health. I'm so stressed out! Fact sheet .
Goldstein DS. Adrenal responses to stress . Cell Mol Neurobiol . 2010;30(8):1433–1440. doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9606-9
Stahl JE, Dossett ML, LaJoie AS, et al. Relaxation response and resiliency training and its effect on healthcare resource utilization [published correction appears in PLoS One . 2017 Feb 21;12 (2):e0172874]. PLoS One . 2015;10(10):e0140212. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0140212
American Heart Association. Stress and Heart Health.
Chi JS, Kloner RA. Stress and myocardial infarction . Heart . 2003;89(5):475–476. doi:10.1136/heart.89.5.475
Salvagioni DAJ, Melanda FN, Mesas AE, González AD, Gabani FL, Andrade SM. Physical, psychological and occupational consequences of job burnout: A systematic review of prospective studies . PLoS One . 2017;12(10):e0185781. Published 2017 Oct 4. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0185781
Bitonte RA, DeSanto DJ 2nd. Mandatory physical exercise for the prevention of mental illness in medical students . Ment Illn . 2014;6(2):5549. doi:10.4081/mi.2014.5549
Ayala EE, Winseman JS, Johnsen RD, Mason HRC. U.S. medical students who engage in self-care report less stress and higher quality of life . BMC Med Educ . 2018;18(1):189. doi:10.1186/s12909-018-1296-x
Richards KC, Campenni CE, Muse-Burke JL. Self-care and well-being in mental health professionals: The mediating effects of self-awareness and mindfulness . J Ment Health Couns . 2010;32(3):247. doi:10.17744/mehc.32.3.0n31v88304423806.
American Psychological Association. 2015 Stress in America .
Krantz DS, Whittaker KS, Sheps DS. Psychosocial risk factors for coronary heart disease: Pathophysiologic mechanisms . In R. Allan & J. Fisher, Heart and mind: The practice of cardiac psychology. American Psychological Association; 2011:91-113. doi:10.1037/13086-004
By Elizabeth Scott, PhD Elizabeth Scott, PhD is an author, workshop leader, educator, and award-winning blogger on stress management, positive psychology, relationships, and emotional wellbeing.
Essay on Stress Management
500 words essay on stress management.
Stress is a very complex phenomenon that we can define in several ways. However, if you put them together, it is basically the wear and tear of daily life. Stress management refers to a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies for controlling a person’s stress level, especially chronic stress . If there is effective stress management, we can help one another break the hold of stress on our lives. The essay on stress management will throw light on the very same thing.

Identifying the Source of Stress
The first step of stress management is identifying the source of stress in your life. It is not as easy as that but it is essential. The true source of stress may not always be evident as we tend to overlook our own stress-inducing thoughts and feelings.
For instance, you might constantly worry about meeting your deadline. But, in reality, maybe your procrastination is what leads to this stress than the actual deadline. In order to identify the source of stress, we must look closely within ourselves.
If you explain away stress as temporary, then it may be a problem. Like if you yourself don’t take a breather from time to time, what is the point? On the other hand, is stress an integral part of your work and you acknowledging it like that?
If you make it a part of your personality, like you label things as crazy or nervous energy, you need to look further. Most importantly, do you blame the stress on people around you or the events surrounding you?
It is essential to take responsibility for the role one plays in creating or maintaining stress. Your stress will remain outside your control if you do not do it.
Strategies for Stress Management
It is obvious that we cannot avoid all kinds of stress but there are many stressors in your life which you can definitely eliminate. It is important to learn how to say no and stick to them. Try to avoid people who stress you out.
Further, if you cannot avoid a stressful situation, try altering it. Express your feelings don’t bottle them up and manage your time better. Moreover, you can also adapt to the stressor if you can’t change it.
Reframe problems and look at the big picture. Similarly, adjust your standards and focus on the positive side. Never try to control the uncontrollable. Most importantly, make time for having fun and relaxing.
Spend some time with nature, go for a walk or call a friend, whatever pleases you. You can also try working out, listening to music and more. As long as it makes you happy, never give up.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Stress Management
All in all, we can control our stress levels with relaxation techniques that evoke the relaxation response of our body. It is the state of restfulness that is the opposite of the stress response. Thus, when you practice these techniques regularly, you can build your resilience and heal yourself.
FAQ of Essay on Stress Management
Question 1: What is the importance of stress management?
Answer 1: Stress management is very efficient as it helps in breaking the hold which stress has on our lives. Moreover, you can also become happy, healthy and more productive because of it. The ultimate goal should be to live a balanced life and have the resilience to hold up under pressure.
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques.
Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- Find Student Housing
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
- Stress Essay
IELTS Stress Essay
This is a model IELTS stress essay. It is about stress in modern society and how to prevent it.
It is a causes and solutions type essay. In other words, you have to identify what causes stressand then suggest solutions.
Stress is now a major problem in many countries around the world.
What are some of the factors in modern society that cause this stress and how can we reduce it?
This type of essay lends itself to two body paragraphs - one explaining the causes and the next discussing some possible solutions.
As is important with any IELTS essay, you must always read the question carefully.
The topic is often narrowed down to a particular group of people or topic.
Narrowing Down the Topic

The key here is that ' modern society ' is mentioned.
If you just talk about stress in general but don't connect it to modern society you may be in danger of not fully answering the question .
You need to brainstorm some issues specific to the world we live in today that may result in stress.
What things effect us today that did not (or not too such an extent) 10, 20, 30 years ago?
Using Personal Pronouns
Also, you may notice that ' we ' is used a lot in the stress essay.
Remember an IELTS essay is not quite the same as an academic essay you will normally write. It is can be more personal as you only have your own experience to support your answer with.
You should avoid too many personal pronouns if possible such as ' I ' throughout the essay but you may wish to use this to give your opinion or examples from your own experience at times. This is ok, but don't overdo it.
This question specifically says how can ' we ' reduce it. So it is already making it personal. So it is ok to write about what all of us, or ' we ', can do.
Model Stress Essay
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
What are some of the factors in modern society that cause this stress, and how can we reduce it?
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Stress Essay Model Answer
Stress is a problem that can have detrimental effects on many people’s lives, and there are various factors in modern society responsible for this. However, there are ways to limit the potential impacts.
The modern world we live in today presents us with many issues that we did not have to cope with in the past. Firstly, there are issues of terrorism that we are constantly confronted with in the media. Whether these are real or not, we are led to believe our lives are in constant danger, be it flying on a plane or travelling on public transport. Climate change is another worry that everyone has to face. The results of a significant rise in temperatures could radically affect our ways of life, and our children’s too. There are also more health issues to be concerned about than in the past, with rises in alzheimer’s, diabetes, and stroke to name but a few. All of these concerns can result in stress.
Tackling such problems will not be easy, but there are measures that can be taken. Governments and the media could play their part by ensuring that instead of persistently bombarding us with such negative images and information about the world in which we live, we are given more positive stories too. However, given this is unlikely to happen, we need to develop our own strategies to distract us from these influences. Of course exercising regularly is one thing we should do as this has been shown to increase endorphin levels and lead to feelings of happiness. Sleeping enough helps us to recuperate and restore our body. Finally, eating properly can improve our health and result in less worry about potential diseases.
All in all, although there are many factors around us today which lead to stress, we can take steps to reduce it. Given that the strains we face in modern society will likely get worse, ignoring it is not an option for many people.
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Causes & Solutions Essays:

Essay: Why are traditional festivals and celebrations disappearing?
IELTS essay on the disappearance of traditional festivals and celebrations - view a model answer and tips on how to answer the question

Why might International travel sometimes make people prejudiced?
This essay is about why international travel might sometimes make people prejudiced rather than broad minded. It's a causes and solutions type IELTS essay.

Why do many children have difficulty paying attention in class?
This IELTS essay is about why many children have difficulty paying attention and concentrating in class in school.

Youth Crime Essay: Why is crime involving the young rising in cities?
This youth crime essay considers why crime involving the young is rising in many cities and what measures there are to reduce it.

Essay on Museums and Historical Places: Why don't local people visit?
Essay on Museums and Historical Places: This is a causes (or 'reasons') and solutions essay as you have to explain why local people visit these places less than tourists, and then present ways to encourage more local people to visit.

Why is there a lack of communication between younger and older people?
This IELTS Essay is about the decline in communication between younger and older people in society. It is a causes and solutions type essay question.

Global Warming Essay: Why is the planet warming & what can be done?
In this global warming essay you are asked in the question to discuss the causes of global warming and possible solutions for individuals and the government.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.

Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Student Housing
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
Decreasing House Sizes Essay
Apr 06, 24 10:22 AM

Latest IELTS Writing Topics - Recent Exam Questions
Apr 04, 24 02:36 AM

IELTS Essay: English as a Global Language
Apr 03, 24 03:49 PM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- AIMS Public Health
- v.8(1); 2021

