Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide

How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Textual Analysis: Definition, Types & 10 Examples
Textual analysis is a research methodology that involves exploring written text as empirical data. Scholars explore both the content and structure of texts, and attempt to discern key themes and statistics emergent from them.
This method of research is used in various academic disciplines, including cultural studies, literature, bilical studies, anthropology , sociology, and others (Dearing, 2022; McKee, 2003).
This method of analysis involves breaking down a text into its constituent parts for close reading and making inferences about its context, underlying themes, and the intentions of its author.
Textual Analysis Definition
Alan McKee is one of the preeminent scholars of textual analysis. He provides a clear and approachable definition in his book Textual Analysis: A Beginner’s Guide (2003) where he writes:
“When we perform textual analysis on a text we make an educated guess at some of the most likely interpretations that might be made of the text […] in order to try and obtain a sense of the ways in which, in particular cultures at particular times, people make sense of the world around them.”
A key insight worth extracting from this definition is that textual analysis can reveal what cultural groups value, how they create meaning, and how they interpret reality.
This is invaluable in situations where scholars are seeking to more deeply understand cultural groups and civilizations – both past and present (Metoyer et al., 2018).
As such, it may be beneficial for a range of different types of studies, such as:
- Studies of Historical Texts: A study of how certain concepts are framed, described, and approached in historical texts, such as the Bible.
- Studies of Industry Reports: A study of how industry reports frame and discuss concepts such as environmental and social responsibility.
- Studies of Literature: A study of how a particular text or group of texts within a genre define and frame concepts. For example, you could explore how great American literature mythologizes the concept of the ‘The American Dream’.
- Studies of Speeches: A study of how certain politicians position national identities in their appeals for votes.
- Studies of Newspapers: A study of the biases within newspapers toward or against certain groups of people.
- Etc. (For more, see: Dearing, 2022)
McKee uses the term ‘textual analysis’ to also refer to text types that are not just written, but multimodal. For a dive into the analysis of multimodal texts, I recommend my article on content analysis , where I explore the study of texts like television advertisements and movies in detail.
Features of a Textual Analysis
When conducting a textual analysis, you’ll need to consider a range of factors within the text that are worthy of close examination to infer meaning. Features worthy of considering include:
- Content: What is being said or conveyed in the text, including explicit and implicit meanings, themes, or ideas.
- Context: When and where the text was created, the culture and society it reflects, and the circumstances surrounding its creation and distribution.
- Audience: Who the text is intended for, how it’s received, and the effect it has on its audience.
- Authorship: Who created the text, their background and perspectives, and how these might influence the text.
- Form and structure: The layout, sequence, and organization of the text and how these elements contribute to its meanings (Metoyer et al., 2018).
Textual Analysis Coding Methods
The above features may be examined through quantitative or qualitative research designs , or a mixed-methods angle.
1. Quantitative Approaches
You could analyze several of the above features, namely, content, form, and structure, from a quantitative perspective using computational linguistics and natural language processing (NLP) analysis.
From this approach, you would use algorithms to extract useful information or insights about frequency of word and phrase usage, etc. This can include techniques like sentiment analysis, topic modeling, named entity recognition, and more.
2. Qualitative Approaches
In many ways, textual analysis lends itself best to qualitative analysis. When identifying words and phrases, you’re also going to want to look at the surrounding context and possibly cultural interpretations of what is going on (Mayring, 2015).
Generally, humans are far more perceptive at teasing out these contextual factors than machines (although, AI is giving us a run for our money).
One qualitative approach to textual analysis that I regularly use is inductive coding, a step-by-step methodology that can help you extract themes from texts. If you’re interested in using this step-by-step method, read my guide on inductive coding here .
See more Qualitative Research Approaches Here
Textual Analysis Examples
Title: “Discourses on Gender, Patriarchy and Resolution 1325: A Textual Analysis of UN Documents” Author: Nadine Puechguirbal Year: 2010 APA Citation: Puechguirbal, N. (2010). Discourses on Gender, Patriarchy and Resolution 1325: A Textual Analysis of UN Documents, International Peacekeeping, 17 (2): 172-187. doi: 10.1080/13533311003625068
Summary: The article discusses the language used in UN documents related to peace operations and analyzes how it perpetuates stereotypical portrayals of women as vulnerable individuals. The author argues that this language removes women’s agency and keeps them in a subordinate position as victims, instead of recognizing them as active participants and agents of change in post-conflict environments. Despite the adoption of UN Security Council Resolution 1325, which aims to address the role of women in peace and security, the author suggests that the UN’s male-dominated power structure remains unchallenged, and gender mainstreaming is often presented as a non-political activity.
Title: “Racism and the Media: A Textual Analysis” Author: Kassia E. Kulaszewicz Year: 2015 APA Citation: Kulaszewicz, K. E. (2015). Racism and the Media: A Textual Analysis . Dissertation. Retrieved from: https://sophia.stkate.edu/msw_papers/477
Summary: This study delves into the significant role media plays in fostering explicit racial bias. Using Bandura’s Learning Theory, it investigates how media content influences our beliefs through ‘observational learning’. Conducting a textual analysis, it finds differences in representation of black and white people, stereotyping of black people, and ostensibly micro-aggressions toward black people. The research highlights how media often criminalizes Black men, portraying them as violent, while justifying or supporting the actions of White officers, regardless of their potential criminality. The study concludes that news media likely continues to reinforce racism, whether consciously or unconsciously.
Title: “On the metaphorical nature of intellectual capital: a textual analysis” Author: Daniel Andriessen Year: 2006 APA Citation: Andriessen, D. (2006). On the metaphorical nature of intellectual capital: a textual analysis. Journal of Intellectual capital , 7 (1), 93-110.
Summary: This article delves into the metaphorical underpinnings of intellectual capital (IC) and knowledge management, examining how knowledge is conceptualized through metaphors. The researchers employed a textual analysis methodology, scrutinizing key texts in the field to identify prevalent metaphors. They found that over 95% of statements about knowledge are metaphor-based, with “knowledge as a resource” and “knowledge as capital” being the most dominant. This study demonstrates how textual analysis helps us to understand current understandings and ways of speaking about a topic.
Title: “Race in Rhetoric: A Textual Analysis of Barack Obama’s Campaign Discourse Regarding His Race” Author: Andrea Dawn Andrews Year: 2011 APA Citation: Andrew, A. D. (2011) Race in Rhetoric: A Textual Analysis of Barack Obama’s Campaign Discourse Regarding His Race. Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection. 120 . https://digitalcommons.butler.edu/ugtheses/120
This undergraduate honors thesis is a textual analysis of Barack Obama’s speeches that explores how Obama frames the concept of race. The student’s capstone project found that Obama tended to frame racial inequality as something that could be overcome, and that this was a positive and uplifting project. Here, the student breaks-down times when Obama utilizes the concept of race in his speeches, and examines the surrounding content to see the connotations associated with race and race-relations embedded in the text. Here, we see a decidedly qualitative approach to textual analysis which can deliver contextualized and in-depth insights.
Sub-Types of Textual Analysis
While above I have focused on a generalized textual analysis approach, a range of sub-types and offshoots have emerged that focus on specific concepts, often within their own specific theoretical paradigms. Each are outlined below, and where I’ve got a guide, I’ve linked to it in blue:
- Content Analysis : Content analysis is similar to textual analysis, and I would consider it a type of textual analysis, where it’s got a broader understanding of the term ‘text’. In this type, a text is any type of ‘content’, and could be multimodal in nature, such as television advertisements, movies, posters, and so forth. Content analysis can be both qualitative and quantitative, depending on whether it focuses more on the meaning of the content or the frequency of certain words or concepts (Chung & Pennebaker, 2018).
- Discourse Analysis : Emergent specifically from critical and postmodern/ poststructural theories, discourse analysis focuses closely on the use of language within a social context, with the goal of revealing how repeated framing of terms and concepts has the effect of shaping how cultures understand social categories. It considers how texts interact with and shape social norms, power dynamics, ideologies, etc. For example, it might examine how gender is socially constructed as a distinct social category through Disney films. It may also be called ‘critical discourse analysis’.
- Narrative Analysis: This approach is used for analyzing stories and narratives within text. It looks at elements like plot, characters, themes, and the sequence of events to understand how narratives construct meaning.
- Frame Analysis: This approach looks at how events, ideas, and themes are presented or “framed” within a text. It explores how these frames can shape our understanding of the information being presented. While similar to discourse analysis, a frame analysis tends to be less associated with the loaded concept of ‘discourse’ that exists specifically within postmodern paradigms (Smith, 2017).
- Semiotic Analysis: This approach studies signs and symbols, both visual and textual, and could be a good compliment to a content analysis, as it provides the language and understandings necessary to describe how signs make meaning in cultural contexts that we might find with the fields of semantics and pragmatics . It’s based on the theory of semiotics, which is concerned with how meaning is created and communicated through signs and symbols.
- Computational Textual Analysis: In the context of data science or artificial intelligence, this type of analysis involves using algorithms to process large amounts of text. Techniques can include topic modeling, sentiment analysis, word frequency analysis, and others. While being extremely useful for a quantitative analysis of a large dataset of text, it falls short in its ability to provide deep contextualized understandings of words-in-context.
Each of these methods has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method depends on the research question, the type of text being analyzed, and the broader context of the research.
See More Examples of Analysis Here
Strengths and Weaknesses of Textual Analysis
When writing your methodology for your textual analysis, make sure to define not only what textual analysis is, but (if applicable) the type of textual analysis, the features of the text you’re analyzing, and the ways you will code the data. It’s also worth actively reflecting on the potential weaknesses of a textual analysis approach, but also explaining why, despite those weaknesses, you believe this to be the most appropriate methodology for your study.
Chung, C. K., & Pennebaker, J. W. (2018). Textual analysis. In Measurement in social psychology (pp. 153-173). Routledge.
Dearing, V. A. (2022). Manual of textual analysis . Univ of California Press.
McKee, A. (2003). Textual analysis: A beginner’s guide. Textual analysis , 1-160.
Mayring, P. (2015). Qualitative content analysis: Theoretical background and procedures. Approaches to qualitative research in mathematics education: Examples of methodology and methods , 365-380. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9181-6_13
Metoyer, R., Zhi, Q., Janczuk, B., & Scheirer, W. (2018, March). Coupling story to visualization: Using textual analysis as a bridge between data and interpretation. In 23rd International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (pp. 503-507). doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3172944.3173007
Smith, J. A. (2017). Textual analysis. The international encyclopedia of communication research methods , 1-7.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”
Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.

The Power of Analysis: Tips and Tricks for Writing Analysis Essays: Home
Crystal sosa.

Helpful Links
- Super Search Webpage Where to start your research.
- Scribbr Textual analysis guide.
- Analyzing Texts Prezi Presentation A prezi presentation on analyzing texts.
- Writing Essays Guide A guide to writing essays/
- Why is it important?
- Explanation & Example
- Different Types of Analysis Essays
Text analysis and writing analysis texts are important skills to develop as they allow individuals to critically engage with written material, understand underlying themes and arguments, and communicate their own ideas in a clear and effective manner. These skills are essential in academic and professional settings, as well as in everyday life, as they enable individuals to evaluate information and make informed decisions.
What is Text Analysis?
Text analysis is the process of examining and interpreting a written or spoken text to understand its meaning, structure, and context. It involves breaking down the text into its constituent parts, such as words, phrases, and sentences, and analyzing how they work together to convey a particular message or idea.
Text analysis can be used to explore a wide range of textual material, including literature, poetry, speeches, and news articles, and it is often employed in academic research, literary criticism, and media analysis. By analyzing texts, we can gain deeper insights into their meanings, uncover hidden messages and themes, and better understand the social and cultural contexts in which they were produced.
What is an Analysis Essay?
An analysis essay is a type of essay that requires the writer to analyze and interpret a particular text or topic. The goal of an analysis essay is to break down the text or topic into smaller parts and examine each part carefully. This allows the writer to make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
In “The Yellow Wallpaper,” Charlotte Perkins Gilman uses the first-person point of view and vivid descriptions of the protagonist’s surroundings to convey the protagonist’s psychological deterioration. By limiting the reader’s understanding of the story’s events to the protagonist’s perspective, Gilman creates a sense of claustrophobia and paranoia, mirroring the protagonist’s own feelings. Additionally, the use of sensory language, such as the “smooch of rain,” and descriptions of the “yellow wallpaper” and its “sprawling flamboyant patterns,” further emphasize the protagonist’s sensory and emotional experience. Through these techniques, Gilman effectively communicates the protagonist’s descent into madness and the effects of societal oppression on women’s mental health.
There are several different types of analysis essays, including:
Literary Analysis Essays: These essays examine a work of literature and analyze various literary devices such as character development, plot, theme, and symbolism.
Rhetorical Analysis Essays: These essays examine how authors use language and rhetoric to persuade their audience, focusing on the author's tone, word choice, and use of rhetorical devices.
Film Analysis Essays: These essays analyze a film's themes, characters, and visual elements, such as cinematography and sound.
Visual Analysis Essays: These essays analyze visual art, such as paintings or sculptures, and explore how the artwork's elements work together to create meaning.
Historical Analysis Essays: These essays analyze historical events or documents and examine their causes, effects, and implications.
Comparative Analysis Essays: These essays compare and contrast two or more works, focusing on similarities and differences between them.
Process Analysis Essays: These essays explain how to do something or how something works, providing a step-by-step analysis of a process.
Analyzing Texts
- General Tips
- How to Analyze
- What to Analyze
When writing an essay, it's essential to analyze your topic thoroughly. Here are some suggestions for analyzing your topic:
Read carefully: Start by reading your text or prompt carefully. Make sure you understand the key points and what the text or prompt is asking you to do.
Analyze the text or topic thoroughly: Analyze the text or topic thoroughly by breaking it down into smaller parts and examining each part carefully. This will help you make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more comprehensive understanding of it.
Identify key concepts: Identify the key concepts, themes, and ideas in the text or prompt. This will help you focus your analysis.
Take notes: Take notes on important details and concepts as you read. This will help you remember what you've read and organize your thoughts.
Consider different perspectives: Consider different perspectives and interpretations of the text or prompt. This can help you create a more well-rounded analysis.
Use evidence: Use evidence from the text or outside sources to support your analysis. This can help you make your argument stronger and more convincing.
Formulate your thesis statement: Based on your analysis of the essay, formulate your thesis statement. This should be a clear and concise statement that summarizes your main argument.
Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to communicate your ideas effectively. Avoid using overly complicated language that may confuse your reader.
Revise and edit: Revise and edit your essay carefully to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Understanding the assignment: Make sure you fully understand the assignment and the purpose of the analysis. This will help you focus your analysis and ensure that you are meeting the requirements of the assignment.
Read the essay multiple times: Reading the essay multiple times will help you to identify the author's main argument, key points, and supporting evidence.
Take notes: As you read the essay, take notes on key points, quotes, and examples. This will help you to organize your thoughts and identify patterns in the author's argument.
Take breaks: It's important to take breaks while reading academic essays to avoid burnout. Take a break every 20-30 minutes and do something completely different, like going for a walk or listening to music. This can help you to stay refreshed and engaged.
Highlight or underline key points: As you read, highlight or underline key points, arguments, and evidence that stand out to you. This will help you to remember and analyze important information later.
Ask questions: Ask yourself questions as you read to help you engage critically with the text. What is the author's argument? What evidence do they use to support their claims? What are the strengths and weaknesses of their argument?
Engage in active reading: Instead of passively reading, engage in active reading by asking questions, making connections to other readings or personal experiences, and reflecting on what you've read.
Find a discussion partner: Find someone to discuss the essay with, whether it's a classmate, a friend, or a teacher. Discussing the essay can help you to process and analyze the information more deeply, and can also help you to stay engaged.
- Identify the author's purpose and audience: Consider why the author wrote the essay and who their intended audience is. This will help you to better understand the author's perspective and the purpose of their argument.
Analyze the structure of the essay: Consider how the essay is structured and how this supports the author's argument. Look for patterns in the organization of ideas and the use of transitions.
Evaluate the author's use of evidence: Evaluate the author's use of evidence and how it supports their argument. Consider whether the evidence is credible, relevant, and sufficient to support the author's claims.
Consider the author's tone and style: Consider the author's tone and style and how it contributes to their argument. Look for patterns in the use of language, imagery, and rhetorical devices.
Consider the context : Consider the context in which the essay was written, such as the author's background, the time period, and any societal or cultural factors that may have influenced their perspective.
Evaluate the evidence: Evaluate the evidence presented in the essay and consider whether it is sufficient to support the author's argument. Look for any biases or assumptions that may be present in the evidence.
Consider alternative viewpoints: Consider alternative viewpoints and arguments that may challenge the author's perspective. This can help you to engage critically with the text and develop a more well-rounded understanding of the topic.

- Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023 1:01 PM
- URL: https://odessa.libguides.com/analysis


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 5 steps to write a great analytical essay.
General Education

Do you need to write an analytical essay for school? What sets this kind of essay apart from other types, and what must you include when you write your own analytical essay? In this guide, we break down the process of writing an analytical essay by explaining the key factors your essay needs to have, providing you with an outline to help you structure your essay, and analyzing a complete analytical essay example so you can see what a finished essay looks like.
What Is an Analytical Essay?
Before you begin writing an analytical essay, you must know what this type of essay is and what it includes. Analytical essays analyze something, often (but not always) a piece of writing or a film.
An analytical essay is more than just a synopsis of the issue though; in this type of essay you need to go beyond surface-level analysis and look at what the key arguments/points of this issue are and why. If you’re writing an analytical essay about a piece of writing, you’ll look into how the text was written and why the author chose to write it that way. Instead of summarizing, an analytical essay typically takes a narrower focus and looks at areas such as major themes in the work, how the author constructed and supported their argument, how the essay used literary devices to enhance its messages, etc.
While you certainly want people to agree with what you’ve written, unlike with persuasive and argumentative essays, your main purpose when writing an analytical essay isn’t to try to convert readers to your side of the issue. Therefore, you won’t be using strong persuasive language like you would in those essay types. Rather, your goal is to have enough analysis and examples that the strength of your argument is clear to readers.
Besides typical essay components like an introduction and conclusion, a good analytical essay will include:
- A thesis that states your main argument
- Analysis that relates back to your thesis and supports it
- Examples to support your analysis and allow a more in-depth look at the issue
In the rest of this article, we’ll explain how to include each of these in your analytical essay.
How to Structure Your Analytical Essay
Analytical essays are structured similarly to many other essays you’ve written, with an introduction (including a thesis), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Below is an outline you can follow when structuring your essay, and in the next section we go into more detail on how to write an analytical essay.
Introduction
Your introduction will begin with some sort of attention-grabbing sentence to get your audience interested, then you’ll give a few sentences setting up the topic so that readers have some context, and you’ll end with your thesis statement. Your introduction will include:
- Brief background information explaining the issue/text
- Your thesis
Body Paragraphs
Your analytical essay will typically have three or four body paragraphs, each covering a different point of analysis. Begin each body paragraph with a sentence that sets up the main point you’ll be discussing. Then you’ll give some analysis on that point, backing it up with evidence to support your claim. Continue analyzing and giving evidence for your analysis until you’re out of strong points for the topic. At the end of each body paragraph, you may choose to have a transition sentence that sets up what the next paragraph will be about, but this isn’t required. Body paragraphs will include:
- Introductory sentence explaining what you’ll cover in the paragraph (sort of like a mini-thesis)
- Analysis point
- Evidence (either passages from the text or data/facts) that supports the analysis
- (Repeat analysis and evidence until you run out of examples)
You won’t be making any new points in your conclusion; at this point you’re just reiterating key points you’ve already made and wrapping things up. Begin by rephrasing your thesis and summarizing the main points you made in the essay. Someone who reads just your conclusion should be able to come away with a basic idea of what your essay was about and how it was structured. After this, you may choose to make some final concluding thoughts, potentially by connecting your essay topic to larger issues to show why it’s important. A conclusion will include:
- Paraphrase of thesis
- Summary of key points of analysis
- Final concluding thought(s)

5 Steps for Writing an Analytical Essay
Follow these five tips to break down writing an analytical essay into manageable steps. By the end, you’ll have a fully-crafted analytical essay with both in-depth analysis and enough evidence to support your argument. All of these steps use the completed analytical essay in the next section as an example.
#1: Pick a Topic
You may have already had a topic assigned to you, and if that’s the case, you can skip this step. However, if you haven’t, or if the topic you’ve been assigned is broad enough that you still need to narrow it down, then you’ll need to decide on a topic for yourself. Choosing the right topic can mean the difference between an analytical essay that’s easy to research (and gets you a good grade) and one that takes hours just to find a few decent points to analyze
Before you decide on an analytical essay topic, do a bit of research to make sure you have enough examples to support your analysis. If you choose a topic that’s too narrow, you’ll struggle to find enough to write about.
For example, say your teacher assigns you to write an analytical essay about the theme in John Steinbeck’s The Grapes of Wrath of exposing injustices against migrants. For it to be an analytical essay, you can’t just recount the injustices characters in the book faced; that’s only a summary and doesn’t include analysis. You need to choose a topic that allows you to analyze the theme. One of the best ways to explore a theme is to analyze how the author made his/her argument. One example here is that Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters (short chapters that didn’t relate to the plot or contain the main characters of the book) to show what life was like for migrants as a whole during the Dust Bowl.
You could write about how Steinbeck used literary devices throughout the whole book, but, in the essay below, I chose to just focus on the intercalary chapters since they gave me enough examples. Having a narrower focus will nearly always result in a tighter and more convincing essay (and can make compiling examples less overwhelming).
#2: Write a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the most important sentence of your essay; a reader should be able to read just your thesis and understand what the entire essay is about and what you’ll be analyzing. When you begin writing, remember that each sentence in your analytical essay should relate back to your thesis
In the analytical essay example below, the thesis is the final sentence of the first paragraph (the traditional spot for it). The thesis is: “In The Grapes of Wrath’s intercalary chapters, John Steinbeck employs a variety of literary devices and stylistic choices to better expose the injustices committed against migrants in the 1930s.” So what will this essay analyze? How Steinbeck used literary devices in the intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants could have it. Crystal clear.
#3: Do Research to Find Your Main Points
This is where you determine the bulk of your analysis--the information that makes your essay an analytical essay. My preferred method is to list every idea that I can think of, then research each of those and use the three or four strongest ones for your essay. Weaker points may be those that don’t relate back to the thesis, that you don’t have much analysis to discuss, or that you can’t find good examples for. A good rule of thumb is to have one body paragraph per main point
This essay has four main points, each of which analyzes a different literary device Steinbeck uses to better illustrate how difficult life was for migrants during the Dust Bowl. The four literary devices and their impact on the book are:
- Lack of individual names in intercalary chapters to illustrate the scope of the problem
- Parallels to the Bible to induce sympathy for the migrants
- Non-showy, often grammatically-incorrect language so the migrants are more realistic and relatable to readers
- Nature-related metaphors to affect the mood of the writing and reflect the plight of the migrants
#4: Find Excerpts or Evidence to Support Your Analysis
Now that you have your main points, you need to back them up. If you’re writing a paper about a text or film, use passages/clips from it as your main source of evidence. If you’re writing about something else, your evidence can come from a variety of sources, such as surveys, experiments, quotes from knowledgeable sources etc. Any evidence that would work for a regular research paper works here.
In this example, I quoted multiple passages from The Grapes of Wrath in each paragraph to support my argument. You should be able to back up every claim you make with evidence in order to have a strong essay.
#5: Put It All Together
Now it's time to begin writing your essay, if you haven’t already. Create an introductory paragraph that ends with the thesis, make a body paragraph for each of your main points, including both analysis and evidence to back up your claims, and wrap it all up with a conclusion that recaps your thesis and main points and potentially explains the big picture importance of the topic.