Risk factors associated with stress, anxiety, and depression among university undergraduate students
Mohammad mofatteh.
1 Lincoln College, University of Oxford, Turl Street, Oxford OX1 3DR, United Kingdom
2 Merton College, University of Oxford, Merton Street, Oxford OX1 4DJ, United Kingdom
3 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3RE, United Kingdom
It is well-known that prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression is high among university undergraduate students in developed and developing countries. Students entering university are from different socioeconomic background, which can bring a variety of mental health risk factors. The aim of this review was to investigate present literatures to identify risk factors associated with stress, anxiety, and depression among university undergraduate students in developed and developing countries. I identified and critically evaluated forty-one articles about risk factors associated with mental health of undergraduate university students in developed and developing countries from 2000 to 2020 according to the inclusion criteria. Selected papers were analyzed for risk factor themes. Six different themes of risk factors were identified: psychological, academic, biological, lifestyle, social and financial. Different risk factor groups can have different degree of impact on students' stress, anxiety, and depression. Each theme of risk factor was further divided into multiple subthemes. Risk factors associated with stress, depression and anxiety among university students should be identified early in university to provide them with additional mental health support and prevent exacerbation of risk factors.
1. Introduction
Mental health is one of the most significant determinants of life quality and satisfaction. Poor mental health is a complex and common psychological problem among university undergraduate students in developed and developing countries [1] . Different psychological and psychiatric studies conducted in multiple developed and developing countries across the past decades have shown that prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression (SAD) is higher among university students compared with the general population [2] – [4] . It is well established that as a multi-factorial problem, SAD cause personal, health, societal, and occupational issues [5] which can directly influence and be influenced by the quality of life. The level of stress cited in self-reported examinations and surveys is inversely correlated with life quality and well-being [6] .
Untreated poor mental health can cause distress among students and, hence, negatively influence their quality of lives and academic performance, including, but not limited to, lower academic integrity, alcohol and substance abuse as well as a reduced empathetic behaviour, relationship instability, lack of self-confidence, and suicidal thoughts [7] – [9] .
A 21-item self-evaluating questionnaire, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), is the most common tool used for diagnoses of depression [10] . A BDI-based survey in five developed countries in Europe (European Outcome of Depression International Network-ODIN in the United Kingdom, Netherlands, Greece, Norway, and Spain) concluded that overall 8.6% (95% CI, 7.95–10.37) of the resident population are dealing with depression [11] . Similar studies confirmed that about 8% of the population in developed and developing countries suffer from depression [12] . Data from systematic review studies revealed that this depression rate is much higher among university students and around one third of all students in the majority of the developed countries have some degree of SAD disorders; and depression prevalence has been increasing in academic environments over the past few decades [3] .
Despite all the efforts to increase awareness and tackle mental health problems among university students, there is still an increasing number of depression and suicide among students [13] , indicating a lack of effectiveness of the measures adopted. In addition to an increase in the prevalence of mental health issues, comparing students and non-college-attending peers demonstrated that the severity of psychological disorders that students receive treatment for has also increased [14] . For example, the rate of suicide among adolescents has increased significantly over the past few decades [15] . In fact, suicide as a result of untreated mental health is the second cause of death among American college students [16] , emphasizing the importance of identifying and treating risk factors associated with SAD.
SAD can be manifested in different forms; however, some common overt symptoms include loss of appetite, sleep disturbance, lack of concentration, apathy (lack of enthusiasm and concern), and poor hygiene. Studying SAD is particularly important among university students who are future representatives and leaders of a country. Furthermore, most undergraduate students enter university at an early age; and dealing with SAD early in life can have long-term negative consequences on the mental and social life of students [3] . For example, a longitudinal study in New Zealand over 25 years demonstrated that depression among people aged 16–21 could increase their unemployment and welfare-dependence in long-term [17] .
A better understanding of SAD among students in developed and developing countries not only helps governments, universities, families, and healthcare agencies to identify risk factors associated with mental health problems in order to minimise such risk factors, but also provides them with an opportunity to study how these factors have been changing in the academia.
This review aims to provide an updated understanding of risk factors associated with SAD among post-secondary undergraduate and college students in developed and developing countries by using existing literature resources available to answer the following question:
“Aetiology of depression and anxiety: What are risk factors associated with stress, anxiety and depression among university and college undergraduate students studying in developed and developing countries?”
It is worth mentioning that this review focuses on SAD risk factors of university students in developed and developed countries, and does not cover underdeveloped countries which can have their own niche problems (such as poverty). However, this review takes into account international students who migrate from underdeveloped countries to developed and developing countries to pursue their education.
2.1. Aims and objectives
The aims of this review were to identifying principal themes associated with depression and anxiety risk factors among university undergraduate students. The objectives of this review are to design a rigorous searching methodology approach by using appropriate inclusion and exclusion criteria, to conduct literature searches of publicly available databases using the designed methodology approach, to investigated collected literature resources to identify risk factors associated with the depression and anxiety which have not changed, and to identify principal themes associated with SAD risk factors among university undergraduate students.
2.2. Designed approach for literature review
A narrative review based on a comprehensive and replicable search strategy is used in this review. This approach is justified and preferred, over other approaches such as primary data gathering, because of the timescale of the research (2000 to 2020-temporal reasons), and extent of the research (developed and developing countries-spatial reasons).
2.3. Criteria for inclusion and exclusion of articles
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for articles and academic writings used in this review are as follows:
2.3.1. Date
2000 to 2020 are included Academic writings which are published between in this review. Initially, during a pilot search, search strategies covered 1990 to 2020. However, the majority of the search results (more than 80% of the search results and more than 88% of applicable search results) were from 2000 to 2020, which indicates the importance of mental health issue and increased awareness over the past two decades. Therefore, for the final search, papers from 2000 to 2020 were included.
2.3.2. Study design
Literatures included in this narrative review were primary research articles, review articles, systematic reviews, mini-reviews, opinion pieces, correspondence, clinical trials, and cases reports published in peer reviewed journals.
2.3.3. Country
The narrative review was limited to developed and developing countries definition by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs [18] . Abstract and method sections of search results were screened to check the country of research.
2.3.4. Language
Peer-reviewed articles published in English were only included in this narrative review.
2.3.5. The explanation for papers exclusion
The main reason for papers excluded from consideration after search results was that they focused on intervention and therapies associated with SAD. Other reasons for exclusion was that studies were conducted on a mixture of undergraduate and graduate students or focused solely only graduate students. Studies which focused on other types of mental disorders such as eating disorders but did not focus on SAD were excluded too. The conducted search did not exclude any gender or specific age category.
2.4. Strategies used for search and limitations
In this review, a robust and replicable search strategy was designed to identify appropriate articles by searching PubMed, MEDLINE via Ovid, and JSTOR electronic databases. These databases were selected because they encompass biopsychosocial papers published on SAD. The date chosen for this search was for articles published between 2000 to 2020 which covers the past two decades. Once key articles were identified, a search for citation of those papers was conducted, and the bibliography of those papers were further screened to identify potential articles which can be relevant.
2.5. Search terminologies used
To conduct searches in databases mentioned above, the following search terms were used: students stress, anxiety, depression risk factors, university stress, anxiety, depression risk factors, student mental health developed and developing countries, students stress, anxiety and depression developed and developing countries. The operation AND was used to connect stress, anxiety, depression, mental health, developed, developing, countries, students. The search for each term was conducted in all fields (title, abstract, full text, etc.).
2.6. Screening, selecting search results, and data extraction
The search results were exported into separate Excel and EndNote X8 files. Titles and abstracts from all articles were screened to determine their relevance to the topic of this review. Potentially relevant articles were fully read to establish their relevance. Each paper which was included according to the inclusion criteria described above was read fully. A word file was created to identify themes associated with SAD risk factors which is included in the Results. An initial search resulted in 1305 articles. The title and abstract of individual papers were read for relevance, resulting in 60 papers which were relevant for the research question asked in this review. All 60 papers were read completely, and from those, 19 were excluded based on the criteria mentioned before. Therefore, the total number of papers for consideration was 41. A flowchart explaining the procedure for identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion of papers is shown in Figure 1 .

Figure 2 provides a quantitative summary of the papers included in this narrative review. In terms of the distribution of the countries where the research was conducted, included papers were mainly articles which carried out studies in the USA (n = 17), followed by China and Canada (each n = 5), UK (n = 4), Japan (n = 3), Germany and Australia (each n = 2), South Korea, Hungary, Switzerland (each n =1) ( Figure 2A ). As for article types included in this review, original research articles, including quantitative and qualitative studies, which relied on obtaining data including cross-sectional studies, interviews, case-control studies, surveys, and questionnaire, were the highest (n = 37) followed by meta-analysis, literature and systematic reviews ( Figure 2B ). Another interesting observation was that although the search was carried out from 2000–2020, most papers were concentrated in the period from 2016 to 2020 ( Figure 2C ). This can be due to the reason that mental health is becoming more important over the past few years. Alternatively, a higher number of papers included from 2016 onward can be due to unintended selection bias. The smallest study covered in this narrative review was conducted on 19 students and the largest one on 153,635 students, adding up to 236,104 students, who were included in articles covered in this narrative review in total. Most studies on mental health, anxiety, and depression use standardised approaches such as patient-filled general health questionnaires, Pearling coping questionnaire, internally regulated surveys, BDI, DSM-IV symptomology, and general anxiety and burnout scales such as Maslach Burnout Inventory.

3.1. Literature search results
Following the search protocol shown in Figure 3 , a list of included papers identified which can be found in the Table 1 .