Analytical Essay Example + Analysis
So that you can see for yourself what a completed analytical essay looks like, here’s an essay I wrote back in my high school days. It’s followed by analysis of how I structured my essay, what its strengths are, and how it could be improved.
One way Steinbeck illustrates the connections all migrant people possessed and the struggles they faced is by refraining from using specific titles and names in his intercalary chapters. While The Grapes of Wrath focuses on the Joad family, the intercalary chapters show that all migrants share the same struggles and triumphs as the Joads. No individual names are used in these chapters; instead the people are referred to as part of a group. Steinbeck writes, “Frantic men pounded on the doors of the doctors; and the doctors were busy. And sad men left word at country stores for the coroner to send a car,” (555). By using generic terms, Steinbeck shows how the migrants are all linked because they have gone through the same experiences. The grievances committed against one family were committed against thousands of other families; the abuse extends far beyond what the Joads experienced. The Grapes of Wrath frequently refers to the importance of coming together; how, when people connect with others their power and influence multiplies immensely. Throughout the novel, the goal of the migrants, the key to their triumph, has been to unite. While their plans are repeatedly frustrated by the government and police, Steinbeck’s intercalary chapters provide a way for the migrants to relate to one another because they have encountered the same experiences. Hundreds of thousands of migrants fled to the promised land of California, but Steinbeck was aware that numbers alone were impersonal and lacked the passion he desired to spread. Steinbeck created the intercalary chapters to show the massive numbers of people suffering, and he created the Joad family to evoke compassion from readers. Because readers come to sympathize with the Joads, they become more sensitive to the struggles of migrants in general. However, John Steinbeck frequently made clear that the Joads were not an isolated incident; they were not unique. Their struggles and triumphs were part of something greater. Refraining from specific names in his intercalary chapters allows Steinbeck to show the vastness of the atrocities committed against migrants.
Steinbeck also creates significant parallels to the Bible in his intercalary chapters in order to enhance his writing and characters. By using simple sentences and stylized writing, Steinbeck evokes Biblical passages. The migrants despair, “No work till spring. No work,” (556). Short, direct sentences help to better convey the desperateness of the migrants’ situation. Throughout his novel, John Steinbeck makes connections to the Bible through his characters and storyline. Jim Casy’s allusions to Christ and the cycle of drought and flooding are clear biblical references. By choosing to relate The Grapes of Wrath to the Bible, Steinbeck’s characters become greater than themselves. Starving migrants become more than destitute vagrants; they are now the chosen people escaping to the promised land. When a forgotten man dies alone and unnoticed, it becomes a tragedy. Steinbeck writes, “If [the migrants] were shot at, they did not run, but splashed sullenly away; and if they were hit, they sank tiredly in the mud,” (556). Injustices committed against the migrants become greater because they are seen as children of God through Steinbeck’s choice of language. Referencing the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s novel and purpose: to create understanding for the dispossessed. It is easy for people to feel disdain for shabby vagabonds, but connecting them to such a fundamental aspect of Christianity induces sympathy from readers who might have otherwise disregarded the migrants as so many other people did.
The simple, uneducated dialogue Steinbeck employs also helps to create a more honest and meaningful representation of the migrants, and it makes the migrants more relatable to readers. Steinbeck chooses to accurately represent the language of the migrants in order to more clearly illustrate their lives and make them seem more like real paper than just characters in a book. The migrants lament, “They ain’t gonna be no kinda work for three months,” (555). There are multiple grammatical errors in that single sentence, but it vividly conveys the despair the migrants felt better than a technically perfect sentence would. The Grapes of Wrath is intended to show the severe difficulties facing the migrants so Steinbeck employs a clear, pragmatic style of writing. Steinbeck shows the harsh, truthful realities of the migrants’ lives and he would be hypocritical if he chose to give the migrants a more refined voice and not portray them with all their shortcomings. The depiction of the migrants as imperfect through their language also makes them easier to relate to. Steinbeck’s primary audience was the middle class, the less affluent of society. Repeatedly in The Grapes of Wrath , the wealthy make it obvious that they scorn the plight of the migrants. The wealthy, not bad luck or natural disasters, were the prominent cause of the suffering of migrant families such as the Joads. Thus, Steinbeck turns to the less prosperous for support in his novel. When referring to the superior living conditions barnyard animals have, the migrants remark, “Them’s horses-we’re men,” (556). The perfect simplicity of this quote expresses the absurdness of the migrants’ situation better than any flowery expression could.
In The Grapes of Wrath , John Steinbeck uses metaphors, particularly about nature, in order to illustrate the mood and the overall plight of migrants. Throughout most of the book, the land is described as dusty, barren, and dead. Towards the end, however; floods come and the landscape begins to change. At the end of chapter twenty-nine, Steinbeck describes a hill after the floods saying, “Tiny points of grass came through the earth, and in a few days the hills were pale green with the beginning year,” (556). This description offers a stark contrast from the earlier passages which were filled with despair and destruction. Steinbeck’s tone from the beginning of the chapter changes drastically. Early in the chapter, Steinbeck had used heavy imagery in order to convey the destruction caused by the rain, “The streams and the little rivers edged up to the bank sides and worked at willows and tree roots, bent the willows deep in the current, cut out the roots of cottonwoods and brought down the trees,” (553). However, at the end of the chapter the rain has caused new life to grow in California. The new grass becomes a metaphor representing hope. When the migrants are at a loss over how they will survive the winter, the grass offers reassurance. The story of the migrants in the intercalary chapters parallels that of the Joads. At the end of the novel, the family is breaking apart and has been forced to flee their home. However, both the book and final intercalary chapter end on a hopeful note after so much suffering has occurred. The grass metaphor strengthens Steinbeck’s message because it offers a tangible example of hope. Through his language Steinbeck’s themes become apparent at the end of the novel. Steinbeck affirms that persistence, even when problems appear insurmountable, leads to success. These metaphors help to strengthen Steinbeck’s themes in The Grapes of Wrath because they provide a more memorable way to recall important messages.
John Steinbeck’s language choices help to intensify his writing in his intercalary chapters and allow him to more clearly show how difficult life for migrants could be. Refraining from using specific names and terms allows Steinbeck to show that many thousands of migrants suffered through the same wrongs. Imitating the style of the Bible strengthens Steinbeck’s characters and connects them to the Bible, perhaps the most famous book in history. When Steinbeck writes in the imperfect dialogue of the migrants, he creates a more accurate portrayal and makes the migrants easier to relate to for a less affluent audience. Metaphors, particularly relating to nature, strengthen the themes in The Grapes of Wrath by enhancing the mood Steinbeck wants readers to feel at different points in the book. Overall, the intercalary chapters that Steinbeck includes improve his novel by making it more memorable and reinforcing the themes Steinbeck embraces throughout the novel. Exemplary stylistic devices further persuade readers of John Steinbeck’s personal beliefs. Steinbeck wrote The Grapes of Wrath to bring to light cruelties against migrants, and by using literary devices effectively, he continuously reminds readers of his purpose. Steinbeck’s impressive language choices in his intercalary chapters advance the entire novel and help to create a classic work of literature that people still are able to relate to today.
This essay sticks pretty closely to the standard analytical essay outline. It starts with an introduction, where I chose to use a quote to start off the essay. (This became my favorite way to start essays in high school because, if I wasn’t sure what to say, I could outsource the work and find a quote that related to what I’d be writing about.) The quote in this essay doesn’t relate to the themes I’m discussing quite as much as it could, but it’s still a slightly different way to start an essay and can intrigue readers. I then give a bit of background on The Grapes of Wrath and its themes before ending the intro paragraph with my thesis: that Steinbeck used literary devices in intercalary chapters to show how rough migrants had it.
Each of my four body paragraphs is formatted in roughly the same way: an intro sentence that explains what I’ll be discussing, analysis of that main point, and at least two quotes from the book as evidence.
My conclusion restates my thesis, summarizes each of four points I discussed in my body paragraphs, and ends the essay by briefly discussing how Steinbeck’s writing helped introduce a world of readers to the injustices migrants experienced during the dust bowl.
What does this analytical essay example do well? For starters, it contains everything that a strong analytical essay should, and it makes that easy to find. The thesis clearly lays out what the essay will be about, the first sentence of each of the body paragraph introduces the topic it’ll cover, and the conclusion neatly recaps all the main points. Within each of the body paragraphs, there’s analysis along with multiple excerpts from the book in order to add legitimacy to my points.
Additionally, the essay does a good job of taking an in-depth look at the issue introduced in the thesis. Four ways Steinbeck used literary devices are discussed, and for each of the examples are given and analysis is provided so readers can understand why Steinbeck included those devices and how they helped shaped how readers viewed migrants and their plight.
Where could this essay be improved? I believe the weakest body paragraph is the third one, the one that discusses how Steinbeck used plain, grammatically incorrect language to both accurately depict the migrants and make them more relatable to readers. The paragraph tries to touch on both of those reasons and ends up being somewhat unfocused as a result. It would have been better for it to focus on just one of those reasons (likely how it made the migrants more relatable) in order to be clearer and more effective. It’s a good example of how adding more ideas to an essay often doesn’t make it better if they don’t work with the rest of what you’re writing. This essay also could explain the excerpts that are included more and how they relate to the points being made. Sometimes they’re just dropped in the essay with the expectation that the readers will make the connection between the example and the analysis. This is perhaps especially true in the second body paragraph, the one that discusses similarities to Biblical passages. Additional analysis of the quotes would have strengthened it.

Summary: How to Write an Analytical Essay
What is an analytical essay? A critical analytical essay analyzes a topic, often a text or film. The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis.
When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps:
Reading analytical essay examples can also give you a better sense of how to structure your essay and what to include in it.
What's Next?
Learning about different writing styles in school? There are four main writing styles, and it's important to understand each of them. Learn about them in our guide to writing styles , complete with examples.
Writing a research paper for school but not sure what to write about? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.
Literary devices can both be used to enhance your writing and communication. Check out this list of 31 literary devices to learn more !

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay: Purposes, Outline, Samples
.png)
Firstly to understand what a literary analysis essay means, it’s a way to determine and understand the work of an author, even if it is a single work or an entire body of work. Literary criticism is a description, analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a particular literary work or an author’s writings as a whole.
Many students, writers, and english scholars are told to write essays on different literary analysis essay topics because this type of assignment helps and makes writers to think about the reason why a poem, short story, novel, or play was written. To analyze literature, writers will need to remember that authors have specific decisions for particular reasons. Your essay should point out the author’s decision and try to explain their intentions.

Learn how to write a book review and check out related guides: poem analysis essay , poetry analysis essay or critical lens essay at EssayHub blog.
What Is A Literary Analysis Essay?
The most comprehensive literary analysis definition goes as follows. It is a text that objectively analyzes the weak and strong points of another text. One author shares their opinion on what another author wrote. The most common literary analysis format is an essay.
The writer examines a novel, short story, or another type of fiction created by someone else. They praise or criticize the plot, style, characters, and other aspects of the text. After reading a piece of literary analysis, people should understand whether the book is worthy or not.
What Is The Purpose Of A Literary Analysis Essay?
When a newbie checks literary analysis examples, they will see that they are very personal. Different people might perceive the same text very differently. It depends on their character, life experience, and cultural background. The aim of writing a literary analysis is to express one’s individual understanding of the text and back it up with facts.
It is not sufficient to say, "I enjoyed every minute of reading this book!" or "It is too dull." All types of literary analysis involve the assessment of both technical and emotional aspects of the text. It implies an impartial balancing of pros and cons.
Imagine that someone is looking for a good book. Their time and finances are limited, so they can afford just one text. They want to avoid hit-or-miss decisions. They prefer an expert to recommend to them what to read.
They do not want this expert to be a high-brow professional critic. They are interested in the opinions of people whose lifestyle and worldview are close to theirs. They read book blogs and unbiased reviews on profile sites. When they finally buy a piece of fiction, they know what to expect of it.
After a reader gains experience, they become ready to share viewpoints with others. They read articles on how to analyze literature and start writing their own reviews. They can post their works in their private blogs or share them on social networks. Plus, literary analysis is an essential part of the educational process in schools and colleges.
Content Of A Literary Analysis Essay
There are many topics for literary analysis, but it all depends on the kind of work that a writer analyzes. For instance, the approach is not the same in poems as it is in the case with a play. Before writing it is important to know what you want to analyze in the literature that you have read. That brings us to types of literature analysis. How can a writer analyze the literature? This is done by:
- Character Analysis
- Symbolism Analysis
- Theme Analysis
- Setting Analysis
- Structure and Style Analysis
- Diction, Imagery, and Denotation Analysis. etc.
How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay?
Read the text critically.
When carrying out literature analysis, a person should read slowly. They should start a notebook where they would put down their thoughts. They should take notes when they find themselves in one of the following situations:
- disagree with the author;
- want to praise the author’s skills;
- come across a plot twist that resembles their own lives;
- have anything to say on the matter.
When people read an interesting text, they have controversial desires. On the one hand, they want to finish it to get to know what happens in the end. On the other hand, they want to enjoy it for as long as possible. When compiling a literary analysis sample, people should focus on their thoughts and not emotions.
Literary Devices
When newbies ask about how to write a good literary analysis, literary devices become the most challenging aspect for them. These devices involve the following terms and notions:
- literary elements, such as plot, mood, and protagonists;
- figurative language, including symbolism and metaphors;
- literary techniques, such as foreshadowing and repetition.
To be able to analyze these aspects, newbies should read theory in textbooks. Also, they should examine enough sample literary analysis essays. They need to see how other writers handle the overview of literary devices without making their texts too formal.
In a literary analysis paper, it is not enough to say that the author has a masterful command of the word. The writer should concentrate on the following important aspects.
- Is the language modern, archaic, or full of slang?
- Does the author use poetic phrases?
- Are the sentences predominantly long or short? How does the rhythm of the text impact its mood?
It would be wise to answer the following question in a literary analysis essay example. Do all characters speak the same language, or does each one have their particular style? Individual speech manners are significant merits of fiction.
Narrative Voice
A text can be written either from a first-person or third-person perspective. In a literary analysis example, the author should explain the position of the narrator. Are they omnipresent, or does the reader hardly notice them? Are they reliable, or do they share a distorted version of events?
Writers with little experience might ask how to do literary analysis when the narrator is absent. In this case, speak about the tone. Is it neutral, comic, or tragic? What emotions does it evoke in the readers from the first passage? How often does the reader come across exaggerations, irony, or incongruities?
In a novel, the key elements of literary analysis are chapters. In a play, these constituents are acts and scenes. In a poem, these are lines and stanzas. The author of the essay should think of how skilfully the writer divided their text into parts.
Chapters, scenes, and stanzas should be interconnected logically and emotionally. The last line of the previous part should motivate the reader to glance through the next one. The structure of the text helps emphasize its conflicts and build up the tension. The pauses between every two parts might speak louder than a thousand words.
Most examples of literary analysis essay include comments on the timeline of the story. Do the events unfold in chronological order? Does the author make the readers travel back and forth in a time machine? How easy is it to switch between different time layers, and which effect does it produce?
The following types of conflicts are most likely to be present in a literary analysis:
- one person versus another;
- person versus society;
- person versus technology;
- person versus supernatural forces;
- an inner conflict within a person (good versus bad intentions).
Instead of one person, there might be a group of people.
Newbies should not get confused about how to write a thesis for a literary analysis. The term "thesis" denotes the main point that they are planning to focus on. Modern books are multifaceted: they feature numerous problems and give readers a lot of food for thought. Yet, the writer should concentrate only on a handful of aspects in their work.
There are three approaches to thesis writing:
- analytical;
- argumentative;
- explanatory.
The literary analysis thesis of the first type strives to answer the questions "why?" and "how?" The writer tries to explain why the author created that book. Why is their perception of the world so unique and innovative? Why do they draw certain parallels and use specific devices?
This sentence might serve as a good example of an analytical thesis: "Outraged by gender inequality in this Eastern country, the author ridicules the problem instead of trying to undermine the traditions."
An argumentative thesis for literary analysis implies that the writer explains their own perception of the text. They take a certain position that might differ from the opinion of the majority. They further prove their point by quoting the book. For instance: "While most critics perceive this novel as an educational one, I believe that the main conflict lies in the lack of tolerance in society."
Literary analysis thesis examples of the explanatory type do not include the author’s opinion at all. They just help other readers understand the message of the book: "The author depicts their ideal political system."
Write A Literary Analysis Essay
Write a title.
After reading the title, the person should understand what the literary analysis paper example is about. The title should contain the digest of the paper. It should reveal the writer’s attitude to the piece of fiction that they criticize.
Those who do not know how to start a literary analysis can use a popular trick that works for any book genre. They can include a short quote from the book in the name of their essay. Then, they should put a colon and accompany the quote with their own comment.
Write An Introduction
The instruction on how to write literary analysis starts with a clear statement of one’s goals. The author should tell their readers what the book they are going to criticize is about and why they chose it. They should share the title of the text and the name of its writer. They might briefly outline the plot and problems of the manuscript. They might focus the readers’ attention on the main points of their essay — language, characters, or conflicts.
Write A Body
All the best examples of literary analysis essay have an identical structure. Each paragraph is focused on one aspect or topic. In the first sentence, the author briefly outlines this topic. That initial phrase should be concise and unambiguous.
The last sentence of each paragraph should summarize its essence. It should not contradict the first phrase and overall logic of the passage.
The writer should avoid lengthy and complicated structures. Even if the author of the book prefers compound sentences, a literary analysis sample should be easier to read. One phrase should contain only one thought. To link sentences, the writer should use transition words.
"The book dissects the impact of virtual reality technologies on the life of single people in cosmopolitan cities" — this is an example of a topic sentence that opens a paragraph. "Nevertheless, its target audience is not geeks or die-hard gamers" — here, the word "nevertheless" serves as a transition.
In any literary analysis template, the writer should back up their opinion with textual evidence. They should quote parts of the original texts only if they contain no more than 30 words. Otherwise, they should reword the quotes to deliver the essence of large passages.\
Write A Conclusion
The answer to the question "How to conclude a literary analysis?" is very simple. The writer needs to reword and sum up everything that they have said above. They should share no original quotes and introduce no new thoughts. It is enough to summarize their main ideas logically and concisely.
Literary Analysis Essay Outline
Introduction.
Introduction should be sophisticated and creative, and it should catch the reader’s attention, so they can read the rest of the essay. A literary analysis should not sound boring. It should create some enthralling and fascinating quotes, reflection or motives. The main sentences of the introduction should give backdrop facts so that the analysis will make sense; facts such as Title of the Book, Name of Author and little information about the book. Don’t write bulky details of the book the reader would have read this book and they just want to read the analysis. Make sure that your backdrop information and your thesis statement are short and transitional. To make the reader understand and connect to the literature and what exactly is been analyzed. The analysis or thesis statement is what you will prove in your essay, and it should come at the end of your introductory paragraph. The Intro could be more than one paragraph but about 5 important sentences.
The body must be very convincing. Here start rendering evidences of the argument. A convincing body will have at least three to four paragraphs or more. Also, do not go out of context the question has to be related. How does it relate to the overall theme of what the analysis? Make emphasis on the ways in which these elements bestow to the entire quality of the book. Emphasize one major point per paragraph in this section. No need to rush all of your evidence into one idea. Do more reading and analyze different factors in your literary analysis. Argue on a character's development, for example how the individual changes from the beginning to the end of the book. Center core on a character's fatal flaw and query or question the person's mistakes.
The conclusion should end dynamically and energetically. Start rounding up the literary essay paper in the last paragraph. It should include all the major points that have been made in the aforementioned statements of your literary analysis. Also, make emphasis on the on the implications of your argument.
.png)
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Symbolism Manifestation in Little Prince By Antoine De Saint-Exupery
The storyline arose from the author's personal experience. He survived an airplane accident in a desert. It happened when the writer served as a pilot during World War II.
A seemingly simple-hearted fairy tale has two main plotlines that uncover deeper problems. The leading one is the pilot-narrator line, lined up with the metaphor of adult reality. The second line dwells on the adventures of the Little Prince. Two protagonists travel to different planets, get acquainted with various characters, both positive and negative.
Each planet introduces the readers to a different philosophical conundrum. Each item and being in the book bear unique symbolic meaning.
The Pilot impersonates the author in his adult years. Antoine de Saint-Exupéry was, in fact, a pilot and survived a plane crash in the desert.
The sudden encounter of an adult and a child (both are metaphors for inner psychological states) occurs in the desert, symbolizing the disastrous inner state of the narrator. The story unravels during the repair of the plane. The maintenance itself is a metaphor for mending the inner traumas through direct dialogue with the inner child.
The Little Prince
The description of the Little Prince gives the readers a hint of its relation to the author in his childhood years. Antoine de Saint-Exupery came from an impoverished aristocratic family. Through the Little Prince, the author shows himself. He reveals his struggle to survive within the boring world of adults.
His visit to our planet is a symbol of birth. The return to the home planet occurs through physical death from the poison of a snake. Here, we can observe the impact of Christian religious thinking on the plotline. The physical death of the protagonist is a reference to the religious idea of an immortal soul. Thus, after receiving knowledge about life from the Fox and Pilot, Little Prince has to die to be reborn into a new state.
The line telling about the love of the Little Prince and Rose shows an allegorical depiction of love. It reveals the ironic unsimilarity of how men and women see and express this feeling.
Rose gets introduced to the readers as a proud and beautiful character who has power over the Little Prince and his feelings. Gentle, timid, dewy-eyed Little Prince suffers from the frivolity of Rose. Because of his naïve perception, the protagonist struggled to see that it was necessary to love her for her essence – for the aroma and the joy she brought him.
When the protagonist sees that roses are abundant in the gardens on Earth, he feels disappointed. Later, he meets the Fox who serves as the guide to the little lost being. Fox explains to the protagonist some basic philosophical truths. He teaches the Little Prince to look with his heart, not his eyes, and be responsible for those we have tamed.
When Little Prince absorbs the knowledge imparted by his new friend, he becomes mortal. This transition symbolizes him growing up and shaking off idealistic world perception.
Planets And Their Inhabitants
The author shows his readers two sorts of evil. The first kind of evil reveals itself in the negative sides of separate people.
The inhabitants of different planets, visited by the protagonist, reveal the most dangerous human vices. It seems relevant to note that all of them are adults. Drunkards, politicians, and selfish people seem quite morally bankrupt.
The author exposes life devoid of meaning as a common vice. The only relatable person to the protagonist is a lamplighter. He differs because his craft is good for others.
Baobab Trees
Another element of evil in the book is macro-evil. Baobabs represent evil in general. This image is a metaphor for fascism. Saint-Exupery gently leads the readers to the idea that such evil endangers the world. It should be extinguished like undesirable plants.
The main idea of the used allegories is the presentation of true values. The author contrasts naive and rational ways of world perception, the individual, and the crowd. In the tale, the unraveling of the main themes is connected with compositional structure, metaphors, and similes used by the author.
The author dwells on deep philosophical issues through similes and symbols. He emphasizes such topics as true love, friendship, and loneliness.
Romantic traditions play a keynote role in the plot formation. Unraveling the deep problems of humanity in a form of the fairytale is the main sign of that. It comprises all typical elements of this genre: child protagonist, fairy-tale characters, and a fantastic journey. These symbolic characters and items introduce the depth to the plot. They make readers see deeper into the book and reconsider their perception of reality.
Do you need assistance with request " write my essay for me " in writing a literary analysis essay or any other kind of essay, academic papers? EssayHub is a genuine essay writing services , providing students with online assistance. We have essay writers who can provide you with an argumentative essay writing service on any topic you want, in any format and at a superior quality. Check the customer reviews who pay for essay on our platform. Seeing is believing. Try it out!

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
Literary Analysis Essay

Literary Analysis Essay - Step by Step Guide
15 min read
Published on: Aug 16, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
Literary Analysis Essay Outline Guide with Examples
Interesting Literary Analysis Essay Topics & Ideas
Share this article
Literature is an art that can inspire, challenge, and transform us. But how do we analyze literature in a way that truly captures its essence?
That's where a literary analysis essay comes in.
Writing a literary analysis essay allows you to delve into the themes, characters, and symbols of a literary work. It's a chance to engage with literature on a deeper level and to discover new insights.
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the process of writing a literary analysis essay, step by step. Plus, you’ll get to read some great examples to help you out!
So let’s dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Literary Analysis Essay?
Literary analysis is a process of examining a literary work in detail to uncover its meaning and significance.
It involves breaking down the various elements of a work, such as plot, character, setting, and theme. And then analyzing how they work together to create a specific effect on the reader.
In other words, literary analysis is an exercise in interpretation. The reader of a work asks questions about what the author means to say, how they are saying it, and why.
A literary analysis essay is an essay where you explore such questions in depth and offer your own insights.
What is the Purpose of a Literary Analysis Essay?
In general, the purpose of a literary analysis essay is as follows:
- To gain a greater understanding and appreciation of the work.
- To be able to think critically and analytically about a text.
Content of a Literary Analysis
A literary analysis essay delves deep into the various aspects of a literary work to examine its meaning, symbolism, themes, and more. Here are the key elements to include in your literary analysis essay:
Plot Analysis
Plot refers to the sequence of events that make up the storyline of a literary work. It encompasses the main events, conflicts, and resolutions that drive the narrative forward.
Elements of Plot Analysis
The elements of a plot typically include:
- Exposition: The introduction of the story that establishes the setting, characters, and initial circumstances.
- Rising action: A set of events or actions that sets the main conflict into motion, often occurring early in the story.
- Conflict: The series of events that build tension and develop the conflict, leading to the story's climax.
- Climax: The turning point of the story, where the conflict reaches its peak and the outcome hangs in the balance.
- Falling Action: The events that occur after the climax, leading towards the resolution of the conflict.
- Resolution: The point in the story where the conflict is resolved, providing closure to the narrative.
Character Analysis
Character analysis involves studying the role, development, and motivations of the characters in a literary work. It explores how characters contribute to the overall narrative and themes of the story.
Elements of Character Analysis
- Identification of major and minor characters.
- Examination of their traits, behaviors, and relationships.
- Analysis of character development and changes throughout the story.
- Evaluation of the character's role in advancing the plot or conveying themes.
Symbolism and Imagery Analysis
Symbolism and imagery analysis focuses on the use of symbols, objects, or images in a work. It analyzes and explores the use of literary devices to convey deeper meanings and evoke emotions.
Elements of Symbolism and Imagery Analysis
- Identification of key symbols or recurring motifs.
- Interpretation of their symbolic significance.
- Analysis of how imagery is used to create vivid mental pictures and enhance the reader's understanding and emotional experience.
Theme Analysis
Analyzing the theme involves exploring the central ideas or messages conveyed in a literary work. It examines the underlying concepts, or messages that the author wants to convey through the story.
Elements of Theme Analysis
- Identification of the main themes or central ideas explored in the text.
- Analysis of how the themes are developed and reinforced throughout the story.
- Exploration of the author's perspective and the intended message behind the themes.
Setting Analysis
The Setting of a story includes the time, place, and social context in which the story takes place. Analyzing the setting involves how the setting influences the characters, plot, and overall atmosphere of the work.
Elements of Setting Analysis
- Description and analysis of the physical, cultural, and historical aspects of the setting.
- Examination of how the setting contributes to the mood, atmosphere, and themes of the work.
- Evaluation of how the setting shapes the characters' actions and motivations.
Structure and Style Analysis
Structure and style analysis involves studying the organization, narrative techniques, and literary devices employed by the author. It explores how the structure and style contribute to the overall impact and effectiveness of the work.
Elements of Structure and Style Analysis
- Analysis of the narrative structure, such as the use of flashbacks, nonlinear timelines, or multiple perspectives.
- Examination of the author's writing style, including the use of language, tone, and figurative language.
- Evaluation of literary devices, such as foreshadowing, irony, or allusion, and their impact on the reader's interpretation.

Paper due? Why Suffer? That's our job.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay?
Writing a great literary analysis piece requires you to follow certain steps. Hereâs what you need to do to write a literary essay:
Preparing for Your Essay
The pre-writing process for writing a literary analysis essay includes the following:
- Choosing a literary work to analyze
- Reading and analyzing the work
- Taking notes and organizing your thoughts
- Creating an outline for your essay
Choosing a Work to Analyze
As a student, you would most probably be assigned a literary piece to analyze. It could be a short story, a novel, or a poem. However, sometimes you get to choose it yourself.
In such a case, you should choose a work that you find interesting and engaging. This will make it easier to stay motivated as you analyze the work and write your essay.
Moreover, you should choose a work that has some depth and complexity. This will give you plenty of material to analyze and discuss in your essay. Finally, make sure that your choice fits within the scope of the assignment and meets the expectations of your instructor.
Reading and Analyzing
Once youâve chosen a literary work, it's time to read the work with careful attention. There are several key elements to consider when reading and analyzing a literary work:
- Plot - The sequence of events that make up the story. Analyzing the plot involves examining the structure of the story, including its exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution.
- Characters - The people or entities that populate the story. Analyzing characters involves examining their motivations, personalities, relationships, and development over the course of the story.
Want to learn more about character analysis? Head to our blog about how to conduct character analysis and learn easy steps with examples.
- Setting - The time, place, and environment in which the story takes place. Analyzing the setting involves examining how the atmosphere contributes to the story's overall meaning.
- Theme - The underlying message or meaning of the story. Analyzing themes involves examining the work's central ideas and how they are expressed through the various elements of the story.
Moreover, it's important to consider the following questions while analyzing:
- What is the central theme or main point the author is trying to make?
- What literary devices and techniques has the author used?
- Why did the author choose to write this particular work?
- What themes and ideas are present in the work?
These questions will help you dive deeper into the work you are writing about.
Take Notes and Gather Material
As you read and analyze the literary work, it's important to take notes so you donât forget important details and ideas. This also helps you identify patterns and connections between different elements of the piece.
One effective way to take notes is to list important elements of the work, such as characters, setting, and theme. You can also use sticky notes, highlighters, or annotations to mark important passages and write down your ideas.
Writing Your Literary Analysis Essay
Once you have read a piece of literature and taken notes, you have all the material you need to write an essay. Follow the simple steps below to write an effective literary analysis essay.
Create an Outline for Your Essay
Firstly, creating an outline is necessary. This will help you to organize your thoughts and ideas and ensure that your essay flows logically and coherently.
This is what your literary essay outline would look like:
Writing the Introduction
Writing your essay introduction involves the three following parts:
- Begin the introductory paragraph with an engaging hook statement that captures the readers' attention. An effective hook statement can take many different forms, such as a provocative quote, an intriguing question, or a surprising fact.
Make sure that your hook statement is relevant to the literary work you are writing about. Here are a few examples of effective hooks:
- Afterward, present the necessary background information and context about the literary work. For instance,
- Talk about the author of the work or when and where it was written.
- Give an overview of the work or why it is significant.
- Provide readers with sufficient context so they can know what the work is generally about.
- Finally, end the introduction with a clear thesis statement . Your thesis statement should be a concise statement that clearly states the argument you will be making in your essay. It should be specific and debatable, and it should provide a roadmap for the rest of your essay.
For example, a thesis statement for an essay on "Hamlet" might be:
Watch this video to learn more about writing an introduction for a literary analysis essay:
Writing the Body
Here are the steps to follow when writing a body paragraph for a literary analysis essay:
- Start with a topic sentence:
The topic sentence should introduce the main point or argument you will be making in the paragraph. It should be clear and concise and should indicate what the paragraph is about.
- Provide evidence:
After you have introduced your main point, provide evidence from the text to support your analysis. This could include quotes, paraphrases, or summaries of the text.
- Explain and discuss the evidence:
Explain how the evidence supports your main point or argument or how it connects back to your thesis statement.
- Conclude the paragraph:
End the paragraph by relating your main point to the thesis and discussing its significance. You should also use transitions to connect the paragraph to your next point or argument.
Writing the Conclusion
The conclusion of a literary analysis essay provides closure to your analysis and reinforces your thesis statement. Hereâs what a conclusion includes:
- Restate your thesis statement:
Start by restating your thesis statement in a slightly different way than in your introduction. This will remind the reader of the argument you made and the evidence you provided to support it.
- Summarize your main points:
Briefly summarize the main points you made in your essay's body paragraphs. This will help tie everything together and provide closure to your analysis.
- Personal reflections:
The conclusion is the best place to provide some personal reflections on the literary piece. You can also explain connections between your analysis and the larger context. This could include connections to other literary works, your personal life, historical events, or contemporary issues.
- End with a strong statement:
End your conclusion with a strong statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a final insight into the significance of your analysis.
Finalizing your Essay
Youâve completed the first draft of your literary analysis essay. Congratulations!
However, itâs not over just yet. You need some time to polish and improve the essay before it can be submitted. Hereâs what you need to do:
Proofread and Revise your Essay
After completing your draft, you should proofread your essay. You should look out for the following aspects:
- Check for clarity:
Make sure that your ideas are expressed clearly and logically. You should also take a look at your structure and organization. Rearrange your arguments if necessary to make them clearer.
- Check for grammar and spelling errors:
Use spelling and grammar check tools online to identify and correct any basic errors in your essay.
- Verify factual information:
You must have included information about the work or from within the work in your essay. Recheck and verify that it is correct and verifiable.
- Check your formatting:
Make sure that your essay is properly formatted according to the guidelines provided by your instructor. This includes requirements for font size, margins, spacing, and citation style.
Helpful Tips for Revising a Literary Essay
Here are some tips below that can help you proofread and revise your essay better:
- Read your essay out loud:
Reading your essay out loud makes it easier to identify awkward phrasing, repetitive language, and other issues.
- Take a break:
It can be helpful to step away from your essay for a little while before starting the editing process. This can help you approach your essay with fresh eyes and a clearer perspective.
- Be concise:
Remove any unnecessary words or phrases that do not add to your argument. This can help to make your essay more focused and effective.
- Let someone else proofread and get feedback:
You could ask a friend or a teacher to read your essay and provide feedback. This way, you can get some valuable insights on what you could include or catch mistakes that you might have missed.
Literary Analysis Essay Examples
Reading a few good examples helps to understand literary analysis essays better. So check out these examples below and read them to see what a well-written essay looks like.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Sample Literary Analysis Essay
Lord of the Rings Literary Analysis
The Great Gatsby Literary Analysis
Literary Analysis Example for 8th Grade
Literary Analysis Essay Topics
Need a topic for your literary analysis essay? You can pick any aspect of any work of literature you like. Here are some example topics that will help you get inspired:
- The use of symbolism in "The Great Gatsby" by F. Scott Fitzgerald.
- The theme of isolation in "The Catcher in the Rye" by J.D. Salinger.
- The portrayal of social class in "Pride and Prejudice" by Jane Austen.
- The use of magical realism in "One Hundred Years of Solitude" by Gabriel Garcia Marquez.
- The role of women in "The Handmaid's Tale" by Margaret Atwood.
- The use of foreshadowing in "Lord of the Flies" by William Golding.
- The portrayal of race and identity in "Invisible Man" by Ralph Ellison.
- The use of imagery in "The Road" by Cormac McCarthy.
- The theme of forgiveness in "The Kite Runner" by Khaled Hosseini.
- The use of allegory in "Animal Farm" by George Orwell.
To conclude,
Writing a literary analysis essay can be a rewarding experience for any student or writer, But itâs not easy. However, by following the steps you learned in this guide, you can successfully produce a well-written literary analysis essay.
Also, you have got some examples of essays to read and topic ideas to get creative inspiration. With these resources, you have all you need to craft an engaging piece. So donât hesitate to start writing your essay and come back to this blog whenever you need.
The deadline is approaching, but you donât have time to write your essay? No worries! Our analytical essay writing service is here to help you out!
At CollegeEssay.org, we have a team of professional and experienced literature writers who can help you craft a compelling literary essay. Our affordable and reliable essay writing website focuses on providing high-quality essays and deliver them timely.
Try our AI essay writing tools today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 components of literary analysis.
The four main components of literary analysis are:
- Conflict
- Characters
- Setting

What is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay?
Interpretive is the fundamental characteristic of a literary analysis essay.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

Introduction
CDHE Nomination
AUCC Requirements
Course Description
Sample Policy Statements
Syllabus Sequencing Strategies
Sample Daily Syllabi
Lesson Plans
Reading Selection Recommendations
Assignments
Response Papers and Discussion Forums
Presentations
Discusssion, Group, WTL Questions
Variations, Misc.
Curbing Plagiarism
Additional Teaching & Course Design Resources
Guide Contributors
E238 Text Analysis Essay Example
Text Analysis Papers
For five of the six texts you read this semester, you will be expected to hand in a corresponding text analysis paper. A text analysis paper will focus upon an area of the work that you find interesting, significant, or feel merits discussion. A text analysis paper should be fairly formal, and should genuinely attempt to shed light on one or more aspects of the work. You may discuss the significance of character, plot, setting, symbol...whatever catches your fancy. Overall, I am looking for interesting and original insights concerning the reading assignment.
An ideal text analysis will be 2 pages in length, double-spaced, and typed. Your paper will explore a problem or point of interest created by a work of literature (this includes, but is not limited to, character motivation, thematic elements, contextual significance, culture, symbol, irony, etc.). Your ideas and insights will be based on information from the pages in the text we have read so far (outside research is encouraged, but not at all necessary), calling upon specific examples to illustrate the idea or issue you are exploring. Your grade will be based on the quality and depth of your insights, and on the use of specific textual evidence as support. Avoid the obvious. Take risks--Make it interesting! This is an issue that the class may be asked to discuss at a later date.
Possible starting places for your text analysis include an author's life, politics, the social context of the work, philosophical musings, how and why the work evokes a particular feeling in you, cultural relevance, or the components of the text such as the significance of setting, narrative voice, imagery, or symbolism. Or, perhaps you will read a critical approach to the text and use it as a springboard for your own ideas (the library database Contemporary Literary Criticism Select is often a nice starting place). Or, you may wish to explore the relationship between various elements of the text (How does setting influence character?). Or, perhaps you would like to build on an idea touched on in class discussion. As we move on into the later weeks of the course, you may even wish to direct your questions toward identifying patterns between texts, and asking what the significance of these patterns might be.
The Dos and Don'ts of Text Analysis Papers:
**Remember: Text analysis papers must be typed and submitted on time. They will be evaluated on the basis of focus, development, use of evidence, creativity, and level of insight. They will count as 30% of your final grade.