3.2. Prevalence of mental health disorders in students
Literature showed that mental health problems are common phenomenon among students with a higher prevalence compared to the general public. For example, surveying more than 2800 students in five American large public universities demonstrated that more than half of them experienced anxiety and depression in their last year of studies [19] . Similarly, a survey of Coventry University undergraduate students in the UK showed that more than one-third of them had experienced mental health issues such as anxiety and depression over the past one year since they were surveyed [20] . In agreements with these results, Maser et al. [21] found that prevalence of mental health disorders including anxiety and depression was higher among medical students compared to the general non-student population of the same age. These studies demonstrated that the prevalence of SAD among students has remained higher than the average population over the past two decades.
SAD are not only prevalent among students, but also persistent. By conducting a follow-up survey study of students over two years, Zivin et al. [19] demonstrated that more than half of students retain their higher levels of anxiety and depression over time. This can be due to a lack of SAD treatment or persistence of existing risk factors over time.
3.3. Risk factors associated with stress, anxiety, and depression
SAD are multifactorial, complex psychological issues which can have underlying biopsychosocial reasons. Multiple risk factors which affect the formation of SAD among undergraduate university students in developed and developing countries were identified in this review. These factors can be categorized into multiple themes including psychological, academic, biological, lifestyle, social and financial. A summary of risk factors and their associated publications are shown in Table 2 .
3.3.1. Psychological factors
Self-esteem, self-confidence, personality types, and loneliness can be associated with SAD among university students. Students who have a lower level of self-esteem are more susceptible to develop anxiety and depression [22] . Also, students with high neuroticism and low extraversion in five-factor personality inventory [23] are more likely to develop SAD during university years [24] . Other psychological factors such as feeling of loneliness plays important roles in increasing SAD risk factors [24] . Moving away from family and beginning an independent life can pose challenges for fresher students such as loneliness until they adjust to university life and expand their social network. Indeed, Kawase et al. [24] showed that students who live in other cities than their hometown for studying purposes are more likely to develop anxiety and depression.
Some students enter the university with underlying mental conditions, which can become exacerbated as they transition into the independent life at university. While depression is higher among university and college students compared to the general public, students with a history of mental health problems, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are more prone to development of anxiety and depression during their university lives compared to students who did not have such experience before starting their degrees [25] . Furthermore, exposure to violence in childhood either at the household or the community correlates with SAD formation later in life and at University [26] . Therefore, low self-esteem and self-confidence, having an underlying mental health condition before beginning the university, personality type (high neuroticism and low extravasation), and loneliness can increase the probability of SAD formation in students.
3.3.2. Academic factors
Multiple university-related academic stressors can lead to SAD among students. One of these factors which was strongly present in many studies evaluated in this review was the subject of the degree. Medical, nursing, and health-related students have a higher prevalence of depression and anxiety compared to their non-medical peers [24] , [27] – [28] . Medical and nursing students who have both theoretical duties and patient-related work usually have the highest level of workload among university students, consequently deal more with anxiety and depression [27] , [29] . In addition, students who major in psychology and philosophy, similar to nursing and medical students, are more likely to develop depression during their studies compared to others [24] . These studies did not identify whether students who have underlying mental health conditions are more likely to choose certain subjects such as philosophy, psychology, or subjects which lead to caring roles such as nursing and medicine. Because of the nature of their work, medical and nursing students who deal with people's health can experience depression and anxiety as a result of fears of making mistakes which can result in harming patients [27] . Students with practical components in their degree are required to travel to unfamiliar places for fieldwork and work experience which can add to their stress and anxiety [27] .
Also, some prospective students, especially those who study nursing and medicine, usually do not have a clear understanding of the curriculum and workload associated with the subject before entering the university, therefore, they can face a state of disillusionment once they begin their studies at university [27] – [29] . It is worth mentioning that not all studies found a significant correlation between the subject of study and SAD development [30] . This can be explained by differences in sample type and size which results in variations existing in the amount of workload and curriculum in similar subjects taught in various universities in different countries.
Studying a higher degree can be a challenging task which requires mental effort. Mastery of the subject can negatively correlate with self-esteem, anxiety, and depression among university students with students who have a mastery of subject demonstrating a lower level of stress and anxiety [31] . Also, students who study in a non-native language report the highest level of anxiety and depression during their freshman years, and their stress levels decrease during the subsequent study years [32] . This can be explained by the fact that students who are studying in a foreign language usually are those who have migrated abroad, therefore, require some time to adjust to their new lives. Different studies showed that the level of anxiety and depression among both international and home students could correlate with the year of study with fresher students who enter the university and students at the final year of their studies experience the greatest amount of anxiety and depression with different risk factors [22] , [32] . While fresher students experience SAD because of challenges in adjustments to university life, past negative family experience, social isolation and not having many friends, final year students report uncertainty about their future, prospective employment, university debt repayment and adjusting to the life after university as major risk factors for their SAD [22] , [32] . Therefore, a shift in SAD risk factors themes are observed as students make a progress in their degrees.
Students spend a significant portion of their time at university being engaged with their academic activities, and unpleasant academic outcomes can influence their mental health. Receiving lower grades during the time of studies can negatively influence students' mental health, causing them to develop SAD [33] , [34] . Academic performance during undergraduate studies can determine the degree classification, which can, subsequently, influence students' opportunities such as employment success rate or access to postgraduate courses [27] . Conversely, both the number of students with mental health problem symptoms and the severity of students' SAD increase during exam time [35] , reflecting a direct relationship between academic pressure and students' mental health states. However, the causal relationship is not well-established; it is possible that depression and associated problems such as temporary memory loss and lack of concentration [36] are reasons for poor academic grades or inversely, students feel stressed leading to depression because of their poor performance in their exams. A mutual relationship can exist between grades and mental health, as having a poor mental health can reciprocally cause students to get lower grades [34] , leading to a vicious cycle of mental health and academic performance. Interestingly, students' sense of social belonging and coherence to the university community was reduced during exam periods [35] . This can be explained by the reduced participation rate of students in university social activities and clubs as well as an increased sense of competition with their peers. Furthermore, students interact directly and indirectly with teachers, lecturers, tutors, and other staff; therefore, the relationship between students and academic staff can influence students' mental health. A negative and abusive relationship with teachers and mentors can be another factor causing SAD among undergraduate students [27] .
On the other hand, being a part-time student is a protective factor for anxiety and depression, and part-time students have better mental health compared to students with full-time status [34] . This can be explained by financial securities which have a source of income can bring or because part-time students are usually older than full-time students [34] , and therefore, more emotionally stable. In conclusion, risk factors increasing SAD among university students include high workload pressure, fear of poor performance in exams and assessments, wrong expectations from the course and university, insufficient mastery in the subject, year of study, and a negative relationship with academic staff.