Analyzing a Text
Written texts.
When you analyze an essay or article, consider these questions:
- What is the thesis or central idea of the text?
- Who is the intended audience?
- What questions does the author address?
- How does the author structure the text?
- What are the key parts of the text?
- How do the key parts of the text interrelate?
- How do the key parts of the text relate to the thesis?
- What does the author do to generate interest in the argument?
- How does the author convince the readers of their argument’s merit?
- What evidence is provided in support of the thesis?
- Is the evidence in the text convincing?
- Has the author anticipated opposing views and countered them?
- Is the author’s reasoning sound?
Visual Texts
When you analyze a piece of visual work, consider these questions:
- What confuses, surprises, or interests you about the image?
- In what medium is the visual?
- Where is the visual from?
- Who created the visual?
- For what purpose was the visual created?
- Identify any clues that suggest the visual’s intended audience.
- How does this image appeal to that audience?
- In the case of advertisements, what product is the visual selling?
- In the case of advertisements, is the visual selling an additional message or idea?
- If words are included in the visual, how do they contribute to the meaning?
- Identify design elements – colors, shapes, perspective, and background – and speculate how they help to convey the visual’s meaning or purpose.
About Writing: A Guide Copyright © 2015 by Robin Jeffrey is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.14: Sample Student Literary Analysis Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 40514

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
While reading these examples, ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the essay's thesis statement, and how do you know it is the thesis statement?
- What is the main idea or topic sentence of each body paragraph, and how does it relate back to the thesis statement?
- Where and how does each essay use evidence (quotes or paraphrase from the literature)?
- What are some of the literary devices or structures the essays analyze or discuss?
- How does each author structure their conclusion, and how does their conclusion differ from their introduction?
Example 1: Poetry
Victoria Morillo
Instructor Heather Ringo
3 August 2022
How Nguyen’s Structure Solidifies the Impact of Sexual Violence in “The Study”
Stripped of innocence, your body taken from you. No matter how much you try to block out the instance in which these two things occurred, memories surface and come back to haunt you. How does a person, a young boy , cope with an event that forever changes his life? Hieu Minh Nguyen deconstructs this very way in which an act of sexual violence affects a survivor. In his poem, “The Study,” the poem's speaker recounts the year in which his molestation took place, describing how his memory filters in and out. Throughout the poem, Nguyen writes in free verse, permitting a structural liberation to become the foundation for his message to shine through. While he moves the readers with this poignant narrative, Nguyen effectively conveys the resulting internal struggles of feeling alone and unseen.
The speaker recalls his experience with such painful memory through the use of specific punctuation choices. Just by looking at the poem, we see that the first period doesn’t appear until line 14. It finally comes after the speaker reveals to his readers the possible, central purpose for writing this poem: the speaker's molestation. In the first half, the poem makes use of commas, em dashes, and colons, which lends itself to the idea of the speaker stringing along all of these details to make sense of this time in his life. If reading the poem following the conventions of punctuation, a sense of urgency is present here, as well. This is exemplified by the lack of periods to finalize a thought; and instead, Nguyen uses other punctuation marks to connect them. Serving as another connector of thoughts, the two em dashes give emphasis to the role memory plays when the speaker discusses how “no one [had] a face” during that time (Nguyen 9-11). He speaks in this urgent manner until the 14th line, and when he finally gets it off his chest, the pace of the poem changes, as does the more frequent use of the period. This stream-of-consciousness-like section when juxtaposed with the latter half of the poem, causes readers to slow down and pay attention to the details. It also splits the poem in two: a section that talks of the fogginess of memory then transitions into one that remembers it all.
In tandem with the fluctuating nature of memory, the utilization of line breaks and word choice help reflect the damage the molestation has had. Within the first couple of lines of the poem, the poem demands the readers’ attention when the line breaks from “floating” to “dead” as the speaker describes his memory of Little Billy (Nguyen 1-4). This line break averts the readers’ expectation of the direction of the narrative and immediately shifts the tone of the poem. The break also speaks to the effect his trauma has ingrained in him and how “[f]or the longest time,” his only memory of that year revolves around an image of a boy’s death. In a way, the speaker sees himself in Little Billy; or perhaps, he’s representative of the tragic death of his boyhood, how the speaker felt so “dead” after enduring such a traumatic experience, even referring to himself as a “ghost” that he tries to evict from his conscience (Nguyen 24). The feeling that a part of him has died is solidified at the very end of the poem when the speaker describes himself as a nine-year-old boy who’s been “fossilized,” forever changed by this act (Nguyen 29). By choosing words associated with permanence and death, the speaker tries to recreate the atmosphere (for which he felt trapped in) in order for readers to understand the loneliness that came as a result of his trauma. With the assistance of line breaks, more attention is drawn to the speaker's words, intensifying their importance, and demanding to be felt by the readers.
Most importantly, the speaker expresses eloquently, and so heartbreakingly, about the effect sexual violence has on a person. Perhaps what seems to be the most frustrating are the people who fail to believe survivors of these types of crimes. This is evident when he describes “how angry” the tenants were when they filled the pool with cement (Nguyen 4). They seem to represent how people in the speaker's life were dismissive of his assault and who viewed his tragedy as a nuisance of some sorts. This sentiment is bookended when he says, “They say, give us details , so I give them my body. / They say, give us proof , so I give them my body,” (Nguyen 25-26). The repetition of these two lines reinforces the feeling many feel in these scenarios, as they’re often left to deal with trying to make people believe them, or to even see them.
It’s important to recognize how the structure of this poem gives the speaker space to express the pain he’s had to carry for so long. As a characteristic of free verse, the poem doesn’t follow any structured rhyme scheme or meter; which in turn, allows him to not have any constraints in telling his story the way he wants to. The speaker has the freedom to display his experience in a way that evades predictability and engenders authenticity of a story very personal to him. As readers, we abandon anticipating the next rhyme, and instead focus our attention to the other ways, like his punctuation or word choice, in which he effectively tells his story. The speaker recognizes that some part of him no longer belongs to himself, but by writing “The Study,” he shows other survivors that they’re not alone and encourages hope that eventually, they will be freed from the shackles of sexual violence.
Works Cited
Nguyen, Hieu Minh. “The Study” Poets.Org. Academy of American Poets, Coffee House Press, 2018, https://poets.org/poem/study-0 .
Example 2: Fiction
Todd Goodwin
Professor Stan Matyshak
Advanced Expository Writing
Sept. 17, 20—
Poe’s “Usher”: A Mirror of the Fall of the House of Humanity
Right from the outset of the grim story, “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Edgar Allan Poe enmeshes us in a dark, gloomy, hopeless world, alienating his characters and the reader from any sort of physical or psychological norm where such values as hope and happiness could possibly exist. He fatalistically tells the story of how a man (the narrator) comes from the outside world of hope, religion, and everyday society and tries to bring some kind of redeeming happiness to his boyhood friend, Roderick Usher, who not only has physically and psychologically wasted away but is entrapped in a dilapidated house of ever-looming terror with an emaciated and deranged twin sister. Roderick Usher embodies the wasting away of what once was vibrant and alive, and his house of “insufferable gloom” (273), which contains his morbid sister, seems to mirror or reflect this fear of death and annihilation that he most horribly endures. A close reading of the story reveals that Poe uses mirror images, or reflections, to contribute to the fatalistic theme of “Usher”: each reflection serves to intensify an already prevalent tone of hopelessness, darkness, and fatalism.
It could be argued that the house of Roderick Usher is a “house of mirrors,” whose unpleasant and grim reflections create a dark and hopeless setting. For example, the narrator first approaches “the melancholy house of Usher on a dark and soundless day,” and finds a building which causes him a “sense of insufferable gloom,” which “pervades his spirit and causes an iciness, a sinking, a sickening of the heart, an undiscerned dreariness of thought” (273). The narrator then optimistically states: “I reflected that a mere different arrangement of the scene, of the details of the picture, would be sufficient to modify, or perhaps annihilate its capacity for sorrowful impression” (274). But the narrator then sees the reflection of the house in the tarn and experiences a “shudder even more thrilling than before” (274). Thus the reader begins to realize that the narrator cannot change or stop the impending doom that will befall the house of Usher, and maybe humanity. The story cleverly plays with the word reflection : the narrator sees a physical reflection that leads him to a mental reflection about Usher’s surroundings.
The narrator’s disillusionment by such grim reflection continues in the story. For example, he describes Roderick Usher’s face as distinct with signs of old strength but lost vigor: the remains of what used to be. He describes the house as a once happy and vibrant place, which, like Roderick, lost its vitality. Also, the narrator describes Usher’s hair as growing wild on his rather obtrusive head, which directly mirrors the eerie moss and straw covering the outside of the house. The narrator continually longs to see these bleak reflections as a dream, for he states: “Shaking off from my spirit what must have been a dream, I scanned more narrowly the real aspect of the building” (276). He does not want to face the reality that Usher and his home are doomed to fall, regardless of what he does.
Although there are almost countless examples of these mirror images, two others stand out as important. First, Roderick and his sister, Madeline, are twins. The narrator aptly states just as he and Roderick are entombing Madeline that there is “a striking similitude between brother and sister” (288). Indeed, they are mirror images of each other. Madeline is fading away psychologically and physically, and Roderick is not too far behind! The reflection of “doom” that these two share helps intensify and symbolize the hopelessness of the entire situation; thus, they further develop the fatalistic theme. Second, in the climactic scene where Madeline has been mistakenly entombed alive, there is a pairing of images and sounds as the narrator tries to calm Roderick by reading him a romance story. Events in the story simultaneously unfold with events of the sister escaping her tomb. In the story, the hero breaks out of the coffin. Then, in the story, the dragon’s shriek as he is slain parallels Madeline’s shriek. Finally, the story tells of the clangor of a shield, matched by the sister’s clanging along a metal passageway. As the suspense reaches its climax, Roderick shrieks his last words to his “friend,” the narrator: “Madman! I tell you that she now stands without the door” (296).
Roderick, who slowly falls into insanity, ironically calls the narrator the “Madman.” We are left to reflect on what Poe means by this ironic twist. Poe’s bleak and dark imagery, and his use of mirror reflections, seem only to intensify the hopelessness of “Usher.” We can plausibly conclude that, indeed, the narrator is the “Madman,” for he comes from everyday society, which is a place where hope and faith exist. Poe would probably argue that such a place is opposite to the world of Usher because a world where death is inevitable could not possibly hold such positive values. Therefore, just as Roderick mirrors his sister, the reflection in the tarn mirrors the dilapidation of the house, and the story mirrors the final actions before the death of Usher. “The Fall of the House of Usher” reflects Poe’s view that humanity is hopelessly doomed.
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Fall of the House of Usher.” 1839. Electronic Text Center, University of Virginia Library . 1995. Web. 1 July 2012. < http://etext.virginia.edu/toc/modeng/public/PoeFall.html >.
Example 3: Poetry
Amy Chisnell
Professor Laura Neary
Writing and Literature
April 17, 20—
Don’t Listen to the Egg!: A Close Reading of Lewis Carroll’s “Jabberwocky”
“You seem very clever at explaining words, Sir,” said Alice. “Would you kindly tell me the meaning of the poem called ‘Jabberwocky’?”
“Let’s hear it,” said Humpty Dumpty. “I can explain all the poems that ever were invented—and a good many that haven’t been invented just yet.” (Carroll 164)
In Lewis Carroll’s Through the Looking-Glass , Humpty Dumpty confidently translates (to a not so confident Alice) the complicated language of the poem “Jabberwocky.” The words of the poem, though nonsense, aptly tell the story of the slaying of the Jabberwock. Upon finding “Jabberwocky” on a table in the looking-glass room, Alice is confused by the strange words. She is quite certain that “ somebody killed something ,” but she does not understand much more than that. When later she encounters Humpty Dumpty, she seizes the opportunity at having the knowledgeable egg interpret—or translate—the poem. Since Humpty Dumpty professes to be able to “make a word work” for him, he is quick to agree. Thus he acts like a New Critic who interprets the poem by performing a close reading of it. Through Humpty’s interpretation of the first stanza, however, we see the poem’s deeper comment concerning the practice of interpreting poetry and literature in general—that strict analytical translation destroys the beauty of a poem. In fact, Humpty Dumpty commits the “heresy of paraphrase,” for he fails to understand that meaning cannot be separated from the form or structure of the literary work.
Of the 71 words found in “Jabberwocky,” 43 have no known meaning. They are simply nonsense. Yet through this nonsensical language, the poem manages not only to tell a story but also gives the reader a sense of setting and characterization. One feels, rather than concretely knows, that the setting is dark, wooded, and frightening. The characters, such as the Jubjub bird, the Bandersnatch, and the doomed Jabberwock, also appear in the reader’s head, even though they will not be found in the local zoo. Even though most of the words are not real, the reader is able to understand what goes on because he or she is given free license to imagine what the words denote and connote. Simply, the poem’s nonsense words are the meaning.
Therefore, when Humpty interprets “Jabberwocky” for Alice, he is not doing her any favors, for he actually misreads the poem. Although the poem in its original is constructed from nonsense words, by the time Humpty is done interpreting it, it truly does not make any sense. The first stanza of the original poem is as follows:
’Twas brillig, and the slithy toves
Did gyre and gimble in the wabe;
All mimsy were the borogroves,
An the mome raths outgrabe. (Carroll 164)
If we replace, however, the nonsense words of “Jabberwocky” with Humpty’s translated words, the effect would be something like this:
’Twas four o’clock in the afternoon, and the lithe and slimy badger-lizard-corkscrew creatures
Did go round and round and make holes in the grass-plot round the sun-dial:
All flimsy and miserable were the shabby-looking birds
with mop feathers,
And the lost green pigs bellowed-sneezed-whistled.
By translating the poem in such a way, Humpty removes the charm or essence—and the beauty, grace, and rhythm—from the poem. The poetry is sacrificed for meaning. Humpty Dumpty commits the heresy of paraphrase. As Cleanth Brooks argues, “The structure of a poem resembles that of a ballet or musical composition. It is a pattern of resolutions and balances and harmonizations” (203). When the poem is left as nonsense, the reader can easily imagine what a “slithy tove” might be, but when Humpty tells us what it is, he takes that imaginative license away from the reader. The beauty (if that is the proper word) of “Jabberwocky” is in not knowing what the words mean, and yet understanding. By translating the poem, Humpty takes that privilege from the reader. In addition, Humpty fails to recognize that meaning cannot be separated from the structure itself: the nonsense poem reflects this literally—it means “nothing” and achieves this meaning by using “nonsense” words.
Furthermore, the nonsense words Carroll chooses to use in “Jabberwocky” have a magical effect upon the reader; the shadowy sound of the words create the atmosphere, which may be described as a trance-like mood. When Alice first reads the poem, she says it seems to fill her head “with ideas.” The strange-sounding words in the original poem do give one ideas. Why is this? Even though the reader has never heard these words before, he or she is instantly aware of the murky, mysterious mood they set. In other words, diction operates not on the denotative level (the dictionary meaning) but on the connotative level (the emotion(s) they evoke). Thus “Jabberwocky” creates a shadowy mood, and the nonsense words are instrumental in creating this mood. Carroll could not have simply used any nonsense words.
For example, let us change the “dark,” “ominous” words of the first stanza to “lighter,” more “comic” words:
’Twas mearly, and the churly pells
Did bimble and ringle in the tink;
All timpy were the brimbledimps,
And the bip plips outlink.
Shifting the sounds of the words from dark to light merely takes a shift in thought. To create a specific mood using nonsense words, one must create new words from old words that convey the desired mood. In “Jabberwocky,” Carroll mixes “slimy,” a grim idea, “lithe,” a pliable image, to get a new adjective: “slithy” (a portmanteau word). In this translation, brighter words were used to get a lighter effect. “Mearly” is a combination of “morning” and “early,” and “ringle” is a blend of “ring” and "dingle.” The point is that “Jabberwocky’s” nonsense words are created specifically to convey this shadowy or mysterious mood and are integral to the “meaning.”
Consequently, Humpty’s rendering of the poem leaves the reader with a completely different feeling than does the original poem, which provided us with a sense of ethereal mystery, of a dark and foreign land with exotic creatures and fantastic settings. The mysteriousness is destroyed by Humpty’s literal paraphrase of the creatures and the setting; by doing so, he has taken the beauty away from the poem in his attempt to understand it. He has committed the heresy of paraphrase: “If we allow ourselves to be misled by it [this heresy], we distort the relation of the poem to its ‘truth’… we split the poem between its ‘form’ and its ‘content’” (Brooks 201). Humpty Dumpty’s ultimate demise might be seen to symbolize the heretical split between form and content: as a literary creation, Humpty Dumpty is an egg, a well-wrought urn of nonsense. His fall from the wall cracks him and separates the contents from the container, and not even all the King’s men can put the scrambled egg back together again!
Through the odd characters of a little girl and a foolish egg, “Jabberwocky” suggests a bit of sage advice about reading poetry, advice that the New Critics built their theories on. The importance lies not solely within strict analytical translation or interpretation, but in the overall effect of the imagery and word choice that evokes a meaning inseparable from those literary devices. As Archibald MacLeish so aptly writes: “A poem should not mean / But be.” Sometimes it takes a little nonsense to show us the sense in something.
Brooks, Cleanth. The Well-Wrought Urn: Studies in the Structure of Poetry . 1942. San Diego: Harcourt Brace, 1956. Print.
Carroll, Lewis. Through the Looking-Glass. Alice in Wonderland . 2nd ed. Ed. Donald J. Gray. New York: Norton, 1992. Print.
MacLeish, Archibald. “Ars Poetica.” The Oxford Book of American Poetry . Ed. David Lehman. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2006. 385–86. Print.
Attribution
- Sample Essay 1 received permission from Victoria Morillo to publish, licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International ( CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 )
- Sample Essays 2 and 3 adapted from Cordell, Ryan and John Pennington. "2.5: Student Sample Papers" from Creating Literary Analysis. 2012. Licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported ( CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 )
The Ultimate Guide to Analytical Essay Writing: How to Craft an A-Grade Paper?
25 January, 2021
17 minutes read
Author: Kate Smith
An analytical essay is often considered the most challenging piece of writing. However, those who have dealt with it at least once are a step closer to calling themselves masters of essay writing. This type of paper requires plenty of analytical skills to carry out an in-depth analysis of the assigned topic. Yet, the main goal of an analytical essay is not only to demonstrate your ability to learn the basics of the theme.

You also need to think critically, analyze facts, express your standpoint, and clearly show a deep understanding of key concepts. In short, your main task as an author is to prove the validity of your views by coming up with strong arguments that do not beg any questions.

The given guide provides a full analytical essay definition, as well as specifies its features and structural aspects. The following information will help you properly start your paper, choose a relevant topic, and come up with compelling conclusions.
What is an Analytical Essay?
An analytical essay is a piece of writing aimed to provide a thorough analysis of a definite phenomenon using persuasive arguments and supporting assertions. Analysis in the analytical essay writing process stands for a method of research that allows one to study specific features of an object. Analytical papers also have to do with analysis of a specific problem; that is consideration of the problem itself and identification of its key patterns. The subject matter of analysis can be a well-known or little-studied scientific phenomenon, artistic work, historical event, social problem, etc.
The content of an analytical essay will totally depend on the object that has been chosen for analysis. Thus, when shedding light on any kind of scientific work, an analytical essay can be devoted to the analysis of research credibility, its relevance, or the adequacy of conclusions. When considering a work of art, an essay writer can focus on the analysis of the author’s artistic techniques or issues raised in the book. For this reason, it is essential to accurately determine the topic and subject matter of your future analytical essay.
Steps to Take Before Writing
The preparational stage of analytical essay writing cannot be omitted. It lays the basis for the A-grade paper and should be carefully completed. If you don’t know how to start an analytical essay, read a few handy tips that will ensure a solid foundation for your paper.
Define a subject matter
You first need to clearly understand the issue you will base your essay on. Since analytical essays imply an in-depth analysis of a specific problem, you need to define its core. Try to split the analysis into several components and provide arguments taken either from a book, a research, a scientific work, or a movie (depending on the subject matter of your analysis), and support your views comprehensively.
Decide on the content of your analytical essay
If you are a student who was given an analytical essay topic, read the task several times before you are 100% sure that you clearly understand the requirements as to the analytical essay format. In case you were lucky to choose the topic of the analytical paper by yourself, make sure the theme you will be dealing with is familiar or at least seems interesting to you.
Remember that different subject matters require a different approach to their analysis. If you examine some literature work, you can prove your opinion based on the deeds of a certain or several characters. But if you have been assigned the task to elaborate on some historic events, analyze their main causes, driving forces that have affected their course, and their global consequences.
Take care of the proper start
Don’t forget to start your analytical essay with a thesis statement. It is a sentence or a couple of sentences that aim to summarize the key statements of your paper. A thesis statement should provide readers with a preliminary idea of what your essay is all about.
Find extra reasoning
Make sure your thesis is supported by compelling arguments. To find enough evidence, you should carry out a thorough analysis of the assigned topic. List the crucial points of your research and ponder over the ways they can be used to prove your final opinion.
Elaborate the outline
A sound outline elaborated at the preparation stage will help you ensure a proper analytical essay structure and make the overall writing process easier. As a rule, an analytical essay consists of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your outline plan should include the key arguments you want to discuss in each paragraph.
Analytical Essay Thesis
A thesis statement represents the central idea of your paper and must serve as strong proof of your standpoint. While elaborating your thesis statement, it is crucial to include it at the end of the first paragraph and thus set a direction for the overall paper.
Analytical Essay Outline
An outline is not a required element of analytical essays writing and should not be included in the text, but it can greatly facilitate the whole process of paper writing.
The analytical essay structure looks as follows:
Introduction
In the introduction of an analytical essay, you will need to identify your paper’s subject matter. Mention the purpose of your work and specify its scope of research. Don’t forget to include a thesis to let readers know what your work is about.
Body Section
As has already been mentioned, the body section covers three or more main paragraphs, each being supported with arguments and details. Besides, you need to provide a small conclusion to each statement to make your essay sound professional and persuasive.
At this stage, you need to summarize the points elucidated in your paper and make sure there is a smooth and logical transition from the body section to the concluding part of the text. If you don’t know how to conclude an analytical essay, try to restate the thesis statement without copying it word for word.
Analytical Essay Examples
Writing an analytical essay may seem to be a thorny way. If you are still not sure how to properly craft one, try to find some examples that will help you go in the right direction. Below, there are some great examples of analytical essays. Take a look at their structure and try to write something similar based on your views and ideas:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JeR4i4RIZIj448W3KVFyHP-eS3QPN7gW/view
https://stlcc.edu/docs/student-support/academic-support/college-writing-center/rhetorical-analysis-sample-essay.pdf
https://www.germanna.eduhttp://handmadewriting.com/wp-content/uploads/tutoring/handouts/Literary-Analysis-Sample-Paper.pdf
30 Analytical Essay Topics
If you were allowed to choose the theme for your paper by yourself, check on the following analytical essay topics. Each of them can bring you the highest score:
General topics
- The influence of social networks on the life of teens
- Are salaries of football players too high?
- Wearing uniforms in schools should be banned
- A person in society: the problems of loneliness and privacy
- Sociology of corporate relationships
- Does the observation of space need more investments?
- Should the voting age in the UK be decreased?
- Reasons why capital punishment should be brought back in the UK
- A world with no rules: a new human era or a road to the global collapse?
- Life without technologies: will modern people survive?
- Should scientists test drugs on animals to fight cancer?
- The problem of keeping the balance between career and family life
- The importance of listening to your body
- Problems caused by the lack of communication
- Food addiction and the problems it causes
- Problems of vaccination in the XXI century
- Does evil really rule the world?
- How does body size affect life quality?
- Pros and cons of video games
- The role of a family model in the life and career of a person
Analytical Essay Topics on Literature
- “Robinson Crusoe”: fantasy vs reality
- Observation of the artistic uniqueness in the comedy by W. Shakespeare “A Midsummer Night’s Dream”
- Observe the social problems in the novel by John Steinbeck “The Grapes of Wrath”
- Convulsions and death of the “little man” in the networks of impersonal, alienated forces in the novel “The Metamorphosis”
- Observation of the problems of a man on a plagued land in the novel “The Plague”
- Revolt of the protagonist in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Observation of friendship and love in the fate of humanity in the XX century
- The triumph of immorality in the novel by F. Sagan “Hello Sadness”
- Observation of the personality of an American student in the novel by J. Salinger “The Catcher in the Rye”
- Eternal tragedies of humanity in the tragedy by W. Shakespeare “The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark”
How to Write a Well-Structured Analytical Essay With a Solid Argument
Writing an analytical essay with a clear structure might be challenging unless you are thoroughly prepared. We decided to help you out and create a detailed guide listing the main things to consider when creating an analytical essay outline. You need to explain your main idea in a concise way to bring your point across. As analytical writing has high requirements, it pays off to find an analytical essay example and analyze how this text was written. It will allow you to understand the analytical essay format better and learn how to provide substantive analysis on various topics. Read on to learn how to write a top-level analytical paper and submit it on time.
Main Tips for Writing an Analytical Essay
An analytical essay should provide a comprehensive analysis of a chosen topic. What makes an analysis essay different from other assignments is that it includes a personal opinion of an author. This is why analytical writing should be persuasive.
Below, we have rounded up the key tips you need to follow when producing an analytical essay outline and the main body of your text. Read on to learn more about the analytical essay format and create a text that will fully meet the requirements.
Select an Analytical Essay Topic
Before creating an analytical essay outline, make sure to pick a topic that you are interested in. It should be provocative enough to engage your readers. A widely-debated topic will help you write an analytical essay that grabs the attention of a wide audience.
Consider your goals and conduct thorough research to see if you have enough sources to support the main thesis of your analysis essay.
Come Up With a Strong Analytical Thesis Statement
When writing an analytical essay, start by formulating a thesis statement that includes the topic and the main goal of your text. It will help you create an analytical essay outline and show your readers what you will discuss in your analysis essay.
Add it to the last paragraph of your analytical essay introduction. Due to this, your analytical essay outline will look better structured. Look at any analytical essay example to see how you can introduce your subject. In most cases, one sentence will suffice to state your analysis essay’s goal. However, a complex analytical essay outline might require you to use two sentences for a thesis statement.
Write an Analytical Essay Body with a Clear Structure
Your analytical essay outline should include 3-4 paragraphs. However, a literary analysis essay usually consists of 5 paragraphs. When it comes to analytical writing, it is important to cover a different point in each section of the main body of an analysis paper.
After writing an analytical essay, check whether each paragraph contains an introduction and the main point. Besides, it should contain evidence. An expertly written analytical essay outline will help you reach out to your target audience more effectively.
Conduct Research Before Writing an Analytical Essay Outline
While this step is preparatory, it is a must for those who want to write a well-grounded analytical paper.
- First, select the best ideas for your essay
- Then, emphasize the problems with works written by other researchers
- Finally, write your analytical essay outline to demonstrate what approach you want to take
Examine the context and find examples to illustrate the scope of the issue. You may draw parallels to emphasize your point and make your topic more relatable.
Analyze the Implications of the Evidence
After listing your pieces of evidence and demonstrating how it is related to your thesis, show why it is important. You need to explore it deeply and use it to support your argument. It will make your analytical essay outline well-grounded facts.
Write an Analytical Essay Conclusion
Whether you write a literary analysis essay or other types of assignments, there is no need to add any new data at the end of your analysis paper. Instead, summarize the arguments you mentioned in your analytical essay outline. The conclusion of your analysis essay should be short and clear. Here, you need to demonstrate that you have achieved your goals.
Analytical Essay Writing Tips
If you want to get the highest grade for your analytical essay, you need to know a little bit more than just the basics of paper writing. Read these handy tips to write a perfect essay you will be proud of:
- Double-check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes. In case your essay contains too many errors, neither an in-depth analysis nor the elaborate writing style will make it look any better. Situations when essays of great value in terms of research and a message they convey are poorly assessed because of the abundance of mistakes are not rare. Make sure you have enough time to proofread your paper before submission. Also, you may consider asking somebody to take a fresh look at your essay and check it for you.
- Reading your analytical essay out loud helps you discover all types of errors or weak phrases. This method might seem a bit uncomfortable, but it has proved to be very effective for many students. Note that silent reading of your paper isn’t even half as helpful as reading it aloud.
- Another great idea to check on the rhythm and flow of your paper is to ask someone to read it for you. While listening to the text, you could perceive it from another perspective and discover even more inconsistencies and mistakes.
- Double-check the facts you use in your analytical essay. The names of people, books, research, publications, as well as dates of historical events are too important to be misspelled. Things like these show your professionalism and the way you treat your readers.
Write an Analytical Essay with HandmadeWriting
Writing an analytical essay requires time, strong writing skills, great attention to detail, and a huge interest in the assigned topic. However, life can be unpredictable sometimes, and students might find themselves at risk of failing their creative assignments. Stress, family issues, poor health, and even unwillingness to work on a certain topic may become significant obstacles on their way to the A-grade work.
If you have similar problems, there is no need to compromise your reputation and grades. You can always refer to HandmadeWriting professionals who are ready to help you with a paper of any type and complexity. They will understand your individual style and totally devote themselv