3.3.3. Biological factors
Mental health can be influenced by ones' physical health. Presence of an underlying health condition or a chronic disease before entering the university can be a predictor of having SAD during university years [31] , [33] . Students with physical and mental disabilities can be in a more disadvantaged position and do not fully participate in university life leading to SAD formation [33] .
An association between gender and depressive disorders have been observed in several studies [21] , [27] , [34] , [37] . Female students had a higher prevalence of SAD compared to male students. Interestingly, while female students demonstrated a higher level of SAD, the dropout rate of female students with a mental health problem from university was lower compared to their male counterparts [33] . On the other hand, while females are at a higher risk of developing depressive disorders, males with depressive disorders are less willing to seek professional help and ask for support due to the stigma attached to mental health [38] , causing exacerbation of their problem over time [20] .
Age can be another factor related to SAD. Younger students report a higher level of SAD compared to older students [34] , [37] . However, other meta-analysis studies did not find a significant correlation between students' age and their mental health which can be due to sampling differences [39] . Some studies showed that while older undergraduate students have a higher determination to do well in the university [40] , those who have family commitments are more prone to develop SAD during their degrees [27] . These discrepancies in findings can be explained by different sample sizes and types of studies which can be influenced by various confounding factors such as nationality, country of study, degree of studies, gender, and socioeconomic status. Similarly, a lack of correlation between depression prevalence and year of study is observed as some studies have reported a higher prevalence among earlier years of studies, while others have shown a higher prevalence among students as they move closer to the end of their studies [41] . These differences can be explained by different causes of depression in a different age; for example, while depression in younger adults can be due to changes in their environment and difficulties in adapting to a new life, older adults can have depression symptoms because of a lack of certainty for their future and employment. Nevertheless, differences exist between SAD risk factors associated with young and older students. Overall, biological risk factors affecting SAD include age of students, gender, and underlying physical conditions before entering the university.
3.3.4. Lifestyle factors
Moving away from families and beginning a new life requires flexibility and adaptation to adjust to a new lifestyle. As most undergraduate students leave their family environment and enter a new life with their peers, friends, and classmates, their behaviour and lifestyle change too. Multiple lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption, tobacco smoking, dietary habits, exercise, and drug abuse can affect SAD. Alcohol consumption is high among students with SAD [28] ; a causal relationship was not been established in this study though.
Tobacco smoking is another risk factor associated with SAD which is common among students, especially students who study in Eastern developed and developing countries such as China, Japan and South Korea [24] , [42] . Most students, especially male students, smoke because of social bonding and the rate of social smoking is directly correlated with SAD [24] , [42] . Social smokers are less willing to quit smoking, and more likely to persist in their habit, resulting in long term negative physical and psychological health consequences [42] . Illegal substance abuse can be another factor important in SAD among young people [43] . Academic-related stress and social environment in university dormitories and student accommodations can encourage students to use illegal drugs, smoke tobacco and consume alcohol excessively as a coping mechanism, resulting in SAD [44] . Interestingly, students who perceived they had support from the university were feeling less stressed and were less at the risk of substance abuse [45] , indicating the important role of social support in preventing and alleviating depression symptoms. This is of particular importance as a new social habit and behaviour adapted early during life can last for a long time. Furthermore, students who do not have a healthy lifestyle can feel guilt, which can worsen their SAD condition [46] . Interestingly, Rosenthal et al. [47] showed that negative behaviours resulting from alcohol consumption such as missing the next day class, careless behaviour and self-harm, verbal argument or physical fight, being involved in unwanted sexual behaviour, and personal regret and shame could be the main reasons for depression associated with drinking alcohol, rather than the amount of alcohol consumed.
In contrast, a moderate to vigorous level of physical activity can be a protective factor against developing SAD during university life [37] , [48] . Students who have a perception of having inadequate time during their studies do not spend enough time for exercise and can develop SAD symptoms [27] .
Another lifestyle-related risk fact associated with SAD is sleep. Many young people do not receive sufficient sleep, and sleep deprivation is a serious risk factor for low mood and depression [28] , [47] . Self-reported high level of stress and sleep deprivation is common among American students [31] , [49] . Insufficient sleep can act as a vicious cycle- academic stress can cause sleep deprivation, and insufficient sleep can cause stress due to poor academic performance since both sleep quality and quantity is associated with academic performance [28] . Overall, poor sleeping habit is associated with a decreased learning ability, increase in anxiety and stress, leading to depression.
Different negative lifestyle behaviours such as tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, lack of adequate physical activity, and insufficient sleep can increase the risk of SAD formation among university students.
3.3.5. Social factors
Having a supportive social network can influence students' social and emotional wellbeing, and subsequently lower their probability of having anxiety and depression in university [27] , [37] , [50] . The quality of relationship with family and friends is important in developing SAD. Having a well-established and supportive relationship with family members can be a protective factor against SAD development, which, in turn, can affect the sense of students' fulfilment from their university life [27] . The frequency of family visits during university years negatively correlates with SAD development [33] . Family visits can be more challenging for international students who live far away from their families, therefore adding to existing problems of international students who live and study abroad.
In contrast, having a negative relationship with family members, especially parents, can cause SAD formation among students in university [51] . Similarly, having a strict family who posed restrictions on behaviours and activities during childhood can be a predictor of developing SAD during university years [51] .
Also, it is shown that being in a committed relationship has a beneficial protective factor against developing depressive symptoms in female, but not male, students [52] . Interestingly, both male and female students who were in committed relationships reported a lower alcohol consumption compared to their peers who were not in committed relationships [52] .
Involvement in social events such as participating in sporting events and engaging in club activities can be a protective factor for mental health [32] , [37] . Assessing preclinical medical students' social, mental, and psychological wellbeing showed that while first year students demonstrate a decrease in their mental wellbeing during the academic year, they have an increase in their social wellbeing and social integration [53] . This can be explained by the time period required for fresher students who enter the university to adjust to the social environment, make new friends, and integrate into the social life of the university.
Access to social support from university is another factor which is negatively correlated with developing anxiety and depression [31] . It is worth mentioning that different universities provide different degrees of social support for students which can reflect on different anxiety and depression observed among students of different universities.
Importantly, sexual victimization during university life can be a predictor of depression. By surveying female Canadian undergraduate students, McDougall et al. [54] found that students who were sexually victimized and had non-consensual sex were at a higher chance of developing depression following their experience, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding mechanism for students at university campuses.