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
How to Write an Analysis Essay: Examples + Writing Guide
An analysis / analytical essay is a standard assignment in college or university. You might be asked to conduct an in-depth analysis of a research paper, a report, a movie, a company, a book, or an event. In this article, you’ll find out how to write an analysis paper introduction, thesis, main body, and conclusion, and analytical essay example.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
So, what is an analytical essay? This type of assignment implies that you set up an argument and analyze it using a range of claims. The claims should be supported by appropriate empirical evidence. Note that you need to explore both the positive and negative sides of the issue fully.
Analytical skills are the key to getting through your academic career. Moreover, they can be useful in many real-life situations. Keep reading this article by Custom-writing experts to learn how to write an analysis!
❓ What Is an Analytical Essay?
- 🤔 Getting Started
📑 Analytical Essay Outline
- 📔 Choosing a Title
- 💁 Writing an Introduction
- 🏋 Writing a Body
- 🏁 Writing a Conclusion
🔗 References
Before you learn how to start an analysis essay, you should understand some fundamentals of writing this type of paper. It implies that you analyze an argument using a range of claims supported by facts . It is essential to understand that in your analysis essay, you’ll need to explore the negative sides of the issue and the positive ones. That’s what distinguishes an analytical essay from, say, a persuasive one.

These are the steps to write an academic paper :
- Review the literature . Before starting any paper, you should familiarize yourself with what has already been written in the field. And the analytical essay is no exception. The easiest way is to search on the web for the information.
- Brainstorm ideas. After you’ve done your search, it is time for a brainstorm! Make a list of topics for your analysis essay, and then choose the best one. Generate your thesis statement in the same way.
- Prepare an outline . Now, when you’ve decided on the topic and the thesis statement of your analytical essay, think of its structure. Below you will find more detailed information on how your paper should be structured.
- Write the first draft. You’ve done a lot of work by now. Congratulations! Your next goal is to write the first version of your analysis essay, using all the notes that you have. Remember, you don’t need to make it perfect!
- Polish your draft. Now take your time to polish and edit your draft to transform it into the paper’s final version.
You are usually assigned to analyze an article, a book, a movie, or an event. If you need to write your analytical essay on a book or an article, you’ll have to analyze the style of the text, its main points, and the author’s purported goals.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
🤔 Analytical Essay: Getting Started
The key to writing an analysis paper is to choose an argument that you will defend throughout it. For example: maybe you are writing a critical analysis paper on George Orwell’s Animal Farm The first and imperative task is to think about your thesis statement. In the case of Animal Farm , the argument could be:
In Orwell’s Animal Farm , rhetoric and language prove to be more effective ways to keep social control than physical power.
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives a great explanation of the thesis statement , how to create one, and what its function is.
But that’s not all. Once you have your thesis statement, you need to break down how you will approach your analysis essay to prove your thesis. To do this, follow these steps:
- Define the main goal(s) of your analysis . Remember that it is impossible to address each and every aspect in a single paper. Know your goal and focus on it.
- Conduct research , both online and offline, to clarify the issue contained within your thesis statement.
- Identify the main parts of the issue by looking at each part separately to see how it works.
- Try to clearly understand how each part works.
- Identify the links between the various aspects of the topic .
- By using the information you found, try to solve your main problem .
At this point, you should have a clear understanding of both the topic and your thesis statement. You should also have a clear direction for your analysis paper firmly planted in your mind and recorded in writing.
This will give you what you need to produce the paper’s outline.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
An outline is the starting point for your work. A typical analytical essay features the usual essay structure. A 500-word essay should consist of a one-paragraph introduction, a three-paragraph body, and a one-paragraph conclusion. Find below a great analytical essay outline sample. Feel free to use it as an example when doing your own work!
Analysis Essay: Introduction
- Start with a startling statement or provocative question.
“All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal”. Animal Farm abounds in ironic and provocative phrases to start an analytical essay.
- Introduce the work and its author.
- Give background information that would help the reader understand your opinion.
- Formulate a thesis statement informing the reader about the purpose of the essay. Essay format does not presuppose telling everything possible on the given topic. Thus, a thesis statement tells what you are going to say, implying what you will not discuss, establishing the limits.
In Animal Farm, Orwell uses different irony types to ridicule totalitarianism to manifest its inability to make every member of society equal and happy.
Analysis Essay: Body
The analytical essay structure requires 2-3 developmental paragraphs, each dedicated to one separate idea confirming your thesis statement. The following template should be used for each of the body paragraphs.
- Start with a topic sentence that supports an aspect of your thesis.
Dramatic irony is used in Animal Farm to point out society’s ignorance.
- Continue with textual evidence (paraphrase, summary, direct quotations, specific details). Use several examples that substantiate the topic sentence.
Animals are unaware of the fact that Boxer was never sent to the hospital. He was sent to the slaughterhouse. However, the reader and writer understand that this is a lie.
- Conclude with an explanation.
By allowing the readers to learn some essential facts before the characters, dramatic irony creates suspense and shows how easy it is to persuade and manipulate the public.
Analysis Essay Conclusion
The next four points will give you a short instruction on how to conclude an analytical essay.
- Never use new information or topics here.
- Restate your thesis in a different formulation.
- Summarize the body paragraphs.
- Comment on the analyzed text from a new perspective.
📔 Choosing a Title for Your Analysis Essay
Choosing a title seems like not a significant step, but it is actually very important. The title of your critical analysis paper should:
- Entice and engage the reader
- Be unique and capture the readers’ attention
- Provide an adequate explanation of the content of the essay in just a few carefully chosen words
In the Animal Farm example, your title could be:
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
“How Do the Pigs Manage to Keep Social Control on Animal Farm?”
Analysis Essay Topics
- Analyze the media content.
- Analyze the specifics and history of hip-hop culture.
- Sociological issues in the film Interstellar .
- Discuss the techniques M. Atwood uses to describe social issues in her novel The Handmaid’s Tale .
- Compare and analyze the paintings of Van Gogh and George Seurat.
- Analysis of Edgar Allan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Examine the juvenile crime rates.
- Describe the influence of different parenting styles on children’s mind.
- Analyze the concept of the Ship of Theseus .
- Compare and analyze the various views on intelligence .
- Analysis of The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman .
- Discuss the techniques used by W. Shakespeare in A Midsummer Night’s Dream .
- Analyze the biography of Frederic Chopin .
- Manifestation of the Chicano culture in the artwork An Ofrenda for Dolores del Rio .
- Similarities and differences of Roman, Anglo-Saxon, and Spanish Empires .
- Describe the problem of stalking and its impact on human mental health.
- Examine the future of fashion .
- Analyze the topicality of the article Effectiveness of Hand Hygiene Interventions in Reducing Illness Absence .
- Discuss Thomas Paine’s impact on the success of American revolution.
- Meaningful messages in Recitatif by Toni Morrison .
- Explore the techniques used by directors in the film Killing Kennedy .
- Compare the leadership styles of Tang Empress Wu Zetian and the Pharaoh Cleopatra .
- Evaluate the credibility of Kristof’s arguments in his article Remote Learning Is Often an Oxymoron .
- Analyze genetically modified food .
- Examine the influence of Europeans on Indian tribes in The Narrative of the Captivity and Restoration of Mrs. Mary Rowlandson .
- Describe the rhetoric techniques used in The Portrait of Dorian Gray by Oscar Wilde .
- The importance of fighting against violence in communities in the documentary film The Interrupters .
- Analyze indoor and outdoor pollution .
- Analyze the issue of overprotective parenthood .
- Explore the connection between eating habits and advertisement.
- Discuss the urgence of global warming issue .
- Influence of sleep on people’s body and mental health.
- Analyze the relationship between Christianity and sports .
- Discuss the concept of leadership and its significance for company efficiency.
- Analyze the key lessons of the book Rich Dad Poor Dad by Robert Kiyosaki .
- Examine the specifics of nursing ethic .
- The theme of emotional sufferings in the short story A Rose for Emily .
- Analysis of bias in books for children .
- Analyze the rhetoric of the article Public Monuments .
- Describe the main messages in Jean-Paul Sartre’s Nausea .
- Explore the problem of structural racism in healthcare .
- The reasons of tango dance popularity.
- The shortcomings of the American educational system in Waiting for Superman.
- Analyze and compare Erin’s Law and Megan’s Law .
- Analyze the James Madison’s essay Federalist 10 .
- Examine symbols in the movie The Joker .
- Compare the thematic connection and stylistic devices in the poems The Road Not Taken and Find Your Way .
- Describe and analyze the life of Eddie Bernice Johnson .
- Explore the social classes in America .
- Crucial strengths and weaknesses of the main translation theories .
💁 Writing Your Analytical Essay Introduction
You must understand how to compose an introduction to an analysis paper. The University of Wollongong describes the introduction as a “map” of any writing. When writing the introduction, follow these steps:
- Provide a lead-in for the reader by offering a general introduction to the topic of the paper.
- Include your thesis statement , which shifts the reader from the generalized introduction to the specific topic and its related issues to your unique take on the essay topic.
- Present a general outline of the analysis paper.
Watch this great video for further instructions on how to write an introduction to an analysis essay.
Example of an Analytical Essay Introduction
“Four legs good, two legs bad” is one of the many postulates invented by George Orwell for his characters in Animal Farm to vest them with socialist ideology and control over the animal population. The social revolution on Manor Farm was built on language instruments, first for the collective success of the animals, and later for the power consolidation by the pigs. The novel was written in 1945 when the transition from limitless freedoms of socialist countries transformed into dictatorship. Through his animal protagonists, the author analyzes the reasons for peoples’ belief in the totalitarian regime. In Orwell’s Animal Farm , rhetoric and language prove to be more effective ways to keep social control than physical power.
🏋 Writing Your Analytical Essay Body
The body of the paper may be compared to its heart. This is the part where you show off your talent for analysis by providing convincing, well-researched, and well-thought-out arguments to support your thesis statement. You have already gathered the information, and now all you may start crafting your paper.
To make the body of an analytical essay, keep the following in mind:
- Discuss one argument per paragraph , although each argument can relate to multiple issues
- Strike a balance between writing in an unbiased tone, while expressing your personal opinion
- Be reasonable when making judgments regarding any of the problems you discuss
- Remember to include the opposing point of view to create a balanced perspective
The bottom line is: you want to offer opposing views, but you must pose your arguments so they will counter those opposing views and prove your point of view. Follow these steps when constructing each body paragraph:
- Choose the main sentence. The main or topic sentence will be the first line in your essay. The topic sentence is responsible for presenting the argument you will discuss in the paragraph and demonstrate how this argument relates to the thesis statement.
- Provide the context for the topic sentence , whether it relates to a quote, a specific incident in society, or something else. Offer evidence on who, what, where, when, why, and how.
- Give your analysis of the argument and how it adequately proves your thesis.
- Write a closing sentence that sums up the paragraph and provides a transition to the following paragraph.
Example of an Analytical Essay Body
Literacy can grant power, provided that there are animals who cannot read or write. In the beginning, the animals’ literacy and intellect are relatively the same. Old Major is the cleverest pig; he is the kind old philosopher, like Karl Marx or Vladimir Lenin. During his retirement, he develops a theory that all humans are the root of evil. His speech was the foundation for the pigs’ assumption of power. They refined his ideas into a new ideology and called it Animalism. They also learned how to read. It allowed the pigs to declare themselves the “mind workers.” Therefore, the pigs’ literacy assured the illiterate animals in their objective superiority.
Meanwhile, as the pigs were the intellectual elite, they were not supposed to work, which raised their social status by itself. Snowball tried to promote education among all the animals, but most of them failed to master the alphabet. This is a metaphor for the general public being predominantly ignorant and easy to manipulate. At the same time, Boxer and other animals that spend most of the day in hard work merely have no time to develop their intellect. Thus, the pigs’ intention to build a school for pig children was highly efficient. Unequal access to education and unequal ability to express one’s thoughts in perspective reinforce the social divide, making the pigs smarter and more powerful and undermining other animals’ self-esteem.
At this point, the pigs resort to propaganda and rhetoric. Squealer uses his oratorical gift to refine the pigs’ message to the other animals. Upon Napoleon’s order, he breaks the Seven Commandments of farm governance. At night, he climbs the ladder to change them, and once even falls from the ladder trying to change the commandment on alcohol. The “proletarian” animals soon forget what the Seven Commandments were like in the first place and are unsure if they have ever been altered. Further on, Minimus writes a poem praising Napoleon. Finally, Squealer replaces the Commandments with a single assertion: “All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others.” Language is no longer used to convince. It is used to control and manipulate.
🏁 Writing Your Analytical Essay Conclusion
The conclusion is short and sweet. It summarizes everything you just wrote in the essay and wraps it up with a beautiful shiny bow. Follow these steps to write a convincing conclusion:
- Repeat the thesis statement and summarize your argument. Even when using the best summary generator for the task, reread it to make sure all the crucial points are included.
- Take your argument beyond what is simply stated in your paper. You want to show how it is essential in terms of the bigger picture. Also, you may dwell on the influence on citizens of the country.
Example of an Analytical Essay Conclusion
Because of everything mentioned above, it becomes clear that language and rhetoric can rise to power, establish authority, and manipulate ordinary people. Animal Farm is the simplified version of a communist society. It shows how wise philosophers’ good intentions can be used by mean leaders to gain unopposed power and unconditional trust. Unfortunately, this can lead to the death of many innocent animals, i.e., people, as totalitarianism has nothing to do with people’s rule. Therefore, language and oratory are potent tools that can keep people oppressed and weak, deprive them of any chance for improvement and growth, and make them think that there is no other possible existence.
Now you are ready to write an analysis essay! See, it’s easier than you thought.
Of course, it’s always helpful to see other analysis essay examples. The University of Arkansas at Little Rock provides some great examples of an analytical paper .
✏️ Analysis Essay FAQ
A great analytical paper should be well-structured, cohesive, and logically consistent. Each part of the essay should be in its place, creating a smooth and easy-to-read text. Most importantly, the statements should be objective and backed by arguments and examples.
It is a paper devoted to analyzing a certain topic or subject. An analysis essay is all about reviewing certain details of the subject and interpreting them. For example, such an analysis for a poem includes a description of artistic means that helped the poet convey the idea.
Writing an analytical essay on a book/movie/poem start with an outline. Point out what catches the eye when reviewing the subject. See how these details can be interpreted. Make sure that you refer to the main idea/message. Add an appropriate introduction and a logical conclusion.
Being more analytical in writing can be essential for a student. This is a skill that can be self-taught: try to start noticing subtle details and describe them. As you write, interpret the facts and strive to draw conclusions. Try to be as objective as possible.
- Elements of Analysis
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay: Bucks.edu
- Essay Structure | – Harvard College Writing Center
- Analytical Writing: Looking Closely (Colostate.edu)
- Analytical Thesis Statements – University of Arizona
- Writing an analytic essay – UTSC – University of Toronto
- Organizing Your Analysis // Purdue Writing Lab
- How to Write an Analytical Essay: 15 Steps (with Pictures)
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

A film analysis essay might be the most exciting assignment you have ever had! After all, who doesn’t love watching movies? You have your favorite movies, maybe something you watched years ago, perhaps a classic, or a documentary. Or your professor might assign a film for you to make a...

A critique paper is an academic writing genre that summarizes and gives a critical evaluation of a concept or work. Or, to put it simply, it is no more than a summary and a critical analysis of a specific issue. This type of writing aims to evaluate the impact of...

What is a creative essay, if not the way to express yourself? Crafting such a paper is a task that allows you to communicate your opinion and tell a story. However, even using your imagination to a great extent doesn’t free you from following academic writing rules. Don’t even get...

A compare and contrast essay — what is it? In this type of paper, you compare two different things or ideas, highlighting what is similar between the two, and you also contrast them, highlighting what is different. The two things might be events, people, books, points of view, lifestyles, or...

What is an expository essay? This type of writing aims to inform the reader about the subject clearly, concisely, and objectively. The keyword here is “inform”. You are not trying to persuade your reader to think a certain way or let your own opinions and emotions cloud your work. Just stick to the...
![what is a text analysis essay Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-sits-end-trolltunga-before-mountains-284x153.jpg)
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation. But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are...

Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding. A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate...
![what is a text analysis essay Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![what is a text analysis essay Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![what is a text analysis essay Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...
This resource helps me a lot. Thanks! You guys have great information. Do you think I can use these steps when taking a test? Could it be known as plagiarized if I just copy and paste the information?

Glad to help, Hazel! You can use it in your test but you should cite it accordingly
Thanks, very good information.
Thank you for your attention, Jaweria🙂!
Thanks for learning how to critique research papers in a proper way! This is what I need to cope with this task successfully! Thanks!
How much is an essay, and is there a chance it can be plagiarized?
You have to remember that the price for our services depends on a lot of factors. You can find the detailed price quote here: https://custom-writing.org/prices (the page will be opened in a new window). You can check out the prices depending on the subjects and deadlines that you choose. No – it can’t be plagiarized: the papers are written from scratch according to your instructions. We also stress the importance of the fact that you CAN’T, under any circumstances, use our final product as your own work – the papers, which we provide, are to be used for research purposes only!
- On My Bookshelf
- Teaching Resources
- Privacy Policy

February 1, 2021
- Tackling the Text Dependent Analysis Essay

You Might Also Like
Post a comment.