While the internet and social media can be great tools for maintaining a social relationship with classmates, pre-university friends and family members, it can have negative mental health effects. Excessive usage of social media and the internet during freshman year can be a predictor of developing SAD during the following years [55] . Students who have a higher dependence on the social media report a higher feeling of loneliness, which can result in SAD [56] . Students with internet addiction and excessive usage of social media are usually in first year of their degrees [55] , [56] which can reflect a lack of adjustment to university life and forming a social network. Also, students who use social media more often have a lower level of self-esteem and prefer to recreate their sense of self [56] , indicating an intertwined relationship between biopsychosocial factors in developing SAD among students.
Demographic status, ethnic and sexual minority groups including international Asian students, black and bisexual students were at an elevated risk of depression and suicidal behaviour [16] , [50] . The frequency of mental health is usually more common among ethnic minorities. For example, Turner et al. [20] showed that ethnic minority students report a higher level of anxiety and depression compared to their white peers; however, they do not ask for help as much. Other studies supported these findings by showing that students from ethnic and religious minorities, regardless of their country of origin and country in which they study, have a higher prevalence of anxiety and depression compared to their peers [50] . Also, students' expectations from university can be different among ethnic minorities students, and most of them do not have a sufficient understanding of the services that university can provide for them [40] .
Therefore, lack of support from family and university, adverse relationships with family, lack of engagement in social activities, sexual victimization, excessive social media usage, belonging to ethnic and religious minority groups, and stigma associated with the mental health are among risk factors for SAD in university students.
3.3.6. Economic factors
Students' family economic status can influence their mental health. A low family income and experiencing poverty can be predictors of SAD development during university years [22] , [50] , [57] , [58] . A higher family income can even ameliorate negative psychological experiences during childhood, which can have long-term negative consequences on the mental health of students once they enter university [57] . Also, experiencing poverty during childhood can have negative long-term consequences on adults, leading to SAD development during university life [58] .
Some students take up part-time job to partially fund their studies. Vaughn et al. [59] showed that relationship of employed students with their colleagues in the workplace could affect students' mental health; and those students who had a poor relationship with their colleagues had worse mental health. However, it is worth mentioning that a causal relationship was not established. It can be possible that students who have poor mental health cannot get along with their co-workers, resulting in an adverse working relationship.
Because of paying higher tuition fees and less access to scholarships and bursaries available, international students can have more financial problems, causing a higher degree of anxiety and depression compared to home students [60] .
Lack of adequate financial support, low family income and poverty during childhood are risk factors of SAD in students of undergraduate courses in developed and developing countries.
3.4. Stigma associated with mental health
While efforts have been put to reduce the stigma associated with receiving help for mental health problems, this still remains a challenge. For example, more than half of students who had SAD did not receive any help or treatment for their condition because of the stigma associated with mental health [19] , [61] . This is not related to the awareness of the availability of mental health resources which was ruled out by authors, as most of the students who did not receive any help for their mental health problem were aware of available help and support to them [19] .
Furthermore, the social stigma associated with receiving help for mental health problems was significantly associated with suicidal behaviour, acting as a preventive barrier to seek help (planning and attempt) [16] . Among students, those with a history of mental health problem such as veterans with PTSD are less likely to seek for help compared to non-veteran students [25] , making them more susceptible to struggling with untreated mental health.
4. Discussion
This review tried to identify and summarise risk factors associated with SAD in undergraduate students studying in developed and developing countries. The prevalence of SAD is high among undergraduate university students who study in developed and developing countries. Untreated SAD can lead to eating disorders, self-harm, suicide, social problems [28] . Similar to a complex society, differences exist among students leading to complicated risk factors causing SAD. Because different themes influencing SAD has been investigated as a distinct body of research by different literature, a concept map is created to demonstrate the relationship between various risk factors contributing to the development of SAD in undergraduate students in developed and developing countries. Figure 3 bridges risk factors concepts between different literature. For most students, entering university is a new step in their lives which is associated with certain challenges such as moving into independent accommodation, social identity, financial management, making decisions, and forming a social network. Different students have different needs depending on the stage of their degree, which needs to be fulfilled. For example, coping with a new university life style can be a challenging task for students who enter the university. This becomes more significant for students moving abroad for their studying who need to adapt to a new lifestyle, speak in a different language, and live away from their families. In agreement with this, different levels of anxiety and depression with different risk factors are observed among students as they progress in their degrees. On the other hand, students who are finishing their degrees can have SAD because of uncertainties about their future.
Students learn different modules in different degrees and have different abilities. Mastery of the subject can be a factor affecting students' sense of self-esteem, influencing their anxiety level and developing depressive symptoms. This partially can explain changes in risk factors observed as students' progress in their degrees. Final year students who adjust to the university environment and develop mastery in their subject can deal with academic pressure better compared to freshers who transform from secondary school life to university lifestyle.
Students can come with a varied and challenging background such as those who experienced household and domestic violence, sexual abuse, and child poverty which can make them susceptible to developing anxiety and depression once academic pressure is mounted. As universities are diverse environment which enrol students from different socioeconomic background and different cultures, universities need to identify risk factors for different students and have robust plans to tackle them to provide a fostering environment for future leaders of the society. Therefore, early mental health screening can help to identify those students who are at risk to provide them with special and additional mental health support. Students not only should be screened for their mental health state as they enter university, but also regular follow up check-ups should be conducted to monitor their conditions as they progress in their degrees to detect early signs of SAD.
University and academic staff can play a significant role in either exaggerating or ameliorating risk factors associated with anxiety and depression. While teachers and mentors can support students to cope with SAD, they can be a source of problem too by discriminating, bullying, and hampering students' progress.
Managing finance and expenses can be a challenging task for students who are stepping into an independent lifestyle and need to pay for their tuitions in addition to their maintenance fees. While some students have access to private funding, bursaries, and scholarships, other students receive loans which they need to pay back or have part-time jobs to meet their expenses. Students who work need to have a work-life balance and the time spent in their jobs can affect the quality of their education.
Fresher students try to establish their social network and might feel isolated, which can push them to excessive usage of social media to fill their social gap. While internet addiction and excessive usage of social media can have a negative impact on students' mental health, technology, such as mobile phone applications can be used in universities campuses to promote a healthier lifestyle and reducing risk factors among students. For example, many students refuse to receive face-to-face mental health counselling support during their anxiety and depression due to stigma associated with disclosure of mental health issues. Providing students with anonymized counselling services through mobile phone applications can be one way of delivering help to students at universities.