Find It Fast
Get support, shop my tpt store, top categories.
- my bookshelf
Post Topics
Blog archive.
- ► December (3)
- ► August (4)
- ► July (10)
- ► June (2)
- ► February (2)
- ► November (3)
- ► October (2)
- ► September (2)
- ► July (2)
- ► June (9)
- ► May (1)
- ► April (1)
- ► March (1)
- ► February (1)
- ► January (1)
- ► December (1)
- ► November (2)
- ► October (1)
- ► September (1)
- ► June (1)
- ► May (3)
- What I'm Reading & Teaching in March
- Everything You Need to Host a March Madness Poetry...
- Teaching Symbolism to Middle & High School Students
- Teaching Theme to Middle & High School Students
- Teaching Point of View to Middle & High School Stu...
- ► January (5)
- ► December (2)
- ► October (6)
- ► September (6)
- ► August (5)
- ► July (6)
- ► May (2)
- ► April (4)
- ► March (4)
- ► February (4)
- ► December (6)
- ► November (10)
- ► October (13)
- ► September (10)
- ► August (14)
- ► July (7)
- ► May (4)
- ► April (7)
- ► March (10)
- ► February (7)
- ► January (7)
- ► November (4)
- ► October (8)
- ► September (13)
- ► August (13)
- ► July (9)
- ► June (6)
- ► May (7)
- ► April (13)
- ► March (12)
- ► February (11)
- ► January (12)
- ► December (7)
- ► November (11)
- ► October (14)
- ► August (12)
- ► July (12)
- ► June (7)
- ► May (8)
- ► April (14)
- ► March (17)
- ► October (12)
- ► July (11)
- ► June (5)
- ► May (14)
- ► February (13)
- ► January (13)
- ► December (8)
- ► November (13)
- ► September (12)
- ► August (11)
- ► May (5)
- ► February (6)
- ► October (4)
- ► September (4)
- ► August (3)
- ► July (4)

What is Text Analysis? A Beginner’s Guide
- How Does It work?
- Use Cases & Applications
- Online Tools

If you receive huge amounts of unstructured data in the form of text (emails, social media conversations, chats), you’re probably aware of the challenges that come with analyzing this data.
Manually processing and organizing text data takes time, it’s tedious, inaccurate, and it can be expensive if you need to hire extra staff to sort through text.
Automate text analysis with a no-code tool
In this guide, learn more about what text analysis is, how to perform text analysis using AI tools, and why it’s more important than ever to automatically analyze your text in real time.
- Text Analysis Basics
- Methods & Techniques
How Does Text Analysis Work?
How to analyze text data.
- Use Cases and Applications
- Tools and Resources
What Is Text Analysis?
Text analysis (TA) is a machine learning technique used to automatically extract valuable insights from unstructured text data. Companies use text analysis tools to quickly digest online data and documents, and transform them into actionable insights.
You can us text analysis to extract specific information, like keywords, names, or company information from thousands of emails, or categorize survey responses by sentiment and topic.
The Text Analysis vs. Text Mining vs. Text Analytics
Firstly, let's dispel the myth that text mining and text analysis are two different processes. The terms are often used interchangeably to explain the same process of obtaining data through statistical pattern learning. To avoid any confusion here, let's stick to text analysis.
So, text analytics vs. text analysis : what's the difference?
Text analysis delivers qualitative results and text analytics delivers quantitative results. If a machine performs text analysis, it identifies important information within the text itself, but if it performs text analytics, it reveals patterns across thousands of texts, resulting in graphs, reports, tables etc.
Let's say a customer support manager wants to know how many support tickets were solved by individual team members. In this instance, they'd use text analytics to create a graph that visualizes individual ticket resolution rates.
However, it's likely that the manager also wants to know which proportion of tickets resulted in a positive or negative outcome?
By analyzing the text within each ticket, and subsequent exchanges, customer support managers can see how each agent handled tickets, and whether customers were happy with the outcome.
Basically, the challenge in text analysis is decoding the ambiguity of human language, while in text analytics it's detecting patterns and trends from the numerical results.
Why Is Text Analysis Important?
When you put machines to work on organizing and analyzing your text data, the insights and benefits are huge.
Let's take a look at some of the advantages of text analysis, below:
Text Analysis Is Scalable
Text analysis tools allow businesses to structure vast quantities of information, like emails, chats, social media, support tickets, documents, and so on, in seconds rather than days, so you can redirect extra resources to more important business tasks.
Analyze Text in Real-time
Businesses are inundated with information and customer comments can appear anywhere on the web these days, but it can be difficult to keep an eye on it all. Text analysis is a game-changer when it comes to detecting urgent matters, wherever they may appear, 24/7 and in real time. By training text analysis models to detect expressions and sentiments that imply negativity or urgency, businesses can automatically flag tweets, reviews, videos, tickets, and the like, and take action sooner rather than later.
AI Text Analysis Delivers Consistent Criteria
Humans make errors. Fact. And the more tedious and time-consuming a task is, the more errors they make. By training text analysis models to your needs and criteria, algorithms are able to analyze, understand, and sort through data much more accurately than humans ever could.
Text Analysis Methods & Techniques

There are basic and more advanced text analysis techniques, each used for different purposes. First, learn about the simpler text analysis techniques and examples of when you might use each one.
Text Classification
Text extraction, word frequency, collocation, concordance, word sense disambiguation.
Text classification is the process of assigning predefined tags or categories to unstructured text. It's considered one of the most useful natural language processing techniques because it's so versatile and can organize, structure, and categorize pretty much any form of text to deliver meaningful data and solve problems. Natural language processing (NLP) is a machine learning technique that allows computers to break down and understand text much as a human would.
Below, we're going to focus on some of the most common text classification tasks, which include sentiment analysis, topic modeling, language detection, and intent detection.
Sentiment Analysis
Customers freely leave their opinions about businesses and products in customer service interactions, on surveys, and all over the internet. Sentiment analysis uses powerful machine learning algorithms to automatically read and classify for opinion polarity (positive, negative, neutral) and beyond, into the feelings and emotions of the writer, even context and sarcasm.
For example, by using sentiment analysis companies are able to flag complaints or urgent requests, so they can be dealt with immediately – even avert a PR crisis on social media . Sentiment classifiers can assess brand reputation, carry out market research, and help improve products with customer feedback.
Try out MonkeyLearn's pre-trained classifier . Just enter your own text to see how it works:
Test with your own text
Topic analysis.
Another common example of text classification is topic analysis (or topic modeling ) that automatically organizes text by subject or theme. For example:
“The app is really simple and easy to use”
If we are using topic categories, like Pricing, Customer Support, and Ease of Use, this product feedback would be classified under Ease of Use .
Try out MonkeyLearn's pre-trained topic classifier , which can be used to categorize NPS responses for SaaS products.
Intent Detection
Text classifiers can also be used to detect the intent of a text. Intent detection or intent classification is often used to automatically understand the reason behind customer feedback. Is it a complaint? Or is a customer writing with the intent to purchase a product? Machine learning can read chatbot conversations or emails and automatically route them to the proper department or employee.
Try out MonkeyLearn's email intent classifier .
Text extraction is another widely used text analysis technique that extracts pieces of data that already exist within any given text. You can extract things like keywords, prices, company names, and product specifications from news reports, product reviews, and more.
You can automatically populate spreadsheets with this data or perform extraction in concert with other text analysis techniques to categorize and extract data at the same time.
Keyword Extraction
Keywords are the most used and most relevant terms within a text, words and phrases that summarize the contents of text. [Keyword extraction] (]( https://monkeylearn.com/keyword-extraction/ ) can be used to index data to be searched and to generate word clouds (a visual representation of text data).
Try out MonkeyLearn's pre-trained keyword extractor to see how it works. Just type in your text below:
Entity Recognition
A named entity recognition (NER) extractor finds entities, which can be people, companies, or locations and exist within text data. Results are shown labeled with the corresponding entity label, like in MonkeyLearn's pre-trained name extractor :
Word frequency is a text analysis technique that measures the most frequently occurring words or concepts in a given text using the numerical statistic TF-IDF (term frequency-inverse document frequency).
You might apply this technique to analyze the words or expressions customers use most frequently in support conversations. For example, if the word 'delivery' appears most often in a set of negative support tickets, this might suggest customers are unhappy with your delivery service.
Collocation helps identify words that commonly co-occur. For example, in customer reviews on a hotel booking website, the words 'air' and 'conditioning' are more likely to co-occur rather than appear individually. Bigrams (two adjacent words e.g. 'air conditioning' or 'customer support') and trigrams (three adjacent words e.g. 'out of office' or 'to be continued') are the most common types of collocation you'll need to look out for.
Collocation can be helpful to identify hidden semantic structures and improve the granularity of the insights by counting bigrams and trigrams as one word.
Concordance helps identify the context and instances of words or a set of words. For example, the following is the concordance of the word “simple” in a set of app reviews:
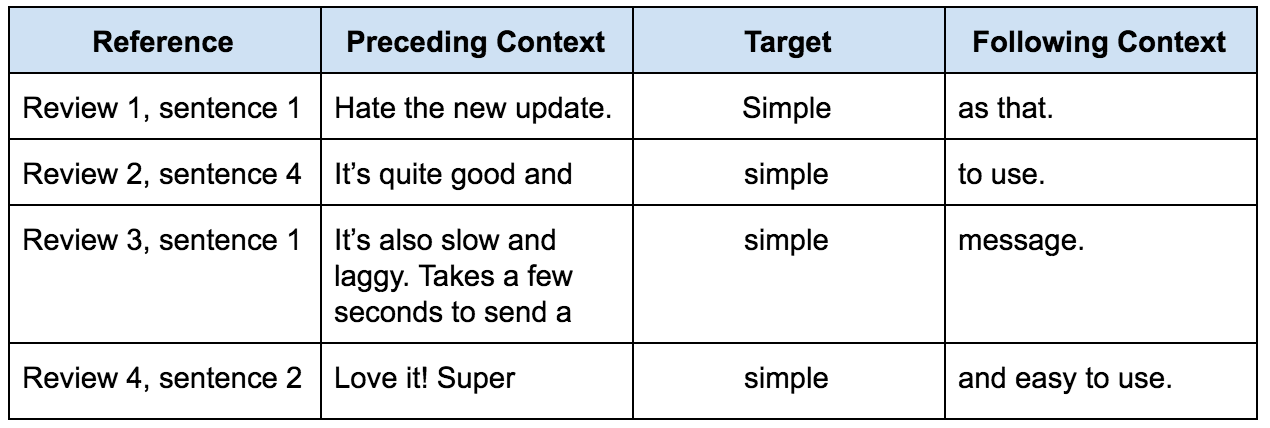
In this case, the concordance of the word “simple” can give us a quick grasp of how reviewers are using this word. It can also be used to decode the ambiguity of the human language to a certain extent, by looking at how words are used in different contexts, as well as being able to analyze more complex phrases.
It's very common for a word to have more than one meaning, which is why word sense disambiguation is a major challenge of natural language processing. Take the word 'light' for example. Is the text referring to weight, color, or an electrical appliance? Smart text analysis with word sense disambiguation can differentiate words that have more than one meaning, but only after training models to do so.
Text clusters are able to understand and group vast quantities of unstructured data. Although less accurate than classification algorithms, clustering algorithms are faster to implement, because you don't need to tag examples to train models. That means these smart algorithms mine information and make predictions without the use of training data, otherwise known as unsupervised machine learning.
Google is a great example of how clustering works. When you search for a term on Google, have you ever wondered how it takes just seconds to pull up relevant results? Google's algorithm breaks down unstructured data from web pages and groups pages into clusters around a set of similar words or n-grams (all possible combinations of adjacent words or letters in a text). So, the pages from the cluster that contain a higher count of words or n-grams relevant to the search query will appear first within the results.
To really understand how automated text analysis works, you need to understand the basics of machine learning . Let's start with this definition from Machine Learning by Tom Mitchell :
"A computer program is said to learn to perform a task T from experience E".
In other words, if we want text analysis software to perform desired tasks, we need to teach machine learning algorithms how to analyze, understand and derive meaning from text. But how? The simple answer is by tagging examples of text. Once a machine has enough examples of tagged text to work with, algorithms are able to start differentiating and making associations between pieces of text, and make predictions by themselves.
It's very similar to the way humans learn how to differentiate between topics, objects, and emotions. Let's say we have urgent and low priority issues to deal with. We don't instinctively know the difference between them – we learn gradually by associating urgency with certain expressions.
For example, when we want to identify urgent issues, we'd look out for expressions like 'please help me ASAP!' or 'urgent: can't enter the platform, the system is DOWN!!' . On the other hand, to identify low priority issues, we'd search for more positive expressions like 'thanks for the help! Really appreciate it' or 'the new feature works like a dream' .
Text analysis can stretch it's AI wings across a range of texts depending on the results you desire. It can be applied to:
- Whole documents : obtains information from a complete document or paragraph: e.g., the overall sentiment of a customer review.
- Single sentences : obtains information from specific sentences: e.g., more detailed sentiments of every sentence of a customer review.
- Sub-sentences : obtains information from sub-expressions within a sentence: e.g., the underlying sentiments of every opinion unit of a customer review.
Once you know how you want to break up your data, you can start analyzing it.
Let’s take a look at how text analysis works, step-by-step, and go into more detail about the different machine learning algorithms and techniques available.
Data Gathering
You can gather data about your brand, product or service from both internal and external sources:
Internal Data
This is the data you generate every day, from emails and chats, to surveys, customer queries, and customer support tickets.
You just need to export it from your software or platform as a CSV or Excel file, or connect an API to retrieve it directly.
Some examples of internal data:
Customer Service Software : the software you use to communicate with customers, manage user queries and deal with customer support issues: Zendesk, Freshdesk, and Help Scout are a few examples.
CRM : software that keeps track of all the interactions with clients or potential clients. It can involve different areas, from customer support to sales and marketing. Hubspot, Salesforce, and Pipedrive are examples of CRMs.
Chat : apps that communicate with the members of your team or your customers, like Slack, Hipchat, Intercom, and Drift.
Email : the king of business communication, emails are still the most popular tool to manage conversations with customers and team members.
Surveys : generally used to gather customer service feedback, product feedback, or to conduct market research, like Typeform, Google Forms, and SurveyMonkey.
NPS (Net Promoter Score) : one of the most popular metrics for customer experience in the world. Many companies use NPS tracking software to collect and analyze feedback from their customers. A few examples are Delighted, Promoter.io and Satismeter.
Databases : a database is a collection of information. By using a database management system, a company can store, manage and analyze all sorts of data. Examples of databases include Postgres, MongoDB, and MySQL.
Product Analytics : the feedback and information about interactions of a customer with your product or service. It's useful to understand the customer's journey and make data-driven decisions. ProductBoard and UserVoice are two tools you can use to process product analytics.
External Data
This is text data about your brand or products from all over the web. You can use web scraping tools, APIs, and open datasets to collect external data from social media, news reports, online reviews, forums, and more, and analyze it with machine learning models.
Web Scraping Tools:
Visual Web Scraping Tools : you can build your own web scraper even with no coding experience, with tools like. Dexi.io, Portia, and ParseHub.e.
Web Scraping Frameworks : seasoned coders can benefit from tools, like Scrapy in Python and Wombat in Ruby, to create custom scrapers.
Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, for example, have their own APIs and allow you to extract data from their platforms. Major media outlets like the New York Times or The Guardian also have their own APIs and you can use them to search their archive or gather users' comments, among other things.
Integrations
SaaS tools, like MonkeyLearn offer integrations with the tools you already use . You can connect directly to Twitter , Google Sheets , Gmail, Zendesk, SurveyMonkey, Rapidminer, and more. And perform text analysis on Excel data by uploading a file.
2. Data Preparation
In order to automatically analyze text with machine learning, you’ll need to organize your data. Most of this is done automatically, and you won't even notice it's happening. However, it's important to understand that automatic text analysis makes use of a number of natural language processing techniques (NLP) like the below.
Tokenization, Part-of-speech Tagging, and Parsing
Tokenization is the process of breaking up a string of characters into semantically meaningful parts that can be analyzed (e.g., words), while discarding meaningless chunks (e.g. whitespaces).
The examples below show two different ways in which one could tokenize the string 'Analyzing text is not that hard' .
(Incorrect): Analyzing text is not that hard. = [“Analyz”, “ing text”, “is n”, “ot that”, “hard.”]
(Correct): Analyzing text is not that hard. = [“Analyzing”, “text”, “is”, “not”, “that”, “hard”, “.”]
Once the tokens have been recognized, it's time to categorize them. Part-of-speech tagging refers to the process of assigning a grammatical category, such as noun, verb, etc. to the tokens that have been detected.
Here are the PoS tags of the tokens from the sentence above:
“Analyzing”: VERB, “text”: NOUN, “is”: VERB, “not”: ADV, “that”: ADV, “hard”: ADJ, “.”: PUNCT
With all the categorized tokens and a language model (i.e. a grammar), the system can now create more complex representations of the texts it will analyze. This process is known as parsing . In other words, parsing refers to the process of determining the syntactic structure of a text. To do this, the parsing algorithm makes use of a grammar of the language the text has been written in. Different representations will result from the parsing of the same text with different grammars.
The examples below show the dependency and constituency representations of the sentence 'Analyzing text is not that hard' .
Dependency Parsing
Dependency grammars can be defined as grammars that establish directed relations between the words of sentences. Dependency parsing is the process of using a dependency grammar to determine the syntactic structure of a sentence:
Constituency Parsing
Constituency phrase structure grammars model syntactic structures by making use of abstract nodes associated to words and other abstract categories (depending on the type of grammar) and undirected relations between them. Constituency parsing refers to the process of using a constituency grammar to determine the syntactic structure of a sentence:
As you can see in the images above, the output of the parsing algorithms contains a great deal of information which can help you understand the syntactic (and some of the semantic) complexity of the text you intend to analyze.
Depending on the problem at hand, you might want to try different parsing strategies and techniques. However, at present, dependency parsing seems to outperform other approaches.
Lemmatization and Stemming
Stemming and lemmatization both refer to the process of removing all of the affixes (i.e. suffixes, prefixes, etc.) attached to a word in order to keep its lexical base, also known as root or stem or its dictionary form or le mma . The main difference between these two processes is that stemming is usually based on rules that trim word beginnings and endings (and sometimes lead to somewhat weird results), whereas lemmatization makes use of dictionaries and a much more complex morphological analysis.
The table below shows the output of NLTK's Snowball Stemmer and Spacy's lemmatizer for the tokens in the sentence 'Analyzing text is not that hard' . The differences in the output have been boldfaced:
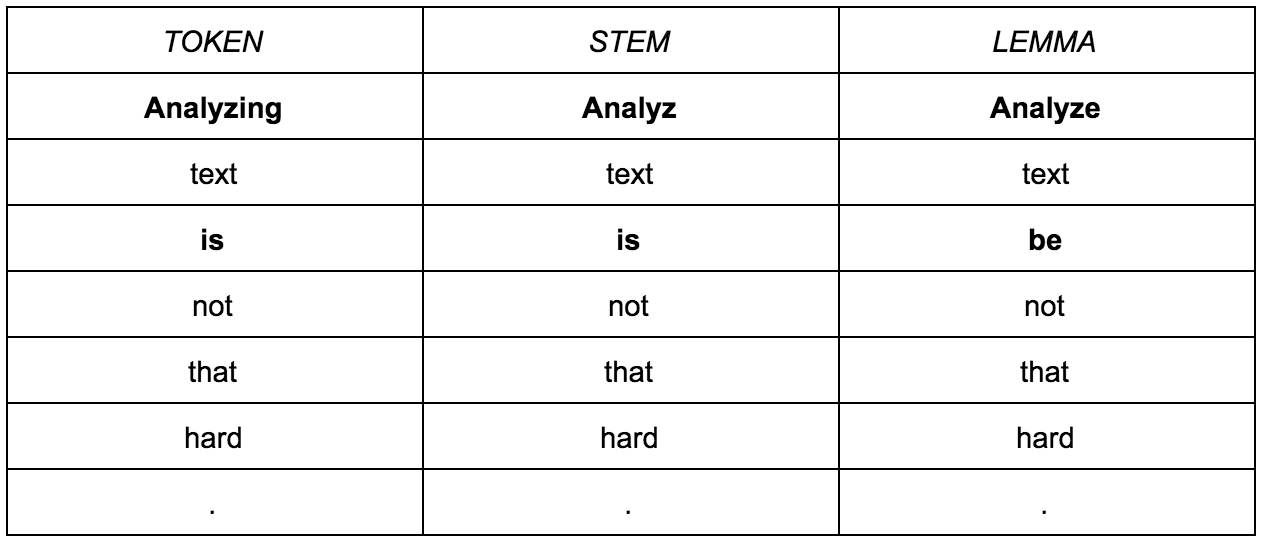
Stopword Removal
To provide a more accurate automated analysis of the text, we need to remove the words that provide very little semantic information or no meaning at all. These words are also known as stopwords: a, and, or, the, etc.
There are many different lists of stopwords for every language. However, it's important to understand that you might need to add words to or remove words from those lists depending on the texts you want to analyze and the analyses you would like to perform.
You might want to do some kind of lexical analysis of the domain your texts come from in order to determine the words that should be added to the stopwords list.
Analyze Your Text Data
Now that you’ve learned how to mine unstructured text data and the basics of data preparation, how do you analyze all of this text?
Well, the analysis of unstructured text is not straightforward. There are countless text analysis methods, but two of the main techniques are text classification and text extraction .
Text classification (also known as text categorization or text tagging ) refers to the process of assigning tags to texts based on its content.
In the past, text classification was done manually, which was time-consuming, inefficient, and inaccurate. But automated machine learning text analysis models often work in just seconds with unsurpassed accuracy.
The most popular text classification tasks include sentiment analysis (i.e. detecting when a text says something positive or negative about a given topic), topic detection (i.e. determining what topics a text talks about), and intent detection (i.e. detecting the purpose or underlying intent of the text), among others, but there are a great many more applications you might be interested in.
Rule-based Systems
In text classification, a rule is essentially a human-made association between a linguistic pattern that can be found in a text and a tag. Rules usually consist of references to morphological, lexical, or syntactic patterns, but they can also contain references to other components of language, such as semantics or phonology.
Here's an example of a simple rule for classifying product descriptions according to the type of product described in the text:
(HDD|RAM|SSD|Memory) → Hardware
In this case, the system will assign the Hardware tag to those texts that contain the words HDD , RAM , SSD , or Memory .
The most obvious advantage of rule-based systems is that they are easily understandable by humans. However, creating complex rule-based systems takes a lot of time and a good deal of knowledge of both linguistics and the topics being dealt with in the texts the system is supposed to analyze.
On top of that, rule-based systems are difficult to scale and maintain because adding new rules or modifying the existing ones requires a lot of analysis and testing of the impact of these changes on the results of the predictions.
Machine Learning-based Systems
Machine learning-based systems can make predictions based on what they learn from past observations. These systems need to be fed multiple examples of texts and the expected predictions (tags) for each. This is called training data . The more consistent and accurate your training data, the better ultimate predictions will be.
When you train a machine learning-based classifier, training data has to be transformed into something a machine can understand, that is, vectors (i.e. lists of numbers which encode information). By using vectors, the system can extract relevant features (pieces of information) which will help it learn from the existing data and make predictions about the texts to come.
There are a number of ways to do this, but one of the most frequently used is called bag of words vectorization . You can learn more about vectorization here .
Once the texts have been transformed into vectors, they are fed into a machine learning algorithm together with their expected output to create a classification model that can choose what features best represent the texts and make predictions about unseen texts:
The trained model will transform unseen text into a vector, extract its relevant features, and make a prediction:
Machine Learning Algorithms
There are many machine learning algorithms used in text classification. The most frequently used are the Naive Bayes (NB) family of algorithms, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and deep learning algorithms.
The Naive Bayes family of algorithms is based on Bayes's Theorem and the conditional probabilities of occurrence of the words of a sample text within the words of a set of texts that belong to a given tag. Vectors that represent texts encode information about how likely it is for the words in the text to occur in the texts of a given tag. With this information, the probability of a text's belonging to any given tag in the model can be computed. Once all of the probabilities have been computed for an input text, the classification model will return the tag with the highest probability as the output for that input.
One of the main advantages of this algorithm is that results can be quite good even if there’s not much training data.
Support Vector Machines (SVM) is an algorithm that can divide a vector space of tagged texts into two subspaces: one space that contains most of the vectors that belong to a given tag and another subspace that contains most of the vectors that do not belong to that one tag.
Classification models that use SVM at their core will transform texts into vectors and will determine what side of the boundary that divides the vector space for a given tag those vectors belong to. Based on where they land, the model will know if they belong to a given tag or not.
The most important advantage of using SVM is that results are usually better than those obtained with Naive Bayes. However, more computational resources are needed for SVM.
Deep Learning is a set of algorithms and techniques that use “artificial neural networks” to process data much as the human brain does. These algorithms use huge amounts of training data (millions of examples) to generate semantically rich representations of texts which can then be fed into machine learning-based models of different kinds that will make much more accurate predictions than traditional machine learning models:
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems usually contain machine learning-based systems at their cores and rule-based systems to improve the predictions
Classifier performance is usually evaluated through standard metrics used in the machine learning field: accuracy , precision , recall , and F1 score . Understanding what they mean will give you a clearer idea of how good your classifiers are at analyzing your texts.
It is also important to understand that evaluation can be performed over a fixed testing set (i.e. a set of texts for which we know the expected output tags) or by using cross-validation (i.e. a method that splits your training data into different folds so that you can use some subsets of your data for training purposes and some for testing purposes, see below ).
Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1 score
Accuracy is the number of correct predictions the classifier has made divided by the total number of predictions. In general, accuracy alone is not a good indicator of performance. For example, when categories are imbalanced, that is, when there is one category that contains many more examples than all of the others, predicting all texts as belonging to that category will return high accuracy levels. This is known as the accuracy paradox . To get a better idea of the performance of a classifier, you might want to consider precision and recall instead.
Precision states how many texts were predicted correctly out of the ones that were predicted as belonging to a given tag. In other words, precision takes the number of texts that were correctly predicted as positive for a given tag and divides it by the number of texts that were predicted (correctly and incorrectly) as belonging to the tag.
We have to bear in mind that precision only gives information about the cases where the classifier predicts that the text belongs to a given tag. This might be particularly important, for example, if you would like to generate automated responses for user messages. In this case, before you send an automated response you want to know for sure you will be sending the right response, right? In other words, if your classifier says the user message belongs to a certain type of message, you would like the classifier to make the right guess. This means you would like a high precision for that type of message.
Recall states how many texts were predicted correctly out of the ones that should have been predicted as belonging to a given tag. In other words, recall takes the number of texts that were correctly predicted as positive for a given tag and divides it by the number of texts that were either predicted correctly as belonging to the tag or that were incorrectly predicted as not belonging to the tag.
Recall might prove useful when routing support tickets to the appropriate team, for example. It might be desired for an automated system to detect as many tickets as possible for a critical tag (for example tickets about 'Outrages / Downtime' ) at the expense of making some incorrect predictions along the way. In this case, making a prediction will help perform the initial routing and solve most of these critical issues ASAP. If the prediction is incorrect, the ticket will get rerouted by a member of the team. When processing thousands of tickets per week, high recall (with good levels of precision as well, of course) can save support teams a good deal of time and enable them to solve critical issues faster.
The F1 score is the harmonic means of precision and recall. It tells you how well your classifier performs if equal importance is given to precision and recall. In general, F1 score is a much better indicator of classifier performance than accuracy is.
Cross-validation
Cross-validation is quite frequently used to evaluate the performance of text classifiers. The method is simple. First of all, the training dataset is randomly split into a number of equal-length subsets (e.g. 4 subsets with 25% of the original data each). Then, all the subsets except for one are used to train a classifier (in this case, 3 subsets with 75% of the original data) and this classifier is used to predict the texts in the remaining subset. Next, all the performance metrics are computed (i.e. accuracy, precision, recall, F1, etc.). Finally, the process is repeated with a new testing fold until all the folds have been used for testing purposes.
Once all folds have been used, the average performance metrics are computed and the evaluation process is finished.
Text Extraction refers to the process of recognizing structured pieces of information from unstructured text. For example, it can be useful to automatically detect the most relevant keywords from a piece of text, identify names of companies in a news article, detect lessors and lessees in a financial contract, or identify prices on product descriptions.
Regular Expressions
Regular Expressions (a.k.a. regexes) work as the equivalent of the rules defined in classification tasks. In this case, a regular expression defines a pattern of characters that will be associated with a tag.
For example, the pattern below will detect most email addresses in a text if they preceded and followed by spaces:
(?i)\b(?: [a-zA-Z0-9_ - .] +)@(?:(?: [ [0-9] {1,3} . [0-9] {1,3} . [0-9] {1,3} . )|(?:(?: [a-zA-Z0-9 -] + . )+))(?: [a-zA-Z] {2,4}| [0-9] {1,3})(?: ] ?)\b
By detecting this match in texts and assigning it the email tag, we can create a rudimentary email address extractor.
There are obvious pros and cons of this approach. On the plus side, you can create text extractors quickly and the results obtained can be good, provided you can find the right patterns for the type of information you would like to detect. On the minus side, regular expressions can get extremely complex and might be really difficult to maintain and scale, particularly when many expressions are needed in order to extract the desired patterns.
Conditional Random Fields
Conditional Random Fields (CRF) is a statistical approach often used in machine-learning-based text extraction. This approach learns the patterns to be extracted by weighing a set of features of the sequences of words that appear in a text. Through the use of CRFs, we can add multiple variables which depend on each other to the patterns we use to detect information in texts, such as syntactic or semantic information.
This usually generates much richer and complex patterns than using regular expressions and can potentially encode much more information. However, more computational resources are needed in order to implement it since all the features have to be calculated for all the sequences to be considered and all of the weights assigned to those features have to be learned before determining whether a sequence should belong to a tag or not.
One of the main advantages of the CRF approach is its generalization capacity. Once an extractor has been trained using the CRF approach over texts of a specific domain, it will have the ability to generalize what it has learned to other domains reasonably well.
Extractors are sometimes evaluated by calculating the same standard performance metrics we have explained above for text classification, namely, accuracy , precision , recall , and F1 score . However, these metrics do not account for partial matches of patterns. In order for an extracted segment to be a true positive for a tag, it has to be a perfect match with the segment that was supposed to be extracted.
Consider the following example:
'Your flight will depart on January 14, 2020 at 03:30 PM from SFO'
If we created a date extractor, we would expect it to return January 14, 2020 as a date from the text above, right? So, if the output of the extractor were January 14, 2020, we would count it as a true positive for the tag DATE .
But, what if the output of the extractor were January 14? Would you say the extraction was bad? Would you say it was a false positive for the tag DATE ? To capture partial matches like this one, some other performance metrics can be used to evaluate the performance of extractors. One example of this is the ROUGE family of metrics.
ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation) is a family of metrics used in the fields of machine translation and automatic summarization that can also be used to assess the performance of text extractors. These metrics basically compute the lengths and number of sequences that overlap between the source text (in this case, our original text) and the translated or summarized text (in this case, our extraction).
Depending on the length of the units whose overlap you would like to compare, you can define ROUGE-n metrics (for units of length n ) or you can define the ROUGE-LCS or ROUGE-L metric if you intend to compare the longest common sequence (LCS).
4.Visualize Your Text Data
Now you know a variety of text analysis methods to break down your data, but what do you do with the results? Business intelligence (BI) and data visualization tools make it easy to understand your results in striking dashboards.
- MonkeyLearn Studio
MonkeyLearn Studio is an all-in-one data gathering, analysis, and visualization tool. Deep learning machine learning techniques allow you to choose the text analyses you need (keyword extraction, sentiment analysis, aspect classification, and on and on) and chain them together to work simultaneously.
You’ll see the importance of text analytics right away. Simply upload your data and visualize the results for powerful insights. It all works together in a single interface, so you no longer have to upload and download between applications.
- Google Data Studio
Google's free visualization tool allows you to create interactive reports using a wide variety of data. Once you've imported your data you can use different tools to design your report and turn your data into an impressive visual story. Share the results with individuals or teams, publish them on the web, or embed them on your website.
Looker is a business data analytics platform designed to direct meaningful data to anyone within a company. The idea is to allow teams to have a bigger picture about what's happening in their company.
You can connect to different databases and automatically create data models, which can be fully customized to meet specific needs. Take a look here to get started.
Tableau is a business intelligence and data visualization tool with an intuitive, user-friendly approach (no technical skills required). Tableau allows organizations to work with almost any existing data source and provides powerful visualization options with more advanced tools for developers.
There's a trial version available for anyone wanting to give it a go. Learn how to perform text analysis in Tableau .
Text Analysis Applications & Examples

Did you know that 80% of business data is text? Text is present in every major business process, from support tickets, to product feedback, and online customer interactions. Automated, real time text analysis can help you get a handle on all that data with a broad range of business applications and use cases. Maximize efficiency and reduce repetitive tasks that often have a high turnover impact. Better understand customer insights without having to sort through millions of social media posts, online reviews, and survey responses.
If you work in customer experience, product, marketing, or sales, there are a number of text analysis applications to automate processes and get real world insights. And best of all you don’t need any data science or engineering experience to do it.
Social Media Monitoring
Let's say you work for Uber and you want to know what users are saying about the brand. You've read some positive and negative feedback on Twitter and Facebook. But 500 million tweets are sent each day , and Uber has thousands of mentions on social media every month. Can you imagine analyzing all of them manually?
This is where sentiment analysis comes in to analyze the opinion of a given text. By analyzing your social media mentions with a sentiment analysis model , you can automatically categorize them into Positive , Neutral or Negative . Then run them through a topic analyzer to understand the subject of each text. By running aspect-based sentiment analysis , you can automatically pinpoint the reasons behind positive or negative mentions and get insights such as:
- The top complaint about Uber on social media?
- The success rate of Uber's customer service - are people happy or are annoyed with it?
- What Uber users like about the service when they mention Uber in a positive way?
Now, let's say you've just added a new service to Uber. For example, Uber Eats. It's a crucial moment, and your company wants to know what people are saying about Uber Eats so that you can fix any glitches as soon as possible, and polish the best features. You can also use aspect-based sentiment analysis on your Facebook, Instagram and Twitter profiles for any Uber Eats mentions and discover things such as:
- Are people happy with Uber Eats so far?
- What is the most urgent issue to fix?
- How can we incorporate positive stories into our marketing and PR communication?
Not only can you use text analysis to keep tabs on your brand's social media mentions, but you can also use it to monitor your competitors' mentions as well. Is a client complaining about a competitor's service? That gives you a chance to attract potential customers and show them how much better your brand is.
Brand Monitoring
Follow comments about your brand in real time wherever they may appear (social media, forums, blogs, review sites, etc.). You’ll know when something negative arises right away and be able to use positive comments to your advantage.
The power of negative reviews is quite strong: 40% of consumers are put off from buying if a business has negative reviews. An angry customer complaining about poor customer service can spread like wildfire within minutes: a friend shares it, then another, then another… And before you know it, the negative comments have gone viral.
- Understand how your brand reputation evolves over time.
- Compare your brand reputation to your competitor's.
- Identify which aspects are damaging your reputation.
- Pinpoint which elements are boosting your brand reputation on online media.
- Identify potential PR crises so you can deal with them ASAP.
- Tune into data from a specific moment, like the day of a new product launch or IPO filing. Just run a sentiment analysis on social media and press mentions on that day, to find out what people said about your brand.
- Repost positive mentions of your brand to get the word out.
Customer Service
Despite many people's fears and expectations, text analysis doesn't mean that customer service will be entirely machine-powered. It just means that businesses can streamline processes so that teams can spend more time solving problems that require human interaction. That way businesses will be able to increase retention, given that 89 percent of customers change brands because of poor customer service. But, how can text analysis assist your company's customer service?
Ticket Tagging
Let machines do the work for you. Text analysis automatically identifies topics, and tags each ticket. Here's how it works:
- The model analyzes the language and expressions a customer language, for example, “I didn't get the right order.”
- Then, it compares it to other similar conversations.
- Finally, it finds a match and tags the ticket automatically. In this case, it could be under a Shipping Problems tag.
This happens automatically, whenever a new ticket comes in, freeing customer agents to focus on more important tasks.
Ticket Routing & Triage: Find the Right Person for the Job
Machine learning can read a ticket for subject or urgency, and automatically route it to the appropriate department or employee .
For example, for a SaaS company that receives a customer ticket asking for a refund, the text mining system will identify which team usually handles billing issues and send the ticket to them. If a ticket says something like “How can I integrate your API with python?” , it would go straight to the team in charge of helping with Integrations.
Ticket Analytics: Learn More From Your Customers
What is commonly assessed to determine the performance of a customer service team? Common KPIs are first response time , average time to resolution (i.e. how long it takes your team to resolve issues), and customer satisfaction (CSAT). And, let's face it, overall client satisfaction has a lot to do with the first two metrics.
But how do we get actual CSAT insights from customer conversations? How can we identify if a customer is happy with the way an issue was solved? Or if they have expressed frustration with the handling of the issue?
In this situation, aspect-based sentiment analysis could be used. This type of text analysis delves into the feelings and topics behind the words on different support channels, such as support tickets, chat conversations, emails, and CSAT surveys. A text analysis model can understand words or expressions to define the support interaction as Positive , Negative , or Neutral , understand what was mentioned (e.g. Service or UI/UX ), and even determine the sentiments behind the words (e.g. Sadness , Anger , etc.).
Urgency Detection: Prioritize Urgent Tickets
“Where do I start?” is a question most customer service representatives often ask themselves. Urgency is definitely a good starting point, but how do we define the level of urgency without wasting valuable time deliberating?
Text mining software can define the urgency level of a customer ticket and tag it accordingly. Support tickets with words and expressions that denote urgency, such as 'as soon as possible' or 'right away' , are duly tagged as Priority .
To see how text analysis works to detect urgency, check out this MonkeyLearn urgency detection demo model .
Voice of Customer (VoC) & Customer Feedback
Once you get a customer, retention is key, since acquiring new clients is five to 25 times more expensive than retaining the ones you already have. That's why paying close attention to the voice of the customer can give your company a clear picture of the level of client satisfaction and, consequently, of client retention. Also, it can give you actionable insights to prioritize the product roadmap from a customer's perspective.
Analyzing NPS Responses
Maybe your brand already has a customer satisfaction survey in place, the most common one being the Net Promoter Score (NPS). This survey asks the question, 'How likely is it that you would recommend [brand] to a friend or colleague?' . The answer is a score from 0-10 and the result is divided into three groups: the promoters , the passives , and the detractors .
But here comes the tricky part: there's an open-ended follow-up question at the end 'Why did you choose X score?' The answer can provide your company with invaluable insights. Without the text, you're left guessing what went wrong. And, now, with text analysis, you no longer have to read through these open-ended responses manually.
You can do what Promoter.io did: extract the main keywords of your customers' feedback to understand what's being praised or criticized about your product. Is the keyword 'Product' mentioned mostly by promoters or detractors? With this info, you'll be able to use your time to get the most out of NPS responses and start taking action.
Another option is following in Retently's footsteps using text analysis to classify your feedback into different topics, such as Customer Support, Product Design, and Product Features, then analyze each tag with sentiment analysis to see how positively or negatively clients feel about each topic. Now they know they're on the right track with product design, but still have to work on product features.
Analyzing Customer Surveys
Does your company have another customer survey system? If it's a scoring system or closed-ended questions, it'll be a piece of cake to analyze the responses: just crunch the numbers.
However, if you have an open-text survey, whether it's provided via email or it's an online form, you can stop manually tagging every single response by letting text analysis do the job for you. Besides saving time, you can also have consistent tagging criteria without errors, 24/7.
Business Intelligence
Data analysis is at the core of every business intelligence operation. Now, what can a company do to understand, for instance, sales trends and performance over time? With numeric data, a BI team can identify what's happening (such as sales of X are decreasing) – but not why . Numbers are easy to analyze, but they are also somewhat limited. Text data, on the other hand, is the most widespread format of business information and can provide your organization with valuable insight into your operations. Text analysis with machine learning can automatically analyze this data for immediate insights.
For example, you can run keyword extraction and sentiment analysis on your social media mentions to understand what people are complaining about regarding your brand.
You can also run aspect-based sentiment analysis on customer reviews that mention poor customer experiences. After all, 67% of consumers list bad customer experience as one of the primary reasons for churning. Maybe it's bad support, a faulty feature, unexpected downtime, or a sudden price change. Analyzing customer feedback can shed a light on the details, and the team can take action accordingly.
And what about your competitors? What are their reviews saying? Run them through your text analysis model and see what they're doing right and wrong and improve your own decision-making.
Sales and Marketing
Prospecting is the most difficult part of the sales process. And it's getting harder and harder. The sales team always want to close deals, which requires making the sales process more efficient. But 27% of sales agents are spending over an hour a day on data entry work instead of selling, meaning critical time is lost to administrative work and not closing deals.
Text analysis takes the heavy lifting out of manual sales tasks, including:
- Updating the deal status as 'Not interested' in your CRM.
- Qualifying your leads based on company descriptions.
- Identifying leads on social media that express buying intent.
GlassDollar , a company that links founders to potential investors, is using text analysis to find the best quality matches. How? They use text analysis to classify companies using their company descriptions. The results? They saved themselves days of manual work, and predictions were 90% accurate after training a text classification model. You can learn more about their experience with MonkeyLearn here .
Not only can text analysis automate manual and tedious tasks, but it can also improve your analytics to make the sales and marketing funnels more efficient. For example, you can automatically analyze the responses from your sales emails and conversations to understand, let's say, a drop in sales:
- What are the blocks to completing a deal?
- What sparks a customer's interest?
- What are customer concerns?
Now, Imagine that your sales team's goal is to target a new segment for your SaaS: people over 40. The first impression is that they don't like the product, but why ? Just filter through that age group's sales conversations and run them on your text analysis model. Sales teams could make better decisions using in-depth text analysis on customer conversations.
Finally, you can use machine learning and text analysis to provide a better experience overall within your sales process. For example, Drift , a marketing conversational platform, integrated MonkeyLearn API to allow recipients to automatically opt out of sales emails based on how they reply.
It's time to boost sales and stop wasting valuable time with leads that don't go anywhere. Xeneta, a sea freight company, developed a machine learning algorithm and trained it to identify which companies were potential customers, based on the company descriptions gathered through FullContact (a SaaS company that has descriptions of millions of companies).
You can do the same or target users that visit your website to:
- Get information about where potential customers work using a service like Clearbit and classify the company according to its type of business to see if it's a possible lead.
- Extract information to easily learn the user's job position, the company they work for, its type of business and other relevant information.
- Hone in on the most qualified leads and save time actually looking for them: sales reps will receive the information automatically and start targeting the potential customers right away.
Product Analytics
Let's imagine your startup has an app on the Google Play store. You're receiving some unusually negative comments. What's going on?
You can find out what’s happening in just minutes by using a text analysis model that groups reviews into different tags like Ease of Use and Integrations. Then run them through a sentiment analysis model to find out whether customers are talking about products positively or negatively. Finally, graphs and reports can be created to visualize and prioritize product problems with MonkeyLearn Studio .
We did this with reviews for Slack from the product review site Capterra and got some pretty interesting insights . Here's how:
We analyzed reviews with aspect-based sentiment analysis and categorized them into main topics and sentiment.
We extracted keywords with the keyword extractor to get some insights into why reviews that are tagged under 'Performance-Quality-Reliability' tend to be negative.
Text Analysis Resources