With the advent of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, etc., more and more students rely on such networks for socialisation. While the internet and online platforms can have beneficial consequences for students, such as rapid access to a variety of online learning resources and keeping in contact with friends and families, excessive usage of social media and internet can have negative consequences on students' academic performance. A poor mental health state at the beginning of university life is a predictor of internet addiction later during the degree. Heavy reliance on the internet can be a coping mechanism for students with anxiety and depression to overcome their mental health problems.
As governments and educational bodies in developed and developing countries are emphasising recruitment of ethnic minority students to university to increase the range of equality and diversity among students, it is important to consider the mental health of those students in the university as well. Students in minority groups such as black, international Chinese and bisexual student report a higher level of anxiety and depression compared to other non-minority group students. This can be due to either pre-existing conditions which student experience before entering the university, and can be exacerbated during the university, or can be because of problems which can develop during university life.
Also, more mental health support is available in universities as the number of university students is increasing, and there is a better understanding of the importance of mental health in academia; however, the stigma associated with mental health has not changed proportionately.
While research and understanding of mental health have changed significantly over the past two decades and many more articles are present, risk factors associated with SAD remain unchanged.
One caveat with studies of mental health among student is that most studies have been conducted among medical and nursing students and neglected non-medical students. One potential explanation for the tendency to conduct depression surveys among medical students is the higher response rate as medical students are more willing to fill out the questionnaires and surveys. It is understandable that students studying medical subjects, who directly interact with the public and treating them once they enter the healthcare profession should have a reasonably sound mental health to be able to conduct their duties, but it does not justify neglecting the mental health of other students. Therefore, more research on mental health and risk factors associated with SAD of non-medical students is required in the future.
Another caveat with most mental health studies is that they are based on self-reports and surveys. Different people can have different perception and understanding of mental health and anxiety, and many confounding factors can influence the response of participants in the time of participation. Furthermore, students with severe mental health conditions are less likely to participate in any activity including surveys and questionnaires, leading to a non-response bias.
Another area which requires improvement in future studies of mental health is the categorisation of different types of depression and their severity. Depression and anxiety are a spectrum which can comprise of minor and major symptoms; however, most studies did not specify the scale of depression in their findings. Furthermore, while various risk factors were identified, a causal relationship between mental health and behaviours were not established.
While counselling services provided by universities in Western countries such as the UK and USA have increased over the past few years [62] , it is still not clear how effective such services are; therefore, more research is required to assess the effectiveness of counselling services at universities.
Therefore, a better understanding of the aetiology, associated factors is required for an effective intervention to reduce the disease incidence and prevalence among students in the population and providing them with a fostering environment to achieve their potential.
University undergraduate students are at a higher risk of developing SAD in developed and developing countries. Promoting the mental health of students is an important issue which should be addressed in the education and healthcare systems of developed and developing countries. Since students entering university are from different socioeconomic background, screening should be carried out early as students.
A personalized approach is required to assess mental health of different students. In addition, a majority of mental health risk factors can be related to the academic environment. A personalised, student-centred approach to include needs and requirements of different students from different background can help students to foster their talent to reach their full potential. Furthermore, more training should be provided for teaching and university staff to help students identify risk factors, and provide appropriate treatment.
5. Conclusion
Despite all the efforts over the past two decades to destigmatise mental health, the stigma associated with mental health is still a significant barrier for students, especially male students and students from ethnic and religious minorities to seek help for SAD treatment. Universities need to continue to destigmatise mental health in university campuses to enable students to receive more in campus support by providing designated time for positive metal health activities such as group exercise, physical activities, and counselling services. There is no shortage of athletic and group activities in form of clubs and social classes in most universities in developed and developing countries; however, more incentives such as athletic bursaries and prizes should be provided to students to encourage their participation in such activities which can act as protective factors against SAD development. Therefore, universities need to allocate more resources for sporting and social activities which can impact the mental health of students. Furthermore, an increase in mental health problems in universities has created a huge burden on university counselling services to meet the demands of students. More novel approaches, such as online counselling services can help universities to meet those increased demands.
Students in different years of studies deal with different risk factors from the time that they enter the university until they graduate, therefore, different coping strategies are required for students at different levels. Universities should be aware of these risk factors and implement measures to minimise those factors while providing mental health treatments to students.
Future studies are required to investigate long-term effects of experiencing SAD on students. A longitudinal study with a large randomly recruited sample size (different age, sex, degree of study, – socioeconomic status, etc.) is required to address how students' mental health change from entering the university until they graduate. Also, more extended follow up studies can be included to address the effect of depression and poor mental health on people's lives after they graduate from the university.
Abbreviations
Conflict of interest: All authors declare no conflicts of interest in this paper.
what are the factors that cause stress and how to cope with stress?
Unauthorized use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Writing9 with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
- overwhelmed
- relaxation techniques
- time management
- support system
- positive thinking
- mindfulness
- healthy habits
- environmental factors
- Check your IELTS essay »
- Find essays with the same topic
- View collections of IELTS Writing Samples
- Show IELTS Writing Task 2 Topics
. Many people these days have computer, laptops, telephones at their home for work. Do you think, working from home has more advantages or disadvantages? Give reasons.
The government should control the amount of violence in films and on television in order to decrease the violent crimes in society. what extent do you agree or disagree , students should not be allowed to use mobile phones at school. do you agree or disagree with this view, some people believe that that childhood is the happiest time of your live. to what extent do your agree , some people think adults should learn practical skills by themselves, while others think they should learn with teachers in the classroom. discuss both views and give your own opinion..
Home Toggle navigation FR Toggle Search Search the site Search About us About us Head office Regional offices History Archives Background materials Photos and videos Accessibility Contact us Corporate governance Board of Directors Governing Council and Senior Management Governance documents Educational resources The Economy, Plain and Simple Explainers Financial education resources Careers Take a central role at the Bank of Canada with our current opportunities and scholarships.
Interest Rate Announcement and Monetary Policy Report
09:45 (ET) On eight scheduled dates each year, the Bank of Canada announces the setting for the overnight rate target in a press release explaining the factors behind the decision. Four times a year, Governing Council presents the Monetary Policy Report : the Bank’s base-case projection for inflation and growth in the Canadian economy, and its assessment of risks.
See the media advisory .
We use cookies to help us keep improving this website.
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Academic Challenges — The Phenomenon of Academic Stress
The Phenomenon of Academic Stress
- Categories: Academic Challenges Stress
About this sample