There are a number of valuable resources out there to help you get started with all that text analysis has to offer.
Text Analysis APIs
You can use open-source libraries or SaaS APIs to build a text analysis solution that fits your needs. Open-source libraries require a lot of time and technical know-how, while SaaS tools can often be put to work right away and require little to no coding experience.
Open Source Libraries
Python is the most widely-used language in scientific computing, period. Tools like NumPy and SciPy have established it as a fast, dynamic language that calls C and Fortran libraries where performance is needed.
These things, combined with a thriving community and a diverse set of libraries to implement natural language processing (NLP) models has made Python one of the most preferred programming languages for doing text analysis.
NLTK , the Natural Language Toolkit, is a best-of-class library for text analysis tasks. NLTK is used in many university courses, so there's plenty of code written with it and no shortage of users familiar with both the library and the theory of NLP who can help answer your questions.
SpaCy is an industrial-strength statistical NLP library. Aside from the usual features, it adds deep learning integration and convolutional neural network models for multiple languages.
Unlike NLTK, which is a research library, SpaCy aims to be a battle-tested, production-grade library for text analysis.
Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn is a complete and mature machine learning toolkit for Python built on top of NumPy, SciPy, and matplotlib, which gives it stellar performance and flexibility for building text analysis models.
Developed by Google, TensorFlow is by far the most widely used library for distributed deep learning. Looking at this graph we can see that TensorFlow is ahead of the competition:
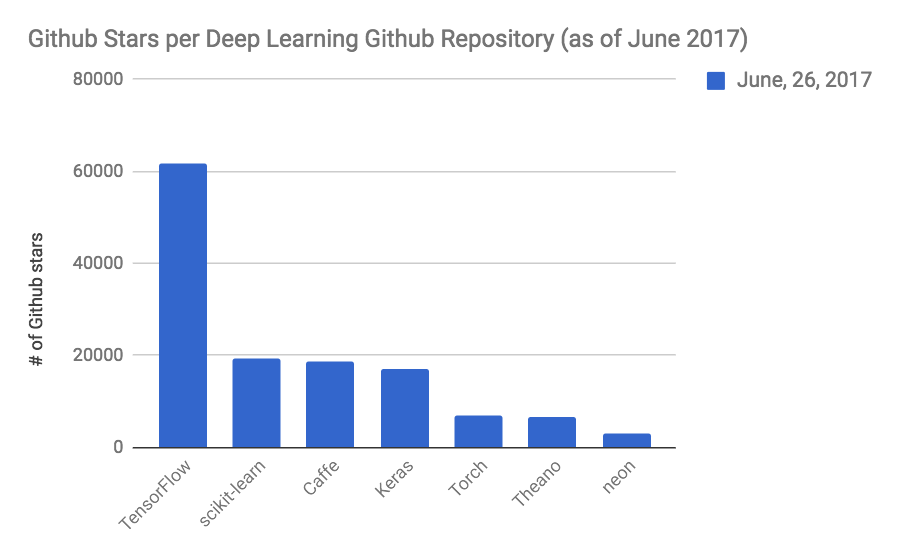
PyTorch is a deep learning platform built by Facebook and aimed specifically at deep learning. PyTorch is a Python-centric library, which allows you to define much of your neural network architecture in terms of Python code, and only internally deals with lower-level high-performance code.
Keras is a widely-used deep learning library written in Python. It's designed to enable rapid iteration and experimentation with deep neural networks, and as a Python library, it's uniquely user-friendly.
An important feature of Keras is that it provides what is essentially an abstract interface to deep neural networks. The actual networks can run on top of Tensorflow, Theano, or other backends. This backend independence makes Keras an attractive option in terms of its long-term viability.
The permissive MIT license makes it attractive to businesses looking to develop proprietary models.
R is the pre-eminent language for any statistical task. Its collection of libraries (13,711 at the time of writing on CRAN far surpasses any other programming language capabilities for statistical computing and is larger than many other ecosystems. In short, if you choose to use R for anything statistics-related, you won't find yourself in a situation where you have to reinvent the wheel, let alone the whole stack.
Caret is an R package designed to build complete machine learning pipelines, with tools for everything from data ingestion and preprocessing, feature selection, and tuning your model automatically.
The Machine Learning in R project (mlr for short) provides a complete machine learning toolkit for the R programming language that's frequently used for text analysis.
Java needs no introduction. The language boasts an impressive ecosystem that stretches beyond Java itself and includes the libraries of other The JVM languages such as The Scala and Clojure . Beyond that, the JVM is battle-tested and has had thousands of person-years of development and performance tuning, so Java is likely to give you best-of-class performance for all your text analysis NLP work.
Stanford's CoreNLP project provides a battle-tested, actively maintained NLP toolkit. While it's written in Java, it has APIs for all major languages, including Python, R, and Go.
The Apache OpenNLP project is another machine learning toolkit for NLP. It can be used from any language on the JVM platform.
Weka is a GPL-licensed Java library for machine learning, developed at the University of Waikato in New Zealand. In addition to a comprehensive collection of machine learning APIs, Weka has a graphical user interface called the Explorer , which allows users to interactively develop and study their models.
Weka supports extracting data from SQL databases directly, as well as deep learning through the deeplearning4j framework.
Using a SaaS API for text analysis has a lot of advantages:
Most SaaS tools are simple plug-and-play solutions with no libraries to install and no new infrastructure.
SaaS APIs provide ready to use solutions. You give them data and they return the analysis. Every other concern – performance, scalability, logging, architecture, tools, etc. – is offloaded to the party responsible for maintaining the API.
You often just need to write a few lines of code to call the API and get the results back.
- Easy Integration:
SaaS APIs usually provide ready-made integrations with tools you may already use. This will allow you to build a truly no-code solution. Learn how to integrate text analysis with Google Sheets .
Some of the most well-known SaaS solutions and APIs for text analysis include:
- MonkeyLearn
- Google Cloud NLP
- MeaningCloud
- Amazon Comprehend
There is an ongoing Build vs. Buy Debate when it comes to text analysis applications: build your own tool with open-source software, or use a SaaS text analysis tool?
Building your own software from scratch can be effective and rewarding if you have years of data science and engineering experience, but it’s time-consuming and can cost in the hundreds of thousands of dollars.
SaaS tools, on the other hand, are a great way to dive right in. They can be straightforward, easy to use, and just as powerful as building your own model from scratch. MonkeyLearn is a SaaS text analysis platform with dozens of pre-trained models. Or you can customize your own, often in only a few steps for results that are just as accurate. All with no coding experience necessary.
Training Datasets
If you talk to any data science professional, they'll tell you that the true bottleneck to building better models is not new and better algorithms, but more data.
Indeed, in machine learning data is king: a simple model, given tons of data, is likely to outperform one that uses every trick in the book to turn every bit of training data into a meaningful response.
So, here are some high-quality datasets you can use to get started:
Topic Classification
Reuters news dataset : one the most popular datasets for text classification; it has thousands of articles from Reuters tagged with 135 categories according to their topics, such as Politics, Economics, Sports, and Business.
20 Newsgroups : a very well-known dataset that has more than 20k documents across 20 different topics.
Product reviews : a dataset with millions of customer reviews from products on Amazon.
Twitter airline sentiment on Kaggle : another widely used dataset for getting started with sentiment analysis. It contains more than 15k tweets about airlines (tagged as positive, neutral, or negative).
First GOP Debate Twitter Sentiment : another useful dataset with more than 14,000 labeled tweets (positive, neutral, and negative) from the first GOP debate in 2016.
Other Popular Datasets
Spambase : this dataset contains 4,601 emails tagged as spam and not spam.
SMS Spam Collection : another dataset for spam detection. It has more than 5k SMS messages tagged as spam and not spam.
Hate speech and offensive language : a dataset with more than 24k tagged tweets grouped into three tags: clean, hate speech, and offensive language.
Finding high-volume and high-quality training datasets are the most important part of text analysis, more important than the choice of the programming language or tools for creating the models. Remember, the best-architected machine-learning pipeline is worthless if its models are backed by unsound data.
Text Analysis Tutorials
The best way to learn is by doing.
First, we'll go through programming-language-specific tutorials using open-source tools for text analysis. These will help you deepen your understanding of the available tools for your platform of choice.
Then, we'll take a step-by-step tutorial of MonkeyLearn so you can get started with text analysis right away.
Tutorials Using Open Source Libraries
In this section, we'll look at various tutorials for text analysis in the main programming languages for machine learning that we listed above.
The official NLTK book is a complete resource that teaches you NLTK from beginning to end. In addition, the reference documentation is a useful resource to consult during development.
Other useful tutorials include:
WordNet with NLTK: Finding Synonyms for words in Python : this tutorial shows you how to build a thesaurus using Python and WordNet .
Tokenizing Words and Sentences with NLTK : this tutorial shows you how to use NLTK's language models to tokenize words and sentences.
spaCy 101: Everything you need to know : part of the official documentation, this tutorial shows you everything you need to know to get started using SpaCy.
This tutorial shows you how to build a WordNet pipeline with SpaCy.
Furthermore, there's the official API documentation , which explains the architecture and API of SpaCy.
If you prefer long-form text, there are a number of books about or featuring SpaCy:
- Introduction to Machine Learning with Python: A Guide for Data Scientists .
- Practical Machine Learning with Python .
- Text Analytics with Python .
The official scikit-learn documentation contains a number of tutorials on the basic usage of scikit-learn, building pipelines, and evaluating estimators.
Scikit-learn Tutorial: Machine Learning in Python shows you how to use scikit-learn and Pandas to explore a dataset, visualize it, and train a model.
For readers who prefer books, there are a couple of choices:
Our very own Raúl Garreta wrote this book: Learning scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python .
Additionally, the book Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow introduces the use of scikit-learn in a deep learning context.
The official Keras website has extensive API as well as tutorial documentation. For readers who prefer long-form text, the Deep Learning with Keras book is the go-to resource. The book uses real-world examples to give you a strong grasp of Keras.
Other tutorials:
Practical Text Classification With Python and Keras : this tutorial implements a sentiment analysis model using Keras, and teaches you how to train, evaluate, and improve that model.
Text Classification in Keras : this article builds a simple text classifier on the Reuters news dataset. It classifies the text of an article into a number of categories such as sports, entertainment, and technology.
TensorFlow Tutorial For Beginners introduces the mathematics behind TensorFlow and includes code examples that run in the browser, ideal for exploration and learning. The goal of the tutorial is to classify street signs.
The book Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow helps you build an intuitive understanding of machine learning using TensorFlow and scikit-learn.
Finally, there's the official Get Started with TensorFlow guide.
The official Get Started Guide from PyTorch shows you the basics of PyTorch. If you're interested in something more practical, check out this chatbot tutorial ; it shows you how to build a chatbot using PyTorch.
The Deep Learning for NLP with PyTorch tutorial is a gentle introduction to the ideas behind deep learning and how they are applied in PyTorch.
Finally, the official API reference explains the functioning of each individual component.
A Short Introduction to the Caret Package shows you how to train and visualize a simple model. A Practical Guide to Machine Learning in R shows you how to prepare data, build and train a model, and evaluate its results. Finally, you have the official documentation which is super useful to get started with Caret.
For those who prefer long-form text, on arXiv we can find an extensive mlr tutorial paper . This is closer to a book than a paper and has extensive and thorough code samples for using mlr.
If interested in learning about CoreNLP, you should check out Linguisticsweb.org's tutorial which explains how to quickly get started and perform a number of simple NLP tasks from the command line. Moreover, this CloudAcademy tutorial shows you how to use CoreNLP and visualize its results. You can also check out this tutorial specifically about sentiment analysis with CoreNLP . Finally, there's this tutorial on using CoreNLP with Python that is useful to get started with this framework.
First things first: the official Apache OpenNLP Manual should be the starting point. The book Taming Text was written by an OpenNLP developer and uses the framework to show the reader how to implement text analysis. Moreover, this tutorial takes you on a complete tour of OpenNLP, including tokenization, part of speech tagging, parsing sentences, and chunking.
The Weka library has an official book Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques that comes handy for getting your feet wet with Weka.
If you prefer videos to text, there are also a number of MOOCs using Weka:
Data Mining with Weka : this is an introductory course to Weka.
More Data Mining with Weka : this course involves larger datasets and a more complete text analysis workflow.
Advanced Data Mining with Weka : this course focuses on packages that extend Weka's functionality.
The Text Mining in WEKA Cookbook provides text-mining-specific instructions for using Weka.
How to Run Your First Classifier in Weka : shows you how to install Weka, run it, run a classifier on a sample dataset, and visualize its results.
Text Analysis Tutorial With MonkeyLearn Templates
MonkeyLearn Templates is a simple and easy-to-use platform that you can use without adding a single line of code.
Follow the step-by-step tutorial below to see how you can run your data through text analysis tools and visualize the results:
1. Choose a template to create your workflow:
2. Upload your data.
We chose the app review template, so we’re using a dataset of reviews.
If you don't have a CSV file:
- You can use our sample dataset .
- Or, download your own survey responses from the survey tool you use with this documentation .
3. Match your data to the right fields in each column:
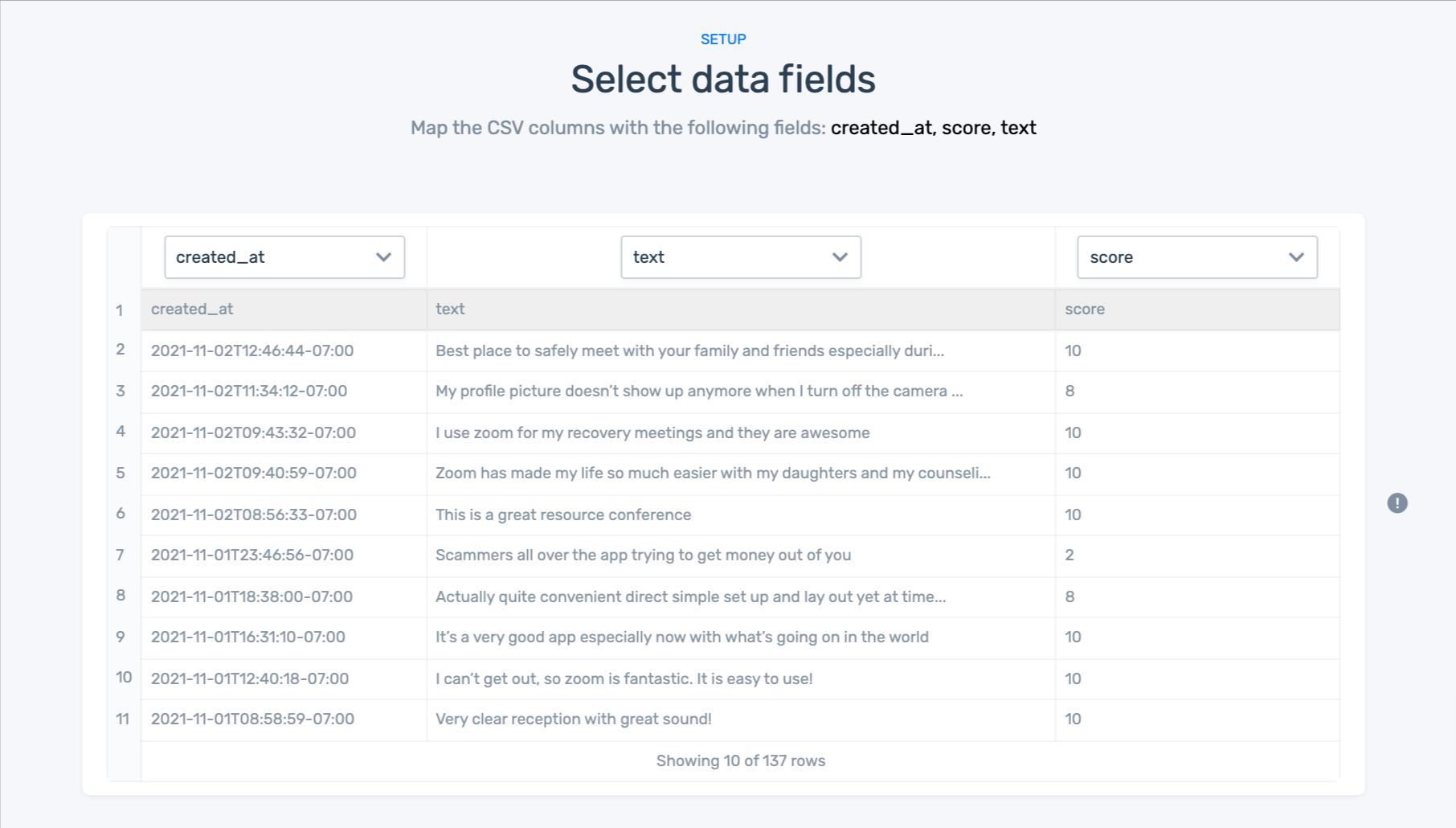
- created_at: Date that the response was sent.
- text: Text of the response.
- rating: Score given by the customer.
4. Name your workflow:
5. Wait for MonkeyLearn to process your data:

6. Explore your dashboard!
MonkeyLearn’s data visualization tools make it easy to understand your results in striking dashboards. Spot patterns, trends, and immediately actionable insights in broad strokes or minute detail.
- Filter by topic, sentiment, keyword, or rating.
- Share via email with other coworkers.
Text analysis is no longer an exclusive, technobabble topic for software engineers with machine learning experience. It has become a powerful tool that helps businesses across every industry gain useful, actionable insights from their text data. Saving time, automating tasks and increasing productivity has never been easier, allowing businesses to offload cumbersome tasks and help their teams provide a better service for their customers.
If you would like to give text analysis a go, sign up to MonkeyLearn for free and begin training your very own text classifiers and extractors – no coding needed thanks to our user-friendly interface and integrations.
And take a look at the MonkeyLearn Studio public dashboard to see what data visualization can do to see your results in broad strokes or super minute detail.
Reach out to our team if you have any doubts or questions about text analysis and machine learning, and we'll help you get started!

MonkeyLearn Inc. All rights reserved 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis, nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Textual analysis is a research methodology that involves exploring written text as empirical data. Scholars explore both the content and structure of texts, and attempt to discern key themes and statistics emergent from them. This method of research is used in various academic disciplines, including cultural studies, literature, bilical studies ...
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Step 1: Read the Text Thoroughly. Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
The term regularly used for the development of the central idea of a literary analysis essay is the body. In this section you present the paragraphs (at least 3 paragraphs for a 500-750 word essay) that support your thesis statement. Good literary analysis essays contain an explanation of your ideas and evidence from the text (short story,
How to Write a Literary Analysis. These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as ...
An analysis essay is a type of essay that requires the writer to analyze and interpret a particular text or topic. The goal of an analysis essay is to break down the text or topic into smaller parts and examine each part carefully. This allows the writer to make connections between different parts of the text or topic and develop a more ...
The analysis paper uses evidence to support the argument, such as excerpts from the piece of writing. All analytical papers include a thesis, analysis of the topic, and evidence to support that analysis. When developing an analytical essay outline and writing your essay, follow these five steps: #1: Choose a topic. #2: Write your thesis.
February 23, 2022. Firstly to understand what a literary analysis essay means, it's a way to determine and understand the work of an author, even if it is a single work or an entire body of work. Literary criticism is a description, analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a particular literary work or an author's writings as a whole.
A literary analysis essay is an essay where you explore such questions in depth and offer your own insights. What is the Purpose of a Literary Analysis Essay? In general, the purpose of a literary analysis essay is as follows: To gain a greater understanding and appreciation of the work. To be able to think critically and analytically about a text.
8.1: Literary Analysis Arguments. Analysis means to break something down in order to better understand how it works. To analyze a literary work is to pull it apart and look at its discrete components to see how those components contribute to the meaning and/or effect of the whole. Thus, a literary analysis argument considers what has been ...
E238 Text Analysis Essay Example. Text Analysis Papers. For five of the six texts you read this semester, you will be expected to hand in a corresponding text analysis paper. A text analysis paper will focus upon an area of the work that you find interesting, significant, or feel merits discussion. A text analysis paper should be fairly formal ...
Written Texts. When you analyze an essay or article, consider these questions: What is the thesis or central idea of the text? Who is the intended audience? What questions does the author address? How does the author structure the text? What are the key parts of the text? How do the key parts of the text interrelate? How do the key parts of the ...
Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
When writing an analytical essay, start by formulating a thesis statement that includes the topic and the main goal of your text. It will help you create an analytical essay outline and show your readers what you will discuss in your analysis essay. Add it to the last paragraph of your analytical essay introduction.
Analysis Essay Conclusion. The next four points will give you a short instruction on how to conclude an analytical essay. Never use new information or topics here. Restate your thesis in a different formulation. Summarize the body paragraphs. Comment on the analyzed text from a new perspective. 📔 Choosing a Title for Your Analysis Essay
This video, part of a series on analytical essay writing, takes you through exactly what it means to analyse a text in an English essay. What does an analyti...
Text-dependent analysis prompts typically follow a three line structure. Line 1 introduces the literary element in focus. Line 2 introduces the task related to that literary element. Line 3 instructs students to use text evidence in their response. Before assigning a text-dependent analysis essay, it may be helpful to review the structure of ...
Text analysis (TA) is a machine learning technique used to automatically extract valuable insights from unstructured text data. Companies use text analysis tools to quickly digest online data and documents, and transform them into actionable insights. You can us text analysis to extract specific information, like keywords, names, or company ...
Analysis is a way of understanding a subject by using each of these elements, expressing an opinion (making assertions), supporting that opinion (including examples), justifying that opinion (explaining the examples), and showing why the opinion matters (extending the significance). A complete analysis relies on these elements, but the reasons ...