Words: 728 |
Published: Aug 31, 2023
Words: 728 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Understanding academic stress, causes of academic stress, effects of academic stress, coping strategies and resilience, support systems and resources, balancing academic demands and well-being, addressing systemic factors, prevention and intervention strategies, conclusion: a call for holistic approaches to education.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1480 words
1 pages / 632 words
1 pages / 554 words
1 pages / 362 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Academic Challenges
Family dynamics can be complex and challenging, especially when dealing with a sibling who may not meet societal expectations of intelligence or competence. In my case, I have a brother who, for the purpose of this essay, I will [...]
Education is a dynamic field marked by constant change, bringing forth both unique opportunities and challenges. In this essay, we will explore the remarkable opportunities presented by diversity and inclusion in education, [...]
One takes on various roles and responsibilities within the academic community. One significant role that a college student embodies is that of a chief legislator. The chief legislator role involves not only abiding by [...]
As a college student, I have experienced firsthand the challenges and pressures of navigating higher education while managing mental health issues. According to the American College Health Association, more than 60% of college [...]
Moving to a new school is a significant life event that can have a profound impact on a person's academic, social, and emotional well-being. As a college student, I have had the opportunity to reflect on my own experience of [...]
Dual enrollment programs have become increasingly popular among high school students, offering them the opportunity to take college-level courses while still in high school. These programs allow students to earn both high school [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Individual response to stressors influences their health. Maladaptive response to stress results in various physical, psychological, and behavioral negative effects. Negative effects of stress on physical health include increased heart rates, sweating, high blood pressure, and long-term development of the cardiac condition. Psychological ...
Narrative Essay on Stress. 2 pages / 716 words. Stress is a universal experience that impacts individuals from all walks of life, regardless of age, gender, or social background. From the pressures of work and school to personal relationships and financial obligations, the sources of stress are vast and varied.
The effects of stress on individuals can be profound and far-reaching, impacting both physical and mental health. Chronic stress has been linked to a range of health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and digestive issues. The constant activation of the body's stress response can lead to a weakened immune system, making ...
1. Injury or infections of the body, dangers in environment, major changes or transitions in life which force us to cope in new ways. 2. Physical stressors like noise, pollutions, climatic changes, etc. 3. Hustles of everyday life centering on work, family, social activities, health and finances. 4.
The essay "Stress and Its Role in Our Life" is a useful introduction to the topic, but it could benefit from some improvements. The writer tends to repeat information in different ways, which can make the essay feel less concise than it could be. ... Psychopathology refers to the study of mental disorders and the factors that contribute to ...
7 Writing Prompts for Essays About Stress. 1. What Is Stress. Use this prompt to help your readers know the early signs of stress. Stress is a person's emotional response to pressure to meet standards, commitments, and responsibilities. It usually occurs in a situation or an outcome we fail to manage or control.
Common relationship stressors include: . Being too busy to spend time with each other and share responsibilities. Intimacy and sex are become rare due to busyness, health problems, and any number of other reasons. There is abuse or control in the relationship. You and your partner are not communicating.
Acute stress: Acute stress is a very short-term type of stress that can either be positive or more distressing; this is the type of stress we most often encounter in day-to-day life.; Chronic stress: Chronic stress is stress that seems never-ending and inescapable, like the stress of a bad marriage or an extremely taxing job; chronic stress can also stem from traumatic experiences and ...
LIFE STRESS, ANXIETY, AND DEPRESSION . It is well known that first depressive episodes often develop following the occurrence of a major negative life event (Paykel 2001).Furthermore, there is evidence that stressful life events are causal for the onset of depression (see Hammen 2005, Kendler et al. 1999).A study of 13,006 patients in Denmark, with first psychiatric admissions diagnosed with ...
loss of your sense of humor. feelings of overwhelm. depression. loss of interest in life or activities. existing mental health conditions get worse. Physical symptoms of stress may include the ...
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques. Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
IELTS Stress Essay. This is a model IELTS stress essay. It is about stress in modern society and how to prevent it. It is a causes and solutions type essay. In other words, you have to identify what causes stressand then suggest solutions. Stress is now a major problem in many countries around the world.
At present, stress is regarded as a public problem for most of employees. People try to find the roots of stress, especially in workplace. Some psychologists say that stressors such as workload, work schedule and conflict at work are the main sources of stress in the workplace (Landy & Conte 2004). Furnham (2005) divides the main stressors into ...
All 60 papers were read completely, and from those, 19 were excluded based on the criteria mentioned before. Therefore, the total number of papers for consideration was 41. ... A lack of self-care and having an unhealthy lifestyle are risk factors for stress and anxiety among students. A lack of self-care can cause sense of guilt which can pose ...
Stress has been considered to be an issue of concern in many wealthy nations. It may be. due to. various factors which could be solved easily. This. essay will indicate the factors that cause stress and how to deal with. this. issue. To start with, pregnancy and becoming a parent are some of the biggest pressures that people have to face up ...
Stress Factors. Stress can be defined as the feeling felt in time of difficulty, fear and when facing challenging situations. Stress is a feeling in which a person feels like they cannot cope with a certain situation. Stress comes in many forms and may be physical, psychological or emotional. Factors that cause stress are known as stressors.
Stress is a universal experience that impacts individuals from all walks of life, regardless of age, gender, or social background. From the pressures of work and school to personal relationships and financial obligations, the sources of stress are vast and varied. In this narrative essay, we will delve into the complex nature of stress, exploring its physical, emotional, and psychological ...
The problem arises when the body's stress response is continuous. A perpetual state of "fight or flight" could lead to many chronic problems. Individuals could experience anxiety and ...
09:45 (ET)On eight scheduled dates each year, the Bank of Canada announces the setting for the overnight rate target in a press release explaining the factors behind the decision. Four times a year, Governing Council presents the Monetary Policy Report: the Bank's base-case projection for inflation and growth in the Canadian economy, and its assessment of risks.
Olive (Olea europaea L.) is a crop of enormous economic and cultural importance. Over the years, the worldwide production of olive oil has been decreasing due to various biotic and abiotic factors. The current drop in olive oil production resulting from climate change raises concerns regarding the fulfillment of our daily demand for olive oil and has led to a significant increase in market prices.
Academic stress encompasses a range of emotional and psychological responses that students experience due to the pressures of their educational journey. It manifests as anxiety, burnout, and an overwhelming sense of pressure to perform. The contributing factors are diverse, encompassing high expectations from oneself and others, heavy workloads ...
This paper has proposed an efficient analysis method to calculate interface stress intensity factors (SIFs) based on a proportional stress field of a reference problem whose exact solution is available. In the previous proportional methods, the same crack length and the same element size were applied to both reference and unknown problems so ...
This paper assesses the state and resilience of corporate and banking sectors in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) in a "higher-for-longer" interest rate environment using granular micro data to conduct the first cross-country corporate and banking sector stress tests for the MENA region. The results suggest that corporate sector debt at risk may increase sizably from 12 to 30 ...